A Multi-Sensor Machine Learning Framework for Field-Scale Soil Salinity Mapping Under Data-Scarce Conditions
Highlights
- Applying explainable machine learning to both proximal and remote sensing data yields strong insights into the dynamics of soil salinity, especially in data-scarce semi-arid regions.
- When used with PLSR, regression kriging is an effective accuracy booster; however, the choice of the underlying predictive model still has a significant impact on how effective it is.
- Topographic features significantly enhance the prediction power of UAV-derived models and are crucial in soil salinization processes.
- PlanetScope and UAV-derived topographic covariates are highly recommended for timely high-resolution monitoring of soil salinity.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
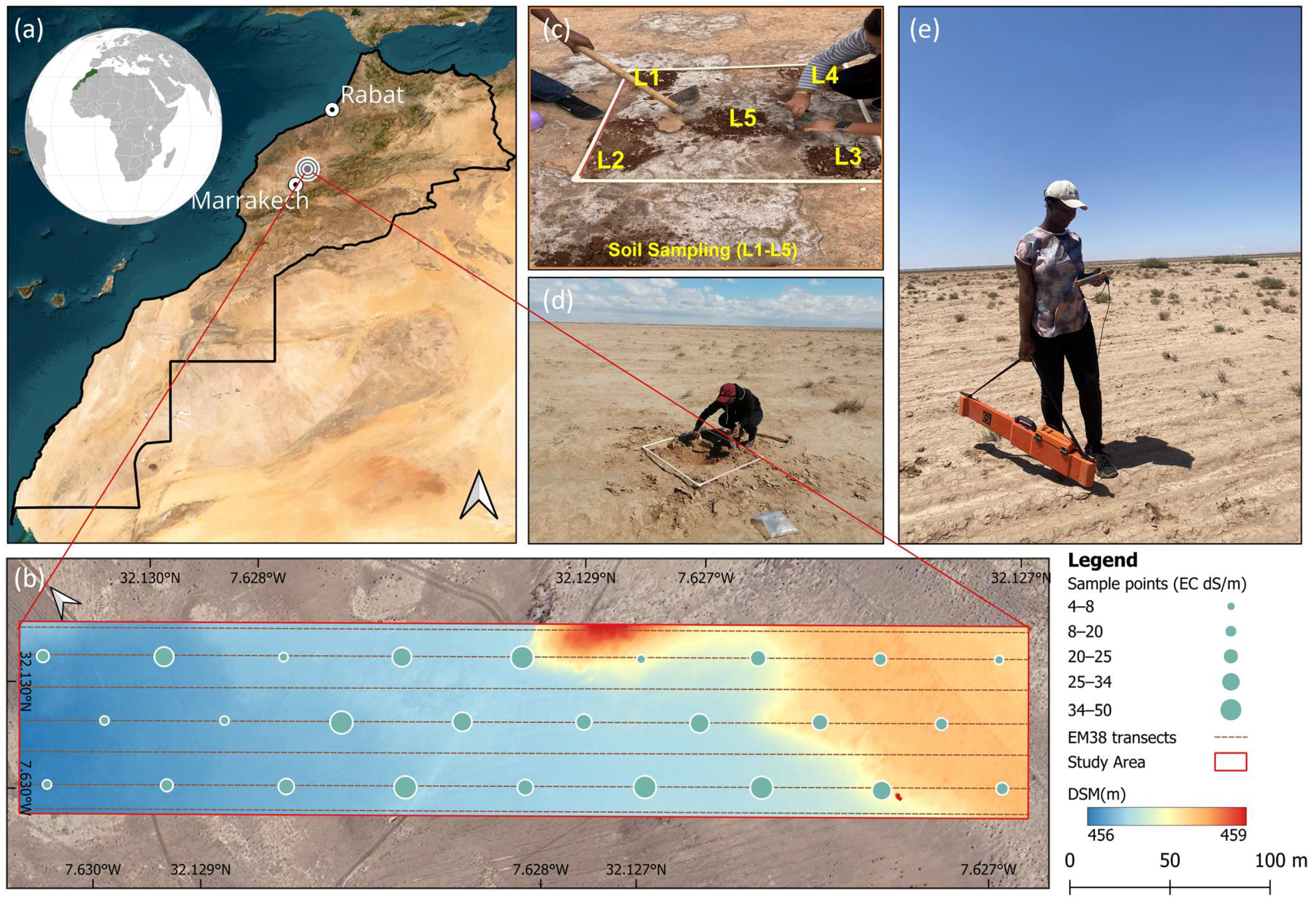
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Field Measurements, Sample Processing and Proximal Data
