MRLF: Multi-Resolution Layered Fusion Network for Optical and SAR Images
Highlights
- The MRLF model outperforms state-of-the-art methods like DenseFuse, SwinFusion, and others on both the Dongying and Xi’an datasets. Quantitatively, it achieves an information entropy (EN) of 6.72 and a structural similarity (SSIM) of 0.63 on the Dongying dataset, indicating enhanced information richness and structural preservation. On the Xi’an dataset, it excels in spatial frequency (SF = 24.10) and gradient similarity (GS = 0.862), highlighting its ability to retain fine details and textures in complex urban scenes.
- The model’s hierarchical fusion mechanism, incorporating multi-resolution decomposition and dual-attention modules, successfully addresses cross-modal radiometric discrepancies and multi-scale mismatches. Ablation experiments confirm that modules like the Complementary Feature Extraction Model (CFEM) and brightness distribution alignment reduce artifacts, with the fusion strategy yielding stable results even on large-pixel data, as shown in quantitative metrics like PSNR and FSIM.
- By integrating optical and SAR images with high radiometric consistency, MRLF provides a robust scheme for continuous environmental monitoring. This is crucial for scenarios like disaster assessment and urban planning, where weather-independent data fusion ensures reliable information extraction under varying conditions, as noted in the document’s emphasis on “all-weather remote sensing monitoring”.
- The model’s ability to preserve complementary features supports downstream applications such as semantic segmentation and target recognition. The document highlights that future work will leverage this fusion technology to improve higher-level tasks, enabling more accurate analysis in fields like agricultural monitoring and resource management.
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A Multi-Resolution Layered Fusion Network (MRLF) is proposed for optical and SAR image fusion. Its multi-resolution module decomposes input features into distinct levels to capture details and semantic information, while intensity and gradient terms ensure controllable fusion across resolutions.
- To coordinate multi-scale mismatches between global structures and local details, spatial and channel attention mechanisms are applied between features at different resolutions, along with designed generation mechanisms for spatial attention tensors and channel attention vectors, enhancing feature interaction under varying resolutions.
- A contrast analysis method is proposed to address brightness discontinuities caused by radiometric inconsistency. By quantifying differences in brightness distribution and feature correlation between SAR images and fused results, this method reduces brightness discontinuity and strengthens the expression of key SAR information during fusion.
