Taiwanese Green Propolis Ethanol Extract Delays the Progression of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Rats Treated with Streptozotocin/High-Fat Diet
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
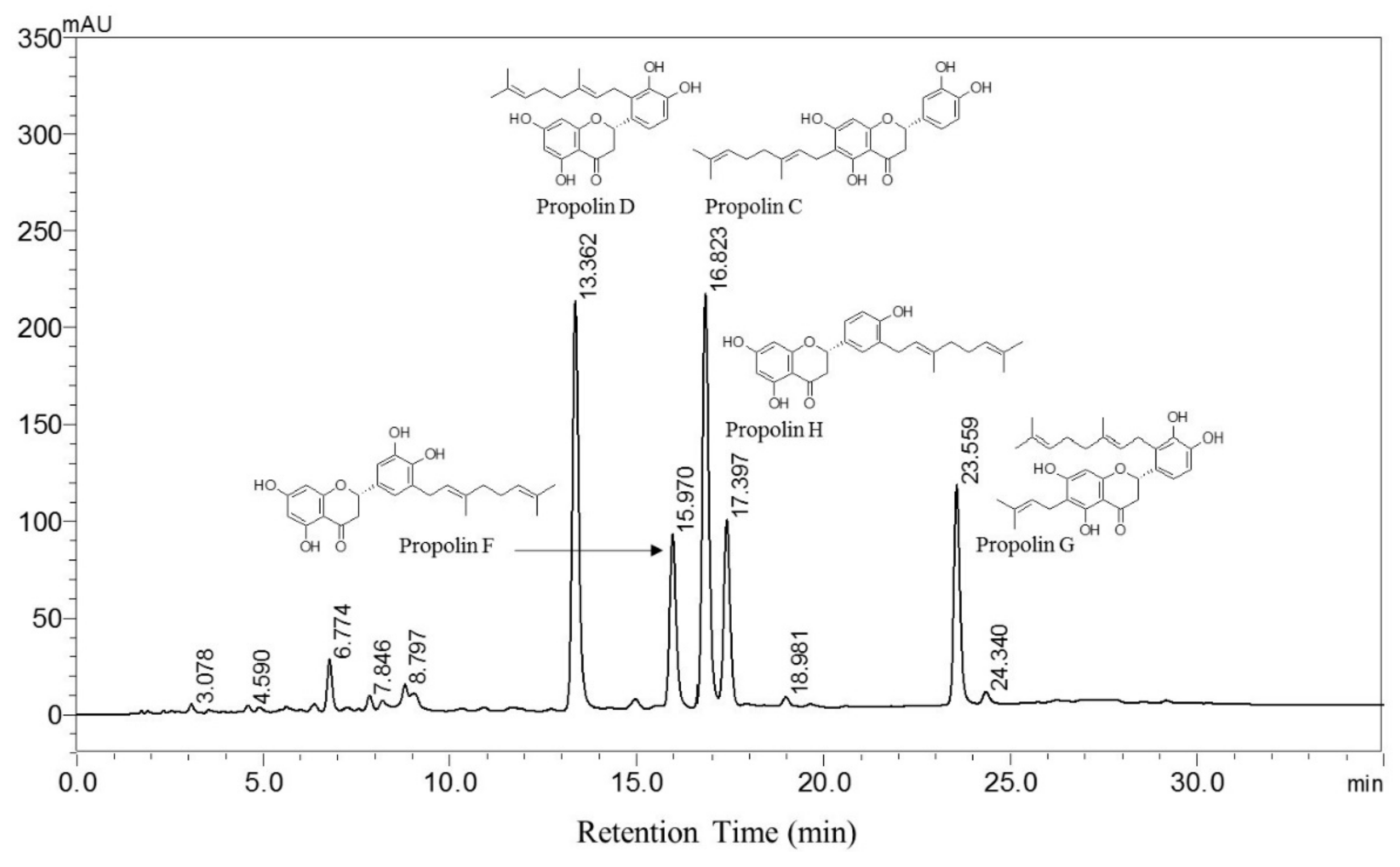
2.1. Sample Preparation and HPLC Analyses
2.2. Animal Model
2.3. Serum Biochemical Analysis
2.4. Insulin Sensitivity Indices (ISI)
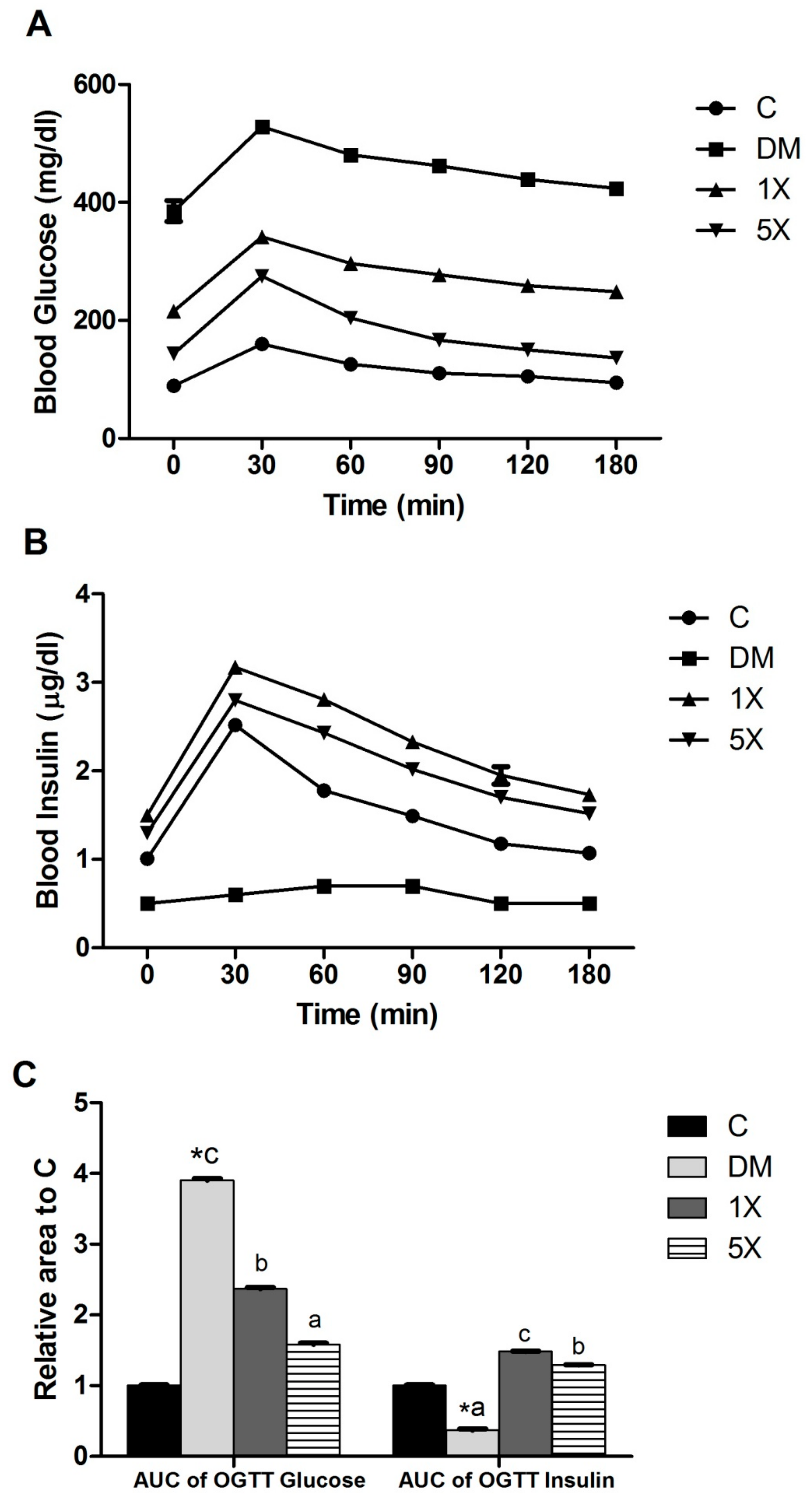
2.5. Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT)
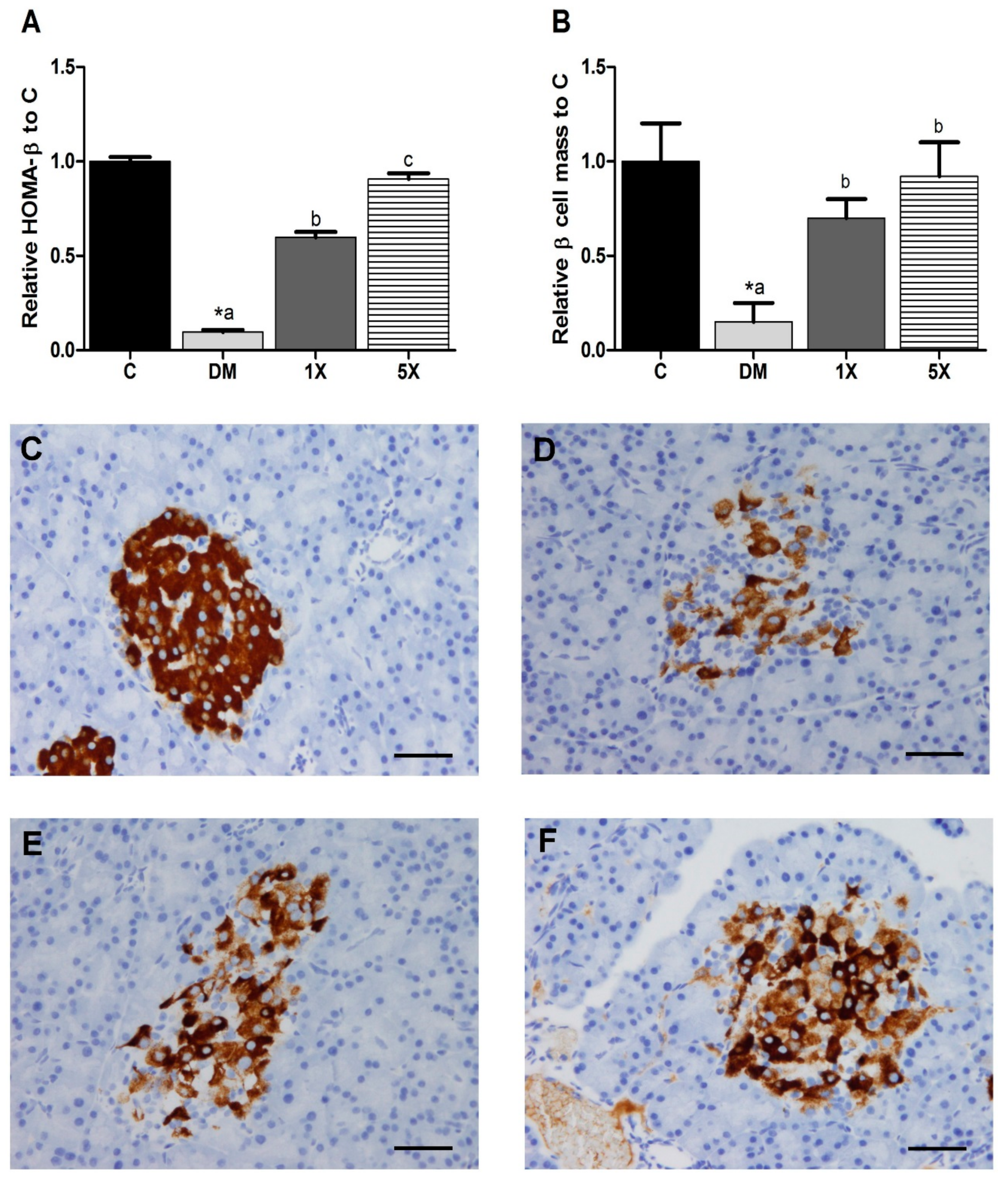
2.6. β-Cell Function and Mass
2.7. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
2.8. Antioxidants Activity and Oxidative Stress Levels
2.9. RNA Extraction and Quantitative RT-PCR
2.10. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Chemical Composition of TGPE
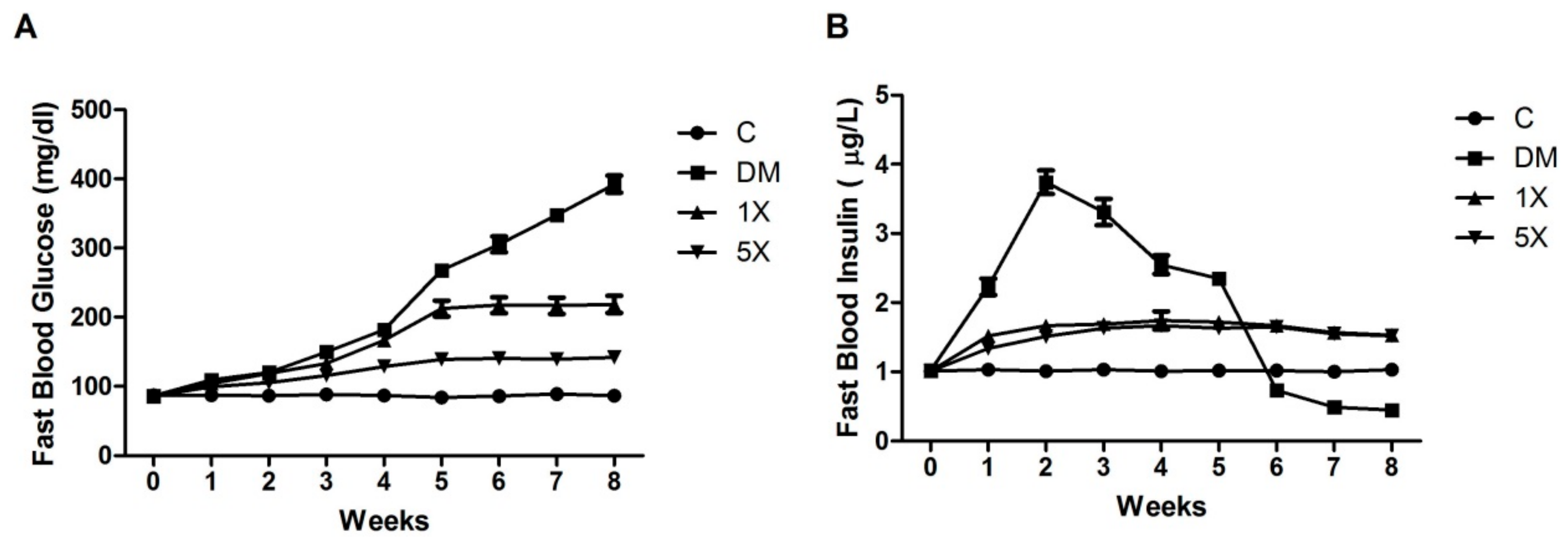
3.2. BW Gain, Feed Conversion Efficiency (FCE), and Water Intake
3.3. Blood Glucose, Insulin, ISI, and OGTT
3.4. β-Cell Function and Mass
3.5. Serum Lipid Biochemical Parameters
