Empirical Estimation of Near-Surface Air Temperature in China from MODIS LST Data by Considering Physiographic Features
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
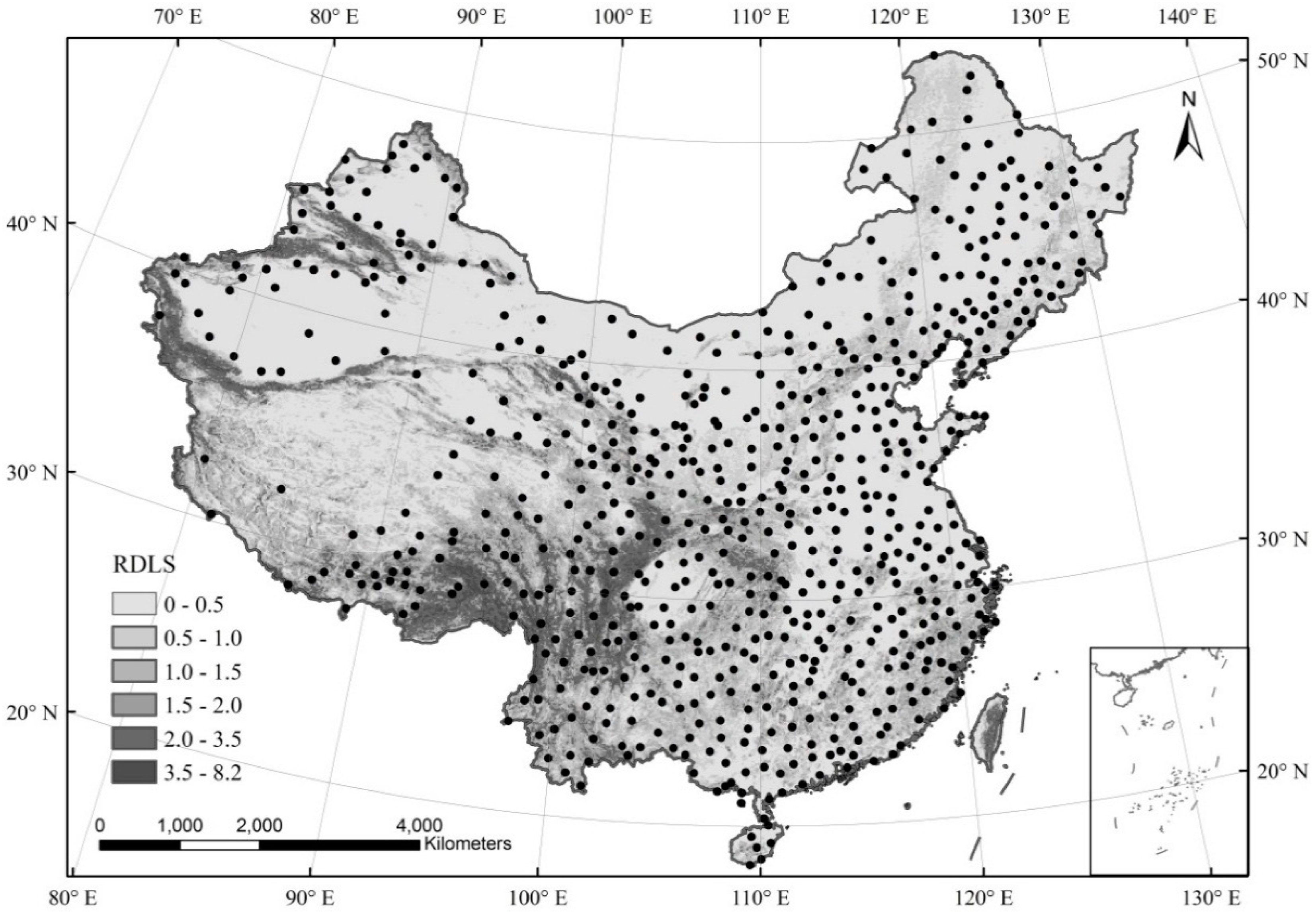
2.1. Meteorological Data
2.2. Satellite Data
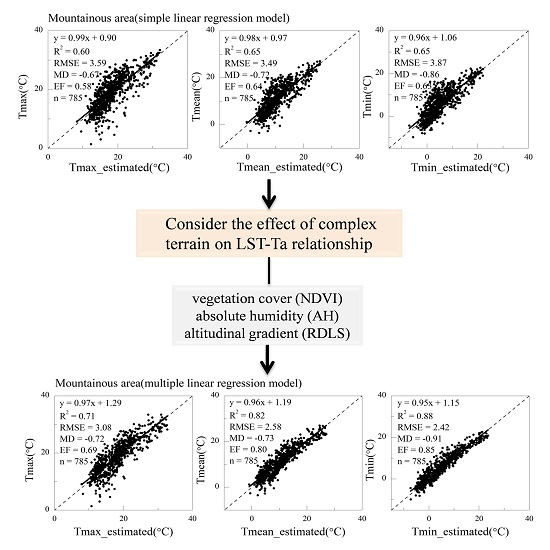
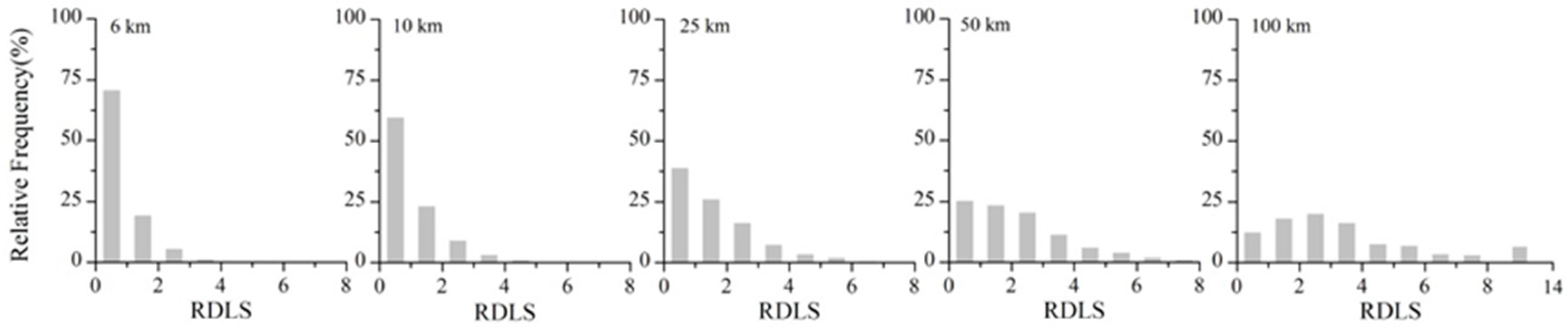
2.3. Relief Degree of the Land Surface
3. Results
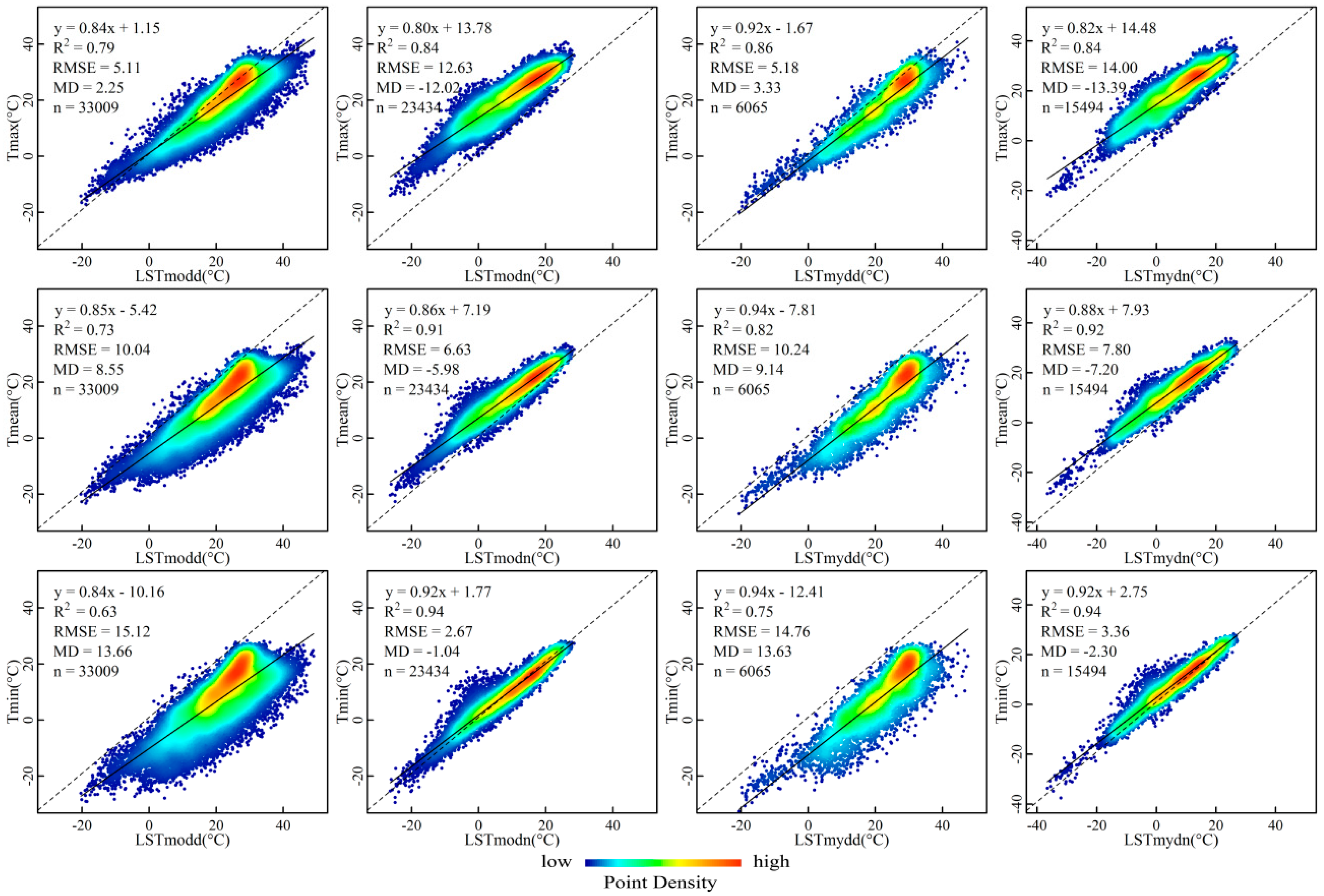
3.1. Relationships between the Ta and the Four LST Products over China
3.2. Model Building
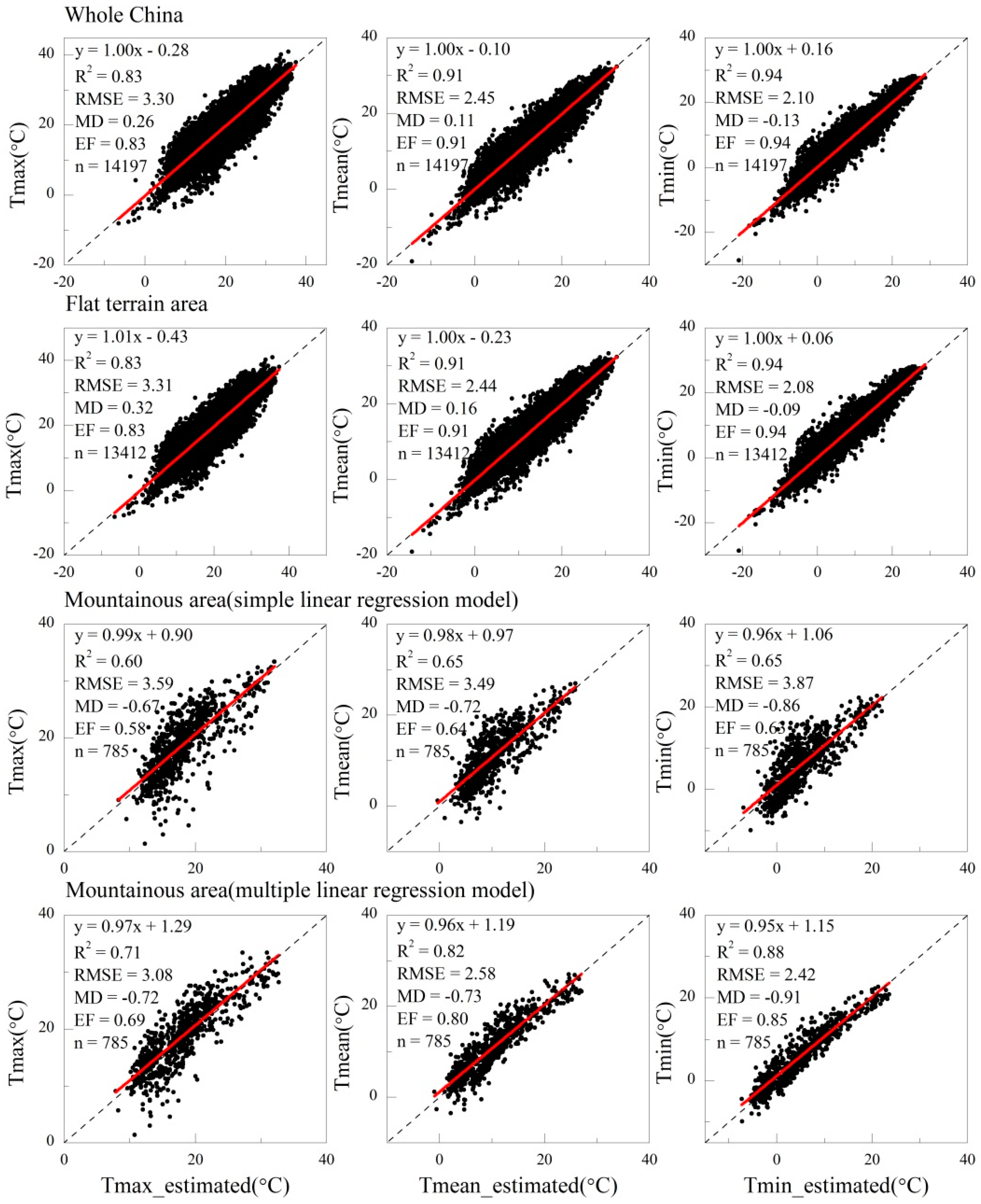
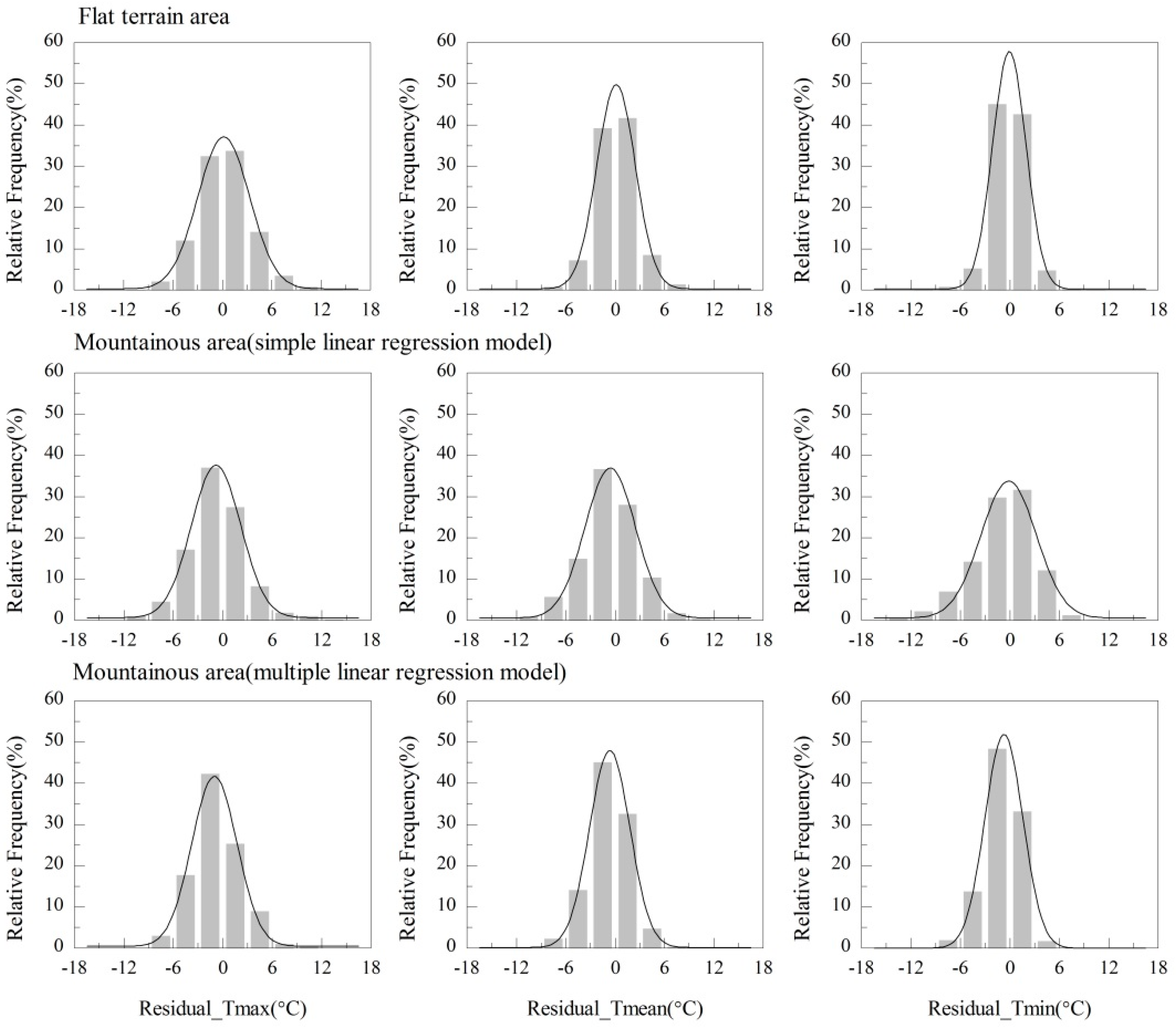
3.3. Model Validation
4. Discussion
4.1. The Accuracy of the Daytime and Nighttime LST for Ta Estimation
4.2. Using the Multiple Linear Regression Model to Derive Ta in Mountainous Areas
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, K.; Li, Z.; Cribb, M. Estimation of evaporative fraction from a combination of day and night land surface temperatures and ndvi: A new method to determine the priestley–taylor parameter. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 102, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, J.M.; Kustas, W.P.; Humes, K.S. Source approach for estimating soil and vegetation energy fluxes in observations of directional radiometric surface temperature. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1995, 77, 263–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betts, A.K.; Ball, J.H.; Beljaars, A.; Miller, M.J.; Viterbo, P.A. The land surfa-ceatmosphere interaction: A review based on observational and global modeling perspectives. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1996, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyler, J.W.; Ballantyne, A.; Jencso, K.; Sweet, M.; Running, S.W. Creating a topoclimatic daily air temperature dataset for the conterminous united states using homogenized station data and remotely sensed land skin temperature. Int. J. Climatol. 