Multi-Instrument Analysis of Ionospheric Equatorial Plasma Bubbles over the Indian and Southeast Asian Longitudes During the 19–20 April 2024 Geomagnetic Storm
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
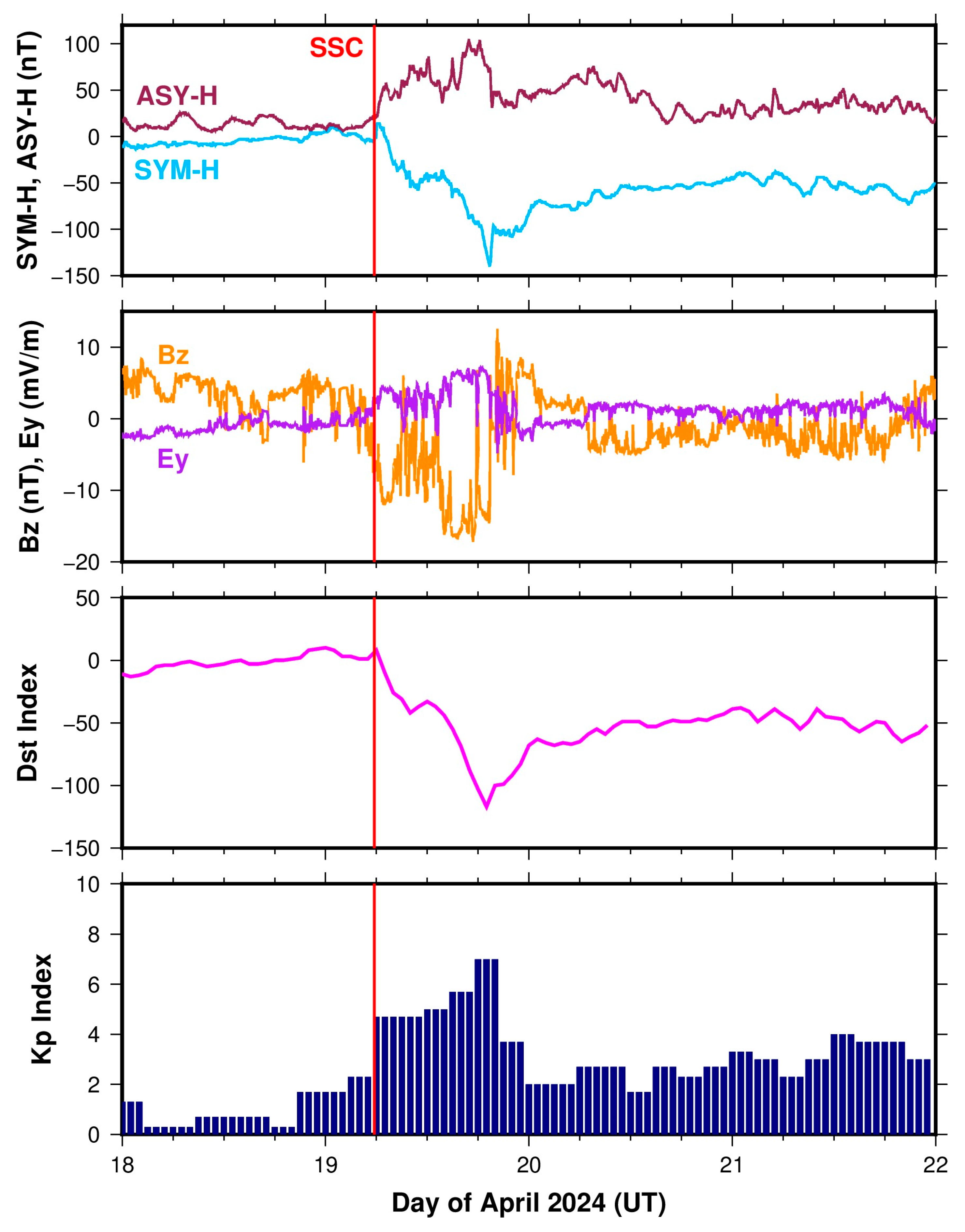
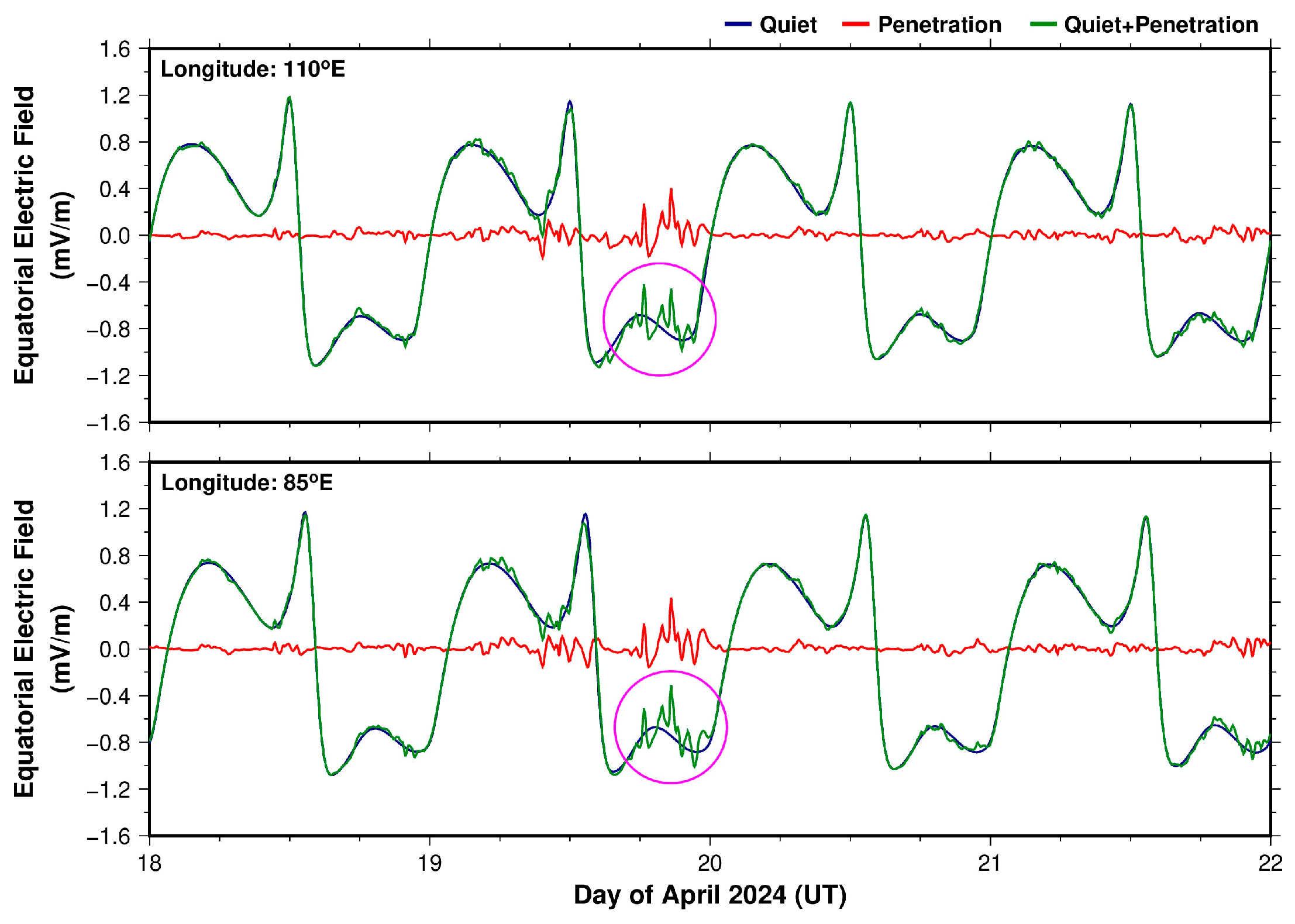
3.1. Geophysical Conditions During the Geomagnetic Storm of 19–20 April 2024
