The Relationship between Generalized and Abdominal Obesity with Diabetic Kidney Disease in Type 2 Diabetes: A Multiethnic Asian Study and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Assessment of Obesity Exposures
2.3. Assessment of DKD
2.4. Assessment of Covariates
2.5. Statistical Analysis
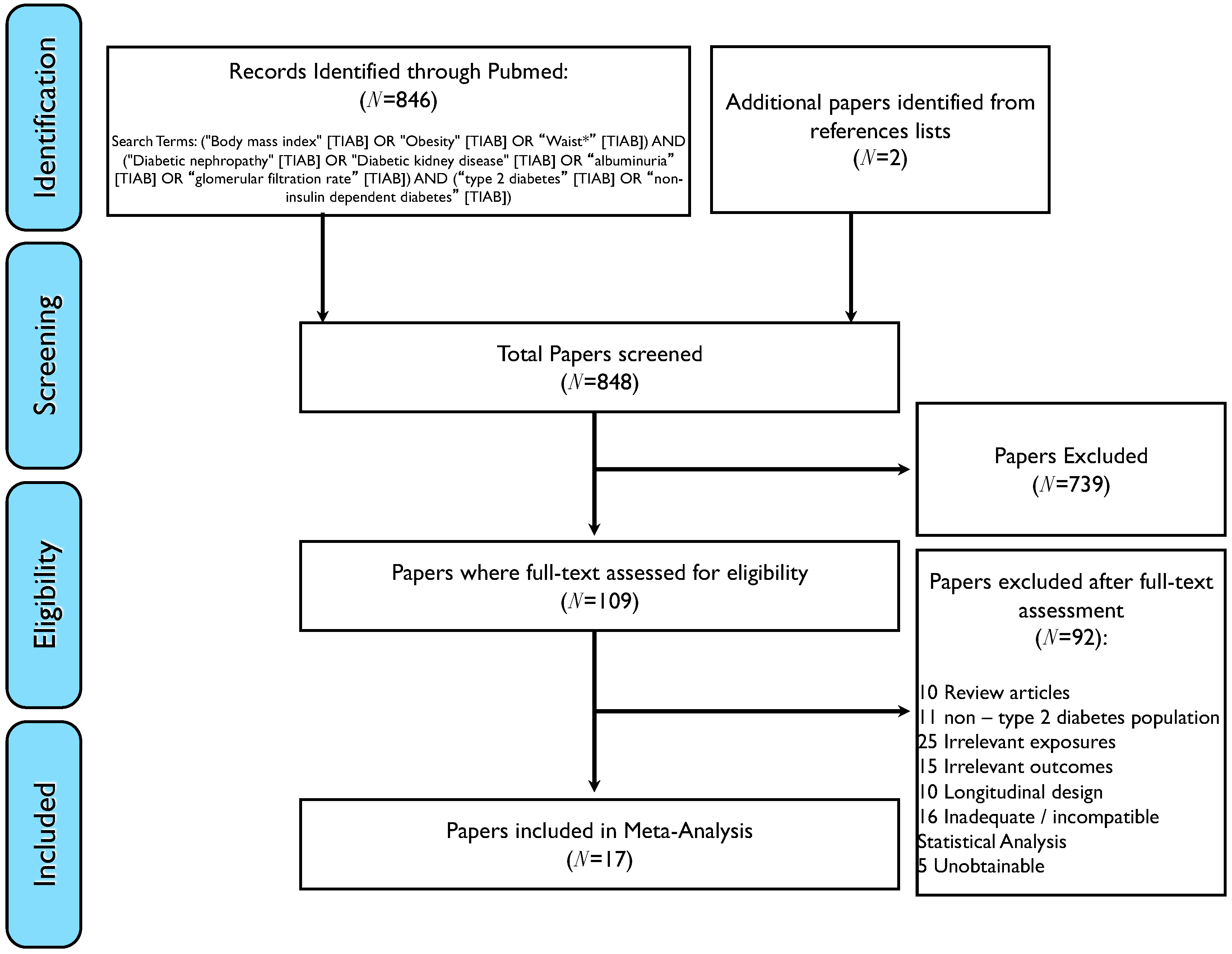
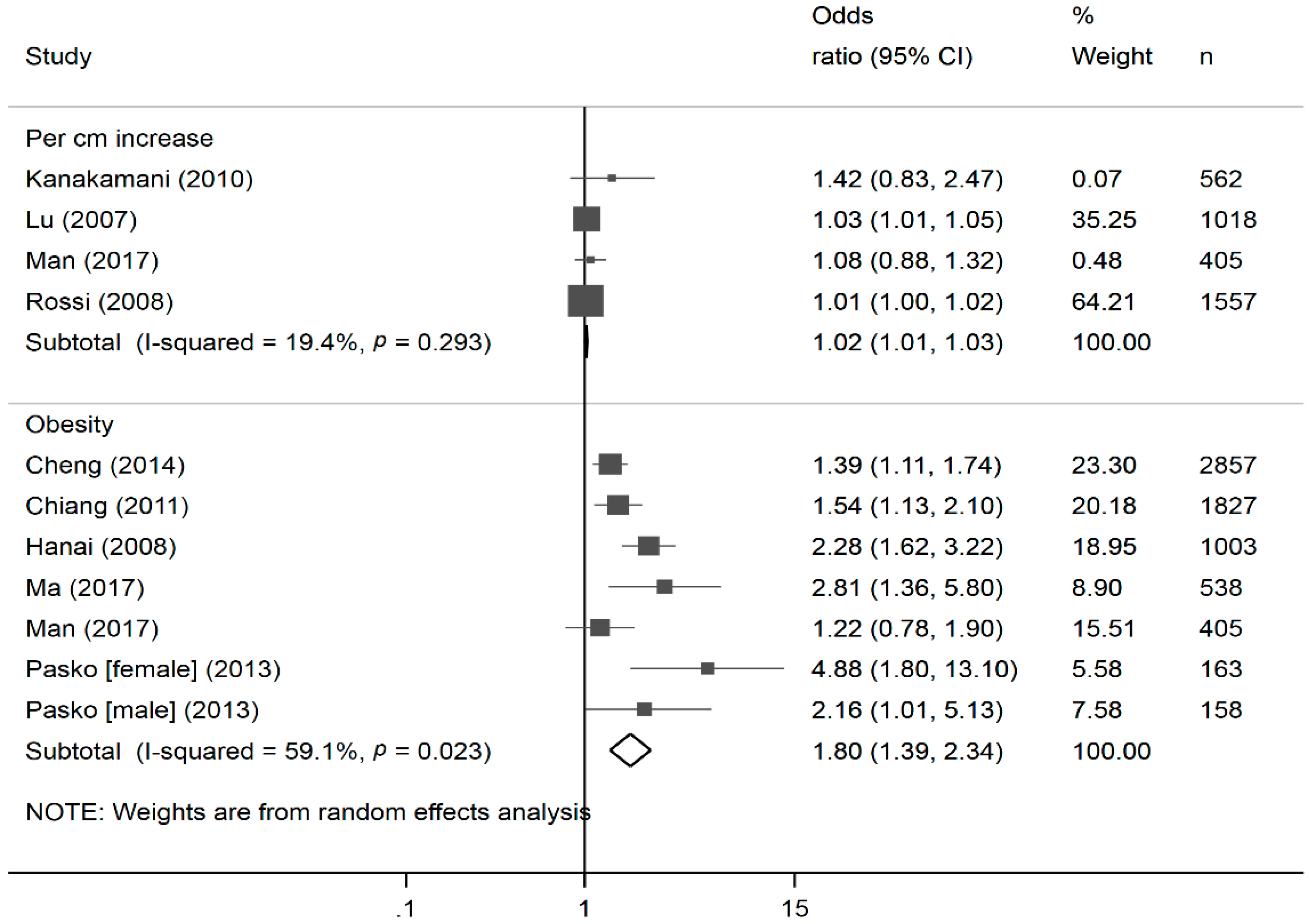
2.6. Meta-Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Macisaac, R.J.; Ekinci, E.I.; Jerums, G. Markers of and risk factors for the development and progression of diabetic kidney disease. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2014, 63, S39–S62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gheith, O.; Farouk, N.; Nampoory, N.; Halim, M.A.; Al-Otaibi, T. Diabetic kidney disease: World wide difference of prevalence and risk factors. J. Nephropharmacol. 2016, 5, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, A.J.; Foley, R.N.; Gilbertson, D.T.; Chen, S.C. United states renal data system public health surveillance of chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2015, 5, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonelli, M.; Muntner, P.; Lloyd, A.; Manns, B.J.; Klarenbach, S.; Pannu, N.; James, M.T.; Hemmelgarn, B.R.; Alberta Kidney Disease, N. Risk of coronary events in people with chronic kidney disease compared with those with diabetes: A population-level cohort study. Lancet 2012, 380, 807–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkoudah, E.; Skali, H.; Uno, H.; Solomon, S.D.; Pfeffer, M.A. Mortality rates in trials of subjects with type 2 diabetes. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2012, 1, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popkin, B.M.; Gordon-Larsen, P. The nutrition transition: Worldwide obesity dynamics and their determinants. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2004, 28, S2–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vazquez, G.; Duval, S.; Jacobs, D.R., Jr.; Silventoinen, K. Comparison of body mass index, waist circumference, and waist/hip ratio in predicting incident diabetes: A meta-analysis. Epidemiol. Rev. 2007, 29, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, N.T.; Nguyen, X.M.; Lane, J.; Wang, P. Relationship between obesity and diabetes in a us adult population: Findings from the national health and nutrition examination survey, 1999–2006. Obes. Surg. 2011, 21, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, M.L.; Dikow, R.; Ritz, E. Diabetic nephropathy: Recent insights into the pathophysiology and the progression of diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2005, 505, S50–S53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organisation. Overweight and Obesity Fact Sheet. Available online: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs311/en/. (accessed on 20 February 2018).
