Multi-Faceted Adaptive Token Pruning for Efficient Remote Sensing Image Segmentation
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We propose a novel multi-faceted adaptive token pruning token pruning method tailored for RS image segmentation. It reduces the inherent token redundancy in vision transformers and provides a new aspect for balancing computational cost and accuracy in RS.
- MATP innovatively employs multi-faceted pruning scores obtained from lightweight auxiliary heads, and utilizes adaptive pruning criteria that change automatically with specific input features to select the proper tokens to prune. And MATP also introduces a train-time retention gate to retain contextual information by stopping pruning of some tokens in the early stages of training.
- We apply MATP to mainstream frameworks with attention mechanisms for RS image interpretation tasks and conduct experiments on three widely used semantic segmentation datasets. The results reveal that MATP decreases FLOPs about 67–70%, with acceptable accuracy degradation, and achieves a better trade-off between computational cost and accuracy.
2. Related Works
2.1. Backbone Networks for RS Image Segmentation
2.2. Lightweight Methods for RS Image Segmentation
2.3. Token Reduction for Semantic Segmentation in Computer Vision
3. Approach
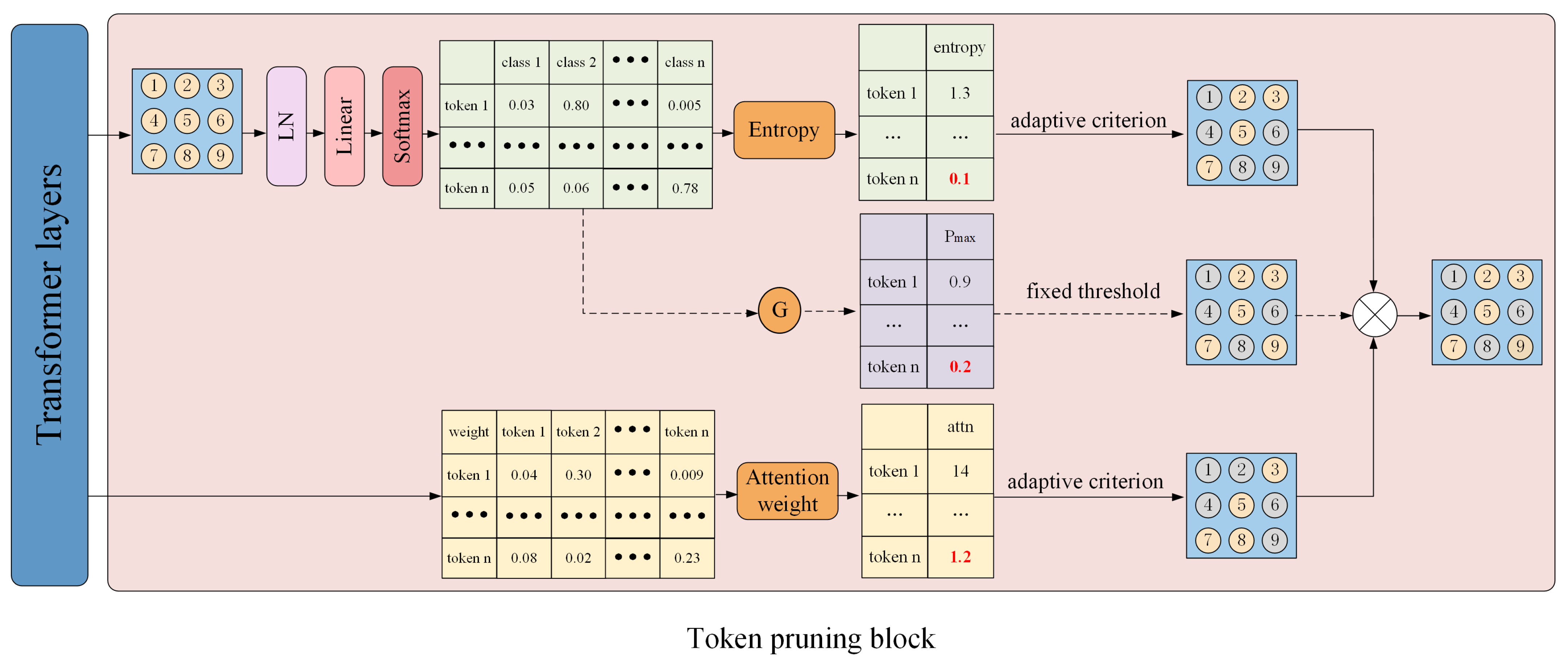
3.1. Architectural Configuration of MATP
3.2. Lightweight Auxiliary Heads
3.3. Multi-Faceted Token Pruning
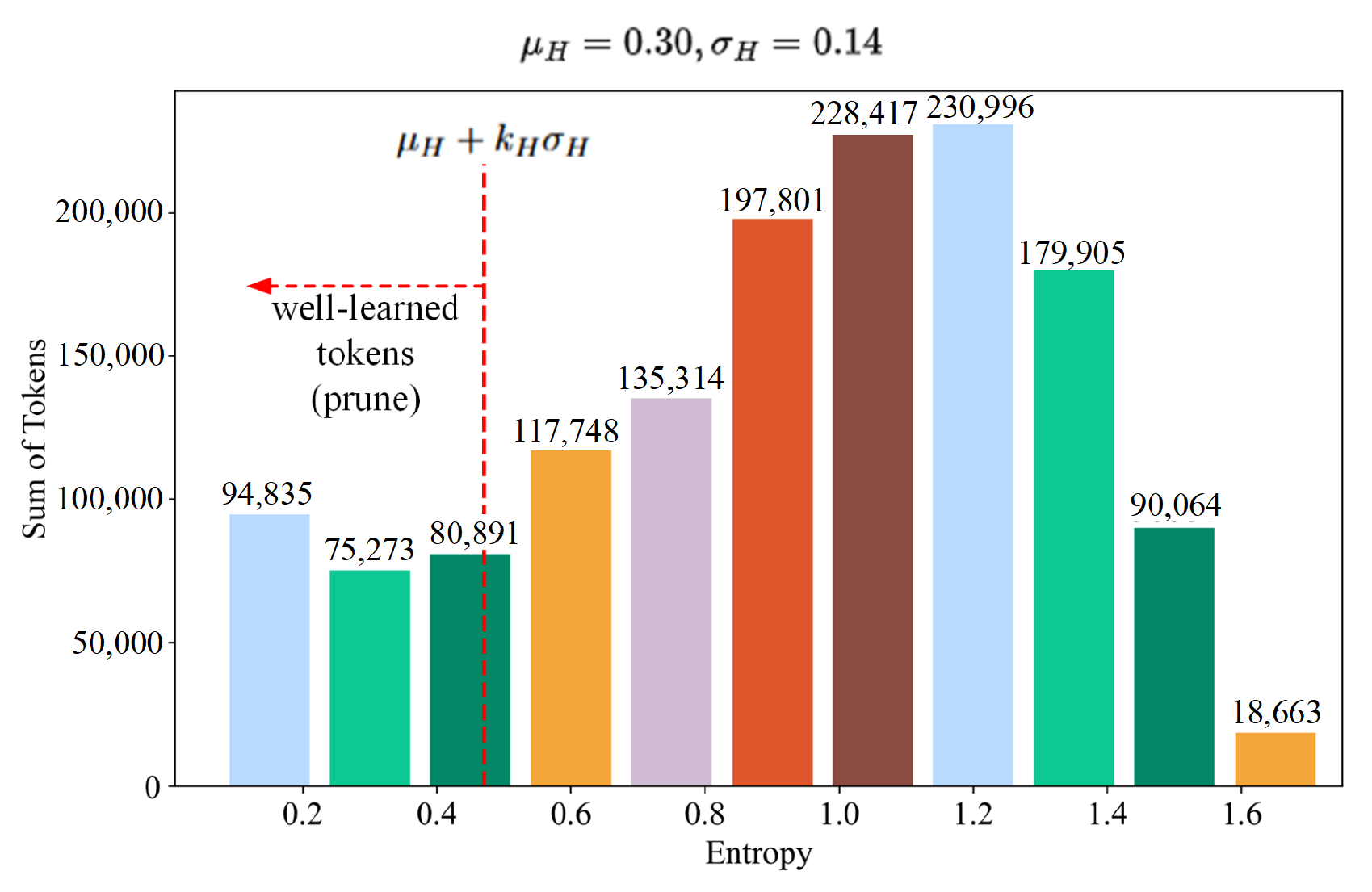
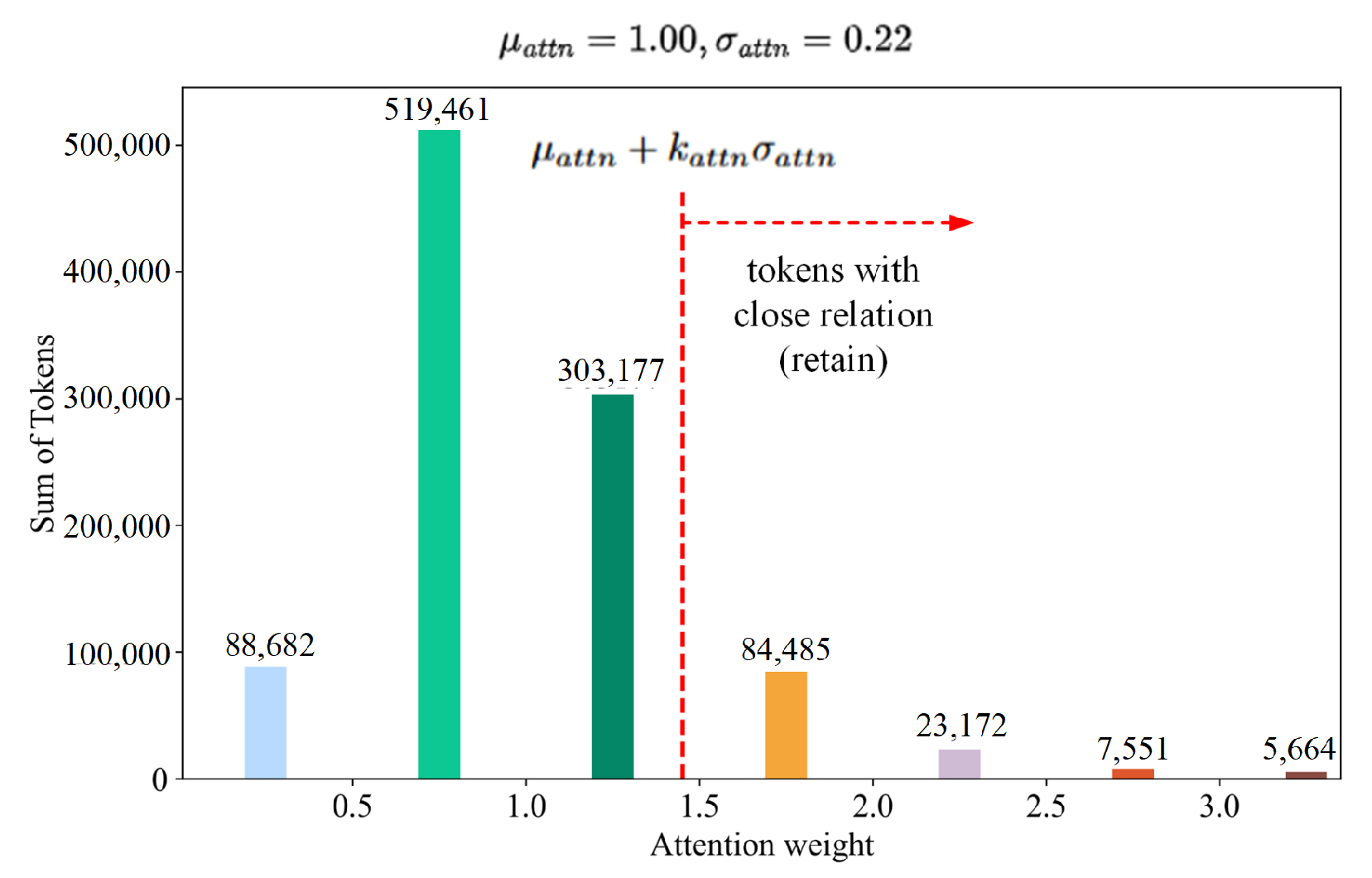
3.4. Adaptive Token Pruning Criteria
4. Experiments
4.1. Segmentation Datasets
4.2. Experimental Setup
4.3. Experimental Results
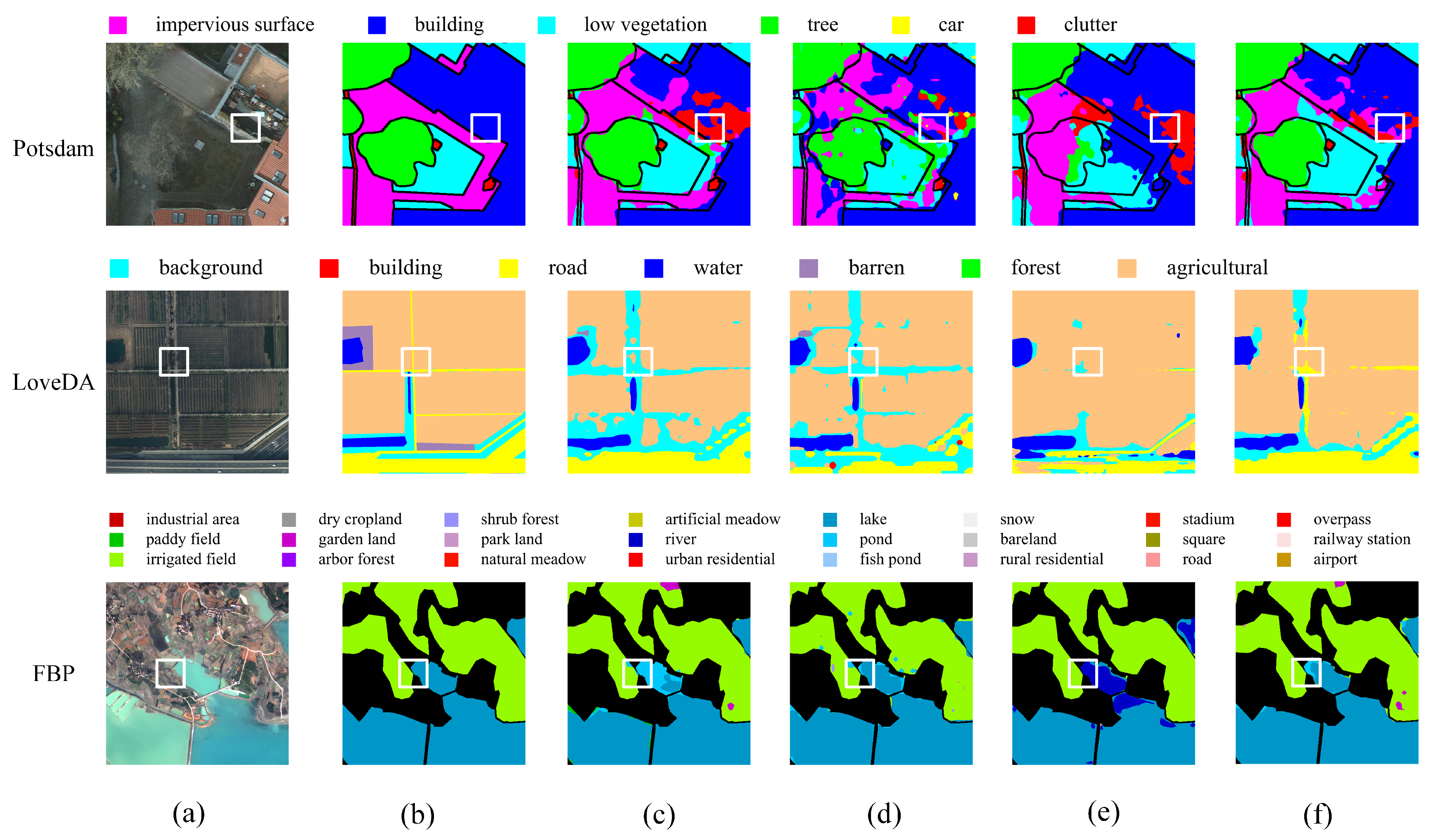
4.4. Visualization Results
4.5. Ablation Studies
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An Image is Worth 16x16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Vienna, Austria, 4 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 10012–10022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Su, J.; Ju, Y.; Lam, K.M.; Wang, Q. Efficient inductive vision transformer for oriented object detection in remote sensing imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5616320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, R.; Zhang, C.; Fang, S.; Duan, C.; Meng, X.; Atkinson, P.M. UNetFormer: A UNet-like transformer for efficient semantic segmentation of remote sensing urban scene imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2022, 190, 