Association between Gestational Weight Gain, Gestational Diabetes Risk, and Obstetric Outcomes: A Randomized Controlled Trial Post Hoc Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
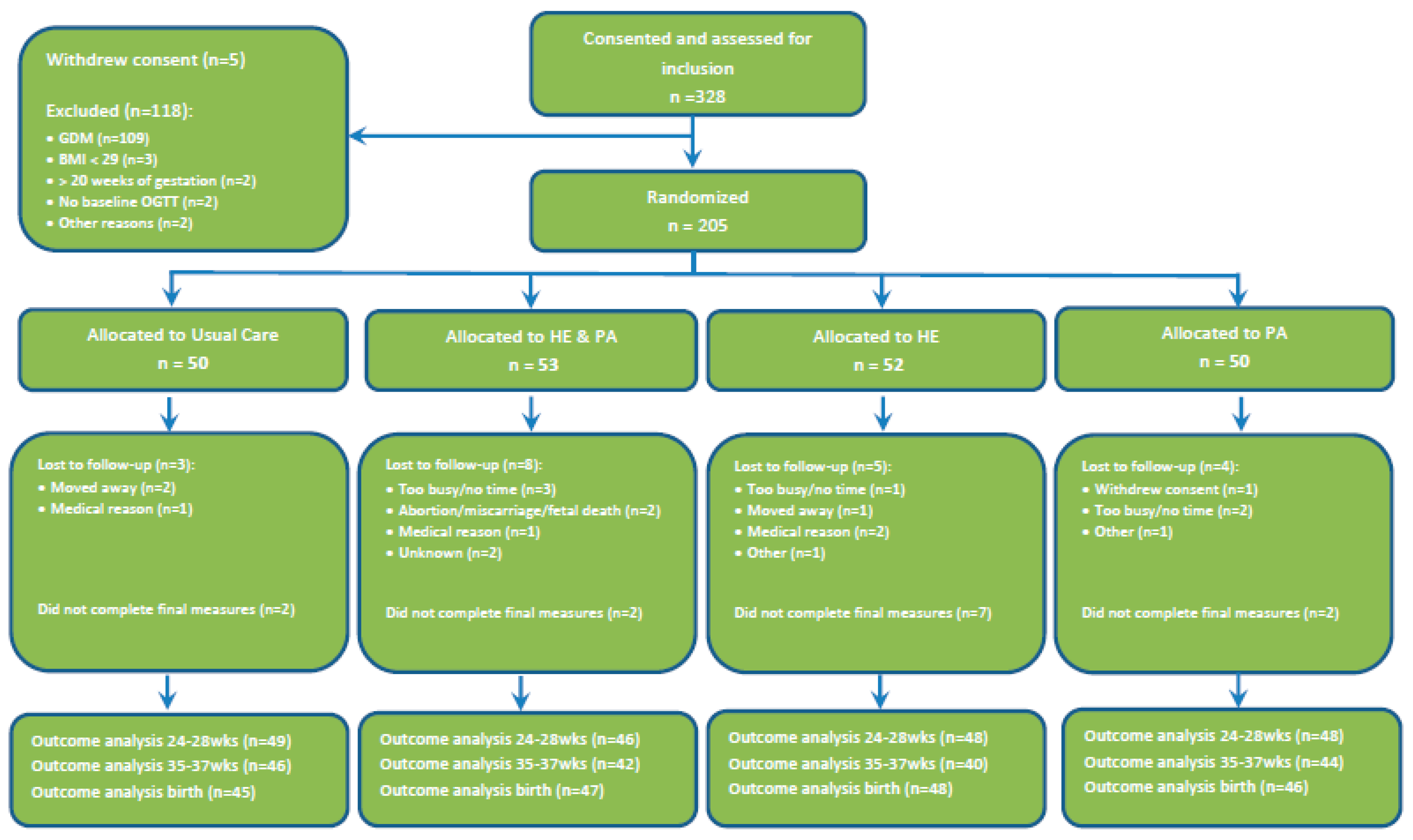
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Overall Study Design
2.2. Statistics
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Simmons, D. Diabetes and obesity in pregnancy. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2011, 25, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmons, D. Prevention of gestational diabetes mellitus: Where are we now? Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2015, 17, 824–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oteng-Ntim, E.; Varma, R.; Croker, H.; Poston, L.; Doyle, P. Lifestyle interventions for overweight and obese pregnant women to improve pregnancy outcome: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med. 2012, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The International Weight Management in Pregnancy (i-WIP) Collaborative Group. Effect of diet and physical activity based interventions in pregnancy on gestational weight gain and pregnancy outcomes: Meta-analysis of individual participant data from randomised trials. BMJ 2017, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, E.; Gomersall, J.C.; Tieu, J.; Han, S.; Crowther, C.A.; Middleton, P. Combined diet and exercise interventions for preventing gestational diabetes mellitus. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.; Li, J.; Leng, J.; Ma, R.C.; Yang, X. Lifestyle intervention can reduce the risk of gestational diabetes: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Obes. Rev. 2016, 17, 960–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koivusalo, S.B.; Rönö, K.; Klemetti, M.M.; Roine, R.P.; Lindström, J.; Erkkola, M.; Kaaja, R.J.; Pöyhönen-Alho, M.; Tiitinen, A.; Huvinen, E.; et al. Gestational diabetes mellitus can be prevented by lifestyle intervention: The Finnish Gestational Diabetes Prevention Study (RADIEL): A randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jelsma, J.G.; van Poppel, M.N.; Galjaard, S.; Desoye, G.; Corcoy, R.; Devlieger, R.; van Assche, A.; Timmerman, D.; Jans, G.; Harreiter, J.; et al. DALI: Vitamin D and lifestyle intervention for gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) prevention: An European multicentre, randomised trial–study protocol. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2013, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmons, D.; Jelsma, J.G.; Galjaard, S.; Devlieger, R.; van Assche, A.; Jans, G.; Corcoy, R.; Adelantado, J.M.; Dunne, F.; Desoye, G.; et al. Results from a european multicenter randomized trial of physical activity and/or healthy eating to reduce the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: The DALI Lifestyle Pilot. