Low-Altitude Multi-Object Tracking via Graph Neural Networks with Cross-Attention and Reliable Neighbor Guidance
Highlights
- A novel multi-object tracking framework, NOWA-MOT, is proposed that leverages stable group context and graph neural networks to resolve tracking ambiguities caused by occlusion and non-linear motion in UAV imagery.
- The framework introduces a cascaded association mechanism using cross-graph attention for robust feature enhancement and reliably matched neighbors as anchors to guide the matching of more difficult, ambiguous targets.
- The proposed approach achieves state-of-the-art performance on challenging UAV datasets (VisDrone, UAVDT), significantly reducing identity switches and improving tracking continuity in dense, dynamic scenes.
- This context-aware tracking paradigm provides a more reliable foundation for downstream remote sensing applications, such as traffic flow analysis and smart city monitoring, by delivering higher-fidelity trajectory data.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Tracking by Detection
2.2. Tracking with Graph Neural Networks
2.3. Tracking Under Occlusion
3. Proposed Method
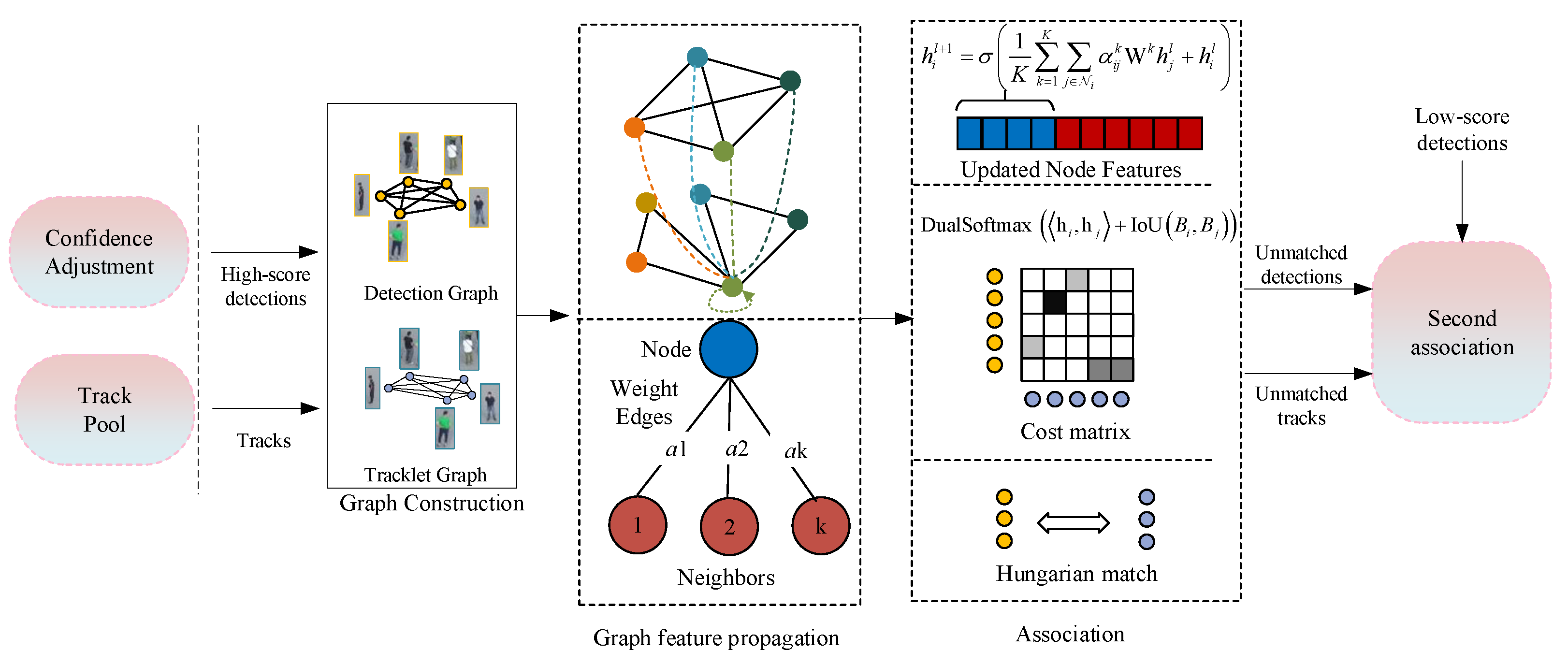
3.1. Overview
3.2. Low-Confidence Object Recovery
3.3. First-Round Association with GCA
3.3.1. Graph Initialization
3.3.2. Cross-Graph Feature Propagation
3.3.3. Training Strategy
3.3.4. First-Round Association Algorithm
| Algorithm 1 First-Round Association with Graph Cross-Attention |
| Require: High-confidence detections ; Active trajectories ; Confidence threshold Ensure: Matched pairs ; Unmatched detections ; Unmatched trajectories
|
3.4. Second-Round Association Based on Reliable Neighbor Guidance
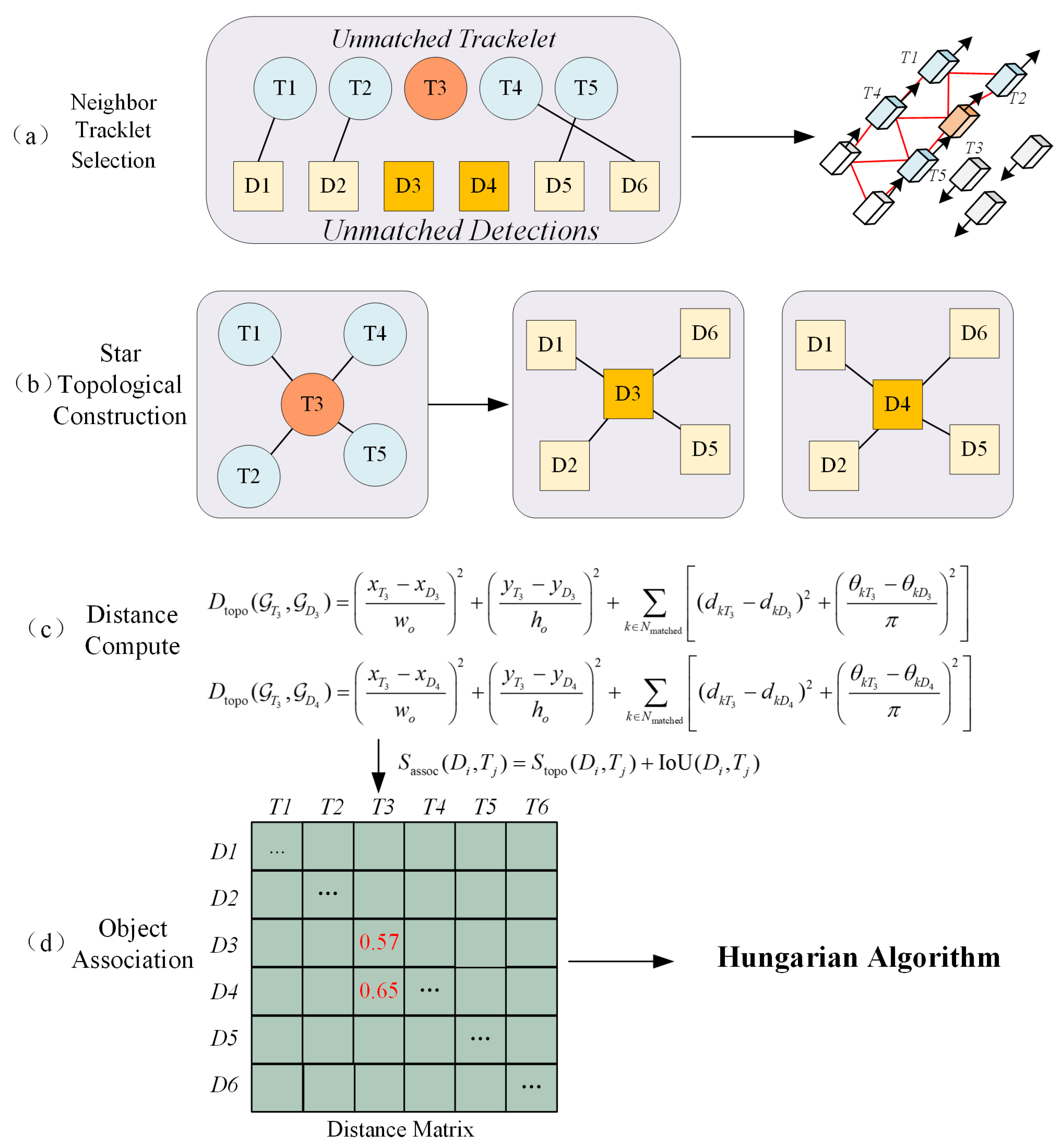
3.4.1. Spatio-Temporally Constrained Neighbor Selection
3.4.2. Star-Shaped Topological Feature Description
3.4.3. Second-Round Association Algorithm
| Algorithm 2 Reliable Neighbor-Guided Second Association |
| Require: : Matched pairs from first round : Unmatched detections : Unmatched tracks Ensure: : Matched pairs from second round : Remaining unmatched sets
|
4. Experiments
4.1. Implementation Details
4.1.1. Datasets and Metrics
4.1.2. Training Details
4.1.3. Inference Details
4.2. Comparison with State of the Art
4.2.1. Results on UAVDT
4.2.2. Results on VisDrone
4.3. Ablation Studies
4.3.1. Effectiveness of Each Module
4.3.2. Composition Analysis of the LOR Module
4.3.3. Analysis of Message Passing Steps
4.3.4. Impact of Data Augmentation on the Graph Network Performance
4.3.5. Impact of Spatio-Temporal Geometric Constraints on Secondary Association
4.3.6. Computational Efficiency Analysis
