The Microbiome and Radiation Induced-Bowel Injury: Evidence for Potential Mechanistic Role in Disease Pathogenesis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
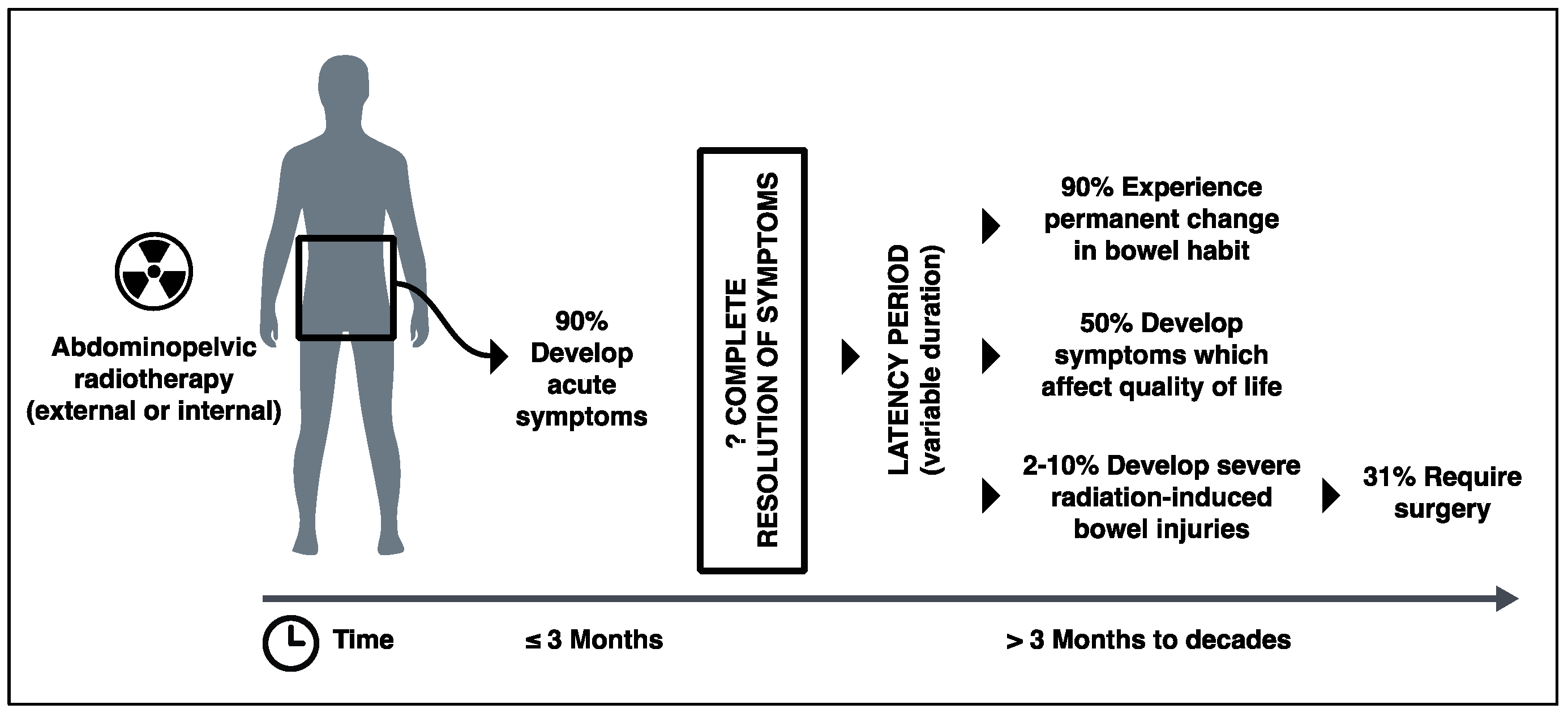
2. Clinical Significance of Radiation-Induced Bowel Injury
3. Pathophysiology of Radiation-Induced Bowel Injury
3.1. Cellular Effect of Radiation
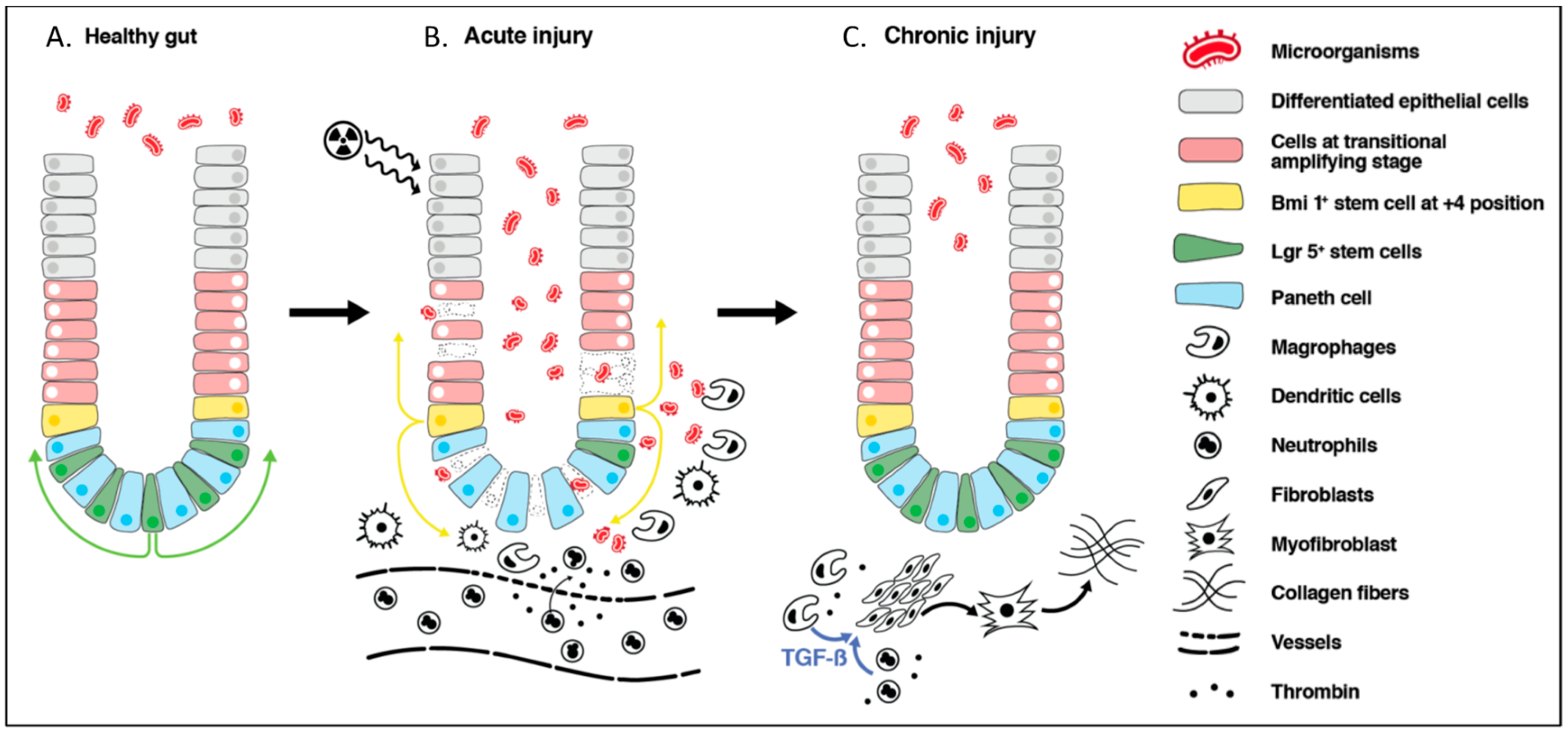
3.2. Radiation-Induced Acute Bowel Injury
3.3. Epithelial Cell Recovery
3.4. Radiation-Induced Chronic Bowel Injury
4. Microbiome and Radiation-Induced Bowel Injury
4.1. Importance of Microbiome in Healthy Gut
4.2. Gut Microbiome of Patients with Cancer
4.3. Effects of Radiation on Gut Microbiome and Incidence of Post-Radiation Diarrhea
4.4. Effects of Probiotics on Acute Radiation-Induced Bowel Injury
4.5. Possible Mechanism of Intestinal Radioprotection Provided by Microbiome
4.6. Effect of Radiation-Induced Dysbiosis and Probiotics on Chronic Radiation-Induced Bowel Injury
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Worldwide Cancer Statistics | Cancer Research UK. Available online: https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/health-professional/cancer-statistics/worldwide-cancer#heading-Zero (accessed on 6 July 2018).
