Highlights
What are the main findings?
- Employ a compact feature extraction scheme.
- Design an out-of-distribution feature inference module.
- Propose a novel knowledge-sharing retraining mechanism.
What is the implication of the main finding?
- The compact feature extraction scheme can constrain intra-class feature compactness to preserve more feature space for unknown classes.
- The out-of-distribution feature inference module can provide the requisite prior knowledge for the ATR model to effectively recognize unknown target samples.
- The knowledge-sharing retraining mechanism ensures that the ATR model can continuously review the knowledge of known samples while learning the knowledge of unknown samples.
Abstract
The efficacy of data-driven automatic target recognition (ATR) algorithms relies on the prior knowledge acquired from the target sample set. However, the lack of knowledge of high-value unknown target samples hinders the practical application of existing ATR models, as the acquisition of this SAR imagery is often challenging. In this paper, we propose an out-of-distribution knowledge inference-based approach for the implementation of open-set-recognition tasks in SAR imagery. The proposed method integrates two modules: out-of-distribution feature inference and a knowledge-sharing retrain mechanism. First, the proposed out-of-distribution feature inference module aims to provide the requisite prior knowledge for the ATR model to effectively recognize unknown target samples. Furthermore, the aforementioned module also employs a compact feature extraction scheme to mitigate the potential overlap between the constructed out-of-distribution feature distribution and the known sample feature distribution. Finally, the proposed method employs the novel knowledge-sharing retraining mechanism to learn prior knowledge of unknown SAR target samples. Several experimental results show the superiority of the proposed approach based on the Moving and Stationary Target Acquisition and Recognition (MSTAR) data set. Some ablation experiments also demonstrate the role of each module of the proposed approach. Even when one category of target sample information is completely absent from the training set, the recognition accuracy of the proposed approach still achieves .
1. Introduction
Synthetic aperture radar (SAR) possesses operational capabilities in all weather conditions, during both day and night, making it an important sensor for remote sensing in the field of earth observation. Automatic target recognition (ATR) in SAR imagery is a crucial application of SAR technology that has been extensively utilized in the domains of military and homeland security [1]. The rapid advancement of machine learning algorithms has significantly propelled the progress of SAR ATR technology over the past decade [2,3,4,5].
Among the many technologies, the data-driven SAR imagery recognition algorithm has made a significant contribution to enhancing the performance of the ATR model. The utilization of data-driven SAR ATR algorithms has a rich historical background, with its evolution being attributed to extensive research endeavors. On the one hand, feature extraction algorithms, including linear discriminant analysis (LDA) [6,7,8], principal component analysis (PCA) [9,10], and nonnegative matrix factorization (NMF) [11,12,13], aim to discover an optimal data representation for SAR target samples. On the other hand, classifier algorithms, such as support vector machine (SVM) [14,15,16] and random forest [17,18,19], can also effectively delineate decision boundaries between distinct target samples based on the acquired data representation. In general, the performance of these methods remains excellent when the SAR target sample categories are comprehensive and the number is sufficiently abundant.
However, training an ATR model using the SAR target sample set containing all categories is a significant challenge or even an unrealistic assumption in practical scenarios [20,21]. This may easily trigger the inherent risks of data-driven algorithms: the SAR ATR model misrecognizes unknown target samples as known target samples with high confidence. Moreover, some infrequent unknown target samples may have extremely important recognition value for the ATR model. Obviously, the open-set-recognition (OSR) problem poses a significant challenge in practical applications of the ATR model.
The essence of the aforementioned phenomenon lies in the failure of the ATR model to acknowledge the open space risks shown in Figure 1 [22,23]. Specifically, ATR models based on the closed-set assumption usually divide the feature space into several regions based on known target samples, including those regions that are far away from various categories of known target samples. The open space risk, which refers to the potential danger introduced to the ATR model when considering samples located in feature space regions significantly distant from known target samples as known samples. This phenomenon is consistent with the logic of human beings recognizing unfamiliar things [24]. Human beings’ understanding of everything exists within boundaries. When this boundary is exceeded, such things may become completely unfamiliar to humans. The open-set assumption is designed to enable the ATR model to recognize and describe this boundary. In other words, the open-set assumptions aim to represent the buffer zone of the target sample data distribution and risk. The ATR model should exercise caution when recognizing target samples that are located significantly distant from the known samples in the feature space.
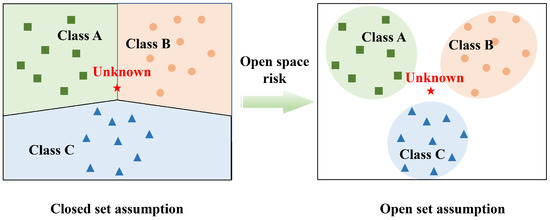
Figure 1.
The differences in the regional division of feature space by the ATR model under different assumptions. Under the assumption of a closed set, the ATR model is limited to recognizing target samples solely as known samples.
Drawing on the current perspective of open-set recognition, the task of unknown SAR target sample recognition can be addressed through a discrimination-based approach as well as a generation-based approach [25]. The discrimination-based approaches aim to construct open space risks and utilize pre-set criteria or thresholds for distinguishing known target samples from unknown target samples [26,27,28,29,30]. For example, the Weibull-calibrated Support Vector Machine (W-SVM) model integrates statistical extreme value theory (EVT) with two separate SVMs, effectively achieving the constraints associated with open space risks [31]. Similarly, Giusti et al. propose the utilization of OpenMax as a replacement for SoftMax in the neural network architecture, aiming to discover unknown target samples by pre-setting a risk threshold [32]. Ma et al. also proposed an incremental open-set-recognition method for the continuous accumulation of unknown samples [33]. However, the efficacy of these methods heavily relies on the appropriate setting of thresholds, which remains a significant challenge that they currently confront.
