Ongoing Conflict Makes Yemen Dark: From the Perspective of Nighttime Light
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
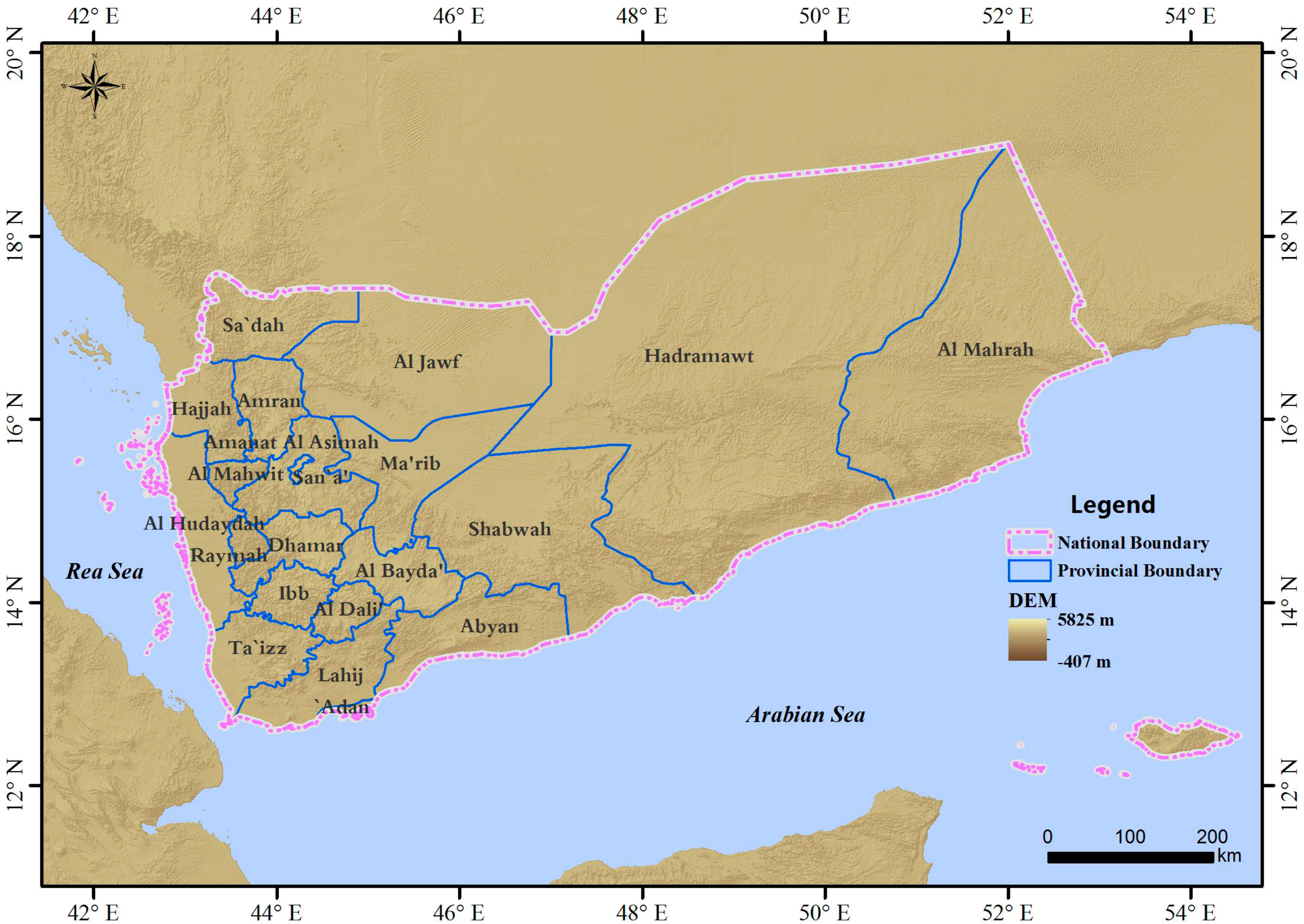
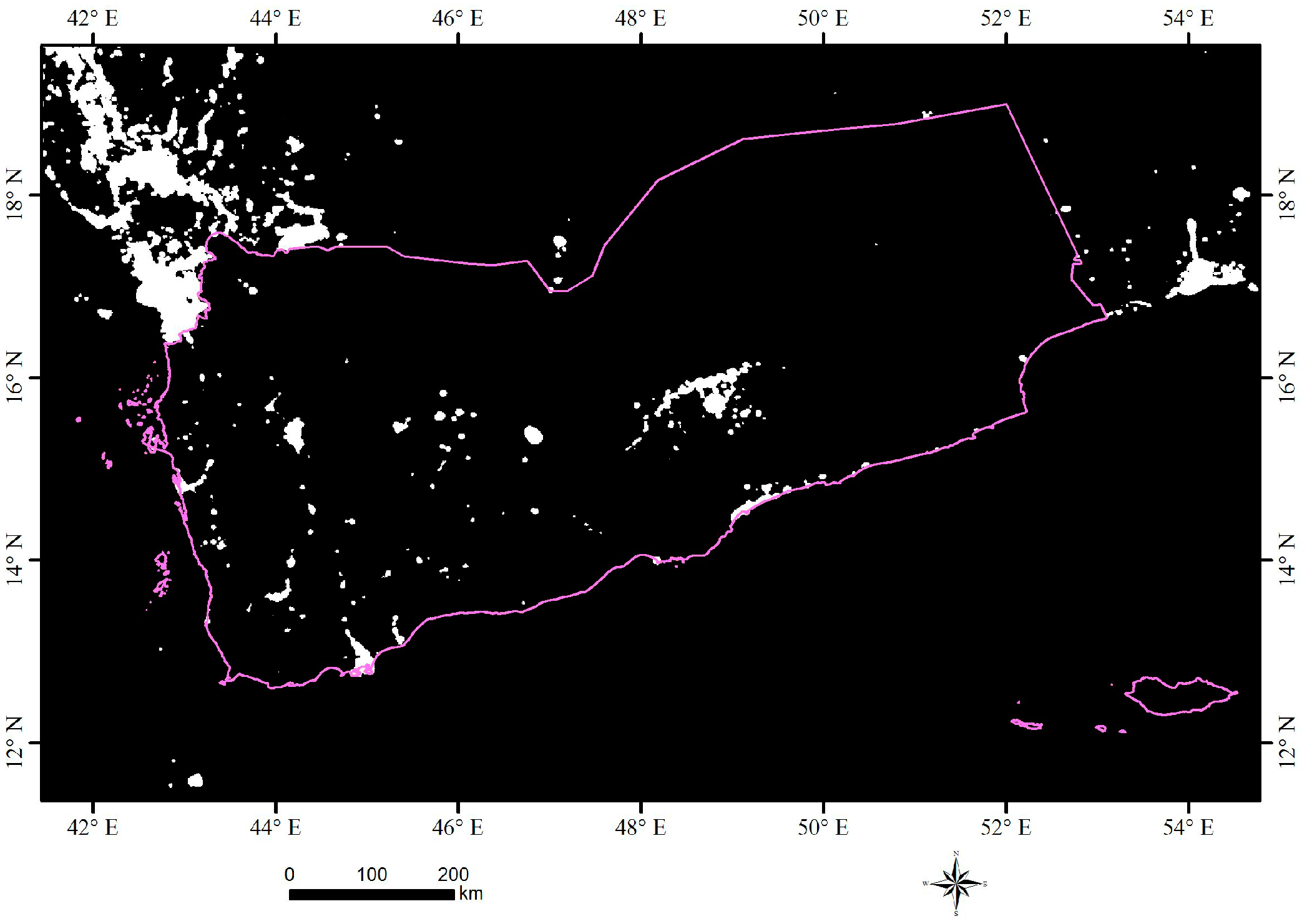