- Cancer Statistics for the UK. | Cancer Research UK. Available online: http://www.cancerresearchuk.org/cancer-info/cancerstats/ (accessed on 7 August 2018).
- Andreyev, J. Gastrointestinal Complications of Pelvic Radiotherapy: Are They of Any Importance? Gut 2005, 54, 1051–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, C.M.; Barnett, G.C. Genetics and Genomics of Radiotherapy Toxicity: Towards Prediction. Genome Med. 2011, 3, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothschild, D.; Weissbrod, O.; Barkan, E.; Kurilshikov, A.; Korem, T.; Zeevi, D.; Costea, P.I.; Godneva, A.; Kalka, I.N.; Bar, N.; et al. Environment Dominates over Host Genetics in Shaping Human Gut Microbiota. Nature 2018, 555, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, L.; Ribeiro, A.L.R.; Levine, A.P.; Pontikos, N.; Balloux, F.; Segal, A.W.; Roberts, A.P.; Smith, A.M. The Human Salivary Microbiome Is Shaped by Shared Environment Rather than Genetics: Evidence from a Large Family of Closely Related Individuals. MBio 2017, 8, e01237-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauer-Jensen, M.; Denham, J.W.; Andreyev, H.J.N. Radiation Enteropathy-Pathogenesis, Treatment and Prevention. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moussa, L.; Usunier, B.; Demarquay, C.; Benderitter, M.; Tamarat, R.; Semont, A.; Mathieu, N. Bowel Radiation Injury: Complexity of the Pathophysiology and Promises of Cell and Tissue Engineering. Cell Transplant. 2016, 25, 1723–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hautmann, M.G.; Hipp, M.; Kölbl, O. Clostridium Difficile-Associated Diarrhea in Radiooncology: An Underestimated Problem for the Feasibility of the Radiooncological Treatment? Radiat. Oncol. 2011, 6, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abayomi, J.; Kirwan, J.; Hackett, A. The Prevalence of Chronic Radiation Enteritis Following Radiotherapy for Cervical or Endometrial Cancer and Its Impact on Quality of Life. Eur. J. Oncol. Nurs. 2009, 13, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gami, B.; Harrington, K.; Blake, P.; Dearnaley, D.; Tait, D.; Davies, J.; Norman, A.R.; Andreyev, H.J.N. How Patients Manage Gastrointestinal Symptoms after Pelvic Radiotherapy. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2003, 18, 987–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreyev, J. Gastrointestinal Symptoms after Pelvic Radiotherapy: A New Understanding to Improve Management of Symptomatic Patients. Lancet Oncol. 2007, 8, 1007–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denton, A.S.; Bond, S.J.; Matthews, S.; Bentzen, S.M.; Maher, E.J.; UK Link Gynaecology–Oncology Group. National Audit of the Management and Outcome of Carcinoma of the Cervix Treated with Radiotherapy in 1993. Clin. Oncol. 2000, 12, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeCosse, J.J.; Rhodes, R.S.; Wentz, W.B.; Reagan, J.W.; Dworken, H.J.; Holden, W.D. The Natural History and Management of Radiation Induced Injury of the Gastrointestinal Tract. Ann. Surg. 1969, 170, 369–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Verhaeghe, M.; Laurent, J.C.; Dupont, A.; Madelain, M.; Rohart, J. Surgical Treatment of Intestinal Radio-Lesions. 53 Patients Operated, out of 171 Radio-Lesions among 7301 Irradiated (Author’s Transl). J. Chir. (Paris) 1981, 118, 221–229. [Google Scholar]
- Regimbeau, J.M.; Panis, Y.; Gouzi, J.L.; Fagniez, P.L. Operative and Long Term Results after Surgery for Chronic Radiation Enteritis. Am. J. Surg. 2001, 182, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harling, H.; Balslev, I. Long-Term Prognosis of Patients with Severe Radiation Enteritis. Am. J. Surg. 1988, 155, 517–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreyev, H.J.N. Gastrointestinal Problems after Pelvic Radiotherapy: The Past, the Present and the Future. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 19, 790–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shadad, A.K.; Sullivan, F.J.; Martin, J.D.; Egan, L.J. Gastrointestinal Radiation Injury: Symptoms, Risk Factors and Mechanisms. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuccio, L.; Guido, A.; Andreyev, H.J.N. Management of Intestinal Complications in Patients with Pelvic Radiation Disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 10, 1326–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riley, P.A. Free Radicals in Biology: Oxidative Stress and the Effects of Ionizing Radiation. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 1994, 65, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azzam, E.I.; Jay-Gerin, J.P.; Pain, D. Ionizing Radiation-Induced Metabolic Oxidative Stress and Prolonged Cell Injury. Cancer Lett. 2012, 327, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, J.F. Biochemistry of DNA Lesions. Radiat. Res. 1985, 104, S103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.F. DNA Damage Produced by Ionizing Radiation in Mammalian Cells: Identities, Mechanisms of Formation, and Reparability. Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol. 1988, 35, 95–125. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Turrens, J.F. Mitochondrial Formation of Reactive Oxygen Species. J. Physiol. 2003, 552, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikkelsen, R.B.; Wardman, P. Biological Chemistry of Reactive Oxygen and Nitrogen and Radiation-Induced Signal Transduction Mechanisms. Oncogene 2003, 22, 5734–5754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, S.; Aykin-Burns, N.; Krager, K.J.; Shah, S.K.; Melnyk, S.B.; Hauer-Jensen, M.; Pawar, S.A. Loss of C/EBPδ Enhances IR-Induced Cell Death by Promoting Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Dysfunction. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2016, 99, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergonié, J.; Tribondeau, L. Interpretation of Some Results from Radiotherapy and an Attempt to Determine a Rational Treatment Techniquea. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2003, 76, 181–182. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rubin, P.; Casarett, G.W. Clinical Radiation Pathology as Applied to Curative Radiotherapy. Cancer 1968, 22, 767–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potten, C.S. Stem Cells in Gastrointestinal Epithelium: Numbers, Characteristics and Death. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 1998, 353, 821–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darwich, A.S.; Aslam, U.; Ashcroft, D.M.; Rostami-Hodjegan, A. Meta-Analysis of the Turnover of Intestinal Epithelia in Preclinical Animal Species and Humans. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2014, 42, 2016–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Porvaznik, M. Tight Junction Disruption and Recovery after Sublethal γ Irradiation. Radiat. Res. 1979, 78, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nejdfors, P.; Ekelund, M.; Weström, B.R.; Willén, R.; Jeppsson, B. Intestinal Permeability in Humans Is Increased after Radiation Therapy. Dis. Colon Rectum 2000, 43, 1582–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, P.K.; Gangwar, R.; Manda, B.; Meena, A.S.; Yadav, N.; Szabo, E.; Balogh, A.; Lee, S.C.; Tigyi, G.; Rao, R. Rapid Disruption of Intestinal Epithelial Tight Junction and Barrier Dysfunction by Ionizing Radiation in Mouse Colon in Vivo: Protection by N-Acetyl-L-Cysteine. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2016, 310, G705–G715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hovdenak, N.; Wang, J.; Sung, C.C.; Kelly, T.; Fajardo, L.F.; Hauer-Jensen, M. Clinical Significance of Increased Gelatinolytic Activity in the Rectal Mucosa during External Beam Radiation Therapy of Prostate Cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2002, 53, 919–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- François, A.; Milliat, F.; Guipaud, O.; Benderitter, M. Inflammation and Immunity in Radiation Damage to the Gut Mucosa. Biomed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 123241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paris, F.; Fuks, Z.; Kang, A.; Capodieci, P.; Juan, G.; Ehleiter, D.; Haimovitz-Friedman, A.; Cordon-Cardo, C.; Kolesnick, R. Endothelial Apoptosis as the Primary Lesion Initiating Intestinal Radiation Damage in Mice. Science 2001, 293, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denham, J.W.; Hauer-Jensen, M. The Radiotherapeutic Injury—A Complex “Wound”. Radiother. Oncol. 2002, 63, 129–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryoo, S.-B.; Kim, J.-S.; Kim, M.-S.; Kim, K.; Yu, S.A.; Bae, M.-J.; Oh, H.-K.; Moon, S.H.; Choe, E.K.; So, I.; et al. High-Dose Radiation-Induced Changes in Murine Small Intestinal Motility: Are the Changes in the Interstitial Cells of Cajal or in the Enteric Nervous System? Radiat. Res. 2016, 185, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erickson, B.A.; Otterson, M.F.; Moulder, J.E.; Sarna, S.K. Altered Motility Causes the Early Gastrointestinal Toxicity of Irradiation. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1994, 28, 905–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, S. Intestinal Stem Cells. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2010, 12, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scoville, D.H.; Sato, T.; He, X.C.; Li, L. Current View: Intestinal Stem Cells and Signaling. Gastroenterology 2008, 134, 849–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, K.S.; Chia, L.A.; Li, X.; Ootani, A.; Su, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Su, N.; Luo, Y.; Heilshorn, S.C.; Amieva, M.R.; et al. The Intestinal Stem Cell Markers Bmi1 and Lgr5 Identify Two Functionally Distinct Populations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schepers, A.G.; Vries, R.; Van Den Born, M.; Van De Wetering, M.; Clevers, H. Lgr5 Intestinal Stem Cells Have High Telomerase Activity and Randomly Segregate Their Chromosomes. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 1104–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potten, C.S.; Hume, W.J.; Reid, P.; Cairns, J. The Segregation of DNA in Epithelial Stem Cells. Cell 1978, 15, 899–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.-K.; Yang, V.W.; Bialkowska, A.B. The Role of Intestinal Stem Cells in Epithelial Regeneration Following Radiation-Induced Gut Injury. Curr. Stem Cell Rep. 2017, 3, 320–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- François, S.; Bensidhoum, M.; Mouiseddine, M.; Mazurier, C.; Allenet, B.; Semont, A.; Frick, J.; Saché, A.; Bouchet, S.; Thierry, D.; et al. Local Irradiation Not Only Induces Homing of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells at Exposed Sites but Promotes Their Widespread Engraftment to Multiple Organs: A Study of Their Quantitative Distribution After Irradiation Damage. Stem Cells 2006, 24, 1020–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sémont, A.; François, S.; Mouiseddine, M.; François, A.; Saché, A.; Frick, J.; Thierry, D.; Chapel, A. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Increase Self-Renewal of Small Intestinal Epithelium and Accelerate Structural Recovery after Radiation Injury. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2006, 585, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Warren, S.; Friedman, N.B. Pathology and Pathologic Diagnosis of Radiation Lesions in the Gastro-Intestinal Tract. Am. J. Pathol. 1942, 18, 499–513. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zheng, H.; Sung, C.C.; Richter, K.K.; Hauer-Jensen, M. Cellular Sources of Transforming Growth Factor-β Isoforms in Early and Chronic Radiation Enteropathy. Am. J. Pathol. 1998, 153, 1531–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strup-Perrot, C.; Mathé, D.; Linard, C.; Violot, D.; Milliat, F.; François, A.; Bourhis, J.; Vozenin-Brotons, M.-C. Global Gene Expression Profiles Reveal an Increase in MRNA Levels of Collagens, MMPs, and TIMPs in Late Radiation Enteritis. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2004, 287, G875–G885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rieder, F.; Brenmoehl, J.; Leeb, S.; Schölmerich, J.; Rogler, G. Wound Healing and Fibrosis in Intestinal Disease. Gut 2007, 56, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Summers, R.W.; Glenn, C.E.; Flatt, A.J.; Elahmady, A. Does Irradiation Produce Irreversible Changes in Canine Jejunal Myoelectric Activity? Dig. Dis. Sci. 1992, 37, 716–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otterson, M.F. Effects of Radiation upon Gastrointestinal Motility. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 2684–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Höckerfelt, U.; Franzén, L.; Norrgard, O.; Forsgren, S. Early Increase and Later Decrease in VIP and Substance P Nerve Fiber Densities Following Abdominal Radiotherapy: A Study on the Human Colon. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2002, 78, 1045–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominguez-Bello, M.G.; Costello, E.K.; Contreras, M.; Magris, M.; Hidalgo, G.; Fierer, N.; Knight, R. Delivery Mode Shapes the Acquisition and Structure of the Initial Microbiota across Multiple Body Habitats in Newborns. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 11971–11975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koenig, J.E.; Spor, A.; Scalfone, N.; Fricker, A.D.; Stombaugh, J.; Knight, R.; Angenent, L.T.; Ley, R.E. Succession of Microbial Consortia in the Developing Infant Gut Microbiome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 4578–4585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Hamady, M.; Yatsunenko, T.; Cantarel, B.L.; Duncan, A.; Ley, R.E.; Sogin, M.L.; Jones, W.J.; Roe, B.A.; Affourtit, J.P.; et al. A Core Gut Microbiome in Obese and Lean Twins. Nature 2009, 457, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommer, F.; Bäckhed, F. The Gut Microbiota-Masters of Host Development and Physiology. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huttenhower, C.; Gevers, D.; Knight, R.; Abubucker, S.; Badger, J.H.; Chinwalla, A.T.; Creasy, H.H.; Earl, A.M.; Fitzgerald, M.G.; Fulton, R.S.; et al. Structure, Function and Diversity of the Healthy Human Microbiome. Nature 2012, 486, 207–214. [Google Scholar]
- Round, J.L.; Mazmanian, S.K. The Gut Microbiota Shapes Intestinal Immune Responses during Health and Disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrams, G.D.; Bishop, J.E. Effect of the Normal Microbial Flora on Gastrointestinal Motility. Exp. Biol. Med. 1967, 126, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wichmann, A.; Allahyar, A.; Greiner, T.U.; Plovier, H.; Lundén, G.Ö.; Larsson, T.; Drucker, D.J.; Delzenne, N.M.; Cani, P.D.; Bäckhed, F. Microbial Modulation of Energy Availability in the Colon Regulates Intestinal Transit. Cell Host Microbe 2013, 14, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carabotti, M.; Scirocco, A.; Maselli, M.A.; Severi, C. The Gut-Brain Axis: Interactions between Enteric Microbiota, Central and Enteric Nervous Systems. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2015, 28, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cryan, J.F.; O’Mahony, S.M. The Microbiome-Gut-Brain Axis: From Bowel to Behavior. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2011, 23, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemente, J.C.; Ursell, L.K.; Parfrey, L.W.; Knight, R. The Impact of the Gut Microbiota on Human Health: An Integrative View. Cell 2012, 148, 1258–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Zhang, J. Role of Intestinal Microbiota and Metabolites on Gut Homeostasis and Human Diseases. BMC Immunol. 2017, 18, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, A.; Vázquez-Baeza, Y.; Knight, R. SnapShot: The Human Microbiome. Cell 2014, 158, 690–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arumugam, M.; Raes, J.; Pelletier, E.; Le Paslier, D.; Yamada, T.; Mende, D.R.; Fernandes, G.R.; Tap, J.; Bruls, T.; Batto, J.M.; et al. Enterotypes of the Human Gut Microbiome. Nature 2011, 473, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ley, R.E.; Mahowald, M.A.; Magrini, V.; Mardis, E.R.; Gordon, J.I. An Obesity-Associated Gut Microbiome with Increased Capacity for Energy Harvest. Nature 2006, 444, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, N.; Vogensen, F.K.; Van Den Berg, F.W.J.; Nielsen, D.S.; Andreasen, A.S.; Pedersen, B.K.; Al-Soud, W.A.; Sørensen, S.J.; Hansen, L.H.; Jakobsen, M. Gut Microbiota in Human Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Differs from Non-Diabetic Adults. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giongo, A.; Gano, K.A.; Crabb, D.B.; Mukherjee, N.; Novelo, L.L.; Casella, G.; Drew, J.C.; Ilonen, J.; Knip, M.; Hyöty, H.; et al. Toward Defining the Autoimmune Microbiome for Type 1 Diabetes. ISME J. 2011, 5, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naseribafrouei, A.; Hestad, K.; Avershina, E.; Sekelja, M.; Linløkken, A.; Wilson, R.; Rudi, K. Correlation between the Human Fecal Microbiota and Depression. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2014, 26, 1155–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, D.; Jia, H.; Feng, Q.; Wang, D.; Liang, D.; Wu, X.; Li, J.; Tang, L.; Li, Y.; et al. The Oral and Gut Microbiomes Are Perturbed in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Partly Normalized after Treatment. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 895–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopalakrishnan, V.; Spencer, C.N.; Nezi, L.; Reuben, A.; Andrews, M.C.; Karpinets, T.V.; Prieto, P.A.; Vicente, D.; Hoffman, K.; Wei, S.C.; et al. Gut Microbiome Modulates Response to Anti-PD-1 Immunotherapy in Melanoma Patients. Science 2018, 359, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matson, V.; Fessler, J.; Bao, R.; Chongsuwat, T.; Zha, Y.; Alegre, M.L.; Luke, J.J.; Gajewski, T.F. The Commensal Microbiome Is Associated with Anti-PD-1 Efficacy in Metastatic Melanoma Patients. Science 2018, 359, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, Y.D.; Kim, H.J.; Seo, J.G.; Kang, S.W.; Bae, J.W. Impact of Pelvic Radiotherapy on Gut Microbiota of Gynecological Cancer Patients Revealed by Massive Pyrosequencing. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hibberd, A.A.; Lyra, A.; Ouwehand, A.C.; Rolny, P.; Lindegren, H.; Cedgård, L.; Wettergren, Y. Intestinal Microbiota Is Altered in Patients with Colon Cancer and Modified by Probiotic Intervention. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2017, 4, e000145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, V.; Moulder, J.E.; Salzman, N.H.; Dubinsky, E.A.; Andersen, G.L.; Baker, J.E. Intestinal Microbiota as Novel Biomarkers of Prior Radiation Exposure. Radiat. Res. 2012, 177, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.S.; Kim, J.; Park, S.J. High-Throughput 16S RRNA Gene Sequencing Reveals Alterations of Mouse Intestinal Microbiota after Radiotherapy. Anaerobe 2015, 33, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manichanh, C.; Varela, E.; Martinez, C.; Antolin, M.; Llopis, M.; Doré, J.; Giralt, J.; Guarner, F.; Malagelada, J.R. The Gut Microbiota Predispose to the Pathophysiology of Acute Postradiotherapy Diarrhea. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 103, 1754–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goudarzi, M.; Mak, T.D.; Jacobs, J.P.; Moon, B.-H.; Strawn, S.J.; Braun, J.; Brenner, D.J.; Fornace, A.J.; Li, H.-H. An Integrated Multi-Omic Approach to Assess Radiation Injury on the Host-Microbiome Axis. Radiat. Res. 2016, 186, 219–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, A.; Ling, Z.; Yang, Z.; Kiela, P.R.; Wang, T.; Wang, C.; Cao, L.; Geng, F.; Shen, M.; Ran, X.; et al. Gut Microbial Dysbiosis May Predict Diarrhea and Fatigue in Patients Undergoing Pelvic Cancer Radiotherapy: A Pilot Study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerassy-Vainberg, S.; Blatt, A.; Danin-Poleg, Y.; Gershovich, K.; Sabo, E.; Nevelsky, A.; Daniel, S.; Dahan, A.; Ziv, O.; Dheer, R.; et al. Radiation Induces Proinflammatory Dysbiosis: Transmission of Inflammatory Susceptibility by Host Cytokine Induction. Gut 2018, 67, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, M.; Xiao, H.; Li, Y.; Zhou, L.; Zhao, S.; Luo, D.; Zheng, Q.; Dong, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; et al. Faecal Microbiota Transplantation Protects against Radiation-induced Toxicity. EMBO Mol. Med. 2017, 9, 448–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, C.; Guarner, F.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Merenstein, D.J.; Pot, B.; Morelli, L.; Canani, R.B.; Flint, H.J.; Salminen, S.; et al. Expert Consensus Document: The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics Consensus Statement on the Scope and Appropriate Use of the Term Probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldenberg, J.Z.; Yap, C.; Lytvyn, L.; Lo, C.K.-F.; Beardsley, J.; Mertz, D.; Johnston, B.C. Probiotics for the Prevention of Clostridium Difficile-Associated Diarrhea in Adults and Children. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 12, CD006095. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alfaleh, K.; Anabrees, J.; Bassler, D.; Al-Kharfi, T. Cochrane Review: Probiotics for Prevention of Necrotizing Enterocolitis in Preterm Infants. Evid-Based Child Heal. 2012, 7, 1807–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cremonini, F.; Di Caro, S.; Nista, E.C.; Bartolozzi, F.; Capelli, G.; Gasbarrini, G.; Gasbarrini, A. Meta-Analysis: The Effect of Probiotic Administration on Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhoea. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2002, 16, 1461–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salminen, E.; Elomaa, I.; Minkkinen, J.; Vapaatalo, H.; Salminen, S. Preservation of Intestinal Integrity during Radiotherapy Using Live Lactobacillus Acidophilus Cultures. Clin. Radiol. 1988, 39, 435–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demers, M.; Dagnault, A.; Desjardins, J. A Randomized Double-Blind Controlled Trial: Impact of Probiotics on Diarrhea in Patients Treated with Pelvic Radiation. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 33, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanarova, C.; Galovicova, A.; Petrasova, D. Use of Probiotics for Prevention of Radiation-Induced Diarrhea. Bratislava Med. J. 2009, 110, 98–104. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.-M.; Li, S.-T.; Shu, Y.; Zhan, H.-Q. Probiotics for Prevention of Radiation-Induced Diarrhea: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbancsek, H.; Kazar, T.; Mezes, I.; Neumann, K. Results of a Double-Blind, Randomized Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of Antibiophilus in Patients with Radiation-Induced Diarrhoea. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2001, 13, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, M.Y.; Chang, T.W.; Gorbach, S.L. Effects of Feeding Lactobacillus GG on Lethal Irradiation in Mice. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 1987, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seal, M.G.; Naito, Y.; Barreto, R.; Lorenzetti, A.; Safran, P.; Marotta, F. Experimental Radiotherapy-Induced Enteritis: A Probiotic Interventional Study. J. Dig. Dis. 2007, 8, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirer, S.; Aydintug, S.; Aslim, B.; Kepenekci, I.; Sengül, N.; Evirgen, O.; Gerceker, D.; Andrieu, M.N.; Ulusoy, C.; Karahüseyinoglu, S. Effects of Probiotics on Radiation-Induced Intestinal Injury in Rats. Nutrition 2006, 22, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ki, Y.; Kim, W.; Cho, H.; Ahn, K.; Choi, Y.; Kim, D. The Effect of Probiotics for Preventing Radiation-Induced Morphological Changes in Intestinal Mucosa of Rats. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2014, 29, 1372–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciorba, M.A.; Riehl, T.E.; Rao, M.S.; Moon, C.; Ee, X.; Nava, G.M.; Walker, M.R.; Marinshaw, J.M.; Stappenbeck, T.S.; Stenson, W.F. Lactobacillus Probiotic Protects Intestinal Epithelium from Radiation Injury in a TLR-2/Cyclo-Oxygenase-2-Dependent Manner. Gut 2012, 61, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burdelya, L.G.; Krivokrysenko, V.I.; Tallant, T.C.; Strom, E.; Gleiberman, A.S.; Gupta, D.; Kurnasov, O.V.; Fort, F.L.; Osterman, A.L.; DiDonato, J.A.; et al. An Agonist of Toll-like Receptor 5 Has Radioprotective Activity in Mouse and Primate Models. Science 2008, 320, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, S.; Bhanja, P.; Liu, L.; Alfieri, A.A.; Yu, D.; Kandimalla, E.R.; Agrawal, S.; Guha, C. Tlr9 Agonist Protects Mice from Radiation-Induced Gastrointestinal Syndrome. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, S.; Fu, Q.; Shah, S.K.; Ponnappan, U.; Melnyk, S.B.; Hauer-Jensen, M.; Pawar, S.A. Role of TLR4 in the Pathogenesis of Radiation-Induced Ibtestinal Injury in C/EBP Delta-Knockout Mice. Shock 2017, 47, 84. [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin, M.; Dacquisto, M.; Jacobus, D.; Horowitz, R. Effects of the Germfree State on Responses of Mice to Whole-Body Irradiation. Radiat. Res. 1964, 23, 333–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cawford, P.A.; Gordon, J.I. From The Cover: Microbial Regulation of Intestinal Radiosensitivity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 13254–13259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selective Microbiota Transplantation for Radiation Enteritis. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03516461 (accessed on 30 July 2018).
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kumagai, T.; Rahman, F.; Smith, A.M. The Microbiome and Radiation Induced-Bowel Injury: Evidence for Potential Mechanistic Role in Disease Pathogenesis. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1405. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10101405
Kumagai T, Rahman F, Smith AM. The Microbiome and Radiation Induced-Bowel Injury: Evidence for Potential Mechanistic Role in Disease Pathogenesis. Nutrients. 2018; 10(10):1405. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10101405
Chicago/Turabian StyleKumagai, Tomoko, Farooq Rahman, and Andrew M. Smith. 2018. "The Microbiome and Radiation Induced-Bowel Injury: Evidence for Potential Mechanistic Role in Disease Pathogenesis" Nutrients 10, no. 10: 1405. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10101405
APA StyleKumagai, T., Rahman, F., & Smith, A. M. (2018). The Microbiome and Radiation Induced-Bowel Injury: Evidence for Potential Mechanistic Role in Disease Pathogenesis. Nutrients, 10(10), 1405. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10101405




