Highlights
What are the main findings?
- Hybrid-SegUFormer achieves effective landslide InSAR deformation detection performance (IoU: 66.74%, F1-score: 80.05%) through synergistic integration of segFormer encoder, multi-scale decoder and self-distillation mechanism.
- Hybrid-SegUFormer demonstrates exceptional multi-scale adaptability with minimal performance degradation and strong cross-regional generalization capability, maintaining superior metrics on unseen datasets and demonstrating its practical utility.
What are the implications of the main findings?
- This study offers a reliable and efficient solution for large-area landslide deformation zone detection using InSAR data in rugged terrains.
- By demonstrating strong cross-regional generalization, Hybrid-SegUFormer reduces the need for localized data collection, facilitating more efficient large-area landslide early warning and risk mitigation.
Abstract
Landslide deformation monitoring via InSAR is crucial for assessing the risk of hazards. Quick and accurate detection of active deformation zones is crucial for early warning and mitigation planning. While the application of deep learning has substantially improved the detection efficiency, several challenges still persist, such as poor multi-scale perception, blurred boundaries, and limited model generalization. This study proposes Hybrid-SegUFormer to address these limitations. The model integrates the SegFormer encoder’s efficient feature extraction with the U-Net decoder’s superior boundary restoration. It introduces a multi-scale fusion decoding mechanism to enhance context perception structurally and incorporates a self-distillation strategy to significantly improve generalization capability. Hybrid-SegUFormer achieves detection performance (98.79% accuracy, 80.05% F1-score) while demonstrating superior multi-scale adaptability (IoU degradation of only 6.99–8.83%) and strong cross-regional generalization capability. The synergistic integration of its core modules enables an optimal balance between precision and recall, making it particularly effective for complex landslide detection tasks. This study provides a new approach for intelligent interpretation of InSAR deformation in complex mountainous areas.
1. Introduction
Landslides refer to the phenomenon where rock, soil, or debris masses on a slope move downward or outward under the influence of gravity, typically triggered by earthquakes, rainfall, or human activities [1,2]. According to the Global Fatal Landslide Database (GFLD, formerly termed the Durham Fatal Landslide Database), spatiotemporal analysis of global fatal non-seismic landslides from 2004 to 2016 revealed that a total of 55,997 people died in 4862 distinct landslide events, with Asia being the high-incidence region. Situated on the eastern edge of the Eurasian Plate, China is significantly influenced by the movements of the Pacific Plate, Indian Ocean Plate, and Eurasian Plate. Its complex topography, geological conditions, and intense tectonic and seismic activity contribute to a high frequency of landslide disasters [2]. In recent years, the continuation of an active seismic period, an increase in extreme rainfall events, and escalating intensity of human engineering activities have further exacerbated landslide risks, making the disaster prevention and reduction situation severe [3,4,5,6].
Deformation magnitude is a key physical quantity characterizing landslide stability and movement state [7]. It can intuitively reveal the deformation evolution process of a slope and serves as a crucial precursor signal for landslide instability. Therefore, deformation monitoring is the most direct and effective means to reveal landslide evolution mechanisms [8], and it is also the critical basis for conducting landslide hazard risk assessment and early warning forecasting. Currently, common surface deformation monitoring methods include ground-based point monitoring techniques such as crack gauges, GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System), rain gauges, inclinometers, and accelerometers. Among these, GNSS is the most widely applied in landslide monitoring due to its global coverage, all-weather operation capability, millimeter-level 3D accuracy, and automation capacity [9,10]. However, ground-based point monitoring methods like GNSS are limited to the locations where equipment is installed, making it difficult to achieve areal coverage. This results in blind spots when monitoring large-scale landslides or risk zones, failing to meet the urgent need for large-scale, high-density monitoring of geological hazards.
The Interferometry Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR) technology developed in recent years possesses capabilities for large-scale, long time-series, and high-temporal-resolution surface deformation monitoring. The abundant availability of SAR satellite data and increasingly mature InSAR processing techniques provide massive deformation information for high-precision monitoring of landslide hazards, serving as critical data support for large-scale geo-hazard monitoring, with accuracy reaching centimeter to millimeter levels. Furthermore, deformation field data acquired through InSAR is crucial for the early identification of potential landslides, serving as a key basis for determining potential landslides, especially in the identification of high-altitude and concentrated distributed landslide hazards [11].
Primary radar satellite methods for landslide deformation monitoring include Differential InSAR (D-InSAR), InSAR Stacking, Multi-Temporal InSAR (MT InSAR), and Pixel Offset Tracking (POT), each playing vital roles in tracking different stages of landslide evolution [12,13,14]. Among these, D-InSAR technology is the earliest application of InSAR and forms the theoretical basis for multi-baseline interferometric measurement methods like PS-InSAR and SBAS-InSAR. As a data approach with relatively simple procedures, SBAS-InSAR has been broadly used in landslide monitoring based on “comprehensive remote sensing” [15,16,17].
Extensive InSAR-based landslide monitoring aims to enhance risk detection accuracy and prevention effectiveness. Quickly and accurately identifying areas of significant deformation is crucial for early warning and mitigation planning [18,19]. Current extraction methods mainly involve manual delineation and threshold segmentation: (1) Manual delineation uses time-series InSAR analysis followed by expert visual interpretation to define deformation zones. This method is subjective, labor-intensive, and inefficient due to dependence on expert judgment [11,20,21]; (2) Threshold segmentation detects deformation areas by applying rate thresholds to coherent targets with spatial clustering. While it allows semi-automated extraction, this approach is sensitive to InSAR noise and limited by region-specific threshold applicability [22]. Therefore, intelligent techniques that balance accuracy and efficiency are urgently needed to fully utilize InSAR data advantages in landslide risk management.
In recent years, deep learning techniques (particularly Convolutional Neural Networks, CNN) have been progressively applied to InSAR deformation area identification and segmentation [23,24,25,26,27,28,29]. Mainstream models such as Mask R-CNN, DeepLabv3+, U-Net, and SegFormer demonstrate notable effectiveness: Mask R-CNN combines object detection and instance segmentation capabilities, generating pixel-level masks to precisely extract landslide deformation boundaries [30,31]; DeepLabv3+ integrates an encoder-decoder structure with an Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling (ASPP) module, employing dilated convolutions to expand the receptive field. This effectively balances local edge features with global topographic context, enhancing deformation zone contour segmentation accuracy [32,33,34]. Given frequent vegetation/topographic occlusion and satellite revisit limitations in InSAR data—where significant surface deformation remains uncommon—U-Net maintains superior segmentation performance even with limited annotated samples. Its encoder-decoder architecture with skip connections preserves both low-level edge details and high-level semantic features, proving particularly adaptive for extracting vague-boundary, irregularly shaped deformation patches [35,36]; SegFormer employs a Transformer-based architecture featuring a multi-scale encoder and lightweight decoder, significantly reducing computational complexity. Its transformer encoder excels at modeling long-range dependencies, enabling efficient perception of multi-scale terrain features while accurately capturing local edges and global spatial relationships within deformation zones—critical for segmenting complex landslide deformation patterns [37,38,39]. The limitation of CNNs in capturing long-range dependencies was addressed through the pioneering integration of the Transformer architecture [40]. A BiFusion module was introduced to enable multi-level feature fusion, forming the TransFuse framework. Building upon this, the novel FSRNet model was developed in 2025, wherein a Feature Symbiosis Coupling (FSC) strategy was employed to combine ResNet50 with a Swin Transformer [41]. The local detail representation of CNNs and the global dependency modeling of Transformers were effectively leveraged, leading to significantly enhanced segmentation accuracy and inference efficiency in orchard extraction tasks. The Mean-Teacher self-distillation framework constructs a teacher network through an exponential moving average (EMA) of the student model’s historical parameters, eliminating dependence on external pre-trained models or additional inference overhead. This framework has been widely adopted in remote sensing applications, such as utilizing the Mean Teacher model to generate pseudo-labels for enhancing model generalization under limited labeled data [42], and developing multi-granularity domain adaptation teacher models to address unsupervised domain adaptation challenges in remote sensing object detection tasks [43].
Despite significant progress in deep learning-based detection of InSAR deformation zones, existing models remain limited in three critical aspects: (1) inadequate perception of landslides with high scale heterogeneity, (2) blurred restoration of deformation boundaries caused by complex slope structures, and (3) limited generalization capability across diverse geological settings. To address these gaps, this study proposes Hybrid-SegUFormer, a novel architecture that integrates a SegFormer encoder with a U-Net–inspired decoder, augmented by a multi-scale decoding mechanism and self-distillation. Our framework introduces two key innovations: first, a hierarchical multi-scale decoder (MSD) that enhances sensitivity to landslides of varying spatial extents and improves boundary precision; and second, a self-distillation strategy that strengthens cross-regional generalization without requiring additional labeled data. Furthermore, we introduce a multi-source auxiliary data preprocessing strategy to suppress non-landslide deformation signals, thereby reducing false detections. Validated on SBAS-InSAR datasets from Zayu County and the Upper Jinsha River, our approach demonstrates superior performance over benchmarks such as Mask R-CNN, DeepLabv3+, U-Net, and SegFormer, offering a more reliable solution for landslide risk monitoring systems.
2. Study Area and Data
2.1. Study Area
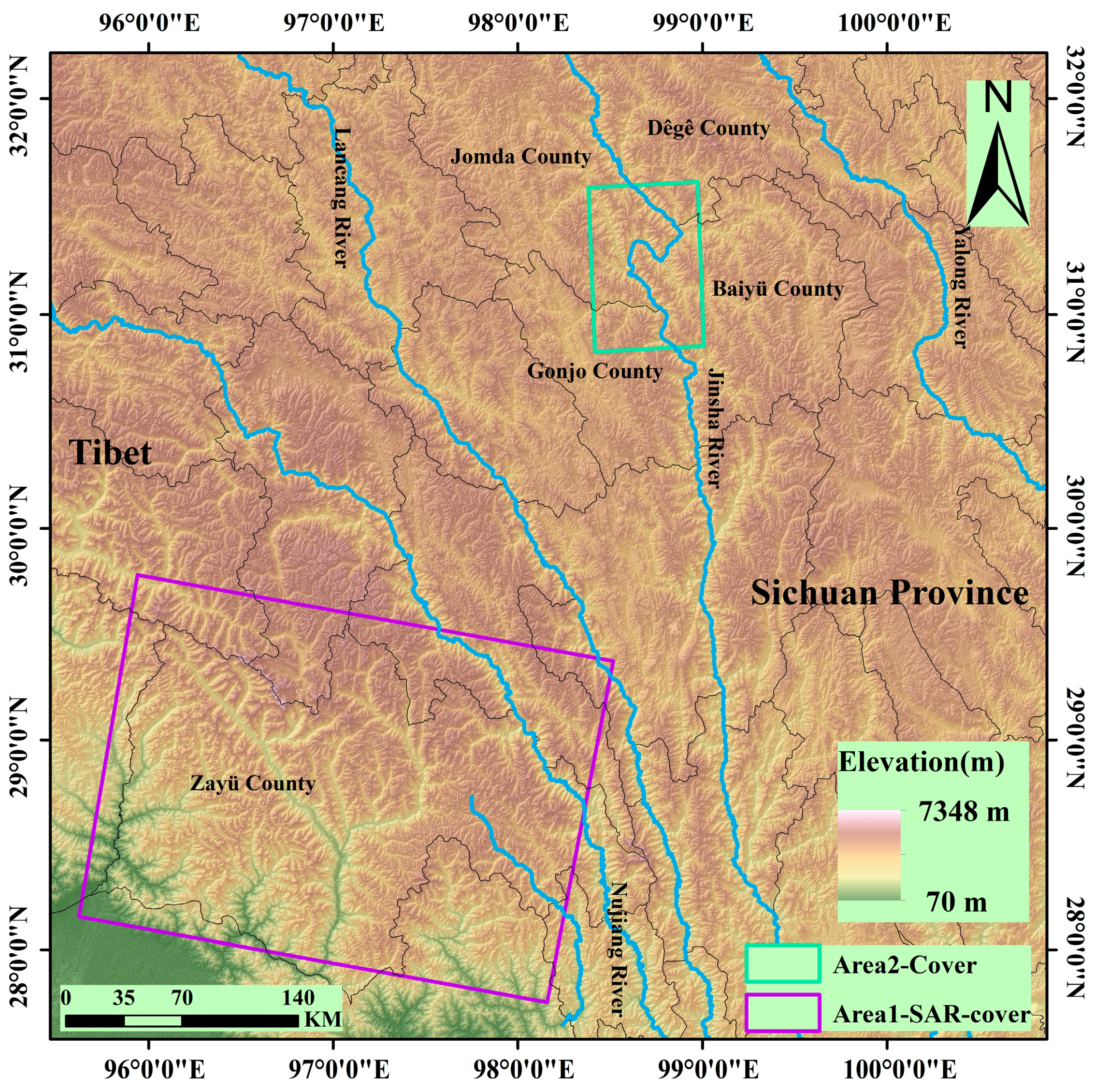
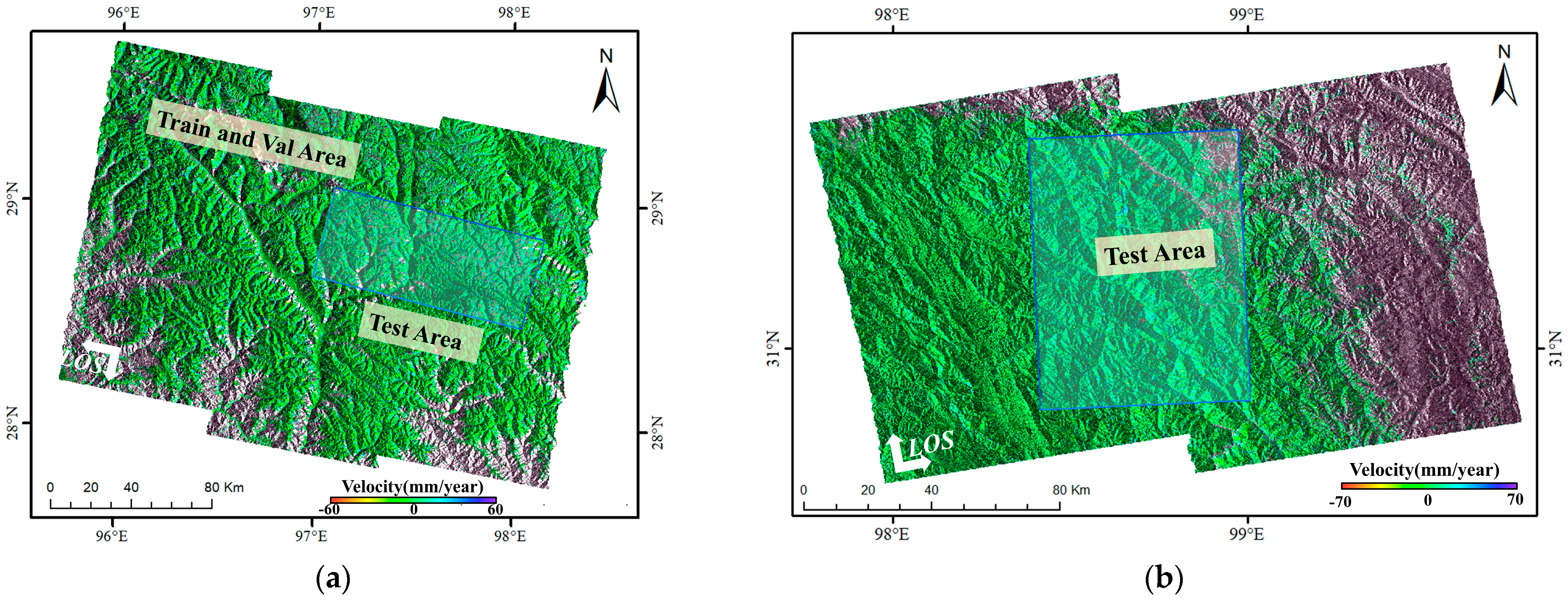
The study areas comprise two representative high-risk geological hazard zones (Figure 1):
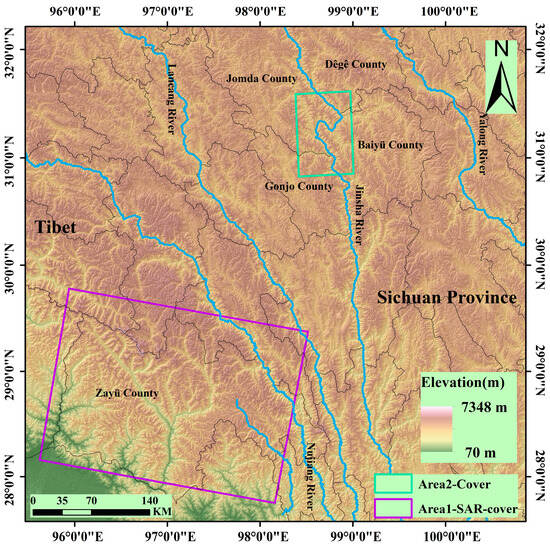
Figure 1.
Location of the study area.
(1) Area 1 (Zayu County): Located in the southeastern Tibet Autonomous Region (average elevation: 2800 m), this area features higher topography in the northwest descending southeastward, with relative relief reaching 3600 m. Dominated by deeply incised V-shaped valleys, it exhibits characteristic high-mountain canyon and fluvial landforms. Controlled by the Jiali-Nujiang Fault Zone, surface cover consists of loose sediments (porosity >35%). Strong precipitation during the rainy season, coupled with tectonic activity, triggers frequent landslides and debris flows [44]. This region was used for model training, validation, and testing.
(2) Area 2 (The Upper Reach (Baiyu-Tange reach section) of the Jinsha River): Situated within the Jinsha River tectonic suture zone at the southeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau (elevation: 2500–4400 m). NW-trending main faults and secondary faults dissect bedrock, forming steep-dipping bank slopes (>45°). It is prone to high-positioned rock landslides (e.g., Bage landslide volume >240 million m3). This area served to validate the model’s cross-regional transfer capability.
2.2. Data
2.2.1. SAR Data and Ancillary Data
This study collected 80 scenes of C-band Sentinel-1A imagery over Area 1, spanning the period from January 2020 to November 2022. The detailed parameters are listed in Table 1. The Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR) data processing employed the European Space Agency (ESA) Precise Orbit products, the 30-m-resolution Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) DEM, and Generic Atmospheric Correction Online Service (GACOS) products [45,46,47].

