Abstract
Remote Sensing Visual Question Answering (RS-VQA) is a research task that combines remote sensing image processing and natural language understanding. The increasing complexity and diversity of question types in Remote Sensing Visual Question Answering (RS-VQA) pose significant challenges for unified multimodal reasoning within a single model architecture. Therefore, we propose the Adaptive Conditional Reasoning (ACR) network, a novel framework that dynamically tailors reasoning pathways to question semantics through type-aware feature fusion. The ACR module selectively applies different reasoning strategies depending on whether the question is open-ended or closed-ended, thereby tailoring the reasoning process to the specific nature of the question. In order to enhance the multimodal fusion process of different types of questions, the ACR model further integrates visual and textual features by leveraging type-guided cross-attention. Meanwhile, we use a Dual-Reconstruction Feature Enhancer that mitigates spatial and channel redundancy in remote sensing images via spatial and channel reconstruction convolution, enhancing discriminative feature extraction for key regions. Experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves 78.5% overall accuracy on the EarthVQA dataset, showcasing the effectiveness of adaptive reasoning in remote sensing application.
1. Introduction
Remote Sensing Visual Question Answering (RS-VQA) is an emerging research area that bridges the fields of computer vision and remote sensing, where the goal is to comprehend complex remote sensing images and provide answers to natural language questions related to those images. With the advent of advanced satellite imaging technologies and the vast volume of remotely sensed data, RS-VQA has gained significant attention due to its potential applications in environmental monitoring [1], disaster management [2], and agricultural surveillance [3]. However, despite recent advancements, RS-VQA still faces significant challenges due to the complexity of remote sensing images, which often contain diverse objects, intricate spatial relationships, and varying scales of features. Remote sensing images often contain diverse and intricate information at multiple spatial and temporal scales. These images typically feature heterogeneous objects, such as buildings, roads and water, with varying textures, shapes, and sizes. Additionally, the vast amount of geospatial data captured from satellites or drones can present difficulties in effectively extracting relevant features that are essential for answering specific questions. For instance, questions related to land cover type recognition may involve differentiating between water, forest, and urban areas, while those focused on environmental changes might require temporal analysis of image sequences. The dynamic nature of these tasks makes RS-VQA a challenging problem, as it demands both precise image understanding and the ability to reason about spatial and contextual relationships between objects in the scene. Furthermore, the inherent multimodal nature of RS-VQA tasks—where both visual content and natural language need to be processed simultaneously—compounds the difficulty of achieving robust and accurate performance.
Recent research in RS-VQA has largely followed the trend of adapting deep learning-based approaches originally designed for image captioning and Visual Question Answering (VQA) to the remote sensing domain [4]. These methods typically rely on convolutional neural networks (CNNs) for visual feature extraction and recurrent neural networks (RNNs) for language understanding. These methods often struggle to effectively handle complex problems that require multi-step reasoning or fine-grained relationship analysis. They tend to perform better when dealing with simpler problems (such as determining the presence of an object), but lack sufficient flexibility and accuracy when it comes to tasks that involve complex reasoning processes (such as dynamic changes in spatial relationships). These methods typically rely on static architectures and fixed spatial hierarchies, which cannot dynamically adjust based on the semantic or contextual dependencies of the problem. They are also unable to automatically adjust the weight of visual features or switch reasoning paths according to the different intents of the problem.
While these models have shown promise, they often struggle to effectively integrate the diverse, multi-scale, and highly detailed information embedded in remote sensing images. Furthermore, existing approaches tend to apply a one-size-fits-all reasoning process across different question types, which may limit their ability to perform nuanced reasoning for complex or context-dependent questions. Existing unified frameworks employ static fusion strategies (e.g., concatenation or fixed attention) that indiscriminately process all question types, leading to suboptimal performance for context-dependent or multi-step queries. For example, a closed-ended question like ‘Is there a hospital near the river?’ requires simple object co-occurrence detection, whereas an open-ended question like ‘How does the distribution of residential areas correlate with road networks in this region?’ demands hierarchical spatial reasoning and semantic grounding. Traditional frameworks fail to distinguish these fundamentally different reasoning requirements, resulting in feature misalignment (e.g., over-emphasizing irrelevant regions for closed-ended tasks) or insufficient interaction depth (e.g., shallow fusion for open-ended tasks).
The unified reasoning framework of traditional VQA struggles to dynamically adjust the feature interaction methods for different types of questions, leading to limited generalization ability of the model for complex questions. Adaptive type judgment alleviates the mismatch between heterogeneous question types and a single reasoning mode by customizing reasoning paths. To address these issues, we propose Adaptive Conditional Reasoning (ACR), which aims to improve the flexibility and precision of reasoning in RS-VQA tasks. Our method consists of two key components: a Type-Driven Conditioned Reasoning module and a Text–Image Cross-Modal Reasoning module based on the type of question. The Type-Driven Conditioned Reasoning module employs Transformer-based type classification before multimodal fusion to adaptively route reasoning procedures based on semantic intent. And the Text–Image Cross-Modal Reasoning module enables fine-grained visual–linguistic interaction through attention-driven joint reasoning. Moreover, to mitigate spatial and channel redundancy in remote sensing images, we utilize Dual-Reconstruction Feature Enhancer (DRE) to enhance visual feature extraction. By leveraging cross-modal attention and adaptive reasoning strategies, our model is capable of providing more accurate, interpretable, and context-sensitive answers. Specifically, our approach excels in handling complex spatial and relational queries, which are common in remote sensing applications. Experimental results on the EarthVQA dataset demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms existing approaches, highlighting the effectiveness of adaptive reasoning in improving the performance of the RS-VQA system.
The key contributions of this paper can be summarized as follows:
- (1)
- We propose an Adaptive Conditional Reasoning process which involves a Type-Driven Conditioned Reasoning module and a text–image cross-modal reasoning method based on the type of question. Before the fusion of multimodal features, incorporating a type judgment process enables adaptive selection of reasoning procedures corresponding to different types of questions. By using image–text and text–image attention, the module achieves symmetric interaction between visual and text features.
- (2)
- In order to mitigate spatial redundancy and channel redundancy during image feature extraction, we employ spatial reconstruction convolution and channel reconstruction convolution, which enhance the model’s ability to focus on key areas in remote sensing images.
- (3)
- To demonstrate the superiority of our proposed framework, we conducted an evaluation, comparing it with the other methods on the EarthVQA dataset. The results confirm the substantial improvement and advancement achieved by the Adaptive Conditional Reasoning framework in Remote Sensing Visual Question Answering tasks.
