Association of Sports Participation and Diet with Motor Competence in Austrian Middle School Students
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Office of the Surgeon General (US and National Institutes of Health). The Surgeon General’s Call to Action to Prevent and Decrease Overweight and Obesity; USDHHS, Office of the Surgeon General: Rockville, MD, USA, 2001.
- Resnick, M.D.; Catalano, R.F.; Sawyer, S.M.; Viner, R.; Patton, G.C. Seizing the opportunities of adolescent health. Lancet 2012, 379, 1564–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawyer, S.M.; Afifi, R.A.; Bearinger, L.H.; Blakemore, S.J.; Dick, B.; Ezeh, A.C.; Patton, G.C. Adolescence: A foundation for future health. Lancet 2012, 379, 1630–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Department of Health and Human Services. Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans, 2nd ed.; US Department of Health and Human Services: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. Available online: https://health.gov/paguidelines/second-edition/pdf/Physical_Activity_Guidelines_2nd_edition.pdf (accessed on 14 November 2018).
- Institute of Medicine. Nutrition Standards for Foods in Schools: Leading the Way Toward Healthier Youth; The National Academic Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser-Jovy, S.; Scheu, A.; Greier, K. Media use, sports activities, and motor fitness in childhood and adolescence. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2017, 129, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biddle, S.J.; Marshall, S.J.; Gorely, T.; Cameron, N. Temporal and environmental patterns of sedentary and active behaviors during adolescents’ leisure time. Int. J. Behav. Med. 2009, 16, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathers, M.; Canterford, L.; Olds, T.; Hesketh, K.; Ridley, K.; Wake, M. Electronic media use and adolescent health and well-being: Cross-sectional community study. Acad. Pediatr. 2009, 9, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mensink, G.B.; Kleiser, C.; Richter, A. [Food consumption of children and adolescents in Germany. Results of the German Health Interview and Examination Survey for Children and Adolescents (KiGGS)]. Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz 2007, 50, 609–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krebs-Smith, S.M.; Guenther, P.M.; Subar, A.F.; Kirkpatrick, S.I.; Dodd, K.W. Americans do not meet federal dietary recommendations. J. Nutr. 2010, 140, 1832–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, L.L.; Barnett, L.; Espinel, P.; Okely, A.D. Thirteen-year trends in child and adolescent fundamental movement skills: 1997–2010. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2013, 45, 1965–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomkinson, G.R.; Olds, T.S. Secular changes in pediatric aerobic fitness test performance: The global picture. Med. Sport Sci. 2007, 50, 46–66. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lubans, D.R.; Morgan, P.J.; Cliff, D.P.; Barnett, L.M.; Okely, A.D. Fundamental movement skills in children and adolescents: Review of associated health benefits. Sports Med. 2010, 40, 1019–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holfelder, B.; Schott, N. Relationship of fundamental movement skills in physical activity in children and adolescents: A systematic review. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 2014, 15, 382–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geidne, S.; Quennerstedt, M.; Eriksson, C. The youth sports club as a health-promoting setting: An integrative review of research. Scand. J. Public Health 2013, 41, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badura, P.; Geckova, A.M.; Sigmundova, D.; van Dijk, J.P.; Reijneveld, S.A. When children play, they feel better: Organized activity participation and health in adolescents. BMC Public Health 2015, 15, 1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, L.L.; O’Hara, B.J.; Rogers, K.; St George, A.; Bauman, A. Contribution of organized and nonorganized activity to children’s motor skills and fitness. J. Sch. Health 2014, 84, 690–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallal, P.C.; Wells, J.C.; Reichert, F.F.; Anselmi, L.; Victora, C.G. Early determinants of physical activity in adolescence: Prospective birth cohort study. BMJ 2006, 332, 1002–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azevedo, M.R.; Araújo, C.L.; Cozzensa da Silva, M.; Hallal, P.C. Tracking of physical activity from adolescence to adulthood: A population-based study. Rev. Saude Publica 2007, 41, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokko, S.; Martin, L.; Geidne, S.; Van Hoye, A.; Lane, A.; Meganck, J.; Scheerder, J.; Seghers, J.; Villberg, J.; Kudlacek, M.; et al. Does sports club participation contribute to physical activity among children and adolescents? A comparison across six European countries. Scand. J. Public Health 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebert, J.J.; Møller, N.C.; Andersen, L.B.; Wedderkopp, N. Organized Sport Participation Is Associated with Higher Levels of Overall Health-Related Physical Activity in Children (CHAMPS Study-DK). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mäkelä, K.; Kokko, S.; Kannas, L.; Villberg, J.; Vasankari, T.; Heinonen, O.; Savonen, K.; Alanko, L.; Korpelainen, R.; Selänne, H.; et al. Physical activity, screen time, and sleep among youth participating and non-participating in organized sports—The Finnish health promoting Sports Club (FHPSC) Study. Adv. Phys. Educ. 2016, 6, 378–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, A.; Ekelund, U.; Sardinha, L. Associations between organized sports participation and objectively measured physical activity, sedentary time and weight status in youth. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2016, 19, 154–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hands, B. Changes in motor skill and fitness measures among children with high and low motor competence: A five-year longitudinal study. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2008, 11, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega, F.B.; Ruiz, J.R.; Castillo, M.J.; Sjöström, M. Physical fitness in childhood and adolescence: A powerful marker of health. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eime, R.M.; Young, J.A.; Harvey, J.T.; Charity, M.J.; Payne, W.R. A systematic review of the psychological and social benefits of participation in sport for adults: Informing development of a conceptual model of health through sport. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2013, 10, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badura, P.; Sigmund, E.; Geckova, A.M.; Sigmundova, D.; Sirucek, J.; van Dijk, J.P.; Reijneveld, S.A. Is Participation in Organized Leisure-Time Activities Associated with School Performance in Adolescence? PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, D. Actively closing the gap? Social class, organized activities, and academic achievement in high school. Youth Soc. 2015, 47, 267–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voráčová, J.; Badura, P.; Hamrik, Z.; Holubčíková, J.; Sigmund, E. Unhealthy eating habits and participation in organized leisure-time activities in Czech adolescents. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2018, 177, 1505–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, L.A.; Rodríguez, G. Dietary risk factors for development of childhood obesity. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2007, 10, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahoz-García, N.; García-Hermoso, A.; Milla-Tobarra, M.; Díez-Fernández, A.; Soriano-Cano, A.; Martínez-Vizcaíno, V. Cardiorespiratory Fitness as a Mediator of the Influence of Diet on Obesity in Children. Nutrients 2018, 10, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuenca-García, M.; Ortega, F.B.; Huybrechts, I.; Ruiz, J.R.; González-Gross, M.; Ottevaere, C.; Sjöström, M.; Dìaz, L.E.; Ciarapica, D.; Molnar, D.; et al. Cardiorespiratory fitness and dietary intake in European adolescents: The Healthy Lifestyle in Europe by Nutrition in Adolescence study. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 107, 1850–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaqout, M.; Vyncke, K.; Moreno, L.A.; De Miguel-Etayo, P.; Lauria, F.; Molnar, D.; Lissner, L.; Hunsberger, M.; Veidebaum, T.; Tornaritis, M.; et al. Determinant factors of physical fitness in European children. Int. J. Public Health 2016, 61, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howe, A.S.; Skidmore, P.M.; Parnell, W.R.; Wong, J.E.; Lubransky, A.C.; Black, K.E. Cardiorespiratory fitness is positively associated with a healthy dietary pattern in New Zealand adolescents. Public Health Nutr. 2016, 19, 1279–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeedi, P.; Black, K.E.; Haszard, J.J.; Skeaff, S.; Stoner, L.; Davidson, B.; Harrex, H.A.L.; Meredith-Jones, K.; Quigg, R.; Wong, J.E.; et al. Dietary Patterns, Cardiorespiratory and Muscular Fitness in 9⁻11-Year-Old Children from Dunedin, New Zealand. Nutrients 2018, 10, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drenowatz, C. A focus on motor competence as alternative strategy for weight management. J. Obes. Chron. Dis. 2017, 1, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kromeyer-Hauschild, K.; Wabitsch, M.; Kunze, D.; Geller, F.; Geiß, H.; Hesse, V.; von Hippel, A.; Jaeger, U.; Johnson, D.; Korte, W.; et al. Perzentile für den Body-mass-Index für das Kindes- und Jugendalter unter Heranziehung verschiedener deutscher Stichproben. Monatsschrift Kinderheilkunde 2001, 149, 807–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bös, K.; Schlenker, L.; Büsch, D.; Lämmle, L.; Müller, H.; Oberger, J.; Seidl, I.; Tittlbach, S. Deutscher Motorik-Test 6-18 (DMT6-18) [German Motor Abilities Test 6-18 (DMT6-18)]; Czwalina: Hamburg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Greier, K.; Ruedl, G.; Weber, C.; Thöni, G.; Riechelmann, H. Ernährungsverhalten und motorische Leistungsfähigkeit von 10- bis 14-jährigen Jugendlichen. Ernährung Medizin 2016, 31, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Hondt, E.; Deforche, B.; Gentier, I.; De Bourdeaudhuij, I.; Vaeyens, R.; Philippaerts, R.; Lenoir, M. A longitudinal analysis of gross motor coordination in overweight and obese children versus normal-weight peers. Int. J. Obes. 2013, 37, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandorpe, B.; Vandendriessche, J.; Vaeyens, R.; Pion, J.; Matthys, S.; Lefevre, J.; Philippaerts, R.; Lenoir, M. Relationship between sports participation and the level of motor coordination in childhood: A longitudinal approach. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2012, 15, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okely, A.D.; Booth, M.L.; Patterson, J.W. Relationship of physical activity to fundamental movement skills among adolescents. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2001, 33, 1899–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaakkola, T.; Kalaja, S.; Liukkonen, J.; Jutila, A.; Virtanen, P.; Watt, A. Relations among physical activity patterns, lifestyle activities, and fundamental movement skills for Finnish students in grade 7. Percept. Mot. Skills 2009, 108, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, C.; Queiroz, D.; Silva, J.; Feitoza, A.; Cattuzzo, M. Relationship between organized physical activity and motor competence in teenagers. Am. J. Sport Sci. Med. 2017, 5, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fransen, J.; Deprez, D.; Pion, J.; Tallir, I.B.; D’Hondt, E.; Vaeyens, R.; Lenoir, M.; Philippaerts, R.M. Changes in physical fitness and sports participation among children with different levels of motor competence: A 2-year longitudinal study. Pediatr. Exerc. Sci. 2014, 26, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stodden, D.; Goodway, J.; Langendorfer, S.; Roberton, M.; Rudisill, M.; Garcia, C.; Garcia, L. A developmental perspective on the role of motor skill competence in physical activity: An emergent relationshihp. Quest 2008, 60, 290–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drenowatz, C.; Greier, K. Cross-sectional and longitudinal assocaition between club sports participation, media consumption and motor competence in adolescents. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2019, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Khodaverdi, Z.; Bahram, A.; Stodden, D.; Kazemnejad, A. The relationship between actual motor competence and physical activity in children: Mediating roles of perceived motor competence and health-related physical fitness. J. Sports Sci. 2016, 34, 1523–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torstveit, M.K.; Johansen, B.T.; Haugland, S.H.; Stea, T.H. Participation in organized sports is associated with decreased likelihood of unhealthy lifestyle habits in adolescents. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2018, 28, 2384–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taliaferro, L.A.; Rienzo, B.A.; Donovan, K.A. Relationships between youth sport participation and selected health risk behaviors from 1999 to 2007. J. Sch. Health 2010, 80, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dortch, K.S.; Gay, J.; Springer, A.; Kohl, H.W.; Sharma, S.; Saxton, D.; Wilson, K.; Hoelscher, D. The association between sport participation and dietary behaviors among fourth graders in the school physical activity and nutrition survey, 2009–2010. Am. J. Health Promot. 2014, 29, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, T.F.; Stovitz, S.D.; Thomas, M.; LaVoi, N.M.; Bauer, K.W.; Neumark-Sztainer, D. Do youth sports prevent pediatric obesity? A systematic review and commentary. Curr. Sports Med. Rep. 2011, 10, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vella, S.A.; Cliff, D.P.; Okely, A.D.; Scully, M.L.; Morley, B.C. Associations between sports participation, adiposity and obesity-related health behaviors in Australian adolescents. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2013, 10, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, K.W.; Larson, N.I.; Nelson, M.C.; Story, M.; Neumark-Sztainer, D. Socio-environmental, personal and behavioural predictors of fast-food intake among adolescents. Public Health Nutr. 2009, 12, 1767–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arriscado, D.; Muros, J.J.; Zabala, M.; Dalmau, J.M. Factors associated with low adherence to a Mediterranean diet in healthy children in northern Spain. Appetite 2014, 80, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greier, K.; Drenowatz, C. Bidirectional association between weight status and motor skills in adolescents: A 4-year longitudinal study. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2018, 130, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kremers, S.P.; van der Horst, K.; Brug, J. Adolescent screen-viewing behaviour is associated with consumption of sugar-sweetened beverages: The role of habit strength and perceived parental norms. Appetite 2007, 48, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utter, J.; Scragg, R.; Schaaf, D. Associations between television viewing and consumption of commonly advertised foods among New Zealand children and young adolescents. Public Health Nutr. 2006, 9, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mota, J.; Ribeiro, J.C.; Carvalho, J.; Santos, M.P.; Martins, J. Television viewing and changes in body mass index and cardiorespiratory