Satellite-Driven Evaluation of Ecological Environmental Quality Based on the PSR Framework
Highlights
- A new remote sensing-based EEQ evaluation indicator system was successfully constructed based on the PSR framework, overcoming the limitations of traditional methods.
- A DNN-based evaluation model was developed and proven effective, achieving more accurate and generally applicable EEQ assessment compared to conventional remote sensing techniques.
- The integration of DNN for data augmentation provides a robust solution to the common challenge of limited samples in remote sensing modeling.
- The spatiotemporal dynamics of EEQ in Guangzhou from 2013 to 2020 were quantitatively revealed, offering critical insights for urban environmental planning and sustainable management.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material
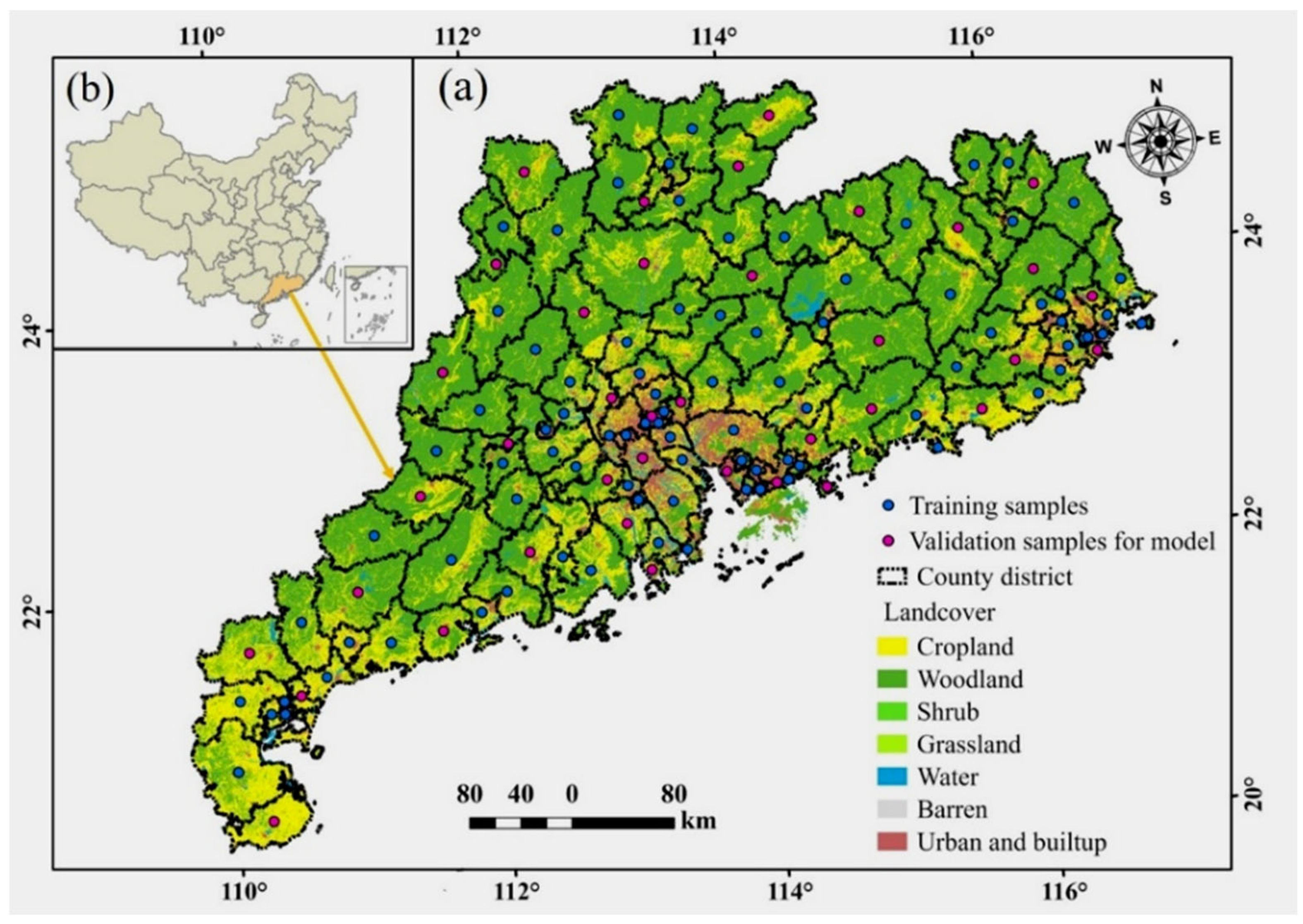
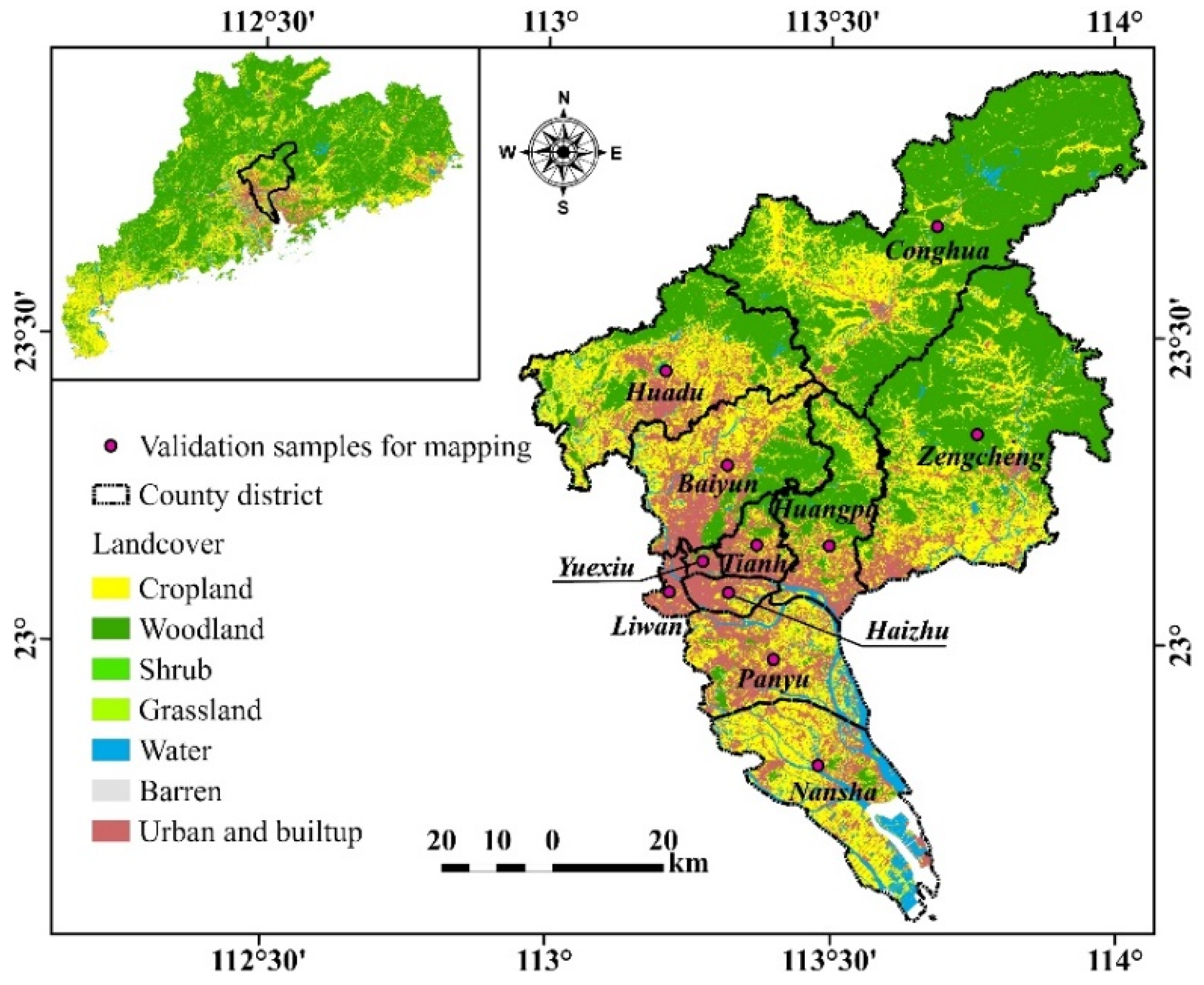
2.1.1. Study Area
2.1.2. Data Collection and Pre-Processing
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Establishment of an RSI System Based on the PSR Framework
- (1)
- The SEI was calculated using the revised universal soil loss equation [27]:
- (2)
- The NDVI and LSM were calculated using Equations (2) and (3), respectively.where and represent the Landsat 8 OLI/TIRS spectral reflectance in the blue, red, near-infrared, shortwave infrared 1, and shortwave infrared 2 bands, respectively.