2. Related Work
2.1. Visual Question Answering
Visual Question Answering (VQA) is a challenging task that requires joint image and language understanding to answer questions about given photographs. Recent research has focused on developing innovative models to improve the performance of VQA systems. Ref. Antol et al. [5] introduced the concept of neural module networks, which compose collections of jointly trained neural modules into deep networks for question answering. By applying this approach, they achieved state-of-the-art results on challenging datasets for VQA, including the VQA natural image dataset and a dataset of complex questions about abstract shapes. The prevalent framework for the general VQA domain is joint embedding [5]. This framework encompasses four key components: an image encoder, question encoder, feature fusion, and answer component tailored to task requirements. Established convolutional neural network (CNN) backbones, such as VGGNet [6] and ResNet [7], function as image feature extractors. For the question encoder, widely adopted language encoding models like LSTM [8] and GRU [9] are employed. Feature encoding models are typically initialized with pre-trained weights and fine-tuned in an end-to-end manner during training for enhanced performance. The fusion of question features and image features is achieved through an attention mechanism. The answer component commonly consists of a neural network classifier.
In summary, the majority of studies employ a transfer learning approach, where models like VGGNet and ResNet are pre-trained on extensive natural image datasets and subsequently fine-tuned using specific data.
2.2. Remote Sensing Visual Question Answering
Remote Sensing Visual Question Answering (RS-VQA) has emerged as a critical area of research, leveraging the synergy between remote sensing imagery and natural language processing to facilitate intelligent interpretation of geospatial data. Numerous advances in deep learning and multimodal reasoning have been pivotal in the development of RS-VQA systems.
Early work [10] introduced an automatic method for generating a dataset for RS-VQA using OpenStreetMap data. This innovative approach utilized deep learning techniques to establish a foundational framework for training models capable of answering questions based on remote sensing images. Expanding on this idea, they developed two distinct RS-VQA datasets containing image–question–answer triplets, derived from both low- and high-resolution satellite imagery. This expansion provided a broader range of data types, facilitating deeper exploration into how image quality impacts the performance of RS-VQA systems. Building upon the need for improved attention mechanisms in deep learning models, Zheng et al. [4] proposed the Mutual Attention Inception Network (MAIN) for RS-VQA. Their approach focused on enhancing the attention mechanism to better fuse visual and textual information, a critical aspect for accurate question answering in remote sensing contexts. Additionally, Lobry et al. [11] introduced a large-scale RS-VQA dataset by extracting image–question–answer triplets from the BigEarthNet dataset. This work highlighted the scalability of deep learning models for RS-VQA tasks, enabling more robust evaluations and improving model generalization across different types of remote sensing data.
In terms of model architectures, recent research has explored more sophisticated approaches to improve performance. Bazi et al. [12] proposed a bimodal Transformer-based approach to RS-VQA. This method utilized contextual representations from both the image and the question, allowing the model to capture intricate relationships between the visual content and the linguistic queries. Similarly, Siebert et al. [13] introduced a multimodal fusion Transformer that learned joint representations of the image and the question modalities, addressing the challenge of aligning and understanding the intricate relations between these two sources of information. In addition to question answering, Zhan et al. [14] explored the task of visual grounding for remote sensing data, focusing on the localization of objects within remote sensing images using natural language queries. Their work extended the idea of integrating language with visual data to not only answer questions but also provide spatial context and precise localization in satellite imagery. This added a layer of complexity to the task, emphasizing the need for fine-grained visual reasoning.
To improve spatial reasoning in RS-VQA systems, Zhang et al. [15] proposed a Spatial Hierarchical Reasoning Network (SHRNet). Their approach enhanced the system’s ability to perform visual–spatial reasoning by breaking down the image into different spatial hierarchies, thus improving model performance on publicly available datasets and facilitating more accurate spatial interpretations in response to complex questions. The application of RS-VQA in specialized domains, such as post-disaster damage assessment, has also garnered attention. Sarkar et al. [16] presented a supervised attention-based VQA model designed for evaluating post-disaster damage from remote sensing imagery. Their approach emphasized the importance of efficient response and recovery strategies following natural disasters, where accurate interpretation of satellite images could significantly aid in emergency management and resource allocation. To extract useful landform information from remote sensing images, many studies use semantic segmentation methods for preprocessing, labeling different landform categories. This process helps the question answering system more accurately locate regions related to the question, thereby improving the relevance and accuracy of the answers. Ran et al. [17] proposed a novel Dual-Domain Image Fusion (DDF) strategy, which leverages original remote sensing images, style-transferred images, and intermediate domain information to enhance the self-training method.
Recent advancements in large-scale vision–language models have begun to influence the field of RS-VQA. Bazi et al. [18] introduced RS-LLaVA, a remote sensing-specific adaptation of the Large Language and Vision Assistant (LLaVA) model. By integrating large-scale vision–language pre-training into the analysis of remote sensing imagery, RS-LLaVA demonstrated substantial improvements in understanding complex remote sensing scenarios. This work showcases the potential of applying cutting-edge multimodal models, like LLaVA, to the specific challenges posed by remote sensing imagery, marking a significant step forward in the development of more powerful and scalable RS-VQA systems. However, the era of large models also brings forth several challenges and issues. For instance, the substantial volume of parameters in training models poses highly demanding research conditions.
2.3. Multimodal Fusion and Reasoning
Multimodal fusion is a key aspect in various fields such as emotion recognition, human activity recognition, affective computing, and sentiment analysis. Different studies have explored the effectiveness of various fusion strategies in improving recognition performance and robustness in multimodal tasks. Jiang et al. [19] conducted a snapshot research on multimodal information fusion for data-driven emotion recognition. They highlighted the importance of integrating multiple modalities to enhance emotion recognition accuracy. Gadzicki et al. [20] compared early vs. late fusion in multimodal convolutional neural networks for human activity recognition. They utilized RGB video, optical flow, and skeleton data as modalities, emphasizing the significance of fusion timing in improving recognition outcomes. Mai et al. [21] proposed a locally confined modality fusion network with a global perspective for multimodal human affective computing. Their framework incorporated bidirectional multiconnected LSTM to address the multimodal affective computing problem, focusing on both local and global fusion for comprehensive information understanding. Huang et al. [22] utilized the Transformer model for multimodal fusion in continuous emotion recognition, showcasing the superiority of model-level fusion over other strategies on the AVEC 2017 database. Additionally, Zhao et al. [23] proposed a Text-guided Coarse-to-Fine Fusion Network for robust RS-VQA, which leverages semantic relationships between question text and multi-source images for feature-level fusion guidance.