fitness over a two-year period in schoolchildren. Pediatr. Exerc. Sci. 2010, 22, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Must, A.; Tybor, D.J. Physical activity and sedentary behavior: A review of longitudinal studies of weight and adiposity in youth. Int. J. Obes. 2005, 29 (Suppl. S2), S84–S96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leek, D.; Carlson, J.A.; Cain, K.L.; Henrichon, S.; Rosenberg, D.; Patrick, K.; Sallis, J.F. Physical activity during youth sports practices. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 2011, 165, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickel, E.E.; Eisenmann, J.C. Contribution of youth sport to total daily physical activity among 6- to 12-yr-old boys. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2007, 39, 1493–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stallmann-Jorgensen, I.S.; Gutin, B.; Hatfield-Laube, J.L.; Humphries, M.C.; Johnson, M.H.; Barbeau, P. General and visceral adiposity in black and white adolescents and their relation with reported physical activity and diet. Int. J. Obes. 2007, 31, 622–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Telford, R.D.; Cunningham, R.B.; Telford, R.M.; Riley, M.; Abhayaratna, W.P. Determinants of childhood adiposity: Evidence from the Australian LOOK study. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGloin, A.F.; Livingstone, M.B.; Greene, L.C.; Webb, S.E.; Gibson, J.M.; Jebb, S.A.; Cole, T.J.; Coward, W.A.; Wright, A.; Prentice, A.M. Energy and fat intake in obese and lean children at varying risk of obesity. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2002, 26, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, S.A.; Truby, H.; Lee, A.; Harper, C.; Abbott, R.A.; Davies, P.S. Associations of body mass index and waist circumference with: Energy intake and percentage energy from macronutrients, in a cohort of Australian children. Nutr. J. 2011, 10, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skinner, A.C.; Steiner, M.J.; Perrin, E.M. Self-reported energy intake by age in overweight and healthy-weight children in NHANES, 2001–2008. Pediatrics 2012, 130, e936–e942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
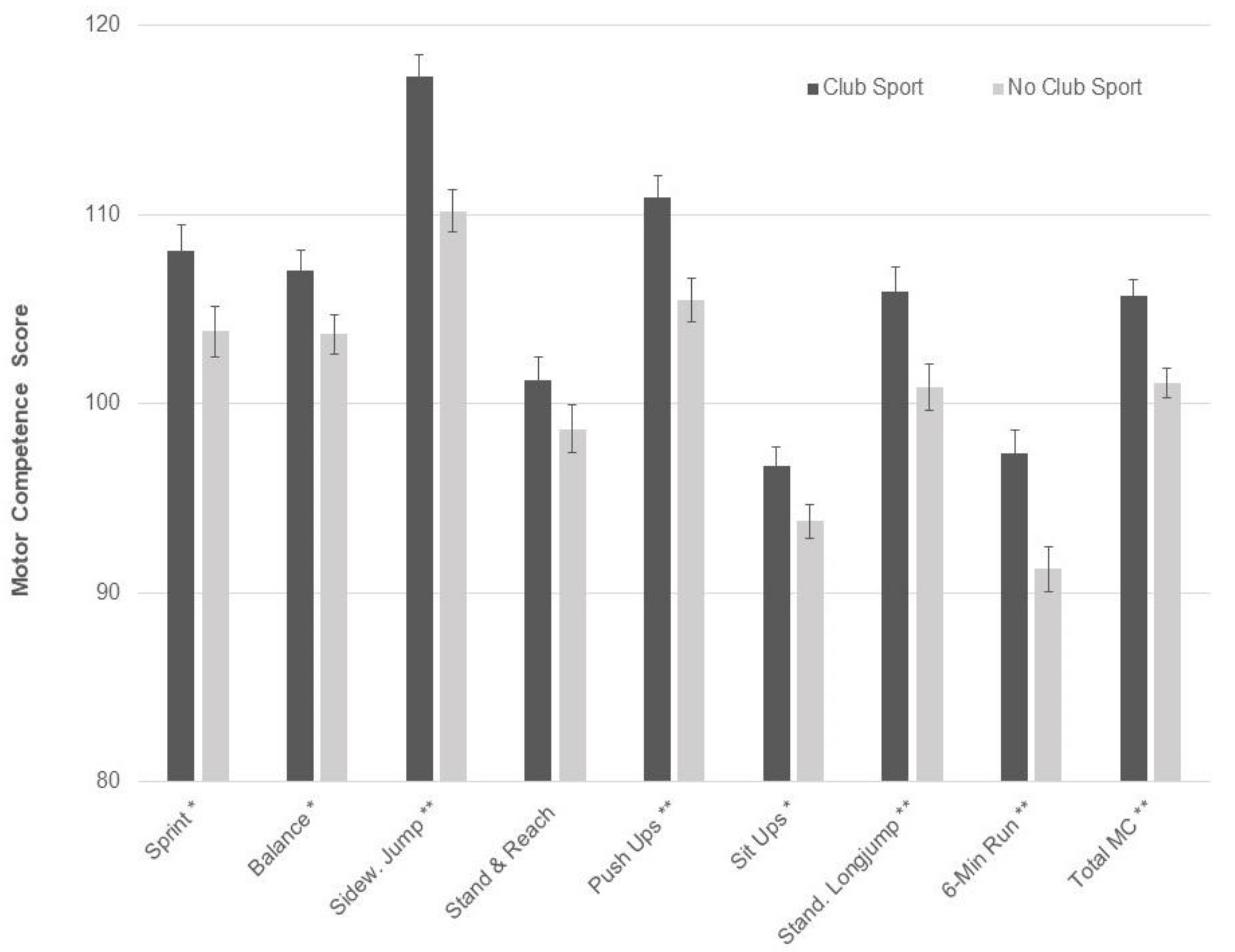
| Total Sample (N = 165) | Girls (N = 74) | Boys (N = 91) | p * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 12.9 ± 1.2 | 12.6 ± 1.1 | 13.1 ± 1.2 | 0.009 |
| Height (cm) | 161.3 ± 8.9 | 158.8 ± 6.8 | 163.4 ± 9.9 | 0.001 |
| Weight (kg) | 53.8 ± 14.3 | 51.3 ± 9.9 | 55.9 ± 16.9 | 0.043 |
| BMI percentile | 59.4 ± 29.4 | 60.9 ± 27.5 | 58.2 ± 31.0 | 0.563 |
| 20 m sprint (sec) | 3.8 ± 0.4 | 3.9 ± 0.4 | 3.7 ± 0.4 | 0.023 |
| Balance (steps) | 38.2 ± 9.1 | 39.5 ± 7.5 | 37.2 ± 10.2 | 0.755 |
| Sideways jump (# in 15 s) | 42.1 ± 7.5 | 41.4 ± 7.0 | 42.6 ± 7.9 | 0.554 |
| Stand and reach (cm) | −0.3 ± 9.7 | 3.8 ± 8.5 | −3.6 ± 9.3 | 0.011 |
| Push-ups (# in 40 s) | 15.6 ± 3.9 | 15.6 ± 3.4 | 15.6 ± 4.2 | 0.067 |
| Sit ups (# in 40 s) | 23.9 ± 4.6 | 22.4 ± 3.8 | 25.1 ± 4.9 | 0.011 |
| Standing long jump (cm) | 171.0 ± 29.7 | 159.5 ± 25.2 | 180.3 ± 29.8 | 0.648 |