The generation-based approaches aim to construct synthetic data and facilitate the recognition model in discovering unknown target samples by providing presumed prior knowledge [34]. Among them, Neal, L. et al. enhance the recognition model by equipping it with the capability to discover unknown target samples through inference of sample data in proximity to the decision boundary [35]. The efficacy of such methodologies hinges upon a sophisticated generation model. To streamline the synthetic data construction process, Schlachter, P. et al. categorize the target samples into typical and atypical data sets, utilizing the latter to substitute for unknown target samples [36,37]. In general, the development of a reasonable synthetic data generation model is evidently the fundamental cornerstone of generation-based approaches.
Overall, discrimination-based approaches that lack prior information tend to lose reference when setting thresholds, thereby compromising the generalization ability of the ATR model. Conversely, generation-based methods that rely solely on prior information are prone to confusion when learning the distributions of both new and old sample data, resulting in degraded recognition performance. Therefore, it is necessary to propose a two-pronged approach to address the open-set-recognition task. This paper proposes an out-of-distribution knowledge inference-based approach for the implementation of open-set-recognition tasks in SAR imagery. First, the proposed approach employs out-of-distribution feature inference to provide the requisite prior knowledge for the model to effectively recognize unknown target samples. Moreover, the proposed method simultaneously considers the risk of potential overlap between the constructed out-of-distribution feature distribution and the known sample feature distribution. In order to overcome the above problems, the proposed method adopts a compact feature extraction scheme of SAR target samples. Finally, based on the compact features of various categories of target samples, the proposed method utilizes a knowledge-sharing retraining mechanism in an innovative manner to recognize unknown SAR target samples.
The remaining section of this paper is organized as follows: In Section 2, the related work of the proposed approach is introduced. In Section 3, the detailed model framework and implementation details of the proposed method is given; Section 4 presents the experimental results of the proposed method, and Section 5 introduces the conclusions of the proposed method.
2. Related Work
2.1. The Necessity of an Open-Set ATR Model
The majority of existing SAR ATR models are developed under the assumption of a closed set. The closed-set ATR models implement the recognition of SAR target samples by partitioning the feature space into a series of predetermined regions. The logical flaw in the aforementioned model lies in the assumption that samples distant from known feature regions in the feature space can be regarded as known target samples. Therefore, the open space risk posed by these regions needs to be accurately measured, which can be expressed in the following form:
where the measurable recognition function is expressed by f. The open space risk expresses the ratio between the relative measure of open space O and the overall measure of feature space . The open-set-recognition aims to make the ATR model aware of this open space risk to discover unknown target samples.
Moreover, merely relying on the open space risk to evaluate the difficulty of an open-set-recognition problem is insufficient. Intuitively, the greater the number of unknown sample categories that require recognition, the more formidable the challenge faced by the ATR model. In this context, the concept of openness is employed to characterize the intricacy associated with the open-set-recognition problem [38]. The openness can be expressed in the following form:
where and represent the number of categories in the training set and test set, respectively. It is evident from the definition of openness that as the degree of openness increases, the complexity of open-set recognition also escalates. Conversely, when the level of openness approaches zero, this problem transforms into closed-set recognition.
Based on the concepts of open space risk and openness , the open-set-recognition problem can be defined as follows:
where denotes the empirical risk of the open-set-recognition model when applied to known target samples in the training set . F represents the function family of measurable recognition functions f contained in the entire feature space. is a regularization constant. In general, the objective of the open-set-recognition model, as demonstrated by Equation (3), is to attain a high recognition accuracy for both known and unknown target samples in diverse scenarios with varying degrees of openness.
2.2. The Current Open-Set Approaches
The current approaches to open-set recognition can be categorized into generation-based and discrimination-based methods. Generation-based methods aim to construct synthetic data and facilitate the recognition model in discovering unknown target samples. In recent years, generative adversarial networks (GANs) have emerged as a prominent research direction in the field of synthetic data generation, exhibiting some advancements in SAR target sample generation [39,40]. The architecture of conventional GANs consists of a deconvolutional and a convolutional network. The deconvolutional network, called generator G, is trained to generate samples from data distribution , by changing the noise z from noise distribution to , where . The convolutional network, called discriminator D, is trained to determine whether the sample generated by the generator is a real or fake sample during the process of training. The loss function of conventional GANs can be expressed as
where refers to the probability that D discriminates that the target sample x comes from the real sample distribution .
The optimization goal of GANs is to simulate known target sample data distribution and generate synthetic data that closely aligns with this distribution. However, the simulation of the unknown target sample data distribution poses a formidable challenge. Although the introduction of OpenGAN [41] offers a potential solution for the aforementioned issues, ongoing research is still being conducted on the generation of unknown SAR target samples. Therefore, the discrimination-based methods for open-set recognition are gradually being employed to discover unknown SAR target samples. The Cevikalp [42] uses support vector machines (SVM) for the recognition of unknown samples, wherein the open space risk is defined in the following form:
where a and b represent the two hyperplanes that are required to be separated using SVM. The marginal distances of the corresponding hyperplane is represented by and , respectively. is the separation needed to account for all positive data. The essence of the aforementioned approach lies in utilizing thresholds and to fine-tune the relative significance attributed to margin spaces and . In this scenario, only target samples located within the region bounded by two hyperplanes can be recognized as known samples, and the remaining samples are considered unknown samples. Moreover, Giusti et al. utilized the OpenMax instead of softmax to achieve open-set recognition of SAR target samples [43]. The open-set-recognition task can be partially addressed through discrimination-based approaches, to a certain degree. However, the generalizability of those methods is often limited due to the application-specific nature of different threshold settings.
3. The Proposed Method
3.1. The Motivations for the Proposed Method
The closed-set recognition models encounter significant challenges when confronted with unknown target samples. The closed-set-based ATR models, including those based on deep learning, fail to address the aforementioned issues. The conventional ATR recognition model discovers that there are two obstacles in unknown target samples. First, the ATR model completely lacks the prior knowledge to recognize unknown target samples. Most ATR models need to rely on data distribution to determine the category of target samples. The absence of prior knowledge regarding unknown target samples hinders the ATR model from comprehending the underlying data distribution of these specific samples. Second, the ATR model fails to comprehend open space risks. The ATR model is accustomed to roughly dividing the feature space into several regions. The number of regions is consistent with the number of target sample categories. However, if the features of the target sample are far away from the feature regions of all known target samples, there is a great risk in recognizing such samples as known target samples.