3.2. Occurrence Characteristics of EPBs During 18–21 April 2024
3.2.1. S4 Index from 80°E Longitude Sector During 18–21 April 2024
3.2.2. ROTI from 70–80°E Longitude Sector During 18–21 April 2024
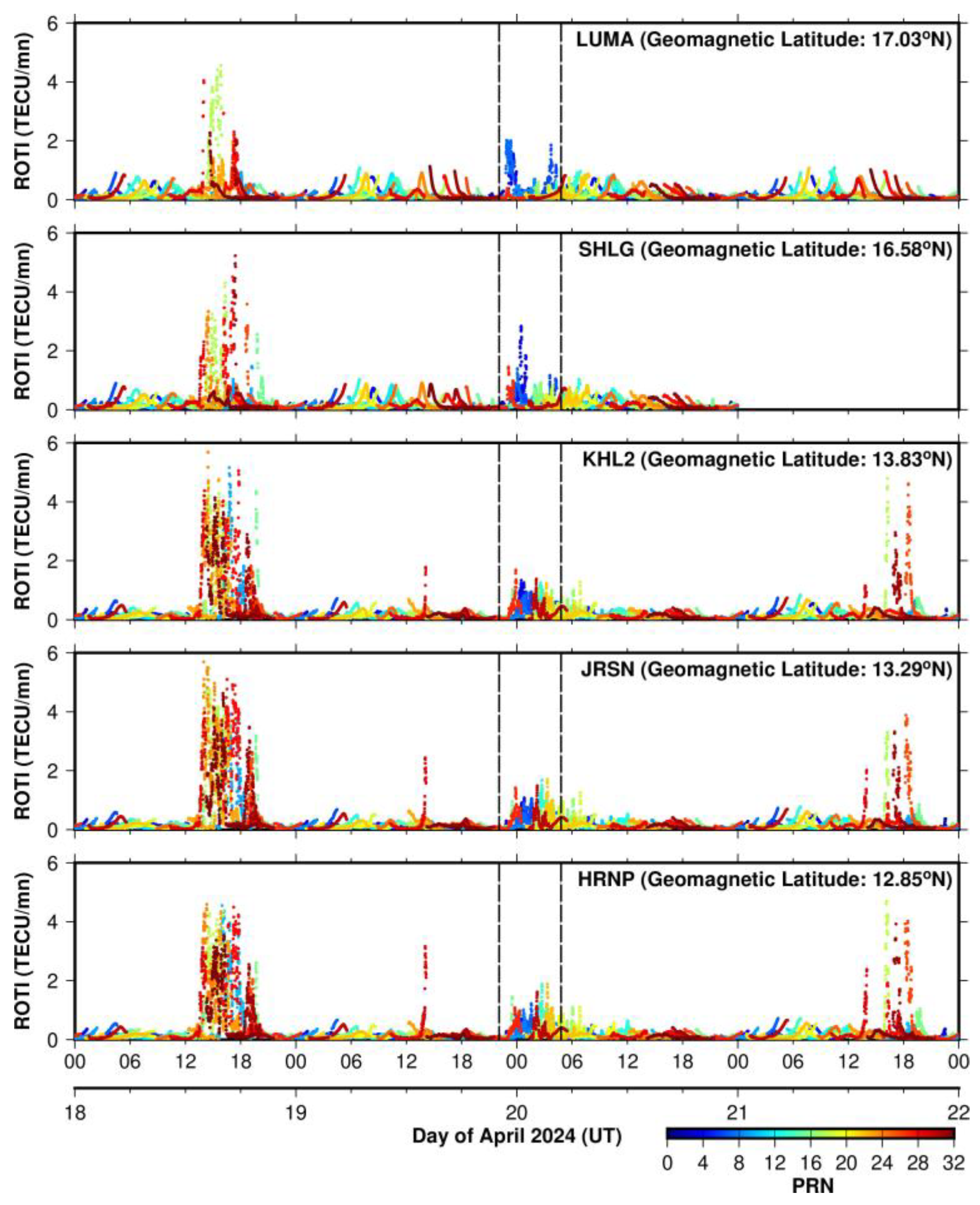
3.2.3. ROTI from 90°E Longitude Sector During 18–21 April 2024
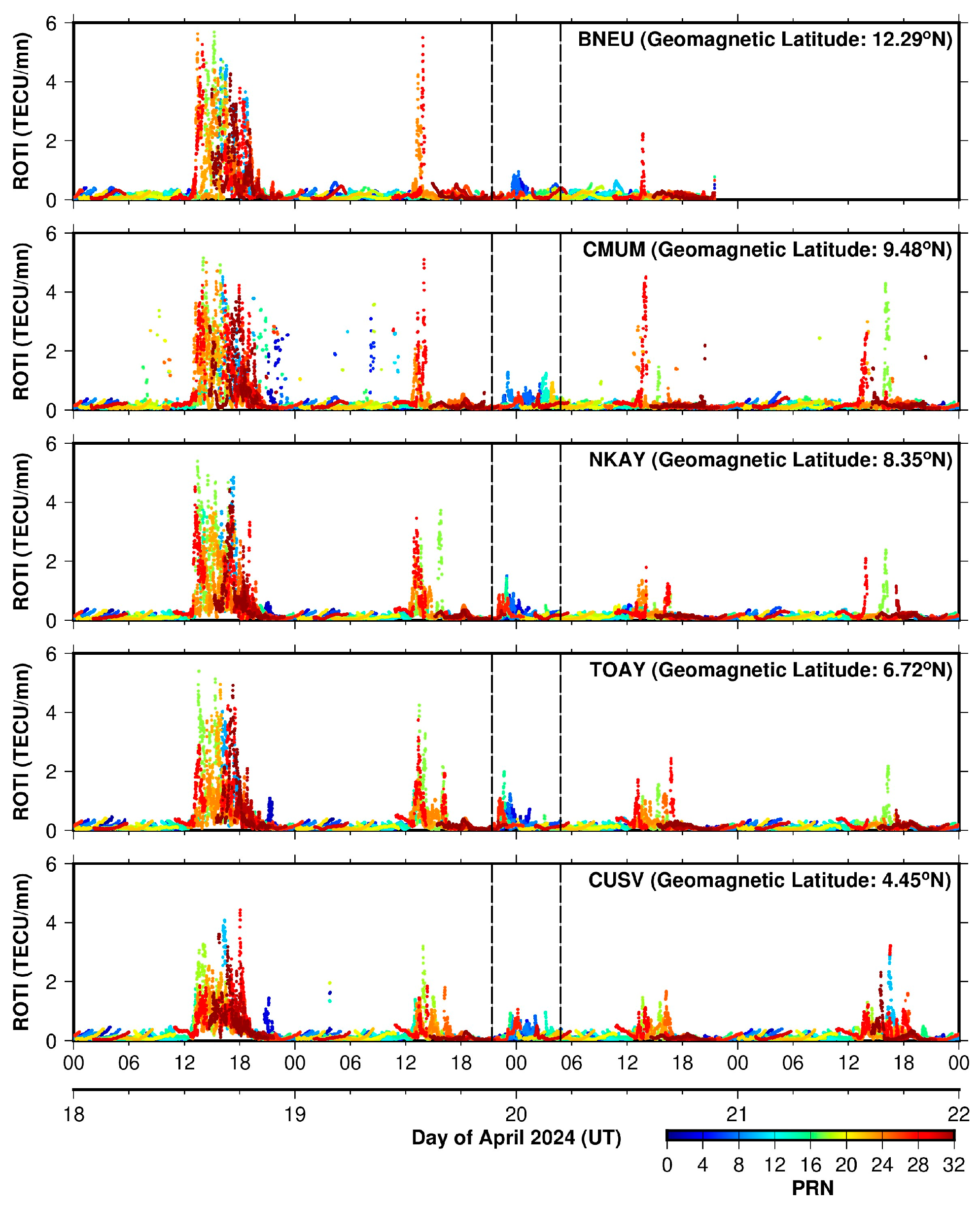
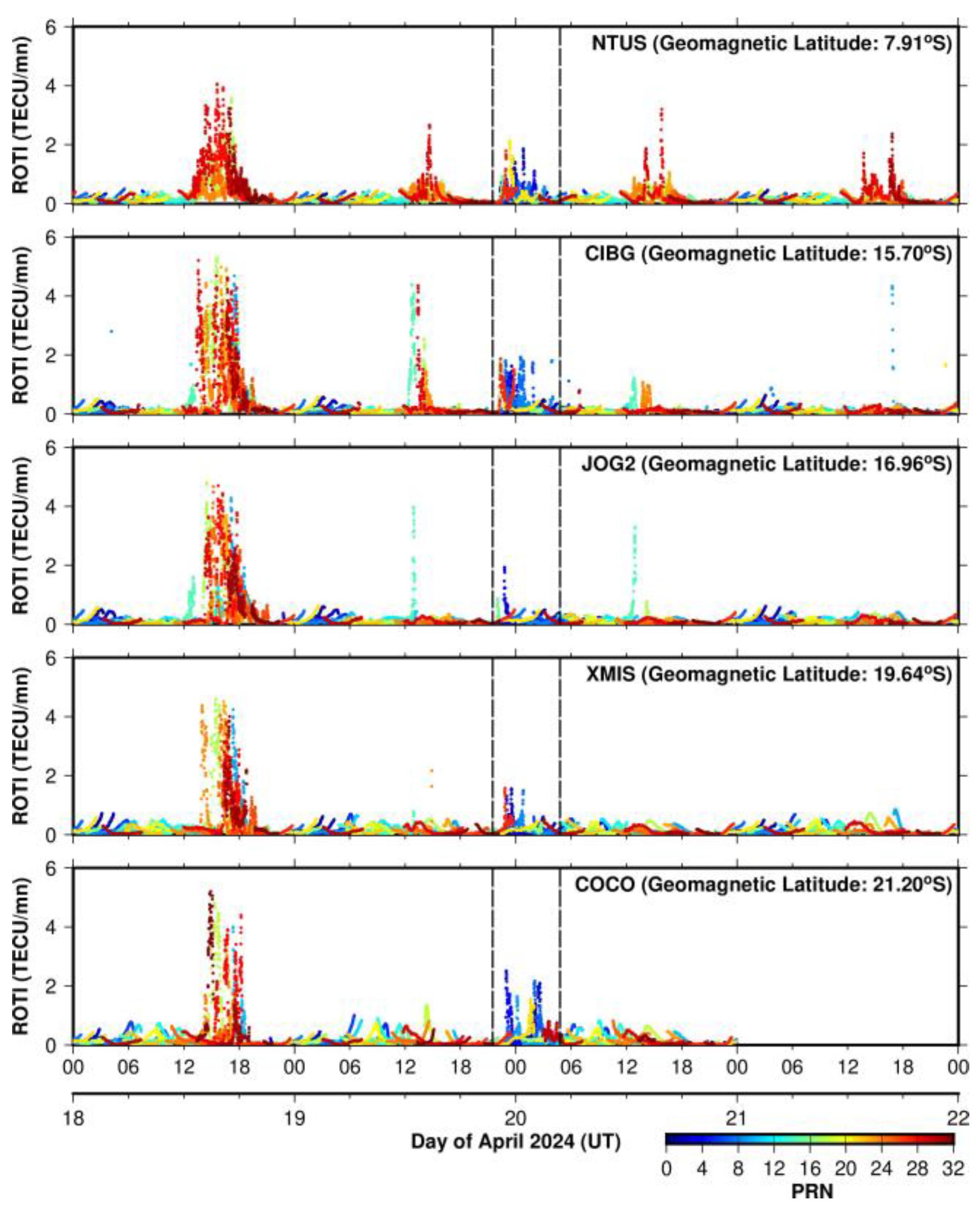
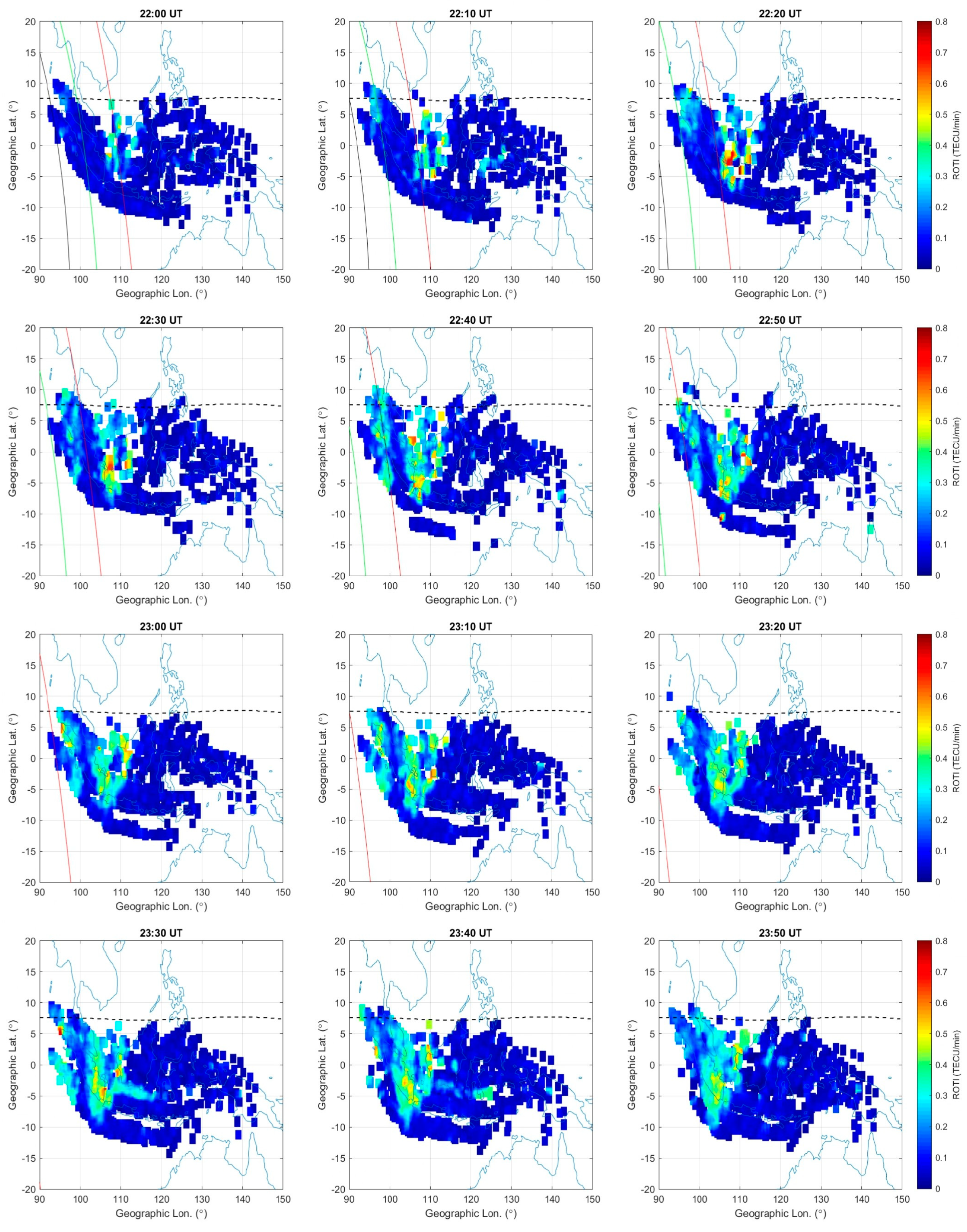