- Experimental validation uses public datasets (Dongying and Xi’an) with large-pixel optical and SAR image pairs to comprehensively evaluate the model’s advantages and effectiveness in practical applications. Results demonstrate strong robustness and accuracy in fusing large-pixel image data.
2. Related Works
2.1. Deep Learning-Based Image Fusion Framework
2.2. Style Features and Feature Correlation
3. Our Proposed Method
3.1. Overall Architecture
3.2. Decomposition and Reconstruction at Multiple Resolution Scales
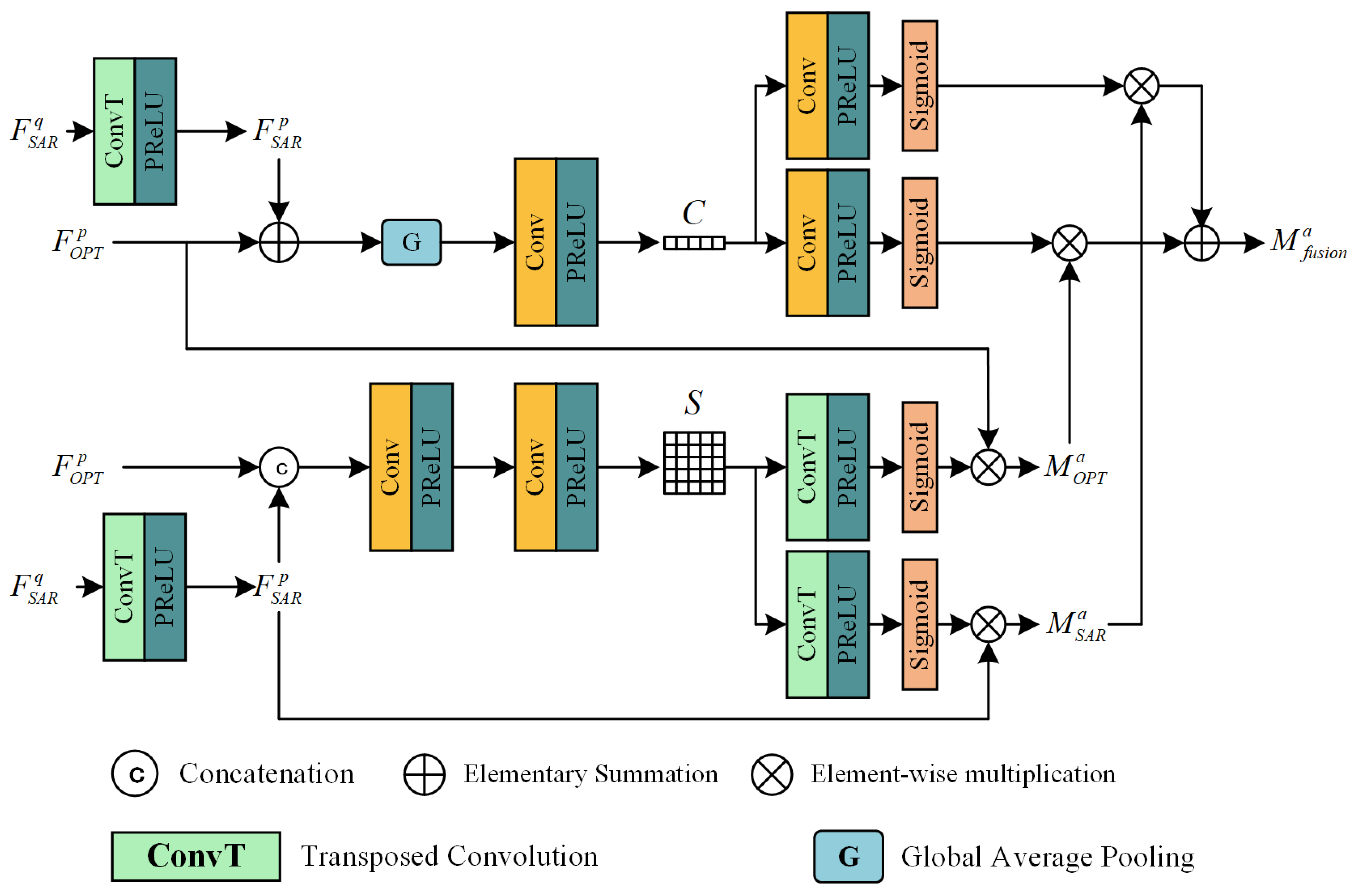
3.3. Multi-Resolution Feature Fusion Module
3.4. Complementary Feature Extraction Model (CFEM) and Radiometric Consistency Enhancement
3.5. Loss Function
4. Implementation
4.1. Preparation for Implementation
4.1.1. Data Description
4.1.2. Training Parameters
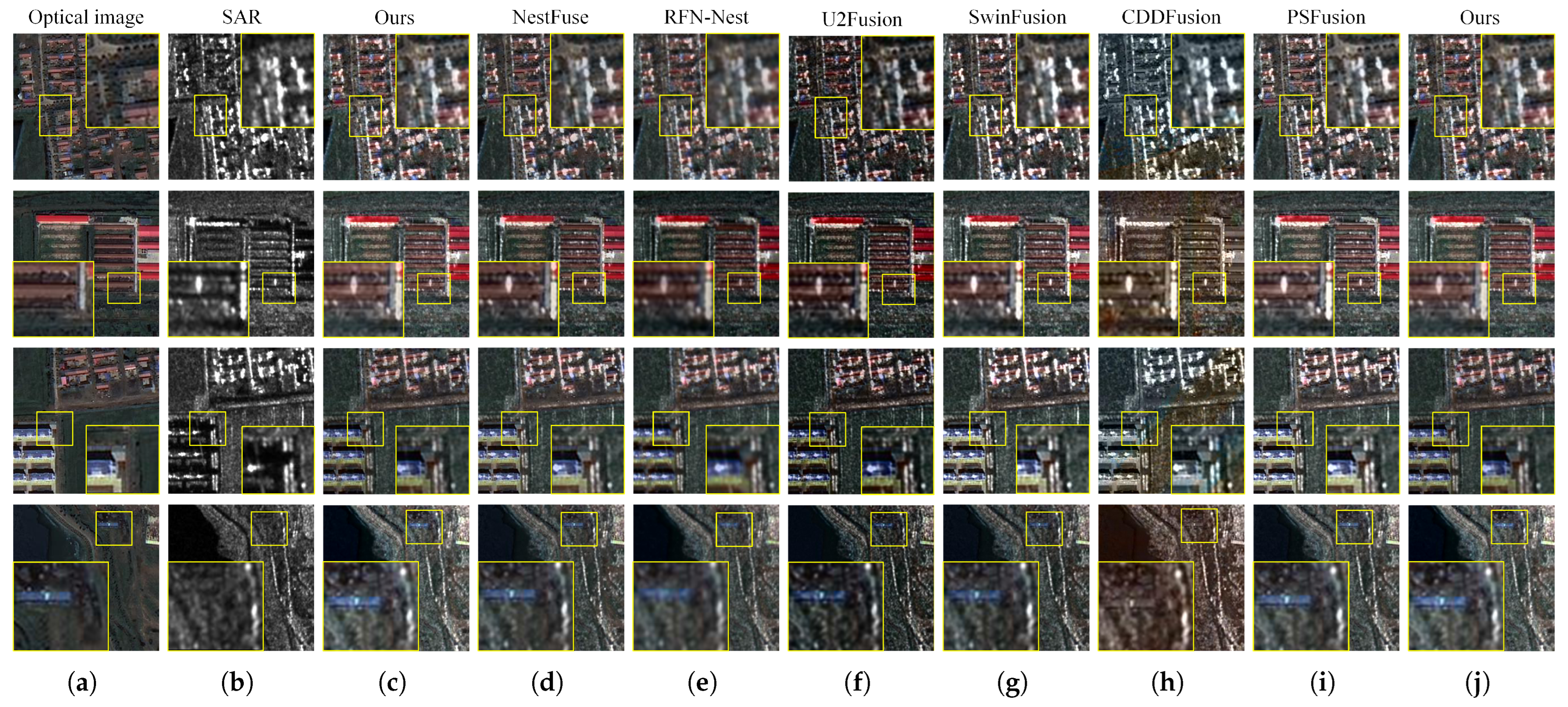
4.2. Comparative Experiments
4.2.1. Comparison Experiments on the Dongying Dataset
4.2.2. Comparison Experiments on the Xi’an Dataset
4.2.3. Comparison Experiments on Larger Pixel Size Data Fusion Tasks
4.3. Ablation Experiment
4.3.1. Multi-Resolution Hierarchical Fusion
4.3.2. Number of Layers in the Complementary Feature Extraction Model
4.3.3. Fusion Strategy
4.3.4. Sampling Strategy
4.3.5. Ablation of and
4.4. Convergence Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, S.; Kang, X.; Fang, L.; Hu, J.; Yin, H. Pixel-level image fusion: A survey of the state of the art. Inf. Fusion 2017, 33, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Sun, Y.; Xu, Y.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, X.; Lei, L.; Kuang, G. A Review of Optical and SAR Image Deep Feature Fusion in Semantic Segmentation. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 12910–12930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, A.; Prats-Iraola, P.; Younis, M.; Krieger, G.; Hajnsek, I.; Papathanassiou, K.P. A tutorial on synthetic aperture radar. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2013, 1, 6–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, Y.; Zhong, B.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Shi, X.; Ji, C.; Wu, S.; Sun, B.; Li, C.; et al. Synergistic Coupling of Multi-Source Remote Sensing Data for Sandy Land Detection and Multi-Indicator Integrated Evaluation. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baier, G.; Deschemps, A.; Schmitt, M.; Yokoya, N. Synthesizing Optical and SAR Imagery From Land Cover Maps and Auxiliary Raster Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 4701312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Liu, M.; Chen, S.; Lu, F.; Xing, M. Ship Detection in SAR Images Based on Multilevel Superpixel Segmentation and Fuzzy Fusion. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5206215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kedar, M.; Rege, P.P. Wavelet Transform-Based Fusion of SAR and Multispectral Images. In Nanoelectronics, Circuits and Communication Systems; Nath, V., Mandal, J.K., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 261–275. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Luo, Z.; Wang, Q. Research on fusion method of SAR and RGB image based on wavelet transform. In Proceedings of the 13h International Conference on Digital Image Processing (ICDIP 2021), Virtual, 20–23 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Chang, F. A Multi-focus Image Fusion Method Based on Laplacian Pyramid. J. Comput. 2011, 6, 2559–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siheng, M.; Li, Z.; Hong, P.; Jun, W. Medical image fusion based on DTNP systems and Laplacian pyramid. J. Membr. Comput. 2021, 3, 284–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tianyong, C.; Yumin, T.; Qiang, L.; Bingxin, B. Novel fusion method for SAR and optical images based on non-subsampled shearlet transform. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 41, 4590–4604. [Google Scholar]
- Bertinetto, L.; Valmadre, J.; Henriques, J.F.; Vedaldi, A.; Torr, P.H.S. Fully-Convolutional Siamese Networks for Object Tracking. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1606.09549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S. Infrared and visible image fusion based on saliency detection and two-scale transform decomposition. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2021, 114, 103626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, L.; Li, J.; Ren, X.; Fan, J. Optical and SAR image fusion based on complementary feature decomposition and visual saliency features. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5205315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batur, E.; Maktav, D. Assessment of Surface Water Quality by Using Satellite Images Fusion Based on PCA Method in the Lake Gala, Turkey. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 2983–2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavirisetti, D.P.; Rajesh, K.N.; Dhuli, R.; Polinati, S. Multimodal Medical Image Fusion Based on Content-based and PCA-sigmoid. Curr. Med. Imaging 2022, 18, 546–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Shi, Z.; An, Z. Hyperspectral and panchromatic image fusion using unmixing-based constrained nonnegative matrix factorization. Optik 2013, 124, 1601–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, J.-J.; Qiu, T.-S. Medical image fusion based on sparse representation of classified image patches. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2017, 34, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Fu, Y.; Li, H.; Zou, J. Dictionary learning method for joint sparse representation-based image fusion. Opt. Eng. 2013, 52, 057006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakar, K.R.; Srikar, V.S.; Babu, R.V. DeepFuse: A Deep Unsupervised Approach for Exposure Fusion with Extreme Exposure Image Pairs. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 4724–4732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, X.J. DenseFuse: A Fusion Approach to Infrared and Visible Images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 28, 2614–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, L.; Lin, L.; Yuli, S.; Ming, L.; Gangyao, K. Multimodal Bilinear Fusion Network With Second-Order Attention-Based Channel Selection for Land Cover Classification. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 1011–1026. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Q.; Zhu, D.; Yang, J.; Li, B. Multisource Hyperspectral and LiDAR Data Fusion for Urban Land-Use Mapping based on a Modified Two-Branch Convolutional Neural Network. ISPRS Int. J.-Geo 2019, 8, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Liu, W.; Zhou, L.; Peng, T.; Xu, Q. An Unsupervised SAR and Optical Image Fusion Network Based on Structure-Texture Decomposition. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 4028305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenwu, W.; Junsheng, W.; Zhixiang, Z.; Hao, C. MSFNet: MultiStage Fusion Network for infrared and visible image fusion. Neurocomputing 2022, 507, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, L.; Yanfeng, T.; Ruiliang, P.; Liang, L. Remotely Sensing Image Fusion Based on Wavelet Transform and Human Vision System. Int. J. Signal Process. Image Process. Pattern Recognit. 2015, 8, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamir, S.W.; Arora, A.; Khan, S.; Hayat, M.; Khan, F.S.; Yang, M.H.; Shao, L. Learning Enriched Features for Real Image Restoration and Enhancement. arXiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, S.C.; Rege, P.P. Pixel level fusion techniques for SAR and optical images: A review. Inf. Fusion 2020, 59, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatys, L.A.; Ecker, A.S.; Bethge, M. Image Style Transfer Using Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NE, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 2414–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrakanth, R.; Saibaba, J.; Varadan, G.; Ananth Raj, P. Feasibility of high resolution SAR and multispectral data fusion. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–29 July 2011; pp. 356–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolme, D.S.; Beveridge, J.R.; Draper, B.A.; Lui, Y.M. Visual object tracking using adaptive correlation filters. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–18 June 2010; pp. 2544–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fein-Ashley, J.; Wickramasinghe, S.; Zhang, B.; Kannan, R.; Prasanna, V. A Single Graph Convolution Is All You Need: Efficient Grayscale Image Classification. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.00564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Guo, W.; Chapman, S.C.; Guo, Y.; Zheng, B. Pixel size of aerial imagery constrains the applications of unmanned aerial vehicle in crop breeding. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 154, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baofeng, T.; Jun, L.; Xin, W. Lossy compression algorithm of remotely sensed multispectral images based on YCrCb transform and IWT. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Photoelectronic Detection and Imaging 2007: Image Processing, Beijing, China, 9–12 September 2007. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Delving Deep into Rectifiers: Surpassing Human-Level Performance on ImageNet Classification. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1502.01852. [Google Scholar]