Therefore, the proposed approach aims to address the aforementioned challenges by adopting two distinct modules, as illustrated in Figure 2. First, the proposed approach utilizes an out-of-distribution feature inference module to estimate the data distribution of unknown target samples. The out-of-distribution feature inference module can provide the necessary prior knowledge for the ATR model to recognize unknown samples. Moreover, merely providing the ATR model with the inferred data distribution of the unknown target samples is insufficient. The unknown target samples may exist in regions far away from all known sample features in the feature space. Second, the ATR model should accurately define the effective discriminatory region for diverse target sample features, encompassing both known target samples and generated unknown target samples. In response to the above motivations, the proposed approach incorporates a knowledge-sharing retraining mechanism to facilitate the ATR model in effectively delimiting discriminatory regions among diverse target samples.
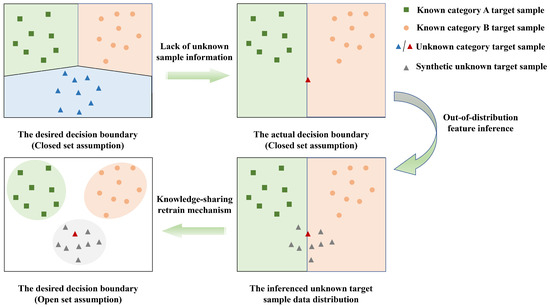
Figure 2.
The detailed motivations about the proposed approach. (1) Upper left: the desired decision boundary of the ATR model under the closed-set assumption. (2) Upper right: the actual decision boundary of the ATR model under the closed-set assumption. (3) Lower right: the inferred distribution of unknown target samples. (4) Lower left: the desired decision boundary of the ATR model under the open-set assumption.
3.2. The Out-of-Distribution Feature Inference of Unknown Target Sample
The objective of out-of-distribution feature inference of unknown target samples is to acquire effective prior knowledge regarding these samples. Moreover, the out-of-distribution feature inference needs to be based on the data distribution of known target samples. Therefore, the proposed method must take into account the potential risk of distribution overlap between the known sample data distribution and the constructed unknown sample data distribution. This prompts out-of-distribution feature inference to be implemented according to the process shown in Figure 3.
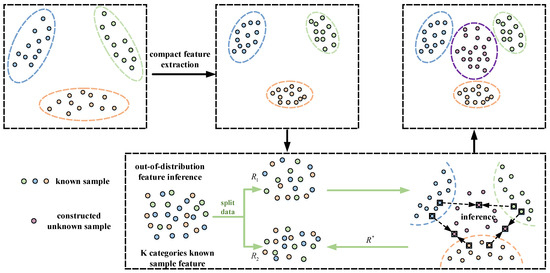
Figure 3.
The detailed scheme of the out-of-distribution feature inference module.
It is crucial to extract the compact feature from the known target sample before inferring the out-of-distribution feature of the unknown target sample. The objective of compact feature extraction for target samples is to acquire discriminative features characterized by high intra-class compactness and low inter-class similarity. The achievement of high intra-class compactness necessitates the aggregation from the same category target samples in the feature space, ensuring the compactness of the feature space of known target samples. Moreover, in order to accommodate unknown target samples, it is essential to enhance the separation of features belonging to different categories in the discriminant space with low inter-class similarity, thereby ensuring sufficient feature space allocation.
Specifically, taking the cross-entropy loss function, which is widely employed in convolutional neural networks, as an illustrative example, its mathematical expression can be formulated as follows:
where is the expected output of the target sample. R represents the known target sample set. is the result of the i-th logical unit corresponding to a target sample. is the result of all the logical units corresponding to a target sample. If is expressed as the feature vector of target samples, and is used as the category center of the is designated as the category center for the category to which the feature vector belongs, and the additional constraints can be expressed in the following form:
Among them, refers to the constraint coefficient. After the ATR model obtains the compact feature of the known target sample, the aforementioned loss function is subsequently reformulated as follows:
The definitions of the above functions are designed to enhance intra-class compactness and inter-class separation.
The compact feature extraction of known target samples is a prerequisite for out-of-distribution feature inference of unknown target samples. The obtained compact features allow for the even division of the known sample feature, belonging to K categories, into two subsets: and . Based on the feature subset , target sample feature vectors and are randomly selected from distinct categories within . Let any , select the manifold mixing-up coefficient that conforms to a specific distribution , and construct the unknown target sample out-of-distribution feature in the manifold space according to the following inference rule:
where i not being equal to j is a strict constraint in Equation (9). Then, the proposed method can construct a new subset R*, which encompasses the data distribution information of unknown target samples, by following the aforementioned steps. Finally, the feature subset is ultimately combined with the feature subset R*, resulting in a -category feature set that encompasses prior information pertaining to the unknown target sample.
3.3. The Knowledge-Sharing Retrain Mechanism for Target Sample Features
The out-of-distribution feature inference can provide the ATR model with essential prior knowledge regarding unknown target samples. However, the utilization of the aforementioned -category feature set alone for training an ATR model fails to meet the anticipated level of recognition performance. As stated in Equation (3), an open-set-recognition model must possess not only high accuracy in recognizing unknown target samples but also the ability to precisely recognize all known target samples. Even if the constructed target sample set is utilized for training the -category recognition model, it remains challenging to achieve the expected recognition performance.
Therefore, the proposed approach employs a knowledge-sharing retraining mechanism for training the open-set-recognition model, as illustrated in Figure 4. The knowledge-sharing retrain mechanism facilitates the ATR model in allocating equal attention to both known and unknown target samples. In essence, the proposed module trains two convolutional neural networks with the same architecture simultaneously. Among them, one neural network is trained using the feature set of known samples from K categories, while the other neural network is trained using the feature set constructed from categories. This allows the two neural networks to receive learning feedback from the K categories recognition results and the -categorhy recognition results, respectively. Moreover, the weights between the two neural networks are shared with each other, which ensures that the ATR model can continuously review the knowledge of known samples while learning unknown sample knowledge.