Table 1.
Detailed parameters of the SAR imagery over Area 1.
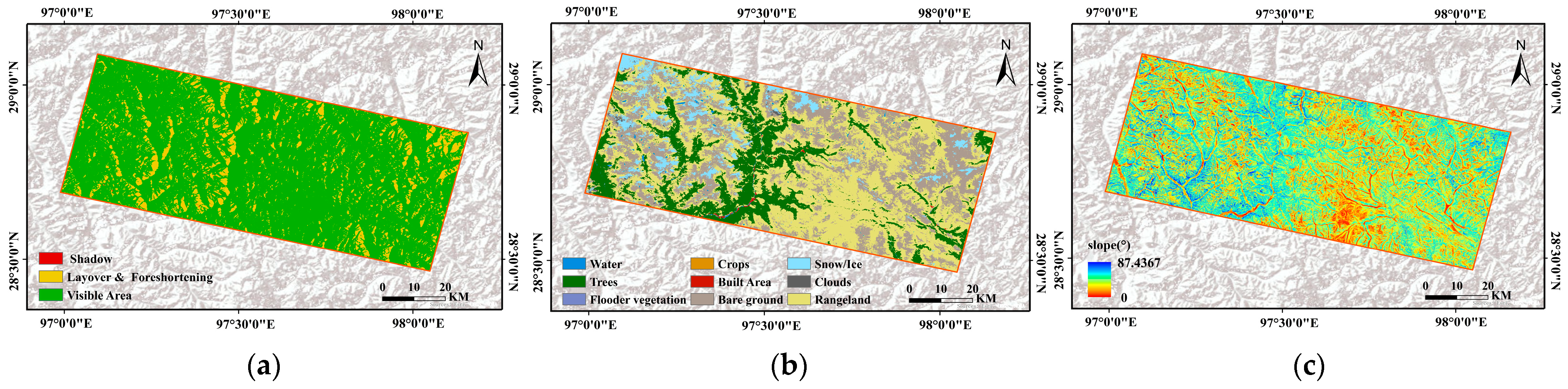
InSAR technology, constrained by the side-looking imaging geometry of SAR sensors, is susceptible to geometric distortions like layover, foreshortening, and shadow in high mountainous canyon areas. To address unreliable deformation values in these regions, this study simulated and calculated the geometric distortion distribution using Sentinel-1A orbital parameters, imaging geometry, and SRTM 30 m DEM. The identified layover, foreshortening, and shadow regions are illustrated in Figure 2a. Additionally, 66 scenes of C-band Sentinel-1A imagery over Area 2 were collected to validate the model’s cross-region transferability. Detailed imagery parameters are provided in Table 2.
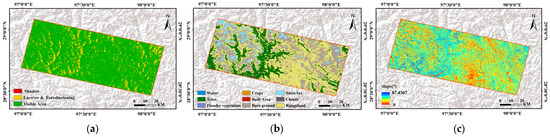
Figure 2.
(a) Sentinel-L geometric distortion map; (b) Land cover; (c) Slope.

Table 2.
Detailed parameters of the SAR imagery over Area 2.
2.2.2. Multi-Source Geo-Data for Eliminating Non-Landslide Deformation Areas
To accurately identify landslide deformation areas, this study utilized multi-source geoscience data to eliminate zones affected by non-landslide factors. Both surface disturbances (e.g., land use changes, vegetation dynamics) and radar geometric distortions can mislead the interpretation of deformation signals. The data sources included land cover from the official ArcGIS website, NDVI data sourced from Google Earth Engine (GEE), and slope information derived from DEM calculations. Figure 2b,c display the land cover and slope, respectively.
3. Methods
To address the limitations of current deep learning models in identifying Landslide InSAR Deformation Detection, including constrained multi-scale object perception, insufficient boundary detail restoration, and weak model generalizability, this study proposes a novel Hybrid-SegUFormer model. Compared with the conventional SegFormer–U-Net hybrid architecture, the proposed model refines the skip-connection mechanism and enhances the decoder design and training stability, enabling more efficient multi-scale feature fusion. Specifically, diagonally-linked skip connections between encoder–decoder pairs allow the decoder to recover full spatial resolution at the D1 stage, where high-resolution semantic features are directly integrated into the multi-scale decoder (MSD). This design improves spatial detail preservation and boundary reconstruction. The integrated MSD further aggregates semantic features from all decoding stages (D4–D1), enhancing cross-scale feature interaction and global-to-local alignment. Moreover, a self-distillation mechanism based on an exponential moving average (EMA) teacher model introduces an auxiliary distillation loss alongside the primary supervised loss, guiding the student model to learn continuously from the teacher’s soft predictions and improving training stability and segmentation accuracy. The model’s effectiveness is validated using SBAS-InSAR surface deformation datasets from the study area. Additionally, multi-source auxiliary data are incorporated to mitigate interference from non-landslide deformations and reduce the misidentification rate of pseudo-landslide deformation areas. The comprehensive technical workflow of Hybrid-SegUFormer for landslide InSAR deformation identification is illustrated in Figure 3 and comprises the following key steps:
Step 1: Acquire Sentinel-1A data and multi-source auxiliary data for the study area, and invert surface deformation rates using GACOS-assisted SBAS-InSAR technology.
Step 2: Integrate the SegFormer and U-Net architectures by combining an MSD with a self-distillation mechanism to construct the Hybrid-SegUFormer model. Train and validate the model using surface deformation rate data from the study area, evaluating its performance through five metrics: accuracy, precision, recall, Intersection over Union (IoU), and F1-score. After testing and assessing the pre-trained model on the test dataset, preliminary extraction of landslide-induced significant deformation areas is conducted based on Hybrid-SegUFormer, followed by further elimination of non-landslide deformation regions using multi-source auxiliary data.
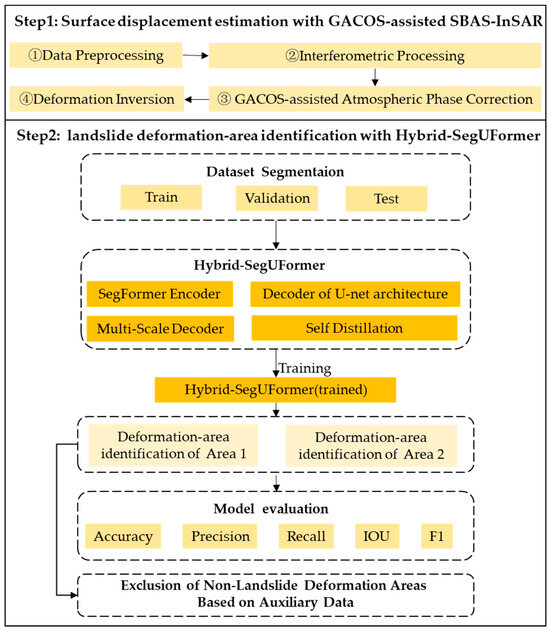
Figure 3.
Hybrid-SegUFormer workflow for landslide deformation identification from InSAR data.
Figure 3.
Hybrid-SegUFormer workflow for landslide deformation identification from InSAR data.
3.1. Surface Displacement Estimation with GACOS-Assisted SBAS-InSAR
To address atmospheric disturbances and spatiotemporal decorrelation caused by rugged terrain and dense vegetation, we used GACOS-assisted SBAS-InSAR for surface displacement estimation. The data processing workflow included the following steps:
(1) Data Preprocessing: Processed Sentinel-1A Single Look Complex (SLC) images using GAMMA software with precise orbit products. Performed SAR image co-registration and terrain phase elimination using a 30-meter Digital Elevation Model (DEM).
(2) Interferometric Processing: Set the temporal-spatial baseline threshold and generate the interferogram using Goldstein adaptive filtering [48].
(3) Conducted atmospheric phase correction using GACOS products for each interferogram. Executed phase unwrapping via the Minimum Cost Flow (MCF) algorithm [49]; Eliminated topographic residuals through linear regression of the unwrapped phase and vertical baseline.
(4) Deformation Inversion: Inverted pixel-wise time-series deformation using Least Squares (LS) with Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) [50].
3.2. Structure of Hybrid-SegUFormer
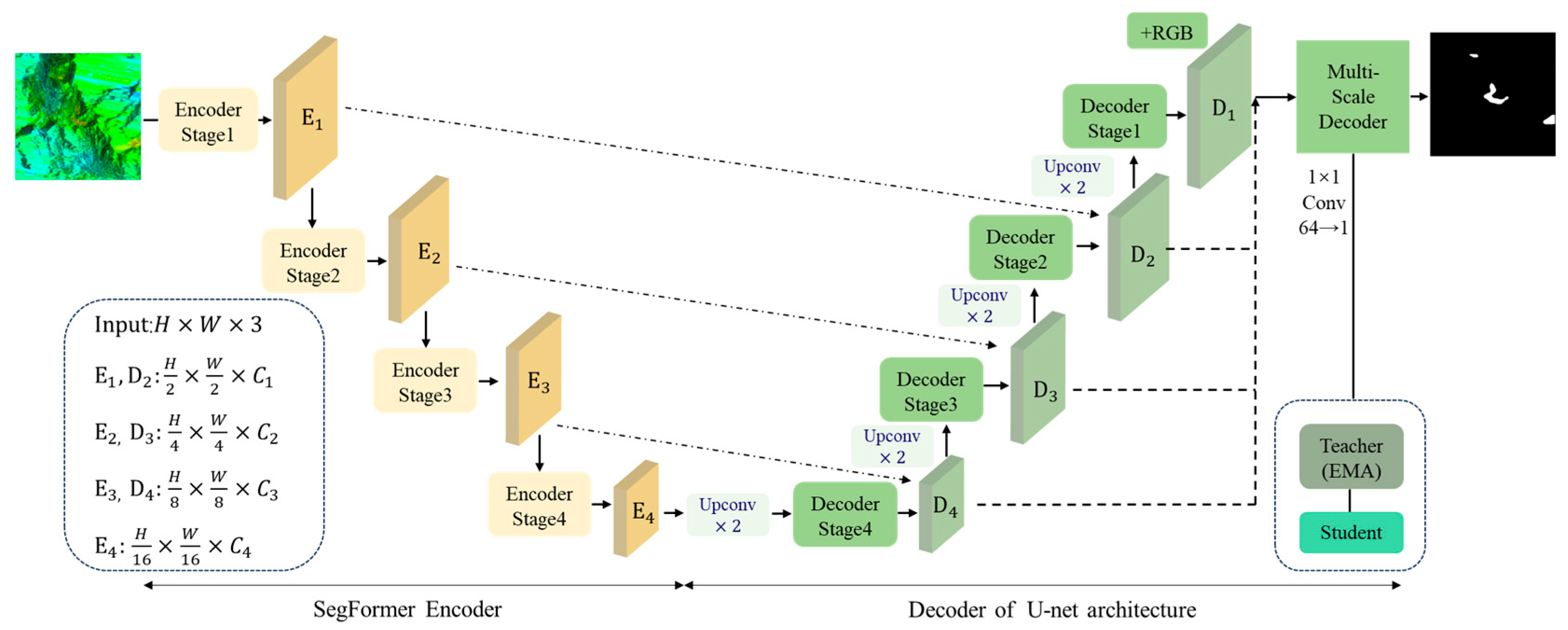
Hybrid-SegUFormer combines the advantages of the SegFormer and U-Net architectures. It incorporates an MSD and a self-distillation mechanism within a four-stage cascade architecture (Figure 4).
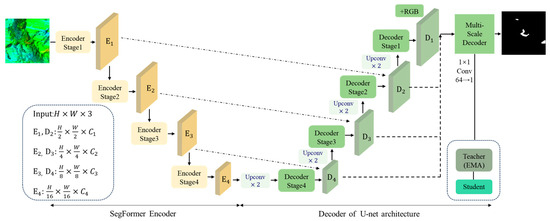
Figure 4.
Structure of Hybrid-SegUFormer.
(1) SegFormer Encoder Layer: A PyTorch-based SegFormer encoder (PySegFormerBackbone) is implemented to extract multi-level features from the input imagery.
(2) U-Net Decoder Layer: Spatial resolution is restored and boundary details are retained through skip connections and layer-wise upsampling.
(3) Multi-Scale Decoder (MSD): Multi-scale semantic features are uniformly projected and fused to generate high-resolution semantic predictions.
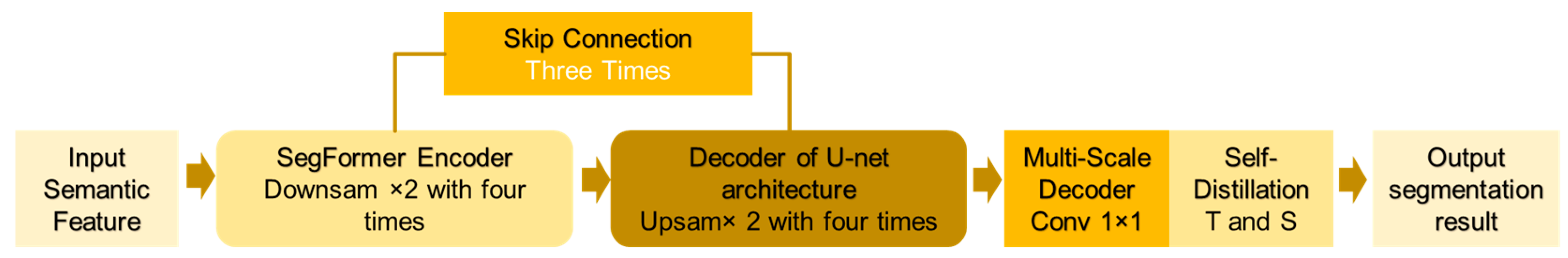
(4) Self-Distillation Optimization Layer: A Teacher-Student self-distillation loop is constructed by using the exponential moving average of the student model’s parameters to update the teacher network. This loop compresses prediction errors and enhances the generalization ability. The complete processing workflow can be expressed as Figure 5.
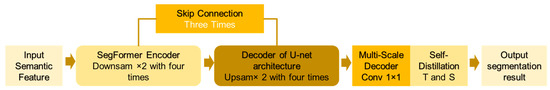
Figure 5.
Complete workflow.
The nomenclature explanation for the Hybrid-SegUFormer model is provided in Table 3.