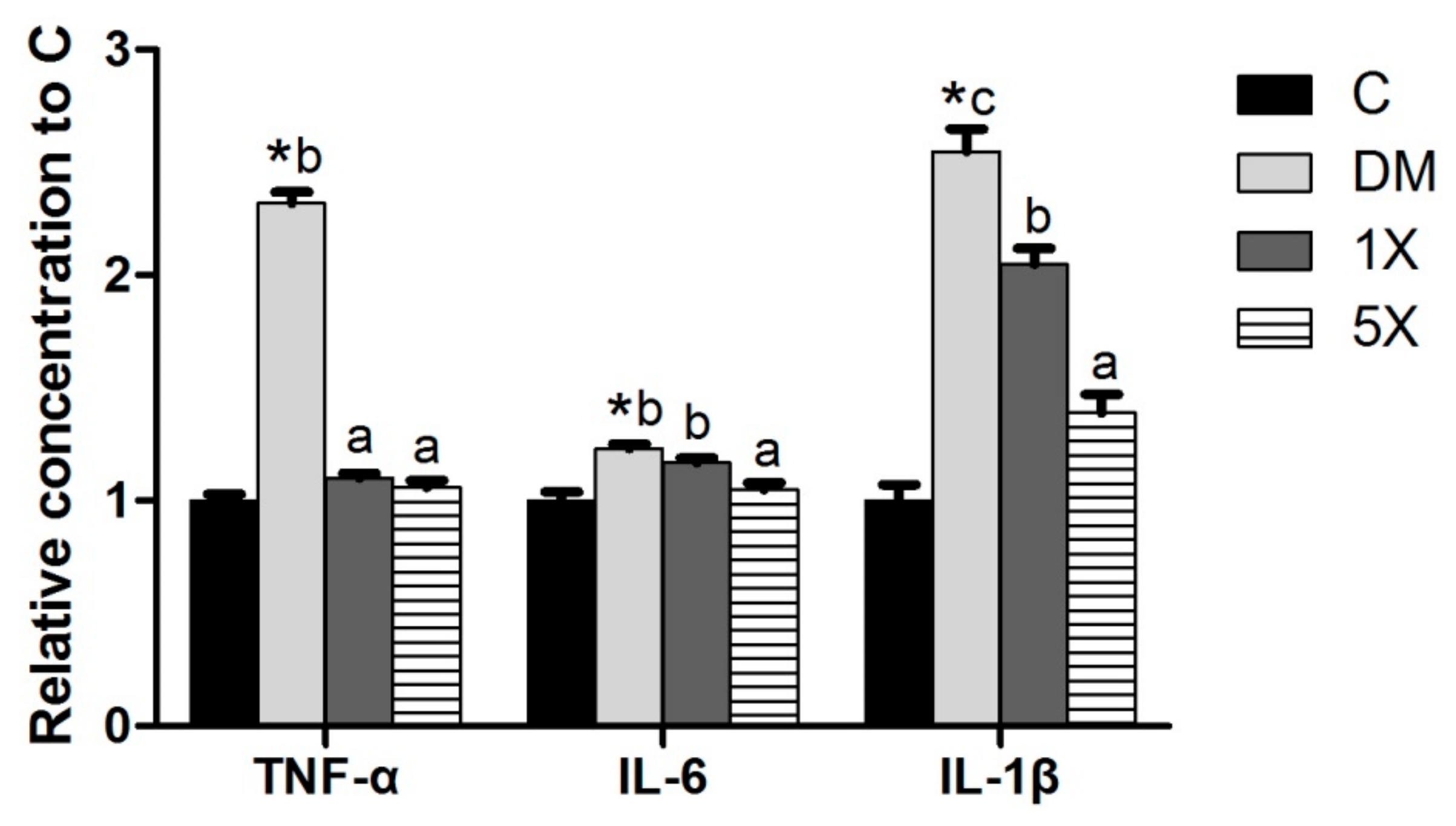
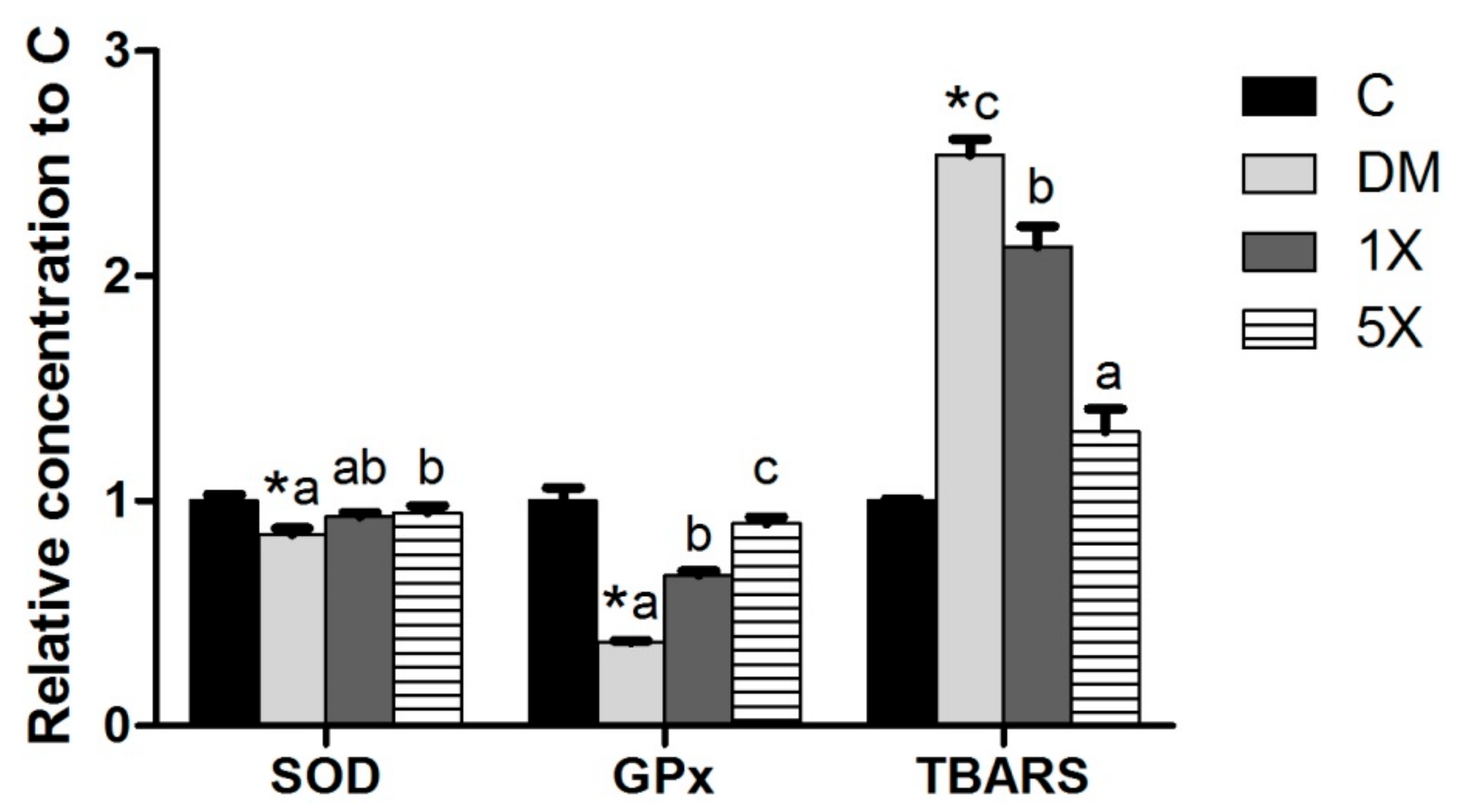
3.6. Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines and Antioxidant Factors
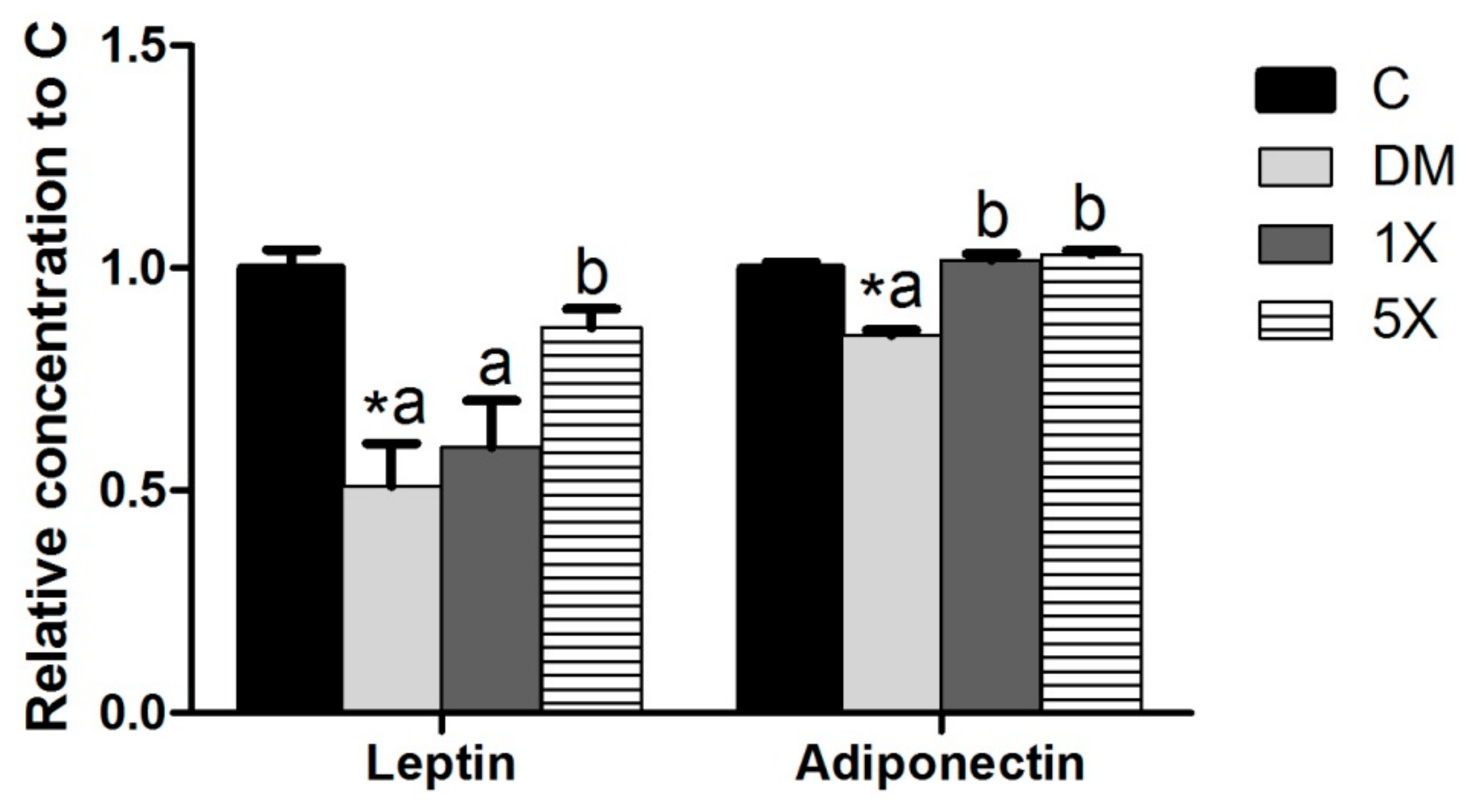
3.7. Leptin and Adiponectin
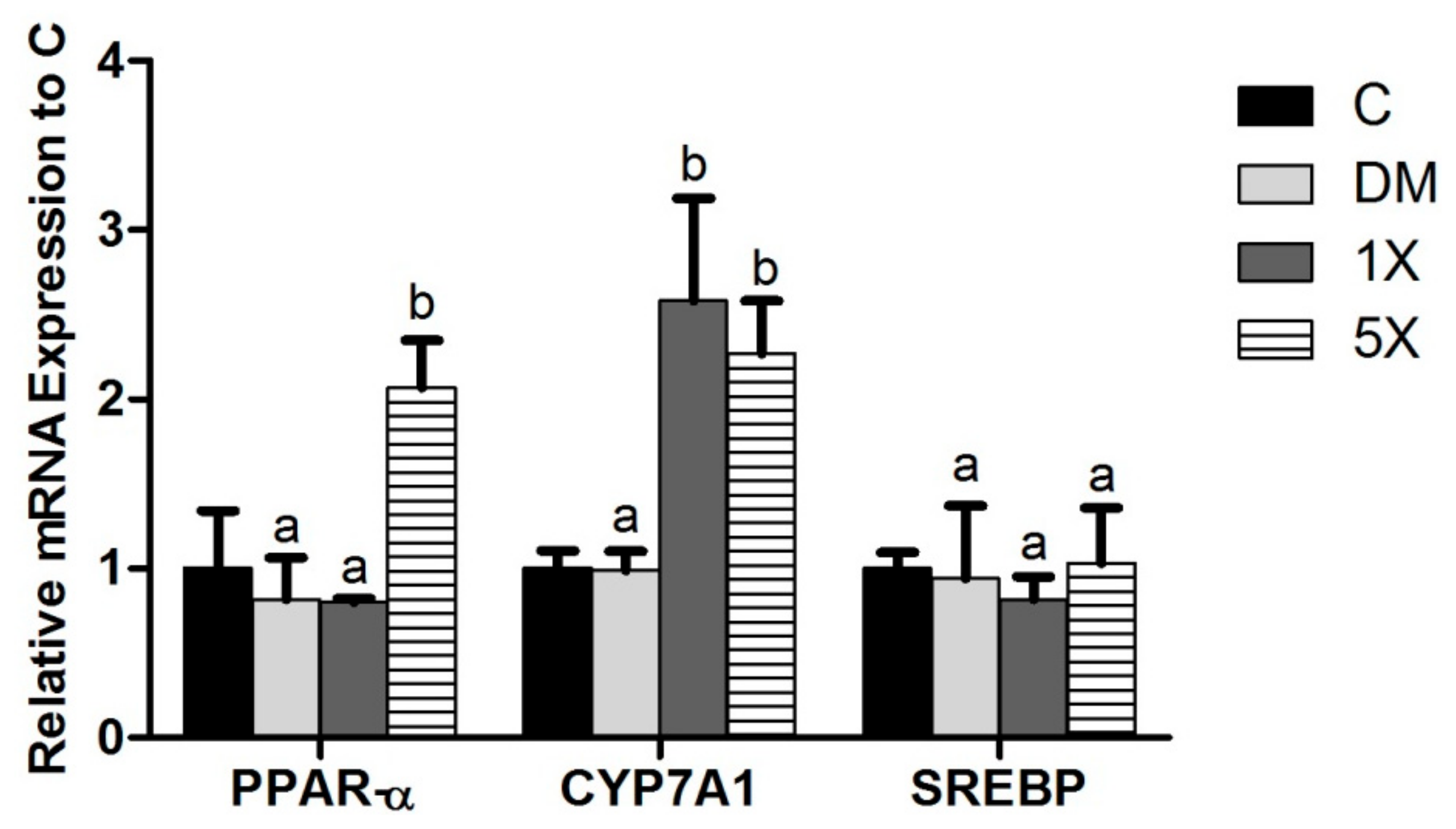
3.8. mRNA Expressions of Lipid Metabolism Genes in the Liver
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ogurtsova, K.; Fernandes, J.D.D.R.; Huang, Y.; Linnenkamp, U.; Guariguata, L.; Cho, N.H.; Cavan, D.; Shaw, J.E.; Makaroff, L.E. Idf diabetes atlas: Global estimates for the prevalence of diabetes for 2015 and 2040. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2017, 128, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NCD Risk Factor Collaboration. Worldwide trends in diabetes since 1980: A pooled analysis of 751 population-based studies with 4.4 million participants. Lancet 2016, 387, 1513–1530. [Google Scholar]