Motivated by the proposed scheme, the loss function of the proposed method is transformed into the following expression:
where refers to the constructed sample feature set. Assume the outputs of the known sample ATR model and the unknown sample ATR model for the Kth category target sample are denoted as and , respectively. The and can be formulated as
The above loss function simultaneously implements out-of-distribution feature inference of an unknown target sample and knowledge-sharing retraining mechanism. The proposed method ensures the accurate discovery of unknown samples while minimizing its impact on the recognition accuracy of known samples.
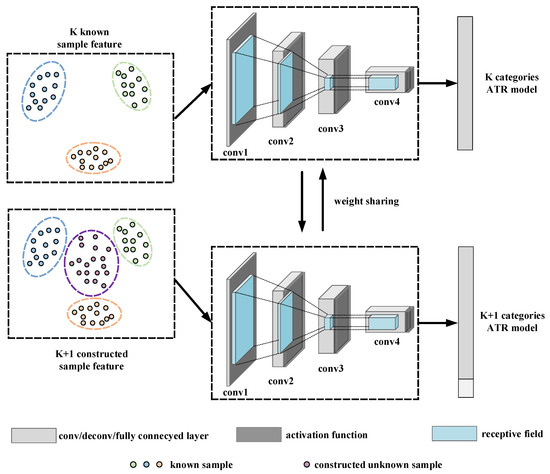
Figure 4.
The detailed scheme of the knowledge-sharing retrain mechanism module.
4. Experimental Results
The proposed method is devised to address the following issues: (1) the proposed method enables the extraction of discrimination knowledge from known data distribution to infer the unknown target sample, (2) the proposed method enables the recognition of unknown samples while preserving the discriminative information of known samples, and (3) the proposed method maintains consistent recognition performance across varying openness conditions. Therefore, the experiments were carried out in terms of the above three aspects to demonstrate the advantages of the proposed method in this paper.
The experiments were performed on the moving and stationary target acquisition and recognition (MSTAR) data set. The MSTAR consists of X-band and HH polarization SAR target samples with a 0.3 m resolution. All the target samples were captured at two different pitch angles, 15 degrees and 17 degrees. All the target slices are RAW data, as shown in Figure 5. In general, the experiment uses the 17-degree pitch angle target samples as the training set and utilizes the 15-degree pitch angle target samples as the test set. The details of various target samples in this paper are shown in Table 1. The training datasets for all experiments notably exclude information on the ZSU23/4 category target sample.

Figure 5.
(Top) optical images and (Bottom) SAR images of ten categories of target samples according to the following order: 2S1, BMP2, BRDM2, BTR60, BTR70, D7, T62, T72, ZIL131 and ZSU23/4.

Table 1.
The details of various target samples in this paper.
4.1. The Validity of Out-of-Distribution Feature Inference
The validity of out-of-distribution feature inference is verified through two sets of experimental results in this subsection. First, the out-of-distribution feature inference is premised on compact feature extraction of known target samples. Therefore, these experiments need to verify the contribution of compact feature extraction to out-of-distribution feature inference. In response to the aforementioned issues, this experiment selected BRDM2, D7, and T62 to try to infer the unknown features of the target sample ZSU23/4. The features initially used in this section were those of the original target samples. Then, the proposed method employed compact features for out-of-distribution feature inference. The compact features were obtained by calculating the original sample features according to Equation (7). This experiment mapped the three categories of known sample features and the inferred unknown sample features into a unified latent feature space, subsequently utilizing the PCA algorithm [44] to condense these sample features into a two-dimensional space, and the results are shown in Figure 6.
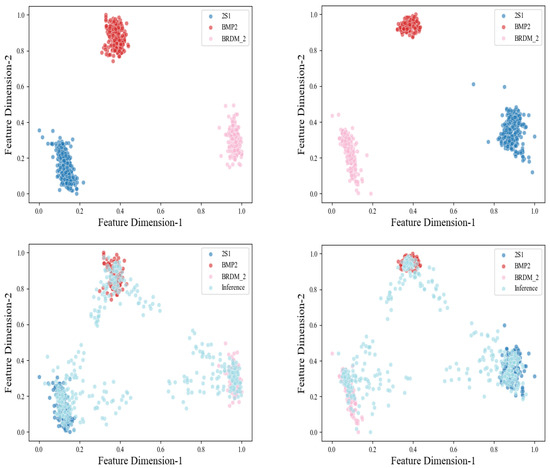
Figure 6.
The contribution of compact feature extraction to out-of-distribution feature inference. (1) Upper left: the original feature distribution of the three categories of known samples. (2) Upper right: the compact feature distribution of the three categories of known samples. (3) Lower left: the unknown sample feature distribution inferred from the original feature distribution. (4) Lower right: the unknown sample feature distribution inferred from compact feature distribution.
The aforementioned experimental results substantiate the merits of compact feature extraction from two perspectives. On the one hand, the compact feature extraction enhances the separation of feature distributions among known samples, thereby facilitating accurate recognition of these samples. On the other hand, the inferred feature distribution region of the unknown sample, derived from the compact feature distribution, is far away from the feature distribution region observed in known category target samples. This effectively mitigates the risk of misrecognizing unknown samples as known ones.
Second, the feature distribution region of the synthetic unknown sample was also compared with that of the real ZSU23/4 sample in this experiment, as illustrated in Figure 7. Obviously, the proposed method can achieve effective out-of-distribution feature inference under the premise of different known feature distributions. There is a clear overlap between the inferred feature distribution of unknown samples and the feature distribution of real ZSU23/4 samples. Moreover, the proposed method also infers that the other two feature regions that are far away from the known samples are also the feature regions of the unknown samples, which also provides a basis for the recognition of other unknown samples. Such feature area inference aligns more closely with common sense. In the feature space, the region that a known target sample can occupy is limited, while different categories of unknown samples occupy more feature regions.