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Source
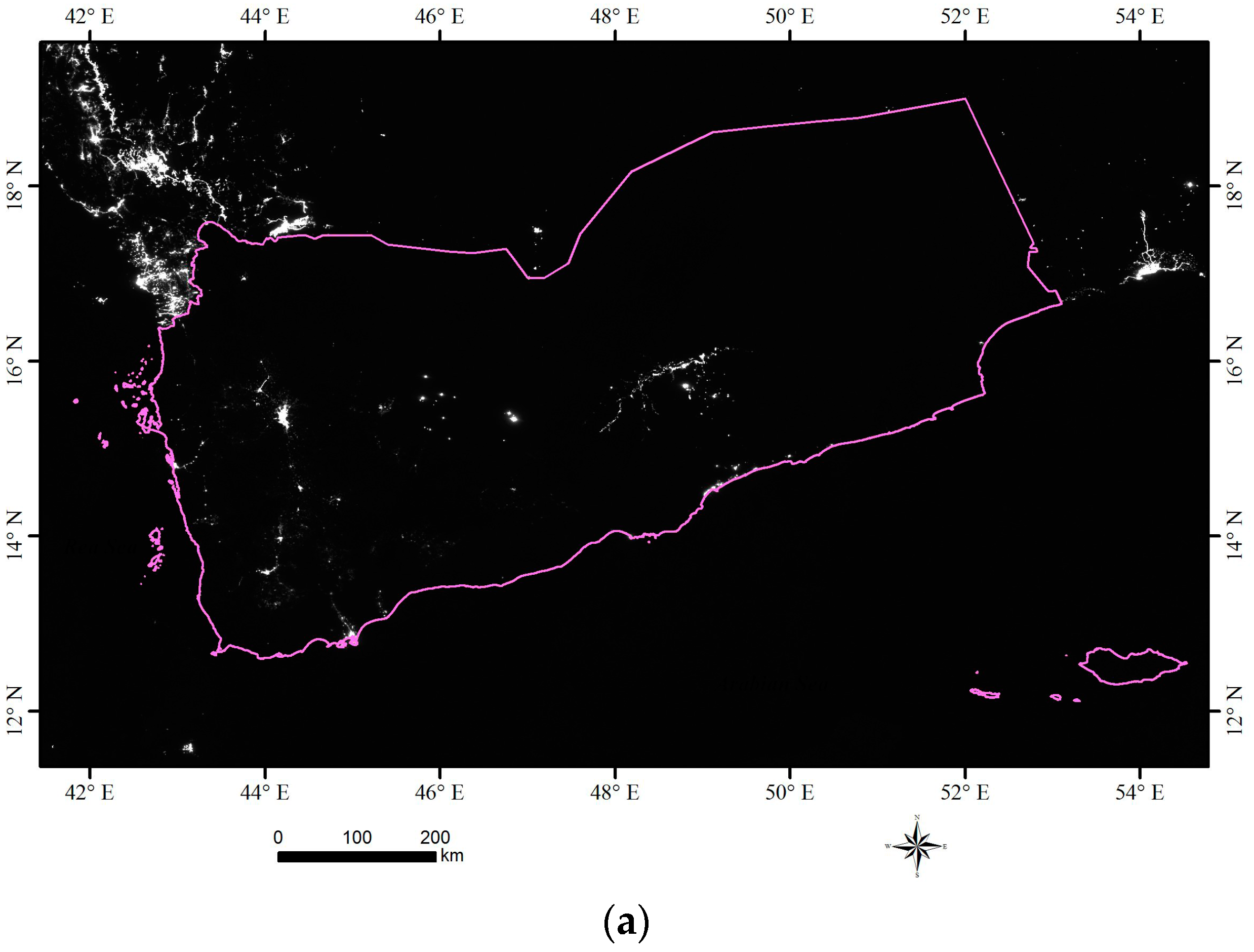
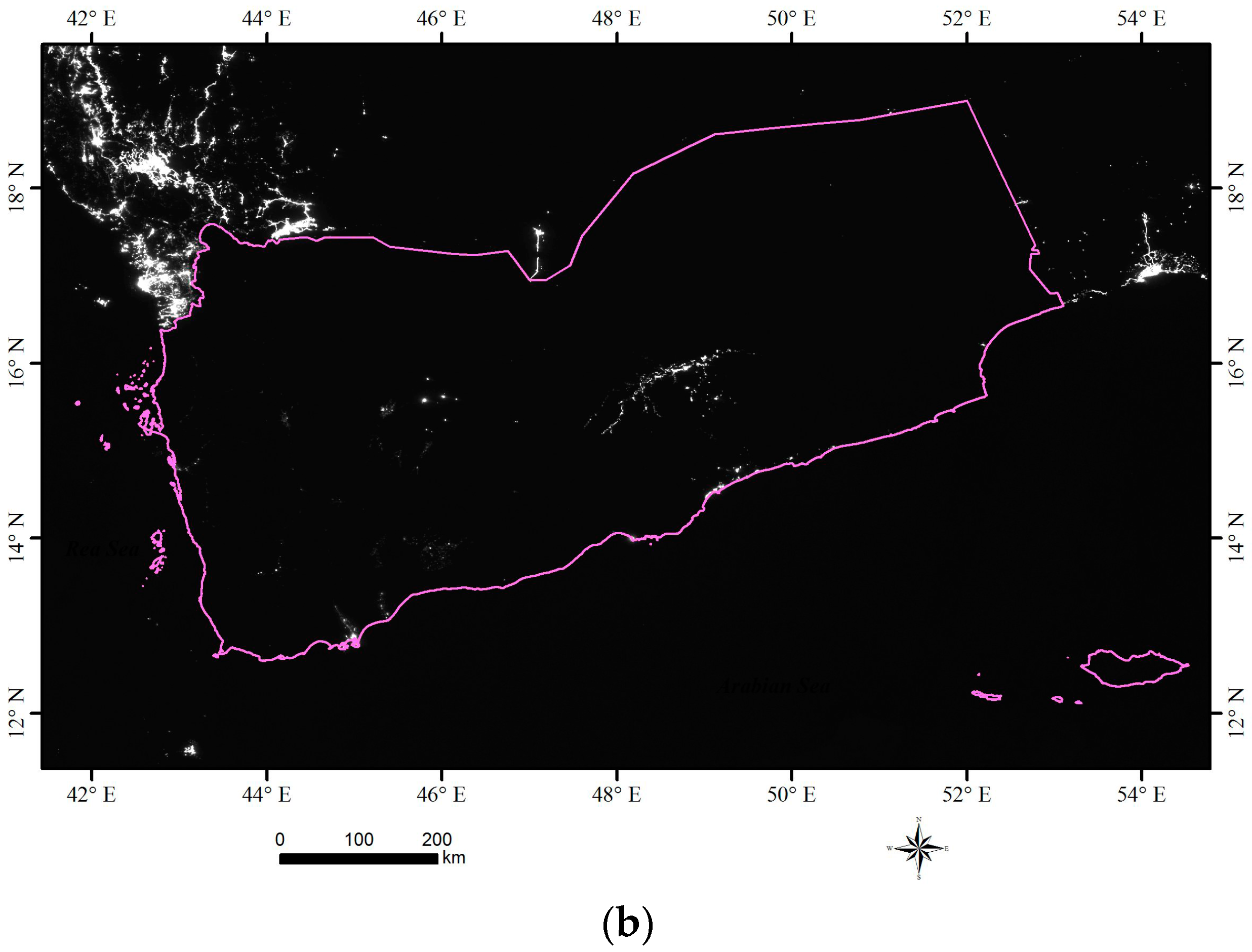
2.2.1. Nighttime Light Imagery
2.2.2. Auxiliary Data
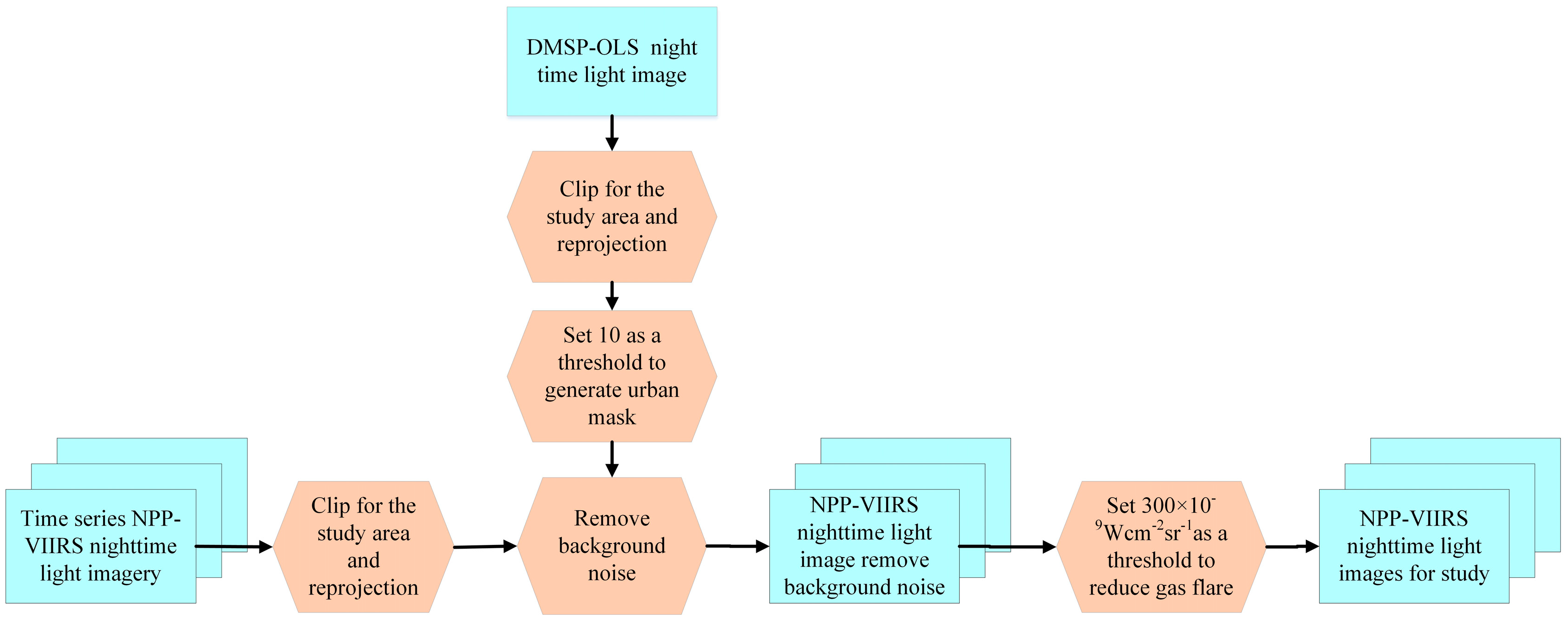