- (3)
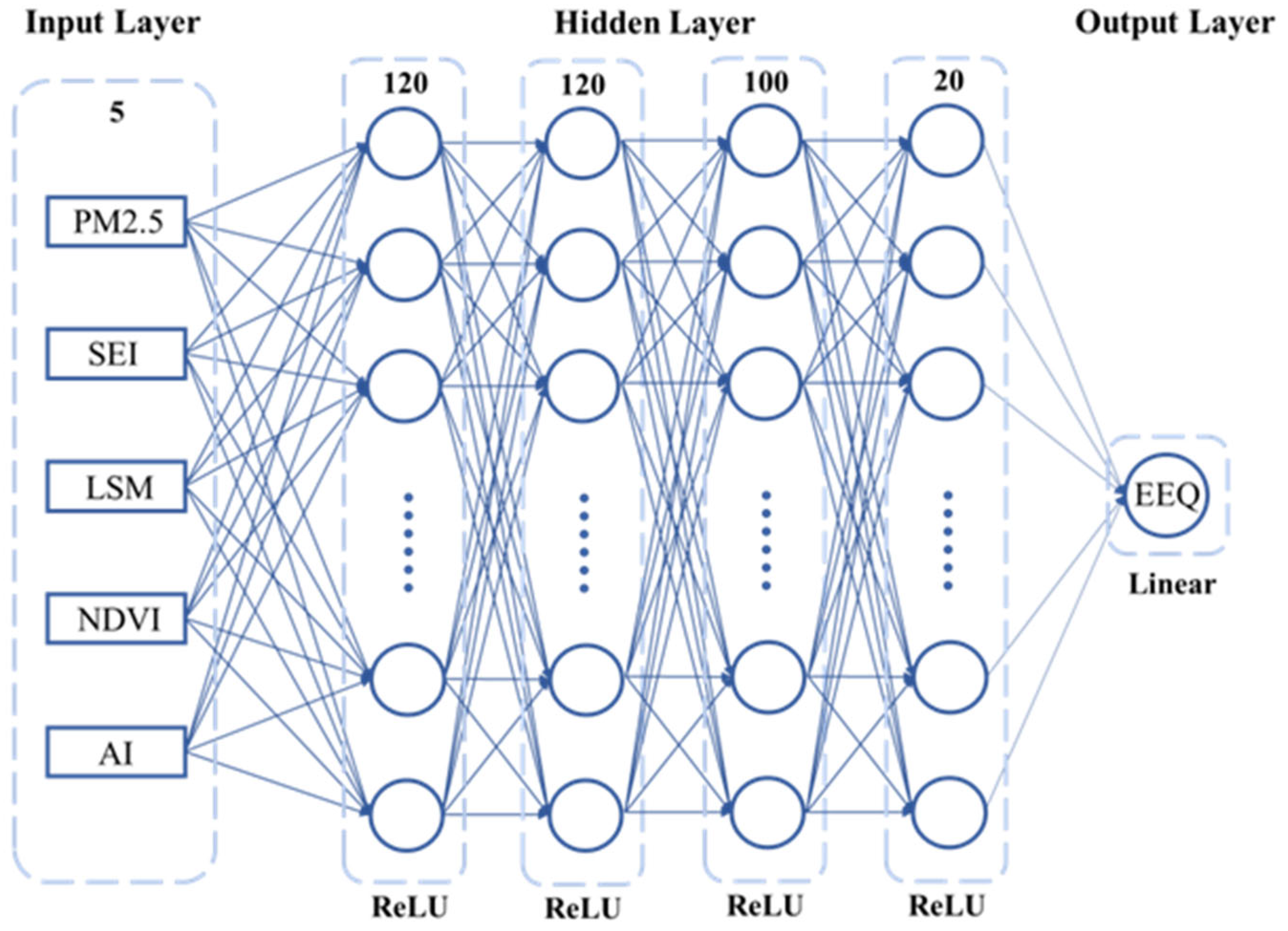
2.2.2. Establishment of the DNN Model for Evaluating EEQ
- (1)
- Forward propagation
- (2)
- Error backpropagation
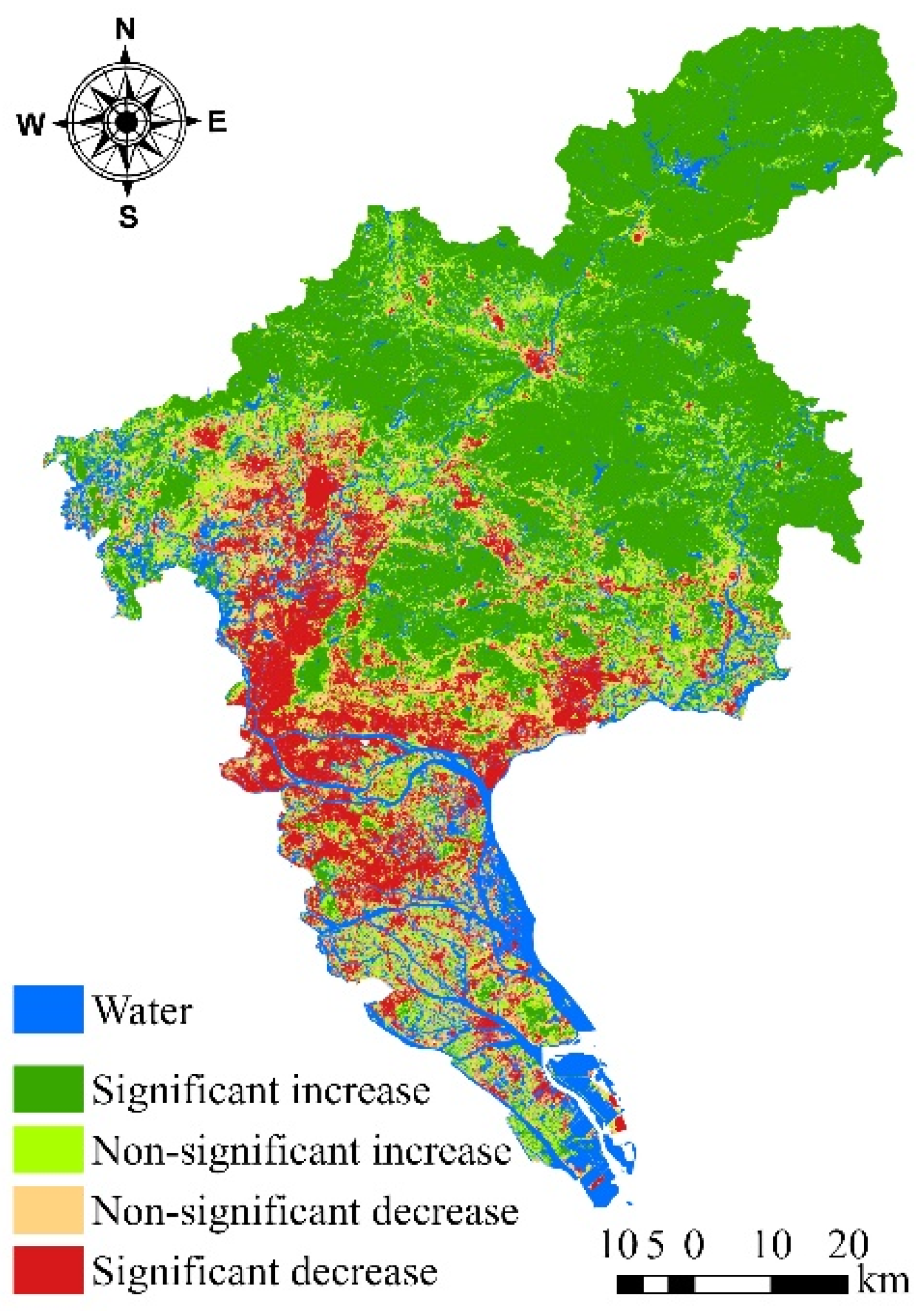
2.2.3. Dynamic Trend Analysis of EEQ
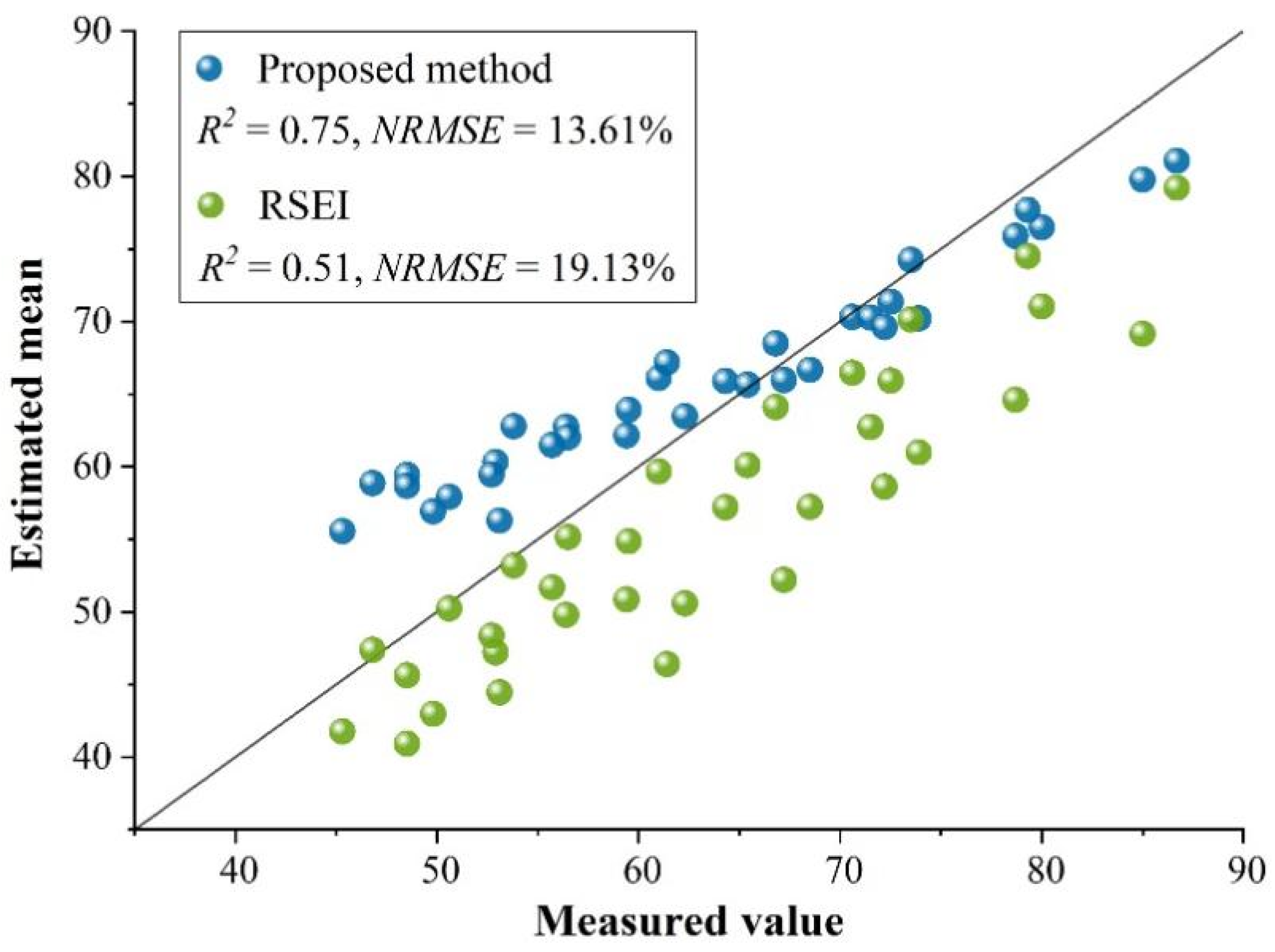
2.2.4. Accuracy Evaluation
3. Results
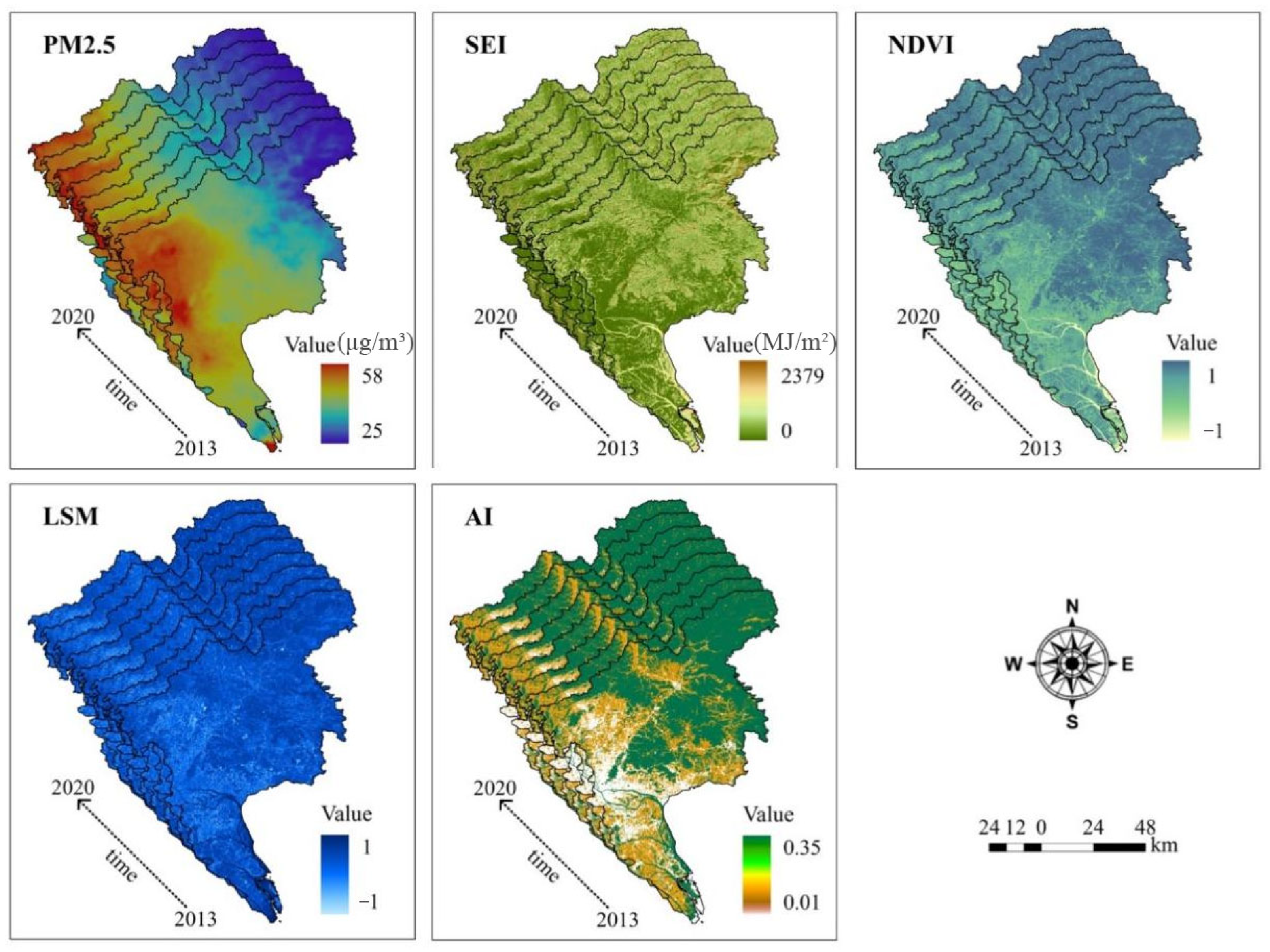
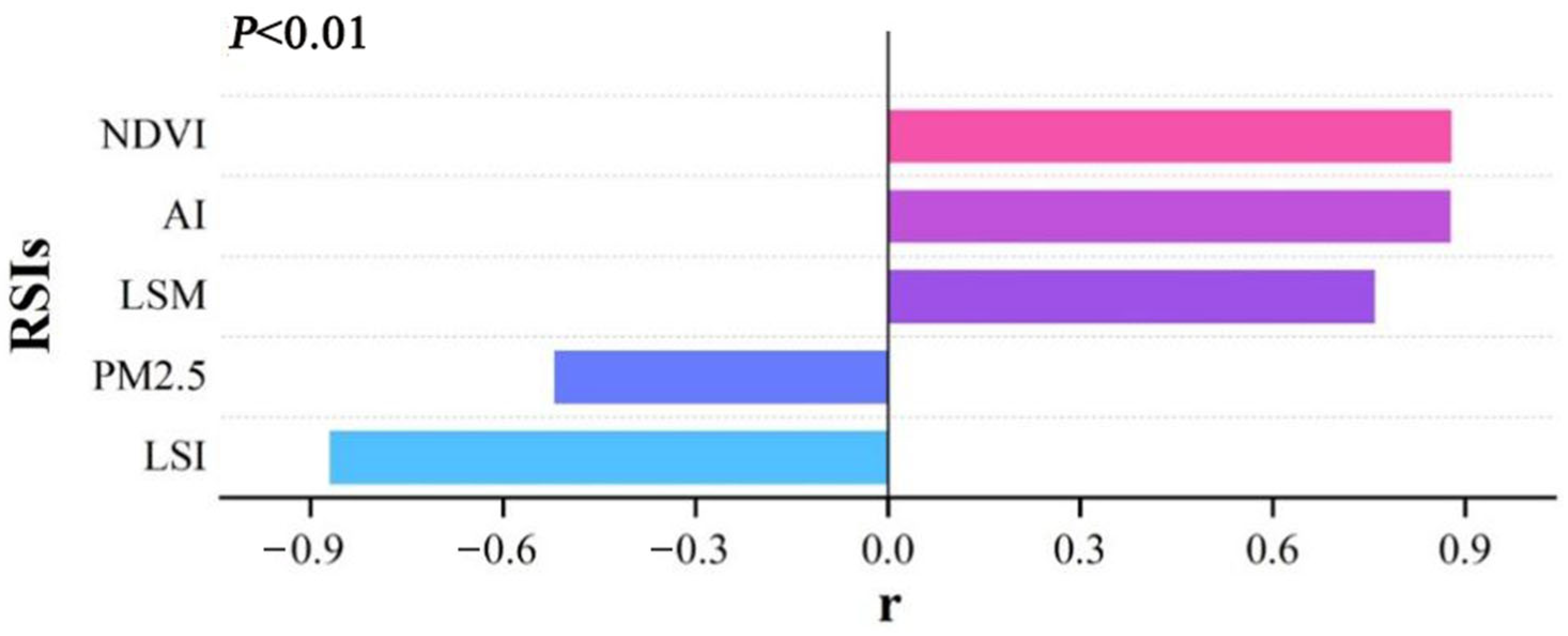
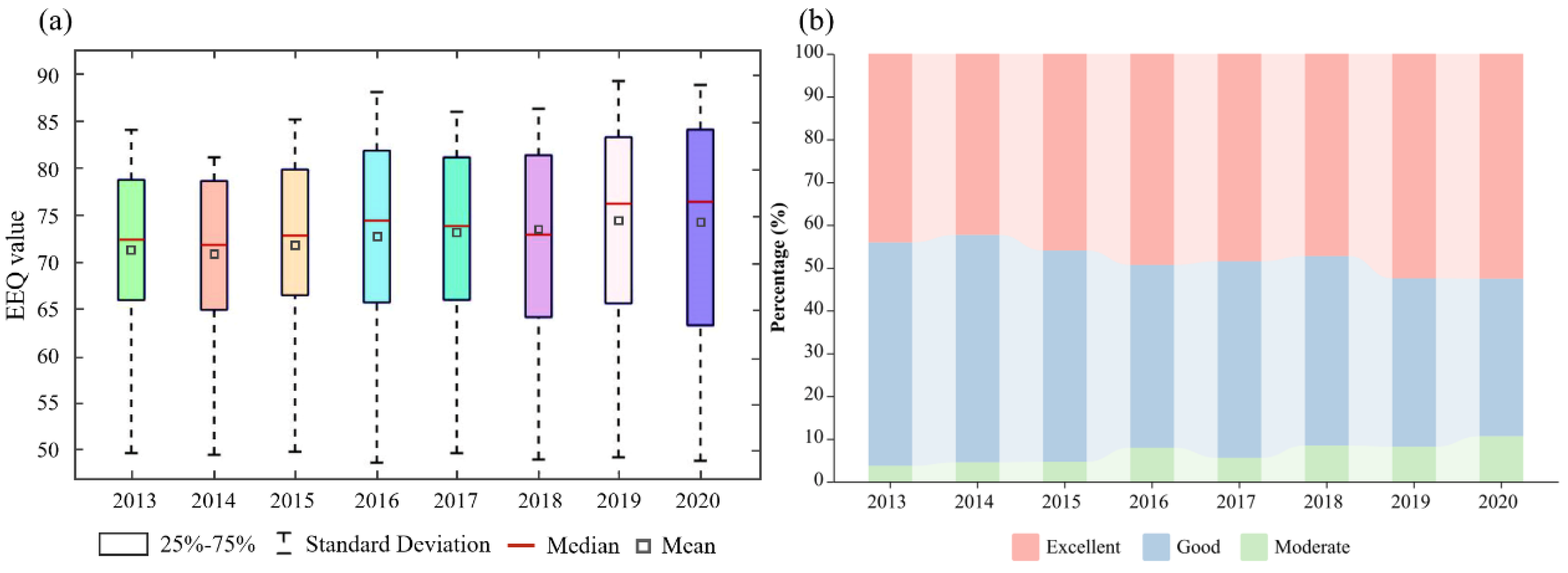
3.1. RSIs in the PSR Framework
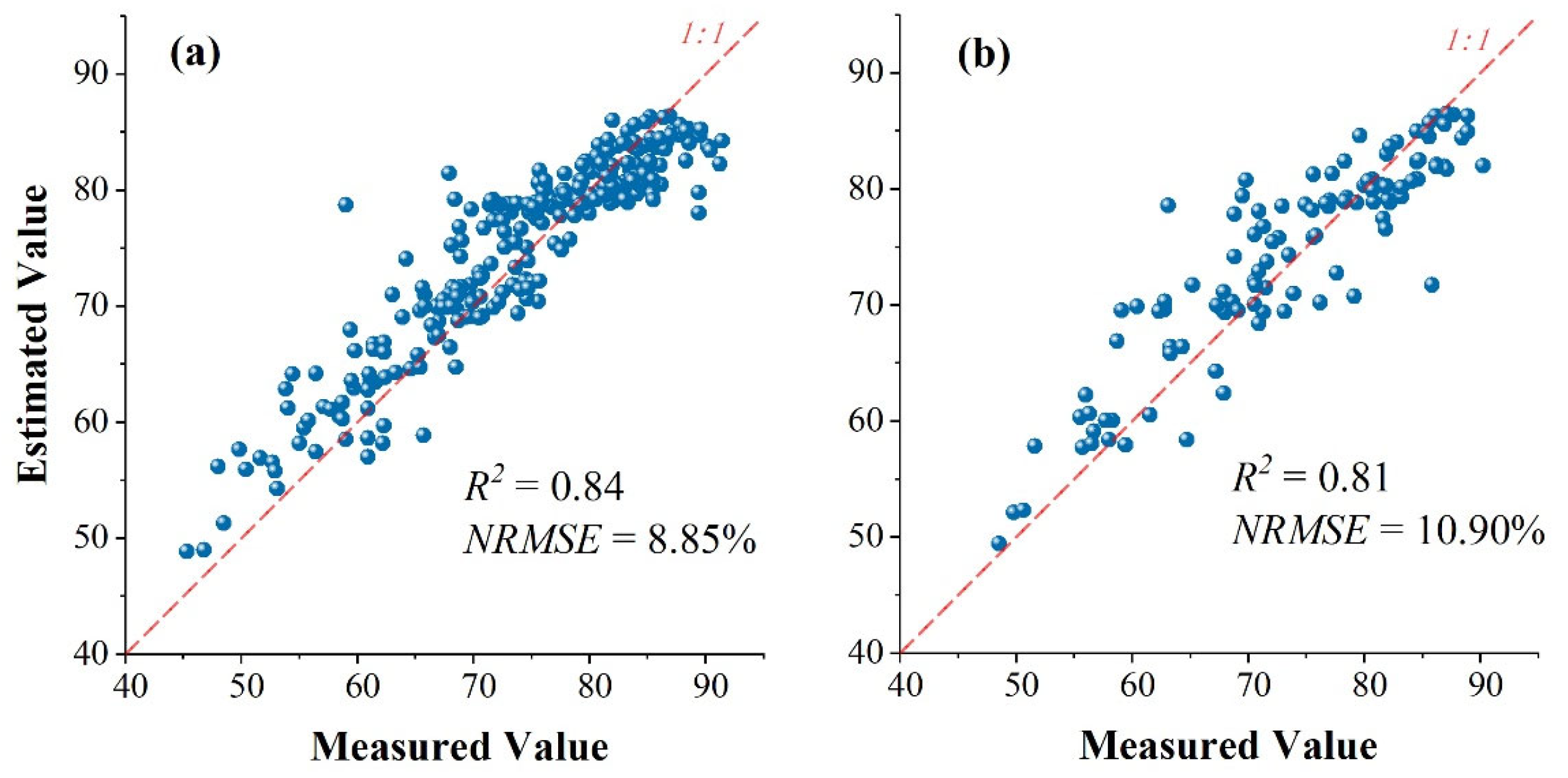
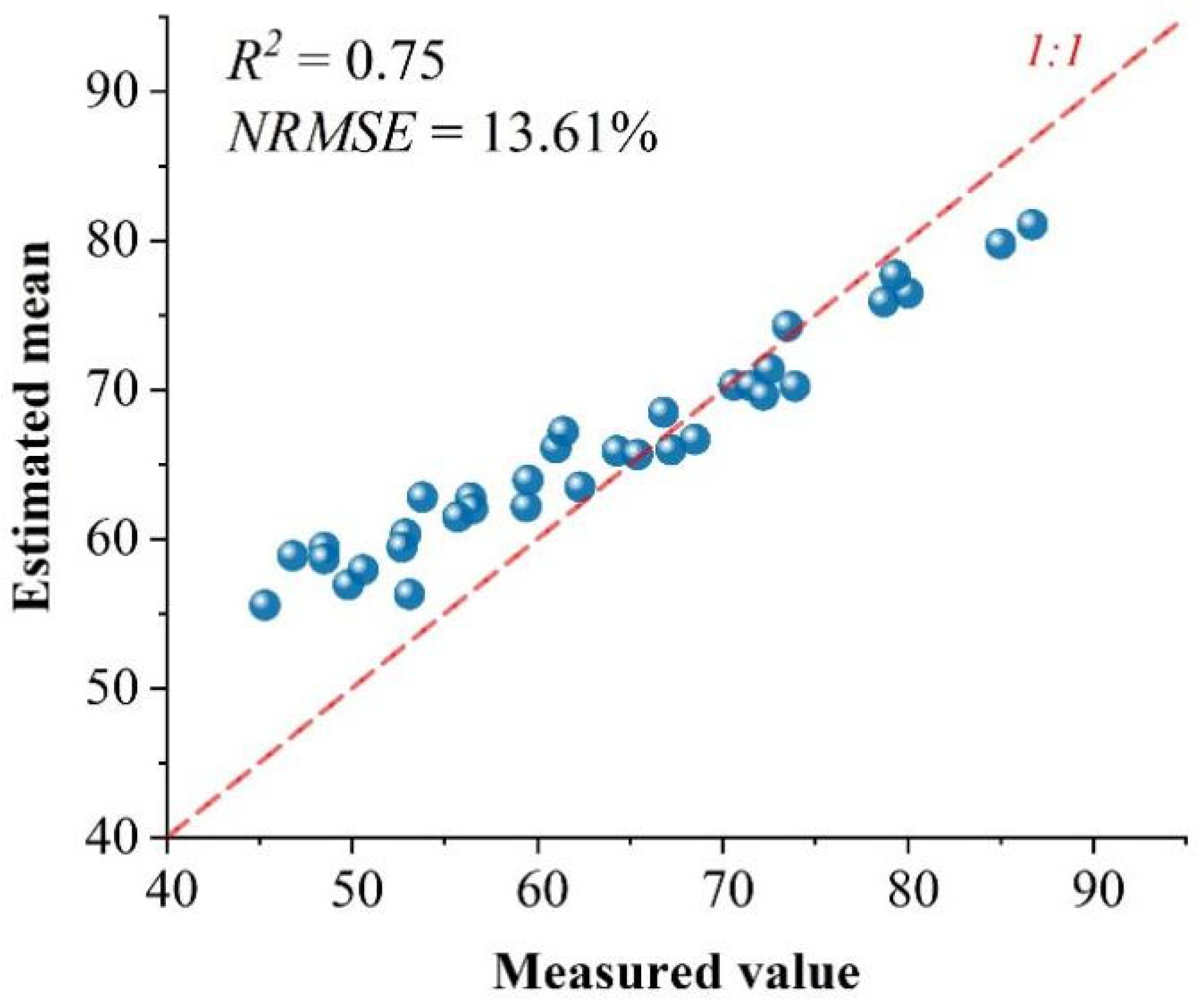
3.2. Performance of the DNN for Evaluating EEQ
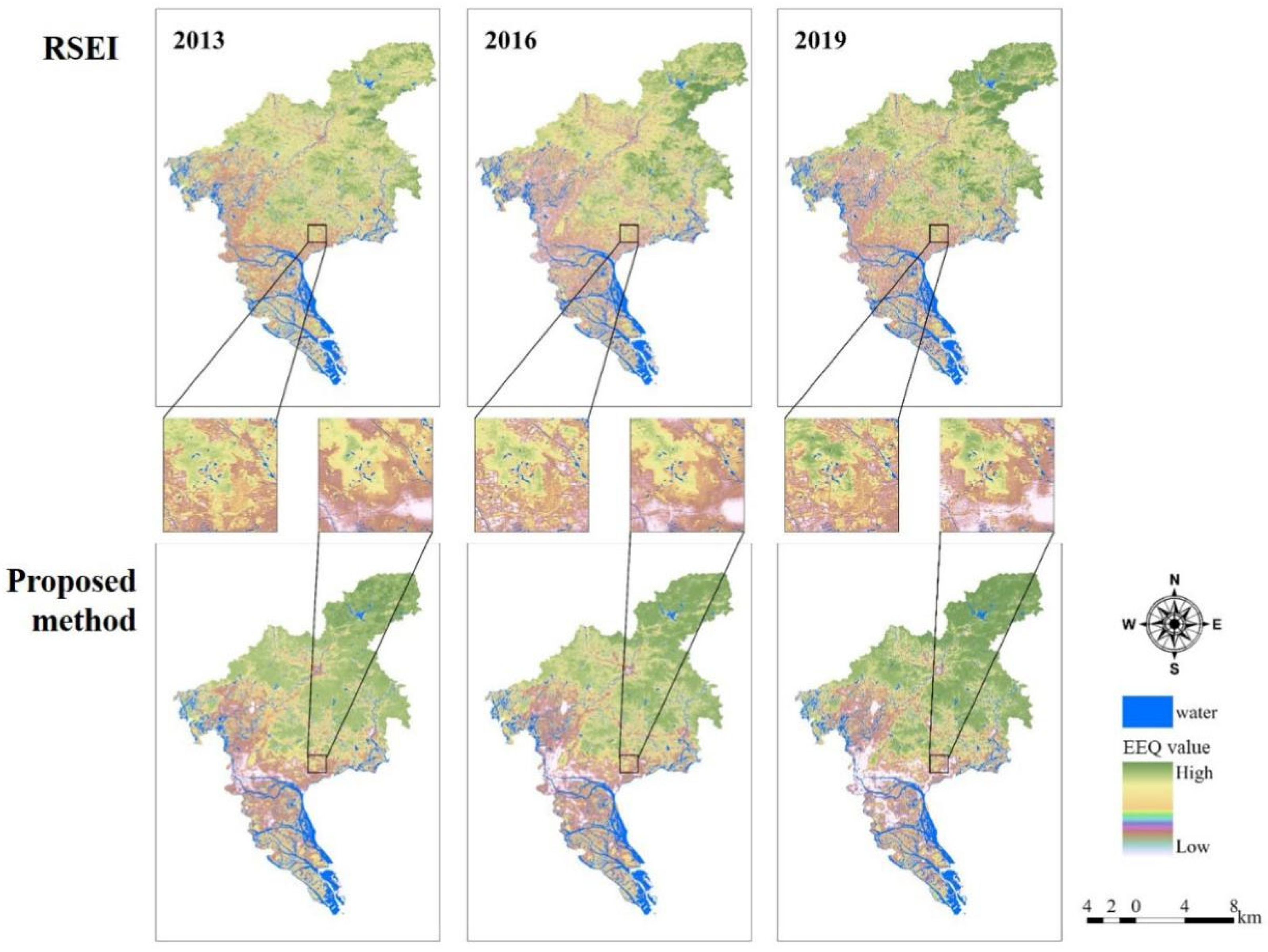
3.3. Spatial Distribution and Dynamic Changes in EEQ in the Guangzhou Study Area
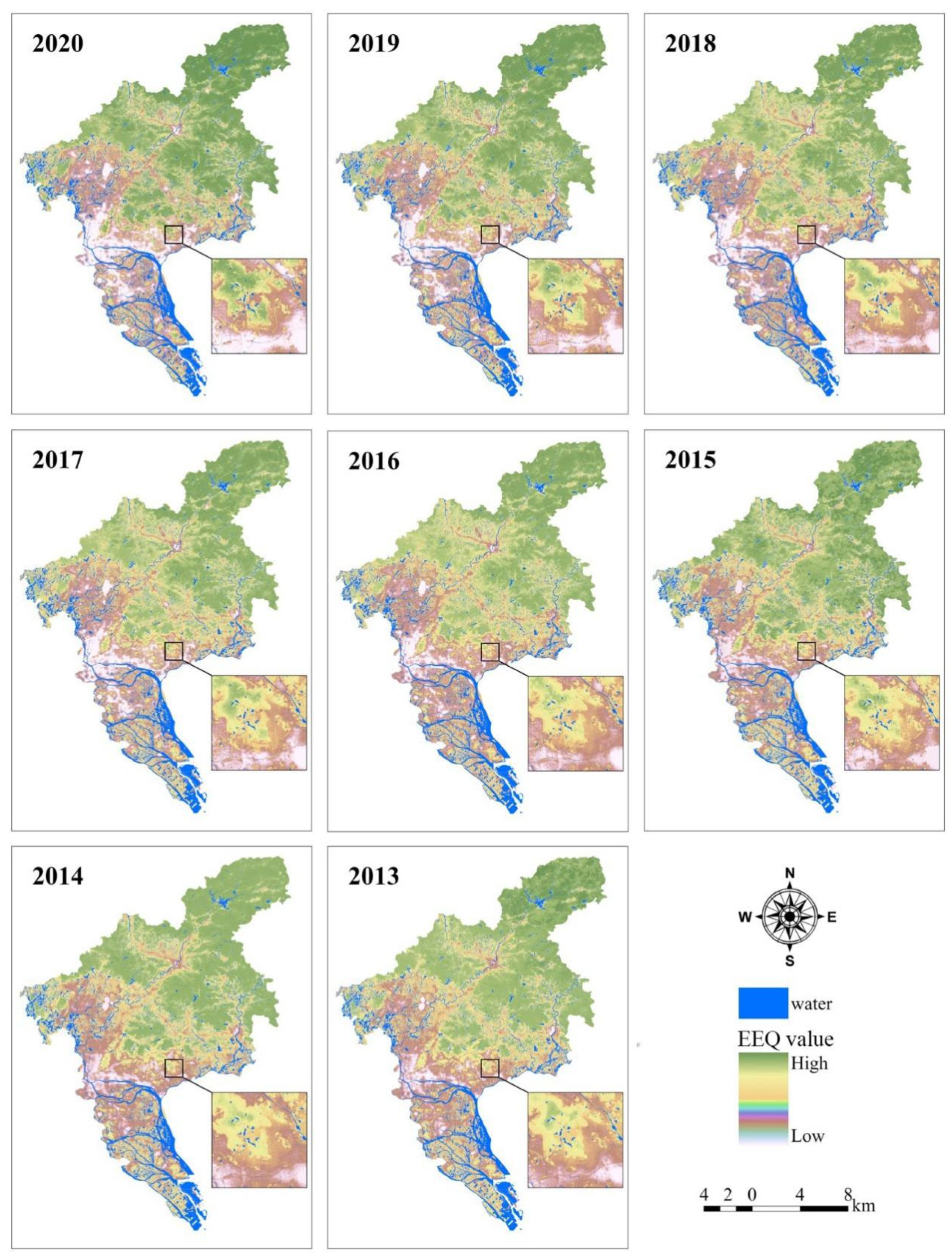
3.3.1. Spatial Distribution of EEQ
3.3.2. Dynamic Changes in EEQ
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison with Similar Studies
4.2. Prospects for Future Studies
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EEQ | Ecological Environmental Quality |
| PSR | Pressure–State–Response |
| DNNs | Deep Neural Networks |
| RSEI | Remote Sensing Ecological Index |
| NDVI | Normalized Difference Vegetation Index |
| LAI | Leaf Area Index |
| CSI | Comprehensive Salinity Index |
| WND | Water Network Density |
| RS | Remote Sensing |
| EI | Ecological Index |
| PM2.5 | Particulate Matter Concentration |
| GPM | Global Precipitation Measurement |
| CLCD | China Land Cover Dataset |
| ASTER GDEM | Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer Global Digital Elevation Model |
| LaSRC | Landsat Surface Reflectance Code |
| GEE | Google Earth Engine |
| CFMASK | C Function of Mask |
| EBK | Empirical Bayesian Kriging |
| OECD | Organization For Economic Cooperation and Development |
| MEP | Environmental Protection |
| BRI | Biological Richness Index |
| VCI | Vegetation Cover Index |
| WNI | Water Network Density Index |
| LSI | Land Stress Index |
| PLI | Pollution Load Index |
| MK | Mann–Kendall |
| R2 | Determination Coefficient |
| NRMSE | Normalized Root Mean Square Error |
References