Multimodal reasoning is a significant area of research in artificial intelligence, aiming to integrate different modes of information processing to solve complex problems. Zhao et al. [24] proposed a framework that combines case-based reasoning, rule-based reasoning, and information retrieval to address challenges in evidence-based medical practice. Marling et al. [25] further explored the role of case-based reasoning in multimodal reasoning integrations, highlighting the various roles that case-based reasoning components can fulfill in integrated systems. Nam et al. [26] introduced Dual-Attention Networks for multimodal reasoning and matching, allowing visual and textual attentions to collaborate during inference tasks like Visual Question Answering. Lippe et al. [27] and Zellers et al. [28] delved into the detection of hateful memes and multimodal script knowledge models, respectively, showcasing the need for joint visual and language understanding in multimodal reasoning. Recent advancements in multimodal reasoning include the development of Socratic Models and MM-REACT [29], which leverage language as an intermediate representation to combine knowledge from different pre-trained models for various tasks. Additionally, Zheng et al. [30] introduced Duty-Distinct Chain-of-Thought Prompting for multimodal reasoning in language models, aiming to mimic human thinking processes in AI systems. These studies collectively highlight the evolving landscape of multimodal reasoning research and its applications across different domains [17].
3. Methods
Currently, the questions in Remote Sensing Visual Question Answering (RS-VQA) are becoming more complex, and the types of questions are no longer uniform. As a result, it is necessary to unify different types of questions within a single model architecture. In response, we propose the Adaptive Conditioned Reasoning (ACR) network (Figure 1), which incorporates type classification during the multimodal feature fusion process to adaptively select the reasoning process for different question types. This approach enables the RS-VQA model to better understand and adapt to the characteristics of diverse question types, thereby enhancing the efficiency and accuracy of the model during multimodal feature integration. Through this mechanism, the model can more precisely select appropriate features and reasoning strategies, ultimately improving the overall performance of the question answering system. The framework consists of three key components: (1) a Dual-Reconstruction Feature Enhancer module for mitigating spatial and channel redundancy in remote sensing images, (2) a Type-Driven Conditional Reasoning module to dynamically select a reasoning procedure based on question semantic, and (3) a Text–Image Cross-Modal Reasoning module for joint visual-linguistic interaction.
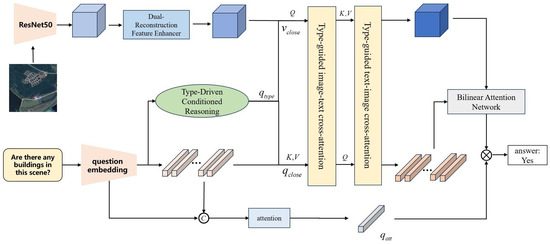
Figure 1.
The framework of the proposed Adaptive Conditional Reasoning module (ACR). We utilize a type judgment process which enables adaptive selection of reasoning procedures corresponding to different types of questions. Then, we use a type-guided cross-attention module with image–text and text–image attention to enhance the representation of visual features and textual features.
3.1. Type-Driven Conditional Reasoning
The Type-Driven Conditional Reasoning module is the core component of our proposed method, designed to dynamically adjust the fusion of visual features based on the semantic content of different types of questions.
Elevating the model’s understanding capability is achievable by leveraging task-specific skills tailored to different tasks. The model enhances multi-level reasoning capabilities through adaptive handling of different tasks based on its judgment of various questions. The structure of the Type-Driven Conditional Reasoning module is shown in Figure 2.
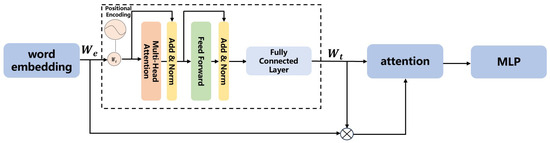
Figure 2.
Type-Driven Conditional Reasoning module.
The role of the question encoding module is to transform natural language questions into high-dimensional semantic vectors, facilitating effective interaction with image features. This semantic vector serves as the input to the Adaptive Conditional Reasoning module, which integrates with the image features to perform subsequent reasoning. The question string is initially converted into a word embedding sequence.
where represents the word embedding of the ith word.
For the word embedding sequence, we further process it to obtain efficient question embedding, facilitating effective feature extraction.
The encoder relies on self-attention mechanisms to process input sequences in parallel, overcoming the sequential nature of RNNs. This architecture is particularly effective for word embedding, as it can simultaneously attend to all words in a sentence, capturing complex relationships between them without relying on sequential processing. The Transformer Encoder consists of multiple stacked layers, each composed of two main components:
The self-attention mechanism enables the model to weigh the importance of each word relative to the others in the input sequence. Specifically, for each word in the input sequence, self-attention computes a weighted sum of all words in the sentence, based on their relevance to . The attention weights are calculated as follows:
where and are the query and key vectors of words i and j, respectively, and is the dimension of the key vectors. The output is a context-sensitive representation of each word.
After applying self-attention, the output is passed through a fully connected feed-forward network. The feed-forward network helps introduce non-linearity, allowing for a richer transformation of the word representations. Each encoder layer also includes residual connections and layer normalization to stabilize training and improve the flow of gradients.
Due to the RS-VQA model’s limited ability to perform multi-layer reasoning, we adopt separate reasoning modules to process closed-ended and open-ended questions.
Closed-ended questions typically start with verbs such as “Is”, “Are”, or “Does”, while open-ended questions usually begin with question words like “How”, “Where”, or “What”. Different question types (such as open-ended questions and closed-ended questions) require different processing approaches. The distinction between these two types can be captured through the use of question embedding. So, the Type-Driven Conditional Reasoning module is responsible for selecting the appropriate reasoning strategy based on the question type. It first classifies the question and then adopts different reasoning paths based on the classification results. Specifically, the module takes the question as input and outputs its question type (either closed-ended or open-ended).
For questions, we utilize the question feature extractor to obtain semantic features. With the multi-head self-attention mechanism as the core, it effectively captures the dependency relationships and semantic information among words in the questions, avoiding long-term dependency on context from a global perspective. Therefore, it can better model the semantics of questions. After extracting question features, an attention mechanism is used to assign important weights to different words to further emphasize the important parts of each problem, such as “What is the area of buildings?”. Then, we further incorporate an attention mechanism:
where represents the concatenation of embedded features and question features along the dimension.
where ⊙ represents the Hadamard product. Next, add attention information to the features:
where represents the attention score.
is the question feature with attention information. The question encoder in the module reduces the long-term dependency of the question context, which is beneficial for subsequent reasoning processes. The obtained question embedding is passed through an MLP to map it to a classification score. The classification probabilities are denoted as p, where represents the probability of the question being a closed-ended question, and represents the probability of the question being an open-ended question. If , it indicates that the question is closed-ended. This can be represented by
where represents the probability that the question is an open-ended question versus a closed-ended question. A of 0 indicates that a question is closed-ended, and a of 1 indicates that a question is open-ended. The visual features and question features are then subjected to corresponding multimodal fusion based on the classification results. The network trains a module effective for open-ended questions ( = 1) and the network trains a module effective only for closed-ended questions ( = 0). Through this module, the model can determine the probability that the input question is an open or closed question, thereby providing guidance for the targeted feature fusion process.