- Davi, G.; Santilli, F.; Patrono, C. Nutraceuticals in diabetes and metabolic syndrome. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2010, 28, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.N.; Weng, M.S.; Wu, C.L.; Lin, J.K. Comparison of radical scavenging activity, cytotoxic effects and apoptosis induction in human melanoma cells by taiwanese propolis from different sources. J. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2004, 1, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vardar-Ünlü, G.; Silici, S.; Ünlü, M. Composition and in vitro antimicrobial activity of populus buds and poplar-type propolis. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 24, 1011–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastos, E.M.; Simone, M.; Jorge, D.M.; Soares, A.E.; Spivak, M. In vitro study of the antimicrobial activity of brazilian propolis against paenibacillus larvae. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2008, 97, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulino, N.; Abreu, S.R.; Uto, Y.; Koyama, D.; Nagasawa, H.; Hori, H.; Dirsch, V.M.; Vollmar, A.M.; Scremin, A.; Bretz, W.A. Anti-inflammatory effects of a bioavailable compound, artepillin C, in brazilian propolis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 587, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajima, M.; Arimatsu, K.; Minagawa, T.; Matsuda, Y.; Sato, K.; Takahashi, N.; Nakajima, T.; Yamazaki, K. Brazilian propolis mitigates impaired glucose and lipid metabolism in experimental periodontitis in mice. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, K.Y.; Hsieh, C.Y.; Chen, Y.W.; Chuang, C.T.; Chen, C.T.; Chen, Y.L. Taiwanese green propolis and propolin G protect the liver from the pathogenesis of fibrosis via eliminating TGF-beta-induced smad2/3 phosphorylation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 3129–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.N.; Wu, C.L.; Shy, H.S.; Lin, J.K. Cytotoxic prenylflavanones from taiwanese propolis. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 503–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popova, M.; Chen, C.N.; Chen, P.Y.; Huang, C.Y.; Bankova, V. A