2.3. Remotely Sensed Data
2.4. Spectral and Topographic Selected Covariates
2.5. Modelling Approaches
2.6. Model Evaluation
2.7. Model Explainability Using SHAP
3. Results
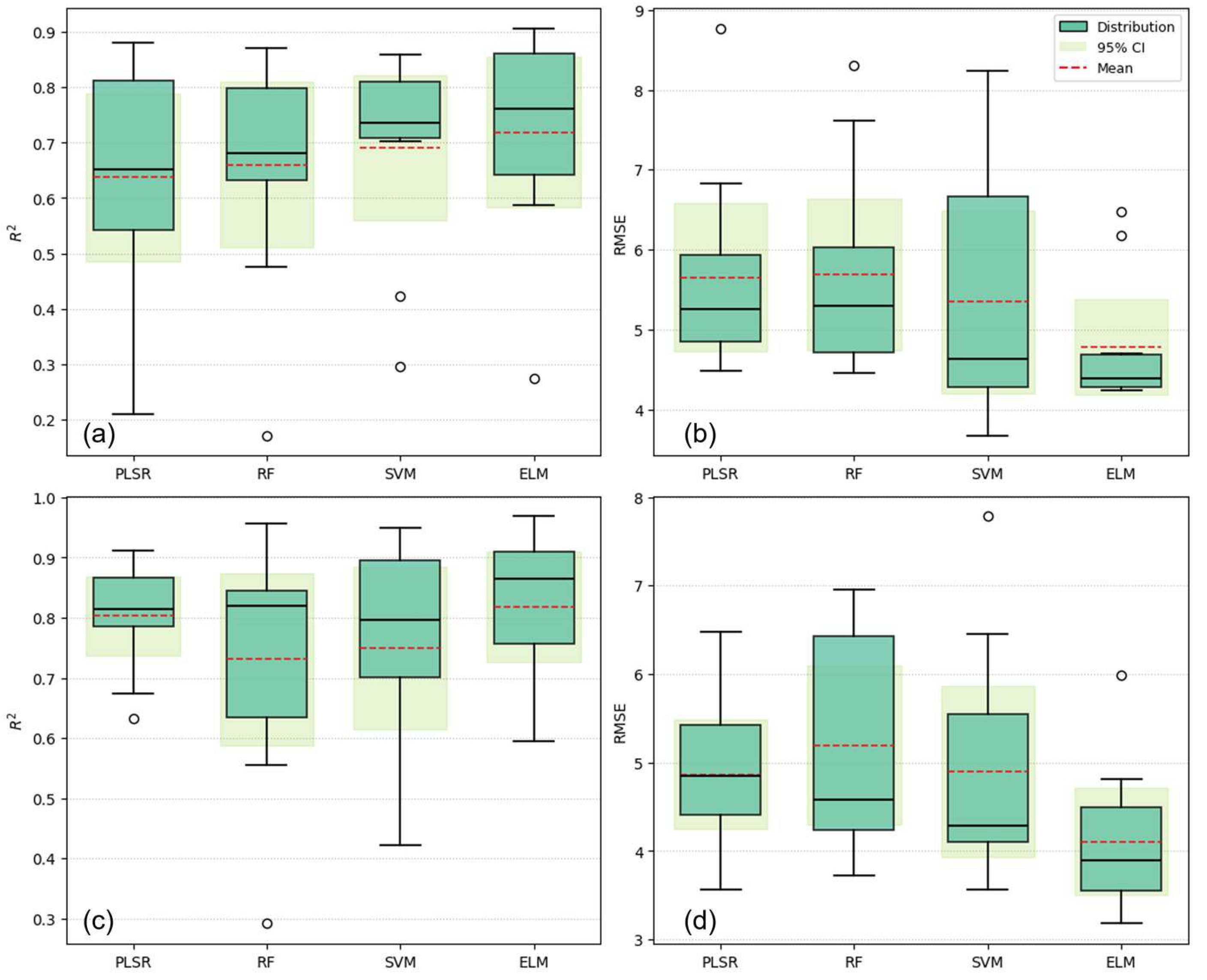
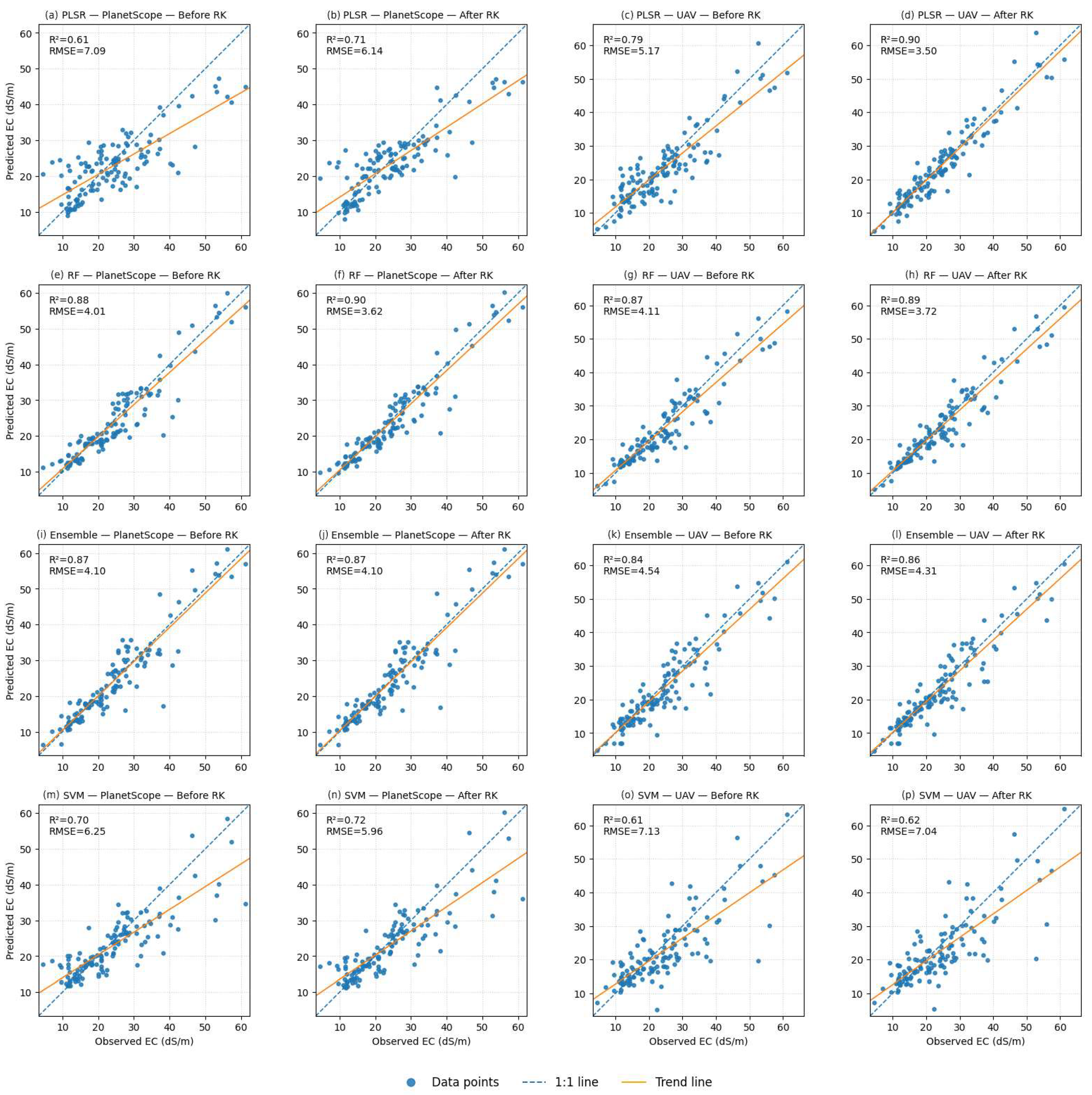
3.1. Model Assessment
3.2. Soil Salinity Mapping
3.3. Results of the SHAP Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Model Performance Hierarchy and Cross-Sensor Stability
4.2. Effects of Regression Kriging on Models
4.3. Topographic Controls, Hydrologic Processes, and Capillarity
4.4. Spectral Behavior and Vegetation Signal
4.5. Sensor-Specific SHAP Patterns and a Tiered Strategy
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. Global Map of Salt-Affected Soils (GSASmap v1.0); Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2021; Available online: https://openknowledge.fao.org/handle/20.500.14283/cb7247en (accessed on 2 June 2025).