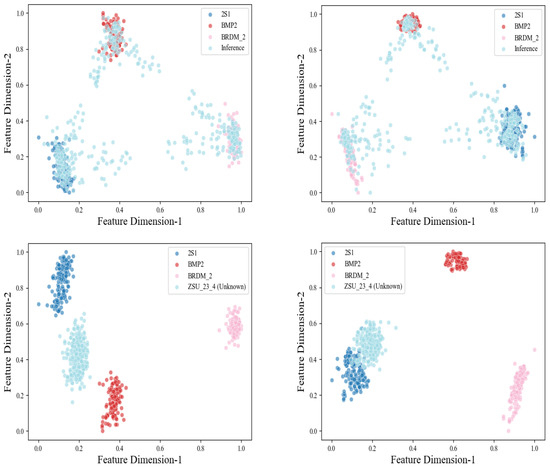
Figure 7.
The contribution of compact feature extraction to out-of-distribution feature inference. (1) Upper left: the unknown sample feature distribution inferred from the original feature distribution. (2) Upper right: the unknown sample feature distribution inferred from the compact feature distribution. (3) Lower left: the relative feature distribution of unknown sample ZSU23/4 under the original feature distribution. (4) Lower right: the relative feature distribution of unknown sample ZSU23/4 under the compact feature distribution.
To verify the superiority of the constructed model architecture, the experiments also executed out-of-distribution (OOD) inference experiments across different network layers. The experiments conducted simulation experiments addressing this problem by introducing out-of-distribution inference at distinct network layers; the experimental results are as shown in Figure 8. It can be observed that our proposed method achieves optimal open-set-recognition results by performing out-of-distribution inference at Network Layer 3.
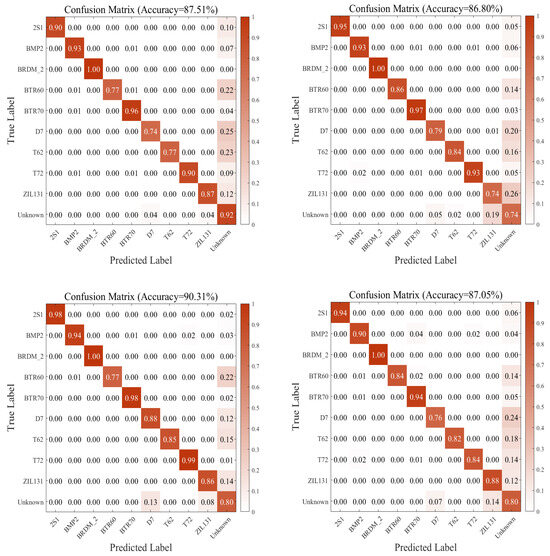
Figure 8.
The out-of-distribution (OOD) inference experiments across different network layers. (1) upper left: Network Layer 1. (2) upper right: Network Layer 2. (3) left lower: Network Layer 3 (proposed method). (4) right lower: Randomly Select Network Layers.
4.2. The Importance of the Knowledge-Sharing Retrain Mechanism
The out-of-distribution feature inference can provide the requisite prior knowledge of unknown samples for the recognition model. However, relying solely on the inference of out-of-distribution feature knowledge is insufficient for accurately recognizing unknown target samples. Moreover, the proposed method aims to enable the ATR model to acquire unknown sample knowledge from out-of-distribution feature inference without forgetting much knowledge from known target samples.
Therefore, this paper proposes a knowledge-sharing retrain mechanism to address the aforementioned issues. The experiment selected nine categories target samples, including 2S1, BMP2, BRDM_2, BTR60, BTR70, D7, T62, T72, and ZIL131 as the training set, aiming to implement ten-category SAR target recognition tasks, including the unknown sample ZSU_23_4. To assess the efficacy of each module within the proposed method, five training schemes were devised to evaluate the ATR model across distinct stages, as outlined below:
Scheme 1: Training the initial nine-category ATR model solely with the dataset comprising the first nine known target samples;
Scheme 2: Expanding the initial nine-category ATR model to encompass ten categories and training it with the aforementioned dataset;
Scheme 3: Training the expanded ten-category ATR model by amalgamating features from the known nine-category target samples with those inferred from out-of-distribution features;
Scheme 4: Introducing the compact feature extraction to enhance the training process of the expanded ten-category ATR model based on Scheme 3;
Scheme 5: Establishing a mechanism for knowledge-sharing retraining to refine the training of the expanded ten-category ATR model.
The five confusion matrices in Figure 9 demonstrate the contributions of different modules in the proposed method to the recognition of ten-category MSTAR data. Figure 9(1) shows the performance of a nine-category closed-set model directly applied to ten-category MSTAR data, achieving an accuracy of 87.51%. Notably, the model exhibited poor performance in recognizing the unknown class (ZSU_23_4 ), failing to distinguish novel data from existing classes. This highlights the necessity of open-set-recognition research. Figure 9(2) presents the results of extending the nine-category model by adding an output unit (ten categories in total), which retained the same accuracy of 87.51%. This indicates that merely expanding the model architecture still suffers from significant misrecognition and remains ineffective in identifying the unknown class (ZSU_23_4 ). Figure 9(3) demonstrates the performance of the ten-category extended model trained with out-of-distribution feature inference (without compact feature extraction), achieving 86.47% accuracy. Here, out-of-distribution feature inference synthesizes non-known-class samples via linear interpolation of inputs and labels, treating them as pseudo-unknown categories during training. This transforms the open-set problem into a closed-set recognition task and moderately improves recognition accuracy, particularly showing notable enhancement in unknown class recognition. Figure 9(4) combines out-of-distribution feature inference, yielding 87.67% accuracy. The compact feature extraction enhances intra-class feature compactness to reserve more feature space for unknown classes. Experimental results reveal that while this method improved the unknown class recognition accuracy from 45% to 77%, it significantly increased the risk of misclassifying known categories. To mitigate this issue, as illustrated in Figure 9(5), the advantage of proposed method is that it incrementally integrates out-of-distribution feature inference and the knowledge-sharing retrain mechanism. This approach achieves a recognition rate of 90.31%. The knowledge-sharing retrain mechanism leverages a knowledge distillation mechanism to guide the training of the extended model, alleviating the degradation in known-category recognition caused by compact feature extraction.