- Tahiru, A.-W.; Cobbina, S.; Asare, W.; Takal, S.U. Advancing Environmental Sustainability through Remote Sensing: A Review of Applications, Limitations, and Emerging Solutions. Preprints 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, R.; Zhao, J. Eco-Environmental Quality Monitoring in Beijing, China, Using an RSEI-Based Approach Combined with Random Forest Algorithms. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 196657–196666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, C.; Zang, F.; Liu, Y.; Chang, Y.; Huang, G.; Fu, G.; Zhao, C.; Liu, X. Remote Sensing-Based Approach for the Assessing of Ecological Environmental Quality Variations Using Google Earth Engine: A Case Study in the Qilian Mountains, Northwest China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimian, H.; Zou, W.; Chen, Y.; Xia, J.; Wang, Z. Landscape Ecological Risk Assessment and Driving Factor Analysis in Dongjiang River Watershed. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boori, M.S.; Choudhary, K.; Paringer, R.; Kupriyanov, A. Eco-Environmental Quality Assessment Based on Pressure-State-Response Framework by Remote Sensing and GIS. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2021, 23, 100530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Gao, X.; Lei, J.; Zhou, N.; Guo, Z.; Shang, B. Ecological Environment Quality Evaluation of the Sahel Region in Africa Based on Remote Sensing Ecological Index. J. Arid Land 2022, 14, 14–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, S.; Das, S.; Pattanayak, J.M.; Bera, B.; Shit, P.K. Assessment of Ecological Environment Quality in Kolkata Urban Agglomeration, India. Urban Ecosyst. 2022, 25, 1137–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Bose, A.; Majumder, S.; Roy Chowdhury, I.; Abdo, H.G.; Almohamad, H.; Abdullah Al Dughairi, A. Evaluating Urban Environment Quality (UEQ) for Class-I Indian City: An Integrated RS-GIS Based Exploratory Spatial Analysis. Geocarto Int. 2022, 38, 2153932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Zhou, W. Ecological Environmental Quality in China: Spatial and Temporal Characteristics, Regional Differences, and Internal Transmission Mechanisms. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, F.; Guo, X.; Zhao, J.; Xu, Y.; Liu, X. Assessment of Eco-Environmental Quality Changes and Spatial Heterogeneity in the Yellow River Delta Based on the Remote Sensing Ecological Index and Geo-Detector Model. Ecol. Inform. 