2015, 35, 2258–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, I.; Jones, P.; Osborn, T.; Lister, D. Updated high-resolution grids of monthly climatic observations-the cru ts3. 10 dataset. Int. J. Climatol. 2014, 34, 623–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stocker, T.; Qin, D.; Plattner, G.; Tignor, M.; Allen, S.; Boschung, J.; Nauels, A.; Xia, Y.; Bex, B.; Midgley, B. IPCC, 2013: Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalnay, E.; Kanamitsu, M.; Kistler, R.; Collins, W.; Deaven, D.; Gandin, L.; Iredell, M.; Saha, S.; White, G.; Woollen, J. The ncep/ncar 40-year reanalysis project. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1996, 77, 437–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uppala, S.M.; Kållberg, P.; Simmons, A.; Andrae, U.; Bechtold, V.D.; Fiorino, M.; Gibson, J.; Haseler, J.; Hernandez, A.; Kelly, G. The era-40 re-analysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2005, 131, 2961–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, K.; Moore, R.; Floyer, J.; Asplin, M.; McKendry, I. Comparison of approaches for spatial interpolation of daily air temperature in a large region with complex topography and highly variable station density. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2006, 139, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, Z.A.; Abatzoglou, J.T.; Luce, C.H.; Baggett, L.S. Empirical downscaling of daily minimum air temperature at very fine resolutions in complex terrain. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2011, 151, 1066–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stisen, S.; Sandholt, I.; Nørgaard, A.; Fensholt, R.; Eklundh, L. Estimation of diurnal air temperature using msg seviri data in west Africa. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 110, 262–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benali, A.; Carvalho, A.; Nunes, J.; Carvalhais, N.; Santos, A. Estimating air surface temperature in portugal using modis lst data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 124, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristóbal, J.; Ninyerola, M.; Pons, X. Modeling air temperature through a combination of remote sensing and gis data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Huang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Sun, W. Empirical models for estimating daily maximum, minimum and mean air temperatures with modis land surface temperatures. Int. J. Remote. Sens. 2011, 32, 9415–9440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Zhu, J.; Yan, Q. Monthly air temperatures over northern China estimated by integrating modis data with gis techniques. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2013, 52, 1987–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Leptoukh, G.G. Estimation of surface air temperature over central and eastern eurasia from modis land surface temperature. Environ. Res. Lett. 2011, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloog, I.; Chudnovsky, A.; Koutrakis, P.; Schwartz, J. Temporal and spatial assessments of minimum air temperature using satellite surface temperature measurements in massachusetts, USA. Sci. Total. Environ. 2012, 432, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Z. New refinements and validation of the modis land-surface temperature/emissivity products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Pu, R. Downscaling thermal infrared radiance for subpixel land surface temperature retrieval. Sensors 2008, 8, 2695–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Dickinson, R.E. Land surface skin temperature climatology: Benefitting from the strengths of satellite observations. Environ. Res. Lett. 2010, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shreve, C. Working towards a community-wide understanding of satellite skin temperature observations. Environ. Res. Lett. 2010, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; Shen, Z.; Zhang, X.; Shi, P.