- Squires, V.R.; Glenn, E.P. Salination, Desertification and Soil Erosion. In The Role of Food, Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries in Human Nutrition; EOLSS Publications: Oxford, UK, 2011; Volume 3, pp. 102–123. [Google Scholar]
- Prăvălie, R.; Patriche, C.; Borrelli, P.; Panagos, P.; Roșca, B.; Dumitraşcu, M.; Nita, I.A.; Săvulescu, I.; Birsan, M.V.; Bandoc, G. Arable Lands under the Pressure of Multiple Land Degradation Processes. A Global Perspective. Environ. Res. 2021, 194, 110697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oussaoui, S.; Boudhar, A.; Hadri, A.; Lebrini, Y.; Houmma, I.H.; Karaoui, I.; El Khalki, E.M.; Ouzemou, J.; Kinnard, C. Mapping Drought Severity Impact on Arboriculture Systems over Tadla and Lower Tassaout Plains in Morocco Using Sentinel-2 Data and Machine Learning Approaches. Geocarto Int. 2025, 40, 2471104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, S.A.; Zaman, M.; Heng, L. Soil Salinity: Historical Perspectives and a World Overview of the Problem. In Guideline for Salinity Assessment, Mitigation and Adaptation Using Nuclear and Related Techniques; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivushkin, K.; Bartholomeus, H.; Bregt, A.K.; Pulatov, A.; Kempen, B.; de Sousa, L. Global Mapping of Soil Salinity Change. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 231, 111260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Standard Operating Procedure for Soil Electrical Conductivity, Soil/Water, 1:5; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Standard Operating Procedure for Saturated Soil Paste Extract; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Nanni, M.R.; Demattê, J.A.M. Spectral Reflectance Methodology in Comparison to Traditional Soil Analysis. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2006, 70, 393–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corwin, D.L.; Scudiero, E. Review of Soil Salinity Assessment for Agriculture across Multiple Scales Using Proximal and/or Remote Sensors. In Advances in Agronomy; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; Volume 158, pp. 1–130. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Ayoubi, S.; Mousavi, S.R.; Mireei, S.A.; Shahpouri, F.; Wu, S.X.; Chen, C.B.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Tian, C.Y. Integrating Proximal Soil Sensing Data and Environmental Variables to Enhance the Prediction Accuracy for Soil Salinity and Sodicity in a Region of Xinjiang Province, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 364, 121311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Harti, A.; Lhissou, R.; Chokmani, K.; Ouzemou, J.E.; Hassouna, M.; Bachaoui, E.M.; El Ghmari, A. Spatiotemporal Monitoring of Soil Salinization in Irrigated Tadla Plain (Morocco) Using Satellite Spectral Indices. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 50, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allbed, A.; Kumar, L.; Aldakheel, Y.Y. Assessing Soil Salinity Using Soil Salinity and Vegetation Indices Derived from IKONOS High-Spatial Resolution Imageries: Applications in a Date Palm Dominated Region. Geoderma 2014, 230–231, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ali, Z.M.; Bannari, A.; Rhinane, H.; El-Battay, A.; Shahid, S.A.; Hameid, N. Remote Sensing Validation and Comparison of Physical Models for Soil Salinity Mapping over an Arid Landscape Using Spectral Reflectance Measurements and Landsat-OLI Data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scudiero, E.; Skaggs, T.H.; Corwin, D.L. Regional Scale Soil Salinity Evaluation Using Landsat 7, Western San Joaquin Valley, California, USA. Geoderma Reg. 2014, 2–3, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Deng, M.; Tang, M.; Liu, R.; Feng, S.; Zhang, C.; Zheng, Z. Estimating Soil Profile Salinity under Vegetation Cover Based on UAV Multi-Source Remote Sensing. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Peng, J.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, D.; Zhao, R.; Jiang, Q.; Fu, T.; Wang, F.; Shi, Z. Quantitative Estimation of Soil Salinity Using UAV-Borne Hyperspectral and Satellite Multispectral Images. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naimi, S.; Ayoubi, S.; Zeraatpisheh, M.; Dematte, J.A.M. Ground Observations and Environmental Covariates Integration for Mapping of Soil Salinity: A Machine Learning-Based Approach. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Sun, J. Estimation of Soil Salinity Using Satellite-Based Variables and Machine Learning Methods. Earth Sci. Inform. 2024, 17, 5049–5061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Peng, J.; Li, H.; Yin, C.; Liu, W.; Wang, T.; Zhang, H. Soil Salinity Mapping Using Machine Learning Algorithms with the Sentinel-2 MSI in Arid Areas, China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Shi, Z.; Biswas, A.; Yang, S.; Ding, J. Multi-Algorithm Comparison for Predicting Soil Salinity. Geoderma 2020, 365, 114211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hengl, T.; Heuvelink, G.B.M.; Stein, A. A Generic Framework for Spatial Prediction of Soil Variables Based on Regression-Kriging. Geoderma 2004, 120, 75–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Xue, J.; Peng, J.; Biswas, A.; He, Y.; Shi, Z. Integrating Remote Sensing and Landscape Characteristics to Estimate Soil Salinity Using Machine Learning Methods: A Case Study from Southern Xinjiang, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 4118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarei, A.; Hasanlou, M.; Mahdianpari, M. A comparison of machine learning models for soil salinity estimation using multi-spectral earth observation data. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2021, V-3–2021, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, G.; Gašparović, M.; Alqasemi, A.S.; Aldhaheri, A.; Abuelgasim, A.; Ibrahim, M. Soil Salinity Prediction Using Machine Learning and Sentinel—2 Remote Sensing Data in Hyper–Arid Areas. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2023, 130, 103400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouzemou, J.E.; Laamrani, A.; El Battay, A.; Whalen, J.K. Predicting Soil Salinity Based on Soil/Water Extracts in a Semi-Arid Region of Morocco. Soil Syst. 2025, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mokhtar, M.; Fakir, Y.; El Mandour, A.; Benavente, J.; Meyer, H.; Stigter, T. Salinisation Des Eaux Souterraines Aux Alentours Des Sebkhas de Sad Al Majnoun et Zima (Plaine de La Bahira, Maroc). Sci. Chang. Planétaires/Sécheresse 2012, 23, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Azhari, A.; Ait Brahim, Y.; Barbecot, F.; Hssaisoune, M.; Berrouch, H.; Laamrani, A.; Hadri, A.; Brouziyne, Y.; Bouchaou, L. Evaluating Groundwater Salinity Patterns and Spatiotemporal Dynamics in Complex Endorheic Aquifer Systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 994, 180055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El hasini, S.; Iben Halima, O.; El Azzouzi, M.; Douaik, A.; Azim, K.; Zouahri, A. Organic and Inorganic Remediation of Soils Affected by Salinity in the Sebkha of Sed El Mesjoune—Marrakech (Morocco). Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 193, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metternicht, G.I.; Zinck, J.A. Remote Sensing of Soil Salinity: Potentials and Constraints. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 85, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silatsa, F.B.T.; Kebede, F. A Quarter Century Experience in Soil Salinity Mapping and Its Contribution to Sustainable Soil Management and Food Security in Morocco. Geoderma Reg. 2023, 34, e00695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Ge, H.; Xu, Y.; Zhuang, L.; Wang, F.; Gu, Q.; Li, X. Estimating Soil Salinity Using Multiple Spectral Indexes and Machine Learning Algorithm in Songnen Plain, China. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2023, 16, 7041–7050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouse, J.W., Jr.; Haas, R.H.; Schell, J.A.; Deering, D.W.; Harlan, J.C. Monitoring the Vernal Advancement and Retrogradation (Green Wave Effect) of Natural Vegetation. Progress Report RSC 1978-1, Remote Sensing Center, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX, USA; Prepared for: NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD, November 1974. Available online: https://ntrs.nasa.gov/api/citations/19750020419/downloads/19750020419.pdf (accessed on 23 December 2024).
- Wu, W. The Generalized Difference Vegetation Index (GDVI) for Dryland Characterization. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 1211–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huete, A.R. A Soil-Adjusted Vegetation Index (SAVI). Remote Sens. Environ. 1988, 25, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Chehbouni, A.; Huete, A.R.; Kerr, Y.H.; Sorooshian, S. A Modified Soil Adjusted Vegetation Index. Remote Sens. Environ. 1994, 48, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henrich, V.; Götze, C.; Jung, A.; Sandow, C.; Thürkow, D.; Glaesser, C. Development of an Online Indices Database: Motivation, Concept and Implementation. In Proceedings of the 6th EARSeL Imaging Spectroscopy SIG Workshop: Innovative Tool for Scientific and Commercial Environment Applications, Tel Aviv, Israel, 16–19 March 2009. [Google Scholar]
- McFeeters, S.K. The Use of the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) in the Delineation of Open Water Features. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.M.; Rastoskuev, V.V.; Shalina, E.V.; Sato, Y. Mapping Salt-Affected Soils Using Remote Sensing Indicators—A Simple Approach with the Use of GIS IDRISI. In Proceedings of the 22nd Asian Conference on Remote Sensing, 5–9 November 2001; National University of Singapore: Singapore, 2001; pp. 25–29. [Google Scholar]
- Douaoui, A.E.K.; Nicolas, H.; Walter, C. Detecting Salinity Hazards within a Semiarid Context by Means of Combining Soil and Remote-Sensing Data. Geoderma 2006, 134, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, R.S. Alkali Land Reclamation: A Boom for Development; Mittal Publications: New Delhi, India, 2009; 305p, ISBN 978-8183242905. [Google Scholar]
- Boettinger, J.L.; Ramsey, R.D.; Bodily, J.M.; Cole, N.J.; Kienast-Brown, S.; Nield, S.J.; Saunders, A.M.; Stum, A.K. Landsat Spectral Data for Digital Soil Mapping. In Digital Soil Mapping with Limited Data; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.; Khan, S. Using Remote Sensing Techniques for Appraisal of Irrigated Soil Salinity. In Proceedings of the Event International Congress on Modelling and Simulation (MODSIM), Christchurch, New Zealand, 10–13 December 2007; pp. 2632–2638. [Google Scholar]