2023, 77, 102203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Li, Z.; Lyapustin, A.; Sun, L.; Peng, Y.; Xue, W.; Su, T.; Cribb, M. Reconstructing 1-Km-Resolution High-Quality PM2.5 Data Records from 2000 to 2018 in China: Spatiotemporal Variations and Policy Implications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 252, 112136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Peijun, D.; Shanchuan, G.; Cong, L.; Hongrui, Z.; Pingjie, F. Enhanced Remote Sensing Ecological Index and Ecological Environment Evaluation in Arid Area. Natl. Remote Sens. Bull. 2023, 27, 299–317. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Xiang, W.; Hu, P.; Gao, P.; Zhang, A. Evaluation of Ecological Environment Quality Using an Improved Remote Sensing Ecological Index Model. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foga, S.; Scaramuzza, P.L.; Guo, S.; Zhu, Z.; Dilley, R.D., Jr.; Beckmann, T.; Schmidt, G.L.; Dwyer, J.L.; Hughes, M.J.; Laue, B. Cloud Detection Algorithm Comparison and Validation for Operational Landsat Data Products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 194, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ding, Q.; Zhuang, D. An Eco-City Evaluation Method Based on Spatial Analysis Technology: A Case Study of Jiangsu Province, China. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 58, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Liu, S.; Xia, Z.; Wang, G.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Z. Crop Growth Stage GPP-Driven Spectral Model for Evaluation of Cultivated Land Quality Using GA-BPNN. Agriculture 2020, 10, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adriaanse, A. Environmental Policy Performance Indicators; Ministerie van Volkshuisvesting, Ruimtelijke Ordening en Milieubeheer: The Hague, The Netherlands, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Wang, M.; Shi, T.; Guan, H.; Fang, C.; Lin, Z. Prediction of Ecological Effects of Potential Population and Impervious Surface Increases Using a Remote Sensing Based Ecological Index (RSEI). Ecol. Indic. 2018, 93, 730–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Chen, L.; Mu, J. Discussion on Construction of Ecological Environment Quality Evaluation System. Meteorol. Environ. Sci 2018, 41, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Lu, Y. Eco-Environmental Quality Assessment in China’s 35 Major Cities Based on Remote Sensing Ecological Index. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 51295–51311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.B.; Jamal, S. Modelling the Present and Future Scenario of Urban Green Space Vulnerability Using PSR Based AHP and MLP Models in a Metropolitan City Kolkata Municipal Corporation. Geol. Ecol. Landsc. 