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 1650–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmons, D.; Devlieger, R.; van Assche, A.; Jans, G.; Galjaard, S.; Corcoy, R.; Adelantado, J.M.; Dunne, F.; Desoye, G.; Harreiter, J.; et al. Effect of physical activity and/or healthy eating on GDM risk: The DALI Lifestyle Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 102, 903–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Institute of Medicine. Weight gain during pregnancy: Reexamining the guidelines. In Institute of Medicine (US) and National Research Council (US) and Committee to Reexamine IOM Pregnancy Weight Guidelines; National Academies Press (US): Washington, DC, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Diagnostic Criteria and Classification of Hyperglycaemia First Detected in Pregnancy; WHO/NMH/MND/13.2; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Matthews, D.R.; Hosker, J.P.; Rudenski, A.S.; Naylor, B.A.; Treacher, D.F.; Turner, R.C. Homeostasis model assessment: Insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 1985, 28, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stumvoll, M.; Mitrakou, A.; Pimenta, W.; Jenssen, T.; Yki-Jarvinen, H.; Van Haeften, T.; Renn, W.; Gerich, J. Use of oral glucose tolerance test to assess insulin release and insulin sensitivity. Diabetes Care 2000, 23, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stumvoll, M.; Van Haeften, T.; Fritsche, A.; Gerich, J. Oral glucose tolerance test indexes for insulin sensitivity and secretion based on various availabilities of sampling times. Diabetes Care 2001, 24, 796–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalano, P.M.; Tyzbir, E.D.; Roman, N.M.; Amini, S.B.; Sims, E.A.H. Longitudinal changes in insulin release and insulin resistance in nonobese pregnant women. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1991, 165, 1667–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratner, R.E.; Christophi, C.A.; Metzger, B.E.; Dabelea, D.; Bennett, P.H.; Pi-Sunyer, X.; Fowler, S.; Kahn, S.E. The Diabetes Prevention Program Research Groupa. Prevention of diabetes in women with a history of gestational diabetes: Effects of metformin and lifestyle interventions. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 4774–4779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiswick, C.; Reynolds, R.M.; Denison, F.; Drake, A.J.; Forbes, S.; Newby, D.E.; Walker, B.R.; Quenby, S.; Wray, S.; Weeks, A.; et al. Effect of metformin on maternal and fetal outcomes in obese pregnant women (EMPOWaR): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015, 3, 778–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syngelaki, A.; Nicolaides, K.H.; Balani, J. Metformin versus placebo in obese pregnant women without diabetes mellitus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balani, J.; Hyer, S.; Syngelaki, A.; Akolekar, R.; Nicolaides, K.H.; Johnson, A.; Shehata, H. Association between insulin resistance and preeclampsia in obese non-diabetic women receiving metformin. Obstet. Med. 2017, 10, 170–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahn, S.E.; Prigeon, R.L.; McCulloch, D.K.; Boyko, E.J.; Bergman, R.N.; Schwartz, M.W.; Neifing, J.L.; Ward, W.K.; Beard, J.C.; Palmer, J.P.; et al. Quantification of the relationship between insulin sensitivity and -cell function in human subjects: Evidence for a hyperbolic function. Diabetes 1993, 42, 1663–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchanan, T.A.; Xiang, A.H.; Peters, R.K.; Kjos, S.L.; Marroquin, A.; Goico, J.; Ochoa, C.; Tan, S.; Berkowitz, K.; Hodis, H.N.; et al. Preservation of pancreatic beta-cell function and prevention of type 2 diabetes by pharmacological treatment of insulin resistance in high-risk hispanic women. Diabetes 2002, 51, 2796–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berkowitz, K.; Peters, R.; Kjos, S.L.; Goico, J.; Marroquin, A.; Dunn, M.E.; Xiang, A.; Azen, S.; Buchanan, T.A. Effect of troglitazone on insulin sensitivity and pancreatic -cell function in women at high risk for non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetes 1996, 45, 1572–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, R.R. Piecing together the puzzle of pancreatic islet adaptation in pregnancy. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2018, 1411, 120–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Q.; Sun, Y.; Su, S.; Zhang, L.; Liu, C.; Feng, Y.; et al. A randomized clinical trial of exercise during pregnancy to prevent gestational diabetes mellitus and improve pregnancy outcome in overweight and obese pregnant women. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2017, 216, 340–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedderson, M.M.; Gunderson, E.P.; Ferrara, A. Gestational weight gain and risk of gestational diabetes mellitus. Obstet. Gynecol. 2010, 115, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodd, J.M.; Turnbull, D.; McPhee, A.J.; Deussen, A.R.; Grivell, R.M.; Yelland, L.N.; Crowther, C.A.; Wittert, G.; Owens, J.A.; Robinson, J.S. Antenatal lifestyle advice for women who are overweight or obese: LIMIT randomised trial. BMJ 2014, 348, g1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowther, C.A.; Hiller, J.E.; Moss, J.R.; McPhee, A.J.; Jeffries, W.S.; Robinson, J.S. Effect