- Ali, A.A.; Al Lami, F.H. Prevalence and determinants of microalbuminurea among type 2 diabetes mellitus patients, baghdad, iraq, 2013. Saudi J. Kidney Dis. Transpl. 2016, 27, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belhatem, N.M.K.; Rouzet, F.; Matallah, N.; Al Baloshi, A.; Travert, F.; Velho, G.; Roussel, R.; Le Guludec, D.; Marre, M.; Hansel, B. Impact of morbid obesity on the kidney function of patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2015, 108, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Low, S.K.; Sum, C.F.; Yeoh, L.Y.; Tavintharan, S.; Ng, X.W.; Lee, S.B.; Tang, W.E.; Lim, S.C. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Ann. Acad. Med. Singap. 2015, 44, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Meguro, S.; Kabeya, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Kawai, T.; Tomita, M.; Katsuki, T.; Oikawa, Y.; Atsumi, Y.; Shimada, A.; Tanaka, M.; et al. Past obesity as well as present body weight status is a risk factor for diabetic nephropathy. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaslov, K.; Bulum, T.; Duvnjak, L. Waist-to-height ratio is independently associated with chronic kidney disease in overweight type 2 diabetic patients. Endocr. Res. 2015, 40, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Yang, S.; Zhang, A.; Yang, P.; Cao, X.; Li, X.; Goswami, R.; Wang, Y.; Luo, T.; Liao, K.; et al. Abdominal obesity is more closely associated with diabetic kidney disease than general obesity. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, e179–e180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, C.H. Waist-to-height ratio is independently and better associated with urinary albumin excretion rate than waist circumference or waist-to-hip ratio in chinese adult type 2 diabetic women but not men. Diabetes Care 2005, 28, 2249–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabbar, A.; Irfanullah, A.; Akhter, J.; Mirza, Y.K. Dyslipidemia and its relation with body mass index versus waist hip ratio. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 1997, 47, 308–310. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brown, C.D.; Higgins, M.; Donato, K.A.; Rohde, F.C.; Garrison, R.; Obarzanek, E.; Ernst, N.D.; Horan, M. Body mass index and the prevalence of hypertension and dyslipidemia. Obes. Res. 2000, 8, 605–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egbe, E.O.; Asuquo, O.A.; Ekwere, E.O.; Olufemi, F.; Ohwovoriole, A.E. Assessment of anthropometric indices among residents of calabar, south-east nigeria. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 18, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Man, R.E.; Sabanayagam, C.; Chiang, P.P.; Li, L.J.; Noonan, J.E.; Wang, J.J.; Wong, T.Y.; Cheung, G.C.; Tan, G.S.; Lamoureux, E.L. Differential association of generalized and abdominal obesity with diabetic retinopathy in asian patients with type 2 diabetes. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2016, 134, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Retnakaran, R.; Cull, C.A.; Thorne, K.I.; Adler, A.I.; Holman, R.R.; Group, U.S. Risk factors for renal dysfunction in type 2 diabetes: U.K. Prospective diabetes study 74. Diabetes 2006, 55, 1832–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laranjinha, I.; Matias, P.; Mateus, S.; Aguiar, F.; Pereira, P.; Perneta Santos, M.; Costa, R.; Lourenco, A.; Guia, J.; Barata, J.D.; et al. Diabetic kidney disease: Is there a non-albuminuric phenotype in type 2 diabetic patients? Nefrologia 2016, 36, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooke, P.; Bullock, R. Validation of a 6 item cognitive impairment test with a view to primary care usage. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 1999, 14, 936–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Waist Circumference and Waist-Hip Ratio: Report of a WHO Expert Consultation, Geneva, 8-11 December 2008; World Health Organization: Albany, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ashwell, M.; Hsieh, S.D. Six reasons why the waist-to-height ratio is a rapid and effective global indicator for health risks of obesity and how its use could simplify the international public health message on obesity. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2005, 56, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browning, L.M.; Hsieh, S.D.; Ashwell, M. A systematic review of waist-to-height ratio as a screening tool for the prediction of cardiovascular disease and diabetes: 0.5 could be a suitable global boundary value. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2010, 23, 247–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levey, A.S.; Stevens, L.A.; Schmid, C.H.; Zhang, Y.L.; Castro, A.F., 3rd; Feldman, H.I.; Kusek, J.W.; Eggers, P.; Van Lente, F.; Greene, T.; et al. A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 150, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kdoqi. Kdoqi clinical practice guidelines and clinical practice recommendations for diabetes and chronic kidney disease. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2007, 49, S12–S154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabanayagam, C.; Wong, T.Y.; Tai, E.S. The ckd-epi equation and mdrd study equation find similar prevalence of chronic kidney disease in asian populations. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 151, 892–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teo, B.W.; Xu, H.; Wang, D.; Li, J.; Sinha, A.K.; Shuter, B.; Sethi, S.; Lee, E.J. Gfr estimating equations in a multiethnic asian population. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2011, 58, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, C.P.; Tan, C.H.; Jacob, E. Haemoglobin a1c: Evaluation of a new hba1c point-of-care analyser bio-rad in2it in comparison with the dca 2000 and central laboratory analysers. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2009, 46, 373–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Ding, L.; Huang, X.; Chen, Y.; Sun, W.; Lin, L.; Huang, Y.; Wang, P.; Peng, K.; Lu, J.; et al. Abdominal adiposity contributes to adverse glycemic control and albuminuria in chinese type 2 diabetic patients: A cross-sectional study. J. Diabetes 2017, 9, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borenstein, M.; Hedges, L.V.; Higgins, J.P.; Rothstein, H.R. Introduction to Meta-Analysis; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hedges, L.V.; Tipton, E.; Johnson, M.C. Robust variance estimation in meta-regression with dependent effect size estimates. Res. Synth. Methods 2010, 1, 39–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tipton, E. Small sample adjustments for robust variance estimation with meta-regression. Psychol. Methods 2015, 20, 375–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, C.M.; Hyun, Y.Y.; Lee, K.B.; Kim, H. The association between underweight and the development of albuminuria is different between sexes in relatively healthy korean subjects. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2014, 29, 2106–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kao, Y.M.; Chen, J.D. Inverse association between body mass index and chronic kidney disease in older diabetic adults. Ann. Epidemiol. 2013, 23, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanakamani, J.A.; Ammini, A.C.; Gupta, N.; Dwivedi, S.N. Prevalence of microalbuminuria among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus—A hospital-based study from north india. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2010, 12, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakabe, K.; Fukui, M.; Ushigome, E.; Hamaguchi, M.; Senmaru, T.; Yamazaki, M.; Hasegawa, G.; Nakamura, N. Low daily salt intake is correlated with albuminuria in patients with type 2 diabetes. Hypertens. Res. 2012, 35, 1176–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, B.; Wen, J.; Song, X.Y.; Dong, X.H.; Yang, Y.H.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Zhao, N.Q.; Ye, H.Y.; Mou, B.; Chen, F.L.; et al. High prevalence of albuminuria in population-based patients diagnosed with type 2 diabetes in the shanghai downtown. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2007, 75, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, M.C.; Nicolucci, A.; Pellegrini, F.; Comaschi, M.; Ceriello, A.; Cucinotta, D.; Giorda, C.; Valentini, U.; Vespasiani, G.; De Cosmo, S. Identifying patients with type 2 diabetes at high risk of microalbuminuria: Results of the DEMAND (developing education on microalbuminuria for awareness of renal and cardiovascular risk in diabetes) study. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2008, 23, 1278–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.Z.; Zhang, H.; Chen, R.; Yang, F.; Li, W.; Chen, L.; Lin, S.; Liang, G.; Cai, D.; Chen, H. Cardiometabolic risk profiles associated with chronic complications in overweight and obese type 2 diabetes patients in south china. PLoS ONE 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, S.C.; Lee, J.K.; Chen, C.H.; Chuang, L.M.; Tsan, K.W.; Sheu, W.H.; Wu, D.A.; Wu, T.J.; Lin, K.C.; Juang, J.H.; et al. Justifying the high prevalence of microalbuminuria for type 2 diabetic patients in taiwan with conditional probability approach—A demand ii study. JCMA 2011, 74, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanai, K.; Babazono, T.; Iwamoto, Y. Renal manifestations of metabolic syndrome in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2008, 79, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.M.; Wang, R.; Liu, X.L.; Lu, N.; Lu, Q.; Yin, F.Z. The relationship between hypertriglyceridemic waist phenotype and early diabetic nephropathy in type 2 diabetes. Cardiorenal Med. 2017, 7, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasko, N.; Toti, F.; Strakosha, A.; Thengjilli, E.; Shehu, A.; Dedej, T.; Ylli, A.; Thereska, N. Prevalence of microalbuminuria and risk factor analysis in type 2 diabetes patients in albania: The need for accurate and early diagnosis of diabetic nephropathy. Hippokratia 2013, 17, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kramer, H.; Luke, A.; Bidani, A.; Cao, G.; Cooper, R.; McGee, D. Obesity and prevalent and incident ckd: The hypertension detection and follow-up program. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2005, 46, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Kopple, J.D. Obesity paradox in patients on maintenance dialysis. Contrib. Nephrol. 2006, 151, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Streja, E.; Kovesdy, C.P.; Oreopoulos, A.; Noori, N.; Jing, J.; Nissenson, A.R.; Krishnan, M.; Kopple, J.D.; Mehrotra, R.; et al. The obesity paradox and mortality associated with surrogates of body size and muscle mass in patients receiving hemodialysis. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2010, 85, 991–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ades, P.A.; Savage, P.D. The obesity paradox: Perception vs knowledge. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2010, 85, 112–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haarbo, J.; Gotfredsen, A.; Hassager, C.; Christiansen, C. Validation of body composition by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (dexa). Clin. Physiol. 1991, 11, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maric-Bilkan, C. Obesity and diabetic kidney disease. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2013, 97, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, M.E.; do Carmo, J.M.; da Silva, A.A.; Juncos, L.A.; Wang, Z.; Hall, J.E. Obesity, hypertension, and chronic kidney disease. Int. J. Nephrol. Renovasc. Dis. 2014, 7, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Mean (SD) or Number (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Overall (N = 405) | No DKD (N = 202) | DKD * (N = 203) | p ^ |
| Age (years) | 58.0 (7.5) | 57.0 (7.4) | 58.9 (7.5) | 0.012 |