3.2. Text–Image Cross-Modal Reasoning Module
If the question type is open-ended (or closed-ended), then the visual feature is (), and the text feature is (). To achieve fine-grained alignment between visual and textual modalities, we design a bidirectional cross-attention architecture shown in Figure 3:
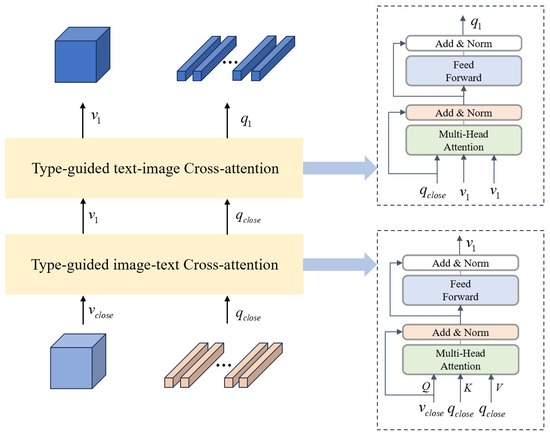
Figure 3.
Text–Image Cross-Modal Reasoning module.
First, map the visual feature to the query vector , with the text feature serving as the key and value .
Then, calculate the cross-attention weights, allowing the visual features to focus on relevant text information and integrate the textual context into the visual features. This helps filter the visual regions that are semantically related to the text:
After the cross-attention operation, the enhanced visual feature is obtained, which contains rich information from the text modality.
Then, the text feature is mapped to the query vector , with the visual feature serving as the key and value .
We calculate the cross-attention weights to optimize the semantic representation through visual features, integrating visual context information.
The cross-attention operation allows the text features to integrate visual information, thereby enhancing the representational power of the text features. After the cross-attention operation, the enhanced text feature is obtained, which contains rich information from the visual modality.
To prevent information loss, residual connections and layer normalization are added to the output of each stage:
In reasoning with the Type-Driven Conditioned Reasoning module, reasoning skill is learned by simultaneously applying importance selection to the fused feature. The module needs to dynamically adjust the handling of image features based on the semantic content of the question. Different types of questions may focus on different regions of the image, requiring the model to selectively attend to specific parts of the image. Through this process, the model can flexibly select the relevant areas of the image based on the semantic information of the question, thereby enhancing the specificity and accuracy of the reasoning.
We combine the language and image features that capture the key information in the problem to obtain a comprehensive feature representation. Specifically, we utilize a common fusion module, denoted as A, to integrate the two modalities effectively. The fused features are then fed into a classifier, denoted as D, for the final prediction.
where ∘ represents the element-wise product, s is the final predicted score, A is a commonly used fusion module, and D is the classifier. Through this approach, the Type-Driven Conditioned Reasoning module ensures that different types of questions are handled with the most suitable reasoning strategy, thereby improving both the efficiency and accuracy of the reasoning process.
The training objective minimizes cross-entropy loss for answer prediction, formulated as
where C is the number of answer classes, is the ground-truth one-hot label for the i-th sample, and is the predicted probability from the classifier D.
3.3. Dual-Reconstruction Feature Enhancer
Objects in remote sensing images often exhibit complex shapes, diverse land cover types, and rich spatial information, making the visual feature extraction module particularly critical. In this study, we employ a convolutional neural network based on the deep residual network (ResNet-50) to extract multi-scale features from the images.
In this process, drawing inspiration from [31] to address spatial and channel redundancy in image features, we devise a Dual-Reconstruction Feature Enhancer through spatial reconstruction units and channel reconstruction units.
In the process of feature extraction from remote sensing images, we incorporate the spatial and channel reconstruction convolution method to enhance the spatial and channel representation capabilities of the features. Specifically, within each residual block of the feature extraction network, spatial and channel reconstruction convolutions are applied after the convolution operation to further process the extracted feature maps. By integrating spatial and channel reconstruction convolution into the feature extraction process of remote sensing images, we can effectively mitigate the impact of redundant features and improve the deep network’s ability to represent remote sensing images. This improvement aids the model in better understanding the types of ground objects, spatial structures, and various environmental features within the images.
Spatial reconstruction convolution aims to enhance the spatial information representation of an image by reconstructing the features along the spatial dimension. In the process of remote sensing image feature extraction, spatial reconstruction convolution can be applied to further process the feature maps, thereby reinforcing the spatial information in important regions and diminishing the influence of redundant areas. For instance, in the case of high-resolution details in remote sensing images, spatial reconstruction convolution enables the model to focus on fine-grained details of ground objects (e.g., buildings, roads, water), while minimizing the interference from irrelevant background regions.
The spatial and channel reconstruction convolution module in the visual feature extraction process is shown in Figure 4. Initially, the assessment of information content in different feature maps is conducted using the scaling factor in Group Normalization. This process separates feature maps with higher information content from those with lower information content.
where represents the standardized input feature X, and obtained from Equation (24) indicates the importance of different feature mappings. The weights of the feature mappings, adjusted through , are mapped to the (0, 1) range by a sigmoid function and gated by a threshold. We set the weights above the threshold to 1, yielding the information weight , and set them to 0, resulting in the non-information weight .
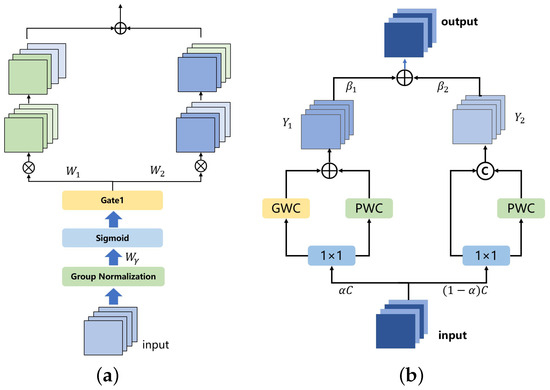
Figure 4.
(a) Spatial reconstruction convolution and (b) Channel reconstruction convolution.
Subsequently, the addition of feature maps with more information and those with less information is performed to generate feature maps with more information while conserving space. The specific operation is cross-reconstruction, involving the weighted combination of two different information features, resulting in a spatially refined feature map. This approach effectively separates feature maps with higher information content from those with lower information content, thus mitigating redundant features in the spatial dimension.
where ∪ represents concatenation, ⊗ represents element-wise multiplication and ⊕ is element-wise summation.