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J. Estimating air temperature of an alpine meadow on the northern tibetan plateau using modis land surface temperature. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2011, 31, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prince, S.D.; Goetz, S.J.; Dubayah, R.; Czajkowski, K.; Thawley, M. Inference of surface and air temperature, atmospheric precipitable water and vapor pressure deficit using advanced very high-resolution radiometer satellite observations: Comparison with field observations. J. Hydrol. 1998, 212, 230–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vancutsem, C.; Ceccato, P.; Dinku, T.; Connor, S.J. Evaluation of modis land surface temperature data to estimate air temperature in different ecosystems over africa. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 449–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recondo, C.; Peón, J.J.; Zapico, E.; Pendás, E. Empirical models for estimating daily surface water vapour pressure, air temperature, and humidity using modis and spatiotemporal variables. Applications to peninsular spain. Int. J. Remote. Sens. 2013, 34, 8051–8080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Gao, S.; Chen, H.; Yu, J.; Tang, Q. Retrieval of the land surface-air temperature difference from high spatial resolution satellite observations over complex surfaces in the Tibetan Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Kafatos, M. Note on the ndvi-lst relationship and the use of temperature-related drought indices over north america. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto, H.; Sandholt, I.; Aguado, I.; Chuvieco, E.; Stisen, S. Air temperature estimation with msg-seviri data: Calibration and validation of the tvx algorithm for the iberian peninsula. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, J.; Mintz, Y. Influence of land-surface evapotranspiration on the earth's climate. Science 1982, 215, 1498–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coll, C.; Caselles, V.; Galve, J.M.; Valor, E.; Niclos, R.; Sánchez, J.M.; Rivas, R. Ground measurements for the validation of land surface temperatures derived from aatsr and modis data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 97, 288–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Muñoz, J.C.; Sobrino, J.A. A generalized single-channel method for retrieving land surface temperature from remote sensing data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, E.E. Downscaling modis lst in the east african mountains using elevation gradient and land-cover information. Int. J. Remote. Sens. 2014, 35, 3094–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroppiana, D.; Antoninetti, M.; Brivio, P.A. Seasonality of modis lst over southern italy and correlation with land cover, topography and solar radiation. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 47, 133–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundquist, J.D.; Cayan, D.R. Surface temperature patterns in complex terrain: Daily variations and long-term change in the central sierra nevada, california. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Liua, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, C. Estimation and Analysis of Land Surface Water and Heat Fluxes in Mountain-Plain Area Based on Remote Sensing and Dem. In Proceedings of the 2009 17th International Conference on Geoinformatics, Fairfax, VA, USA, 12–14 August 2009.