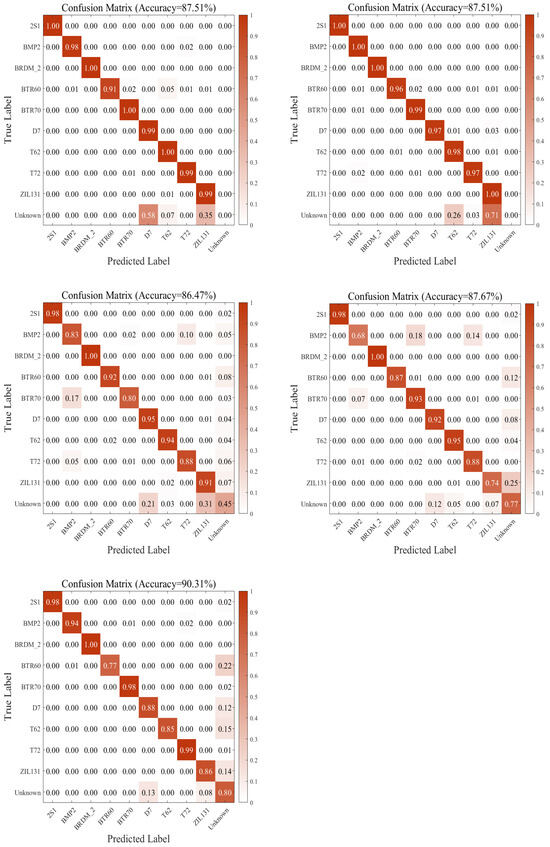
Figure 9.
The importance of knowledge-sharing retrain mechanism. (1) row1 left: the confusion matrix of the initial nine-category ATR model. (2) row1 right: the confusion matrix of the ten-category ATR model extended by the initial model. (3) row2 left: the confusion matrix of the extended ATR model with out-of-distribution feature inference (without compact feature extraction). (4) row2 right: the confusion matrix of the extended ATR model with out-of-distribution feature inference. (5) row3 left: the confusion matrix of the proposed method. Compared with (4), it adds the additional knowledge-sharing retrain mechanism.
The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method progressively enhances open-set-recognition performance on the MSTAR dataset, with particularly significant improvements in novel class identification. This strongly validates the importance of the knowledge-sharing retraining mechanism in boosting open-set-recognition accuracy.
4.3. The Recognition Performance Across Varying Openness Conditions
The proposed method has demonstrated its capability to infer out-of-distribution feature knowledge and effectively learn corresponding unknown target sample knowledge. Subsequently, the experiments investigate the recognition performance of the proposed method under varying openness conditions to verify its generalization to different open-set problems. To simulate these scenarios, this experiment adjusted the proportions of known and unknown classes in the MSTAR dataset according to the openness level defined in Formula (13).
where denotes the number of classes in the training set and denotes the number of classes in the test set.
In this experiment, the first five classes of the ten-category MSTAR dataset were selected as known categories. The number of unknown categories was dynamically adjusted based on predefined known category configurations (5, 6, 7, 8, and 9), generating test sets with controlled openness levels ranging from 5.13% to 29.29%. A systematic comparative analysis was performed between the proposed method and four benchmark open-set-recognition approaches: Softmax [45], OpenMax [21], G-OpenMax [46], and Placeholder [47]. To maintain the fairness of the experimental setup, all comparative methods shared identical backbone network architectures and hyperparameter configurations. All methods set the mini-batch size to 64 during the model pre-training phase, and the recognition model was optimized and updated for 100 epochs using the Adam optimizer with a learning rate of 0.001. Moreover, in the open-set training phase, the tail size parameter of the OpenMax and G-OpenMax methods was set to 30, and the optimal decision threshold for distinguishing known classes from unknown classes was determined through traversal search in the [0.1, 0.9] interval. The mixup alpha parameter of the Placeholder method was set to 0.5. Quantitative evaluation using accuracy and macro F1-score metrics was conducted to assess performance across incremental openness levels. The experimental results are shown in Table 2 and Table 3 and Figure 10.

Table 2.
Comparison of Accuracy Results for Various OSR Methods on the MSTAR Dataset.

Table 3.
Comparison of F1-Score Results for Various OSR Methods on the MSTAR Dataset.
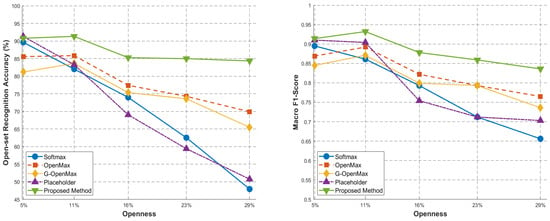
Figure 10.
Comparison of Open-set-Recognition Performance for Various OSR Methods on the MSTAR Dataset. (1) Left: the comparison results of open-set-recognition accuracy at different openness levels. (2) Right: the comparison results of macro F1-Score at different openness levels.
Figure 10(1,2) present the comparative open-set-recognition performance between the proposed method and various state-of-the-art OSR methods under incremental openness conditions on the MSTAR dataset. More detailed data descriptions for Figure 10 are provided in Table 2 and Table 3. It can be seen that the experimental results reveal progressive declines in both accuracy and macro F1-score metrics across all methods as openness levels increase. Analysis of the subfigures demonstrates significant performance variations: Placeholder and Softmax exhibit the most substantial fluctuation amplitudes, whereas G-OpenMax and OpenMax maintain relative stability. Notably, the proposed method achieves minimal performance degradation, validating its enhanced capability in out-of-distribution knowledge inference. These experimental findings confirm that our approach outperforms contemporary open-set-recognition benchmarks, surpassing existing methods.