196–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Naseer, M.; Hayat, M.; Zamir, S.W.; Khan, F.S.; Shah, M. Transformers in vision: A survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2022, 54, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Zhang, B.; Liu, J.; Liu, F.; Liu, Y. Dynamic token pruning in plain vision transformers for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 777–786. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, T.; Geng, X.; Ning, H.; Lv, Z.; Gong, M.; Jin, Y.; Nandi, A.K. Ultralightweight spatial—Spectral feature cooperation network for change detection in remote sensing images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 4402114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, C. Transformer and CNN Hybrid Deep Neural Network for Semantic Segmentation of Very-High-Resolution Remote Sensing Imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 4408820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Huang, P.; Zhang, M.; Tang, W.; Yu, X. CMTFNet: CNN and multiscale transformer fusion network for remote-sensing image semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 2004612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, C.; Duan, C.; Wang, L.; Atkinson, P.M. ABCNet: Attentive bilateral contextual network for efficient semantic segmentation of Fine-Resolution remotely sensed imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 181, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Qi, Z.; Shi, Z. Remote sensing image change detection with transformers. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 5900318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Chen, S.B.; Shu, Q.L.; Tang, J.; Luo, B. DecoupleNet: A Lightweight Backbone Network With Efficient Feature Decoupling for Remote Sensing Visual Tasks. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5935411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Chen, S.B.; Ding, C.H.; Tang, J.; Luo, B. LWGANet: A Lightweight Group Attention Backbone for Remote Sensing Visual Tasks. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2501.10040. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, Y.; Zhao, W.; Liu, B.; Lu, J.; Zhou, J.; Hsieh, C.J. DynamicViT: Efficient vision transformers with dynamic token sparsification. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 13937–13949. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, H.; Vahdat, A.; Alvarez, J.M.; Mallya, A.; Kautz, J.; Molchanov, P. A-ViT: Adaptive tokens for efficient vision transformer. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 10809–10818. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.; Ge, C.; Tong, Z.; Song, Y.; Wang, J.; Xie, P. EViT: Expediting Vision Transformers via Token Reorganizations. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Online, 25–29 April 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, C.; de Geus, D.; Dubbelman, G. Content-aware token sharing for efficient semantic segmentation with vision transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 23631–23640. [Google Scholar]
- Norouzi, N.; Orlova, S.; De Geus, D.; Dubbelman, G. ALGM: Adaptive Local-then-Global Token Merging for Efficient Semantic Segmentation with Plain Vision Transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 15773–15782. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, D.; Yao, R.; Xue, Y. Swin Transformer Embedding UNet for Remote Sensing Image Semantic Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 4408715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Z.; Dong, P.; Ma, X.; Meng, X.; Niu, W.; Sun, M.; Shen, X.; Yuan, G.; Ren, B.; Tang, H.; et al. SpViT: Enabling faster vision transformers via latency-aware soft token pruning. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; pp. 620–640. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, W.; Yuan, Y.; Ding, H.; Luo, X.; Lin, W.; Jia, D.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Hu, H. Expediting large-scale vision transformer for dense prediction without fine-tuning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 35462–35477. [Google Scholar]
- Shannon, C.E. A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, F.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W. Dynamic token-pass transformers for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2024; pp. 1827–1836. [Google Scholar]
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Zhmoginov, A.; Chen, L.C. MobileNetV2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 4510–4520. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, N.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, H.T.; Sun, J. ShuffleNet v2: Practical guidelines for efficient cnn architecture design. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 116–131. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, X.; Lin, M.; Sun, J. ShuffleNet: An extremely efficient convolutional neural network for mobile devices. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 6848–6856. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.; Chen, B.; Pang, R.; Vasudevan, V.; Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Le, Q.V. Mnasnet: Platform-aware neural architecture search for mobile. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 2820–2828. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Yuan, G.; Wen, Y.; Hu, J.; Evangelidis, G.; Tulyakov, S.; Wang, Y.; Ren, J. EfficientFormer: Vision transformers at MobileNet speed. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 12934–12949. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Hu, J.; Wen, Y.; Evangelidis, G.; Salahi, K.; Wang, Y.; Tulyakov, S.; Ren, J. Rethinking vision transformers for MobileNet size and speed. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 16889–16900. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, X.; Zhang, X.; Ma, N.; Han, J.; Ding, G.; Sun, J. RepVGG: Making VGG-style convnets great again. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 13733–13742. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, L.; Chen, Y.; Wang, T.; Yu, W.; Shi, Y.; Jiang, Z.H.; Tay, F.E.; Feng, J.; Yan, S. Tokens-to-token ViT: Training vision transformers from scratch on ImageNet. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 558–567. [Google Scholar]
- Carion, N.; Massa, F.; Synnaeve, G.; Usunier, N.; Kirillov, A.; Zagoruyko, S. End-to-end object detection with transformers. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; pp. 213–229. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Su, W.; Lu, L.; Li, B.; Wang, X.; Dai, J. DETR: Deformable Transformers for End-to-End Object Detection. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Vienna, Austria, 4 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, B.; Misra, I.; Schwing, A.G.; Kirillov, A.; Girdhar, R. Masked-attention mask transformer for universal image segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 1290–1299. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, B.; Schwing, A.; Kirillov, A. Per-pixel classification is not all you need for semantic segmentation. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 17864–17875. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, X.; Bao, J.; Chen, D.; Zhang, W.; Yu, N.; Yuan, L.; Chen, D.; Guo, B. CSWin transformer: A general vision transformer backbone with cross-shaped windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 12124–12134. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, A.; Wang, J.; Zhong, Y.; Zheng, Z. FactSeg: Foreground activation-driven small object semantic segmentation in large-scale remote sensing imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 5606216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhong, Y.; Ma, A.; Zheng, Z.; Wan, Y.; Zhang, L. LoveNAS: Towards multi-scene land-cover mapping via hierarchical searching adaptive network. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2024, 209, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Zou, Z.; Shi, Z. Building Extraction from Remote Sensing Images with Sparse Token Transformers. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Liu, C.; Chen, B.; Li, W.; Zou, Z.; Shi, Z. Dynamicvis: An efficient and general visual foundation model for remote sensing image understanding. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2503.16426. [Google Scholar]
- Bolya, D.; Fu, C.Y.; Dai, X.; Zhang, P.; Feichtenhofer, C.; Hoffman, J. Token Merging: Your ViT But Faster. In Proceedings of the Eleventh International Conference on Learning Representations, Kigali, Rwanda, 1–5 May 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Liu, Z.; Tang, H.; Yi, L.; Zhao, H.; Han, S. SparseViT: Revisiting activation sparsity for efficient high-resolution vision transformer. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 2061–2070. [Google Scholar]
- Ba, J.L.; Kiros, J.R.; Hinton, G.E. Layer normalization. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1607.06450. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Bergner, B.; Lippert, C.; Mahendran, A. Token Cropr: Faster ViTs for Quite a Few Tasks. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2412.00965. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Tian, Z.; Tang, Q.; Chu, X.; Wei, X.; Shen, C. Segvit: Semantic segmentation with plain vision transformers. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 4971–4982. [Google Scholar]
- Weidner, D.; Liao, M.; Roth, P.; Schindler, K. ISPRS Potsdam: A New 2D Semantic Labeling Benchmark for Remote Sensing. In Proceedings of the 23rd ISPRS Symposium, Melbourne, Australia, 25 August–1 September 2012; p. 5. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zheng, Z.; Ma, A.; Lu, X.; Zhong, Y. LoveDA: A Remote Sensing Land-Cover Dataset for Domain Adaptive Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the Neural Information Processing Systems Track on Datasets and Benchmarks, Online, 6–14 December 2021; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, X.Y.; Xia, G.S.; Zhu, X.X. Enabling country-scale land cover mapping with meter-resolution satellite imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2023, 196, 178–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, T.