Table 3.
Nomenclature of Hybrid-SegUFormer.
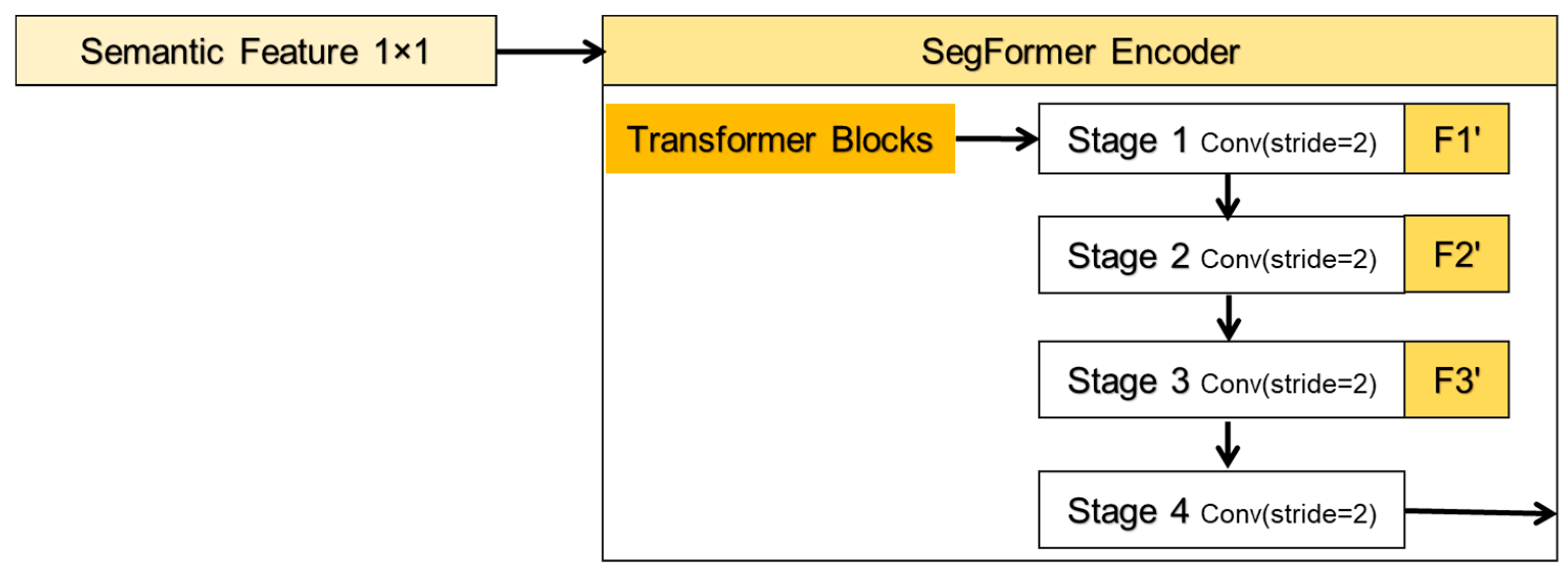
3.3. Encoder
The PyTorch-implemented PySegFormerBackbone encoder uses a four-stage hybrid architecture that combines convolutional downsampling for local feature extraction, lightweight multi-head self-attention for global context modeling, and feed-forward networks (FFNs) for feature refinement. The overall decoding process is illustrated in Figure 6, where F1′, F2′, and F3′ denote the nodes of the skip connections. In each stage, convolutional blocks first reduce spatial dimensions and capture local receptive fields, then flatten feature maps into sequences processed by Transformer blocks to establish long-range dependencies, thereby synthesizing CNN’s computational efficiency with Transformer’s global representation capabilities. The convolutional block at the *l*-th decoder level includes a single 3 × 3 convolution with a stride of 2, performing the mapping defined in Equation (1):
where denotes convolution, and represent the output feature maps at levels and respectively. is batch normalization. the nonlinear activation, and the convolutional kernel parameters. Channel dimensions ensure exponential channel growth while halving spatial resolution per level, generating pyramidal features.
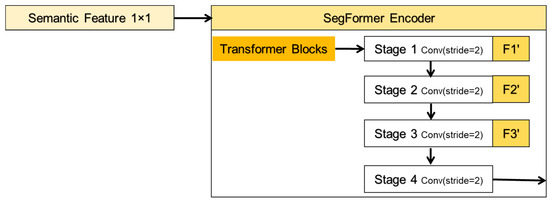
Figure 6.
Processing flow of the encoder.
The resulting tensor is reshaped according to Equation (2) before Transformer processing:
where represents flattened token count, the feature map height, the feature map width, and the reshaped 3D tensor. This implementation eliminates explicit positional encoding by leveraging convolution-derived implicit location information. This not only reduces parameters and computation but also maintains SegFormer’s position-agnostic design. Subsequently, the flattened features are subjected to multi-head self-attention (Equation (3)):
where are query/key/value vectors for head , the key dimension, head output, projection matrix, and head count. Subsequent feed-forward networks (Equation (4)) apply:
where z represents input features, and are the linear weights. The complete Transformer block integrates GELU activation, residual connections, and layer normalization. The encoder ultimately outputs four-level features , combining convolutional local perception with self-attention global representation.
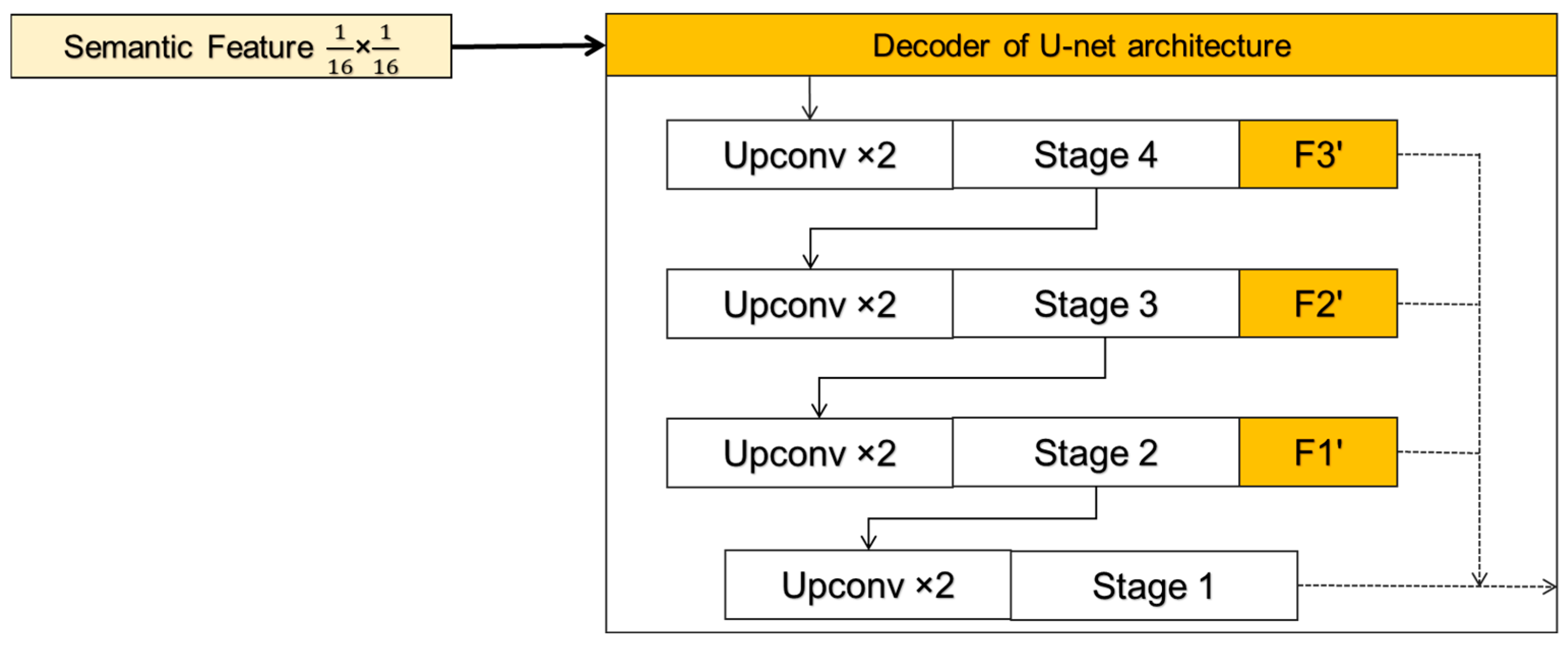
3.4. Hierarchical U-Net Decoder
The Hybrid-SegUFormer decoder incorporates U-Net’s paradigm of “Upsampling-Concatenation-Convolution”, constructing four decoding stages () for quad-level encoder features (Figure 7). At each level, transposed convolution () doubles spatial resolution, followed by skip connections with the same-resolution encoder features for semantic-detail alignment and fusion. The final decoder stage fuses with bilinearly upsampled original path features, integrating low-level texture details. This structure maintains deep semantics while gradually restoring fine-grained edges through shallow layers, achieving a unified resolution and semantics.
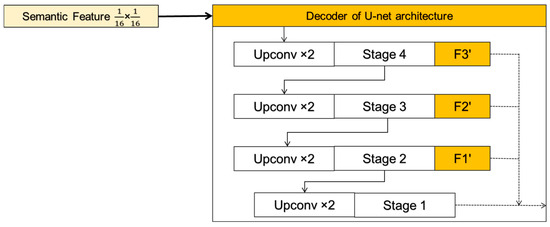
Figure 7.
Processing flow of the decoder.
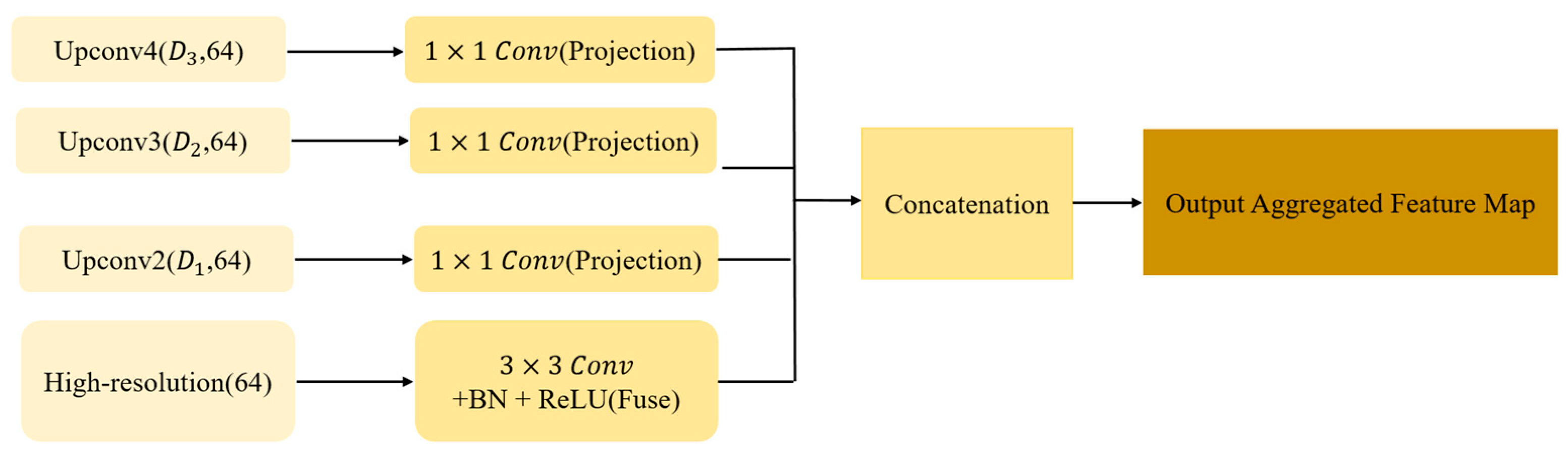
3.5. Multi-Scale Decoder
Due to the significant cross-scale variations in spatial patterns of landslide deformation areas, single-scale semantic features struggle to capture both macro and micro targets simultaneously. To address this limitation, Hybrid-SegUFormer includes the MSD (Figure 8). This module performs channel projection and convolutional fusion across different semantic hierarchies while maintaining a uniform output resolution, ultimately generating scale-sensitive yet spatially consistent prediction maps. The four-level features derived from the U-Net decoder still exhibit scale and channel discrepancies, specifically:.
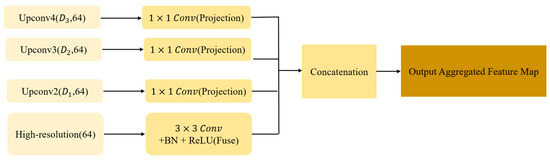
Figure 8.
Core technical workflow of the multi-scale decoder.
The MSD first projects all feature scales to 64 channels using 1 × 1 convolutions. Subsequently, all multi-scale feature maps are upsampled to match the spatial resolution of the input image and concatenated along the channel dimension to fuse multi-scale information.
The integrated feature is obtained through 3 × 3 convolutional fusion, followed by projection to a single-channel segmentation map via 1 × 1 convolution. This design explicitly models diverse receptive fields, significantly enhancing detection capabilities for multi-scale targets (Large-scale landslides and Slender slope toes).
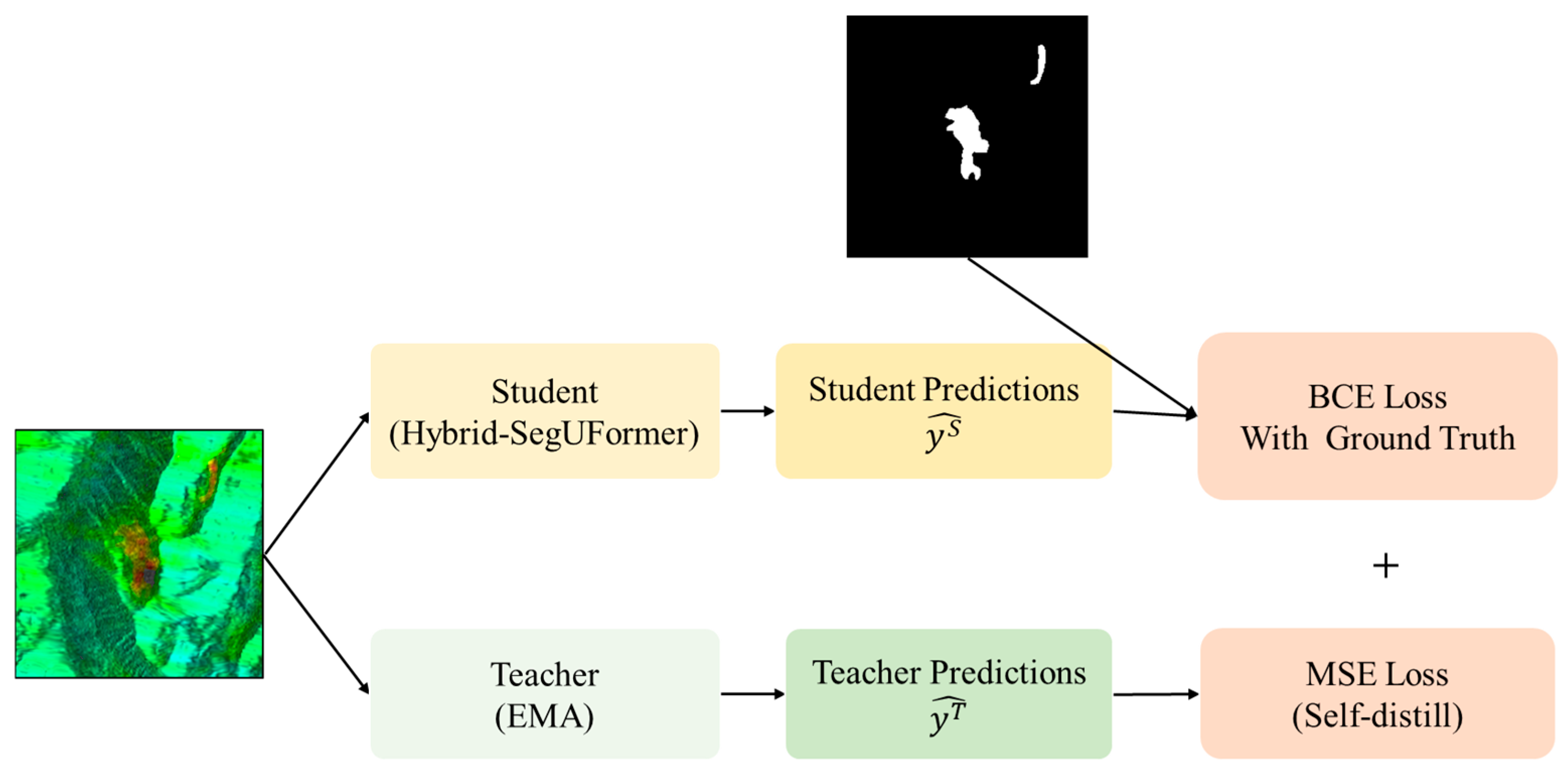
3.6. Online Self-Distillation Mechanism
To mitigate overfitting risks in landslide deformation area extraction under limited annotated samples, this study integrates a Mean Teacher self-distillation framework (Figure 9) into the Hybrid-SegUFormer backbone, enhancing model generalization. This framework constructs the teacher network via an exponential moving average (EMA) of student model parameters, offering dual advantages:
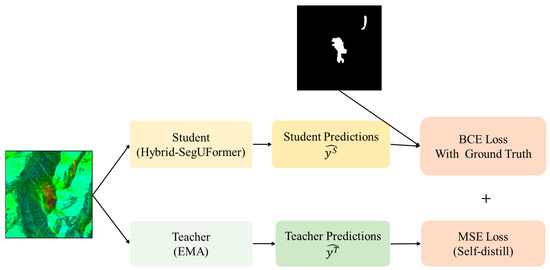
Figure 9.
Self-Distillation Architecture Schematic.
(1) Pre-training Independence: The teacher network is constructed via the exponential moving average (EMA) of historical student parameters, thereby eliminating dependence on external pre-trained models. Builds the teacher network through EMA of historical student parameters, eliminating reliance on external pre-trained models;
(2) Zero Inference Overhead: The teacher network operates solely during training, adding no computational burden during inference.
The teacher model’s predictions serve as stable soft labels, enforcing consistency constraints on the student model. This introduces an adaptive distillation consistency loss alongside traditional hard-label supervised loss, with the joint loss function formulated as follows (Equation (5)):
where is the Sigmoid function, and process the prediction outputs of the student and teacher networks, respectively. Teacher model weights are updated via the exponential moving average (EMA) of student parameters , without direct backpropagation.
InSAR deformation maps fundamentally differ from natural images: they contain multiplicative speckle, spatially varying coherence (γ), atmospheric phase-screen residuals, and phase-wrapping discontinuities that obscure deformation boundaries and produce sparse, noise-prone labels. The model employs a self-distillation mechanism, in which an EMA-based teacher (α = 0.99) generates temporally averaged soft masks, while the student is optimized using a BCE loss against binary labels together with an MSE consistency term to the teacher’s outputs. The teacher’s smoothed predictions suppress speckle-induced fluctuations and capture uncertainty in low-coherence regions, guiding the student toward spatially coherent deformation patterns. This mechanism reduces false detections in decorrelated or layover–shadow areas, preserves boundary continuity along interferometric fringes, and enhances cross-pair generalization under varying baselines and atmospheric conditions.
3.7. Evaluation Metrics
To assess the performance of the recognition method, this study uses five metrics: accuracy, precision, recall, Intersection over Union (IoU), and F1-score. Accuracy measures the proportion of correctly predicted pixels out of the total pixels. Precision quantifies the percentage of true deformation pixels among those predicted as salient deformation areas. Recall represents the fraction of actual deformation pixels that were correctly identified. IoU evaluates the overlap between predicted and ground-truth deformation regions. The F1-score is the harmonic mean of precision and recall, providing a comprehensive reflection of the model’s precision and completeness in identifying salient deformation areas. The formulae for each metric are provided below.
where:
- TP (True Positives): Correctly predicted landslide deformation pixels;
- TN (True Negatives): Correctly predicted non-landslide pixels;
- FP (False Positives): Non-landslide pixels misclassified as deformation;
- FN (False Negatives): Landslide deformation pixels missed by the prediction.
4. Results and Analysis
4.1. Results of the SBAS-InSAR Deformation Estimation
The annual line-of-sight (LOS) deformation velocity under periodic color mapping was shown in Figure 10 (Area 1) and (Area 2).
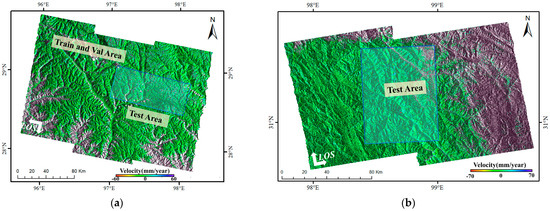
Figure 10.
Surface deformation velocity map. (a) is for Area 1 and (b) for Area 2.
Figure 10a illustrates the surface deformation monitoring results of Zayu County. Positive deformation velocity indicates ground movement toward the radar sensor, whereas negative deformation indicates movement away from it. The results show that during the period from 2 January 2020, to 23 November 2022, the maximum annual deformation velocity away from the LOS reached approximately 170 mm/y, while that toward the LOS reached approximately 110 mm/y. Overall, the applicability of InSAR in Zayu County is higher in the eastern region than in the western region, and higher in the northern region than in the southern region. This spatial variation was primarily attributed to the dense vegetation in the western and southern areas. The abundant vegetation caused multiple scattering, occlusion effects, and seasonal growth variations, resulting in complex phase changes of the C-band radar signal during propagation. Consequently, maintaining phase coherence between radar echoes acquired at different times and locations became difficult, ultimately leading to decorrelation.
Figure 10b presents the surface deformation estimation results for Area-2. The maximum deformation velocity away from the sensor reached 134 mm/y, while the maximum deformation velocity toward the sensor reached 52 mm/y. Owing to the sparse vegetation in this area, a high density of monitoring points is observed. Notably, the landslide deformation zone in this area exhibits a chair-shaped pattern, characterized by pronounced deformation features and clearly defined spatial boundaries.
4.2. Sample Preparation
Using Google Earth optical imagery as a supplementary reference along with InSAR deformation phase maps, we extracted significant landslide deformation areas on the ArcGIS platform. Initial interferometric processing of the study-area SAR imagery produced deformation phase and average velocity maps. Deformation-concentrated zones were identified through overlay analysis and visual interpretation. These areas were then vectorized using ArcGIS tools to create polygon vector datasets of significant deformation regions (Figure 11), providing high-quality sample labels for subsequent landslide detection. To manage GPU memory constraints during training, deformation phase images were cropped into 256 × 256-pixel samples (total: 1975 samples). The dataset was partitioned into 5:1 (train: test) and 8.5:1 (train: val) ratios, with sample ground truths comprising InSAR significant deformation areas and background values.