of treatment of gestational diabetes mellitus on pregnancy outcomes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 2477–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landon, M.B.; Spong, C.Y.; Thom, E.; Carpenter, M.W.; Ramin, S.M.; Casey, B.; Wapner, R.J.; Varner, M.W.; Rouse, D.J.; Thorp, J.M., Jr.; et al. A multicenter, randomized trial of treatment for mild gestational diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 1339–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gestational Weight Gain Group | <1.80 kg at Baseline | ≥1.80 kg at Baseline | <5.65 kg to 24–28 Weeks | ≥5.65 kg to 24–28 Weeks | <9.5 kg to 35–37 Weeks † | ≥9.5 kg to 35–37 Weeks † |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 215 | n = 216 | n = 203 | n = 201 | n = 158 | n = 159 | |
| Age (years) | 31.5 ± 5.3 | 32.4 ± 5.4 | 32.0 ± 5.2 | 32.1 ± 5.4 | 32.7 ± 5.1 | 31.7±5.4 |
| Pre-pregnancy weight (kg) | 94.1 ± 14.0 | 91.4 ± 12.0 * | 94.9 ± 14.0 | 90.5 ± 11.9 *** | 94.7 ± 13.9 | 90.8 ± 11.4 ** |
| Pre-pregnancy BMI (kg/m2) | 34.2 ± 4.2 | 33.3 ± 3.6 ** | 34.6 ± 4.2 | 33.0 ± 3.5 *** | 34.4 ± 4.1 | 33.0 ± 3.5 ** |
| European descent | 184/215 (86%) | 189/216 (88%) | 177/203 (87%) | 176/201 (88%) | 137/158 (87%) | 142/159 (89%) |
| Nullipara | 109/215 (51%) | 106/216 (49%) | 100/203 (49%) | 102/201 (51%) | 69/158 (44%) | 84/159 (53%) * |
| Smokers | 26/215 (12%) | 41/216 (19%) | 19/203 (9%) | 42/201 (21%) ** | 14/158 (9%) | 29/159 (18%) * |
| First degree relative with diabetes | 52/215 (24%) | 48/216 (22%) | 48/2103 (24%) | 41/201 (20%) | 33/158 (21%) | 38/159 (24%) |
| Previous GDM | 7/136 (5%) | 10/137 (7%) | 8/133 (6%) | 5/120 (4%) | 4/112 (4%) | 6/91(7%) |
| Fasting glucose (mmol/L) | 4.6 ± 0.4 | 4.6 ± 0.4 | 4.7 ± 0.4 | 4.6 ± 0.4 | 4.7 ± 0.3 | 4.6 ± 0.4 ** |
| 1-h glucose (mmol/L) | 6.9 ± 1.4 | 6.7 ± 1.3 | 6.9 ± 1.4 | 6.7 ± 1.4 | 6.9 ± 1.3 | 6.5 ± 1.3 ** |
| 2-h glucose (mmol/L) | 5.9 ± 1.2 | 5.8 ± 1.0 | 5.9 ± 1.1 | 5.8 ± 1.1 | 5.9 ± 1.0 | 5.7 ± 1.1 * |
| HOMA-IR (IQR) | 2.5 (2.0, 3.4) | 2.8 (2.0, 3.7) | 2.7 (2.0, 3.6) | 2.6 (2.0, 2.4) | 2.7 (2.1, 3.4) | 2.5 (1.9, 3.4) |
| HOMA insulin secretion (IQR) | 217 (170, 312) | 256 (180, 363) | 220 (166, 324) | 245 (181, 346) | 215 (158, 295) | 251 (180, 358) |
| Stumvoll phase 1 (IQR) | 1590 (1221, 2067) | 1521 (1255, 2045) | 1560 (1219, 2083) | 1502 (1258, 2016) | 1595 (1224, 2099) | 1507 (1261, 2042) |
| Stumvoll phase 2 (IQR) | 409 (318, 532) | 388 (327, 520) | 408 (319, 533) | 386 (326, 519) | 410 (319, 534) | 388 (327, 519) |
| Gestational Weight Gain Group | <1.80 kg at Baseline | ≥1.80 kg at Baseline | <5.65 kg to 24–28 Weeks | ≥5.65 kg to 24–28 Weeks | <9.5 kg to 35–37 Weeks † | ≥9.5 kg to 35–37 Weeks † |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 215 | n = 216 | n = 203 | n = 201 | n = 156 | n = 158 | |