Channel reconstruction convolution optimizes feature representation by reconstructing the channel dimension, thereby reducing redundancy between channels. In the context of remote sensing images, channel reconstruction convolution adjusts the weights of different feature channels, compressing or optimizing redundant channel information. For the extracted multi-scale feature maps, some feature channels may contain duplicate or overly similar information. Channel reconstruction convolution can adaptively learn which channels are most critical for the final task, automatically suppressing redundant channels, thus enhancing the expressiveness of the feature maps.
In the channel dimension, the spatially refined features of the input are split into two segments: one with channels and the other with channels, where is a hyper-parameter, and , convolution kernels are employed to compress the channel numbers of the two sets of features, resulting in and .
We perform GWC and PWC separately, followed by adding the outputs. The fusion operation utilizes global average pooling to integrate global spatial information and channel statistics, yielding pooled and .
Then, we obtain feature weight vectors and .
Finally, the output Y is acquired using the feature weight vectors, representing the channel-refined features.
where Y represents the visual features extracted by the model.
4. Experiment and Results
4.1. Setting
The model is implemented using pytorch and trained on a single GPU in the Ubuntu 22.04 environment. During the model training process, the learning rate decay algorithm is employed, and the Adam [32] optimizer is used. During training, the batch size is set to 16, and the initial learning rate of the model is set to 5 .
The accuracy of the model’s answers to questions is the most important and sole evaluation metric, which is the mainstream evaluation standard for RS-VQA models. We also use accuracy as the evaluation metric for the model, and it is calculated as follows:
where represents the number of correctly answered questions, and represents the total number of questions.
4.2. Dataset
In this study, we use the EarthVQA [33] dataset as the primary data source for the Visual Question Answering model.
The EarthVQA dataset consists of 6000 high-resolution remote sensing images, corresponding semantic masks, and 208,593 question–answer pairs. These QA pairs are closely related to urban and rural governance requirements, covering a wide range of tasks from simple judgments and counting to more complex relational analysis. The dataset is an extension of the LoveDA dataset and includes 18 urban and rural areas from cities in China, namely Nanjing, Changzhou, and Wuhan. Similar to common Visual Question Answering (VQA) datasets, the distribution of answers in EarthVQA is imbalanced, posing additional challenges for practical applications in the Earth’s environmental contexts. Figure 5 shows an example image from the EarthVQA dataset along with the corresponding QA pairs.

Figure 5.
Example image and corresponding QA pairs from the EarthVQA dataset.
4.3. Accuracy Evaluation with Other Methods
To better evaluate the RS-VQA model’s robustness to various types of questions, the accuracy is typically analyzed from six perspectives: basic counting, relational-based counting, basic judging, relational-based judging, comprehensive analysis and object situation analysis. All types of questions encompass both open-ended and closed-ended questions. Open-ended questions are defined as question types without fixed answers, meaning that the type of answer changes with the question, while closed-ended questions are defined as question types with fixed answers, meaning that the type of answer remains the same regardless of how the question changes (e.g., yes/no).
To comprehensively evaluate the performance of the ACR module, we conducted comparative experiments with other methods on the EarthVQA dataset. Table 1 presents the results of the EarthVQA dataset. The compared models include both general VQA frameworks and specialized RS-VQA approaches:

Table 1.
Accuracy of the existing methods on the EarthVQA dataset.
- (1)
- SAN [34]: SAN processes the input image and question through stacked attention mechanisms, progressively enhancing the model’s focus on different visual information, thereby enabling more accurate reasoning and answering in the given visual scene.
- (2)
- MAC [35]: MAC introduces a memory module, which is used to store and transfer relevant features of the image. The model gradually reads the image features and stores them in the “memory” for subsequent reasoning and answering.
- (3)
- MCAN [36]: MCAN is composed of a series of Modular Co-Attention (MCA) layers. Each MCA layer is capable of modeling the attention between the image and the question.
- (4)
- BUTD [37]: BUTD combines bottom-up and top-down attention mechanisms to compute the salient regions in the image at the object level.
- (5)
- D-VQA [38]: D-VQA constructs branches from questions to answers and from visuals to answers, capturing the biases in language and vision, and applies two unimodal bias detection modules to explicitly identify and remove negative biases.
- (6)
- RSVQA [39]: A baseline model constrained by its shallow CNN feature extractor in capturing high-resolution RS image details.
- (7)
- SOBA [33]: SOBA generates object semantics using a segmentation network and aggregates internal object features through pseudo-masks.
Our experiments on the EarthVQA dataset demonstrate the superior performance of the proposed ACR model in Remote Sensing Visual Question Answering tasks. ACR achieves an overall accuracy of 78.5%, surpassing all baseline methods, particularly excelling in tasks requiring complex spatial relational reasoning (68.0% for relational-based counting and 83.6% for relational-based judging), outperforming the suboptimal model SOBA by +0.2% and +1.0%, respectively. With only 47.9 M parameters (81.6% of BAN’s 58.7 M), ACR maintains leadership in high-level semantic tasks such as object situation analysis (61.6%) through its dynamic relational reasoning module and multimodal feature fusion strategy, achieving an optimal balance between parameter efficiency and task performance. While slightly trailing behind specialized models like BUTD in basic tasks (79.7% for counting and 89.8% for judging), ACR validates the effectiveness of its unified architecture for multi-granularity geospatial reasoning. This work establishes a new paradigm for building efficient and interpretable remote sensing QA systems.
While ACR achieves great performance in complex tasks (e.g., relational reasoning), its modest improvement in Bas Co (79.7%) compared to MCAN (79.8%) and SOBA (80.1%) stems from the inherent simplicity of basic counting tasks. These tasks often require localized object detection rather than adaptive reasoning. TCR’s adaptive reasoning pathways are more impactful for open-ended or relation-heavy questions, where nuanced cross-modal interaction is critical. Future work will explore task-specific feature enhancement to better balance performance across simple and complex tasks.
Based on the experimental evaluation results, we can make the following analysis. First, the results for basic condition-type questions indicate that, in fundamental analyses of remote sensing images (such as terrain type, vegetation cover, and building presence), our method is able to effectively understand and reason about the basic condition information within the image, accurately identifying the geographic phenomena queried by the question. Secondly, for basic judging-type questions, our method achieves an accuracy of 89.8%, demonstrating its effectiveness in reasoning about simple judgments within the image (such as whether a specific feature is present or whether climatic conditions are met). In making basic judgments on remote sensing images, particularly in low-resolution images or those significantly affected by weather conditions, the model can make relatively accurate inferences by carefully processing image features. Third, relational-based counting-type questions typically involve reasoning about the relationships between multiple variables, such as identifying spatial relationships between different features in remote sensing images (e.g., the relative position of water and urban areas). Our method performs well in reasoning across complex geographical and spatial information. Finally, our method exhibits significantly higher accuracy than other methods in answering comprehensive analysis-type questions. This suggests that our approach is particularly effective in integrating multidimensional information from remote sensing images, such as considering vegetation, buildings, road networks, and climatic conditions simultaneously, to conduct comprehensive reasoning for complex questions.
