Dietary Treatment of Metabolic Acidosis in Chronic Kidney Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Metabolic Acidosis
3. Dietary Acid Load
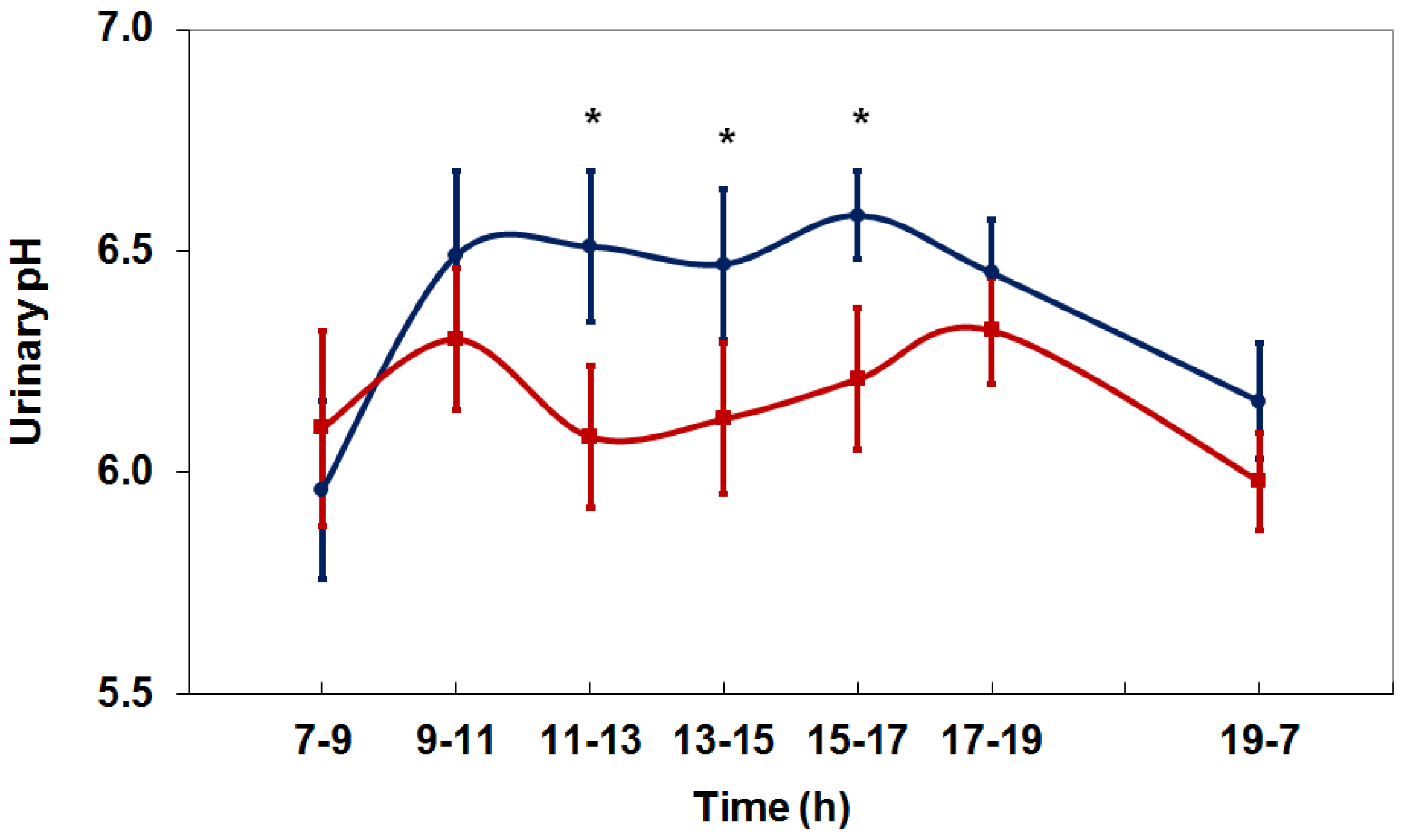
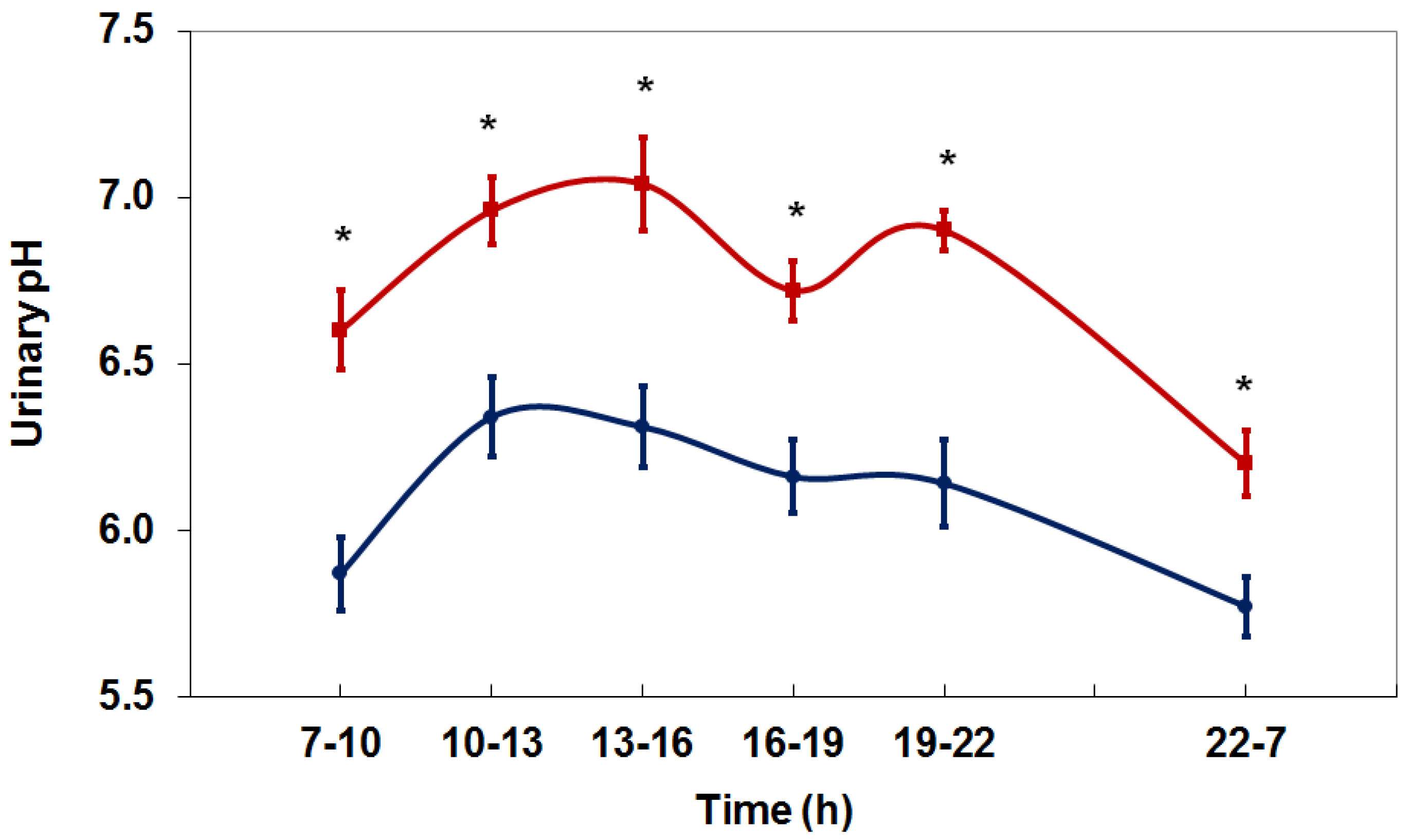
4. Net Acid Excretion and Urinary pH
5. Beverages
5.1. Fruit Juices
5.2. Bicarbonate-Rich Beverages
6. Dietary Acid Load and Risk of Chronic Kidney Disease
7. Diet versus Supplementation
8. Conclusions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dhondup, T.; Qian, Q. Electrolyte and acid-base disorders in chronic kidney disease and end-stage kidney failure. Blood Purif. 2017, 43, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, B.D.; Post, T.W. Clinical Physiology of Acid-Base and Electrolyte Disorders, 5th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2001; ISBN-10: 0071346821, ISBN-13: 9780071346825. [Google Scholar]
- Kazancioglu, R. Risk factors for chronic kidney disease: An update. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2013, 3, 368–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Q. Inflammation: A key contributor to the genesis and progression of chronic kidney disease. In Expanded Hemodialysis—Innovative Clinical Approach in Dialysis Contributions to Nephrology; Ronco, C., Ed.; Karger: Basel, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 191, pp. 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambaro, G.; Croppi, E.; Bushinsky, D.; Jaeger, P.; Cupisti, A.; Ticinesi, A.; Mazzaferro, S.; D’Addessi, A.; Ferraro, P.M. The risk of chronic kidney disease associated with urolithiasis and its urological treatments: A review. J. Urol. 2017, 198, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovesdy, C.P. Metabolic acidosis and kidney disease: Does bicarbonate therapy slow the progression of CKD? Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012, 27, 3056–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaqoob, M.M. Acidosis and progression of chronic kidney disease. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2010, 19, 489–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobre, M.; Rahman, M.; Hostetter, T.H. Current status of bicarbonate in CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO); CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2012 clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2013, 3, 1–150. [Google Scholar]
- Nagami, G.T.; Hamm, L.L. Regulation of acid-base balance in chronic kidney disease. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2017, 24, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eustace, J.A.; Astor, B.; Muntner, P.M.; Ikizler, A.; Coresh, J. Prevalence of acidosis and inflammation and their association with low serum albumin in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2004, 65, 1031–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballmer, P.E.; McNurlan, M.A.; Hulter, H.N.; Anderson, S.E.; Garlick, P.J.; Krapf, R. Chronic metabolic acidosis decreases albumin synthesis and induces negative nitrogen balance in humans. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 95, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopple, J.D.