2.3. Nighttime Light Imagery Processing
2.4. Method
2.4.1. Theil-Sen Median Trend Method
2.4.2. Nighttime Light Indexes
3. Results
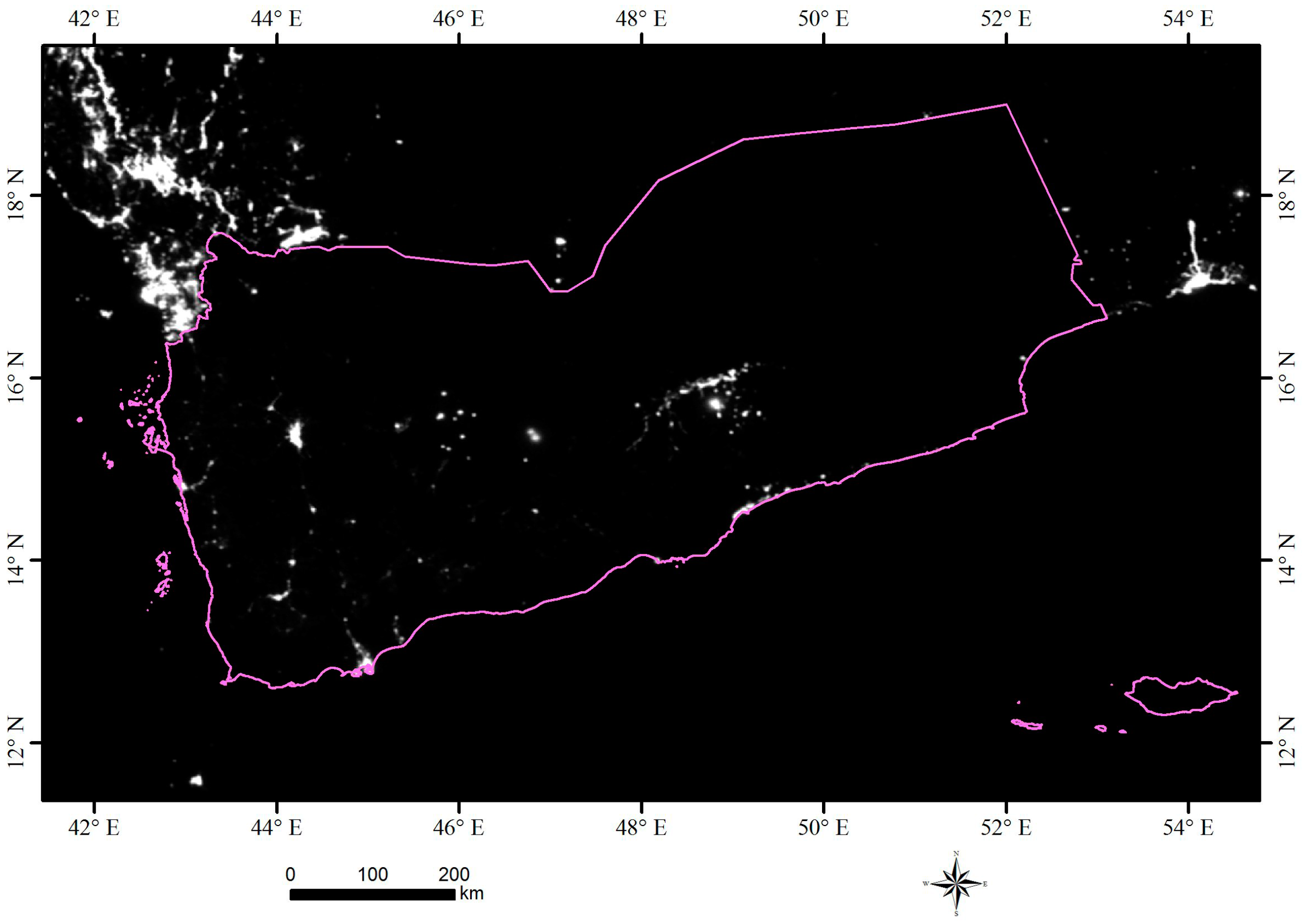
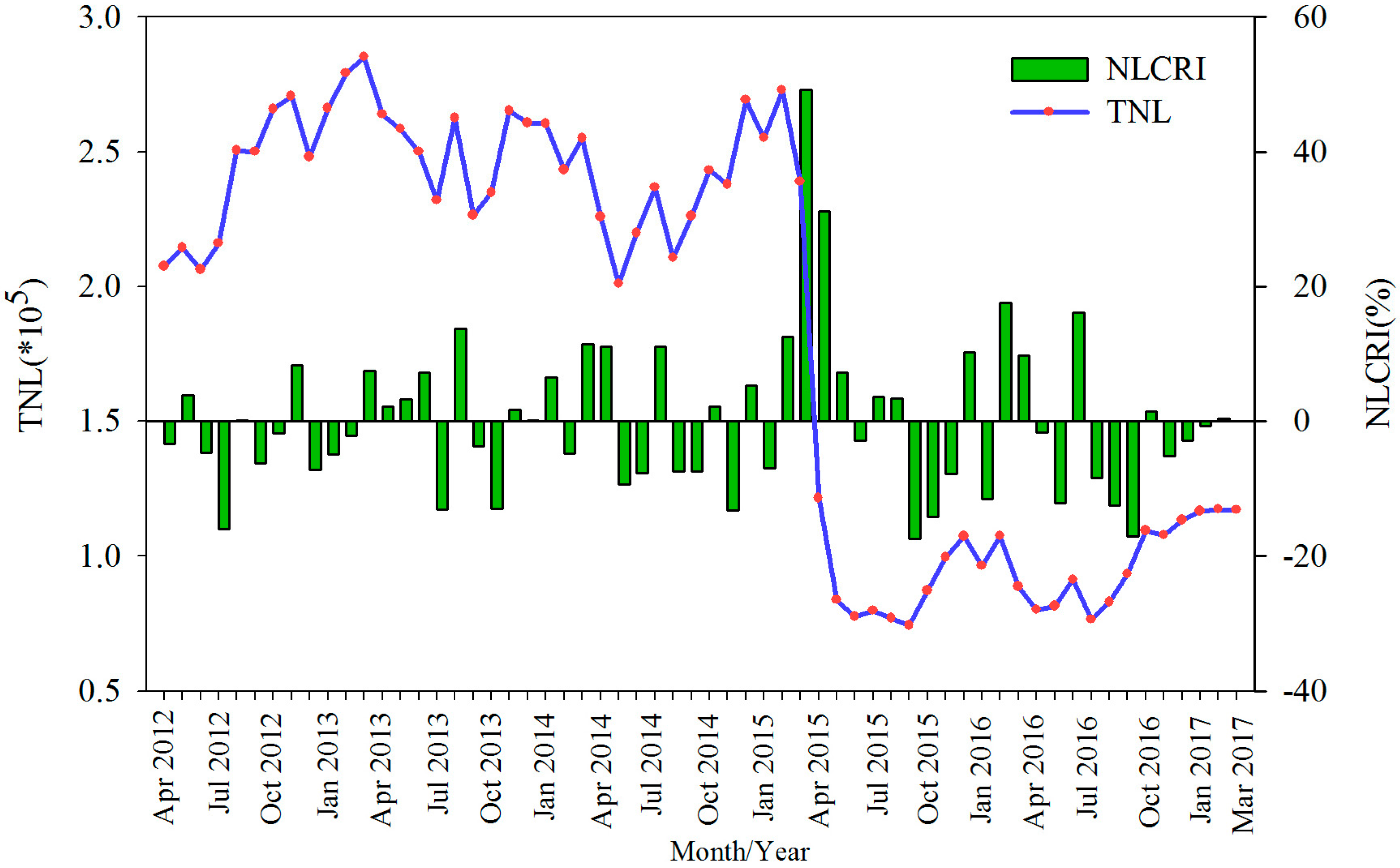