validated spectrophotometric method for quantification of prenylated flavanones in pacific propolis from Taiwan. Phytochem. Anal. 2010, 21, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahn, S.E.; Halban, P.A. Release of incompletely processed proinsulin is the cause of the disproportionate proinsulinemia of niddm. Diabetes 1997, 46, 1725–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabak, A.G.; Jokela, M.; Akbaraly, T.N.; Brunner, E.J.; Kivimaki, M.; Witte, D.R. Trajectories of glycaemia, insulin sensitivity, and insulin secretion before diagnosis of type 2 diabetes: An analysis from the whitehall ii study. Lancet 2009, 373, 2215–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Sanchez, A.; Madrigal-Santillan, E.; Bautista, M.; Esquivel-Soto, J.; Morales-Gonzalez, A.; Esquivel-Chirino, C.; Durante-Montiel, I.; Sanchez-Rivera, G.; Valadez-Vega, C.; Morales-Gonzalez, J.A. Inflammation, oxidative stress, and obesity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 3117–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.C.; Wang, D.P.; Chiang, J.Y. Regulation of cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase in the liver. Cloning, sequencing, and regulation of cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase mrna. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 12012–12019. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Matozel, M.; Boehme, S.; Kong, B.; Nilsson, L.M.; Guo, G.; Ellis, E.; Chiang, J.Y. Overexpression of cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase promotes hepatic bile acid synthesis and secretion and maintains cholesterol homeostasis. Hepatology 2011, 53, 996–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, D.W. The enzymes, regulation, and genetics of bile acid synthesis. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2003, 72, 137–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rockville, M. Guidance for Industry: Estimating the Maximum Safe Starting Dose in Adult Healthy Volunteer; USFDA: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2005.
