A Microwave–Optical Multi-Stage Synergistic Daily 30 m Soil Moisture Downscaling Framework
Highlights
- The microwave–optical multi-stage synergistic downscaling framework (MMSDF) generates daily 30 m soil moisture products by integrating SMAP, optical, and SAR data.
- Using an intermediate 1 km estimate, reliance on in situ stations was reduced to achieve 30-meter data extraction by calibrating the Water Cloud Model (WCM).
- MMSDF improves correlation from 0.34 to 0.54 compared to SMAP L4, enhancing agricultural and drought monitoring.
- In situ independent calibration enables large-scale operational deployment for high-resolution soil moisture monitoring.
Abstract
1. Introduction
- To develop a residual-constrained downscaling approach using a random forest model to enhance SMAP L4 SSM from a 9 km to a 1 km daily resolution, addressing the spatial limitations of passive microwave data.
- To calibrate a Water Cloud Model (WCM) for Sentinel-1 SAR data using intermediate 1 km SSM estimates, enabling 30 m SSM retrieval without in situ measurements and mitigating cloud-induced gaps in optical data.
- To implement a spatiotemporal fusion model (ESTARFM) that combines 1 km downscaled SSM with intermittent 30 m WCM-derived SSM, generating a seamless daily 30 m product and validating its accuracy against in situ networks.
2. Study Area and Data
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Remote Sensing and Auxiliary Data
2.3. Data Processing Framework
3. Methods
3.1. Stage 1: Residual Correction-Based Soil Moisture Downscaling (9 km to 1 km)
3.2. Stage 2: Water Cloud Model-Based Soil Moisture Inversion (30 m, Intermittent)
3.3. Stage 3: Spatiotemporal Fusion-Based Soil Moisture Inversion (30 m, Daily)
3.4. Experimental Setup
3.4.1. Downscaling 1 km Soil Moisture with Residual Correction
3.4.2. Inversion of 30 m Soil Moisture Using Water Cloud Model
3.4.3. Spatial–Temporal Fusion Parameter Settings
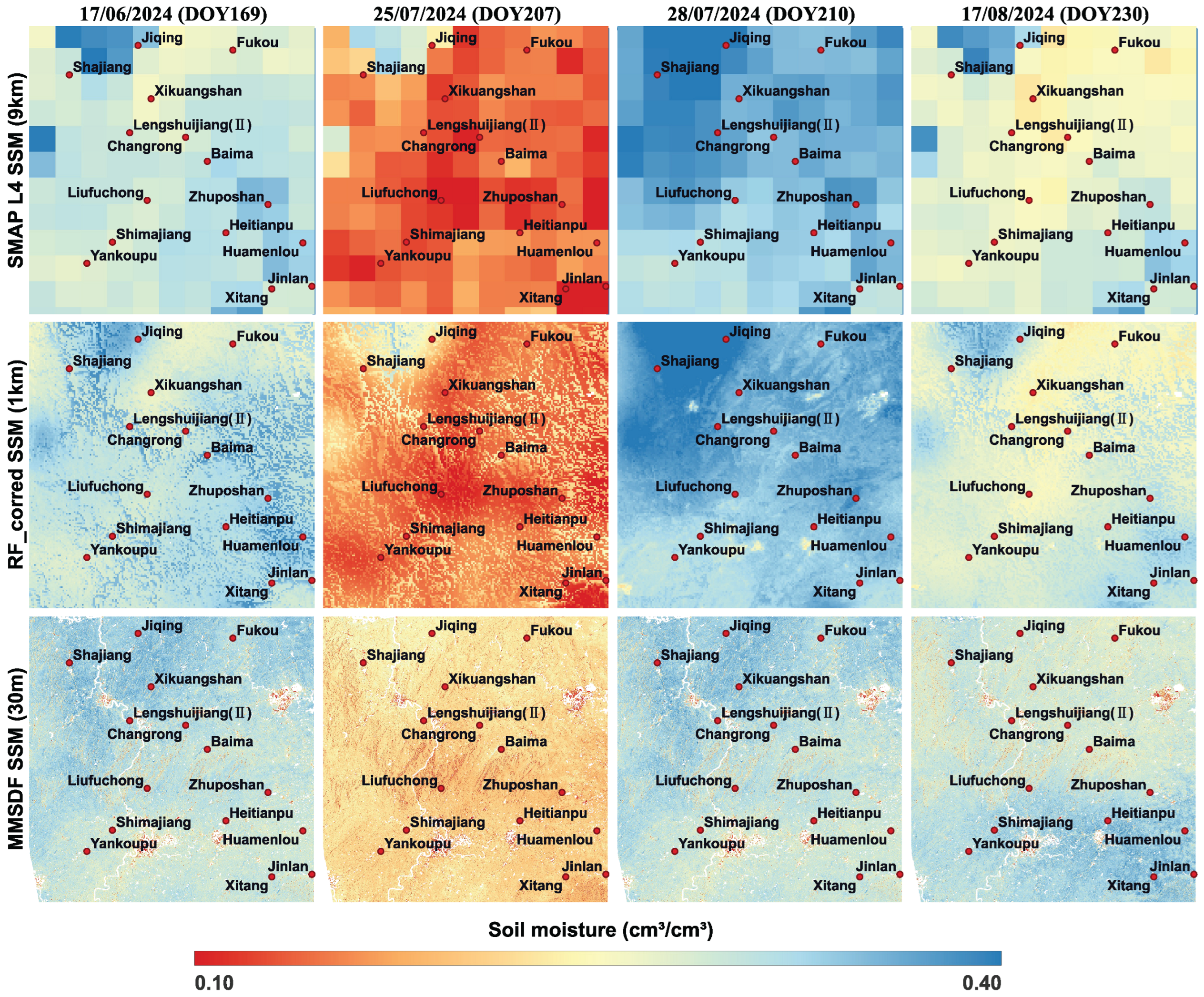
4. Results
4.1. Performance of Stage 1: Residual-Constrained Downscaling to 1 km Resolution
4.2. Performance of Stage 2: WCM Calibration for 30 m Retrieval
4.3. Performance of Stage 3: Daily 30 m Product via Spatiotemporal Fusion
4.4. Overall Framework Validation and Component Analysis
5. Discussion
5.1. Methodological Advancements and Framework Performance
5.2. Spatial Heterogeneity and Accuracy Analysis