3.2.4. ROTI from the 100 to 110°E Longitude Sector During 18–21 April 2024
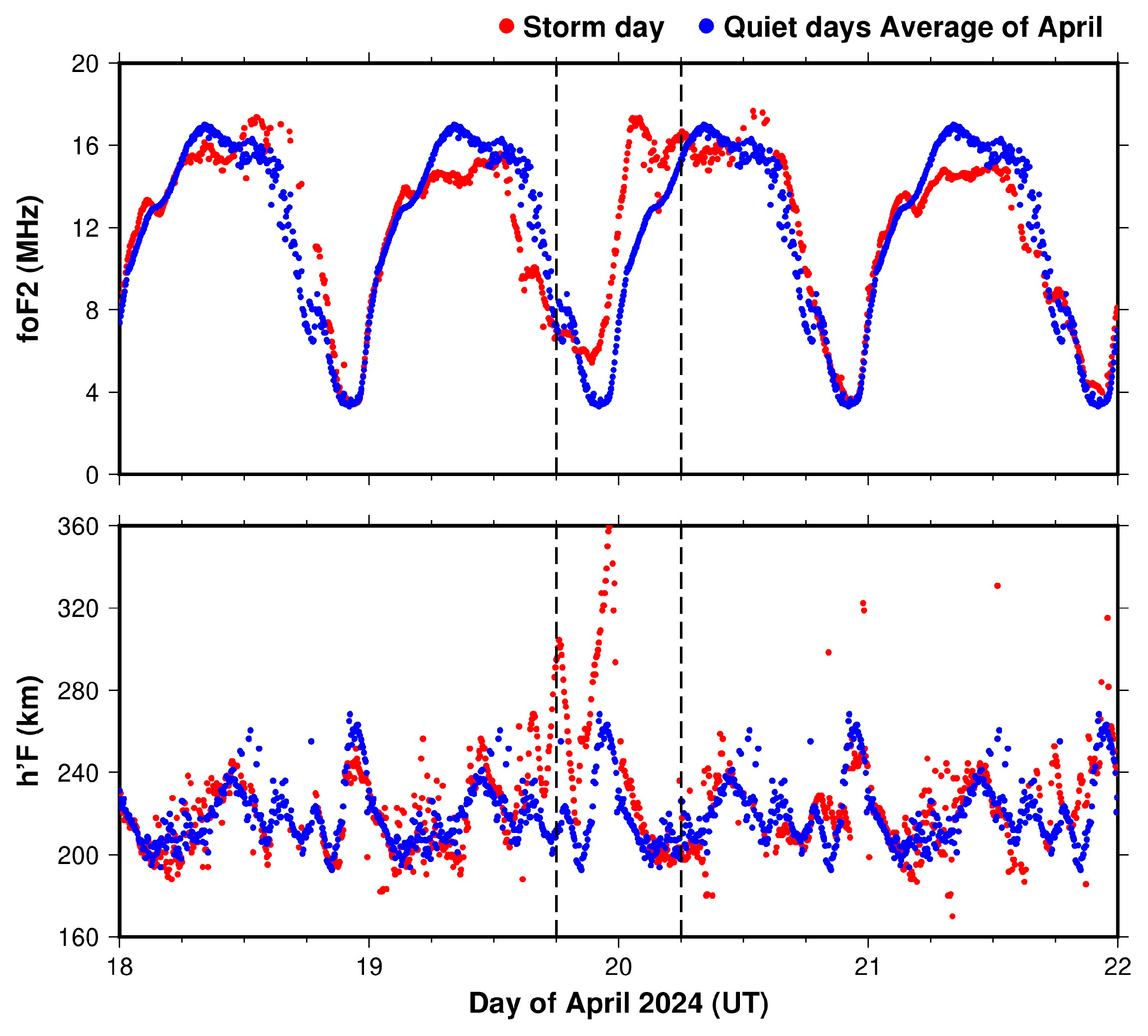
3.2.5. foF2 and h’F Variations at Cocos Island from 18 to 21 April 2024
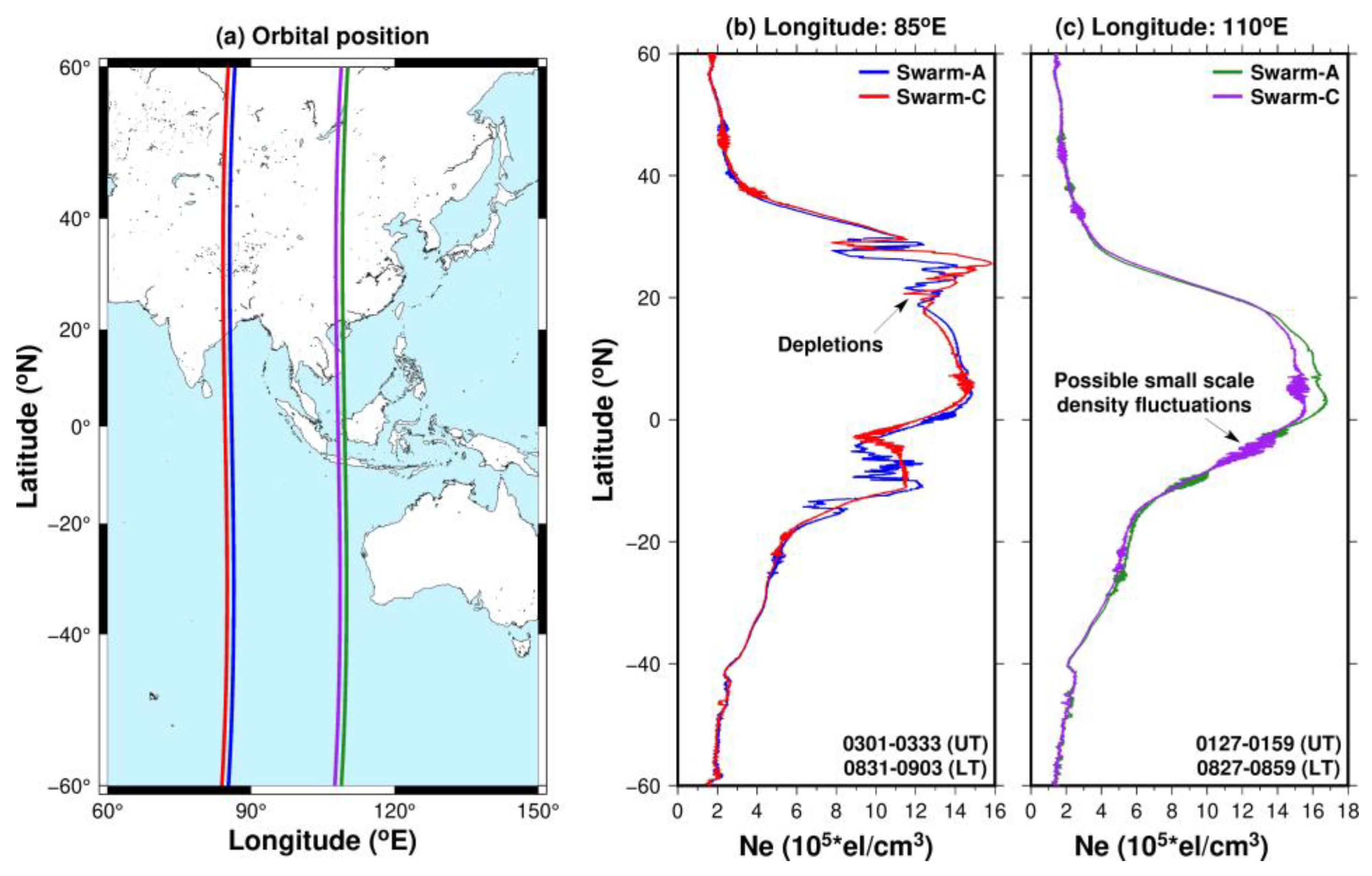
3.2.6. Swarm Satellite-Derived Electron Density Variations at 85°E and 85°E Longitudes on 20 April
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- i.
- Despite the significant southward turning of IMF Bz (Dst minimum: −117 nT) during the main phase of the above-mentioned storm event, there were hardly any significant disturbances in the electric fields observed during the local post-sunset to midnight sector over the whole 70–110°E longitude region.
- ii.
- The formation of EPBs during the near-sunrise period was mainly linked to the northward shift in IMF Bz associated with the rapid penetration of overshielding electric fields during the storm recovery phase.
- iii.
- EPBs were more intense at the geomagnetic southern latitudes compared to the northern latitudes in the 90–110°E longitude region. Additionally, the EPBs that initially developed in the Southeast Asian region drifted toward the Indian longitude region, along with the sunrise terminator.