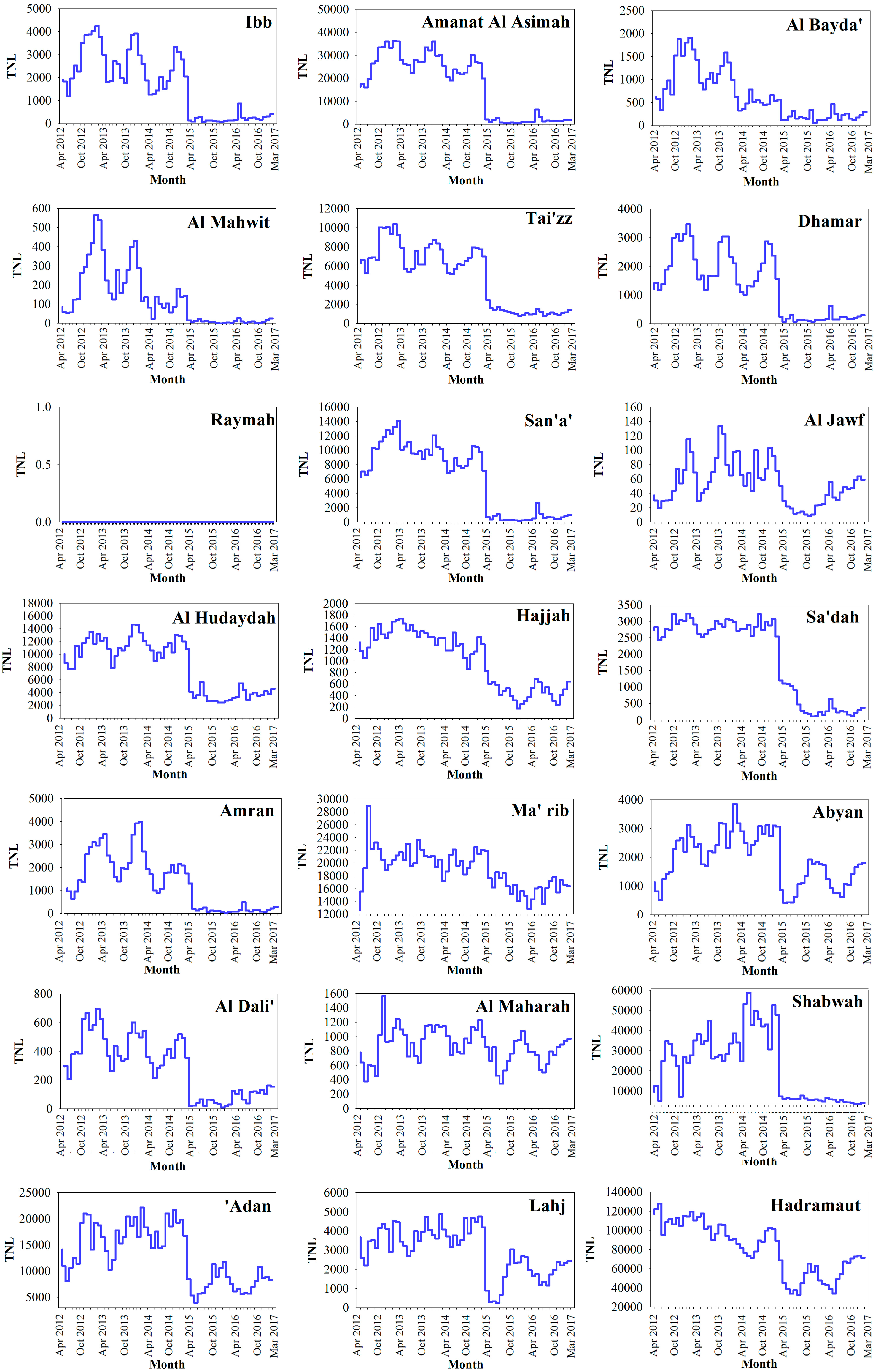
3.1. Time Series Analysis
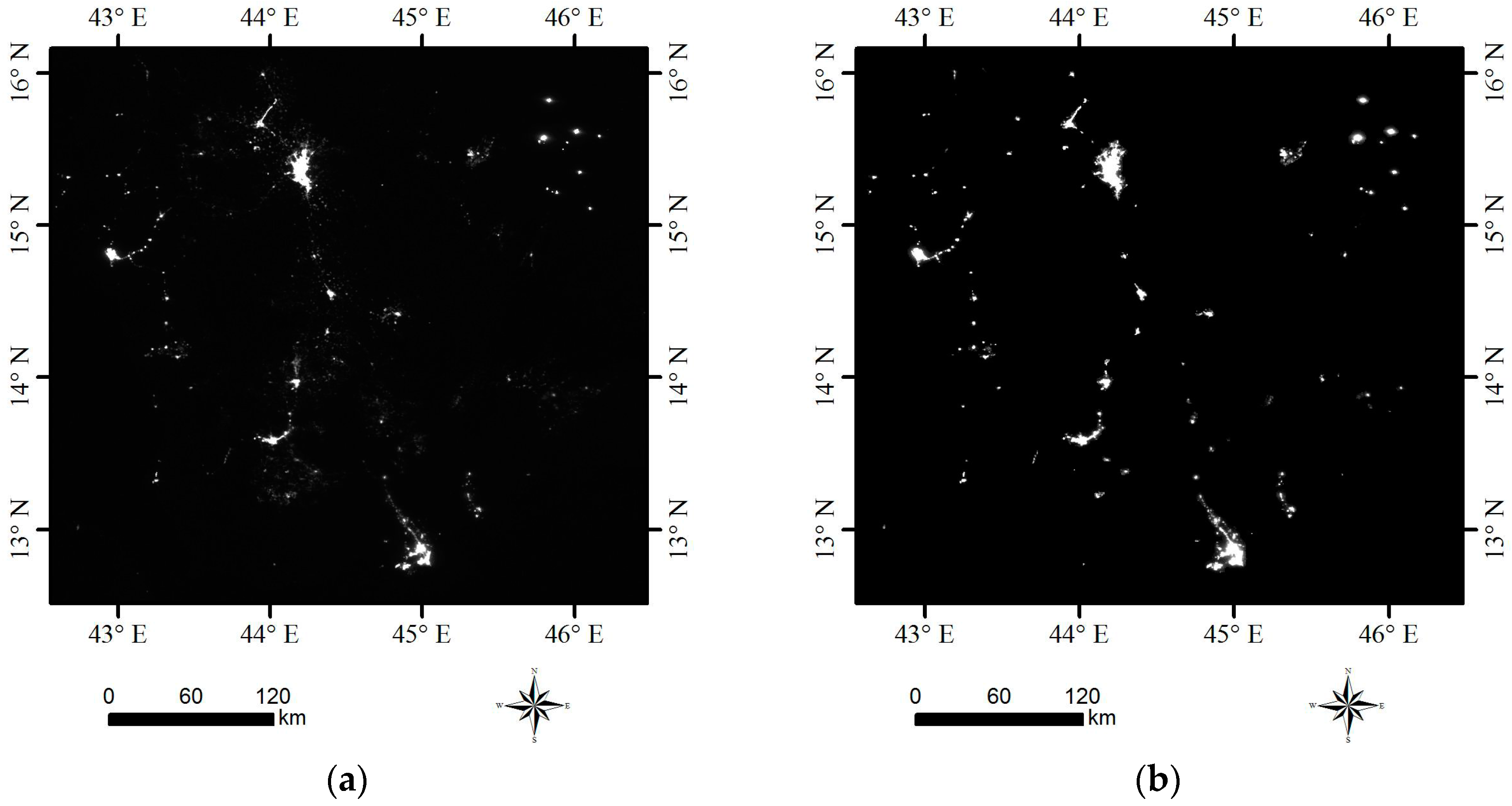
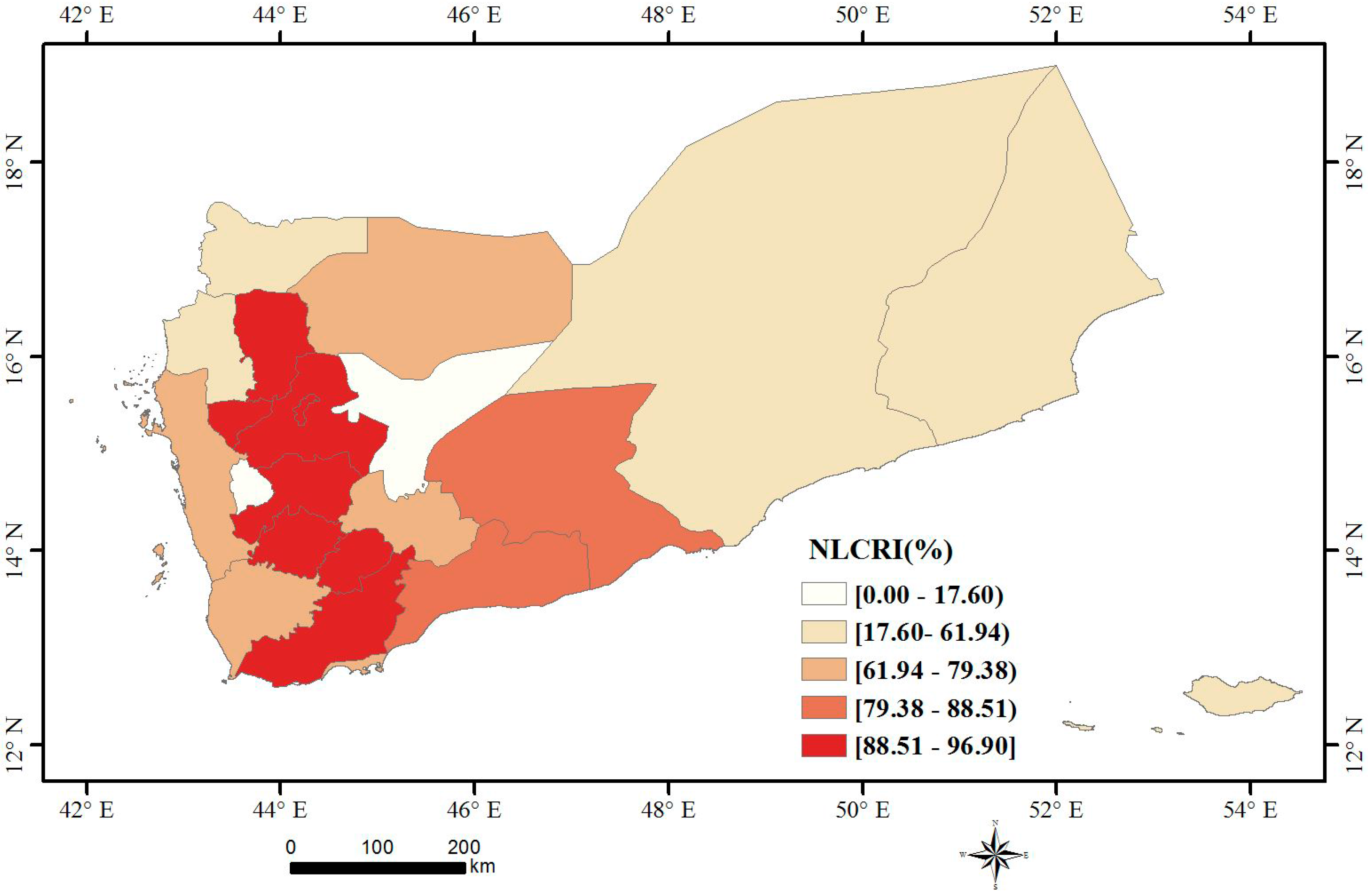
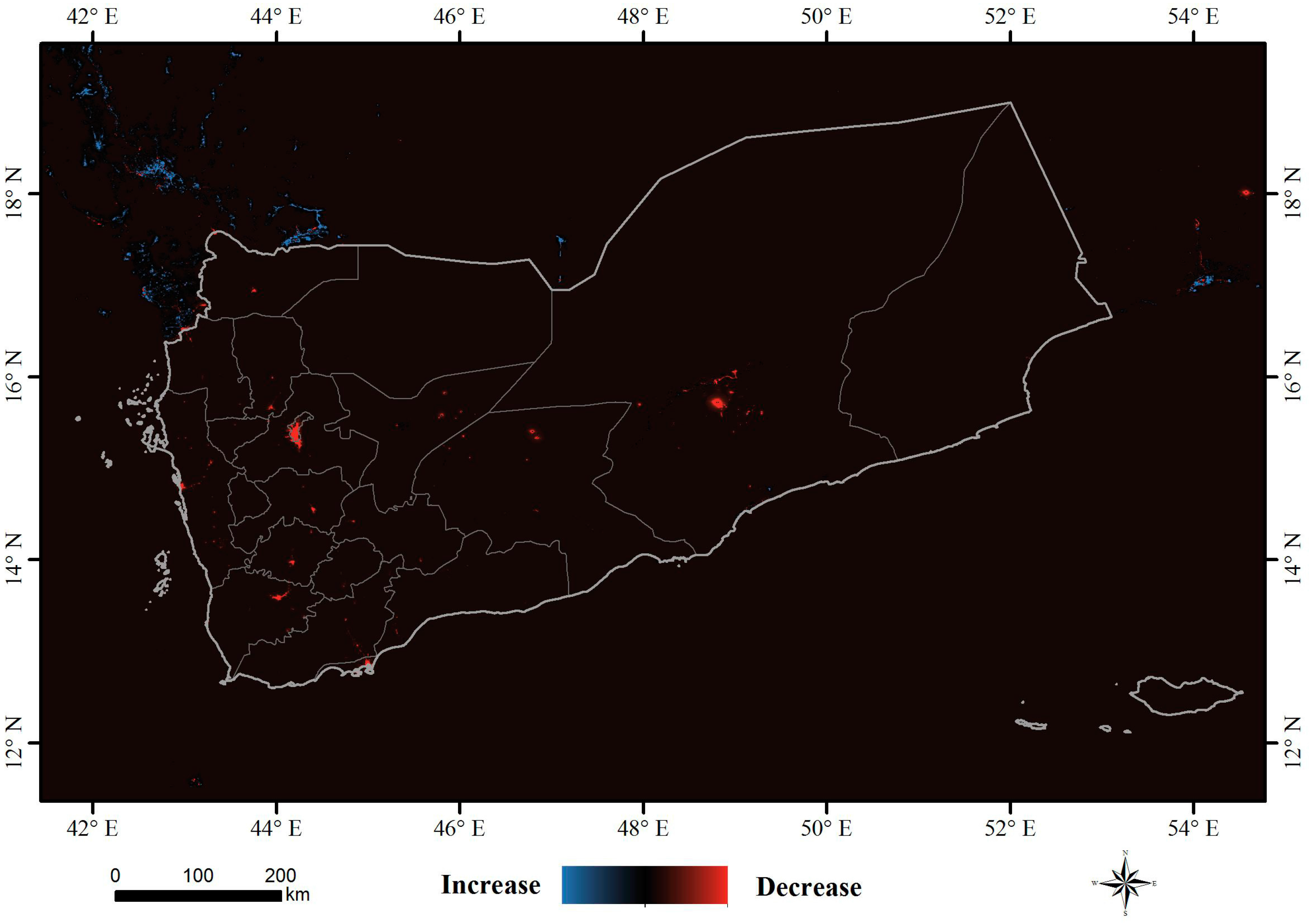
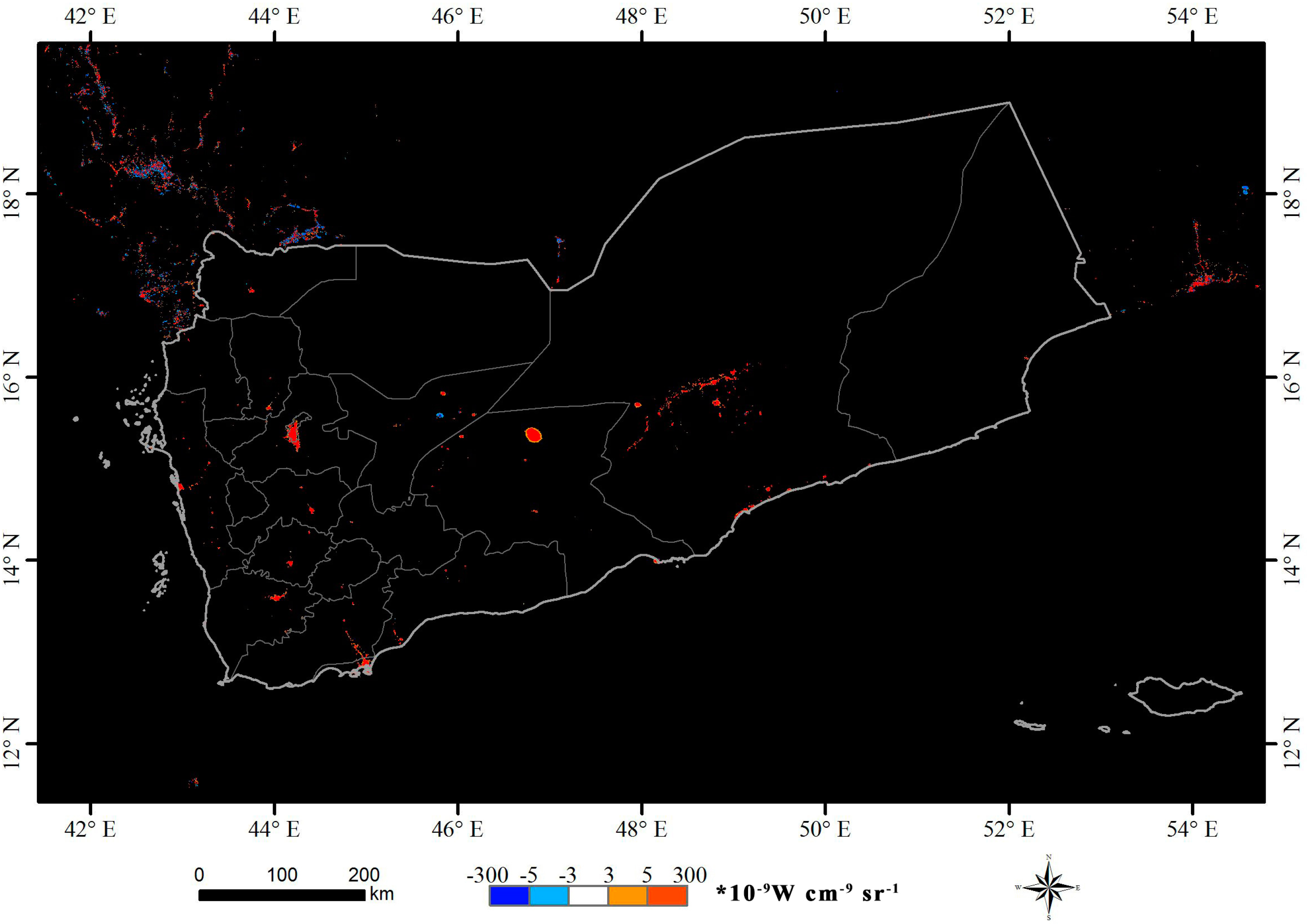