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Mehrotra, R. Risks of chronic metabolic acidosis in patients with chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2005, 67 (Suppl. 95), S21–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krieger, N.S.; Frick, K.K.; Bushinsky, D.A. Mechanism of acid-induced bone resorption. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2004, 13, 423–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovesdy, C.P.; Anderson, J.E.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Association of serum bicarbonate levels with mortality in patients with non-dialysis-dependent CKD. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2009, 24, 1232–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abramowitz, M.K.; Melamed, M.L.; Bauer, C.; Raff, A.C.; Hostetter, T.H. Effects of oral sodium bicarbonate in patients with CKD. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 8, 714–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domrongkitchaiporn, S.; Pongskul, C.; Sirikulchayanonta, V.; Stitchantrakul, W.; Leeprasert, V.; Ongphiphadhanakul, B.; Radinahamed, P.; Rajatanavin, R. Bone histology and bone mineral density after correction of acidosis in distal renal tubular acidosis. Kidney Int. 2002, 62, 2160–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, P.L.; Frassetto, L.A. Management of osteoporosis in CKD stages 3 to 5. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2010, 55, 941–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Susantitaphong, P.; Sewaralthahab, K.; Balk, E.M.; Jaber, B.L.; Madias, N.E. Short- and long-term effects of alkali therapy in chronic kidney disease: A systematic review. Am. J. Nephrol. 2012, 35, 540–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.N.; Abramowitz, M.; Hostetter, T.H.; Melamed, M.L. Serum bicarbonate levels and the progression of kidney disease: A cohort study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2009, 54, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Brito-Ashurst, I.; Varagunam, M.; Raftery, M.J.; Yaqoob, M.M. Bicarbonate supplementation slows progression of CKD and improves nutritional status. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 2075–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobre, M.; Yang, W.; Pan, Q.; Appel, L.; Bellovich, K.; Chen, J.; Feldman, H.; Fischer, M.J.; Ham, L.L.; Hostetter, T.; et al. Persistent high serum bicarbonate and the risk of heart failure in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD): A report from the Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort (CRIC) Study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2015, 4, e001599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raphael, K.L. Approach to the treatment of chronic metabolic acidosis in CKD. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2016, 67, 696–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remer, T.; Manz, F. Estimation of the renal net acid excretion by adults consuming diets containing variable amounts of protein. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1994, 59, 1356–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remer, T.; Manz, F. Potential renal acid load of foods and its influence on urine pH. J. Am. Diet Assoc. 1995, 95, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frassetto, L.A.; Todd, K.M.; Morris, R.C., Jr.; Sebastian, A. Estimation of net endogenous noncarbonic acid production in humans from diet potassium and protein contents. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1998, 68, 576–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remer, T. Influence of diet on acid-base balance. Semin. Dial. 2000, 13, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Relman, A.S.; Lennon, E.J.; Lemann, J. Endogenous production of fixed acid and the measurement of the net balance of acid in normal subjects. J. Clin. Investig. 1961, 40, 1621–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovesdy, C.P. Metabolic acidosis as a possible cause of CKD: What should clinicians do? Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2014, 64, 481–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siener, R.; Hesse, A. The effect of a vegetarian and different omnivorous diets on urinary risk factors for uric acid stone formation. Eur. J. Nutr. 2003, 42, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siener, R.; Struwe, F.; Hesse, A. Effect of l-methionine on the risk of phosphate stone formation. Urology 2016, 98, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souci, S.W.; Fachmann, W.; Kraut, H. Food Composition and Nutrition Tables 1986/87, 3rd ed.; Wissenschaftliche Verlagsgesellschaft mbH: Stuttgart, Germany, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Penniston, K.L.; Nakada, S.Y.; Holmes, R.P.; Assimos, D.G. Quantitative assessment of citric acid in lemon juice, lime juice, and commercially-available fruit juice products. J. Endourol. 2008, 22, 567–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamm, L.L.; Hering-Smith, K.S. Pathophysiology of hypocitraturic nephrolithiasis. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2002, 31, 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hönow, R.; Laube, N.; Schneider, A.; Keßler, T.; Hesse, A. Influence of grapefruit-, orange- and apple-juice consumption on urinary variables and risk of crystallization. Br. J. Nutr. 2003, 90, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Siener, R.; Jahnen, A.; Hesse, A. Influence of a mineral water rich in calcium, magnesium and bicarbonate on urine composition and the risk of calcium oxalate crystallization. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 58, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keßler, T.; Hesse, A. Cross-over study of the influence of bicarbonate-rich mineral water on urinary composition in comparison with sodium potassium citrate in healthy male subjects. Br. J. Nutr. 2000, 84, 865–871. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pinheiro, V.B.; Baxmann, A.C.; Tiselius, H.G.; Heilberg, I.P. The effect of sodium bicarbonate upon urinary citrate excretion in calcium stone formers. Urology 2013, 82, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, T.; Crews, D.C.; Wesson, D.E.; Tilea, A.; Saran, R.; Burrows, N.R.; Williams, D.E.; Powe, N.R. Dietary acid load and chronic kidney disease among adults in the United States. BMC Nephrol. 