4.3.7. Parameter Sensitivity Analysis
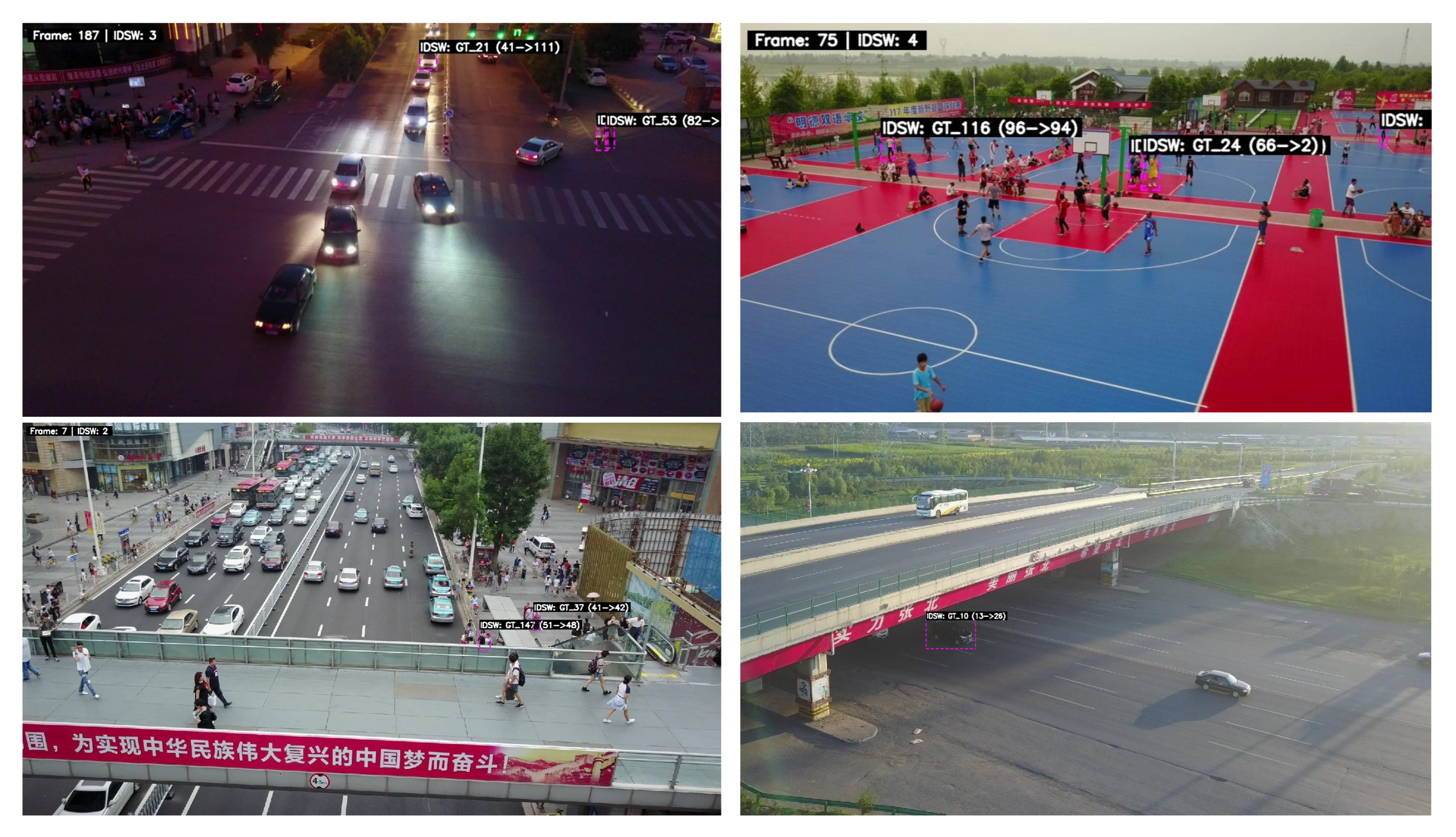
4.4. Qualitative Comparisons with State-of-the-Art Trackers
4.5. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Sun, K.; Liu, M.; Wang, Z. Pedestrian multi-object tracking combining appearance and spatial characteristics. Expert Syst. Appl. 2025, 272, 126772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, Y.; Yang, Y. Advancing multi-object tracking through occlusion-awareness and trajectory optimization. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2025, 310, 112930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, J. Co-MOT: Exploring the Collaborative Relations in Traffic Flow for 3D Multi-Object Tracking. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transport. Syst. 2025, 26, 4744–4756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidenschwarz, J.; Brasó, G.; Serrano, V.C.; Elezi, I.; Leal-Taixé, L. Simple Cues Lead to a Strong Multi-Object Tracker. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 13813–13823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Naphade, M.; Liu, M.Y.; Yang, X.; Birchfield, S.; Wang, S.; Kumar, R.; Anastasiu, D.; Hwang, J.N. CityFlow: A City-Scale Benchmark for Multi-Target Multi-Camera Vehicle Tracking and Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 8789–8798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aharon, N.; Orfaig, R.; Bobrovsky, B.Z. Bot-sort: Robust associations multi-pedestrian tracking. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2206.14651. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Song, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Su, F.; Gong, T.; Meng, H. StrongSORT: Make DeepSORT Great Again. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2023, 25, 8725–8737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, P.; Jiang, Y.; Yu, D.; Weng, F.; Yuan, Z.; Luo, P.; Liu, W.; Wang, X. ByteTrack: Multi-object Tracking by Associating Every Detection Box. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2022, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Avidan, S., Brostow, G., Cissé, M., Farinella, G.M., Hassner, T., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Wei, G.; Fu, W.; Ye, M.; Jiang, K.; Liang, C.; Zhu, T.; He, T.; Mukherjee, M. Multiple Pedestrian Tracking Under Occlusion: A Survey and Outlook. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2025, 35, 1009–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Leng, J.; Wang, Z. SCGTracker: Spatio-temporal correlation and graph neural networks for multiple object tracking. Pattern Recognit. 