2025, 9, 1141–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zeng, Q.; Geng, B.; Lin, X.; Sude, B.; Chen, L. Deep Learning Architecture for Estimating Hourly Ground-Level PM 2.5 Using Satellite Remote Sensing. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 16, 1343–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Huang, K.; Tang, W.; Liang, X.; Wu, W.; Huang, G. Discussion on the Construction of Ecological Water Network in Guangxi Province of China. Res. Ecol. 2021, 3, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peri, P.; Lasagno, R.; Chartier, M.; Roig, F.; Rosas, Y.; Pastur, G. Soil Erosion Rates and Nutrient Loss in Rangelands of Southern Patagonia; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 102–110. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, W.; Jin, X.; Ren, J.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Fan, Y.; Gu, Z.; Hong, C.; Lin, J.; Zhou, Y. Ecological Environment Quality Assessment Based on Remote Sensing Data for Land Consolidation. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 239, 118126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Yang, F.; Yu, L.; Zhou, Y.; Li, H.; Ma, J.; Huang, J.; Wei, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, C.; et al. Quantization of the Coupling Mechanism between Eco-Environmental Quality and Urbanization from Multisource Remote Sensing Data. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 321, 128948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Niu, R.; Li, P.; Zhang, L.; Du, B. Regional Soil Erosion Risk Mapping Using RUSLE, GIS, and Remote Sensing: A Case Study in Miyun Watershed, North China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 63, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.; Renard, K.; Dyke, P. EPIC: A New Method for Assessing Erosion’s Effect on Soil Productivity. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1983, 38, 381–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulibaly, L.K.; Guan, Q.; Assoma, T.V.; Fan, X.; Coulibaly, N. Coupling Linear Spectral Unmixing and RUSLE2 to Model Soil Erosion in the Boubo Coastal Watershed, Côte d’ivoire. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 130, 108092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kefi, M.; Yoshino, K.; Setiawan, Y. Assessment and Mapping of Soil Erosion Risk by Water in Tunisia Using Time Series MODIS Data. Paddy Water Environ. 