4.4. Computational Complexity of the Proposed Method
In this section, time complexity (measured by floating-point operations, FLOPs) and space complexity (quantified by model parameters, Params) are used as key metrics to assess the computational efficiency of our method. FLOPs serve as an indicator of computational workload, providing an estimate of processing speed, while Params reflect the memory footprint of the model. As shown in Table 4, evaluation results for openness levels of 5.13%, 10.56%, 16.33%, and 22.54% demonstrate that both total Params and total FLOPs remain relatively stable with increasing known categories. This indicates that the proposed method can maintain stable time and space complexity even with an increasing number of known categories, thereby avoiding the exponential growth of computing resources typically associated with large-scale SAR datasets.

Table 4.
Computational Complexity under Varying Openness.
Furthermore, Figure 11 presents a comparative analysis of the running time (in seconds) for various open-set-recognition (OSR) methods on the MSTAR dataset. The running time of the proposed method is 2.27 s, which is significantly lower than that of OpenMax (28.62 s) and G-OpenMax (24.44 s). Softmax achieves a running time of 2.72 s, while Placeholder exhibits a running time of 2.49 s. Error bars are included to indicate the variability in running time across multiple trials, suggesting that the proposed method not only achieves the shortest running time but also demonstrates consistent computational efficiency.
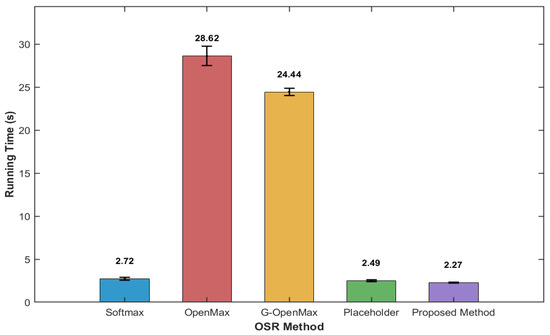
Figure 11.
Comparison of Running Time for Various OSR Methods on the MSTAR Dataset.
5. Conclusions and Discussion
The efficacy of data-driven ATR algorithms relies on the prior knowledge acquired from the target sample set. However, the absence of prior knowledge regarding unknown target samples hinders the ATR model from comprehending the underlying data distribution of target samples. This paper proposed an out-of-distribution knowledge inference-based approach for the implementation of open-set-recognition tasks in SAR imagery. The experimental results visually demonstrate the necessity of adopting out-of-distribution feature inference in the proposed method. Through the comparison of recognition performance under different schemes, the experimental results have demonstrated the value of the knowledge distillation mechanism. Notably, the proposed method consistently outperforms other OSR methods in recognition performance across varying openness conditions. Even when one category of target sample information is completely absent from the training set, the recognition accuracy of the proposed approach still achieves . Additionally, the proposed method also demonstrates superior operational efficiency, outperforming other approaches in terms of running speed. Overall, this paper demonstrated that the proposed method is an effective approach to deal with SAR imagery open-set recognition.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.C. and Y.Y.; methodology, C.C., Y.Y. and Z.Z.; software, Y.Y., C.C. and B.W.; validation, C.C., Y.Y. and Z.Z.; formal analysis, C.C., Y.Y., Z.Z. and B.L.; investigation, Z.Z. and B.L.; resources, C.C., Z.Z., and B.W.; data curation, C.C.; writing—original draft preparation, C.C. and Y.Y.; writing—review and editing, C.C. and Y.Y.; visualization, C.C., Y.Y., B.W. and C.L.; supervision, Z.Z., B.L. and Y.K.; project administration, C.C. and Z.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work is fully supported by the National Science and Technology Major Project (Grant 2024ZD1003206), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grants 2023YFC2906403 and 2022YFC2905002).
Data Availability Statement
The MSTAR dataset used in this study is a publicly available SAR image dataset provided by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) and Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL). This dataset contains high-resolution X-band SAR images of various military targets (e.g., tanks, armored vehicles). The raw data can be obtained through public sharing platforms. This research complies with all dataset usage restrictions, including non-commercial use only for academic purposes.
Acknowledgments
Thanks for the technical support provided by the Geomathematics Key Laboratory of Sichuan Provience, Chengdu University of Technology.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Bizao Wu was employed by China Mobile IoT Company Limited. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Choi, J.H.; Lee, M.J.; Jeong, N.H.; Lee, G.; Kim, K.T. Fusion of target and shadow regions for improved SAR ATR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5226217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Du, L.; Wei, D. Multiscale CNN based on component analysis for SAR ATR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 5211212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, B.; Wen, G.; Zhong, J.; Ma, C.; Yang, X. A robust similarity measure for attributed scattering center sets with application to SAR ATR. Neurocomputing 2017, 219, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, B.; Wen, G. Target reconstruction based on 3-D scattering center model for robust SAR ATR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 3772–3785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, N.; Chen, C.; Qiu, T.; Sangaiah, A.K. Deep learning and superpixel feature extraction based on contractive autoencoder for change detection in SAR images. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2018, 14, 5530–5538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, G.D.A.; Minnett, P.J.; Paes, E.T.; de Miranda, F.P.; Landau, L. Oil-Slick Category Discrimination (Seeps vs. Spills): A Linear Discriminant Analysis Using RADARSAT-2 Backscatter Coefficients (σ∘, β∘, and γ∘) in Campeche Bay (Gulf of Mexico). Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Fang, X.; Cui, J.; Fei, L.; Yan, K.; Chen, Y.; Xu, Y. Robust sparse linear discriminant analysis. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2018, 29, 390–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, Z.; Nie, F. A new formulation of linear discriminant analysis for robust dimensionality reduction. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2018, 31, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, A.; Zhang, M.J.; Bagaria, V.K.; Zou, J. Exploring patterns enriched in a dataset with contrastive principal component analysis. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Woźniak, M.; Wu, J.; Li, W.; Bai, Z. Denoising aggregation of graph neural networks by using principal component analysis. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 19, 2385–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.R.; Li, H.C.; Wang, R.; Du, Q.; Jia, X.; Plaza, A. Hyperspectral unmixing based on nonnegative matrix factorization: A comprehensive review. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 4414–4436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoruso, A.; Crescentini, L.; Costa, R. Spatial Dispersion and Non-Negative Matrix Factorization of SAR Backscattering as Tools for Monitoring Snow Depth Evolution in Mountain Areas: A Case Study at Central Pyrenees (Spain). Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Cao, Z.; Cui, Z.; Wang, L. Incremental robust non-negative matrix factorization for SAR image recognition. In Proceedings of the 2019 6th Asia-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar (APSAR), Xiamen, China, 26–29 November 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Okwuashi, O.; Ndehedehe, C.E. Deep support vector machine for hyperspectral image classification. Pattern Recognit. 