5.3. Limitations and Future Research Directions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peng, J.; Loew, A.; Merlin, O.; Verhoest, N.E. A review of spatial downscaling of satellite remotely sensed soil moisture. Rev. Geophys. 2017, 55, 341–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sishodia, R.P.; Ray, R.L.; Singh, S.K. Applications of remote sensing in precision agriculture: A review. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Shen, H.; Li, T.; Li, Z.; Li, S.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, H.; Tan, W.; Yang, Q.; Wang, J.; et al. Deep learning in environmental remote sensing: Achievements and challenges. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 241, 111716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Jia, L. A method for downscaling FengYun-3B soil moisture based on apparent thermal inertia. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.W.; Bindlish, R.; O’Neill, P.; Fang, B.; Lakshmi, V.; Yang, Z.; Cosh, M.H.; Bongiovanni, T.; Collins, C.H.; Starks, P.J.; et al. Thermal hydraulic disaggregation of SMAP soil moisture over the continental United States. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 4072–4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, J.; Prasad, R.; Srivastava, P.K.; Yadav, S.A.; Yadav, V.P. Improving spatial representation of soil moisture through the incorporation of single-channel algorithm with different downscaling approaches. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, T.; Chen, G.; Zhu, K.; Wang, Q.; Wang, J. Detection of vegetation coverage changes in the Yellow River Basin from 2003 to 2020. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 138, 108818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, X.; Xie, H.; Yang, H.; Tan, X.; Wang, T.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Q.; Cao, J.; et al. Enhancing terrestrial net primary productivity estimation with EXP-CASA: A novel light use efficiency model approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2025, 326, 114790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Loew, A.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Niesel, J. Spatial downscaling of satellite soil moisture data using a vegetation temperature condition index. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 54, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Cai, C.; Liu, H.; Yang, B. Microwave and meteorological fusion: A method of spatial downscaling of remotely sensed soil moisture. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 1107–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, S.; Gunn, G.; Joosse, P.; Russell, H.A. A model for downscaling SMOS soil moisture using Sentinel-1 SAR data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 72, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Cui, Q.; Zhang, W.; Meng, L. An approach for downscaling SMAP soil moisture by combining Sentinel-1 SAR and MODIS data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, R.; Zhang, W.; Kragh, S.J.; Andreasen, M.; Jensen, K.H.; Fensholt, R.; Stisen, S.; Looms, M.C. Exploring the combined use of SMAP and Sentinel-1 data for downscaling soil moisture beyond the 1 km scale. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2021, 26, 3337–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojha, N.; Merlin, O.; Molero, B.; Suere, C.; Olivera-Guerra, L.; Ait Hssaine, B.; Amazirh, A.; Al Bitar, A.; Escorihuela, M.J.; Er-Raki, S. Stepwise disaggregation of SMAP soil moisture at 100 m resolution using Landsat-7/8 data and a varying intermediate resolution. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; He, Y.; Zhang, X. Nir-red spectra-based disaggregation of smap soil moisture to 250 m resolution based on oznet in southeastern australia. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, A.A.; Zha, Y.; Shi, L.; Ali, S.; Wang, X.; Zafar, Z.; Afzal, Z.; Tariq, M.A.U.R. Spatial downscaling and gap-filling of SMAP soil moisture to high resolution using MODIS surface variables and machine learning approaches over ShanDian River Basin, China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemohammad, S.H.; Kolassa, J.; Prigent, C.; Aires, F.; Gentine, P. Global downscaling of remotely sensed soil moisture using neural networks. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 5341–5356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colliander, A.; Fisher, J.B.; Halverson, G.; Merlin, O.; Misra, S.; Bindlish, R.; Jackson, T.J.; Yueh, S. Spatial downscaling of SMAP soil moisture using MODIS land surface temperature and NDVI during SMAPVEX15. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 2107–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, T.; Chen, G.; Tan, X.; Zhu, K. Convective clouds extraction from Himawari–8 satellite images based on double-stream fully convolutional networks. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 17, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Wen, F.; Wang, Q.; Sanchez, N.; Piles, M. Seamless downscaling of the ESA CCI soil moisture data at the daily scale with MODIS land products. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 126930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Zhao, T.; Shi, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, J. A Novel Downscaling Approach based on Multi-Frequency Microwave Radiometry toward Finer Scale Global Soil Moisture Mapping. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5302915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakigari, S.A.; Leconte, R. Enhancing spatial resolution of SMAP soil moisture products through spatial downscaling over a large watershed: A case study for the Susquehanna River Basin in the Northeastern United States. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eweys, O.A.; Escorihuela, M.J.; Villar, J.M.; Er-Raki, S.; Amazirh, A.; Olivera, L.; Jarlan, L.; Khabba, S.; Merlin, O. Disaggregation of SMOS soil moisture to 100 m resolution using MODIS optical/thermal and Sentinel-1 radar data: Evaluation over a bare soil site in Morocco. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Walker, J.P.; Rüdiger, C.; Panciera, R.; Gao, Y. Intercomparison of alternate soil moisture downscaling algorithms using active–passive microwave observations. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 14, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiß, T.; Jagdhuber, T.; Ramsauer, T.; Löw, A.; Marzahn, P. RTM-based downscaling of medium resolution soil moisture using Sentinel-1 data over agricultural fields. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 15463–15479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zhang, Z.; Long, Z.; Qin, Q. Downscaling SMAP soil moisture products with convolutional neural network. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 4051–4062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jing, W.; Wang, Q.; Xia, X. Generating high-resolution daily soil moisture by using spatial downscaling techniques: A comparison of six machine learning algorithms. Adv. Water Resour. 2020, 141, 103601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, T.; Shangguan, W.; Li, Q.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, F.; Li, J.; Liu, W.; Zhang, R. A spatial downscaling method for remote sensing soil moisture based on random forest considering soil moisture memory and mass conservation. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Sun, H.; Gao, J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, D.; Zhang, T.; Xu, H. PhySoilNet: A deep learning downscaling model for microwave satellite soil moisture with physical rule constraint. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2024, 135, 104290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Ge, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Heuvelink, G.B.; Atkinson, P.M. Downscaling AMSR-2 soil moisture data with geographically weighted area-to-area regression kriging. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 56, 2362–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Huang, J.; Mansaray, L.R. An improved surface soil moisture downscaling approach over cloudy areas based on geographically weighted regression. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 275, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, F.; Zhao, W.; Wang, Q.; Sánchez, N. A value-consistent method for downscaling SMAP passive soil moisture with MODIS products using self-adaptive window. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 58, 913–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Sánchez, N.; Lu, H.; Li, A. A spatial downscaling approach for the SMAP passive surface soil moisture product using random forest regression. J. Hydrol. 2018, 563, 1009–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Meng, Y.; Zhang, W.; Peng, J.; Meng, L. Downscaling SMAP soil moisture estimation with gradient boosting decision tree regression over the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 225, 30–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, W.; Dorjee, D.; Meng, L. A spatial downscaling method for SMAP soil moisture through visible and shortwave-infrared remote sensing data. J. Hydrol. 2020, 590, 125360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, J.; Park, S.; Rhee, J.; Baik, J.; Choi, M. Downscaling of AMSR-E soil moisture with MODIS products using machine learning approaches. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Jeong, J.; Zohaib, M.; Choi, M. Spatial disaggregation of ASCAT soil moisture under all sky condition using support vector machine. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2018, 32, 3455–3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Ge, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, H.; Heuvelink, G.B. A machine learning-based geostatistical downscaling method for coarse-resolution soil moisture products. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 14, 1025–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaszadeh, P.; Moradkhani, H.; Zhan, X. Downscaling SMAP radiometer soil moisture over the CONUS using an ensemble learning method. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 324–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, A.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, H. A neural-network based spatial resolution downscaling method for soil moisture: Case study of qinghai province. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Chen, G.; Zhang, X.; Liu, C.; Wang, J.; Tan, X.; Zhou, W.; He, C. LMFNet: Lightweight Multimodal Fusion Network for high-resolution remote sensing image segmentation. Pattern Recognit. 2025, 164, 111579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, S.; Judge, J.; Bongiovanni, T.; Rangarajan, A.; Ranka, S. Disaggregation of remotely sensed soil moisture in heterogeneous landscapes using holistic structure-based models. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 4629–4641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamouz, M.; Alipour, R.S.; Roohinia, M.; Fereshtehpour, M. A remote sensing driven soil moisture estimator: Uncertain downscaling with geostatistically based use of ancillary data. Water Resour. Res. 2022, 58, e2022WR031946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entekhabi, D.; Njoku, E.G.; O’neill, P.E.; Kellogg, K.H.; Crow, W.T.; Edelstein, W.N.; Entin, J.K.; Goodman, S.D.; Jackson, T.J.; Johnson, J.; et al. The soil moisture active passive (SMAP) mission. Proc. IEEE 2010, 98, 704–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claverie, M.; Ju, J.; Masek, J.G.; Dungan, J.L.; Vermote, E.F.; Roger, J.C.; Skakun, S.V.; Justice, C. The Harmonized Landsat and Sentinel-2 surface reflectance data set. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 219, 145–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiroma, G.H.; Fattahi, H.; Meyer, F.; Jeong, S.H.; Cinquini, L.; Collins, S.; Chapman, B.; Chan, S.K.; Handwerger, A.L.; Bekaert, D. The opera radiometric terrain corrected SAR backscatter from Sentinel-1 (RTC-S1) product. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2023-2023 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Pasadena, CA, USA, 16–21 July 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 880–883. [Google Scholar]
- Attema, E.; Ulaby, F.T. Vegetation modeled as a water cloud. Radio Sci. 1978, 13, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasirzadehdizaji, R.; Balik Sanli, F.; Abdikan, S.; Cakir, Z.; Sekertekin, A.; Ustuner, M. Sensitivity analysis of multi-temporal Sentinel-1 SAR parameters to crop height and canopy coverage. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, T.; Shi, J.; Wang, H.; Ji, D.; Yao, P.; Zheng, J.; Zhao, X.; Xu, X. 1-km soil moisture retrieval using multi-temporal dual-channel SAR data from Sentinel-1 A/B satellites in a semi-arid watershed. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 284, 113334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindlish, R.; Barros, A.P. Parameterization of vegetation backscatter in radar-based, soil moisture estimation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2001, 76, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Chen, J.; Gao, F.; Chen, X.; Masek, J.G. An enhanced spatial and temporal adaptive reflectance fusion model for complex heterogeneous regions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2610–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, J.; Chen, G.; Wang, T.; Wang, Q.; Wang, K.; Miao, T. Spatio-Temporal Fusion of Landsat and MODIS Data for Monitoring of High-Intensity Fire Traces in Karst Landscapes: A Case Study in China. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanaga, D.; Van De Kerchove, R.; Daems, D.; De Keersmaecker, W.; Brockmann, C.; Kirches, G.; Wevers, J.; Cartus, O.; Santoro, M.; Fritz, S.; et al. ESA WorldCover 10 m 2021 v200. Zenodo 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