Overall, our method outperforms traditional approaches such as SAN, MAC, and MCAN on the EarthVQA dataset, demonstrating strong reasoning capabilities in Remote Sensing Visual Question Answering. Remote sensing images often contain complex information related to terrain, climate, and human activities. Our method is able to effectively integrate image and question information, extracting key geographical details from these complex data, thereby enabling more accurate reasoning.
4.4. Ablation Study
In order to evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed Adaptive Conditional Reasoning network and new image feature extraction module, we conducted ablation experiments on the model by removing the Dual-Reconstruction Feature Enhancer (DRE) and the Type-Driven Conditioned Reasoning (TCR) module separately. We evaluated the performance of the model in both cases, as shown in Table 2. “DRE” represents the accuracy after adding the Dual-Reconstruction Feature Enhancer to the model. “TCR” represents the accuracy after adding the Type-Driven Conditioned Reasoning module to the model. It can be observed that removing both modules resulted in a decrease in the prediction accuracy of the model to varying degrees.

Table 2.
Ablation study of the proposed modules.
The ablation results in Table 2 reveal nuanced contributions of the Dual-Reconstruction Feature Enhancer (DRE) and Type-Driven Conditional Reasoning (TCR) modules. The results of the ablation study reveal that when the DRE module is used individually, the overall performance of the model is 77.4%. When the TCR module is enabled, the performance slightly improves to 78.4%. The DRE improves basic counting questions (+0.3% without DRE) and comprehensive analysis questions (+0.7%) by suppressing spatial–channel redundancies, which is critical for tasks requiring fine-grained localization (e.g., counting scattered buildings). However, its impact on relational-based judging questions is limited, as relational judgments rely more on cross-modal interaction than spatial refinement. TCR significantly boosts relational-based counting questions (+3.3%) and object situation analysis questions (+2.9%) by dynamically aligning visual–textual features based on question semantics. However, TCR provides minimal gains for basic judging questions (+0.9%), as closed-ended questions (e.g., ‘Is there a road?’) depend less on adaptive reasoning. However, when both modules are used together, the overall performance significantly increases to 78.5%. This indicates that both DRE and TCR modules contribute to performance enhancement when used individually, but their combined use demonstrates a synergistic effect, leading to a substantial optimization of the model’s performance. This highlights that DRE optimizes low-level feature discriminability, while TCR governs high-level reasoning pathways—both are essential for complex tasks. Therefore, it can be concluded that all the proposed modules contribute to the performance improvement of the Remote Sensing Visual Question Answering system, with the most significant contribution coming from the conditionally adaptive reasoning module, which effectively enhances the inference capability of the Remote Sensing Visual Question Answering model.
While ACR achieves great performance in complex tasks, its modest improvement in Bas Co (79.7%) compared to MCAN (79.8%) and SOBA (80.1%) stems from the inherent simplicity of basic counting tasks. These tasks often require localized object detection rather than adaptive reasoning. TCR’s adaptive reasoning pathways are more impactful for open-ended or relation-heavy questions, where nuanced cross-modal interaction is critical. Future work will explore task-specific feature enhancement to better balance performance across simple and complex tasks.
4.5. Accuracy of Different Types of Questions
To validate the adaptive reasoning capability of ACR for open-ended (closed-ended) questions, we conducted fine-grained evaluation on the EarthVQA dataset, with results shown in Figure 6 and Table 3. Case 1 corresponds to the ACR model’s average answer accuracy for both open-ended and closed-ended questions, while case 2 represents the average accuracy of open-ended or closed-ended questions when the ACR module is removed. The experimental results demonstrate that the ACR model achieves improved answer accuracy for both question types, with a particularly pronounced enhancement observed for open-ended questions.
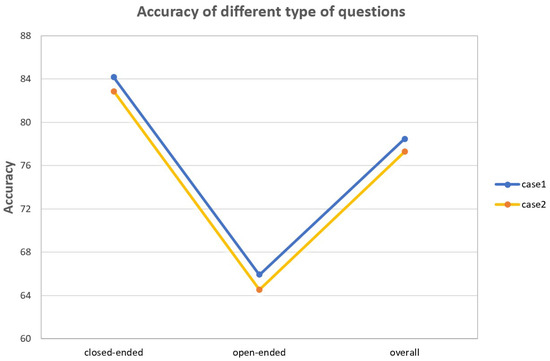
Figure 6.
The accuracy of open-ended and closed-ended questions. Case 1 represents ACR model’s average answer accuracy and case 2 represents the accuracy without the ACR module.

Table 3.
The accuracy of different types of questions.
5. Discussion
A comparison of various Visual Question Answering (VQA) methods on the EarthVQA dataset reveals that the method proposed in this study outperforms others in multiple task types, particularly in relational-based judging, where it shows superior performance. Additionally, it demonstrates a relatively balanced performance in more complex tasks such as object situation analysis and comprehensive analysis, with an overall accuracy of 78.5%, surpassing SOBA [33] (78.1%). While traditional methods such as SAN, BAN, and MCAN excel in basic tasks like basic counting and basic judging, they show weaker performance in complex scenario analysis. In contrast, RSVQA [39] consistently exhibits lower accuracy across all task types, particularly struggling with more complex problem-solving tasks. Overall, the proposed method exhibits strong capabilities in handling complex VQA tasks, establishing itself as a competitive approach in the field. This indicates that our proposed framework, utilizing Adaptive Conditional Reasoning at multiple levels, enables the model to better comprehend questions during the VQA process, thereby enhancing the model’s multi-level reasoning capability.
Moreover, ACR’s adaptive reasoning capabilities hold significant practical value in disaster response. For instance, during post-earthquake assessments, emergency teams could input a satellite image of an affected area and ask questions like ‘How many buildings show severe structural damage?’ or ‘Are there accessible roads connecting evacuation zones?’. ACR’s ability to dynamically parse spatial relationships (e.g., collapsed buildings blocking roads) and quantify damage (e.g., counting damaged roofs) would enable rapid, actionable insights. VQA systems accelerated post-disaster damage assessment, but ACR’s adaptive reasoning offers superior scalability for complex, dynamic scenarios.