- Huang, H.Y.; Korivi, M.; Chaing, Y.Y.; Chien, T.Y.; Tsai, Y.C. Pleurotus tuber-regium polysaccharides attenuate hyperglycemia and oxidative stress in experimental diabetic rats. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 2012, 856381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.M.; Bong, H.Y.; Jeong, H.I.; Kim, Y.K.; Kim, J.Y.; Kwon, O. Postprandial hypoglycemic effect of mulberry leaf in goto-kakizaki rats and counterpart control wistar rats. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2009, 3, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peth, J.A.; Kinnick, T.R.; Youngblood, E.B.; Tritschler, H.J.; Henriksen, E.J. Effects of a unique conjugate of alpha-lipoic acid and gamma-linolenic acid on insulin action in obese zucker rats. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2000, 278, R453–R459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panes, J.; Kurose, I.; Rodriguez-Vaca, D.; Anderson, D.C.; Miyasaka, M.; Tso, P.; Granger, D.N. Diabetes exacerbates inflammatory responses to ischemia-reperfusion. Circulation 1996, 93, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiganis, T. Reactive oxygen species and insulin resistance: The good, the bad and the ugly. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2011, 32, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.A.; Zhang, C.P.; Wang, K.; Li, G.Q.; Hu, F.L. Recent advances in the chemical composition of propolis. Molecules 2014, 19, 19610–19632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yakushijin, K.; Shibayama, K.; Murata, H.; Furukawa, H. New prenylflavanones from hernandia-nymphaefolia (presl) kubitzki. Heterocycles 1980, 14, 397–402. [Google Scholar]
- Kumazawa, S.; Goto, H.; Hamasaka, T.; Fukumoto, S.; Fujimoto, T.; Nakayama, T. A new prenylated flavonoid from propolis collected in Okinawa, Japan. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2004, 68, 260–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.J.; Huang, C.H.; Wu, C.L.; Lin, J.K.; Chen, Y.W.; Lin, C.L.; Chuang, S.E.; Huang, C.Y.; Chen, C.N. Propolin G, a prenylflavanone, isolated from taiwanese propolis, induces caspase-dependent apoptosis in brain cancer cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 7366–7376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, M.S.; Liao, C.H.; Chen, C.N.; Wu, C.L.; Lin, J.K. Propolin H from taiwanese propolis induces G1 arrest in human lung carcinoma cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 5289–5298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.J.; Chen, M.L.; Xuan, H.Z.; Hu, F.L. Effects of encapsulated propolis on blood glycemic control, lipid metabolism, and insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes mellitus rats. J. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 2012, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, G.I.; Polonsky, K.S. Diabetes mellitus and genetically programmed defects in beta-cell function. Nature 2001, 414, 788–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tangvarasittichai, S. Oxidative stress, insulin resistance, dyslipidemia and type 2 diabetes mellitus. World J. Diabetes 2015, 6, 456–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, F.C.; Lee, C.L.; Chai, C.Y.; Chen, W.T.; Lu, Y.C.; Wu, C.S. Oral administration of lactobacillus reuteri gmnl-263 improves insulin resistance and ameliorates hepatic steatosis in high fructose-fed rats. Nutr. Metab. 2013, 10, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.H.; Chen, Y.H.; Cheng, K.C.; Chien, T.Y.; Chan, C.H.; Tsao, S.P.; Huang, H.Y. Antiobesity effect of lactobacillus reuteri 263 associated with energy metabolism remodeling of white adipose tissue in high-energy-diet-fed rats. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2017, 54, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabu, M.C.; Smitha, K.; Ramadasan, K. Anti-diabetic activity of green tea polyphenols and their role in reducing oxidative stress in experimental diabetes. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2002, 83, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sathishsekar, D.; Subramanian, S. Antioxidant properties of momordica charantia (bitter gourd) seeds on streptozotocin induced diabetic rats. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 14, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kumazawa, S.; Ueda, R.; Hamasaka, T.; Fukumoto, S.; Fujimoto, T.; Nakayama, T. Antioxidant prenylated flavonoids from propolis collected in okinawa, Japan. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 7722–7725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akash, M.S.H.; Rehman, K.; Chen, S.Q. Role of inflammatory mechanisms in pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Cell. Biochem. 2013, 114, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boden, G.; Shulman, G.I. Free fatty acids in obesity and type 2 diabetes: Defining their role in the development of insulin resistance and beta-cell dysfunction. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 32 (Suppl. S3), 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kersten, S. Integrated physiology and systems biology of PPARalpha. Mol. Metab. 