| Gender | ||||
| Male | 277 (68.4) | 130 (64.4) | 147 (72.4) | 0.081 |
| Female | 128 (31.6) | 72 (35.6) | 56 (27.6) | |
| Race | ||||
| Chinese | 303 (74.8) | 149 (73.8) | 154 (75.9) | 0.193 |
| Malay | 35 (8.6) | 14 (6.9) | 21 (10.3) | |
| Indian | 67 (16.5) | 39 (19.3) | 28 (13.8) | |
| Total to HDL cholesterol ratio | 4.2 (1.3) | 4.0 (1.1) | 4.4 (1.4) | 0.004 |
| ACR (mg/mmoL) | 22.2 (62.8) | 1.3 (0.8) | 43.0 (83.8) | <0.001 |
| HbA1C (%) | 7.8 (1.6) | 7.5 (1.4) | 8.1 (1.6) | <0.001 |
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 136.3 (17.8) | 132.2 (16.4) | 140.5 (18.2) | <0.001 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 77.3 (9.8) | 76.4 (9.1) | 78.2 (10.5) | 0.058 |
| Diabetes duration (years) | 13.3 (9.3) | 11.1 (8.5) | 15.6 (9.5) | <0.001 |
| Insulin use | ||||
| No insulin use | 347 (85.7) | 183 (90.6) | 164 (80.8) | 0.005 |
| Insulin use | 58 (14.3) | 19 (9.4) | 39 (19.2) | |
| Presence of DR | ||||
| No | 178 (44.0) | 106 (52.5) | 72 (35.5) | 0.001 |
| Yes | 227 (56.0) | 96 (47.5) | 131 (64.5) | |
| Anti-hypertensive medication use | ||||
| No | 259 (64.0) | 137 (67.8) | 122 (60.1) | 0.106 |
| Yes | 146 (36.0) | 65 (32.2) | 81 (39.9) | |
| Generalized Obesity categories | ||||
| Normal or underweight (BMI < 25 kg/m2) | 168 (41.5) | 94 (46.5) | 74 (36.5) | 0.104 |
| Overweight (BMI 25–29.9 kg/m2) | 160 (39.5) | 71 (35.1) | 89 (43.8) | |
| Obese (BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2) | 77 (19.0) | 37 (18.3) | 40 (19.7) | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 26.5 (4.2) | 26.3 (4.3) | 26.7 (4.1) | 0.331 |
| Abdominal Obesity categories | ||||
| Normal or underweight | 127 (31.4) | 66 (32.7) | 61 (30.0) | 0.569 |
| Overweight or obese (waist circumference >90 cm for males; >80 cm for females | 278 (68.6) | 136 (67.3) | 142 (70.0) | |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 93.3 (10.6) | 92.7 (10.7) | 94.0 (10.4) | 0.206 |
| Waist-hip ratio quantiles | ||||
| Lower quantile (0.72–0.94) | 203 (50.1) | 112 (55.4) | 91 (44.8) | 0.033 |
| Upper quantile (0.95–1.13) | 202 (49.9) | 90 (44.6) | 112 (55.2) | |
| Waist-hip ratio | 0.9 (0.1) | 0.9 (0.1) | 1.0 (0.1) | 0.017 |
| Waist-height ratio quantiles | ||||
| Lower quantile (0.41–0.56) | 203 (50.1) | 109 (54.0) | 94 (46.3) | 0.123 |
| Upper quantile (0.57–0.80) | 202 (49.9) | 93 (46.0) | 109 (53.7) | |
| Waist-height ratio | 0.6 (0.1) | 0.6 (0.1) | 0.6 (0.1) | 0.168 |
| Odds Ratio (95% CI) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1 | p | Model 2 | p | ||
| Body mass index | Overweight or obese | 1.69 (1.12 to 2.55) | 0.012 | 1.59 (1.04 to 2.41) | 0.030 |
| Per SD increase | 1.20 (0.97 to 1.47) | 0.091 | 1.14 (0.93 to 1.42) | 0.213 | |
| Waist circumference | Overweight or obese | 1.62 (0.94 to 2.78) | 0.084 | 1.25 (0.70 to 2.24) | 0.457 |
| Per SD increase | 1.13 (0.93 to 1.38) | 0.228 | 1.08 (0.88 to 1.32) | 0.484 | |