| 24–28 weeks | ||||||
| Weight (kg) | 96.5 ± 12.4 | 100.7 ± 12.8 ** | 96.7±12.7 | 100.4±12.7* | 96.7 ± 12.7 | 100.2 ± 12.6 * |
| Gestational weight gain (kg) # | 2.3 ± 3.9 | 9.3 ± 4.3 *** | 1.7±3.3 | 9.9±3.8*** | 2.0 ± 3.5 | 9.4 ± 4.3 *** |
| Fasting blood glucose (BG) (mmol/l) # | 4.62 ± 0.40 | 4.66 ± 0.42 * | 4.61±0.40 | 4.66±0.43** | 4.58 ± 0.36 | 4.57 ± 0.37 * |
| 1-h glucose (mmol/l) # | 7.73 ± 1.58 | 7.81 ± 1.66 | 7.74±1.59 | 7.83±1.68 | 7.52 ± 1.29 | 7.39 ± 1.49 |
| 2-h glucose (mmol/l) # | 6.34 ± 1.23 | 6.21 ± 1.24 | 6.33±1.26 | 6.22±1.19 | 6.18 ± 1.02 | 5.98 ± 1.13 |
| HOMA-IR # | 2.88 (2.17, 3.83) | 3.13 (2.39, 4.45) * | 2.80 (2.07, 3.76) | 3.15 (2.46, 4.47) *** | 2.84 (2.17, 3.69) | 3.03 (2.26, 4.29) *** |
| HOMA insulin secretion # | 256 (190, 366) | 285 (200, 393) | 264 (189, 345) | 283 (204, 407) * | 269 (193, 343) | 300 (208, 420) |
| Stumvoll phase 1 # | 1757 (1292, 2308) | 1888 (1404, 2347) * | 1675 (1276, 2256) | 1919 (1403, 2378) *** | 1612 (1287, 2255) | 1929 (1494, 2366) *** |
| Stumvoll phase 2 # | 454 (337, 588) | 484 (365, 598) * | 433 (335, 576) | 496 (368, 607) *** | 418 (336, 576) | 495 (380, 604) *** |
| 35–37 weeks | ||||||
| Weight (kg)† | 100.3 ± 12.3 | 104.9 ± 13.0 ** | 100.1 ± 12.6 | 105.2 ± 12.8 ** | 99.4 ± 12.8 | 105.7 ± 12.3 *** |
| Gestational weight gain (kg) #† | 6.2 ± 5.3 | 13.4 ± 5.7 *** | 5.4 ± 4.5 | 14.5 ± 4.9 *** | 4.7 ± 3.7 | 14.9 ± 4.4 *** |
| Fasting BG (mmol/l) #$ | 4.57 ± 0.45 | 4.60 ± 0.51 | 4.55 ± 0.45 | 4.61 ± 0.51 * | 4.49 ± 0.43 | 4.53 ± 0.43 ** |
| 1-h glucose (mmol/l) #$ | 8.20 ± 1.61 | 8.46 ± 1.57 | 8.21 ± 1.54 | 8.45 ± 1.67 * | 8.01 ± 1.37 | 8.17 ± 1.47 * |
| 2-h glucose (mmol/l) #$ | 6.74 ± 1.28 | 6.58 ± 1.21 | 6.82 ± 1.31 | 6.51 ± 1.14 * | 6.63 ± 1.21 | 6.43 ± 1.09 |
| HOMA-IR #$ | 3.11 (2.35, 4.46) | 3.38 (2.55, 4.60) | 2.96 (2,25, 4.32) | 3.45 (2.62, 4.76) ** | 2.66 (2.21, 4.04) | 3.47 (2.70, 4.74) *** |
| HOMA insulin secretion #$ | 345 (234, 565) | 354 (250, 483) | 346 (227, 478) | 351 (252, 531) | 324 (217, 445) | 367 (256, 531) |
| Stumvoll phase 1 #$ | 2469 (1722, 3174) | 2518 (1898, 3117) | 2403 (1723, 3124) | 2561 (1917, 3200) ** | 2383 (1732, 3026) | 2684 (2162, 3354) *** |
| Stumvoll phase 2 #$ | 629 (441, 801) | 639 (497, 786) | 618 (450, 790) | 652 (497, 810) ** | 608 (452, 766) | 684 (554, 841) *** |
| Birth | N = 198 | N = 195 | N = 194 | N = 194 | N = 154 | N = 158 |
| Gestation at birth (weeks) | 39.5 ± 2.6 | 39.6 ± 1.7 | 39.8 ± 1.6 | 39.5 ± 1.7 | 39.8 ± 1.4 | 39.8 ± 1.3 |
| Gender (male) | 102/198 (52%) | 94/195 (48%) | 101/194 (52%) | 94/194 (49%) | 84/154 (55%) | 74/158 (47%) |