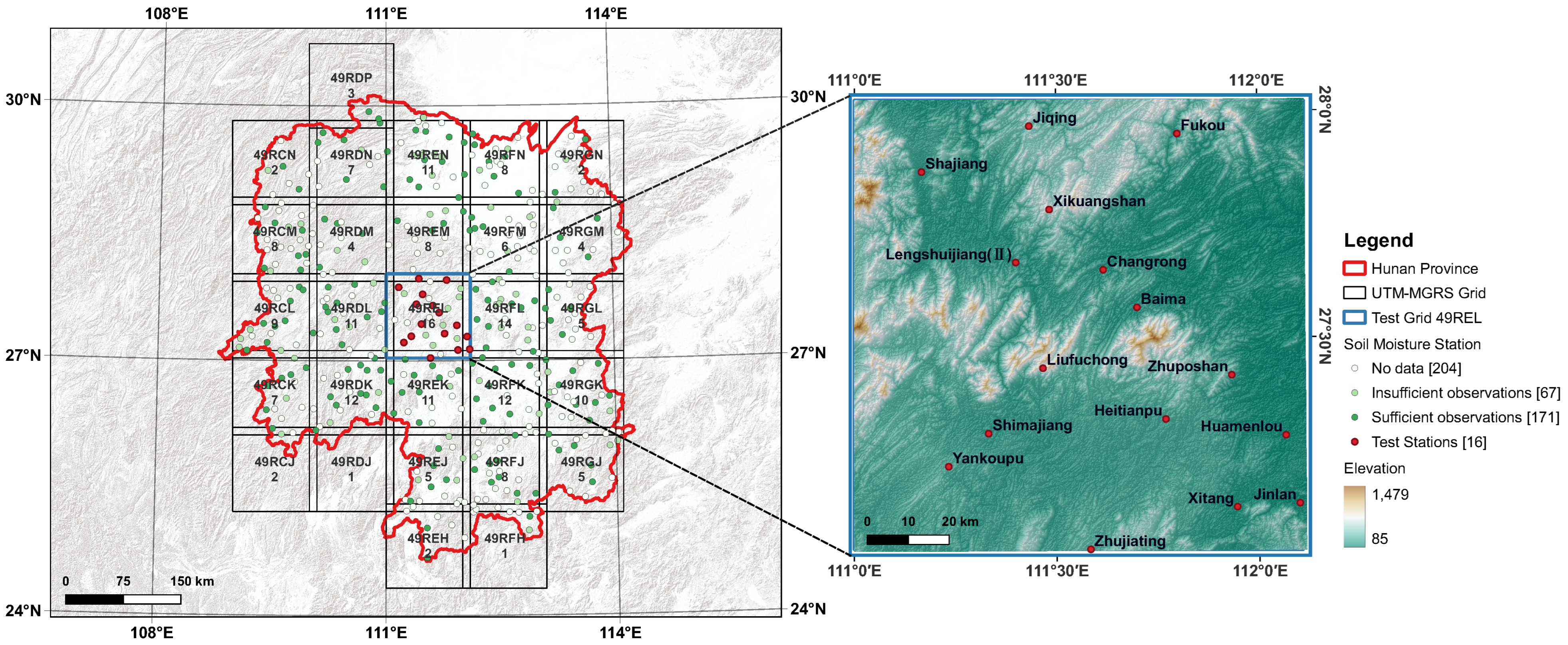
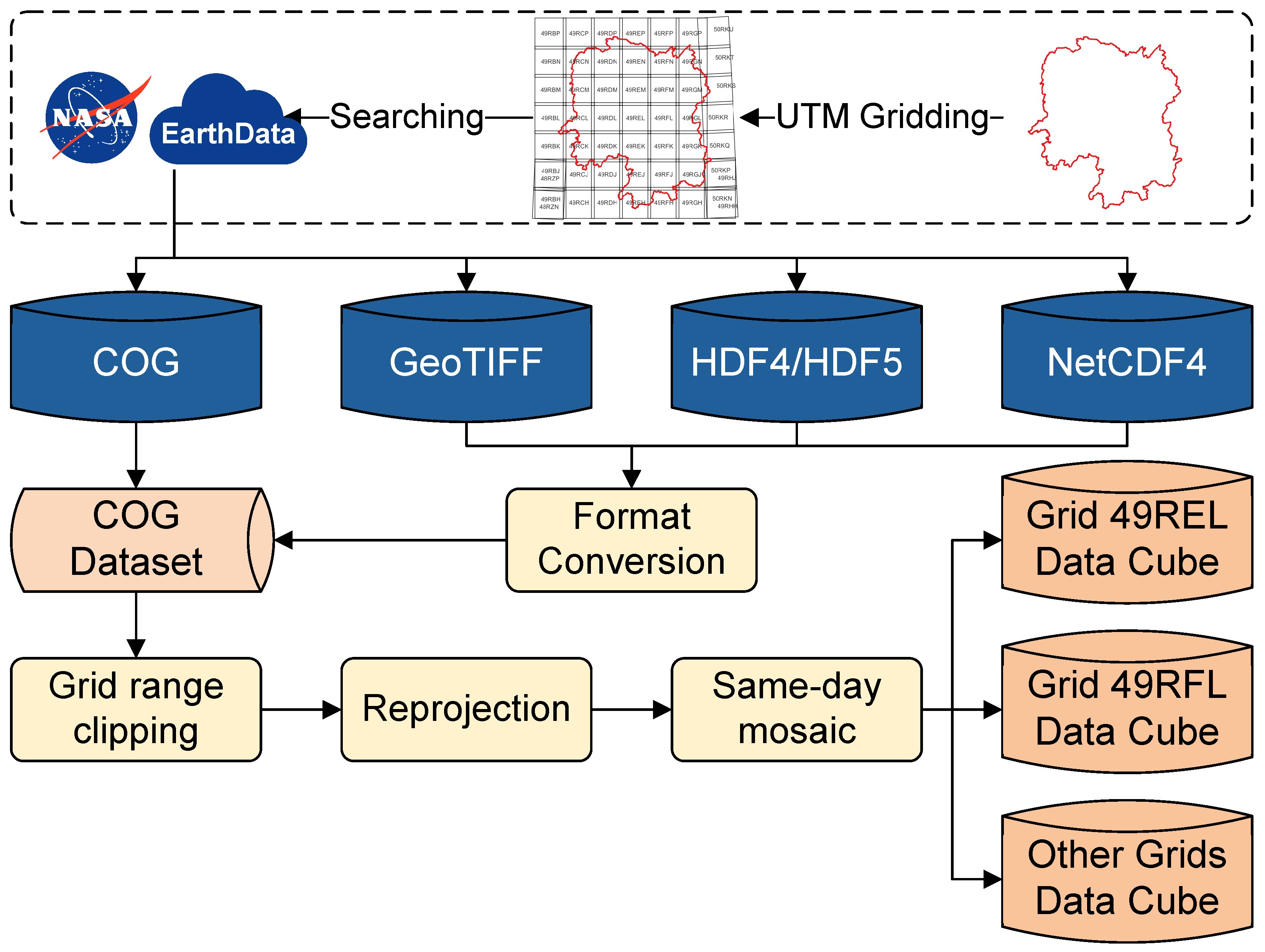
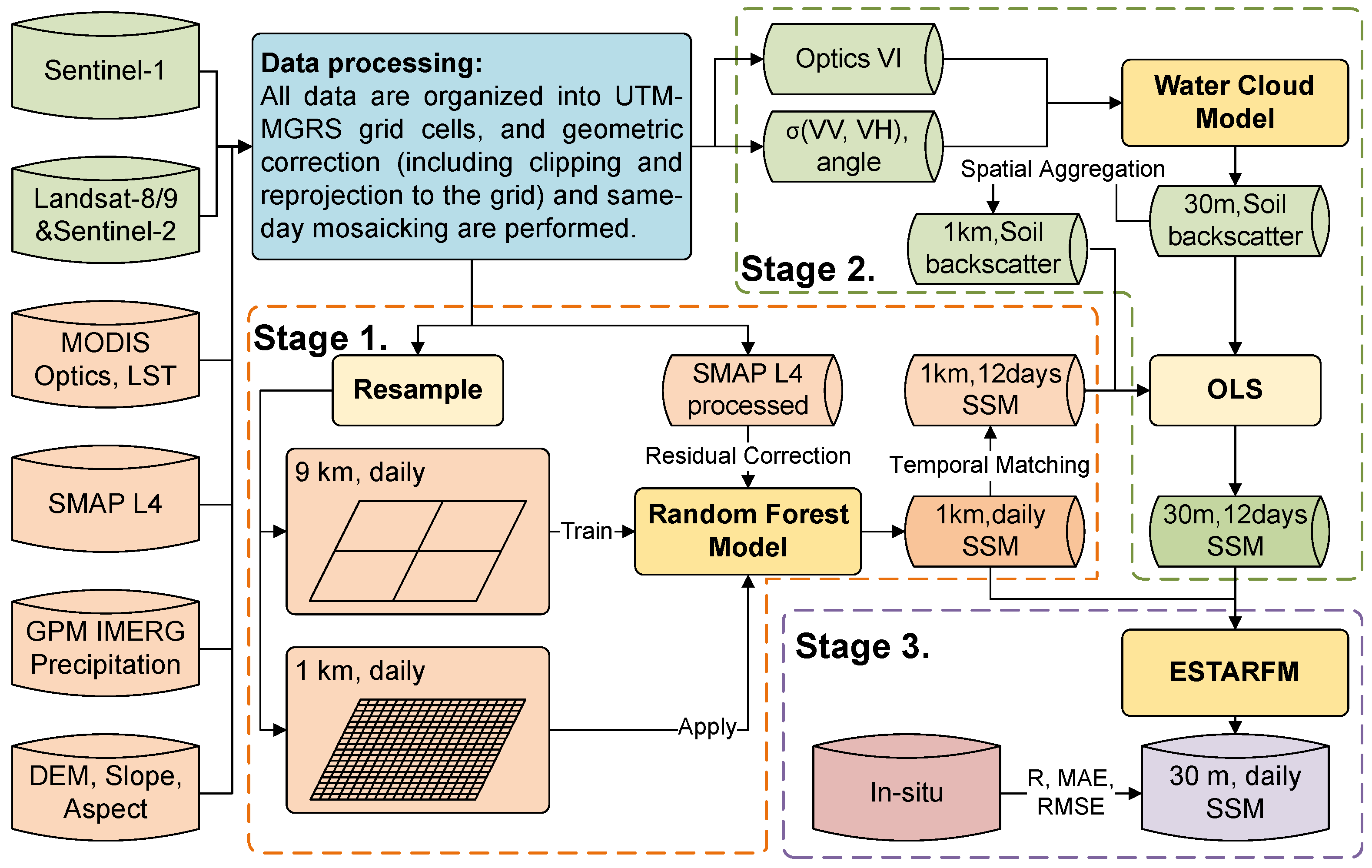

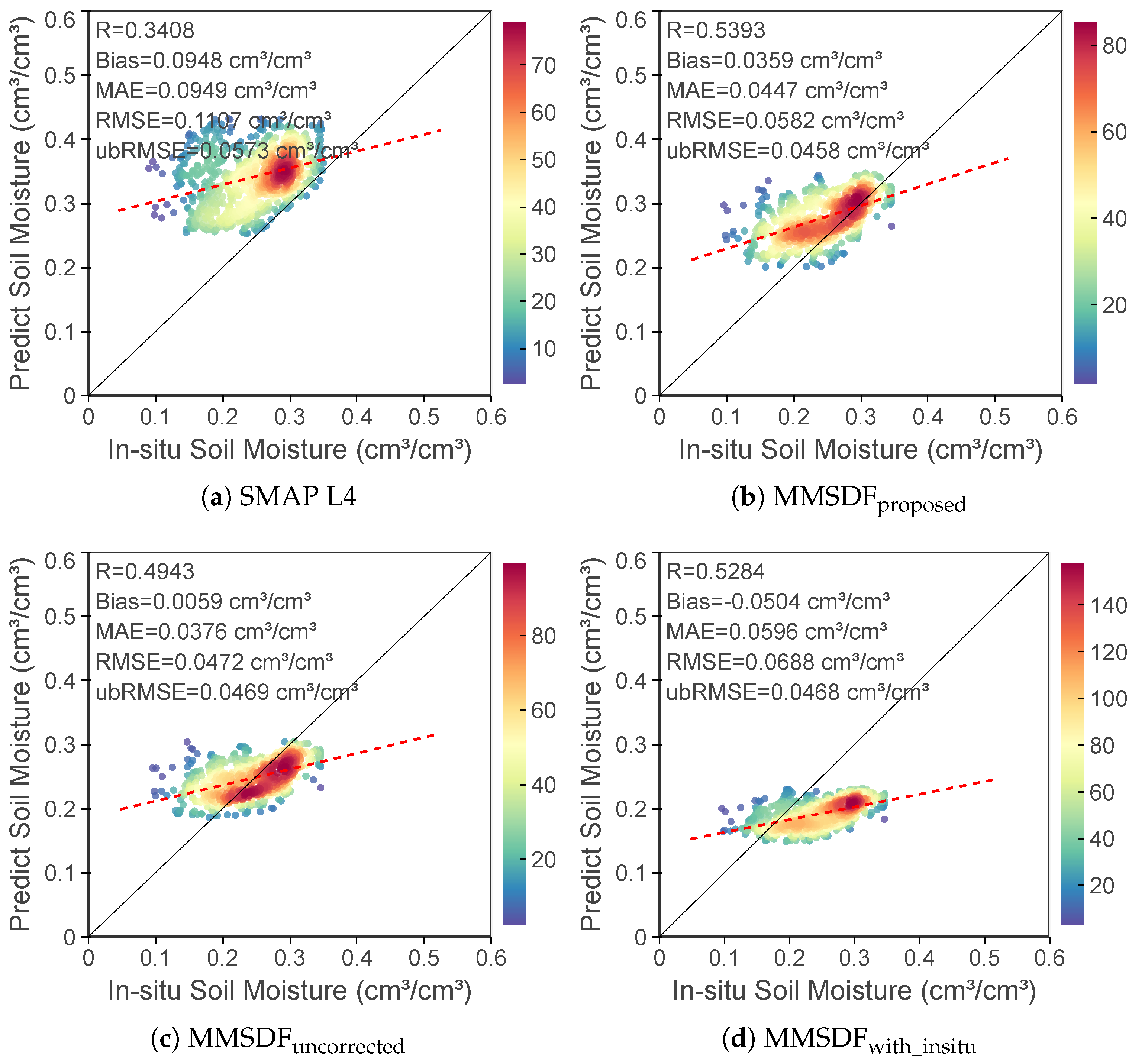


| Station Name | Location | Elevation (m) | R with SMAP L4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Jinlan | (112.1000, 27.1333) | 157 | 0.7403 |
| Changrong | (111.6167, 27.6500) | 176 | 0.7609 |
| Baima | (111.7000, 27.5667) | 186 | 0.7045 |
| Huamenlou | (112.0667, 27.2833) | 122 | 0.8176 |
| Zhuposhan | (111.9333, 27.4167) | 266 | 0.8359 |
| Xitang | (111.9455, 27.1257) | 156 | 0.7779 |
| Lengshuijiang (II) | (111.4000, 27.6667) | 187 | 0.6939 |
| Heitianpu | (111.7700, 27.3200) | 275 | 0.7974 |
| Zhujiating | (111.5833, 27.0333) | 343 | 0.7252 |
| Liufuchong | (111.4667, 27.4333) | 529 | 0.7969 |
| Yankoupu | (111.2333, 27.2167) | 344 | 0.8396 |
| Xikuangshan | (111.4833, 27.7833) | 575 | 0.7568 |
| Shajiang | (111.1667, 27.8667) | 213 | 0.7977 |
| Shimajiang | (111.3319, 27.2894) | 212 | 0.8215 |
| Jiqing | (111.4336, 27.9675) | 390 | 0.7389 |
| Fukou | (111.8015, 27.9496) | 336 | 0.3638 |
| Data Type | Data Product | Time Range | Spatial Res. | Temporal Res. | Latency | Effective Period |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil Moisture | SPL4SMGP | 2015–present | 9 km | 3 h | 1.5 d | 2-3 d |
| Medium-res. N-BRDF | HLS L30 | 2013–present | 30 m | 8 d | 1.7 d | 10 d |
| HLS S30 | 2015–present | 30 m | 5 d | 1.7 d | 7 d | |
| Low-res. N-BRDF | MCD43A4 | 2000–present | 500 m | 1 d | 12 d | 13 d |
| SAR | RTC-S1 | 2013–present | 30 m | 12 d | 3 d | 15 d |
| LST | MOD11A1 | 2000–present | 1 km | 1 d | 5 d | 6 d |
| Precipitation | GPM IMERGDL | 1998–present | 0.1° | 1 d | 2 d | 3 d |
| Terrain | NASADEM | – | 30 m | – | – | – |
| Configuration | R | Bias | MAE | RMSE | ubRMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SMAP L4 | 0.34 | 0.095 | 0.095 | 0.111 | 0.057 |
| SMAP L | 0.38 | 0.096 | 0.096 | 0.111 | 0.055 |
| 0.53 | 0.112 | 0.112 | 0.122 | 0.048 | |
| 0.44 | 0.106 | 0.106 | 0.119 | 0.054 |
| Station Name | R | Bias | MAE | RMSE | ubRMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jinlan | 0.6030 | 0.0078 | 0.0200 | 0.0298 | 0.0288 |
| Changrong | 0.7113 | 0.0294 | 0.0503 | 0.0609 | 0.0533 |
| Baima | 0.6564 | 0.0733 | 0.0882 | 0.1104 | 0.0826 |
| Huamenlou | 0.6608 | 0.1935 | 0.1935 | 0.2011 | 0.0550 |
| Zhuposhan | 0.7900 | 0.0593 | 0.0593 | 0.0637 | 0.0232 |
| Xitang | 0.7025 | 0.1103 | 0.1103 | 0.1139 | 0.0284 |