2012, 10, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Liu, B.; Zhou, G.; Sun, Z.; Zhu, X. Calculation Tool of Topographic Factors. Sci. Soil Water Conserv. 2015, 13, 105–110. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Knijff, J.; Jones, R.; Montanarella, L. Soil Erosion Risk Assessment in Europe; European Soil Bureau: Ispra, Italy, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, G.; Yuan, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wen, X.; Lin, R. Integrated Study on Soil Erosion Using RUSLE and GIS in Yangtze River Basin of Jiangsu Province (China). Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Li, D.; Wei, X.; Zhang, H. The Current Situation of Soil Erodibility (K) Value and Its Impact Factors in Guangdong Province. Subtrop. Soil Water Conserv. 2007, 19, 4–7. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Q.; Shen, H.; Li, T.; Li, Z.; Li, S.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, H.; Tan, W.; Yang, Q.; Wang, J.; et al. Deep Learning in Environmental Remote Sensing: Achievements and Challenges. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 241, 111716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuan, C.; Zheng, C.; Bo, L.; Ligang, L. Computation of Atmospheric Optical Parameters Based on Deep Neural Network and PCA. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 102256–102262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Wang, Z.; Li, J. Application of the Deep Neural Network in Retrieving the Atmospheric Temperature and Humidity Profiles from the Microwave Humidity and Temperature Sounder Onboard the Feng-Yun-3 Satellite. Sensors 2021, 21, 4673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Yuan, L.; Wang, W.; Cao, R.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, W. Spatio-Temporal Analysis of Vegetation Variation in the Yellow River Basin. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 51, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wang, Y.; Guan, H.; Shi, T.; Hu, X. Detecting Ecological Changes with a Remote Sensing Based Ecological Index (RSEI) Produced Time Series and Change Vector Analysis. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, R.O. Statistical Methods for Environmental Pollution Monitoring; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Xu, H.; Xu, D.; Ji, W.; Li, S.; Yang, M.; Hu, B.