| Birthweight | 3490 ± 538 | 3479 ± 557 | 3457 ± 541 | 3505 ± 551 | 3477 ± 503 | 3602 ± 515 |
| Birthweight ≥4 (kg) | 37/195 (19%) | 34/195 (17%) | 33/192 (17%) | 35/193 (18%) | 25/153 (16%) | 39/157 (25%) * |
| Birthweight <2.5 (kg) | 8/195 (4%) | 8/195 (4%) | 8/192 (4%) | 8/193 (4%) | 5/153 (3%) | 2/157 (1%) |
| Large for Gestational Age | 26/187 (14%) | 25/186 (13%) | 23/186 (12%) | 26/182 (14%) | 13/150 (9%) | 31/150 (21%) ** |
| Small for Gestational Age | 12/186 (7%) | 16/186 (9%) | 15/186 (8%) | 13/182 (7%) | 10/150 (7%) | 9/150 (6%) |
| Preterm birth | 8/194 (4%) | 14/195 (7%) | 8/192 (4%) | 14/192 (7%) | 2/153 (1%) | 4/157 (3%) |
| Induction of labor or planned caesarean section | 70/188 (37%) | 82/187 (44%) | 76/186 (41%) | 75/184 (41%) | 61/151 40% | 60/148 41% |
| Caesarean section | 51/190 (27%) | 73/190 (38%) * | 58/188 (31%) | 65/187 (35%) | 45/153 (29%) | 53/151 (35%) |
| Pre-eclampsia | 4/181 (2%) | 10/187 (5%) | 7/181 (4%) | 8/183 (4%) | 4/147 (3%) | 5/148 (3%) |
| Neonatal Intensive Care Unit admission | 19/170 (11%) | 18/185 (10%) | 19/173 (11%) | 19/179 (11%) | 14/145 (10%) | 14/144 (10%) |
| GDM total | 71/183 (39%) | 61/175 (35%) | 68/185 (37%) | 63/175 (36%) | 40/153 (26%) | 45/155 (29%) |
| Baseline | UC | HE + PA |
|---|---|---|
| n = 50 | n = 53 | |
| Age (years) | 32.1 ± 6.0 | 31.9 ± 5.0 |
| Pre-pregnancy weight (kg) | 94.7 ± 11.4 | 94.7 ± 13.6 |
| Pre- pregnancy BMI (kg/m2) | 33.6 ± 3.3 | 34.8 ± 4.1 |
| Fasting (F) BG (mmol/L) | 4.69 ± 0.33 | 4.64 ± 0.36 |
| 1-h BG (mmol/L) | 6.80 ± 1.36 | 6.84 ± 1.23 |
| 2-h BG (mmol/L) | 5.69 ± 1.25 | 5.72 ± 0.99 |
| HOMA-IR | 2.62 (1.94, 4.30) | 2.49 (2.19, 2.82) |
| HOMA insulin secretion | 229 (142, 365) | 215 (168, 313) |
| Stumvoll phase 1 | 1498 (1211, 2144) | 1489 (1236, 1948) |
| Stumvoll phase 2 | 379 (313, 554) | 382 (322, 501) |
| European descent | 45/50 90.0% | 47/53 88.7% |
| Nullipara | 27/50 46.2% | 27/53 49.1% |
| Smokers | 6/50 12.0% | 5/53 9.4% |
| First degree relative with diabetes | 13/50 26.0% | 6/53 11.3% |
| 24–28 weeks | n = 50 | n = 53 |
| Weight gain from pre-pregnancy | 6.7 ± 5.9 (n = 49) | 4.1 ± 5.0 (n = 46) * |
| Fasting Blood Glucose (BG) | 4.59 ± 0.40 | 4.57 ± 0.43 |
| 1-h BG | 7.86 ± 1.64 | 7.93 ± 1.60 |
| 2-h BG | 6.23 ± 1.31 | 6.09 ± 1.20 |
| HOMA-Insulin Resistance | 2.86 (2.18, 3.82) | 2.54 (2.16, 3.02) |
| HOMA-Insulin secretion | 284 (203, 394) | 249 (198, 352) |
| Stumvoll phase 1 | 1762 (1386, 2371) | 1943 (1311, 2327) |
| Stumvoll phase 2 | 455 (359, 606) | 501 (346, 594) |
| GDM at 24–28 weeks | 9/49 (18.4%) | 9/45 (20.0%) |
| 35–37 weeks | N = 46 | N = 42 |
| Weight gain from pre-pregnancy † | 11.3 ± 6.7 (n = 40) | 7.0 ± 6.0 (n = 36) * |
| FBG & | 4.53 ± 0.46 | 4.49 ± 0.51 |