| Waist-hip-ratio | Upper quantile (0.95–1.13) | 1.39 (0.92 to 2.10) | 0.114 | 1.27 (0.83 to 1.93) | 0.271 |
| Per SD increase | 1.23 (0.97 to 1.55) | 0.086 | 1.14 (0.90 to 1.45) | 0.281 | |
| Waist-height-ratio | Upper quantile (0.57–0.80) | 1.41 (0.95 to 2.10) | 0.091 | 1.28 (0.85 to 1.92) | 0.239 |
| Per SD increase | 1.18 (0.97 to 1.45) | 0.099 | 1.11 (0.91 to 1.37) | 0.304 | |
| Male | Female | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Odds Ratio (95% CI) | p | Odds Ratio (95% CI) | p | ||
| Body mass index | Overweight or obese | 1.45 (0.88 to 2.39) | 0.149 | 1.88 (0.86 to 4.13) | 0.115 |
| Per SD increase | 1.08 (0.82 to 1.42) | 0.581 | 1.23 (0.87 to 1.73) | 0.240 | |
| Waist circumference | Overweight or obese | 1.45 (0.88 to 2.37) | 0.141 | 1.69 (0.56 to 5.11) | 0.356 |
| Per SD increase | 0.71 (0.42 to 1.18) | 0.188 | 1.35 (0.91 to 1.98) | 0.133 | |
| Waist-hip-ratio | Upper quantile (0.95–1.13) | 1.12 (0.68 to 1.85) | 0.662 | 1.71 (0.78 to 3.73) | 0.181 |
| Per SD increase | 0.99 (0.70 to 1.39) | 0.932 | 1.41 (0.93 to 2.14) | 0.106 | |
| Waist-height-ratio | Upper quantile (0.57–0.80) | 1.13 (0.69 to 1.85) | 0.632 | 1.68 (0.81 to 3.50) | 0.164 |
| Per SD increase | 1.08 (0.62 to 1.85) | 0.794 | 1.18 (0.83 to 1.69) | 0.360 | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Man, R.E.K.; Gan, A.T.L.; Fenwick, E.K.; Gupta, P.; Wong, M.Y.Z.; Wong, T.Y.; Tan, G.S.W.; Teo, B.W.; Sabanayagam, C.; Lamoureux, E.L. The Relationship between Generalized and Abdominal Obesity with Diabetic Kidney Disease in Type 2 Diabetes: A Multiethnic Asian Study and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1685. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10111685
Man REK, Gan ATL, Fenwick EK, Gupta P, Wong MYZ, Wong TY, Tan GSW, Teo BW, Sabanayagam C, Lamoureux EL. The Relationship between Generalized and Abdominal Obesity with Diabetic Kidney Disease in Type 2 Diabetes: A Multiethnic Asian Study and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients. 2018; 10(11):1685. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10111685
Chicago/Turabian StyleMan, Ryan Eyn Kidd, Alfred Tau Liang Gan, Eva Katie Fenwick, Preeti Gupta, Mark Yu Zheng Wong, Tien Yin Wong, Gavin Siew Wei Tan, Boon Wee Teo, Charumathi Sabanayagam, and Ecosse Luc Lamoureux. 2018. "The Relationship between Generalized and Abdominal Obesity with Diabetic Kidney Disease in Type 2 Diabetes: A Multiethnic Asian Study and Meta-Analysis" Nutrients 10, no. 11: 1685. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10111685
APA StyleMan, R. E. K., Gan, A. T. L., Fenwick, E. K., Gupta, P., Wong, M. Y. Z., Wong, T. Y., Tan, G. S. W., Teo, B. W., Sabanayagam, C., & Lamoureux, E. L. (2018). The Relationship between Generalized and Abdominal Obesity with Diabetic Kidney Disease in Type 2 Diabetes: A Multiethnic Asian Study and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients, 10(11), 1685. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10111685