Figure 11.
Examples of deformation area masks.
4.3. Model Comparative Experiments
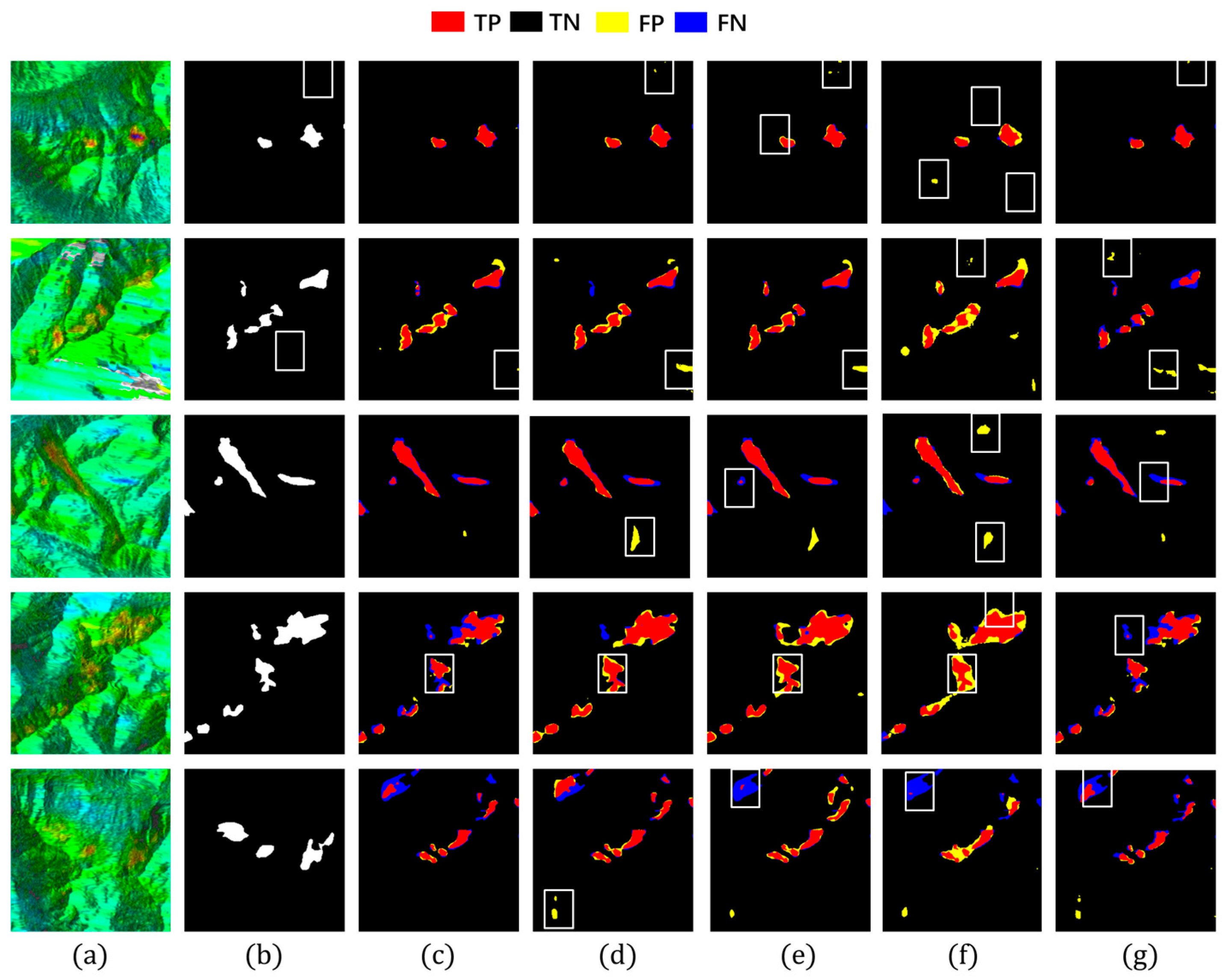
To assess model performance, we compared Hybrid-SegUFormer with several mainstream semantic segmentation models, including U-Net, DeepLabV3+, Mask R-CNN, and Seg-Former. The results of landslide deformation area identification across these models are illustrated in Figure 12, with quantitative evaluation metrics provided in Table 4 and Table 5. Both Figure 12 and Table 4 and Table 5 show that Hybrid-SegUFormer outperforms the others in both qualitative visual assessment and quantitative metrics.
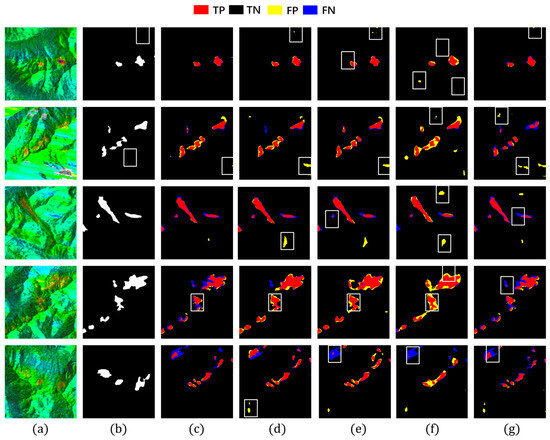
Figure 12.
Detection results of different detection models. (a) InSAR displacement velocity map; (b) Ground truth label; (c) Hybrid-SegUFormer; (d) U-net; (e) DeepLabV3+; (f) Mask R-CNN; (g) SegFormer.