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, N.; Arrouays, D.; et al. Evaluating Validation Strategies on the Performance of Soil Property Prediction from Regional to Continental Spectral Data. Geoderma 2021, 400, 115159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, H.; Kang, S.; Li, F.; Du, T.; Tong, L.; Li, S.; Ding, R.; Zhang, X. Parameterization of the AquaCrop Model for Full and Deficit Irrigated Maize for Seed Production in Arid Northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 203, 438–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Xu, W.; Lu, N.; Huang, S.; Wu, C.; Wang, L.; Dai, F.; Kou, W. Assessment of Spatial–Temporal Changes of Ecological Environment Quality Based on RSEI and GEE: A Case Study in Erhai Lake Basin, Yunnan Province, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 125, 107518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furberg, D.; Ban, Y.; Nascetti, A. Monitoring of Urbanization and Analysis of Environmental Impact in Stockholm with Sentinel-2A and SPOT-5 Multispectral Data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Xu, H. A New Remote Sensing Index for Assessing the Spatial Heterogeneity in Urban Ecological Quality: A Case from Fuzhou City, China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 89, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Data | Spatial Resolution | Time Resolution | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| EEQ measurements | County unit | Annual | Department of Ecology and Environment of Guangdong province (http://gdee.gd.gov.cn/ (accessed on 11 December 2025)) |
| Soil type and property data | 1:1 million | — | Soil Science Datasets (http://vdb3.soil.csdb.cn/ (accessed on 11 December 2025)) |
| PM2.5 | 1 km | Annual | China High PM2.5 dataset (https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6398971) |
| Land cover | 30 m | Annual | CLCD (https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5210928) |
| ASTER GDEM | 30 m | 2011 | NASA http://reverb.echo.nasa.gov/reverb/ (accessed on 11 December 2025) |
| GPM_3IMERGM L3 1-month V06 | 0.1° | Monthly | GEE (https://code.earthengine.google.com/ (accessed on 11 December 2025)) |
| Landsat 8 OLI/TIRS | 30 m | 16-Day |
| Target Layer | Project Layer | RSIs | Corresponding Traditional EEQ Indicators |
|---|---|---|---|