| Lengshuijiang (II) | 0.5142 | 0.0551 | 0.0592 | 0.0696 | 0.0426 |
| Heitianpu | 0.7511 | 0.0774 | 0.0774 | 0.0843 | 0.0333 |
| Zhujiating | 0.6386 | 0.0279 | 0.0302 | 0.0369 | 0.0241 |
| Liufuchong | 0.7430 | 0.0061 | 0.0263 | 0.0307 | 0.0301 |
| Yankoupu | 0.6847 | 0.0143 | 0.0201 | 0.0238 | 0.0191 |
| Xikuangshan | 0.7285 | 0.0691 | 0.0699 | 0.0829 | 0.0458 |
| Shajiang | 0.5298 | 0.1026 | 0.1039 | 0.1182 | 0.0587 |
| Shimajiang | 0.8207 | 0.0064 | 0.0151 | 0.0187 | 0.0176 |
| Jiqing | 0.6410 | 0.0817 | 0.0817 | 0.0846 | 0.0221 |
| Fukou | 0.2474 | 0.0147 | 0.0574 | 0.0628 | 0.0611 |
| Case | Configuration | In Situ | R | Bias | MAE | RMSE | ubRMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (a) | SMAP L4 | × | 0.34 | 0.095 | 0.095 | 0.111 | 0.057 |
| (b) | × | 0.54 | 0.036 | 0.045 | 0.058 | 0.046 | |
| (c) | × | 0.49 | 0.006 | 0.038 | 0.047 | 0.047 | |
| (d) | ✔ | 0.53 | 0.060 | 0.069 | 0.047 |
| Land Cover Class | Number of In Situ | R | Bias | MAE | RMSE | ubRMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Built-up | 4 | 0.694 ± 0.042 | 0.053 ± 0.061 | 0.054 ± 0.058 | 0.061 ± 0.058 | 0.026 ± 0.007 |
| Tree cover | 5 | 0.656 ± 0.229 | 0.055 ± 0.045 | 0.059 ± 0.002 | 0.064 ± 0.007 | 0.043 ± 0.031 |
| Grassland | 4 | 0.686 ± 0.069 | 0.049 ± 0.076 | 0.060 ± 0.058 | 0.072 ± 0.059 | 0.050 ± 0.012 |
| Cropland | 3 | 0.641 ± 0.145 | 0.082 ± 0.048 | 0.082 ± 0.044 | 0.085 ± 0.050 | 0.022 ± 0.021 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, H.; Wang, T.; Xiong, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, G.; Zhang, K.; Wang, Q. A Microwave–Optical Multi-Stage Synergistic Daily 30 m Soil Moisture Downscaling Framework. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 3677. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17223677
Xie H, Wang T, Xiong Y, Zhang X, Zhang Y, Chen G, Zhang K, Wang Q. A Microwave–Optical Multi-Stage Synergistic Daily 30 m Soil Moisture Downscaling Framework. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(22):3677. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17223677
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Hong, Tong Wang, Yujiang Xiong, Xiaodong Zhang, Yu Zhang, Guanzhou Chen, Kaiqi Zhang, and Qing Wang. 2025. "A Microwave–Optical Multi-Stage Synergistic Daily 30 m Soil Moisture Downscaling Framework" Remote Sensing 17, no. 22: 3677. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17223677
APA StyleXie, H., Wang, T., Xiong, Y., Zhang, X., Zhang, Y., Chen, G., Zhang, K., & Wang, Q. (2025). A Microwave–Optical Multi-Stage Synergistic Daily 30 m Soil Moisture Downscaling Framework. Remote Sensing, 17(22), 3677. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17223677