Table 4.
Evaluation metrics of Hybrid-SegUFormer across multiple runs.

Table 5.
Evaluation metrics of Hybrid-SegUFormer and other models on the dataset.
To verify the stability of the proposed model, we conducted four independent training experiments to obtain four distinct pre-trained weights. The corresponding performance data and statistical metrics are summarized in Table 4. As shown, the deviations across all evaluation indicators are minimal, indicating that the model consistently achieves comparable performance across multiple runs. This experiment provides strong evidence of the model’s stability and confirms that its performance improvement is reproducible rather than incidental. Among these four trained versions, the model achieving the best test performance was selected for comparison with other benchmark methods, as presented in Table 5.
(1) Based on a comprehensive evaluation of metrics (Table 5), the proposed Hybrid-SegUFormer achieves optimal overall performance, attaining the highest scores in accuracy (98.79%), IoU (66.74%), precision (81.78%), and F1-score (80.05%), which reflects superior detection precision, the lowest false positive rate, and an optimal balance between precision and recall. Although U-Net exhibits a slightly higher recall (82.52%), its lower precision may increase false alarms. Overall, Hybrid-SegUFormer outperforms other models in accuracy, segmentation detail, and reliability.
(2) Both DeepLabv3+ and SegFormer exhibit considerable missed detections within landslide deformation zones (blue-highlighted regions in Figure 12e,g), along with inadequate boundary localization precision. Their lower recall values further corroborate these models’ limitations in effectively identifying positive samples. Architectural analysis indicates that DeepLabv3+ suffers from progressive decay of critical semantic information throughout the encoder–decoder process, largely due to the absence of an efficient multi-scale feature fusion mechanism and explicit boundary modeling. This results in distorted reconstructions of landslide spatial morphology. Although SegFormer leverages a Transformer-based architecture to capture global contextual information, it remains deficient in recovering fine-grained spatial details.
(3) Both U-Net and Mask R-CNN generate a significant number of false detections in non-landslide areas (yellow-marked areas in Figure 12d,f), primarily stemming from their insufficient ability to discriminate between background and target features. U-Net’s symmetric encoder–decoder design lacks sufficient global contextual understanding, leading to frequent misclassification of spectrally similar background textures as landslides. Meanwhile, Mask R-CNN, dependent on region proposal mechanisms and RoI-based feature extraction, shows reduced sensitivity to landslides with ambiguous boundaries or irregular geometries. This results in a pronounced increase in false positive rates under noisy imaging conditions.
Meanwhile, we have also added comparative experiments to evaluate the computational costs of different models (Table 6). While the proposed Hybrid-SegUFormer has a slower inference speed (125.27 ms) than lightweight models like U-Net and SegFormer, it achieves a superior balance between performance and efficiency. Its parameter count (12.55 M) and computational cost (32.56 G FLOPs) are significantly lower than those of larger models like DeepLabV3+ and Mask R-CNN. This strategic trade-off is enabled by its core design: a dual-branch hybrid encoder and an attention-guided multi-scale decoder. This architecture effectively captures richer multi-scale contextual features and finer boundary details without excessive computational overhead. The result is substantially improved segmentation accuracy and robustness in complex scenarios, affirming Hybrid-SegUFormer’s advanced and well-balanced design.

Table 6.
Comparative analysis of model complexity and inference performance.
4.4. Ablation Studies
To validate the contributions of individual modules in Hybrid-SegUFormer, ablation studies demonstrate that the complete model (c) achieves the best overall balance, attaining the highest scores in accuracy, recall, IoU, and F1. Notably, the F1-score reaches as high as 80.05%, confirming that the synergistic effect of these three components achieves the best overall performance balance. Although its precision is not the single highest value, it remains well-balanced with recall. This indicates that the model produces fewer false positives and missed detections in practical applications, making it more suitable for robust recognition requirements in complex scenarios. The visualization results in Figure 13 provide intuitive corroboration of the model’s advantage in reducing both false detection phenomena.
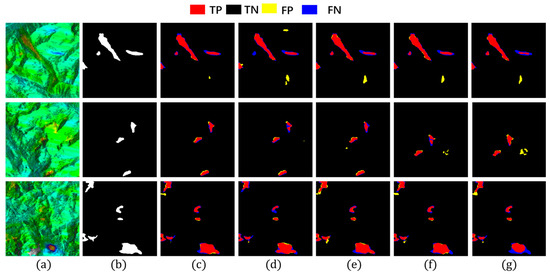
Figure 13.
Ablation study results. (a) InSAR displacement velocity map; (b) Landslide label; (c) Hybrid-SegUFormer; (d) w/o SegFormer encoder (using U-net encoder instead); (e) w/o MSD; (f) w/o self-distillation; (g) w/o MSD and self-distillation.
The ablation study systematically analyzes the impact of each submodule in Hybrid-SegUFormer on landslide deformation area identification, demonstrating that all modules effectively enhance performance (Table 7). Comparing Figure 13e (w/o MSD) with Figure 13c (complete model) reveals that the MSD improves precision by 0.81 percentage points to 81.78% while significantly reducing false detection areas, proving its effectiveness in refining detailed segmentation. A comparison between configurations (c) and (f) demonstrates the specific contribution of the self-distillation module. While recall remains virtually unchanged (78.39% vs. 78.30%), removing this module causes a notable precision decrease from 81.78% to 80.14%, ultimately reducing both F1-score (80.05% to 79.21%) and IoU (66.74% to 65.58%). This indicates that the self-distillation module primarily enhances model performance by effectively suppressing false positives, thus playing a crucial role in maintaining the optimal precision-recall balance in the complete model. The comparison between Figure 13g (w/o MSD and self-distillation) and Figure 13e (w/o MSD) shows that the self-distillation module increases recall from 75.33% to 77.64%, with visually observable reductions in missed detection areas. This indicates its primary contribution lies in enhancing model generalization and detection sensitivity for potential landslides to reduce omissions, though it has a limited impact on precision improvement.

Table 7.
Evaluation metrics for ablation study.
A further comparison between Figure 13c (complete model) and Figure 13d (U-Net encoder replacing SegFormer) reveals that the model employing the SegFormer encoder demonstrates significantly superior performance across all five evaluation metrics. Visually, Figure 13c exhibits fewer false detections and missed identifications, along with more precise delineation of landslide boundaries. These observations collectively demonstrate that the SegFormer encoder effectively enhances the model’s global contextual awareness, and the most significant improvements in fine boundary delineation are attributed to the synergistic interaction between the SegFormer encoder and our proposed decoder architecture.
It is noteworthy that when configured with only the SegFormer encoder (without the MSD and self-distillation), the model achieves its highest precision of 83.49% (the best among all configurations), demonstrating its extremely conservative prediction of foreground areas and effective suppression of false positives. However, this configuration shows suboptimal recall (75.33%) and IoU (65.57%), revealing significant missed detection issues (false negatives). This reflects the model’s strong conservatism: it sacrifices detection completeness in pursuit of high precision. Mechanistically, while SegFormer’s global attention mechanism can abstract semantic information and suppress background noise to reduce false alarms, the absence of boundary detail supplementation from the MSD and feature enhancement for weak semantic regions through self-distillation results in the model only recognizing the most prominent and definite landslide areas, consequently exacerbating missed detections.
4.5. Evaluation of Multi-Scale Perception Capabilities Across Models
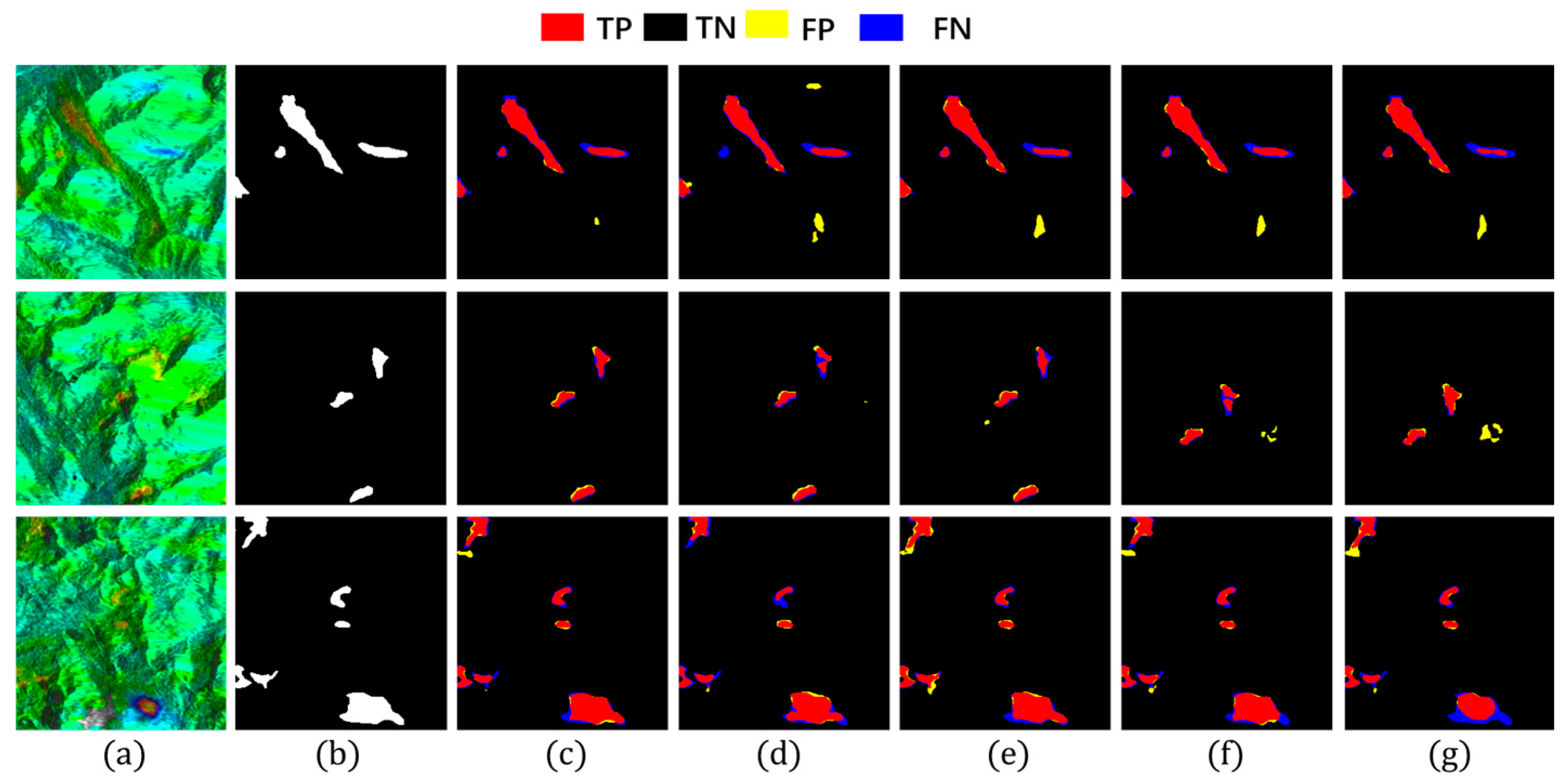
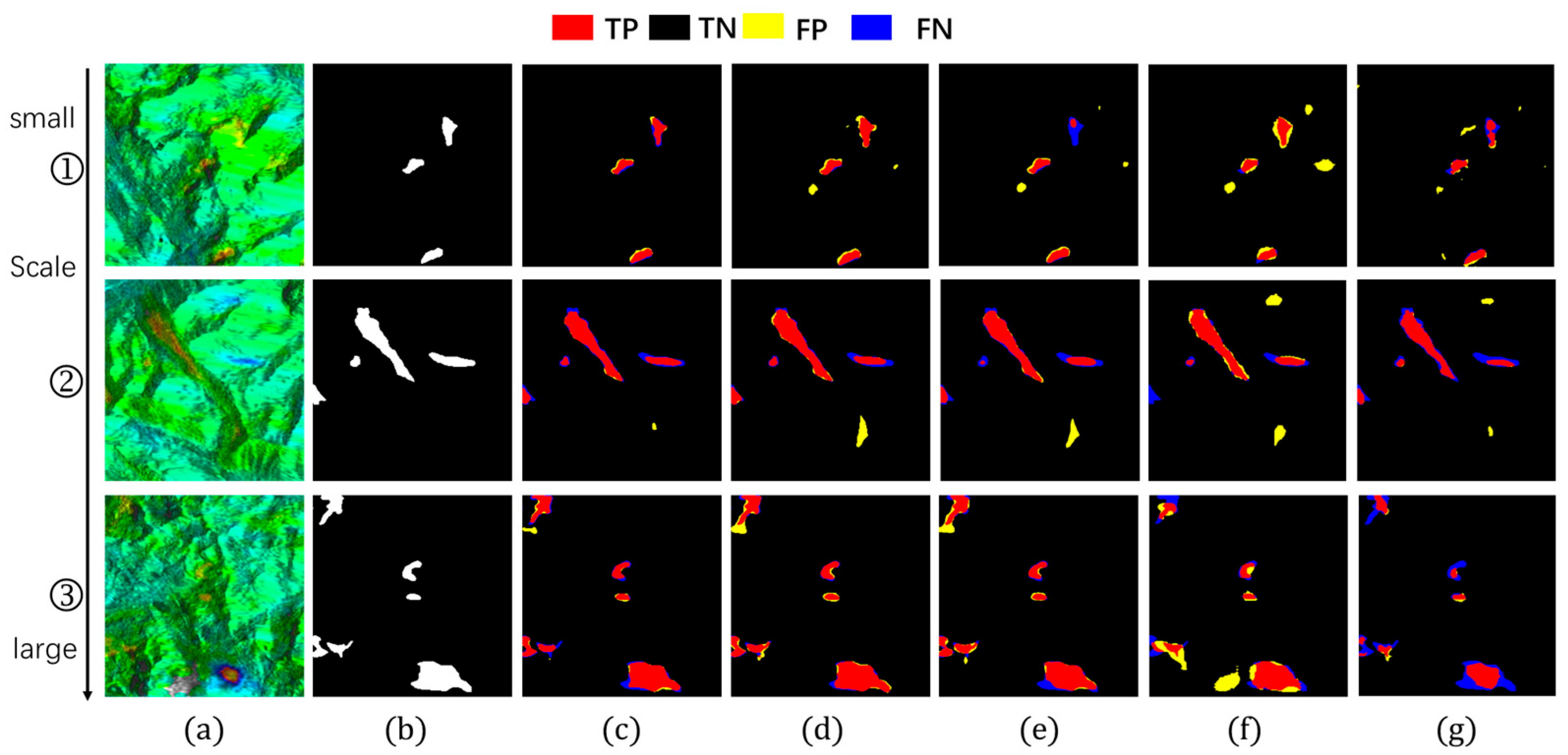
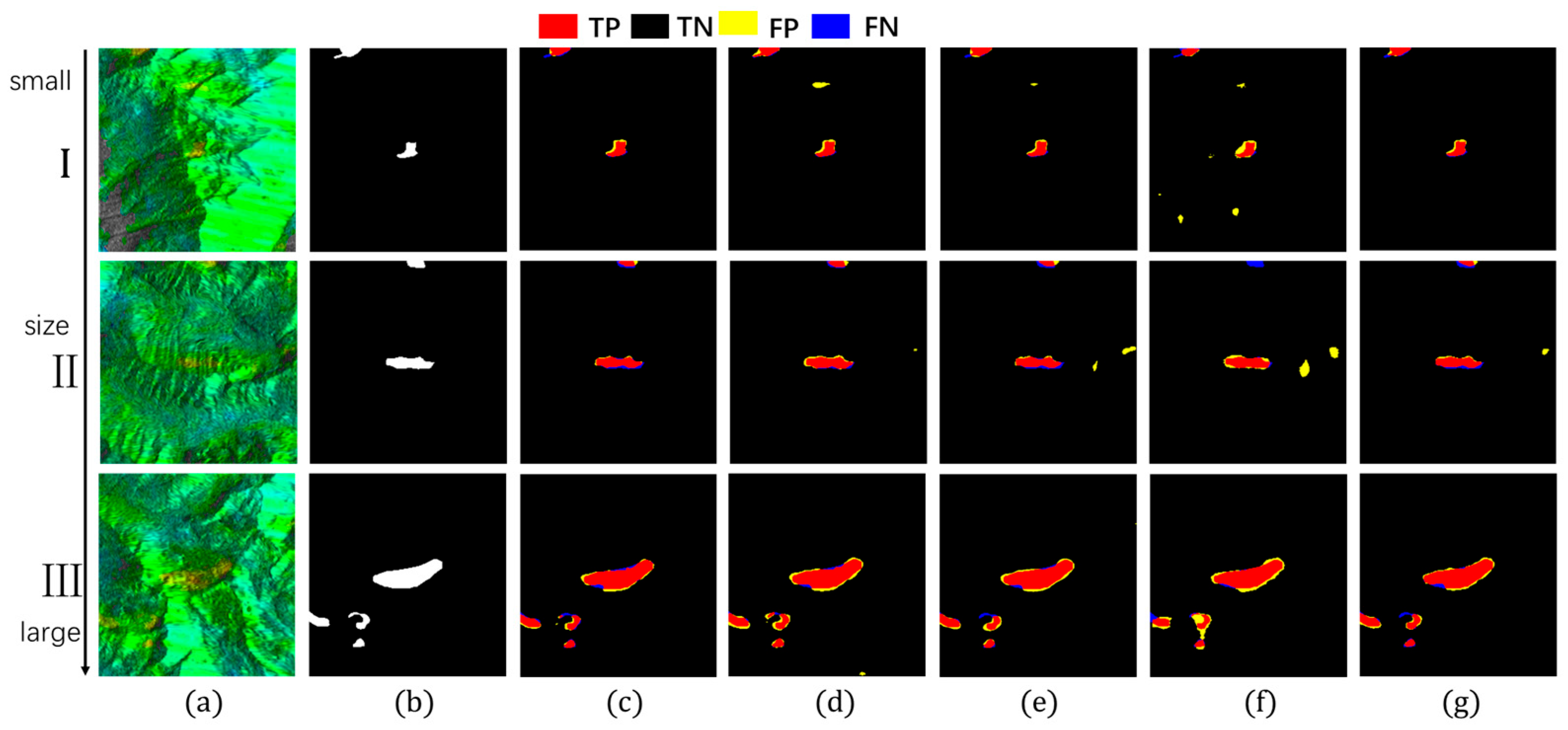
This section demonstrates Hybrid-SegUFormer’s multi-scale perception capability and its advantages over comparative models. Models with robust multi-scale perception typically exhibit three key characteristics: (1) higher recall and F1-scores for small-scale targets; (2) relative insensitivity of IoU metrics to target size variations; and (3) extensive spatial distribution of true positive (TP) regions, indicating strong spatial consistency between predictions and ground truth annotations. To quantitatively evaluate this capability, we selected sample images from Figure 14 and Figure 15, calculating recall, IoU, and F1-scores for each case. The corresponding quantitative results are systematically summarized in Table 8, Table 9 and Table 10.
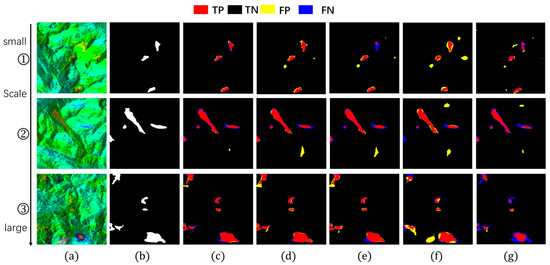
Figure 14.
Detection images at different scales (group1). (a) InSAR displacement velocity map; (b) Landslide ground truth; (c) Hybrid-SegUFormer; (d) U-net; (e) DeepLabV3+; (f) Mask R-CNN; (g) SegFormer.
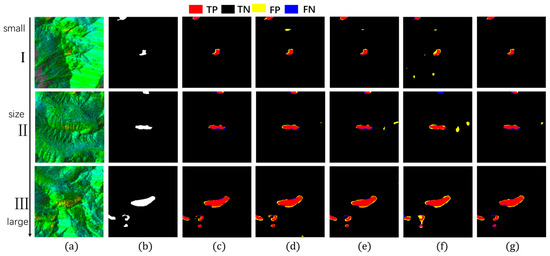
Figure 15.
Detection images at different scales (group2). (a) InSAR displacement velocity map; (b) Landslide ground truth; (c) Hybrid-SegUFormer; (d) U-net; (e) DeepLabV3+; (f) Mask R-CNN; (g) SegFormer.