- Sonobe, R.; Yamaya, Y.; Tani, H.; Wang, X.; Kobayashi, N.; Mochizuki, K.-i. Mapping crop cover using multi-temporal Landsat 8 OLI imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 4348–4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Diwakar, M.; Shankar, A.; Shree, R.; Kumar, M. A Review on SAR Image and its Despeckling. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2021, 28, 4633–4653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, W.; Hu, X.; Yang, J. Selective Kernel Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Jie, H.; Li, S.; Samuel, A.; Gang, S.; Enhua, W. Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2019, 42, 2011–2023. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. CBAM: Convolutional Block Attention Module. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.06521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, N.; Jahan, I.; Nadeem, M.R.; Sharma, V. A Comparative Study of ResNet50, EfficientNetB7, InceptionV3, VGG16 models in Crop and Weed classification. In Proceedings of the 2023 4th International Conference on Intelligent Engineering and Management (ICIEM), London, UK, 9–11 May 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Zhang, J.Q.; Wang, X.R.; Liu, X. A novel similarity based quality metric for image fusion. Inf. Fusion 2008, 9, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonato, L.G.; do Carmo, F.P.; Silva, C.T. GLoG: Laplacian of Gaussian for Spatial Pattern Detection in Spatio-Temporal Data. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2021, 27, 3481–3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, J.W.; van Aardt, J.; Ahmed, F. Assessment of image fusion procedures using entropy, image quality, and multispectral classification. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2008, 2, 023522. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, B.; Ma, S.; Hou, B.; Hong, D.; Chanussot, J.; Wang, J.; Jiao, L. A dual-stream high resolution network: Deep fusion of GF-2 and GF-3 data for land cover classification. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 112, 102896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Ma, J.; Jiang, J.; Guo, X.; Ling, H. U2Fusion: A Unified Unsupervised Image Fusion Network. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 44, 502–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Bai, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, S.; Lin, Z.; Timofte, R.; Van Gool, L. CDDFuse: Correlation-Driven Dual-Branch Feature Decomposition for Multi-Modality Image Fusion. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 5906–5916. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, L.; Zhang, H.; Xu, H.; Ma, J. Rethinking the necessity of image fusion in high-level vision tasks: A practical infrared and visible image fusion network based on progressive semantic injection and scene fidelity. Inf. Fusion 2023, 99, 101870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Shao, W.; Li, H.; Zhang, L. SwinFuse: A Residual Swin Transformer Fusion Network for Infrared and Visible Images. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 5016412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Ma, Y.; Li, C. Infrared and visible image fusion methods and applications: A survey. Inf. Fusion 2019, 45, 153–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Mou, X.; Zhang, D. FSIM: A Feature Similarity Index for Image Quality Assessment. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2011, 20, 2378–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Layer | Type | Channel (Input) | Channel (Output) | Output Feature Map |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 1 | Conv + ReLU | 3 | 64 | , |
| Conv + ReLU | 64 | 64 | ||
| n = 2 | Conv + ReLU | 64 | 128 | , |
| Conv + ReLU | 128 | 128 | ||
| n = 3 | Conv + ReLU | 128 | 256 | , |
| Conv + ReLU | 256 | 256 | ||
| n = 4 | Conv + ReLU | 256 | 512 | , |
| Conv + ReLU | 512 | 512 |
| EN | SF | SSIM | FSIM | GS | PSNR (dB) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DensFuse | 6.33 | 14.21 | 0.61 | 0.588 | 0.845 | 19.897 |
| NestFuse | 6.31 | 16.60 | 0.62 | 0.600 | 0.852 | 20.060 |
| RFN-Nest | 6.32 | 11.49 | 0.57 | 0.559 | 0.836 | 20.010 |
| U2Fusion | 6.09 | 18.53 | 0.60 | 0.567 | 0.844 | 20.448 |
| SwinFusion | 6.46 | 18.86 | 0.61 | 0.605 | 0.847 | 21.502 |
| CDDFusion | 6.41 | 19.87 | 0.61 | 0.591 | 0.839 | 19.839 |
| PSFusion | 6.63 | 19.89 | 0.59 | 0.601 | 0.841 | 19.438 |
| Ours | 6.72 | 19.36 | 0.63 | 0.600 | 0.853 | 21.325 |
| EN | SF | SSIM | FSIM | GS | PSNR (dB) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DensFuse | 6.65 | 15.51 | 0.61 | 0.595 | 0.860 | 19.165 |
| NestFuse | 6.74 | 18.75 | 0.62 | 0.609 | 0.859 | 19.839 |
| RFN-Nest | 6.70 | 13.59 | 0.59 | 0.573 | 0.847 | 19.235 |
| U2Fusion | 6.55 | 20.92 | 0.60 | 0.573 | 0.852 | 19.451 |
| SwinFusion | 6.91 | 21.60 | 0.60 | 0.617 | 0.853 | 19.829 |
| CDDFusion | 6.95 | 23.17 | 0.60 | 0.600 | 0.846 | 18.905 |
| PSFusion | 6.97 | 22.09 | 0.61 | 0.611 | 0.853 | 18.147 |
| Ours | 6.95 | 24.10 | 0.62 | 0.602 | 0.862 | 19.625 |
| EN | SF | SSIM | FSIM | GS | PSNR (dB) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DensFuse | 6.73 | 8.01 | 0.61 | 0.634 | 0.816 | 20.241 |
| NestFuse | 6.68 | 12.00 | 0.68 | 0.517 | 0.754 | 19.919 |
| RFN-Nest | 6.86 | 12.19 | 0.57 | 0.522 | 0.749 | 20.353 |
| U2Fusion | 6.94 | 18.21 | 0.52 | 0.568 | 0.774 | 19.518 |
| SwinFusion | 6.54 | 10.55 | 0.68 | 0.525 | 0.746 | 20.117 |
| CDDFusion | 6.92 | 18.23 | 0.54 | 0.631 | 0.816 | 20.543 |
| PSFusion | 6.75 | 12.77 | 0.66 | 0.680 | 0.826 | 20.848 |