5.1. Qualitative Result Visualization
In order to demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed Adaptive Conditional Reasoning method in remote sensing image Visual Question Answering, we present six remote sensing images along with their corresponding questions, predicted results, and correct answers (Figure 7). In these examples, the predicted results are fully consistent with the correct answers, which validates the outstanding performance of our method in complex remote sensing image analysis tasks.

Figure 7.
Qualitative result visualization on the EarthVQA dataset.
Our method introduces two key components: the question-based conditional Transformer reasoning module and the type-based conditional Transformer reasoning module. The synergy between these modules enables the model to flexibly adjust its reasoning strategy when facing different types of questions, thereby enhancing the accuracy of remote sensing image interpretation. The question-based conditional reasoning module dynamically adjusts the fusion of image features based on the semantic content of the question, allowing the model to more accurately focus on and process contextually relevant information. In remote sensing tasks, images contain vast amounts of geospatial information, and questions may concern specific geographic areas or particular object features. The question-based conditional reasoning module adapts the selection and processing of image features based on the specific requirements of the question, ensuring that the final prediction is closely aligned with the actual query.
The type-based conditional reasoning module selectively applies different reasoning strategies depending on whether the question is open-ended or closed-ended. Open-ended questions typically require the model to provide detailed explanations or reasoning processes, whereas closed-ended questions demand a clear, definitive answer. In Remote Sensing Visual Question Answering tasks, the difference in question types may involve tasks such as land cover type recognition, regional change analysis, or classification based on specific conditions. The type-based conditional reasoning module ensures that the model selects the appropriate reasoning path based on the nature of the question, thus improving both the accuracy and interpretability of the predictions.
Through the collaboration of these two modules, our method is able to flexibly adapt to the diverse demands of different questions and achieve strong performance in remote sensing image VQA tasks. In the demonstrated examples, our model successfully identifies key features in the images and performs reasonable inferences based on the content of the question, ultimately generating predictions that are consistent with the actual answers. For instance, in a remote sensing image of urban buildings, the question “How many eutrophic waters are in this scene?” is answered by the question-based conditional reasoning module, which allows the model to focus on the water bodies in the image and accurately extract relevant information. In another closed-ended question regarding buildings, the model uses the type-based conditional reasoning module to directly provide a clear answer on the presence of buildings.
5.2. Attention Visualization on the EarthVQA Dataset
To validate the effectiveness of Adaptive Conditional Reasoning in Remote Sensing Visual Question Answering tasks, we designed a multi-level attention visualization scheme to intuitively demonstrate the model’s ability to model cross-modal associations (Figure 8). The first column displays the input original images, the second column shows the attention maps from the first cross-attention layer, and the third column presents the attention maps from the final layer. As illustrated in the figure, as the network depth increases, the model progressively focuses on semantically relevant regions while suppressing attention to irrelevant areas. This gradual shift in focus illustrates the model’s ability to dynamically adjust its attention, ensuring that it selectively emphasizes the most pertinent visual information based on the given textual input. This observation demonstrates the effectiveness of our proposed model in Remote Sensing Visual Question Answering tasks.
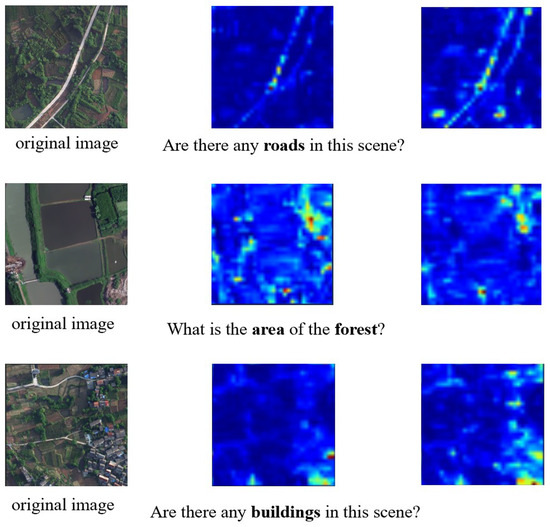
Figure 8.
Attention map visualization of the EarthVQA dataset. The darker the red color, the higher the attention level in that area.
6. Conclusions
In this paper, we propose Adaptive Conditional Reasoning that effectively solves the lack of multi-level reasoning capabilities in Remote Sensing Visual Question Answering tasks. The primary goal of our research was to develop a more effective and contextually aware VQA model that can reason both with the content of images and the specific nature of the questions. Through this approach, we aim to improve the accuracy and relevance of answers provided by VQA systems, particularly for complex questions that involve various reasoning types and multiple object relationships.
Our method consists of two key components: a Type-Driven Conditioned Reasoning module and Text–Image Cross-Modal Reasoning module based on the type of question. The Type-Driven Conditioned Reasoning module employs transformer-based type classification before multimodal fusion to adaptively route reasoning procedures based on semantic intent. And the Text–Image Cross-Modal Reasoning module enables fine-grained visual–linguistic interaction through attention-driven joint reasoning. Moreover, to mitigate spatial and channel redundancy in remote sensing images, we utilize the Dual-Reconstruction Feature Enhancer to enhance visual feature extraction. By leveraging cross-modal attention and adaptive reasoning strategies, our model is capable of providing more accurate, interpretable, and context-sensitive answers.
Despite the promising results, our method has several limitations. First, the binary classification of question types (open-ended and closed-ended) may oversimplify the diversity of real-world queries, especially for ambiguous questions that blend both types. Future work will explore finer-grained question categorization. Expanding the model to handle more diverse and nuanced question types—such as those involving complex multi-step inference—would provide significant improvements in real-world applicability. Finally, we aim to investigate the generalization capability of our model across various datasets and domains, ensuring that the proposed method is robust and adaptable to different VQA tasks.
Author Contributions
Methodology, Y.G.; software, Y.G. and B.J.; investigation, Y.G., Z.B. and P.G.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.G.; writing—review and editing, Y.G. and R.Z.; supervision, Z.B. and M.Z.; project administration, Z.B.; funding acquisition, Z.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2022YFE0138600) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 62266045).