Table 8.
IoU range across scales (%) for Hybrid-SegUFormer and other models on the dataset.

Table 9.
Multi-scale recall comparison (%).

Table 10.
Multi-scale F1-score comparison (%).
In the evaluation of IoU metrics (Table 8), all models exhibited performance degradation as target scales decreased, but with markedly different attenuation magnitudes. Hybrid-SegUFormer demonstrated significantly lower total IoU attenuation (6.99% and 8.83% respectively) compared to benchmark models: U-Net (11.80%/11.75%), DeepLabV3+ (27.92%/15.04%), Mask R-CNN (16.15%/20.71%), and SegFormer (19.03%/12.90%). These results indicate that Hybrid-SegUFormer maintains superior stability and robustness across scales, exhibiting more effective adaptation to varying landslide sizes while preserving higher segmentation accuracy for small targets—a compelling validation of its multi-scale fusion architecture’s efficacy.
The recall analysis (Table 9) reveals significant disparities among models in detecting small targets (Image ①). While U-Net demonstrates high sensitivity to small targets with a 94.66% recall rate, its substantially degraded IoU and F1-scores indicate that this high recall comes at the cost of significant false positives. In contrast, Hybrid-SegUFormer maintains a balanced detection capability, achieving both considerable recall (81.70%) and segmentation accuracy (IoU/F1). DeepLabV3+ (59.94%) and SegFormer (74.68%), however, show markedly lower recall rates for small targets, reflecting their inadequate recognition capacity for small-scale landslide areas.
The F1-score effectively balances recall and precision. Hybrid-SegUFormer maintains consistently high F1-scores across all scales (peaking at 89.52% with a minimum of 82.97%, Table 10), demonstrating minimal performance decline and superior overall capability for multi-scale target recognition. In contrast, while U-Net achieves higher recall rates (Table 9), its F1-score drops to 67.30% on Image ①, indicating significant false positive issues with small targets. SegFormer, although showing less F1-score degradation, has generally lower absolute values (Table 10), highlighting the inherent limitations of single-scale architectures in managing target size variability.
By integrating these analyses (Table 8, Table 9 and Table 10), this study systematically compares Hybrid-SegUFormer with benchmark models (U-Net, DeepLabV3+, Mask R-CNN, SegFormer) across multiple scales using IoU, recall, and F1 metrics. It conclusively validates Hybrid-SegUFormer’s superior multi-scale perception capability. The proposed model not only achieves outstanding performance across all target scales but also strikes an optimal balance between precision and recall, effectively addressing the critical limitations of comparative models in handling varying target sizes.
4.6. Ablation Study on Multi-Scale Perception Capabilities
To systematically evaluate the multi-scale perception capability of the proposed Hybrid-SegUFormer in detecting landslide deformation areas, a comparative ablation experiment was conducted with a focus on the multi-scale decoder module. The experiment utilized 20 landslide deformation velocity maps, comprising 10 large-scale and 10 small-scale images, to comprehensively assess performance across varying spatial extents. For each image, the IoU, recall, and F1-score were calculated, and the average values for each scale category were summarized to provide a robust statistical comparison, as presented in Table 11, Table 12 and Table 13. This multi-faceted evaluation with aggregated metrics verifies that the performance enhancement of the proposed model in multi-scale perception is not occasional or limited to specific cases.

Table 11.
IMulti-scale IoU comparison of Hybrid-SegUFormer with or without the self-distillation module

Table 12.
Recall range across scales (%) for different models.

Table 13.
F1 range across scales (%) for different models.
The results in Table 11 (IoU across scales) demonstrate the model’s stability. The complete Hybrid-SegUFormer model exhibits a smaller performance range (2.36%) between large and small scales compared to the variant without the multi-scale decoder (3.08%) in the first set, indicating superior scale robustness.
Analysis of Table 12 (recall across scales) reveals a nuanced role of the multi-scale decoder. In the first set, the complete model achieves lower recall on both large (89.13%) and small scales (84.85%) compared to the ablated version. This indicates that the multi-scale decoder’s primary contribution is not necessarily to increase raw detection sensitivity but potentially to refine the quality of detections.
The data in Table 13 (F1-score across scales) provides the most critical insight into overall performance. The complete Hybrid-SegUFormer achieves higher F1-scores on both large (87.34%) and small (85.72%) scales than its counterpart, alongside a smaller performance range between scales (1.62% vs. 2.62%). This conclusively demonstrates that the integration of the multi-scale decoder enhances the model’s comprehensive performance and ensures more consistent and reliable detection across diverse spatial scales.
In summary, the ablation study confirms that while the multi-scale decoder may not uniformly boost individual metrics like recall, it plays an indispensable role in achieving a superior balance between precision and recall. This is evidenced by the higher and more stable F1-scores across scales, validating its effectiveness in enabling robust multi-scale landslide detection. The synergistic integration of the multi-scale decoder is thus crucial for handling the complex multi-scale characteristics inherent in landslide deformation areas.
4.7. Model Transferability Validation
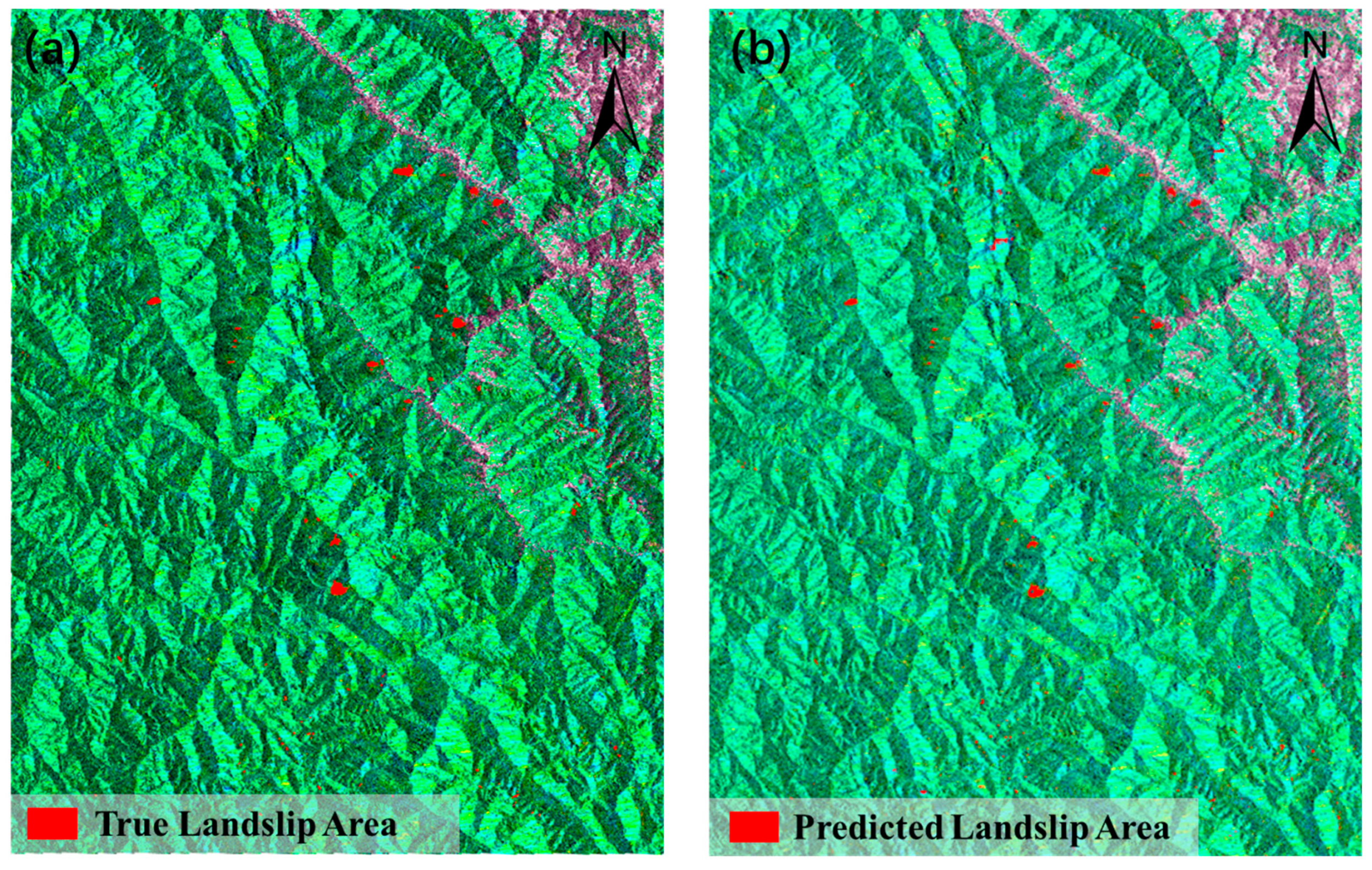
To evaluate the generalization capability of the Hybrid-SegUFormer model, the pre-trained model was transferred to Study Area II (the Baige-Tangge section of the Jinsha River), which is geographically distant from the original training area. The landslide deformation area identification results based on the Hybrid-SegUFormer model are presented in Figure 16 and Table 14.
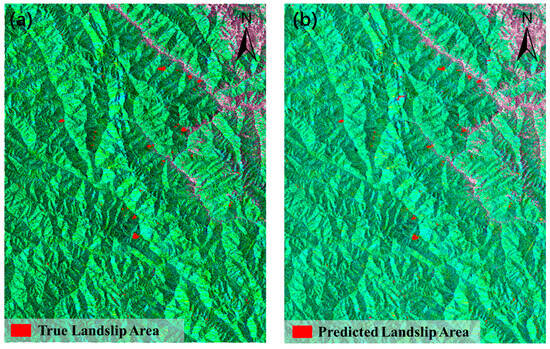
Figure 16.
Partial identification of migrated dataset compared with the true value. (a) Ground truth of the test dataset, (b) Prediction part of the test dataset.