- Van De Kerchove, R.; Lhermitte, S.; Veraverbeke, S.; Goossens, R. Spatio-temporal variability in remotely sensed land surface temperature, and its relationship with physiographic variables in the russian altay mountains. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2013, 20, 4–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noetzli, J.; Gruber, S.; Kohl, T.; Salzmann, N.; Haeberli, W. Three-dimensional distribution and evolution of permafrost temperatures in idealized high-mountain topography. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mittaz, C.; Hoelzle, M.; Haeberli, W. First results and interpretation of energy-flux measurements over alpine permafrost. Ann. Glaciol. 2000, 31, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoldi, G.; Notarnicola, C.; Leitinger, G.; Endrizzi, S.; Zebisch, M.; Della Chiesa, S.; Tappeiner, U. Topographical and ecohydrological controls on land surface temperature in an alpine catchment. Ecohydrology 2010, 3, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Mohammat, A.; Feng, J.; Zhou, R.; Fang, J. Storage, patterns and environmental controls of soil organic carbon in China. Biogeochemistry 2007, 84, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y. Estimation of monthly mean daily diffuse radiation in china. Appl. Energ. 2009, 86, 1458–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, R.L.; Melo-Abreu, J.P. Frost Protection: Fundamentals, Practice and Economics. Volume 1; Environment and Natural Resources Service Series; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2005; pp. 219–221. [Google Scholar]
- Reber, E.E.; Swope, J.R. On the correlation of the total precipitable water in a vertical column and absolute humidity at the surface. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1972, 11, 1322–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (Modis). Available online: Https://ladsweb.Nascom.Nasa.Gov/data/ (accessed on 6 September 2015).