| Ours | 6.95 | 13.73 | 0.63 | 0.660 | 0.835 | 20.383 |
| EN | SF | SSIM | FSIM | GS | PSNR (dB) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NO.1 | 6.71 | 18.32 | 0.63 | 0.596 | 0.854 | 21.201 |
| NO.2 | 6.71 | 18.05 | 0.63 | 0.598 | 0.846 | 21.123 |
| NO.3 | 6.72 | 17.33 | 0.63 | 0.600 | 0.847 | 21.157 |
| NO.4 | 6.68 | 16.61 | 0.63 | 0.600 | 0.847 | 21.288 |
| a = 1 | 6.65 | 16.96 | 0.63 | 0.592 | 0.853 | 21.340 |
| a = 2 | 6.72 | 18.31 | 0.63 | 0.601 | 0.851 | 21.342 |
| a = 3 | 6.68 | 16.90 | 0.63 | 0.601 | 0.849 | 21.335 |
| a = 4 | 6.68 | 15.04 | 0.60 | 0.602 | 0.848 | 21.235 |
| a = 5 | 6.68 | 15.48 | 0.61 | 0.594 | 0.853 | 21.012 |
| Ours | 6.72 | 19.36 | 0.63 | 0.600 | 0.853 | 21.325 |
| EN | SF | FSIM | PSNR (dB) | PM (MB) | pGPUu | Time | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N = 1 (Ours) | 6.72 | 19.36 | 0.600 | 21.324 | 1380.8 | 76.8 % | 334 s |
| N = 2 | 6.71 | 19.36 | 0.591 | 21.324 | 1444.7 | 82.5 % | 488 s |
| N = 3 | 6.68 | 18.33 | 0.602 | 21.057 | 1445.1 | 87 % | 708 s |
| N = 4 | 6.72 | 17.41 | 0.592 | 21.524 | 1450.1 | 87 % | 1180 s |
| EN | SF | SSIM | FSIM | GS | PSNR (dB) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| summation | 4.83 | 17.52 | 0.62 | 0.465 | 0.859 | 21.047 |
| concatenation | 4.61 | 11.14 | 0.43 | 0.347 | 0.797 | 16.169 |
| stride = 4 × 4 | 6.69 | 19.33 | 0.63 | 0.597 | 0.847 | 21.224 |
| = 1 × | 3.95 | 13.10 | 0.23 | 0.161 | 0.722 | 14.555 |
| = 1 × | 2.03 | 0.55 | 0.07 | 0.048 | 0.711 | 12.650 |
| = 1 × 10 | 6.71 | 17.35 | 0.62 | 0.582 | 0.847 | 20.150 |
| = 1 × | 6.68 | 16.32 | 0.58 | 0.577 | 0.831 | 20.512 |
| = 1 × | 6.69 | 16.36 | 0.58 | 0.601 | 0.842 | 20.437 |
| = 1 × | 6.70 | 17.41 | 0.62 | 0.583 | 0.841 | 20.105 |
| = 1 × | 6.71 | 17.45 | 0.61 | 0.583 | 0.847 | 20.190 |
| = 1 × | 4.66 | 22.88 | 0.58 | 0.547 | 0.810 | 20.690 |
| Ours | 6.72 | 19.36 | 0.63 | 0.600 | 0.853 | 21.325 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Ma, L.; Zhao, B.; Gou, Z.; Yin, Y.; Sun, G. MRLF: Multi-Resolution Layered Fusion Network for Optical and SAR Images. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 3740. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17223740
Wang J, Ma L, Zhao B, Gou Z, Yin Y, Sun G. MRLF: Multi-Resolution Layered Fusion Network for Optical and SAR Images. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(22):3740. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17223740
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jinwei, Liang Ma, Bo Zhao, Zhenguang Gou, Yingzheng Yin, and Guangcai Sun. 2025. "MRLF: Multi-Resolution Layered Fusion Network for Optical and SAR Images" Remote Sensing 17, no. 22: 3740. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17223740
APA StyleWang, J., Ma, L., Zhao, B., Gou, Z., Yin, Y., & Sun, G. (2025). MRLF: Multi-Resolution Layered Fusion Network for Optical and SAR Images. Remote Sensing, 17(22), 3740. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17223740