Data Availability Statement
The EarthVQA dataset was obtained from Datasets at Intelligent Data Extraction, Analysis and Applications of Remote Sensing (http://rsidea.whu.edu.cn/EarthVQA.htm accessed on 7 December 2024).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Qing, Y.; Ming, D.; Wen, Q.; Weng, Q.; Xu, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, B. Operational earthquake-induced building damage assessment using CNN-based direct remote sensing change detection on superpixel level. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 112, 102899. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, T.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Wang, W.; Shao, C.; Liu, B. Flood disaster monitoring and emergency assessment based on multi-source remote sensing observations. Water 2022, 14, 2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wu, S.; Qin, M.; Fu, Z.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Du, Z. A deep learning crop model for adaptive yield estimation in large areas. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 110, 102828. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.; Wang, B.; Du, X.; Lu, X. Mutual attention inception network for remote sensing visual question answering. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 5606514. [Google Scholar]
- Antol, S.; Agrawal, A.; Lu, J.; Mitchell, M.; Batra, D.; Zitnick, C.L.; Parikh, D. Vqa: Visual question answering. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 2425–2433. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.; Gulcehre, C.; Cho, K.; Bengio, Y. Empirical evaluation of gated recurrent neural networks on sequence modeling. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.3555. [Google Scholar]
- Lobry, S.; Tuia, D. Visual question answering on remote sensing images. In Advances in Machine Learning and Image Analysis for GeoAI; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 237–254. [Google Scholar]
- Lobry, S.; Demir, B.; Tuia, D. RSVQA meets BigEarthNet: A new, large-scale, visual question answering dataset for remote sensing. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium IGARSS, Brussels, Belgium, 11–16 July 2021; pp. 1218–1221. [Google Scholar]
- Bazi, Y.; Al Rahhal, M.M.; Mekhalfi, M.L.; Al Zuair, M.A.; Melgani, F. Bi-modal transformer-based approach for visual question answering in remote sensing imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 4708011. [Google Scholar]
- Siebert, T.; Clasen, K.N.; Ravanbakhsh, M.; Demir, B. Multi-modal fusion transformer for visual question answering in remote sensing. In Image and Signal Processing for Remote Sensing XXVIII; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2022; Volume 12267, pp. 162–170. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Yuan, Y. Rsvg: Exploring data and models for visual grounding on remote sensing data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5604513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Jiao, L.; Li, L.; Liu, X.; Chen, P.; Liu, F.; Li, Y.; Guo, Z. A spatial hierarchical reasoning network for remote sensing visual question answering. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 4400815. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar, A.; Chowdhury, T.; Murphy, R.R.; Gangopadhyay, A.; Rahnemoonfar, M. Sam-vqa: Supervised attention-based visual question answering model for post-disaster damage assessment on remote sensing imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 4702716. [Google Scholar]
- Ran, L.; Wang, L.; Zhuo, T.; Xing, Y.; Zhang, Y. DDF: A Novel Dual-Domain Image Fusion Strategy for Remote Sensing Image Semantic Segmentation with Unsupervised Domain Adaptation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 4708113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazi, Y.; Bashmal, L.; Al Rahhal, M.M.; Ricci, R.; Melgani, F. Rs-llava: A large vision-language model for joint captioning and question answering in remote sensing imagery. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1477. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Li, W.; Hossain, M.S.; Chen, M.; Alelaiwi, A.; Al-Hammadi, M. A snapshot research and implementation of multimodal information fusion for data-driven emotion recognition. Inf. Fusion 2020, 53, 209–221. [Google Scholar]
- Gadzicki, K.; Khamsehashari, R.; Zetzsche, C. Early vs late fusion in multimodal convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 23rd International Conference on Information Fusion (FUSION), Rustenburg, South Africa, 6–9 July 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Mai, S.; Xing, S.; Hu, H. Locally confined modality fusion network with a global perspective for multimodal human affective computing. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2019, 22, 122–137. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Tao, J.; Liu, B.; Lian, Z.; Niu, M. Multimodal transformer fusion for continuous emotion recognition. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2020-2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 4–8 May 2020; pp. 3507–3511. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Ma, X.; Tang, J. Text-Guided Coarse-to-Fine Fusion Network for Robust Remote Sensing Visual Question Answering. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2411.15770. [Google Scholar]
- Bichindaritz, I.; Kansu, E.; Sullivan, K.M. Case-based reasoning in care-partner: Gathering evidence for evidence-based medical practice. In Proceedings of the European Workshop on Advances in Case-Based Reasoning, Dublin, Ireland, September 23–25 1998; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998; pp. 334–345. [Google Scholar]
- Marling, C.; Sqalli, M.; Rissland, E.; Muñoz-Avila, H.; Aha, D. Case-based reasoning integrations. AI Mag. 2002, 23, 69. [Google Scholar]
- Nam, H.; Ha, J.W.; Kim, J. Dual attention networks for multimodal reasoning and matching. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 299–307. [Google Scholar]
- Lippe, P.; Holla, N.; Chandra, S.; Rajamanickam, S.; Antoniou, G.; Shutova, E.; Yannakoudakis, H. A multimodal framework for the detection of hateful memes. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2012.12871. [Google Scholar]
- Zellers, R.; Lu, X.; Hessel, J.; Yu, Y.; Park, J.S.; Cao, J.; Farhadi, A.; Choi, Y. Merlot: Multimodal neural script knowledge models. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 23634–23651. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Li, L.; Wang, J.; Lin, K.; Azarnasab, E.; Ahmed, F.; Liu, Z.; Liu, C.; Zeng, M.; Wang, L. Mm-react: Prompting chatgpt for multimodal reasoning and action. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.11381. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, G.; Yang, B.; Tang, J.; Zhou, H.Y.; Yang, S. Ddcot: Duty-distinct chain-of-thought prompting for multimodal reasoning in language models. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2023, 36, 5168–5191. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Wen, Y.; He, L. Scconv: Spatial and channel reconstruction convolution for feature redundancy. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 6153–6162. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zheng, Z.; Chen, Z.; Ma, A.; Zhong, Y. Earthvqa: Towards queryable earth via relational reasoning-based remote sensing visual question answering. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 20–27 February 2024; Volume 38, pp. 5481–5489. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; He, X.; Gao, J.; Deng, L.; Smola, A. Stacked attention networks for image question answering. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 21–29. [Google Scholar]
- Hudson, D.A.; Manning, C.D. Compositional Attention Networks for Machine Reasoning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 30 April–3 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.; Yu, J.; Cui, Y.; Tao, D.; Tian, Q. Deep modular co-attention networks for visual question answering. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 6281–6290. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, P.; He, X.; Buehler, C.; Teney, D.; Johnson, M.; Gould, S.; Zhang, L. Bottom-Up and Top-Down Attention for Image Captioning and Visual Question Answering. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Z.; Xu, G.; Tan, M.; Wu, Q.; Wu, Q. Debiased Visual Question Answering from Feature and Sample Perspectives. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Beygelzimer, A., Dauphin, Y., Liang, P., Vaughan, J.W., Eds.; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Lobry, S.; Marcos, D.; Murray, J.; Tuia, D. RSVQA: Visual Question Answering for Remote Sensing Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 8555–8566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).