- Wan, Z.; Dozier, J. A generalized split-window algorithm for retrieving land-surface temperature from space. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1996, 34, 892–905. [Google Scholar]
- Crosson, W.L.; Al-Hamdan, M.Z.; Hemmings, S.N.; Wade, G.M. A daily merged modis aqua–terra land surface temperature data set for the conterminous united states. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 119, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, Y.; Kang, S.; Moon, S.-K.; Kim, J. Evaluation of land surface radiation balance derived from moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer (modis) over complex terrain and heterogeneous landscape on clear sky days. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2008, 148, 1538–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blandford, T.R.; Humes, K.S.; Harshburger, B.J.; Moore, B.C.; Walden, V.P.; Ye, H. Seasonal and synoptic variations in near-surface air temperature lapse rates in a mountainous basin. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2008, 47, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolland, C. Spatial and seasonal variations of air temperature lapse rates in alpine regions. J. Clim. 2003, 16, 1032–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Leclerc, M.Y. How large must surface inhomogeneities be before they influence the convective boundary layer structure? A case study. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1995, 121, 1209–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldocchi, D.; Falge, E.; Gu, L.; Olson, R. Fluxnet: A new tool to study the temporal and spatial variability of ecosystem-scale carbon dioxide, water vapor, and energy flux densities. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2001, 82, 2415–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepin, N.; Lundquist, J. Temperature trends at high elevations: Patterns across the globe. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohrabinia, M.; Zawar-Reza, P.; Rack, W. Spatio-temporal analysis of the relationship between lst from modis and air temperature in New Zealand. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2014, 119, 567–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, M.; Hall, A.; Fovell, R.G. Dynamical controls on the diurnal cycle of temperature in complex topography. Clim. Dyn. 2007, 29, 277–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Tang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, D. The relief degree of land surface in china and its correlation with population distribution. Acta Geol. Sin. 2007, 62, 1073–1082. (in Chinese) . [Google Scholar]
- Julien, Y.; Sobrino, J.A.; Verhoef, W. Changes in land surface temperatures and ndvi values over europe between 1982 and 1999. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 103, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julien, Y.; Sobrino, J.A. The yearly land cover dynamics (ylcd) method: An analysis of global vegetation from ndvi and lst parameters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtslag, A.; De Bruin, H. Applied modeling of the nighttime surface energy balance over land. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1988, 27, 689–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamir, E.; Georgakakos, K.P. Modis land surface temperature as an index of surface air temperature for operational snowpack estimation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 152, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liang, S.; Meyers, T. Validating modis land surface temperature products using long-term nighttime ground measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 623–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kestens, Y.; Brand, A.; Fournier, M.; Goudreau, S.; Kosatsky, T.; Maloley, M.; Smargiassi, A. Modelling the variation of land surface temperature as determinant of risk of heat-related health events. Int. J. Health Geogr. 2011, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mildrexler, D.J.; Zhao, M.; Running, S.W. A global comparison between station air temperatures and modis land surface temperatures reveals the cooling role of forests. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, A.C.; Privette, J.L.; Mahoney, R.; Tucker, C.J. Directional effects in a daily avhrr land surface temperature dataset over Africa. IEEE. Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 1941–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Wardlow, B.D.; Tadesse, T.; Shan, J.; Hayes, M.J.; Li, D.; Xiang, D. Estimation of daily air temperature based on modis land surface temperature products over the corn belt in the us. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 951–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Lű, A.; Jia, S. Estimation of daily maximum and minimum air temperature using modis land surface temperature products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 130, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Moore, N.J.; Messina, J.P.; DeVisser, M.H.; Wu, J. Evaluation of estimating daily maximum and minimum air temperature with modis data in east africa. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2012, 18, 128–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Zhang, C.; Huang, J.; Zhu, D.; Wang, L.; Liu, J. Mapping of daily mean air temperature in agricultural regions using daytime and nighttime land surface temperatures derived from terra and aqua modis data. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 8728–8756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostovoy, G.V.; King, R.L.; Reddy, K.R.; Kakani, V.G.; Filippova, M.G. Statistical estimation of daily maximum and minimum air temperatures from modis lst data over the state of mississippi. Gisci. Remote Sens. 2006, 43, 78–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Qin, F. A statistical method based on remote sensing for the estimation of air temperature in china. Int. J. Climatol. 2015, 35, 2131–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Qin, Z.; Shen, Y. Study on the estimation of near-surface air temperature from modis data by statistical methods. Int. J. Remote. Sens. 2012, 33, 7629–7643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Zhang, B. Modis-based air temperature estimation in the southeastern tibetan plateau and neighboring areas. J. Geogr. Sci. 2012, 22, 152–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhong, H.; Wu, Q.; zhang, Y.; Hou, Y.; Tang, M. Analyses on changes of surface temperature over qinghai-xizang plateau. Plateau Meteorol. 2005, 24, 291–298. [Google Scholar]
- Norman, J.M.; Becker, F. Terminology in thermal infrared remote sensing of natural surfaces. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1995, 77, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T. Influence of the seasonal snow cover on the ground thermal regime: An overview. Rev. Geophys. 2005, 43, RG4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Li, C.; Lin, P.; Wey, T.; Chang, C. Comparison of modis land surface temperature and ground-based observed air temperature in complex topography. Int. J. Remote. Sens. 2012, 33, 7685–7702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombi, A.; De Michele, C.; Pepe, M.; Rampini, A. Estimation of daily mean air temperature from modis lst in alpine areas. EARSeL eProc. 2007, 6, 38–46. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, T.; Vivoni, E.R.; Gochis, D.J. Seasonal evolution of ecohydrological controls on land surface temperature over complex terrain. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 3852–3874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Q.; Lu, D.; Schubring, J. Estimation of land surface temperature–vegetation abundance relationship for urban heat island studies. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 89, 467–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Q. Thermal infrared remote sensing for urban climate and environmental studies: Methods, applications, and trends. Isprs J. Photogramm. 2009, 64, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.; Ishikawa, H.; Hayashi, T.; Tamagawa, I.; Ma, Y. Surface energy budget at amdo on the tibetan plateau using game/tibet iop98 data. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2001, 79, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.; Tamagawa, I.; Ishikawa, H.; Ma, Y.; Hu, Z. Surface energy budget and closure of the eastern tibetan plateau during the game-tibet iop 1998. J. Hydrol. 2003, 283, 169–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jixi, J.; Meizhu, F. Convective clouds and mesoscale convective systems over the tibetan plateau in summer. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2002, 26, 263–270. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zi, Y.; Feng, S.; Li, Y.; Liu, G. Summer precipitation and latent heating over the tibetan plateau based on trmm measurements. Plateau Mountain Meteorol. Res. 2008, 28, 8–18. (in Chinese) . [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Bao, Q.; Hoskins, B.; Wu, G.; Liu, Y. Tibetan plateau warming and precipitation changes in east asia. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L14702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulley, G.C.; Hughes, C.G.; Hook, S.J. Quantifying uncertainties in land surface temperature and emissivity retrievals from aster and modis thermal infrared data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mira, M.; Valor, E.; Boluda, R.; Caselles, V.; Coll, C. Influence of soil water content on the thermal infrared emissivity of bare soils: Implication for land surface temperature determination. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Flat Terrain Area | Mountainous Area | |
|---|---|---|
| (Growing Season) | (Non-Growing Season) | |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, X.; Zhang, W.; Huang, Y.; Sun, W.; Han, P.; Yu, L.; Sun, F. Empirical Estimation of Near-Surface Air Temperature in China from MODIS LST Data by Considering Physiographic Features. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 629. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8080629
Lin X, Zhang W, Huang Y, Sun W, Han P, Yu L, Sun F. Empirical Estimation of Near-Surface Air Temperature in China from MODIS LST Data by Considering Physiographic Features. Remote Sensing. 2016; 8(8):629. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8080629
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Xiaohui, Wen Zhang, Yao Huang, Wenjuan Sun, Pengfei Han, Lingfei Yu, and Feifei Sun. 2016. "Empirical Estimation of Near-Surface Air Temperature in China from MODIS LST Data by Considering Physiographic Features" Remote Sensing 8, no. 8: 629. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8080629
APA StyleLin, X., Zhang, W., Huang, Y., Sun, W., Han, P., Yu, L., & Sun, F. (2016). Empirical Estimation of Near-Surface Air Temperature in China from MODIS LST Data by Considering Physiographic Features. Remote Sensing, 8(8), 629. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8080629