2014, 15, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirmiran, P.; Yuzbashian, E.; Bahadoran, Z.; Asghari, G.; Azizi, F. Dietary acid-base load and risk of chronic kidney disease in adults: Tehran Lipid and Glucose Study. Iran. J. Kidney Dis. 2016, 10, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rebholz, C.M.; Coresh, J.; Grams, M.E.; Steffen, L.M.; Anderson, C.A.M.; Appel, L.J.; Crews, D.C. Dietary acid load and incident chronic kidney disease: Results from the ARIC Study. Am. J. Nephrol. 2015, 42, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goraya, N.; Simoni, J.; Jo, C.H.; Wesson, D.E. Treatment of metabolic acidosis in patients with stage 3 chronic kidney disease with fruits and vegetables or oral bicarbonate reduces urine angiotensinogen and preserves glomerular filtration rate. Kidney Int. 2014, 86, 1031–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahajan, A.; Simoni, J.; Sheather, S.J.; Broglio, K.R.; Rajab, M.H.; Wesson, D.E. Daily oral sodium bicarbonate preserves glomerular filtration rate by slowing its decline in early hypertensive nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2010, 78, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goraya, N.; Simoni, J.; Jo, C.H.; Wesson, D.E. A comparison of treating metabolic acidosis in CKD stage 4 hypertensive kidney disease with fruits and vegetables or sodium bicarbonate. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 8, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bovio, G.; Esposito, C.; Montagna, G.; Brazzo, S.; Esposito, V.; Torreggiani, M.; Semeraro, L.; Cena, H. Inadequate macronutrient and micronutrient intakes in hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis patients: Data from a seven-day weighed dietary record. Nephron 2016, 133, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Food Group | PRAL (mEq/100 g) |
|---|---|
| Fruits and fruit juices | −3.1 |
| Vegetables | −2.8 |
| Fats and oils | 0 |
| Milk and whey based products | +1.0 |
| Bread | +3.5 |
| Noodles, spaghetti | +6.7 |
| Fish | +7.9 |
| Cheese (protein <15 g/100 g) | +8.0 |
| Meat and meat products | +9.5 |
© 2018 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Siener, R. Dietary Treatment of Metabolic Acidosis in Chronic Kidney Disease. Nutrients 2018, 10, 512. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10040512
Siener R. Dietary Treatment of Metabolic Acidosis in Chronic Kidney Disease. Nutrients. 2018; 10(4):512. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10040512
Chicago/Turabian StyleSiener, Roswitha. 2018. "Dietary Treatment of Metabolic Acidosis in Chronic Kidney Disease" Nutrients 10, no. 4: 512. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10040512
APA StyleSiener, R. (2018). Dietary Treatment of Metabolic Acidosis in Chronic Kidney Disease. Nutrients, 10(4), 512. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10040512