| 1-h BG & | 8.57 ± 1.31 | 8.32 ± 1.44 |
| 2-h BG & | 6.70 ± 1.23 | 6.59 ± 1.01 |
| HOMA-Insulin Resistance & | 2.89 (2.07, 4.44) | 2.56 (2.28, 3.84) |
| HOMA insulin secretion & | 309 (233, 504) | 337 (242, 411) |
| Stumvoll phase 1 & | 2644 (1793, 3179) | 2577 (2001, 3189) |
| Stumvoll phase 2 & | 674 (457, 802) | 654 (512, 811) |
| GDM at 35–37 weeks | 9/39(23.1%) | 5/36 (13.9%) |
| Birth outcomes | N = 45 | N = 47 |
| Gestational age at birth | 39.8 ± 1.5 | 39.8 ±1.2 |
| LGA | 7/42 16.7% | 2/44 4.5% * |
| SGA | 1/42 2.4% | 4/44 9.1% |
| Birthweight | 3588 ± 524 | 3455 ± 463 |
| Preterm birth | 2/44 4.5% | 0/45 0% |
| Caesarean section | 14/43 30.2% | 14/47 29.8% |
| Pre-eclampsia | 4/42 9.5% | 2/43 4.7% |
| Birthweight ≥4 kg | 9/45 20.0% | 7/45 15.6% |
| Birthweight <2.5 kg | 1/45 2.2% | 1/45 2.2% |
| NICU admission | 7/41 17.1% | 6/44 13.6% |
| GDM total | 15/46 32.6% | 13/44 29.5% |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Simmons, D.; Devlieger, R.; Van Assche, A.; Galjaard, S.; Corcoy, R.; Adelantado, J.M.; Dunne, F.; Desoye, G.; Kautzky-Willer, A.; Damm, P.; et al. Association between Gestational Weight Gain, Gestational Diabetes Risk, and Obstetric Outcomes: A Randomized Controlled Trial Post Hoc Analysis. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1568. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10111568
Simmons D, Devlieger R, Van Assche A, Galjaard S, Corcoy R, Adelantado JM, Dunne F, Desoye G, Kautzky-Willer A, Damm P, et al. Association between Gestational Weight Gain, Gestational Diabetes Risk, and Obstetric Outcomes: A Randomized Controlled Trial Post Hoc Analysis. Nutrients. 2018; 10(11):1568. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10111568
Chicago/Turabian StyleSimmons, David, Roland Devlieger, Andre Van Assche, Sander Galjaard, Rosa Corcoy, Juan M. Adelantado, Fidelma Dunne, Gernot Desoye, Alexandra Kautzky-Willer, Peter Damm, and et al. 2018. "Association between Gestational Weight Gain, Gestational Diabetes Risk, and Obstetric Outcomes: A Randomized Controlled Trial Post Hoc Analysis" Nutrients 10, no. 11: 1568. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10111568
APA StyleSimmons, D., Devlieger, R., Van Assche, A., Galjaard, S., Corcoy, R., Adelantado, J. M., Dunne, F., Desoye, G., Kautzky-Willer, A., Damm, P., Mathiesen, E. R., Jensen, D. M., Andersen, L. L. T., Lapolla, A., Dalfra, M. G., Bertolotto, A., Wender-Ozegowska, E., Zawiejska, A., Hill, D., ... Van Poppel, M. N. M. (2018). Association between Gestational Weight Gain, Gestational Diabetes Risk, and Obstetric Outcomes: A Randomized Controlled Trial Post Hoc Analysis. Nutrients, 10(11), 1568. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10111568