- Alhammadi, M.S.; Glenn, E.P. Detecting Date Palm Trees Health and Vegetation Greenness Change on the Eastern Coast of the United Arab Emirates Using SAVI. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 1745–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, A.; Kumar, N.; Sinha, N.K.; Kumar, J. Identification of Salt-Affected Soils Using Remote Sensing Data through Random Forest Technique: A Case Study from India. Arab. J. Geosci. 2022, 15, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, O.; Bechtel, B.; Bock, M.; Dietrich, H.; Fischer, E.; Gerlitz, L.; Wehberg, J.; Wichmann, V.; Böhner, J. System for Automated Geoscientific Analyses (SAGA) v. 2.1.4. Geosci. Model Dev. 2015, 8, 1991–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van’T Veen, K.M.; Ferré, T.P.A.; Iversen, B.V.; Børgesen, C.D. Using Machine Learning to Predict Optimal Electromagnetic Induction Instrument Configurations for Characterizing the Shallow Subsurface. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 26, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolpert, D.H. Stacked Generalization. Neural Netw. 1992, 5, 241–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Heap, A.D.; Potter, A.; Daniell, J.J. Application of Machine Learning Methods to Spatial Interpolation of Environmental Variables. Environ. Model. Softw. 2011, 26, 1647–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, S.M.; Lee, S.I. A Unified Approach to Interpreting Model Predictions. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 30 (NIPS 2017), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 4766–4775. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, J.; Shi, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhong, Z.; He, S.; Wang, X. Soil Salinization Prediction through Feature Selection and Machine Learning at the Irrigation District Scale. Front. Earth Sci. 2024, 12, 1488504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghizadeh-Mehrjardi, R.; Schmidt, K.; Toomanian, N.; Heung, B.; Behrens, T.; Mosavi, A.; Band, S.S.; Amirian-Chakan, A.; Fathabadi, A.; Scholten, T. Improving the Spatial Prediction of Soil Salinity in Arid Regions Using Wavelet Transformation and Support Vector Regression Models. Geoderma 2021, 383, 114793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, T.; Shao, Y.; Ju, Z. Comparing Machine Learning Algorithms for Soil Salinity Mapping Using Topographic Factors and Sentinel-1/2 Data: A Case Study in the Yellow River Delta of China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ul Haq, Y.; Shahbaz, M.; Asif, H.M.S.; Al-Laith, A.; Alsabban, W.H. Spatial Mapping of Soil Salinity Using Machine Learning and Remote Sensing in Kot Addu, Pakistan. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ding, J.; Tan, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, T.; Cai, W.; Meng, S. UAV Hyperspectral Analysis of Secondary Salinization in Arid Oasis Cotton Fields: Effects of FOD Feature Selection and SOA-RF. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1358965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandak, S.; Movahedi-Naeini, S.A.; Mehri, S.; Lotfata, A. A Longitudinal Analysis of Soil Salinity Changes Using Remotely Sensed Imageries. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 10383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Ding, J.; Han, L.; Ge, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, R.; Qin, S.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y. Exploring PlanetScope Satellite Capabilities for Soil Salinity Estimation and Mapping in Arid Regions Oases. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goovaerts, P. Geostatistics for Natural Resources Evaluation by Pierre Goovaerts. Math. Geol. 1999, 31, 349–350. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, S.; Bian, J.; Zhou, Y. Estimating the Spatial Distribution of Soil Salinity with Geographically Weighted Regression Kriging and Its Relationship to Groundwater in the Western Jilin Irrigation Area, Northeast China. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2020, 30, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahbeni, G. A PLSR Model to Predict Soil Salinity Using Sentinel-2 MSI Data. Open Geosci. 2021, 13, 977–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medhat Saleh, A.; Abd-Elwahed, M.; Metwally, Y.; Arafat, S. Capabilities of hyperspectral remote sensing data to detect soil salinity. Arab. Univ. J. Agric. Sci. 2021, 29, 943–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, J.; Wang, N.; Hu, B.; Han, J.; Feng, C.; Peng, J.; Luo, D.; Shi, Z. Estimation of Soil Salinity by Combining Spectral and Texture Information from UAV Multispectral Images in the Tarim River Basin, China. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.P.; Gallant, J.C. Terrain Analysis: Principles and Applications; Wilson, J.P., Gallant, J.C., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2000; 520p. [Google Scholar]
- Beven, K.J.; Kirkby, M.J. A Physically Based, Variable Contributing Area Model of Basin Hydrology. Hydrol. Sci. Bull. 1979, 24, 43–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarboton, D.G. A New Method for the Determination of Flow Directions and Upslope Areas in Grid Digital Elevation Models. Water Resour. Res. 1997, 33, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawar, S.; Buddenbaum, H.; Hill, J. Estimation of Soil Salinity Using Three Quantitative Methods Based on Visible and Near-Infrared Reflectance Spectroscopy: A Case Study from Egypt. Arab. J. Geosci. 2015, 8, 5127–5140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzeri, G.; Milewski, R.; Foerster, S.; Moretti, S.; Chabrillat, S. Early Detection of Soil Salinization by Means of Spaceborne Hyperspectral Imagery. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farifteh, J.; Van der Meer, F.; Atzberger, C.; Carranza, E.J.M. Quantitative Analysis of Salt-Affected Soil Reflectance Spectra: A Comparison of Two Adaptive Methods (PLSR and ANN). Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 110, 59–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization). Salt-Affected Soils and Their Management; Bulletin 39 FAO; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1988; 148p. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, X.; Ding, J.; Teng, D.; Xie, B.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Han, L.; Bao, Q.; Wang, J. Exploring the Capability of Gaofen-5 Hyperspectral Data for Assessing Soil Salinity Risks. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 112, 102969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, P.; Zhang, J.; He, W.; Yuan, D.; Hu, Y.; Zamanian, K.; Jia, K.; Zhao, X. Inversion of Different Cultivated Soil Types’ Salinity Using Hyperspectral Data and Machine Learning. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, M.; Wang, S.; Li, K.; Li, Y. Improving Estimates of Soil Salt Content by Using Two-Date Image Spectral Changes in Yinbei, China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, T.; Schmidt, K.; Viscarra Rossel, R.A.; Gries, P.; Scholten, T.; MacMillan, R.A. Spatial Modelling with Euclidean Distance Fields and Machine Learning. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2018, 69, 757–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
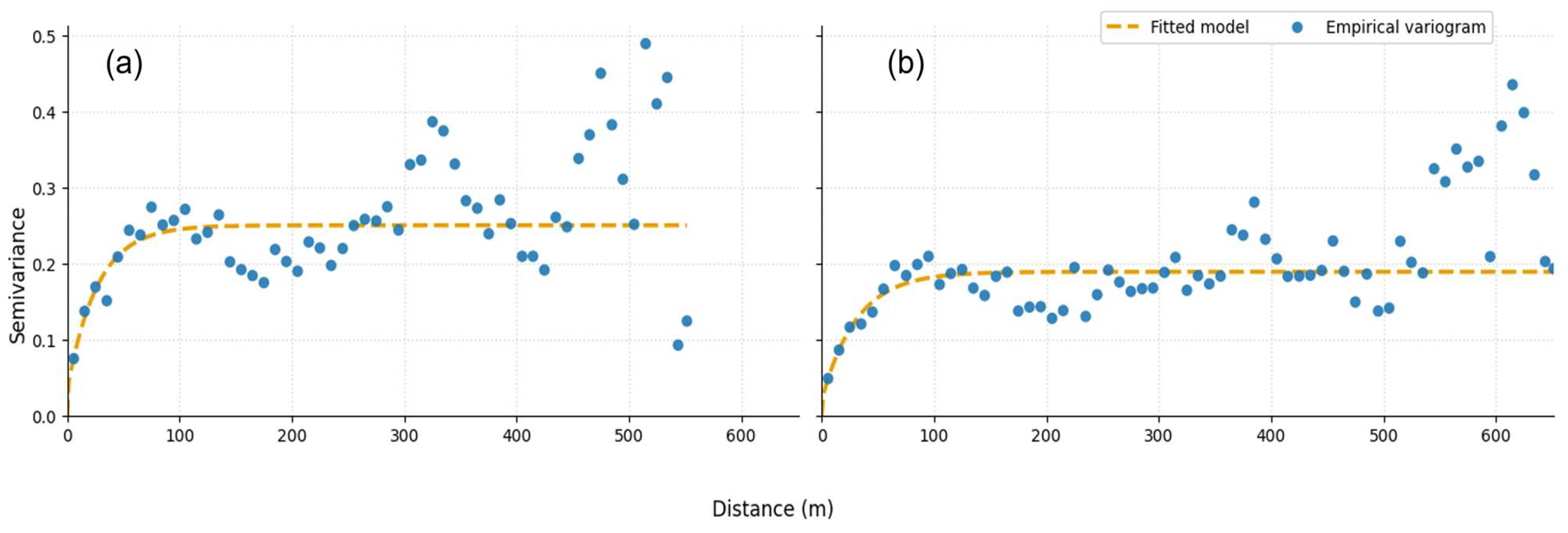
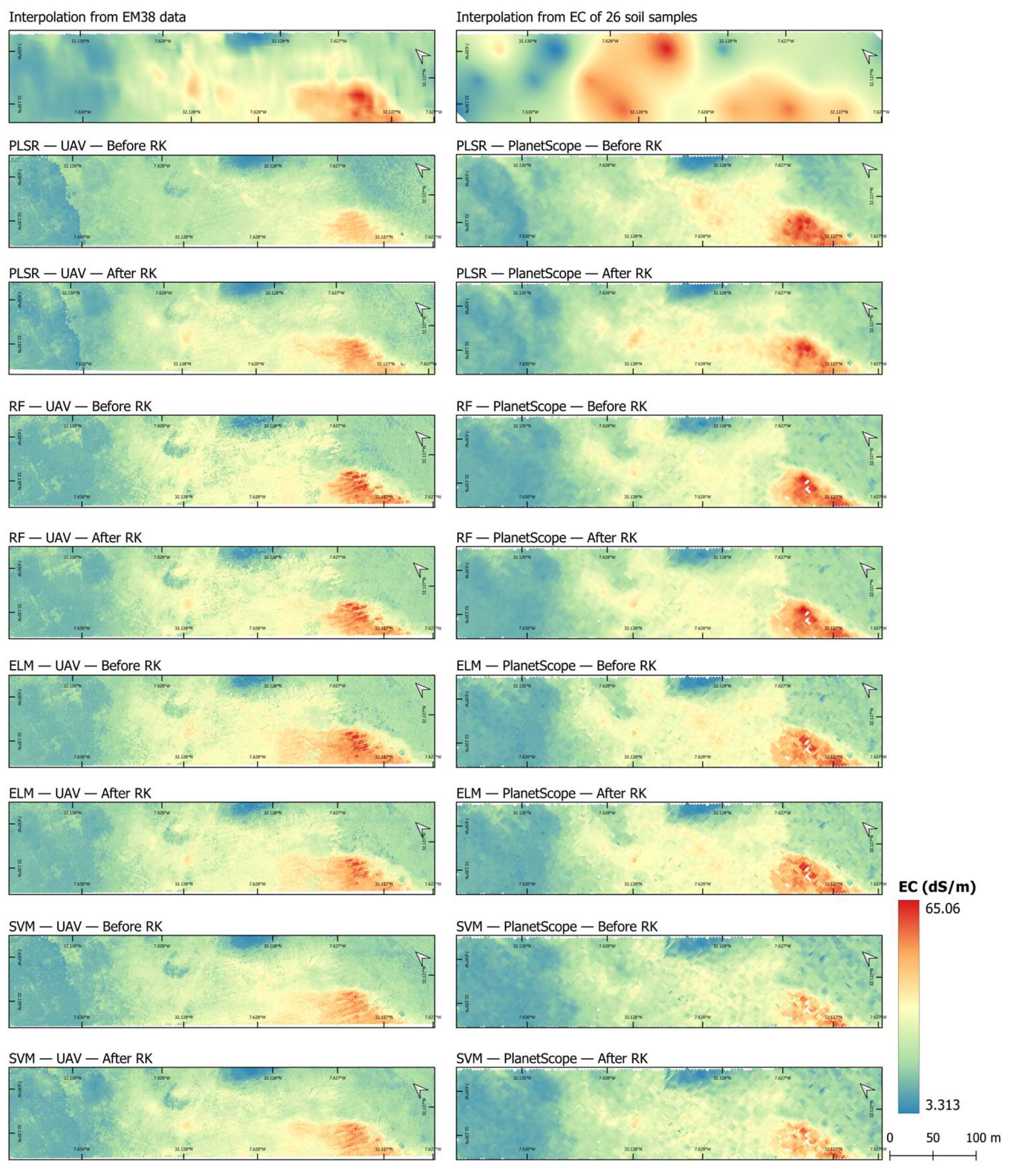
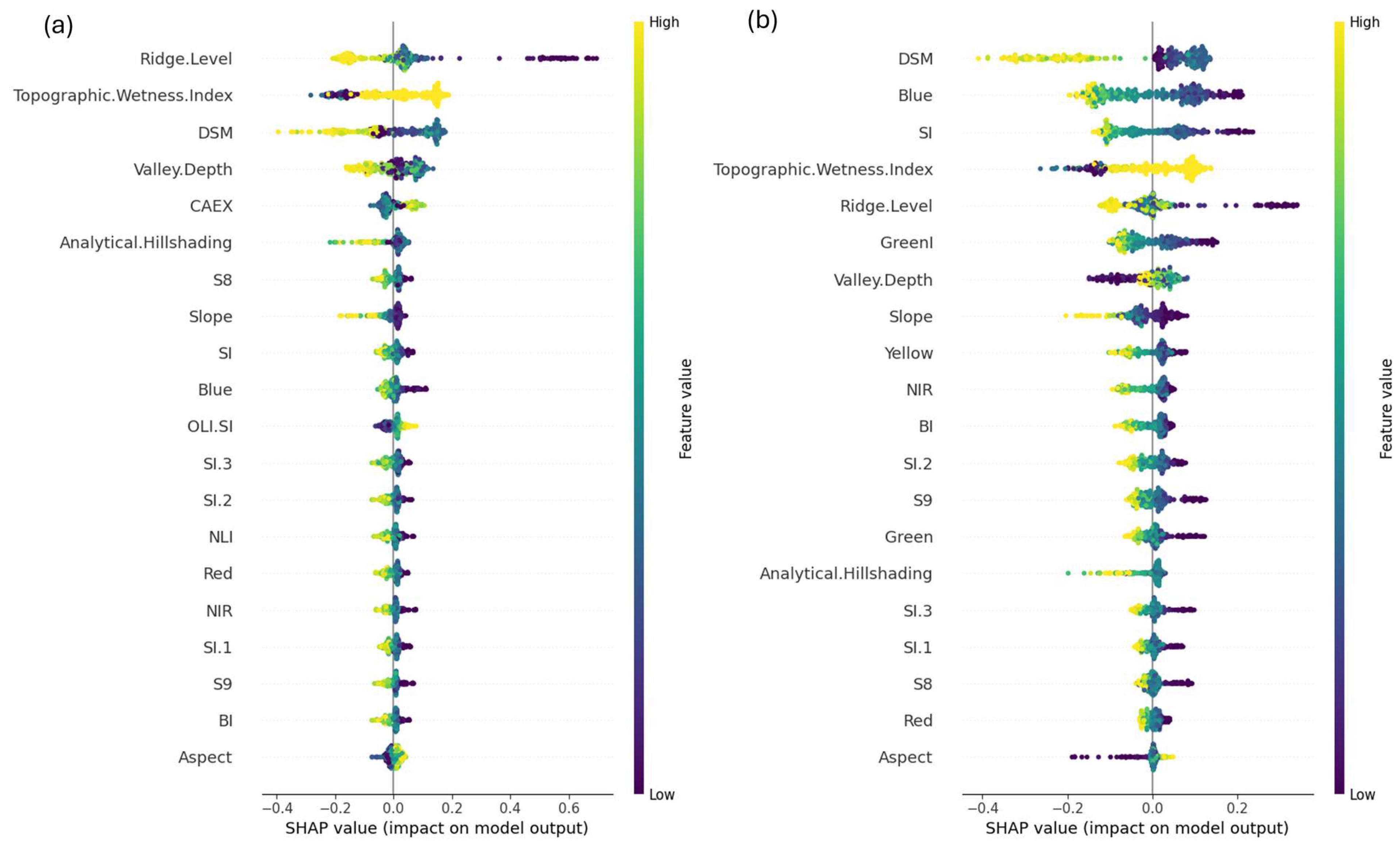
| Sensor | PlanetScope SuperDove | RedEdge-P | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spectral bands | Band Name | Wavelength * (nm) | Bandwidth (nm) | Wavelength * (nm) | Bandwidth (nm) |