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, B.; Jiang, Y.; Sun, J. Unified perceptual parsing for scene understanding. In Proceedings of the PEuropean Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 418–434. [Google Scholar]



| Training Config | MATP |
|---|---|
| Image size | 512 × 512 |
| Train and validation size | 512 × 512 |
| Patch size | 16 |
| Number of heads | 12 |
| Prune layers | 3, 6, 8 |
| Optimizer | AdamW |
| Learning rate | 2 × 10−4 |
| Weight decay | 0.01 |
| Batch size | 4 |
| Training iterations | 40,000 |
| Main loss | Cross-entropy loss |
| Auxiliary loss | Attention to mask loss |
| Method | Decoder | Dataset | Publication | Params. (M)↓ | mIoU (%)↑ | FLOPs (G)↓ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ViT-B [1] | SegViT [46] | Potsdam [47] | NIPS2022 | 93.83 | 79.20 | 108.27 |
| +ToMe [41] | SegViT [46] | Potsdam [47] | ICLR2023 | 93.80 | 62.55 (−16.65%) | 62.40 (−42.4%) |
| +DToP [6] | SegViT [46] | Potsdam [47] | IEEE ICCV2023 | 109.00 | 74.43 (−4.77%) | 33.51 (−69.0%) |
| +ALGM [18] | SegViT [46] | Potsdam [47] | IEEE CVPR2024 | 93.83 | 74.88 (−4.32%) | 30.49 (−71.8%) |
| +ours | SegViT [46] | Potsdam [47] | - | 94.75 | 76.33 (−2.87%) | 33.97 (−68.6%) |
| ViT-B [1] | SegViT [46] | LoveDA [48] | NIPS2022 | 93.83 | 52.75 | 108.28 |
| +ToMe [41] | SegViT [46] | LoveDA [48] | ICLR2023 | 93.80 | 41.25 (−11.5%) | 62.42 (−42.4%) |
| +DToP [6] | SegViT [46] | LoveDA [48] | IEEE ICCV2023 | 109.00 | 49.37 (−3.38%) | 33.43 (−69.1%) |
| +ALGM [18] | SegViT [46] | LoveDA [48] | IEEE CVPR2024 | 93.83 | 49.20 (−3.55%) | 34.23 (−68.4%) |
| +ours | SegViT [46] | LoveDA [48] | - | 94.75 | 49.83 (−2.92%) | 33.57 (−69.0%) |
| ViT-B [1] | SegViT [46] | FBP [49] | NIPS2022 | 93.83 | 60.74 | 108.44 |
| +ToMe [41] | SegViT [46] | FBP [49] | ICLR2023 | 93.80 | 37.49 (−23.25%) | 62.58 (−42.3%) |
| +DToP [6] | SegViT [46] | FBP [49] | IEEE ICCV2023 | 109.00 | 51.99 (−8.75%) | 41.28 (−61.9%) |
| +ALGM [18] | SegViT [46] | FBP [49] | IEEE CVPR2024 | 93.83 | 52.56 (−8.18%) | 30.77 (−71.6%) |
| +ours | SegViT [46] | FBP [49] | − | 94.75 | 54.64 (−6.10%) | 35.05 (−67.7%) |