Table 14.
Evaluation metrics for different detection models.
The training results and statistical metrics of the proposed model over four independent runs are summarized in Table 15 below. As observed, although certain training iterations exhibited a slight decline in overall performance, the variations among different runs remain minor. These consistent outcomes substantiate the stability and robustness of the proposed model, indicating that its performance is not sensitive to random initialization or training variations.

Table 15.
Multiple-run parameters and statistical parameters of Hybrid-SegUFormer.
Evaluation results on the newly migrated landslide dataset (Table 13) demonstrate Hybrid-SegUFormer’s significant advantages: it achieves top performance in both IoU (69.47%) and F1-score (81.99%), surpassing classical models U-Net (IoU 69.34%, F1 81.89%) and DeepLabV3+ (IoU 67.09%, F1 80.31%). Notably, compared to the widely used Transformer model SegFormer (IoU 56.06%, F1 71.84%), Hybrid-SegUFormer shows remarkable improvements of 13.41% in IoU and 10.15% in F1-score, highlighting its exceptional generalization capability. Furthermore, the model maintains an optimal balance between precision (89.81%) and recall (75.42%), indicating more balanced control over false positives and missed detections. These comprehensive metrics conclusively validate Hybrid-SegUFormer’s effectiveness and robustness for transferred landslide recognition tasks.
4.8. Exclusion of Non-Landslide Deformation Areas Based on Auxiliary Data
In landslide deformation area identification, study areas often contain various non-landslide surface disturbance sources (such as agricultural activities, seasonal vegetation variations, construction activities, and radar geometric distortions), which can easily lead to misinterpretations. To improve identification accuracy and practical utility, this study uses a systematic procedure for removing non-landslide deformation areas based on multi-source auxiliary data, after initially extracting prominent landslide deformation regions using Hybrid-SegUFormer. The specific steps of this procedure include the following: ① combining land cover data to exclude human-disturbed areas such as permanent croplands, water bodies, and construction zones; ② incorporating NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index) data to exclude regions with high vegetation coverage (threshold greater than 0.5), thereby reducing false deformation signals caused by normal seasonal vegetation changes or forest dynamics; ③ using radar geometric distortion data to identify and exclude observation-unreliable areas such as layover and shadow zones; and finally, applying slope information to filter out areas with excessively gentle slopes, minimizing false alarms due to insufficient topographic relief. This systematic elimination strategy reduces the proportion of false landslide deformation areas, significantly decreases misjudgments, and provides crucial data preprocessing support for building a highly reliable automated monitoring system for geological hazards.
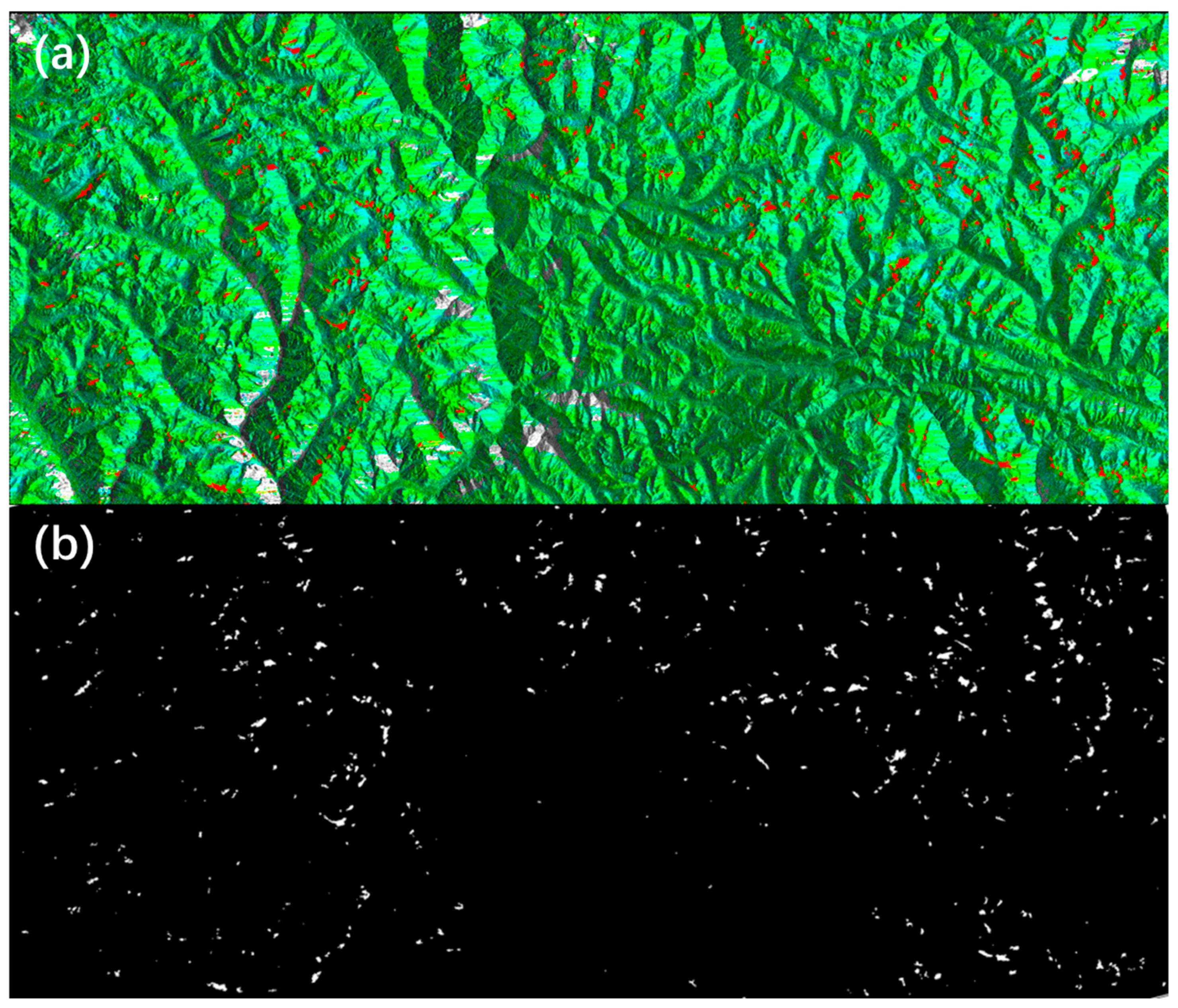
Before implementing the aforementioned filtering procedures, the patch-based predictions generated by the Hybrid-SegUFormer model are first mosaicked into large-scale GeoTIFF images with precise geospatial coordinates (as illustrated in Figure 17). This critical preprocessing step establishes the foundation for subsequent multi-source data spatial registration and overlay analysis.
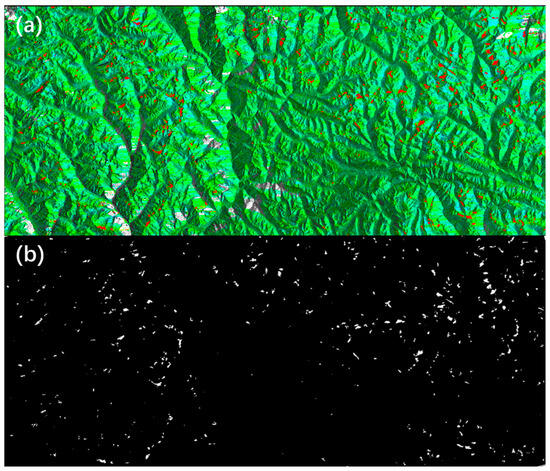
Figure 17.
(a) Landslide deformation area identification results; (b) Landslide deformation area mask.
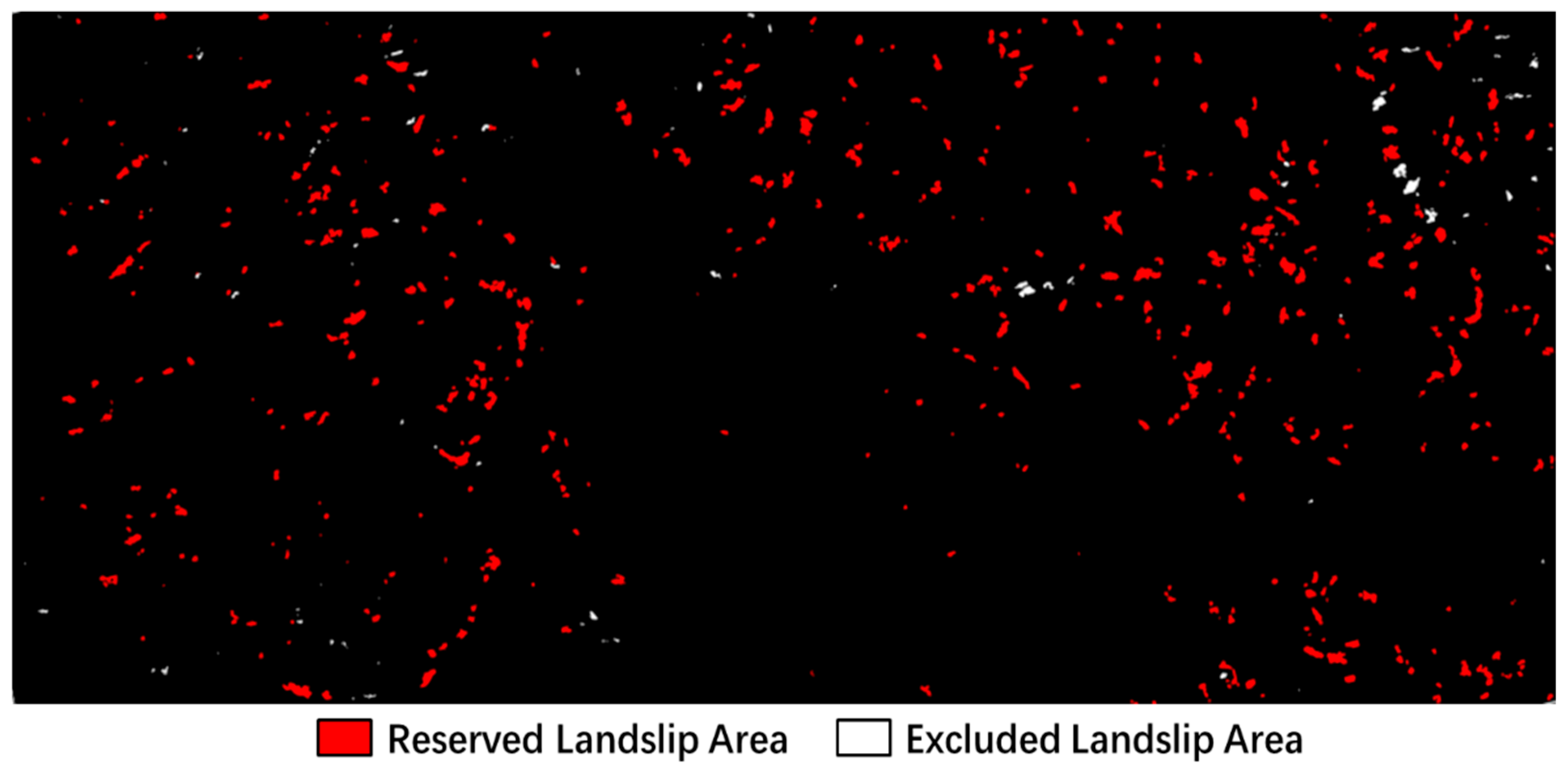
The Python script was then employed to extract white significant deformation areas from the landslide mask and convert them into Shapefile format for ArcGIS 10.8 integration. We run the script in Python 3.11. Subsequently, multi-source auxiliary data were incorporated to eliminate non-significant deformation areas through the editing of Shapefile attributes, with the refined results presented in Figure 18.