2020, 103, 107298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostami, O.; Kaveh, M. Optimal feature selection for SAR image classification using biogeography-based optimization (BBO), artificial bee colony (ABC) and support vector machine (SVM): A combined approach of optimization and machine learning. Comput. Geosci. 2021, 25, 911–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.M.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Q. Extraction of sea ice cover by Sentinel-1 SAR based on support vector machine with unsupervised generation of training data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 59, 3040–3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conceição, M.R.A.; de Mendonça, L.F.F.; Lentini, C.A.D.; da Cunha Lima, A.T.; Lopes, J.M.; de Vasconcelos, R.N.; Porsani, M.J. SAR oil Spill detection system through random forest classifiers. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Magagi, R.; Goïta, K.; Trudel, M.; McNairn, H.; Powers, J. Crop phenology retrieval via polarimetric SAR decomposition and Random Forest algorithm. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 231, 111234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastro, P.; Masiello, G.; Serio, C.; Pepe, A. Change Detection Techniques with Synthetic Aperture Radar Images: Experiments with Random Forests and Sentinel-1 Observations. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, T.; Guo, W.; Luo, Y. Transferable SAR image classification crossing different satellites under open set condition. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 4506005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendale, A.; Boult, T.E. Towards open set deep networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 1563–1572. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Ji, K.; Zhang, L.; Feng, S.; Xiong, B.; Kuang, G. An open set recognition method for SAR targets based on multitask learning. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 19, 4014005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevikalp, H.; Uzun, B.; Salk, Y.; Saribas, H.; Köpüklü, O. From anomaly detection to open set recognition: Bridging the gap. Pattern Recognit. 2023, 138, 109385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheirer, W.J.; Jain, L.P.; Boult, T.E. Probability models for open set recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2014, 36, 2317–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, C.; Huang, S.J.; Chen, S. Recent advances in open set recognition: A survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 43, 3614–3631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Fehérvári, I.; Zhao, X.; Macedo, I.; Appalaraju, S. Seetek: Very large-scale open-set logo recognition with text-aware metric learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 4–8 January 2022; pp. 2544–2553. [Google Scholar]
- Rudd, E.M.; Jain, L.P.; Scheirer, W.J.; Boult, T.E. The extreme value machine. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 762–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes Júnior, P.R.; De Souza, R.M.; Werneck, R.D.O.; Stein, B.V.; Pazinato, D.V.; De Almeida, W.R.; Rocha, A. Nearest neighbors distance ratio open-set classifier. Mach. Learn. 2017, 106, 359–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, S.A.; Shin, A.H.; Park, K.H.; Choi, J.; Park, G.M. Open-set domain adaptation for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 17–21 June 2024; pp. 23943–23953. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Ji, K.; Zhang, L.; Feng, S.; Xiong, B.; Kuang, G. SAR target open-set recognition based on joint training of class-specific sub-dictionary learning. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 21, 3500805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, S.; Coleman, C.; Rudd, E.M.; Boult, T.E. Open set intrusion recognition for fine-grained attack categorization. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Technologies for Homeland Security (HST), Waltham, MA, USA, 25–26 April 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Giusti, E.; Ghio, S.; Oveis, A.H.; Martorella, M. Open set recognition in synthetic aperture radar using the openmax classifier. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf22), New York, NY, USA, 21–25 March 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Ji, K.; Feng, S.; Zhang, L.; Xiong, B.; Kuang, G. Open set recognition with incremental learning for SAR target classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5106114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, I.; Kim, J.; Kang, H.; Kim, Y.D.; Choi, S. Open set recognition by regularising classifier with fake data generated by generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Calgary, AB, Canada, 15–20 April 2018; pp. 2686–2690. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Hou, C.; Lang, Y.; Guan, D.; Huang, D.; Xu, J. Open-set human activity recognition based on micro-Doppler signatures. Pattern Recognit. 2019, 85, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, L.; Olson, M.; Fern, X.; Wong, W.K.; Li, F. Open set learning with counterfactual images. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 613–628. [Google Scholar]
- Schlachter, P.; Liao, Y.; Yang, B. Open-set recognition using intra-class splitting. In Proceedings of the 2019 27th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), A Coruna, Spain, 2–6 September 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Cardoso, D.O.; Gama, J.; França, F.M. Weightless neural networks for open set recognition. Mach. Learn. 2017, 106, 1547–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Cao, Z.; Cui, Z. LDGAN: A synthetic aperture radar image generation method for automatic target recognition. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 58, 3495–3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Cui, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Cao, Z.; Yang, J. A demand-driven SAR target sample generation method for imbalanced data learning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 5219315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, S.; Ramanan, D. Opengan: Open-set recognition via open data generation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 813–822. [Google Scholar]
- Cevikalp, H. Best fitting hyperplanes for classification. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 39, 1076–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giusti, E.; Ghio, S.; Oveis, A.H.; Martorella, M. Proportional similarity-based Openmax classifier for open set recognition in SAR images. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, H.; Williams, L.J. Principal component analysis. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Stat. 2010, 4, 433–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Deng, W.; Du, J. Noisy softmax: Improving the generalization ability of dcnn via postponing the early softmax saturation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 5372–5381. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, Z.; Demyanov, S.; Chen, Z.; Garnavi, R. Generative openmax for multi-class open set classification. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1707.07418. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, D.W.; Ye, H.J.; Zhan, D.C. Learning placeholders for open-set recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 4401–4410. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).