| Coastal Blue | 443 | 20 | -- | -- | |
| Blue | 490 | 50 | 475 | 32 | |
| Green I | 531 | 36 | -- | -- | |
| Green | 565 | 36 | 560 | 27 | |
| Yellow | 610 | 20 | -- | -- | |
| Red | 665 | 31 | 668 | 16 | |
| Red Edge | 705 | 15 | 717 | 12 | |
| NIR | 865 | 40 | 842 | 57 | |
| Spatial resolution | 3 m | ~2 cm (altitude dependent) | |||
| Temporal resolution | Near daily revisit | -- | |||
| Category | Covariates | References |
|---|---|---|
| Vegetation Indices | [33] | |
| [34] | ||
| [35] | ||
| [36] | ||
| [37] | ||
| Water Index | [38] | |
| Salinity/Soil-related indices | [39] | |
| [40] | ||
| [41] | ||
| [15] | ||
| [42] | ||
| [12] | ||
| [43] | ||
| SRSI = | [44] | |
| [45] | ||
| Topographic Attributes | Analytical Hillshading | [46] |
| Aspect | ||
| Convergence Index | ||
| Flow Accumulation | ||
| Longitudinal Curvature | ||
| Profile Curvature | ||
| Ridge Level | ||
| Slope | ||
| Tangential Curvature | ||
| Topographic Wetness Index (TWI) | ||
| Valley Depth |
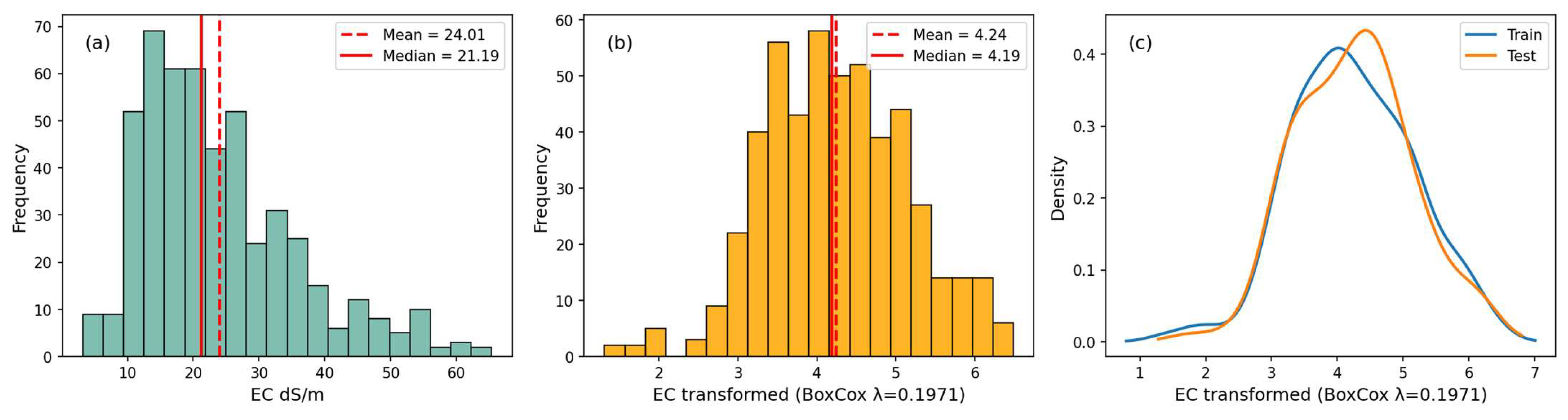
| Value | EC (26 Tested Samples) | EC (500 Calibrated Samples) | EC (BoxCox, λ = 0.1971) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Min | 4.47 | 3.206719 | 1.309918 |
| Max | 49.99 | 65.36646 | 6.4907 |
| Mean | 24.087 | 24.02738 | 4.238627 |
| Median | 24.082 | 20.996781 | 4.171470 |
| SD | 13.281 | 11.97944 | 0.925357 |
| Skewness | 0.163 | 0.98413 | −0.02564 |
| PLSR | RF | SVR | ELM | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PlanetScope | 10-fold spatial CV | R2 | 0.79 | 0.73 | 0.75 | 0.82 |
| RMSE | 5.00 | 5.18 | 4.9 | 4.11 | ||
| Test before RK | R2 | 0.81 | 0.88 | 0.83 | 0.89 | |
| RMSE | 4.98 | 3.99 | 4.64 | 3.84 | ||
| Test after RK | R2 | 0.9 | 0.91 | 0.87 | 0.90 | |
| RMSE | 3.54 | 3.46 | 4.13 | 3.56 | ||
| % Improvement | %↑ R2 | 11.11% | 3.41% | 4.82% | 1.12% | |
| %↓ RMSE | 28.91% | 13.29% | 10.99% | 7.29% | ||
| UAV | 10-fold spatial CV | R2 | 0.64 | 0.66 | 0.69 | 0.78 |
| RMSE | 5.65 | 5.68 | 5.35 | 4.65 | ||
| Test before RK | R2 | 0.79 | 0.83 | 0.76 | 0.85 | |
| RMSE | 5.16 | 4.68 | 5.51 | 4.42 | ||
| Test after RK | R2 | 0.91 | 0.87 | 0.81 | 0.86 | |
| RMSE | 3.43 | 4.13 | 4.93 | 4.27 | ||
| % Improvement | %↑ R2 | 15.19% | 4.82% | 6.58% | 1.18% | |
| %↓ RMSE | 33.53% | 11.75% | 10.53% | 3.39% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chindong, J.M.; Ouzemou, J.-E.; Laamrani, A.; El Battay, A.; Hajaj, S.; Rhinane, H.; Chehbouni, A. A Multi-Sensor Machine Learning Framework for Field-Scale Soil Salinity Mapping Under Data-Scarce Conditions. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 3778. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17223778
Chindong JM, Ouzemou J-E, Laamrani A, El Battay A, Hajaj S, Rhinane H, Chehbouni A. A Multi-Sensor Machine Learning Framework for Field-Scale Soil Salinity Mapping Under Data-Scarce Conditions. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(22):3778. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17223778
Chicago/Turabian StyleChindong, Joyce Mongai, Jamal-Eddine Ouzemou, Ahmed Laamrani, Ali El Battay, Soufiane Hajaj, Hassan Rhinane, and Abdelghani Chehbouni. 2025. "A Multi-Sensor Machine Learning Framework for Field-Scale Soil Salinity Mapping Under Data-Scarce Conditions" Remote Sensing 17, no. 22: 3778. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17223778
APA StyleChindong, J. M., Ouzemou, J.-E., Laamrani, A., El Battay, A., Hajaj, S., Rhinane, H., & Chehbouni, A. (2025). A Multi-Sensor Machine Learning Framework for Field-Scale Soil Salinity Mapping Under Data-Scarce Conditions. Remote Sensing, 17(22), 3778. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17223778