Figure 18.
Results before/after non-landslide deformation area excluded.
5. Discussion
This study addresses the challenges of multi-scale target perception, boundary detail restoration, and insufficient model generalization performance in the detection of landslide InSAR Deformation areas. We propose the Hybrid-SegUFormer model, which integrates a SegFormer encoder, a U-Net decoder structure, an MSD, and a self-distillation mechanism. Through systematic experimental validation, Hybrid-SegUFormer demonstrates superior performance in complex landslide scenarios, and an in-depth analysis of its advantages is provided.
5.1. Superiority of Model Performance
Comparative experiments with mainstream semantic segmentation models (U-Net, DeepLabV3+, Mask R-CNN, SegFormer) show that Hybrid-SegUFormer performs excellently in both qualitative and quantitative evaluations. Specifically, DeepLabV3+ and SegFormer exhibit significant missed detections and boundary localization deviations; U-Net and Mask R-CNN suffer from high false detection rates due to insufficient background discrimination ability. In contrast, Hybrid-SegUFormer effectively balances missed and false detections through its hybrid architecture, achieving more accurate identification of landslide deformation areas and boundary characterization. This capability offers essential geometric parameters for volume estimation and kinematic analysis, thereby greatly improving the utility of InSAR data in landslide risk assessment.
5.2. Synergistic Contribution of Core Modules
Ablation studies quantify the contribution of each module to the model’s performance. The full model (F1: 80.05%) achieves the best overall balance, attaining the highest scores in accuracy, recall, IoU, and F1, verifying the importance of the synergistic effects of the SegFormer encoder, MSD, and self-distillation module. Among them, the SegFormer encoder significantly enhances the model’s global context modeling capability and generalization performance; the MSD effectively improves the segmentation precision of detailed regions (especially boundaries); the self-distillation module strengthens the model’s generalization ability and detection sensitivity to potential landslide areas, effectively reducing the missed detection rate. The three together form a “global-local-knowledge distillation” closed-loop optimization, breaking through the performance limitations of individual modules.
5.3. Exceptional Multi-Scale Perception Ability
The experimental results demonstrate Hybrid-SegUFormer’s competent multi-scale perception capability for landslide detection. While all models showed performance degradation with decreasing target scales, Hybrid-SegUFormer exhibited relatively attenuated performance reduction (IoU range: 6.99–8.83% versus 11.80–27.92% in benchmarks), indicating better scale adaptability. The model maintains a balance between detection sensitivity and accuracy, achieving reasonable recall (81.70% for small targets) while avoiding the significant false positive issues observed in U-Net. The ablation study further reveals that the multi-scale decoder contributes to performance stability across scales (F1-range: 1.62% versus 2.62% without decoder), though its impact varies across different metrics. These consistent results across multiple evaluation metrics suggest that Hybrid-SegUFormer’s architecture effectively addresses scale variance challenges in landslide detection tasks.
5.4. Validation of Model Transferability
Evaluation results on the newly constructed transfer landslide dataset demonstrate that Hybrid-SegUFormer exhibits exceptional cross-regional recognition capability. It outperforms all comparison models in two key metrics: Intersection over Union (IoU: 69.47%) and F1-score (81.99%). Particularly when compared to the SegFormer model, it achieves significant improvements (13.41% increase in IoU and 10.15% increase in F1-score). Furthermore, the model maintains an excellent balance between precision (89.81%) and recall (75.42%), indicating more balanced control over false positives and missed detections for landslide targets. These results strongly validate the effectiveness and robustness of the model in transfer landslide identification tasks. This generalization ability can reduce dependency on extensive, region-specific data collection, thereby accelerating large-scale regional landslide screening and geohazard assessment.
5.5. Comparative Analysis with Related Studies
Compared to related studies, the innovations and distinctive features of this model are mainly reflected in three aspects: In terms of architectural fusion, it creatively combines the SegFormer’s advantages in global long-range context modeling with the U-Net decoder’s ability to restore fine-grained local features; in module enhancement, the introduction of the MSD significantly improves perception ability for multi-scale landslide areas in complex terrain, and the self-distillation mechanism further enhances boundary precision and model robustness; in multi-source information utilization, it effectively integrates multi-source auxiliary data (geometric distortion, terrain slope, NDVI, land use type), and by incorporating non-visual prior information, it accurately filters out non-landslide areas, significantly reducing the false detection rate and improving the reliability and practicality of the results.
5.6. Limitations and Future Work
While Hybrid-SegUFormer demonstrates strong multi-scale perception and cross-regional transferability, several limitations persist. First, the model’s performance remains constrained by input data quality, including SAR coherence/resolution and DEM accuracy, where poor-quality inputs in rugged terrain can introduce artifacts and reduce boundary precision. Second, detection challenges remain for small, elongated, or blurry-boundary landslides due to Transformers’ local detail constraints, error propagation in self-distillation, and inherent InSAR resolution limits. Finally, the lack of comprehensive ground-truth validation in truly unseen regions hinders the precise quantification of operational performance in new geological settings.
Based on these limitations, our future work will pursue three key directions: (1) optimizing the model through lightweight Transformers and boundary-focused loss functions to enhance efficiency and detail capture; (2) rigorously validating generalization capability across diverse terrains and data qualities; (3) advancing transfer learning techniques while initiating field campaigns for ground-truth collection, ultimately bridging the gap toward operational landslide monitoring systems; (4) integrating multi-source data (e.g., LiDAR-derived topography and SAR coherence) to enhance feature discrimination and improve model robustness against vegetation, shadows, and complex terrain.
6. Conclusions
Hybrid-SegUFormer is proposed to address the challenges of multi-scale target perception, inadequate recovery of boundary details, and limited generalization capability in the identification of landslide InSAR deformation areas. The model integrates a SegFormer encoder, a U-Net-based decoder, a multi-scale feature decoding module, and a self-distillation mechanism. Through systematic experiments and comprehensive evaluation, the following key conclusions are drawn:
(1) Comprehensive evaluation demonstrated that Hybrid-SegUFormer achieves state-of-the-art performance in landslide deformation area identification, outperforming benchmark models (U-Net, DeepLabV3+, Mask R-CNN, SegFormer) across key metrics, including accuracy (98.79%), IoU (66.74%), and F1-score (80.05%). While maintaining reasonable computational efficiency, the model effectively addresses critical limitations observed in comparative approaches: reducing false detections through enhanced global context understanding, improving boundary precision via multi-scale feature fusion, and maintaining robust performance across multiple training runs. The results confirm Hybrid-SegUFormer’s superior capability in balancing segmentation accuracy, operational efficiency, and operational stability for complex landslide detection tasks.
(2) Ablation studies confirm that the complete Hybrid-SegUFormer achieves optimal performance balance (F1-score: 80.05%) through synergistic module integration. The multi-scale decoder enhances precision (81.78%) and reduces false detections, while the self-distillation module effectively suppresses false positives and maintains precision-recall balance. The SegFormer encoder provides superior global contextual awareness, though its standalone use yields high precision (83.49%) at the cost of significantly reduced recall (75.33%). These findings demonstrated that the architectural components collectively address both boundary precision and detection sensitivity, with their integration being crucial for robust landslide identification.
(3) Comprehensive evaluations demonstrated Hybrid-SegUFormer’s superior multi-scale perception capability, showing significantly smaller IoU degradation across scales (6.99–8.83%) compared to benchmark models (11.80–27.92%). While maintaining balanced recall-precision trade-offs, the model achieves consistently high F1-scores (82.97–89.52%) across all target sizes. Ablation studies further confirm the multi-scale decoder’s crucial role in enhancing performance stability, yielding improved F1-scores (85.72–87.34%) and reduced performance variance (1.62% range) across scales. These results collectively validate the architecture’s effectiveness in handling scale variations while maintaining robust detection accuracy for landslide identification tasks.
(4) Evaluation results on a transferred landslide dataset indicate that Hybrid-SegUFormer possesses strong cross-regional recognition capability. Its IoU and F1-score are significantly higher than those of comparative models, demonstrating that the model can effectively adapt to different geographical environments and data distributions, highlighting its considerable practical value and potential for broad application.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.Z. and D.M.; methodology, W.Z. and D.M.; software, J.Z.; validation, W.Z. and J.C.; formal analysis, W.Z.; investigation, J.Z.; resources, W.Z.; data curation, J.C.; writing—original draft preparation, W.Z.; writing—review and editing, D.M.; visualization, W.Z. and J.Z.; supervision, D.M.; project administration, D.M.; funding acquisition, D.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Geological Survey Program “Support for Geo-hazard monitoring, early warning and prevention” (DD20230085) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42371379).
Data Availability Statement
The data are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors want to thank the ESA for providing the satellite radar data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Hungr, O.; Leroueil, S.; Picarelli, L. The Varnes Classification of Landslide Types, an Update. Landslides 2014, 11, 167–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R. Large-scale landslides and their sliding mechanisms in china since the 20th century. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2007, 26, 433–454. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Y.; Wang, F.; Ping, S. Landslide Hazards Triggered by the 2008 Wenchuan Earthquake, Sichuan, China. Landslides 2009, 6, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschbaum, D.; Kapnick, S.B.; Stanley, T.; Pascale, S. Changes in Extreme Precipitation and Landslides Over High Mountain Asia. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2019GL085347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, T.; Guo, Z.; Wang, L.; Jin, B.; Wu, F.; Guo, R. Tempo-Spatial Landslide Susceptibility Assessment from the Perspective of Human Engineering Activity. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hürlimann, M.; Guo, Z.; Puig-Polo, C.; Medina, V. Impacts of Future Climate and Land Cover Changes on Landslide Susceptibility: Regional Scale Modelling in the Val d’Aran Region (Pyrenees, Spain). Landslides 2022, 19, 99–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Wang, H.; Gao, Y.; Li, X. Real-Time Monitoring and Early Warning of Landslides at Relocated Wushan Town, the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Landslides 2010, 7, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Zhu, X.; Li, W.; Dong, X.; Dai, K.; Jiang, Y.; Lu, H.; Guo, C. Technical Progress of Space-Air Ground Collaborative Monitoring of Landslide. Acta Gcodaetica Cartogr. Sin. 2022, 51, 1416–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Zhang, M.; Ma, J.; Qi, G.; Zhu, S.; Huang, Z. Research, Development, and Field Trial of the Universal Global Navigation Satellite System Receivers. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 570, 62048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Zhang, M.; Ma, J.; Han, B.; Ye, S.; Huang, Z. Application of CORS in Landslide Monitoring. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 861, 42049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, L.; Su, F.; Wu, W. Application of InSAR Technology in Landslide Hazard: Progress and Prospects. Natl. Remote Sens. Bull. 2021, 25, 614–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vern, S.; Pierre-Jean, A.; Rejean, C.; Valentin, P. InSAR Monitoring of Landslides on Permafrost Terrain in Canada. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS 2007), Barcelona, Spain, 23 July 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Antoni, W.; Zbigniew, P.; Ramon, H. InSAR Analyses of Terrain Deformation near the Wieliczka Salt Mine, Poland. Eng. Geol. 2009, 106, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Xie, M.; Chai, X.; Wang, L.; Dong, C. Application of D-InSAR Technique to Landslide Monitoring in Wide Reservoir Area. China Min. Mag. 2011, 20, 94–101. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H.; Li, W.; Xu, Q.; Dong, X.; Dai, C.; Wang, D. Early Detection of Landslides in the Upstream and Downstream Areas of the Baige Landslide, the Jinsha River Based on Optical Remote Sensing and InSAR Technologies. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2019, 44, 1342–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Xu, S.; Wang, J.; Hu, K. Identification and Time Series Monitoring of Hidden Dangers of Geological Hazards in the Typical Loess Hilly Regions. Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. 2023, 50, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, Z.; Li, Z.; Yang, C.; Zhu, W.; Liu-Zeng, J.; Chen, L.; Liu, C. Integration of Sentinel-1 and ALOS/PALSAR-2 SAR Datasets for Mapping Active Landslides along the Jinsha River Corridor, China. Eng. Geol. 2021, 284, 106033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondini, A.C.; Guzzetti, F.; Chang, K.-T.; Monserrat, O.; Martha, T.R.; Manconi, A. Landslide Failures Detection and Mapping Using Synthetic Aperture Radar: Past, Present and Future. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2021, 216, 103574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Zhang, L.; Dong, J.; Dong, X.; Li, M.; Xu, Q.; Liao, M. Detection and Characterization of Slow-Moving Landslides in the 2017 Jiuzhaigou Earthquake Area by Combining Satellite SAR Observations and Airborne Lidar DSM. Eng. Geol. 2022, 305, 106730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liao, M.; Dong, J.; Xu, Q.; Gong, J. Early Detection of Landslide Hazards in Mountainous Areas of West China Using Time Series SAR Interferometry-A Case Study of Danba, Sichuan. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2018, 43, 2039–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomás, R.; Pagán, J.I.; Navarro, J.A.; Cano, M.; Pastor, J.L.; Riquelme, A.; Cuevas-González, M.; Crosetto, M.; Barra, A.; Monserrat, O.; et al. Semi-Automatic Identification and Pre-Screening of Geological–Geotechnical Deformational Processes Using Persistent Scatterer Interferometry Datasets. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, M.; Dong, J.; LI, M.; Ao, M.; Zhang, L.; Shi, X. Radar Remote Sensing for Potential Landslides Detection and Deformation Monitoring. Natl. Remote Sens. Bull. 2021, 25, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anantrasirichai, N.; Biggs, J.; Kelevitz, K.; Sadeghi, Z.; Wright, T.; Thompson, J.; Achim, A.M.; Bull, D. Detecting Ground Deformation in the Built Environment Using Sparse Satellite InSAR Data With a Convolutional Neural Network. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 2940–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Ge, D.; Yu, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, M.; Liu, B.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Liu, H. Deep Learning Identification Technology of InSAR Significant Deformation Zone of Potential Landslide Hazard at Large Scale. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2022, 51, 2046–2055. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, S.; Guo, X.; Sun, J.; Qiao, S.; Zhang, L.; Yao, J.; Cheng, Q.; Zhang, Y. Landslide Detection from Open Satellite Imagery Using Distant Domain Transfer Learning. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Shi, A.; Li, X.; Dou, J.; Li, S.; Chen, T.; Chen, T. Deep Learning-Based Landslide Recognition Incorporating Deformation Characteristics. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, W.; Cao, D.; Yi, Y.; Wu, X. A New Deep Learning Neural Network Model for the Identification of InSAR Anomalous Deformation Areas. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashutosh, T.; Manoochehr, S. A Novel Machine Learning and Deep Learning Semi-Supervised Approach for Automatic Detection of InSAR-Based Deformation Hotspots. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2023, 126, 103611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shan, X.; Wang, Z.; Gong, W.; Zhang, G. Deep Learning for Automatic Detection of Volcanic and Earthquake-Related InSAR Deformation. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Xi, J.; Li, Z.; Ding, M.; Yang, L.; Xie, D. Landslide Detection and Segmentation Using Mask R-CNN with Simulated Hard Samples. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2023, 48, 1931–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, C.; Gan, J.; Chen, A.; Acharya, P.; Li, F.; Yu, W.; Liu, F. A Novel Method for Identifying Landslide Surface Deformation via the Integrated YOLOX and Mask R-CNN Model. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 2024, 17, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-Decoder with Atrous Separable Convolution for Semantic Image Segmentation. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2018, 11211, 833–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y. The Research on Landslide Detection in Remote Sensing Images Based on Improved DeepLabv3+ Method. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 7957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, X.; Yang, S. Semantic Segmentation of Landslide Image Using DeepLabv3+ and Completed Local Binary Pattern. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2024, 19, 14502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, J.; Palomino-Ángel, S.; Hidalgo, C. Exploring U-Net Deep Learning Model for Landslide Detection Using Optical Imagery, Geo-Indices, and SAR Data in a Data Scarce Tropical Mountain Region. PFG-J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Geoinf. Sci. 2025, 93, 251–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Zeng, S.; Xiao, K.; Yang, D.; Yao, G.; Yang, R. A Novel Landslide Identification Method for Multi-Scale and Complex Background Region Based on Multi-Model Fusion: YOLO + U-Net. Landslides 2024, 21, 901–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, K.; Liu, X.; Mu, J.; Zhao, X. Partial Convolution-Simple Attention Mechanism-SegFormer: An Accurate and Robust Model for Landslide Identification. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2025, 151, 110612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Zhang, R.; Wu, R.; Bao, X.; Liu, G. Landslide Detection Based on Pixel-Level Contrastive Learning for Semi-Supervised Semantic Segmentation in Wide Areas. Landslides 2025, 22, 1087–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opara, J.; Moriwaki, R.; Chun, P. Automated Landslide Mapping in Japan Using the Segformer Model: Enhancing Accuracy and Efficiency in Disaster Management. Intell. Inform. Infrastruct. 2023, 4, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Hu, Q. Transfuse: Fusing transformers and cnns for medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Strasbourg, France, 27 September 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, B.; Wang, Z.; Chen, C.; Wang, K.; Zhang, J. An Improved Backbone Fusion Neural Network for Orchard Extraction. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2025, 18, 17961–17974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Z.; Tong, X.; Luo, Z. Semi-Supervised Remote Sensing Image Change Detection Using Mean Teacher Model for Constructing Pseudo-Labels. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2023–2023 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Rhodes Island, Greece, 4 June 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, F.; Kang, J.; Li, S.; Tian, P.; Liu, Y.; Luo, C.; Zhou, S. Multi-Granularity Domain-Adaptive Teacher for Unsupervised Remote Sensing Object Detection. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Ming, D.; Zhao, W.; Ling, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X. Integrated Remote Sensing-Based Hazard Identification and Disaster-Causing Mechanisms of Landslides in Zayu County. Remote Sens. Nat. Resour. 2024, 36, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Li, Z.; Penna Nigel, T.; Crippa, P. Generic Atmospheric Correction Model for Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar Observations. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2018, 123, 9202–9222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Penna, N.T.; Li, Z. Generation of Real-Time Mode High-Resolution Water Vapor Fields from GPS Observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 2008–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; He, X. Statistical Assessment Metrics for InSAR Atmospheric Correction: Applications to Generic Atmospheric Correction Online Service for InSAR (GACOS) in Eastern China. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 96, 102289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, R.; Werner, C. Radar Interferogram Filtering for Geophysical Applications. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1998, 25, 4035–4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, M. A Novel Phase Unwrapping Method Based on Network Programming. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R. A New Algorithm for Surface Deformation Monitoring Based on Small Baseline Differential SAR Interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).