3.2. Spatial Pattern Analysis
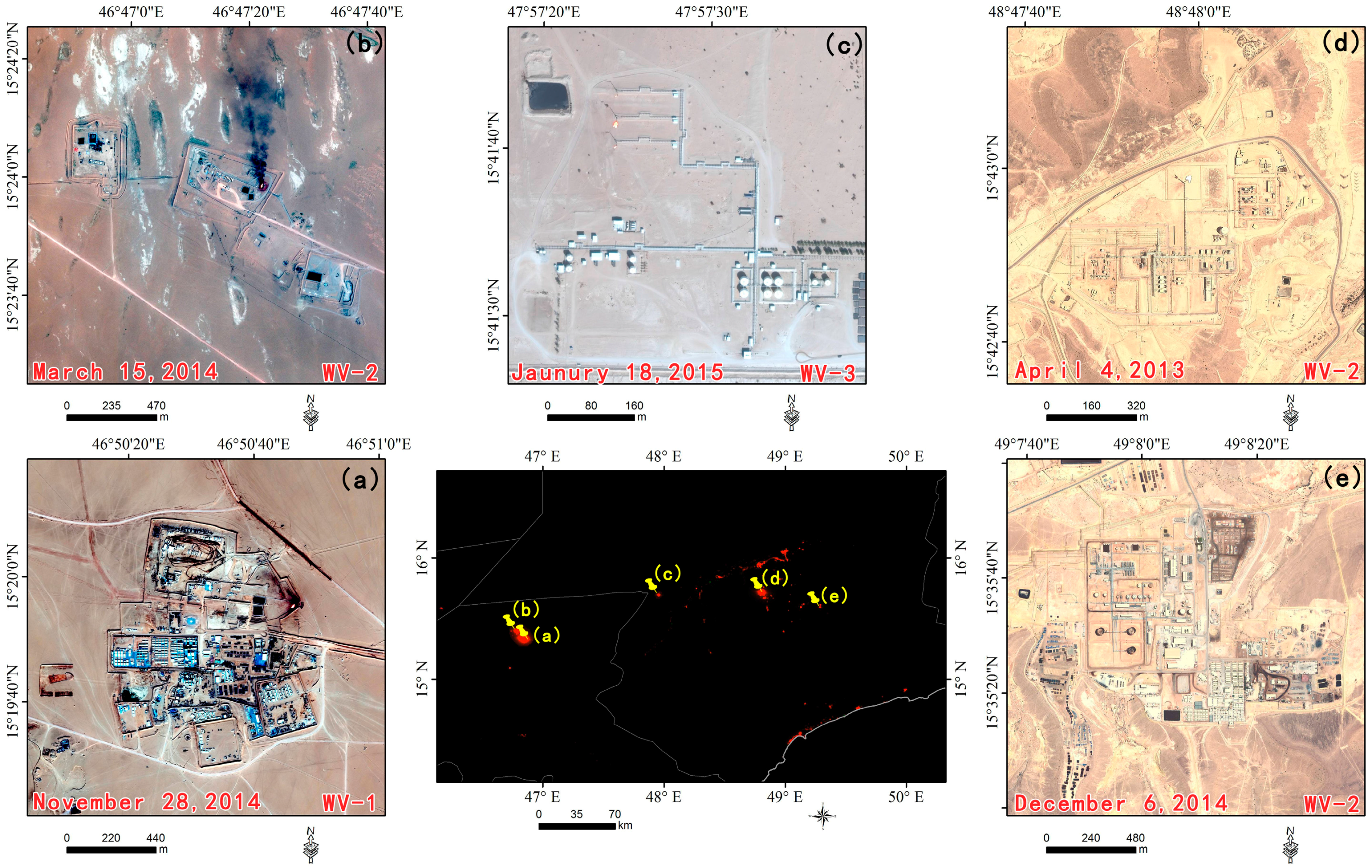
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- At the national scale, nighttime light showed a sharp decline from February 2015 to June 2015, and TNL lost 71.60%. The nighttime light in all provinces also showed the decline period. These findings reflect that the Saudi-led airstrikes caused widespread and severe humanitarian crisis in Yemen.