| 6 min run (m) | 997 ± 157 | 988 ± 119 | 1005 ± 183 | <0.001 |
| Total motor competence | 103.3 ± 7.7 | 104.6 ± 6.9 | 102.3 ± 8.1 | 0.056 |
| Total Sample | Girls | Boys | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Meat | 2.5 ± 1.2 | 2.1 ± 1.1 | 2.7 ± 1.2 | 0.002 |
| Fish & Eggs | 1.8 ± 1.2 | 1.6 ± 1.0 | 2.0 ± 1.3 | 0.051 |
| Milk | 2.2 ± 1.0 | 2.2 ± 1.1 | 2.3 ± 1.0 | 0.458 |
| Carbs | 2.2 ± 1.1 | 2.2 ± 1.0 | 2.2 ± 1.1 | 0.702 |
| Bread | 3.2 ± 0.9 | 3.3 ± 0.8 | 3.1 ± 1.0 | 0.371 |
| Nuts & Seeds | 1.2 ± 0.9 | 1.2 ± 1.0 | 1.2 ± 0.9 | 0.662 |
| Fast Food | 1.6 ± 0.9 | 1.5 ± 0.8 | 1.7 ± 0.9 | 0.105 |
| Sweets | 2.6 ± 1.1 | 2.5 ± 1.1 | 2.7 ± 1.2 | 0.420 |
| Fruits | 2.7 ± 1.2 | 2.9 ± 1.3 | 2.6 ± 1.1 | 0.044 |
| Veggie | 2.5 ± 1.5 | 2.9 ± 1.6 | 2.2 ± 1.4 | 0.003 |
| Soft Drink | 2.3 ± 1.3 | 2.0 ± 1.1 | 2.6 ± 1.3 | 0.001 |
| Water | 4.4 ± 1.6 | 4.6 ± 1.7 | 4.2 ± 1.5 | 0.126 |
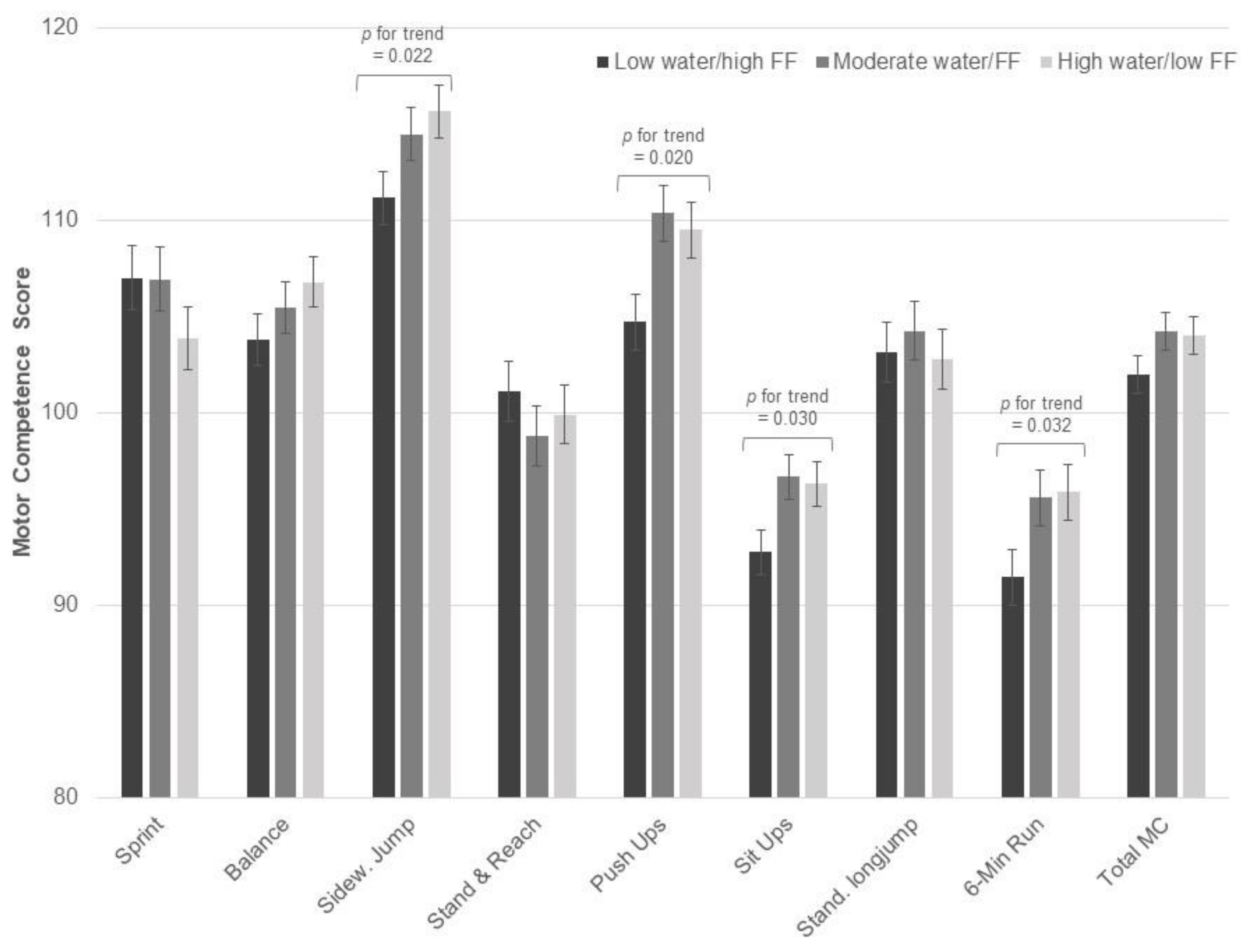
| Low Milk/Cereal | Moderate Milk/Cereal | High Milk/Cereal | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Club Sports | No Club Sports | Club Sports | No Club Sports | Club Sports | No Club Sports | |
| 20 m sprint 1 | 108.9 ± 13.0 | 107.5 ± 9.5 | 106.9 ± 10.7 | 103.8 ± 14.1 | 108.1 ± 12.5 | 99.5 ± 13.0 |
| Balance 1,3,* | 104.6 ± 9.6 | 107.6 ± 8.2 | 107.8 ± 8.8 | 99.4 ± 10.2 | 108.4 ± 9.8 | 103.6 ± 11.1 |
| Sideways jump 1,* | 118.0 ± 6.9 | 111.6 ± 9.7 | 116.7 ± 7.9 | 111.7 ± 12.6 | 117.6 ± 7.9 | 110.1 ± 12.3 |
| Stand and reach | 101.5 ± 12.1 | 102.0 ± 9.3 | 101.9 ± 12.0 | 97.8 ± 12.3 | 100.3 ± 11.8 | 98.7 ± 11.1 |
| Push-ups 1,* | 111.2 ± 9.6 | 109.1 ± 7.9 | 110.1 ± 11.5 | 104.3 ± 13.3 | 111.5 ± 10.8 | 102.2 ± 10.9 |
| Sit ups 1 | 97.3 ± 8.7 | 96.9 ± 7.7 | 96.0 ± 9.2 | 92.1 ± 10.4 | 97.0 ± 7.4 | 91.8 ± 7.5 |
| Standing long jump 1,*,2 | 107.2 ± 9.2 | 104.2 ± 9.2 | 105.5 ± 12.6 | 100.6 ± 13.7 | 105.1 ± 11.0 | 97.4 ± 11.7 |
| 6 min run 1,* | 97.0 ± 10.1 | 94.1 ± 11.4 | 98.3 ± 9.1 | 89.3 ± 12.2 | 97.0 ± 9.6 | 89.8 ± 11.6 |
| Total motor competence† 1,*,2 | 105.8 ± 6.4 | 104.2 ± 5.8 | 105.5 ± 6.3 | 100.0 ± 9.4 | 105.8 ± 7.1 | 98.4 ± 7.5 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Drenowatz, C.; Greier, K. Association of Sports Participation and Diet with Motor Competence in Austrian Middle School Students. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1837. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10121837
Drenowatz C, Greier K. Association of Sports Participation and Diet with Motor Competence in Austrian Middle School Students. Nutrients. 2018; 10(12):1837. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10121837
Chicago/Turabian StyleDrenowatz, Clemens, and Klaus Greier. 2018. "Association of Sports Participation and Diet with Motor Competence in Austrian Middle School Students" Nutrients 10, no. 12: 1837. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10121837
APA StyleDrenowatz, C., & Greier, K. (2018). Association of Sports Participation and Diet with Motor Competence in Austrian Middle School Students. Nutrients, 10(12), 1837. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10121837