- iv.
- Further, these near-sunrise EPBs persisted for more than three hours after the sunrise terminator.
- v.
- Additionally, altering electric fields in the dip equatorial region suppressed the formation of dusk-time EPBs during the storm recovery period across the 70–90°E longitude region.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Woodman, R.F.; La Hoz, C. Radar observations of F region equatorial irregularities. J. Geophys. Res. 1976, 81, 5447–5466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, M.C. The Earth’s Ionosphere: Plasma Physics and Electrodynamics; Academic Press: Cambridge, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Abdu, M.A. Outstanding problems in the equatorial ionosphere–thermosphere electrodynamics relevant to spread F. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2012, 63, 869–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, A. Equatorial Plasma Bubbles: A Review. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, A.S.; Nade, D.P.; Taori, A.; Pawar, R.P.; Pawar, S.M.; Nikte, S.S.; Pawar, S.D. A Brief Review of Equatorial Plasma Bubbles. Space Sci. Rev. 2023, 219, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kil, H. The Morphology of Equatorial Plasma Bubbles—A Review. J. Astron. Space Sci. 2015, 32, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.Y.; Burke, W.J.; Machuzak, J.S.; Gentile, L.C.; Sultan, P.J. Equatorial Plasma Bubbles Observed by DMSP Satellites during a Full Solar Cycle: Toward a Global Climatology. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2002, 107, SIA 7-1–SIA 7-10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotulak, K.; Zakharenkova, I.; Krankowski, A.; Cherniak, I.; Wang, N.; Fron, A. Climatology Characteristics of Ionospheric Irregularities Described with GNSS ROTI. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vital, L.F.R.; Takahashi, H.; Barros, D.; Carmo, S.C.; Carrasco, A.J.; Wrasse, C.M.; Figueiredo, C.A.O.B. Seasonal and Solar Cycle Dependency of Relationship Between Equatorial Plasma Bubbles and Rayleigh-Taylor Instability Growth Rate. Space Weather 2024, 22, e2024SW003959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajana, S.S.K.; Panda, S.K.; Jade, S.; Vivek, C.G. Morphology of Equatorial F-Region Irregularities over the Indian Longitude Sector Using GPS-Derived ROTI Observations. Adv. Space Res. 2024, 74, 3361–3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fejer, B.G.; Scherliess, L.; de Paula, E.R. Effects of the Vertical Plasma Drift Velocity on the Generation and Evolution of Equatorial Spread F. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1999, 104, 19859–19869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, L.C.; Burke, W.J.; Roddy, P.A.; Retterer, J.M.; Tsunoda, R.T. Climatology of Plasma Density Depletions Observed by DMSP in the Dawn Sector. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2011, 116, A03321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.S. Occurrence of Equatorial Plasma Bubbles during Intense Magnetic Storms. Int. J. Geophys. 2011, 2011, 401858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherniak, I.; Zakharenkova, I.; Sokolovsky, S. Multi-Instrumental Observation of Storm-Induced Ionospheric Plasma Bubbles at Equatorial and Middle Latitudes. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2019, 124, 1491–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdu, M.A.; Kherani, E.A.; Batista, I.S.; Sobral, J.H.A. Equatorial Evening Prereversal Vertical Drift and Spread F Suppression by Disturbance Penetration Electric Fields. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L19103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Xiong, C.; Wang, H.; Zhang, K.; Zheng, Z.; He, Y.; Yu, L. A Statistical Study on the Climatology of the Equatorial Plasma Depletions Occurrence at Topside Ionosphere During Geomagnetic Disturbed Periods. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2019, 124, 8023–8038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimoh, O.; Lei, J.; Huang, F.; Zhong, J. The Study of Topside Ionospheric Irregularities during Geomagnetic Storms in 2015. J. Space Weather Space Clim. 2022, 12, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, C.; Tsai, L.C.; Su, S.Y.; Galkin, I.A.; Caton, R.G.; Groves, K.M. Suppression of Ionospheric Scintillation during St. Patrick’s Day Geomagnetic Super Storm as Observed over the Anomaly Crest Region Station Pingtung, Taiwan: A Case Study. Adv. Space Res. 2017, 60, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajana, S.S.K.; Panda, S.K.; Jade, S.; Vivek, C.G.; Upadhayaya, A.K.; Bhardwaj, A.; Jorphail, S.; Seemala, G.K. Impact of Two Severe Geomagnetic Storms on the Ionosphere over Indian Longitude Sector during March-April 2023. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2024, 369, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdu, M.A.; Sorral, J.H.A.; Nelson, R.; Bat, I.S. Solar Cycle Related Range Type Spread-F Occurrence Characteristics over Equatorial and Low Latitude Stations in Brazil. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 1985, 47, 901–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, W.J.; Gentile, L.C.; Huang, C.Y.; Valladares, C.E.; Su, S.Y. Longitudinal Variability of Equatorial Plasma Bubbles Observed by DMSP and ROCSAT-1. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2004, 109, A12301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, B.A.; Yizengaw, E.; Pradipta, R.; Retterer, J.M.; Groves, K.; Valladares, C.; Caton, R.; Bridgwood, C.; Norman, R.; Zhang, K. Global Equatorial Plasma Bubble Occurrence during the 2015 St. Patrick’s Day Storm. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2016, 121, 894–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulasi Ram, S.; Yokoyama, T.; Otsuka, Y.; Shiokawa, K.; Sripathi, S.; Veenadhari, B.; Heelis, R.; Ajith, K.K.; Gowtam, V.S.; Gurubaran, S.; et al. Duskside Enhancement of Equatorial Zonal Electric Field Response to Convection Electric Fields during the St. Patrick’s Day Storm on 17 March 2015. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2016, 121, 538–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, K.; Tulasi Ram, S.; Fagundes, P.R.; Seemala, G.K.; Batista, I.S. Electrodynamic Disturbances in the Brazilian Equatorial and Low-Latitude Ionosphere on St. Patrick’s Day Storm of 17 March 2015. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2017, 122, 4553–4570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vankadara, R.K.; Panda, S.K.; Amory-Mazaudier, C.; Fleury, R.; Devananboyina, V.R.; Pant, T.K.; Jamjareegulgarn, P.; Haq, M.A.; Okoh, D.; Seemala, G.K. Signatures of Equatorial Plasma Bubbles and Ionospheric Scintillations from Magnetometer and GNSS Observations in the Indian Longitudes during the Space Weather Events of Early September 2017. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugassa, T.; Habarulema, J.B.; Nigussie, M. Longitudinal Variability of Occurrence of Ionospheric Irregularities over the American, African and Indian Regions during Geomagnetic Storms. Adv. Space Res. 2019, 63, 2609–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulasi Ram, S.; Ajith, K.K.; Yamamoto, M.; Otsuka, Y.; Yokoyama, T.; Niranjan, K.; Gurubaran, S. Fresh and Evolutionary-Type Field-Aligned Irregularities Generated near Sunrise Terminator Due to Overshielding Electric Fields. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2015, 120, 5922–5930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharenkova, I.; Astafyeva, E.; Cherniak, I. Early Morning Irregularities Detected with Spaceborne GPS Measurements in the Topside Ionosphere: A Multisatellite Case Study. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2015, 120, 8817–8834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Xu, J.; Yue, X.; Xiong, C.; Wang, W.; Yuan, W.; Wang, C.; Zhu, Y.; Luo, J. Equatorial Plasma Bubbles Developing around Sunrise Observed by an All-Sky Imager and Global Navigation Satellite System Network during Storm Time. Ann. Geophys. 2020, 38, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Xiong, C.; Xu, J.; Zhu, Z.; Chang, S. The Low-Latitude Plasma Irregularities after Sunrise from Multiple Observations in Both Hemispheres during the Recovery Phase of a Storm. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Li, G.; Lei, J.; Zhao, B.; Hu, L.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Xie, H.; Li, Y.; Ning, B.; et al. Ionospheric Super Bubbles Near Sunset and Sunrise During the 26–28 February 2023 Geomagnetic Storm. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2023, 128, e2023JA031864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmo, C.; Denardini, C.; Figueiredo, C.; Resende, L.; Moro, J.; Silva, R.; Nogueira, P.; Chen, S.; Picanço, G.; Neto, P.B. Findings of the unusual plasma bubble occurrences at dawn during the recovery phase of a moderate geomagnetic storm over the Brazilian sector. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2022, 235, 105908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.Q.; Lei, J.H.; Xiong, C.; Zhong, J.H.; Li, G.Z. Observations of Equatorial Plasma Bubbles during the Geomagnetic Storm of October 2016. Earth Planet. Phys. 2021, 5, 416–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, X.; Mannucci, A.J.; Lindqwister, U.J.; Ho, C.M. Monitoring of Global Ionospheric Irregularities Using the Worldwide GPS Network. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1997, 24, 2283–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S.; Groves, K.M.; Quinn, J.M.; Doherty, P. A Comparison of TEC fluctuations and Scintillations at Ascension Island. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 1999, 61, 1219–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen Thanh, D.; Le Huy, M.; Amory-Mazaudier, C.; Fleury, R.; Saito, S.; Nguyen Chien, T.; Pham Thi Thu, H.; Le Truong, T.; Nguyen Thi, M. Characterization of Ionospheric Irregularities over Vietnam and Adjacent Region for the 2008–2018 Period Characterization of Ionospheric Irregularities over Vietnam and Adjacent Region for the Characterization of Ionospheric Irregularities over Vietnam and Adjacent Region for the 2008-2018 Period. Vietnam J. Earth Sci. 2008, 43, 465–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessel, P.; Luis, J.F.; Uieda, L.; Scharroo, R.; Wobbe, F.; Smith, W.H.F.; Tian, D. The Generic Mapping Tools Version 6. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 2019, 20, 5556–5564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abadi, P.; Muafiry, I.N.; Pratama, T.N.; Putra, A.Y.; Suraina. Database of Ionospheric Rate of TEC Change Index (ROTI) Map Derived from Indonesian GNSS Receiver Network [Data set]. Zenodo 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, A. Coherence of Geomagnetic DP 2 Fluctuations with Interplanetary Magnetic Variations. J. Geophys. Res. 1968, 73, 5549–5559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, T.; Lühr, H.; Kitamura, T.; Saka, O.; Schlegel, K. Direct Penetration of the Polar Electric Field to the Equator during a DP 2 Event as Detected by the Auroral and Equatorial Magnetometer Chains and the EISCAT Radar. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1996, 101, 17161–17173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, M.C.; Fejer, B.G.; Gonzales, C.A. An Explanation for Anomalous Equatorial Ionospheric Electric Fields Associated with a Northward Turning of the Interplanetary Magnetic Field. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1979, 6, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sripathi, S.; Abdu, M.A.; Patra, A.K.; Ghodpage, R.N. Unusual Generation of Localized EPB in the Dawn Sector Triggered by a Moderate Geomagnetic Storm. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2018, 123, 9697–9710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fejer, B.G.; Gonzales, C.A.; Farley, D.T.; Kelley, M.C.; Woodman, R.F. Equatorial electric fields during magnetically disturbed conditions 1. The effect of the interplanetary magnetic field. J. Geophys. Res. 1979, 84, 5797–5802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, R.G.; Patel, V.L. Effect of interplanetary magnetic field on ionosphere over the magnetic equator. Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. 1975, 82, 121–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdu, M.A. Equatorial Spread F/Plasma Bubble Irregularities under Storm Time Disturbance Electric Fields. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2012, 75–76, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
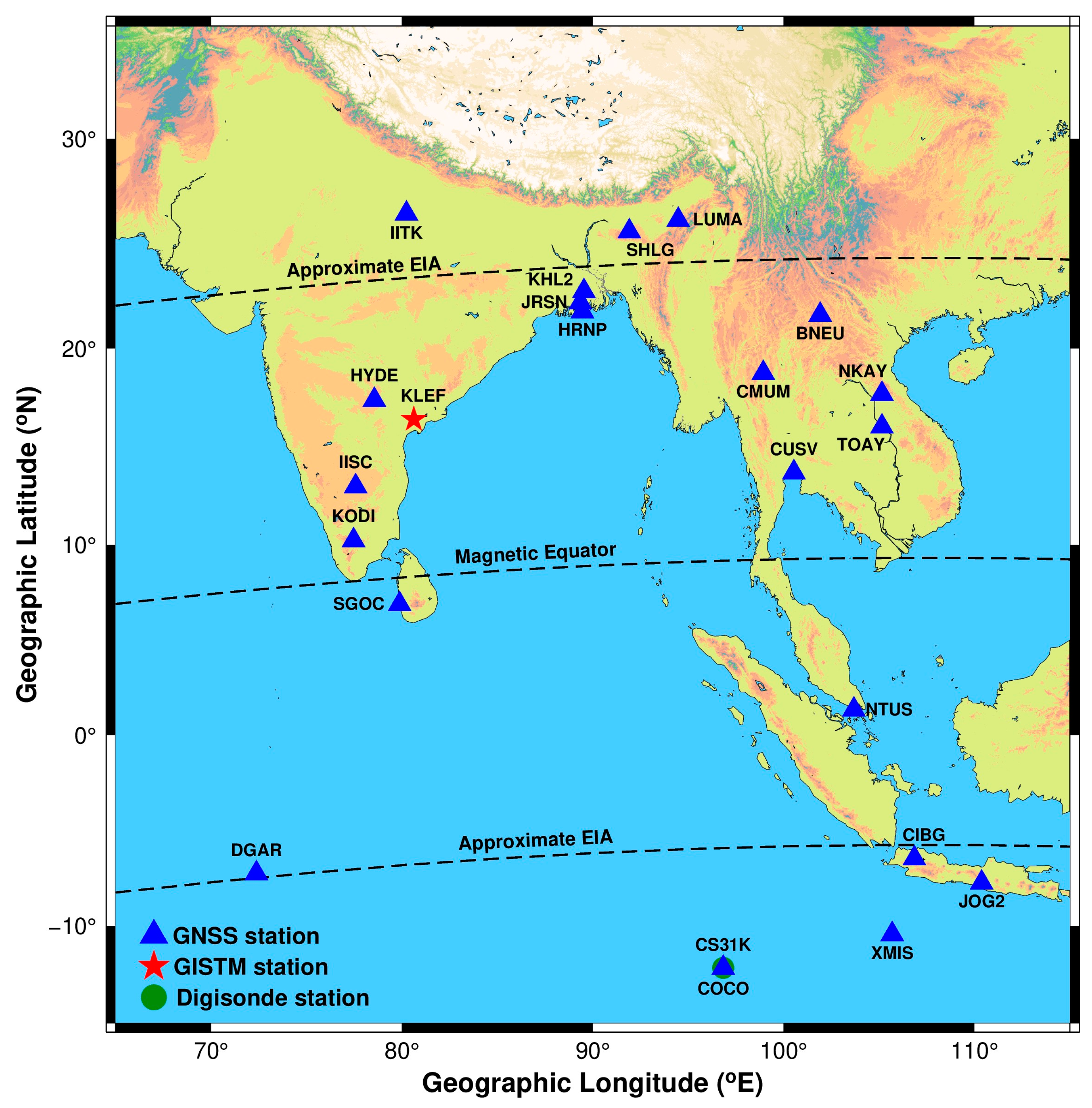


| Station Code | Geographic Latitude (°N) | Geographic Longitude (°E) | Geomagnetic Latitude (°N) | Geomagnetic Longitude (°E) | Observation Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DGAR | 7.27 | 72.37 | −14.77 | 144.07 | GNSS |
| SGOC | 6.89 | 79.87 | −1.38 | 152.73 | GNSS |
| KODI | 10.23 | 77.46 | 2.11 | 150.70 | GNSS |
| IISC | 13.02 | 77.57 | 4.86 | 150.94 | GNSS |
| KLEF | 16.44 | 80.62 | 8.03 | 154.25 | GISTM |
| HYDE | 17.42 | 78.55 | 9.15 | 152.24 | GNSS |
| IITK | 26.52 | 80.23 | 18.06 | 154.65 | GNSS |
| HRNP | 21.82 | 89.46 | 12.85 | 163.06 | GNSS |
| JRSN | 22.25 | 89.35 | 13.29 | 162.98 | GNSS |
| KHL2 | 22.80 | 89.53 | 13.83 | 163.19 | GNSS |
| SHLG | 25.67 | 91.91 | 16.58 | 165.57 | GNSS |
| LUMA | 26.22 | 94.48 | 17.03 | 168.01 | GNSS |
| COCO | −12.18 | 96.83 | −21.20 | 169.07 | GNSS |
| CS31K | −12.18 | 96.83 | −21.20 | 169.07 | Digisonde |
| XMIS | −10.450 | 105.69 | −19.64 | 178.27 | GNSS |
| JOG2 | −7.76 | 110.37 | −16.96 | −176.86 | GNSS |
| CIBG | −6.49 | 106.85 | −15.70 | 179.58 | GNSS |
| NTUS | 1.35 | 103.68 | −7.91 | 171.74 | GNSS |
| CUSV | 13.74 | 100.53 | 4.45 | 173.36 | GNSS |
| TOAY | 16.07 | 105.15 | 6.72 | 177.88 | GNSS |
| NKAY | 17.72 | 105.15 | 8.35 | 178.24 | GNSS |
| CMUM | 18.76 | 98.93 | 9.48 | 171.92 | GNSS |
| BNEU | 21.64 | 101.92 | 12.29 | 174.83 | GNSS |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Panda, S.K.; Rajana, S.S.K.; Vivek, C.G.; Dabbakuti, J.R.K.K.; Jamir, W.; Jamjareegulgarn, P. Multi-Instrument Analysis of Ionospheric Equatorial Plasma Bubbles over the Indian and Southeast Asian Longitudes During the 19–20 April 2024 Geomagnetic Storm. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17061100
Panda SK, Rajana SSK, Vivek CG, Dabbakuti JRKK, Jamir W, Jamjareegulgarn P. Multi-Instrument Analysis of Ionospheric Equatorial Plasma Bubbles over the Indian and Southeast Asian Longitudes During the 19–20 April 2024 Geomagnetic Storm. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(6):1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17061100
Chicago/Turabian StylePanda, Sampad Kumar, Siva Sai Kumar Rajana, Chiranjeevi G. Vivek, Jyothi Ravi Kiran Kumar Dabbakuti, Wangshimenla Jamir, and Punyawi Jamjareegulgarn. 2025. "Multi-Instrument Analysis of Ionospheric Equatorial Plasma Bubbles over the Indian and Southeast Asian Longitudes During the 19–20 April 2024 Geomagnetic Storm" Remote Sensing 17, no. 6: 1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17061100
APA StylePanda, S. K., Rajana, S. S. K., Vivek, C. G., Dabbakuti, J. R. K. K., Jamir, W., & Jamjareegulgarn, P. (2025). Multi-Instrument Analysis of Ionospheric Equatorial Plasma Bubbles over the Indian and Southeast Asian Longitudes During the 19–20 April 2024 Geomagnetic Storm. Remote Sensing, 17(6), 1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17061100