- (2)
- From spatial pattern analysis, the areas of decline were found to be mainly located in Sana’a, Dhamar, Ibb, Ta’izz, ’Adan, Shabwah and Hadramawt. The validation results show that the nighttime light declines in western cities and eastern cities are due to the damage of urban infrastructure and decreased oil exploration, respectively. In addition, a nighttime curfew policy and electrical blackouts are also key factors in the decline of nighttime light in Yemen.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yemen Humanitarian Response. Available online: https://www.humanitarianresponse.info/en/home (accessed on 29 August 2016).
- Humanitarian Information Unit. Available online: https://hiu.state.gov/ (accessed on 29 August 2016).
- State of Crisis: Explosive Weapons in Yemen. Available online: https://aoav.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2015/09/State-of-Crisis-A4.pdf (accessed on 29 August 2016).
- Li, X.; Zhang, R.; Huang, C.Q.; Li, D.R. Detecting 2014 northern Iraq insurgency using nighttime light imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 36, 3446–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witmer, F.D.W. Remote sensing of violent conflict: Eyes from above. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 36, 2326–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, A.J. Detecting urban destruction in Syria: A landsat-based approach. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2016, 4, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giada, S.; De Groeve, T.; Ehrlich, D.; Soille, P. Information extraction from very high resolution satellite imagery over Lukole refugee camp, Tanzania. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 4251–4266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagenlocher, M.; Lang, S.; Tiede, D. Integrated assessment of the environmental impact of an IDP Camp in Sudan based on very high resolution multi-temporal satellite imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 126, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, I.A. Assessing eco-scarcity as a cause of the outbreak of conflict in Darfur: A remote sensing approach. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 31, 2513–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, K.; Campbell, L.; Urquhart, G.; Kramer, D.; Qi, J.G. Examining complexities of forest cover change during armed conflict on Nicaragua's Atlantic Coast. Biodivers. Conserv. 2011, 20, 2597–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorsevski, V.; Kasischke, E.; Dempewolf, J.; Loboda, T.; Grossmann, F. Analysis of the impacts of armed conflict on the eastern afromontane forest region on the South Sudan—Uganda border using multitemporal landsat imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 118, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nackoney, J.; Molinario, G.; Potapov, P.; Turubanova, S.; Hansen, M.C.; Furuichi, T. Impacts of civil conflict on primary forest habitat in Northern Democratic Republic of the Congo, 1990–2010. Biol. Conserv. 2014, 170, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Cinzano, P.; Pettit, D.R.; Arvesen, J.; Sutton, P.; Small, C.; Nemani, R.; Longcore, T.; Rich, C.; Safran, J.; et al. The nightsat mission concept. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 2645–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, T.; Elvidge, C.D.; Sutton, P.C.; Baugh, K.E.; Ziskin, D.; Tuttle, B.T. Creating a global grid of distributed fossil fuel CO2 emissions from nighttime satellite imagery. Energies 2010, 3, 1895–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.F.; Chen, Y.; Yu, B.L.; Xu, T.B.; Yang, C.S.; Li, L.Y.; Huang, C.; Chen, Z.Q.; Liu, R.; Wu, J.P. Detecting spatiotemporal dynamics of global electric power consumption using DMSP-OLS nighttime stable light data. Appl. Energy 2016, 184, 450–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Yu, B.; Hu, Y.; Huang, C.; Chen, Y.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wu, J. Modeling and mapping total freight traffic in China using NPP-VIIRS nighttime light composite data. GISci. Remote Sens. 2015, 52, 274–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.Y.; Shi, P.J.; Li, J.G.; Chen, J.; Pan, Y.Z.; Li, J.; Zhuo, L.; Toshiaki, I. Restoring urbanization process in China in the 1990s by using non-radiance calibrated DMSP/OLS nighttime light imagery and statistical data. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2006, 51, 1614–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.L.; Shu, S.; Liu, H.X.; Song, W.; Wu, J.P.; Wang, L.; Chen, Z.Q. Object-based spatial cluster analysis of urban landscape pattern using nighttime light satellite images: A case study of China. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2014, 28, 2328–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, P.; Wang, X.; Feng, X.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y. Detecting China’s urban expansion over the past three decades using nighttime light data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 4095–4106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Yin, Z.; Li, B.; Zhou, C.; Haynie, S. Quantitative estimation of the velocity of urbanization in China using nighttime luminosity data. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.Y.; Smith, S.J.; Elvidge, C.D.; Zhao, K.G.; Thomson, A.; Imhoff, M. A cluster-based method to map urban area from DMSP/OLS nightlights. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 147, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Ziskin, D.; Baugh, K.E.; Tuttle, B.T.; Ghosh, T.; Pack, D.W.; Erwin, E.H.; Zhizhin, M. A fifteen year record of global natural gas flaring derived from satellite data. Energies 2009, 2, 595–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Scheving, B.; Shoghli, B.; Zygarlicke, C.; Wocken, C. Quantifying gas flaring CH4 consumption using VIIRS. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 9529–9541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaston, K.J.; Duffy, J.P.; Bennie, J. Quantifying the erosion of natural darkness in the global protected area system. Conserv. Biol. 2015, 29, 1132–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyba, C.C.M.; Ruhtz, T.; Fischer, J.; Hoelker, F. Lunar skylight polarization signal polluted by urban lighting. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennie, J.; Duffy, J.P.; Davies, T.W.; Correa-Cano, M.E.; Gaston, K.J. Global trends in exposure to light pollution in natural terrestrial ecosystems. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 2715–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; He, G.J.; Long, T.F.; Wang, C.; Ni, Y.; Ma, R.Q. Assessing light pollution in China based on nighttime light imagery. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, F.; Chen, X. Satellite-observed nighttime light variation as evidence for global armed conflicts. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2013, 6, 2302–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, C.R.; Zullo, J.; Elvidge, C. Brazil’s 2001 energy crisis monitored from space. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 25, 2475–2482. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Li, D. Can nighttime light images play a role in evaluating the Syrian crisis? Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 6648–6661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, D.; Xu, H.; Wu, C. Intercalibration between DMSP/OLS and VIIRS nighttime light images to evaluate city light dynamics of Syria’s major human settlement during Syrian civil war. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witmer, F.D.W.; O’Loughlin, J. Detecting the effects of wars in the caucasus regions of Russia and Georgia using radiometrically normalized DMSP-OLS nighttime lights imagery. GISci. Remote Sens. 2011, 48, 478–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coscieme, L.; Sutton, P.C.; Anderson, S.; Liu, Q.; Elvidge, C.D. Dark times: Nighttime satellite imagery as a detector of regional disparity and the geography of conflict. GISci. Remote Sens. 2017, 54, 118–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.F.; Yu, B.L.; Huang, Y.X.; Hu, Y.J.; Yin, B.; Chen, Z.Q.; Chen, L.J.; Wu, J.P. Evaluating the ability of NPP-VIIRS nighttime light data to estimate the gross domestic product and the electric power consumption of China at multiple scales: A comparison with DMSP-OLS data. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 1705–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, H.M.; Chen, X.L.; Li, C. Potential of NPP-VIIRS nighttime light imagery for modeling the regional economy of China. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 3057–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, X.L.; Zhao, Y.S.; Xu, J.; Chen, F.R.; Li, H. Automatic intercalibration of nighttime light imagery using robust regression. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 4, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.F.; Huang, C.; Yu, B.L.; Yin, B.; Huang, Y.X.; Wu, J.P. Evaluation of NPP-VIIRS nighttime light composite data for extracting built-up urban areas. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 5, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Shi, K.; Hu, Y.; Huang, C.; Chen, Z.; Wu, J. Poverty evaluation using NPP-VIIRS nighttime light composite data at the county level in China. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 1217–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yemeni Crisis (2011–Present). Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Yemeni_Crisis_(2011-present) (accessed on 29 August 2016).