2024, 149, 110249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Zhou, S.; Wang, L.; Duan, J.; Hua, G.; Tang, W. MotionTrack: Learning Robust Short-Term and Long-Term Motions for Multi-Object Tracking. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 17939–17948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Ren, W.; Sun, G.; Ji, H.; Gao, Y.; Liu, H. GroupTrack: Multi-Object Tracking by Using Group Motion Patterns. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), 14–18 October 2024; pp. 4896–4903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Shen, X.; Xiao, S.; Li, H.; Tao, H. A Multi-Scale Feature-Fusion Multi-Object Tracking Algorithm for Scale-Variant Vehicle Tracking in UAV Videos. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Guan, J.; Jing, F.; Wang, C.; Ma, H. A real-time multi-vehicle tracking framework in intelligent vehicular networks. China Commun. 2021, 18, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Pang, J.; Weng, X.; Khirodkar, R.; Kitani, K. Observation-centric sort: Rethinking sort for robust multi-object tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2023; pp. 9686–9696. [Google Scholar]
- Bochinski, E.; Eiselein, V.; Sikora, T. High-Speed tracking-by-detection without using image information. In Proceedings of the 2017 14th IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video and Signal Based Surveillance (AVSS), Lecce, Italy, 29 August–1 September 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojke, N.; Bewley, A.; Paulus, D. Simple online and realtime tracking with a deep association metric. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Beijing, China, 17–20 September 2017; pp. 3645–3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, M.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, X.; Yan, C.; Zeng, D. STAT: Multi-Object Tracking Based on Spatio-Temporal Topological Constraints. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2024, 26, 4445–4457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Han, G.; Yan, B.; Zhang, W.; Qi, J.; Lu, H.; Wang, D. Hybrid-sort: Weak cues matter for online multi-object tracking. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 20–27 February 2024; Volume 38, pp. 6504–6512. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Q.; Hu, H. ArbiTrack: A Novel Multi-Object Tracking Framework for a moving UAV to Detect and Track Arbitrarily Oriented Targets. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2025, 27, 5387–5397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Wu, J.; Han, Y.; Wang, W.; Chanussot, J. Learning a robust topological relationship for online multi-object tracking in uav scenarios. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5628615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, I.; Lee, J. SFTrack: A Robust Scale and Motion Adaptive Algorithm for Tracking Small and Fast Moving Objects. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 14–18 October 2024; pp. 10870–10877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Nevatia, R. Global data association for multi-object tracking using network flows. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Anchorage, AK, USA, 23–28 June 2008; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Andriluka, M.; Andres, B.; Schiele, B. Multiple People Tracking by Lifted Multicut and Person Re-identification. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 3701–3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshan Zamir, A.; Dehghan, A.; Shah, M. GMCP-Tracker: Global Multi-object Tracking Using Generalized Minimum Clique Graphs. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2012; Fitzgibbon, A., Lazebnik, S., Perona, P., Sato, Y., Schmid, C., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 7573, pp. 343–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Andres, B.; Andriluka, M.; Schiele, B. Subgraph decomposition for multi-target tracking. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 5033–5041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetintas, O.; Brasó, G.; Leal-Taixé, L. Unifying Short and Long-Term Tracking with Graph Hierarchies. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 22877–22887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasó, G.; Leal-Taixé, L. Learning a Neural Solver for Multiple Object Tracking. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 6246–6256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Chu, Q.; Liu, B.; Yu, N. GSM: Graph Similarity Model for Multi-Object Tracking. In Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Yokohama, Japan, 11–17 July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Gao, X.; Jiang, T. Graph Networks for Multiple Object Tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Snowmass Village, CO, USA, 1–5 March 2020. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Huang, Z.; Wang, N.; Zhang, Z. Learnable Graph Matching: Incorporating Graph Partitioning with Deep Feature Learning for Multiple Object Tracking. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 5295–5305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, J.; Kang, M.; Wee, D.; Yeung, D.Y. Detection Recovery in Online Multi-Object Tracking with Sparse Graph Tracker. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Waikoloa, HI, USA, 2–7 January 2023; pp. 4839–4848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Liang, G.; Zhang, R. LTTrack: Rethinking the Tracking Framework for Long-Term Multi-Object Tracking. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2024, 34, 9866–9881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Wang, L. MeMOTR: Long-term memory-augmented transformer for multi-object tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2–6 October 2023; pp. 9901–9910. [Google Scholar]
- You, S.; Yao, H.; Xu, C. Multi-Object Tracking With Spatial-Temporal Topology-Based Detector. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2022, 32, 3023–3035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaquero, L.; Xu, Y.; Alameda-Pineda, X.; Brea, V.M.; Mucientes, M. Lost and Found: Overcoming Detector Failures in Online Multi-object Tracking. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2024; Leonardis, A., Ricci, E., Roth, S., Russakovsky, O., Sattler, T., Varol, G., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; Volume 15131, pp. 448–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanojević, V.; Todorović, B. BoostTrack++: Using tracklet information to detect more objects in multiple object tracking. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2408.13003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Nie, X.; Yan, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhu, Z.; Qi, D. AHOR: Online Multi-Object Tracking With Authenticity Hierarchizing and Occlusion Recovery. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2024, 34, 8253–8265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Yang, Y.; Cavallaro, A.; Xiang, T. Omni-Scale Feature Learning for Person Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 3701–3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarlin, P.E.; DeTone, D.; Malisiewicz, T.; Rabinovich, A. SuperGlue: Learning Feature Matching With Graph Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Wang, W.; He, Z.; Wang, L.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, P.; Van Gool, L.; Han, J.; et al. VisDrone-MOT2021: The Vision Meets Drone Multiple Object Tracking Challenge Results. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCVW), Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 2839–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Li, G.; Zhang, W.; Huang, Q.; Du, D.; Tian, Q.; Sebe, N. The Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Benchmark: Object Detection, Tracking and Baseline. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2020, 128, 1141–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Li, X.; Lu, H.; He, Y. Multi-Object Tracking Meets Moving UAV. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 8866–8875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Zeng, W.; Liu, W. FairMOT: On the Fairness of Detection and Re-identification in Multiple Object Tracking. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2021, 129, 3069–3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Wang, Y.; Li, D. DroneMOT: Drone-based Multi-Object Tracking Considering Detection Difficulties and Simultaneous Moving of Drones and Objects. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Yokohama, Japan, 13–17 May 2024; pp. 7397–7404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Zhang, Q.; Pan, B.; Zhang, J.; Su, Y. Global-Local and Occlusion Awareness Network for Object Tracking in UAVs. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2023, 16, 8834–8844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bewley, A.; Ge, Z.; Ott, L.; Ramos, F.; Upcroft, B. Simple online and realtime tracking. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Phoenix, AZ, USA, 25–28 September 2016; pp. 3464–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, M.; Wang, J.; Peng, J.; Chi, M.; Liu, C. FOLT: Fast Multiple Object Tracking from UAV-captured Videos Based on Optical Flow. In Proceedings of the 31st ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 29 October–3 November 2023; pp. 3375–3383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Yin, W.; Diao, W.; Fu, K.; Sun, X. SuperMOT: Decoupling Motion and Fusing Temporal Pyramid Features for UAV Multiobject Tracking. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2025, 18, 14188–14202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, M.; Peng, J.; He, Q.; Peng, B.; Chen, H.; Chi, M.; Liu, C.; Benediktsson, J.A. MM-Tracker: Motion Mamba for UAV-platform Multiple Object Tracking. AAAI 2025, 39, 9409–9417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, K.; Ko, K.; Yang, Y.; Kim, C. Focusing on Tracks for Online Multi-Object Tracking. In Proceedings of the 2025 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 10–17 June 2025; pp. 11687–11696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
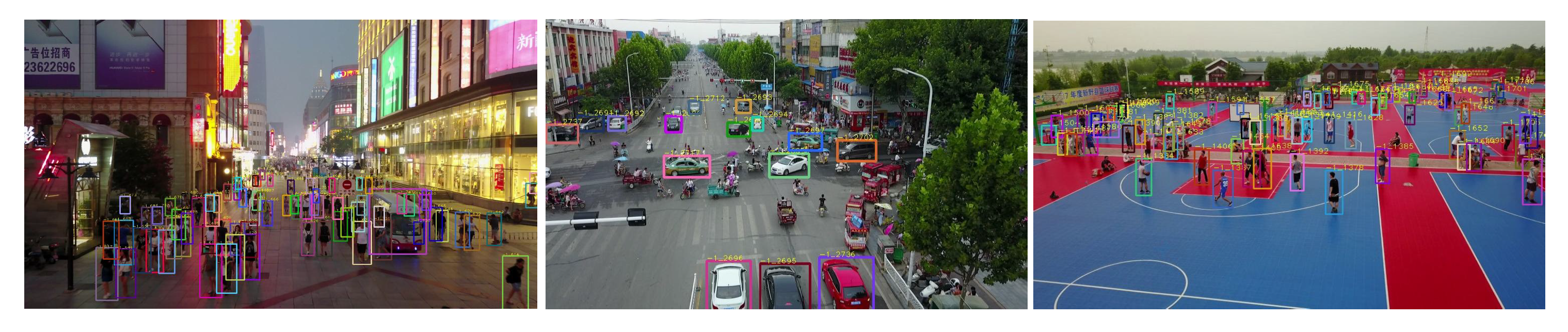




| Method | HOTA ↑ | MOTA ↑ | IDF1 ↑ | MOTP ↑ | MT ↑ | ML ↓ | FP ↓ | FN ↓ | IDs ↓ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SORT [47] | 41.24 | 38.99 | 43.71 | 74.28 | 493 | 410 | 33,037 | 172,628 | 2350 |
| DeepSORT[17] | 61.48 | 68.45 | 78.38 | 80.03 | 817 | 114 | 36,670 | 70,044 | 850 |
| ByteTrack [8] | 61.25 | 67.19 | 78.86 | 79.93 | 830 | 109 | 43,056 | 68,509 | 305 |