| EEQ evaluation indicator system | Pressure | PM2.5 | PLI |
| SEI | LSI | ||
| State | NDVI | VCI | |
| LSM | WNI | ||
| Response | AI | BRI |
| Land Cover Type | Urban and Built-up | Water | Woodland | Grassland | Cropland | Barren |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p value | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0.3 | 1 |
| Soil Type | K Value | Soil Type | K Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Humid-thermo ferralitic | 0.233 | Skeletal soils | 0.252 |
| Lateritic red earth | 0.234 | Litho soils | 0.268 |
| Red earth | 0.250 | Mountain meadow soils | 0.259 |
| Yellow earth | 0.209 | Fluvo-aquic soils | 0.284 |
| Coastal sandy soils | 0.134 | Bog soils | 0.303 |
| Limestone soils | 0.292 | Coastal solonchaks | 0.310 |
| Purplish soils | 0.299 | Acid sulfate soil | 0.327 |
| Volcanic soils | 0.268 | Paddy soils | 0.295 |
| Land Cover Type | Urban and Built-up | Water | Woodland | Grassland | Cropland | Barren |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.11 | 0.35 | 0.21 | 0.28 |
| Judgment Criterion | Dynamic EEQ Trend |
|---|---|
| β > 0 and |S| > 14 | Significant increase |
| β > 0 and |S| ≤ 14 | Non-significant increase |
| β < 0 and |S| ≤ 14 | Non-significant decrease |
| β < 0 and |S| > 14 | Significant decrease |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Xie, S.; Cheng, X.; Jin, M.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, Z. Satellite-Driven Evaluation of Ecological Environmental Quality Based on the PSR Framework. Remote Sens. 2026, 18, 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs18010031
Xie S, Cheng X, Jin M, Jiang Y, Liu J, Liu Z. Satellite-Driven Evaluation of Ecological Environmental Quality Based on the PSR Framework. Remote Sensing. 2026; 18(1):31. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs18010031
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Shujuan, Xingrong Cheng, Mingzhe Jin, Yifan Jiang, Jinlong Liu, and Zhenhua Liu. 2026. "Satellite-Driven Evaluation of Ecological Environmental Quality Based on the PSR Framework" Remote Sensing 18, no. 1: 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs18010031
APA StyleXie, S., Cheng, X., Jin, M., Jiang, Y., Liu, J., & Liu, Z. (2026). Satellite-Driven Evaluation of Ecological Environmental Quality Based on the PSR Framework. Remote Sensing, 18(1), 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs18010031