- Yemen Profile—Timeline. Available online: http://www.bbc.com/news/world-middle-east-14704951 (accessed on 19 June 2017).
- Version 1 VIIRS Day/Night Band Nighttime Lights. Available online: https://ngdc.noaa.gov/eog/viirs/download_dnb_composites.html (accessed on 18 June 2017).
- Version 4 DMSP-OLS Nighttime Lights Time Series. Available online: https://ngdc.noaa.gov/eog/dmsp/downloadV4composites.html (accessed on 16 June 2017).
- Gadm Database of Global Administrative Areas. Available online: http://www.gadm.org/ (accessed on 29 August 2016).
- Zhao, N.Z.; Samson, E.L. Estimation of virtual water contained in international trade products using nighttime imagery. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2012, 18, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Zhizhin, M.; Baugh, K.; Hsu, F.C.; Ghosh, T. Methods for global survey of natural gas flaring from visible infrared imaging radiometer suite data. Energies 2016, 9, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- How Much Oil Is Daesh Producing? Evidence From Remote Sensing. Available online: https://www.aeaweb.org/conference/2017/preliminary/paper/Drey9fyy (accessed on 18 June 2017).
- Viirs Nightfire. Available online: https://ngdc.noaa.gov/eog/viirs/download_viirs_fire.html (accessed on 29 August 2016).
- Ma, T.; Zhou, C.H.; Pei, T.; Haynie, S.; Fan, J.F. Responses of Suomi-NPP VIIRS-derived nighttime lights to socioeconomic activity in China’s cities. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 5, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.G.; Yuan, L.H.; Wang, W.J.; Cao, R.; Zhang, Y.F.; Shen, W.M. Spatio-temporal analysis of vegetation variation in the Yellow River basin. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 51, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.C.; Bai, X.Y.; Wang, S.J.; Qin, L.Y.; Li, Y. Spatial-temporal changes of vegetation cover in Guizhou Province, Southern China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2017, 27, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, S. Analysing temporal trends in the ratios of PM2.5/PM10 in the UK. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2017, 17, 34–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Jiang, W.G.; Yuan, L.H.; Wang, W.J.; Lv, Z.L.; Chen, Z. Inter-annual variations in vegetation and their response to climatic factors in the upper catchments of the Yellow River from 2000 to 2010. J. Geogr. Sci. 2014, 24, 963–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, P.; Sarkar, S.; Basistha, A.; Sachdeva, K. Trend analysis and forecast of pre-monsoon rainfall over India. Weather 2016, 71, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, L.; Ichinose, T.; Zheng, J.; Chen, J.; Shi, P.J.; Li, X. Modelling the population density of China at the pixel level based on DMSP/OLS non-radiance-calibrated nighttime light images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 1003–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ge, L.L.; Chen, X.L. Detecting Zimbabwe’s decadal economic decline using nighttime light imagery. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 4551–4570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, N. The impact of seasonal changes on observed nighttime brightness from 2014 to 2015 monthly VIIRS DNB composites. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 193, 150–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yemen 2017 Humanitarian Response Plan. Available online: http://www.unocha.org/yemen (accessed on 2 May 2017).
- Saudi Arabia Launches Air Strikes in Yemen. Available online: http://www.bbc.com/news/world-us-canada-32061632 (accessed on 18 June 2017).
- U.S. Fingerprints on Attacks Obliterating Yemen’s Economy. Available online: https://www.nytimes.com/2016/11/14/world/middleeast/yemen-saudi-bombing-houthis-hunger.html?_r=0 (accessed on 19 June 2017).
- Yemen Conflict: Twin Suicide Bombings Hit Aden Base. Available online: http://www.bbc.com/news/world-middle-east-36722447 (accessed on 19 June 2017).
- Saudi Coalition Bombs Yemen Water Bottling Plant, Killing Dozens of Civilians. Available online: https://www.commondreams.org/news/2015/08/31/saudi-coalition-bombs-yemen-water-bottling-plant-killing-dozens-civilians (accessed on 19 June 2017).
- Yemen Crude Oil Production. Available online: http://www.tradingeconomics.com/yemen/crude-oil-production (accessed on 2 May 2017).
- Monitoring the Syrian Humanitarian Crisis with the JRC’s Global Human Settlement Layer and Nighttime Satellite Data. Available online: http://publications.jrc.ec.europa.eu/repository/bitstream/JRC101733/syria_ghsl-template%20jrc%20technical%20reports-online.pdf (accessed on 2 May 2017).
- Yemen Enforces Curfew in Sanaa amid Clashes with Shiite Rebels. Available online: https://www.thestar.com/news/world/2014/09/20/yemen_enforces_curfew_in_sanaa_amid_clashes_with_shiite_rebels.html (accessed on 19 June 2017).
- Yemen Declares Nighttime Curfew in Port City of Aden. Available online: http://wtop.com/world/2016/01/yemen-declares-nighttime-curfew-in-port-city-of-aden/ (accessed on 2 May 2017).
- Visible Light at Night over Yemen as of 21 July 2015. Available online: http://www.unitar.org/unosat/node/44/2243?utm_source=unosat-unitar&utm_medium=rss&utm_campaign=maps (accessed on 2 May 2017).


| Parameters | NPP-VIIRS | DMSP-OLS |
|---|---|---|
| Operator | National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) | Department of Defense, United States |
| Orbit | Polar orbit satellite | Polar orbit satellite |
| Overpass time | 13:30 and 1:30 | 8:30–9:30 and 20:30–21:30 |
| Width | 3040 km | 3000 km |
| Temporal resolution | 12 h | 12 h |
| Spatial resolution | 742 m | 2.7 km |
| Wavelength range | 0.5–0.9 µm | 0.4–1.1 µm |
| Radiation resolution | 14 bit | 6 bit |
| Unit | W·cm−2·sr−1·μm−1 | Relative (0–63 scale) |
| On-board calibration | Yes | No |
| Pixel saturated | No saturated | Saturated |
| Available product | December 2011–now | 1992–2013 |
| Product cycle | Month | Year |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, W.; He, G.; Long, T.; Liu, H. Ongoing Conflict Makes Yemen Dark: From the Perspective of Nighttime Light. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 798. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9080798
Jiang W, He G, Long T, Liu H. Ongoing Conflict Makes Yemen Dark: From the Perspective of Nighttime Light. Remote Sensing. 2017; 9(8):798. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9080798
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Wei, Guojin He, Tengfei Long, and Huichan Liu. 2017. "Ongoing Conflict Makes Yemen Dark: From the Perspective of Nighttime Light" Remote Sensing 9, no. 8: 798. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9080798
APA StyleJiang, W., He, G., Long, T., & Liu, H. (2017). Ongoing Conflict Makes Yemen Dark: From the Perspective of Nighttime Light. Remote Sensing, 9(8), 798. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9080798