| Method | Decoder | Dataset | Publication | Params. (M)↓ | mIoU (%)↑ | FLOPs (G)↓ (Encoder) | FLOPs (G)↓ (Decoder) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Swin-T [2] | UPerNet [50] | Potsdam [47] | IEEE ICCV2021 | 59.83 | 80.03 | 25.61 | 210.36 |
| +ELViT [21] | UPerNet [50] | Potsdam [47] | NIPS2022 | 52.80 | 67.08 | 17.39 | 210.36 |
| +SparseViT [42] | UPerNet [50] | Potsdam [47] | IEEE CVPR2023 | 59.85 | 76.99 | 14.61 | 210.36 |
| +ours | UPerNet [50] | Potsdam [47] | - | 59.31 | 77.89 | 17.76 | 210.36 |
| Swin-T [2] | UPerNet [50] | LoveDA [48] | IEEE ICCV2021 | 59.83 | 52.36 | 25.61 | 210.38 |
| +ELViT [21] | UPerNet [50] | LoveDA [48] | NIPS2022 | 52.80 | 38.80 | 17.49 | 210.38 |
| +SparseViT [42] | UPerNet [50] | LoveDA [48] | IEEE CVPR2023 | 59.85 | 48.36 | 14.63 | 210.38 |
| +ours | UPerNet [50] | LoveDA [48] | - | 59.31 | 49.31 | 16.96 | 210.38 |
| Swin-T [2] | UPerNet [50] | FBP [49] | IEEE ICCV2021 | 59.83 | 60.48 | 25.62 | 210.51 |
| +ELViT [21] | UPerNet [50] | FBP [49] | NIPS2022 | 52.80 | 31.50 | 17.49 | 210.51 |
| +SparseViT [42] | UPerNet [50] | FBP [49] | IEEE CVPR2023 | 59.85 | 50.27 | 14.63 | 210.51 |
| +ours | UPerNet [50] | FBP [49] | - | 59.31 | 52.05 | 17.25 | 210.51 |
| Method | Decoder | Dataset | Publication | Params. (M)↓ | mIoU (%)↑ | FLOPs (G)↓ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ResNet50 [44] | FactSeg [37] | Potsdam [47] | TGRS2021 | 33.46 | 76.61 | 68.08 |
| ResNet18 [44] | UnetFormer [4] | Potsdam [47] | ISPRS2022 | 12.31 | 60.82 | 13.01 |
| DecoupleNet-D2 [12] | UnetFormer [4] | Potsdam [47] | TGRS2024 | 7.33 | 65.21 | 8.11 |
| ResNet50 [44] | LoveNAS [38] | Potsdam [47] | ISPRS2024 | 30.51 | 75.93 | 44.40 |
| ViT-B [1] +ours | SegViT [46] | Potsdam [47] | - | 94.75 | 76.33 | 33.97 |
| ResNet50 [44] | FactSeg [37] | LoveDA [48] | TGRS2021 | 33.46 | 48.07 | 68.09 |
| ResNet18 [44] | UnetFormer [4] | LoveDA [48] | ISPRS2022 | 12.31 | 37.91 | 13.02 |
| DecoupleNet-D2 [12] | UnetFormer [4] | LoveDA [48] | TGRS2024 | 7.33 | 43.88 | 8.12 |
| ResNet50 [44] | LoveNAS [38] | LoveDA [48] | ISPRS2024 | 30.51 | 48.86 | 44.40 |
| ViT-B [1] +ours | SegViT [46] | LoveDA [48] | - | 94.75 | 49.83 | 33.57 |
| ResNet50 [44] | FactSeg [37] | FBP [49] | TGRS2021 | 33.46 | 54.78 | 68.14 |
| ResNet18 [44] | UnetFormer [4] | FBP [49] | ISPRS2022 | 12.31 | 32.94 | 13.05 |
| DecoupleNet-D2 [12] | UnetFormer [4] | FBP [49] | TGRS2024 | 7.33 | 26.00 | 8.15 |
| ResNet50 [44] | LoveNAS [38] | FBP [49] | ISPRS2024 | 30.51 | 32.75 | 44.45 |
| ViT-B [1] +ours | SegViT [46] | FBP [49] | - | 94.75 | 54.64 | 35.05 |