2014, 3, 354–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, M.E.; Marcucci, M.J.; Cline, G.W.; Bell, K.; Barucci, N.; Lee, D.; Goodyear, L.J.; Kraegen, E.W.; White, M.F.; Shulman, G.I. Free fatty acid-induced insulin resistance is associated with activation of protein kinase c theta and alterations in the insulin signaling cascade. Diabetes 1999, 48, 1270–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiomi, Y.; Yamauchi, T.; Iwabu, M.; Okada-Iwabu, M.; Nakayama, R.; Orikawa, Y.; Yoshioka, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Ueki, K.; Kadowaki, T. A novel peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)alpha agonist and PPARgamma antagonist, Z-551, ameliorates high-fat diet-induced obesity and metabolic disorders in mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 14567–14581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, S.Y.; He, H.; Nguyen, T.; Mennone, A.; Boyer, J.L. Retinoic acid represses CYP7A1 expression in human hepatocytes and hepg2 cells by FXR/RXR-dependent and independent mechanisms. J. Lipid Res. 2010, 51, 2265–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quang, T.H.; Ngan, N.T.; Minh, C.V.; Kiem, P.V.; Tai, B.H.; Nhiem, N.X.; Thao, N.P.; Luyen, B.T.; Yang, S.Y.; Kim, Y.H. Anti-inflammatory and PPAR transactivational properties of flavonoids from the roots of sophora flavescens. Phytother. Res. 2013, 27, 1300–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Bei, W.; Hu, Y.; Tang, C.; He, W.; Liu, X.; Huang, L.; Cao, Y.; Hu, X.; Zhong, X.; et al. A new tcm formula ftz lowers serum cholesterol by regulating HMG-CoA reductase and CYP7A1 in hyperlipidemic rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 135, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.Q.; Ding, J.; Zhao, H.; Liu, C.M. Puerarin attenuates carbon tetrachloride-induced liver oxidative stress and hyperlipidaemia in mouse by JNK/c-jun/CYP7A1 pathway. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2014, 115, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koya-Miyata, S.; Arai, N.; Mizote, A.; Taniguchi, Y.; Ushio, S.; Iwaki, K.; Fukuda, S. Propolis prevents diet-induced hyperlipidemia and mitigates weight gain in diet-induced obesity in mice. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2009, 32, 2022–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppari, R.; Bjorbaek, C. Leptin revisited: Its mechanism of action and potential for treating diabetes. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2012, 11, 692–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasler, C.M. Functional foods: Their role in disease prevention and health promotion. Food Technol. 1998, 52, 63–70. [Google Scholar]
| Parameter | C | DM | 1X | 5X |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BW gain (g)/rat | 195.5 ± 12.8 | 174.0 ± 12.1 *,a | 190.4 ± 11.6 b | 196.6 ± 8.5 b |
| Food intake (Kcal)/day/rat | 98.3 ± 1.6 | 119.4 ± 1.8 *,a | 118.9 ± 1.8 a | 118.9 ± 1.7 a |
| FCE (%) | 3.16 ± 0.06 | 2.22 ± 0.04 *,a | 2.45 ± 0.05 b | 2.53 ± 0.03 b |
| Water intake w0 | 34.8 ± 1.1 | 32.8 ± 0.8 a | 33.6 ± 1.0 a | 34.2 ± 1.0 a |
| Water intake w8 | 34.3 ± 0.7 | 146.2 ± 4.3 *,c | 104.3 ± 3.1 b | 65.4 ± 2.7 a |
| Parameter | C | DM | 1X | 5X |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FBG (mg/dL) | 89.2 ± 1.5 | 415.3 ± 50.3 *,c | 214.2 ± 19.0 b | 144.2 ± 8.1 a |
| FBI (μg/L) | 1.02 ± 0.01 | 0.41 ± 0.11 *,a | 1.53 ± 0.22 b | 1.52 ± 0.09 b |
| HbA1c (%) | 4.33 ± 0.07 | 8.51 ± 0.27 *,c | 6.91 ± 0.44 b | 5.49 ± 0.26 a |
| TC | 62.4 ± 2.07 | 85.4 ± 3.91 *,b | 75.7 ± 3.90 b | 64.0 ± 4.43 a |
| TG | 46.0 ± 2.36 | 132.1 ± 3.06 *,c | 72.9 ± 3.19 b | 51.2 ± 0.69 a |
| HDL | 28.0 ± 0.34 | 15.3 ± 0.14 *,a | 17.2 ± 0.20 b | 22.2 ± 0.39 c |
| LDL | 4.1 ± 0.15 | 8.4 ± 0.16 *,c | 7.8 ± 0.30 b | 5.3 ± 0.19 a |
| ISI W5 | −4.4 ± 0.1 | −6.4 ± 0.2 *,a | −5.9 ± 0.2 b | −5.4 ± 0.1 c |
| HOMA-IR W5 | 5.05 ± 0.28 | 37.59 ± 7.18 *,c | 21.66 ± 5.18 b | 13.36 ± 1.84 a |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, L.-H.; Chien, Y.-W.; Chang, M.-L.; Hou, C.-C.; Chan, C.-H.; Tang, H.-W.; Huang, H.-Y. Taiwanese Green Propolis Ethanol Extract Delays the Progression of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Rats Treated with Streptozotocin/High-Fat Diet. Nutrients 2018, 10, 503. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10040503
Chen L-H, Chien Y-W, Chang M-L, Hou C-C, Chan C-H, Tang H-W, Huang H-Y. Taiwanese Green Propolis Ethanol Extract Delays the Progression of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Rats Treated with Streptozotocin/High-Fat Diet. Nutrients. 2018; 10(4):503. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10040503
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Li-Han, Yi-Wen Chien, Mei-Ling Chang, Chia-Chung Hou, Ching-Hung Chan, Hung-Wei Tang, and Hui-Yu Huang. 2018. "Taiwanese Green Propolis Ethanol Extract Delays the Progression of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Rats Treated with Streptozotocin/High-Fat Diet" Nutrients 10, no. 4: 503. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10040503
APA StyleChen, L.-H., Chien, Y.-W., Chang, M.-L., Hou, C.-C., Chan, C.-H., Tang, H.-W., & Huang, H.-Y. (2018). Taiwanese Green Propolis Ethanol Extract Delays the Progression of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Rats Treated with Streptozotocin/High-Fat Diet. Nutrients, 10(4), 503. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10040503