| UAVMOT [43] | 57.74 | 66.51 | 71.98 | 80.04 | 822 | 113 | 43,191 | 68,869 | 2100 |
| StrongSORT [7] | 61.37 | 68.32 | 78.17 | 80.12 | 808 | 113 | 36,517 | 70,485 | 985 |
| FLOT * [48] | – | 48.5 | 68.3 | 80.1 | – | – | 24,105 | 107,630 | 800 |
| DroneMOT * [45] | – | 50.10 | 69.60 | 74.50 | 638 | 178 | 57,411 | 112,548 | 129 |
| GLOA * [46] | – | 49.60 | 68.90 | 79.80 | 626 | 220 | 55,822 | 115,567 | 433 |
| BOT-SORT [6] | 61.99 | 67.86 | 79.73 | 80.45 | 763 | 127 | 31,035 | 78,439 | 184 |
| SuperMOT * [49] | – | 50.60 | 70.60 | 75.70 | 674 | 227 | 60,587 | 107,538 | 407 |
| MM-tracker [50] | 58.87 | 62.48 | 76.13 | 79.99 | 723 | 168 | 31,649 | 95,958 | 295 |
| Tracktrack [51] | 57.62 | 58.16 | 70.96 | 77.68 | 723 | 168 | 30,547 | 101,132 | 781 |
| Ours | 62.69 | 69.01 | 80.58 | 80.13 | 814 | 114 | 36,098 | 69,407 | 131 |
| Method | HOTA ↑ | MOTA ↑ | IDF1 ↑ | MOTP ↑ | MT ↑ | ML ↓ | FP ↓ | FN ↓ | IDs ↓ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SORT [47] | 33.29 | 32.18 | 21.61 | 68.51 | 318 | 511 | 64,548 | 85,453 | 5728 |
| DeepSORT [17] | 45.75 | 43.27 | 55.91 | 75.06 | 849 | 249 | 50,118 | 60,436 | 4616 |
| ByteTrack [8] | 47.38 | 45.68 | 60.37 | 74.89 | 872 | 285 | 45,211 | 62,800 | 2274 |
| UAVMOT [43] | 39.43 | 36.10 | 51.00 | 74.20 | 520 | 574 | 27,983 | 115,925 | 2775 |
| StrongSORT [7] | 46.03 | 43.16 | 56.40 | 75.07 | 846 | 251 | 49,716 | 60,672 | 5013 |
| Unigraph [21] | 47.66 | 47.61 | 60.01 | 75.62 | 895 | 290 | 42,527 | 61,532 | 2306 |
| FOLT * [48] | – | 42.1 | 56.9 | 77.6 | – | – | 24,105 | 107,630 | 800 |
| DroneMOT* [45] | – | 43.7 | 58.6 | 71.4 | 689 | 397 | 41,998 | 86,177 | 1112 |
| GLOA * [46] | – | 39.1 | 46.2 | 76.1 | 581 | 824 | 18,715 | 158,043 | 4426 |
| BOT-SORT [6] | 50.29 | 49.55 | 65.72 | 76.90 | 716 | 471 | 14,260 | 88,377 | 483 |
| SuperMOT * [49] | – | 51.70 | 66.70 | 77.2 | 892 | 407 | 30528 | 79579 | 1105 |
| MM-tracker [50] | 50.54 | 50.61 | 65.59 | 75.12 | 715 | 443 | 15,934 | 83,781 | 558 |
| Tracktrack [51] | 50.75 | 51.54 | 67.03 | 75.86 | 810 | 337 | 27,608 | 69,558 | 1202 |
| Ours | 51.34 | 50.47 | 67.33 | 76.40 | 883 | 289 | 23,239 | 76,524 | 793 |
| LOR | GCA | MNG | HOTA ↑ | MOTA ↑ | IDF1 ↑ | IDs ↓ | FPS ↑ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 47.38 | 45.68 | 60.37 | 2274 | 37.25 | |||
| ✓ | 47.68 | 47.53 | 59.89 | 2140 | 35.44 | ||
| ✓ | 49.62 | 48.63 | 61.81 | 1105 | 21.71 | ||
| ✓ | 48.13 | 47.56 | 61.84 | 1564 | 34.09 | ||
| ✓ | ✓ | 49.97 | 49.23 | 65.87 | 862 | 19.38 | |
| ✓ | ✓ | 48.34 | 47.63 | 62.25 | 1477 | 32.68 | |
| ✓ | ✓ | 50.88 | 49.56 | 65.88 | 937 | 19.76 | |
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 51.34 | 50.47 | 67.33 | 793 | 18.05 |