| Method | mIoU (%)↑ with 0 Pixels Noise | mIoU (%)↑ with 100 Pixels Noise | mIoU (%)↑ with 1000 Pixels Noise |
|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 79.20 | 79.17 | 78.04 |
| +MATP | 76.33 | 76.25 | 74.66 |
| Random Token Pruning | Adaptive Entropy-Based Token Pruning | Lightweight Auxiliary Heads | Relation-Based Tokens Retained | Gradient Stop | mIoU (%)↑ | FLOPs (G)↓ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| × | × | × | × | × | 79.35 | 108.27 |
| ✓ | × | × | × | × | 75.60 | 38.01 |
| × | ✓ | × | × | × | 75.21 | 33.05 |
| × | ✓ | ✓ | × | × | 75.91 | 32.88 |
| × | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | × | 76.25 | 33.93 |
| × | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 76.33 | 33.97 |
| Method | mIoU (%)↑ | FLOPs (G)↓ |
|---|---|---|
| ViT-B [1] | 79.35 | 108.27 |
| Random | 78.54 | 70.80 |
| Pruning topk () | 78.51 | 64.78 |
| Fix threshold () | 77.82 | 65.63 |
| Adaptive entropy-based | 78.64 | 58.65 |
| mIoU (%)↑ | |
|---|---|
| 0 | 75.54 |
| 0.2 | 76.11 |
| 0.4 | 75.47 |
| 0.6 | 75.59 |
| 0.8 | 74.09 |
| 1.0 | 18.50 |
| lpruning | mIoU (%)↑ | FLOPs (G)↓ |
|---|---|---|
| 6 | 78.52 | 63.62 |
| 8 | 79.02 | 77.89 |
| 6, 8 | 78.51 | 59.24 |
| 3, 6, 8 | 76.33 | 33.97 |
| mIoU (%)↑ | FLOPs (G)↓ | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.3 | 2.0 | 77.24 | 44.29 |
| 0.6 | 2.0 | 77.05 | 39.99 |
| 0.9 | 2.0 | 76.69 | 36.39 |
| 1.2 | 0.5 | 77.08 | 44.29 |
| 1.2 | 1.0 | 76.47 | 36.31 |
| 1.2 | 1.5 | 76.37 | 34.67 |
| 1.2 | 2.0 | 76.33 | 33.97 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, C.; Yao, J. Multi-Faceted Adaptive Token Pruning for Efficient Remote Sensing Image Segmentation. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2508. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17142508
Zhang C, Yao J. Multi-Faceted Adaptive Token Pruning for Efficient Remote Sensing Image Segmentation. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(14):2508. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17142508
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Chuge, and Jian Yao. 2025. "Multi-Faceted Adaptive Token Pruning for Efficient Remote Sensing Image Segmentation" Remote Sensing 17, no. 14: 2508. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17142508
APA StyleZhang, C., & Yao, J. (2025). Multi-Faceted Adaptive Token Pruning for Efficient Remote Sensing Image Segmentation. Remote Sensing, 17(14), 2508. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17142508