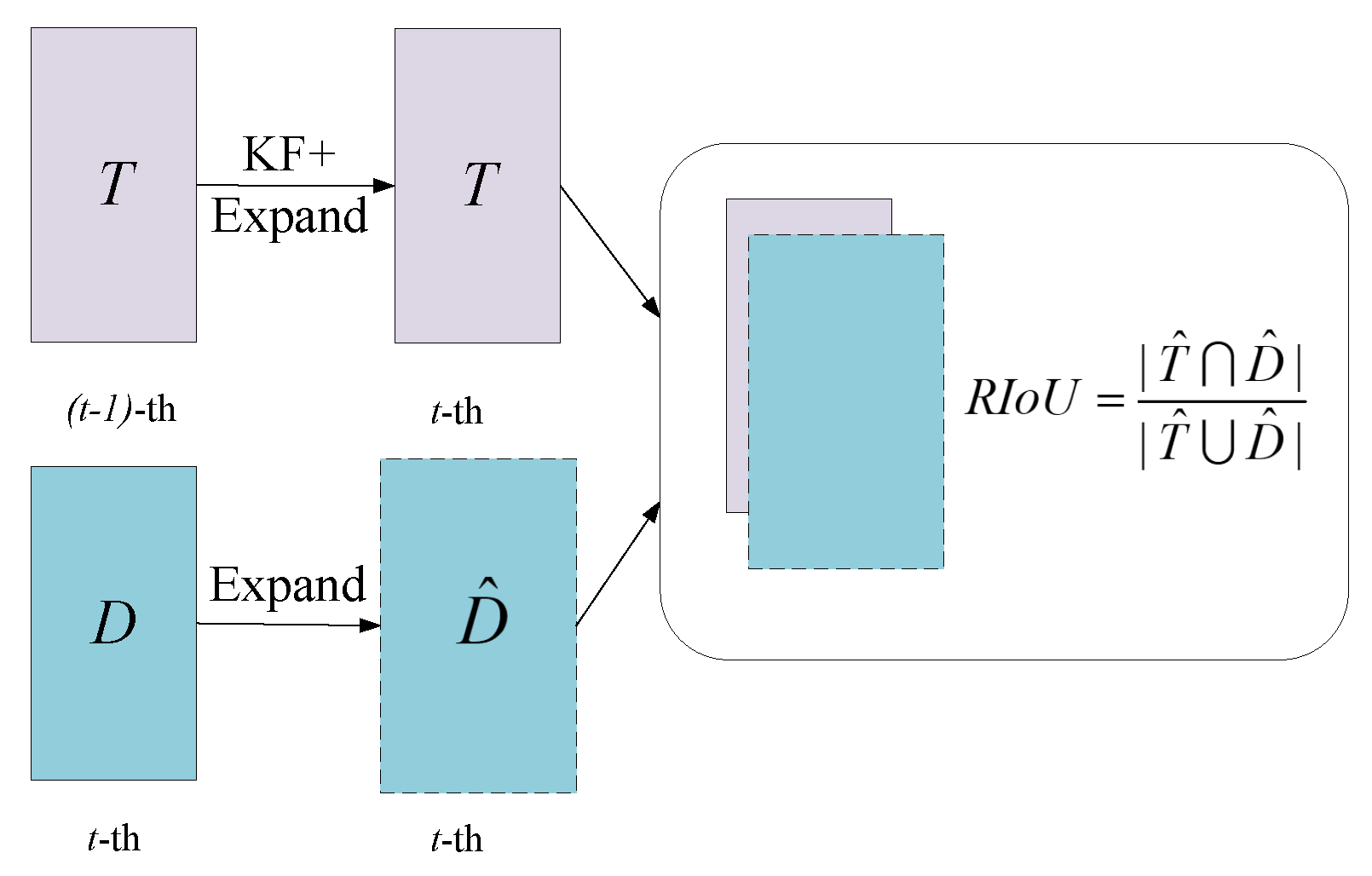
| IoU | RIoU | HOTA ↑ | MOTA ↑ | IDF1 ↑ | IDs ↓ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ✓ | 47.38 | 45.68 | 60.37 | 2274 | ||
| ✓ | ✓ | 47.05 | 46.12 | 59.16 | 2377 | |
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 47.68 | 47.53 | 59.89 | 2140 |
| L | HOTA ↑ | MOTA ↑ | IDF1 ↑ |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 45.54 | 47.56 | 57.78 |
| 2 | 49.62 | 48.63 | 61.81 |
| 3 | 46.17 | 48.24 | 58.48 |
| Augmentation | HOTA ↑ | MOTA ↑ | IDF1 ↑ |
|---|---|---|---|
| w/o | 48.29 | 47.16 | 60.01 |
| w/ | 49.62 | 48.63 | 61.81 |
| Constraints | HOTA ↑ | MOTA ↑ | IDF1 ↑ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nearest Neighbor | 47.24 | 47.54 | 58.36 |
| Proposed (w/ Constraints) | 48.13 | 47.56 | 61.84 |
| Methods | HOTA ↑ | MOTA ↑ | IDF1 ↑ | FPS ↑ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ByteTrack [8] | 47.38 | 45.68 | 60.37 | 37.25 |
| BOT-SORT [6] | 50.29 | 49.55 | 65.72 | 24.16 |
| MM-tracker [50] | 50.54 | 50.61 | 65.59 | 31.89 |
| NOWA-MOT | 51.34 | 50.47 | 67.33 | 18.05 |
| Module | N | HOTA ↑ | MOTA ↑ | IDF1 ↑ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GCA | 3 | 49.13 | 50.08 | 66.53 |
| 5 | 51.34 | 50.47 | 67.33 | |
| 7 | 50.72 | 50.35 | 66.84 | |
| 9 | 47.29 | 48.02 | 65.21 | |
| MNG | 2 | 49.51 | 48.24 | 62.75 |
| 4 | 51.34 | 50.47 | 67.33 | |
| 6 | 49.64 | 49.39 | 64.91 | |
| 8 | 48.42 | 49.11 | 63.48 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qian, H.; Sun, X.; Guo, R.; Su, S.; Ding, B.; Guo, X. Low-Altitude Multi-Object Tracking via Graph Neural Networks with Cross-Attention and Reliable Neighbor Guidance. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 3502. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17203502
Qian H, Sun X, Guo R, Su S, Ding B, Guo X. Low-Altitude Multi-Object Tracking via Graph Neural Networks with Cross-Attention and Reliable Neighbor Guidance. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(20):3502. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17203502
Chicago/Turabian StyleQian, Hanxiang, Xiaoyong Sun, Runze Guo, Shaojing Su, Bing Ding, and Xiaojun Guo. 2025. "Low-Altitude Multi-Object Tracking via Graph Neural Networks with Cross-Attention and Reliable Neighbor Guidance" Remote Sensing 17, no. 20: 3502. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17203502
APA StyleQian, H., Sun, X., Guo, R., Su, S., Ding, B., & Guo, X. (2025). Low-Altitude Multi-Object Tracking via Graph Neural Networks with Cross-Attention and Reliable Neighbor Guidance. Remote Sensing, 17(20), 3502. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17203502






