Advancing Water Quality Management: Harnessing the Synergy of Remote Sensing, Process-Based Models, and Machine Learning to Enhance Monitoring and Prediction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Current Developments in RS Applications for Water Quality Monitoring and Modeling
2.1. Applications of RS in Water Quality Monitoring and Prediction
- Optically Active Constituents
- Non-Optically Active Constituents
| Satellite (Sensor) | Water Quality Parameter | Retrieval Algorithm Formula | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Landsat-8 OLI | TSS | [24] | |
| Landsat-8 OLI, GF-1 WFV | Chl-a | [24,25] | |
| Advanced Land Imager (ALI) | CDOM | [44] | |
| Landsat-8 OLI, Landsat-5 TM | SDD | [26,27] |
- Delineation of Water Boundaries and Monitoring of Changes
| Index | Full Name | Formula | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| NDWI | Normalized Difference Water Index | NDWI = (Green − NIR)/(Green + NIR) | Index DataBase |
| MNDWI | Modified Normalized Difference Water Index | MNDWI = (Green − SWIR)/(Green + SWIR) | Index DataBase |
| NDMI | Normalized Difference Moisture Index | NDMI = (NIR − SWIR)/(NIR + SWIR) | Index DataBase |
| AWEI | Automated Water Extraction Index | AWEI = 4(Green − SWIR1) − (0.25 × NIR + 2.75 × SWIR2); AWEI = Blue + 2.5 × Green − 1.5(NIR + SWIR1) − 0.25 × SWIR2 | Feyisa et al. (2014) [48] |
| WI | Water Index | WI = (Blue + Green)/(NIR + SWIR) | Fisher et al. (2016) [49] |
- Analysis of Water Quality Trends and Monitoring of Emergencies
2.2. The Trend of Multi-Technology Integration in Assessing Water Quality
- The Coupling of RS and ML
- The Coupling of RS and PBMs
3. Leveraging ML in RS for Water Quality Monitoring: From Data Processing to Predictive Accuracy
3.1. Processing RS Data Using ML Techniques
3.2. Modeling and Prediction of Water Quality Parameters Driven by ML Techniques
4. Integrating RS and PBMs for Enhanced Understanding of Water Quality Dynamics and Mechanisms
4.1. Application of PBMs in Water Quality Simulation
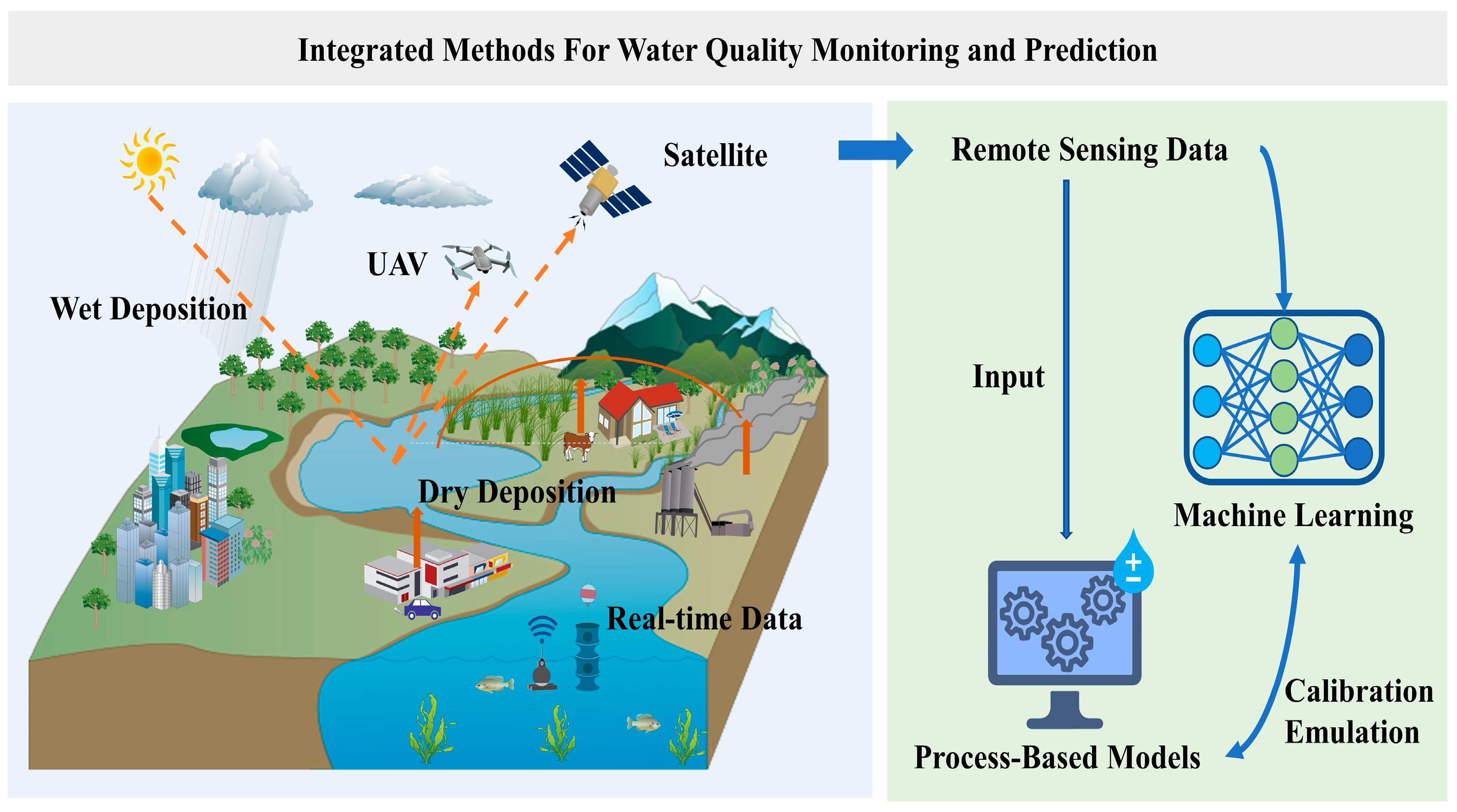
4.2. Integrated Methods for Water Quality Monitoring and Retrieval
5. A Synergistic Framework Integrating ML, RS, and PBMs for Enhanced Water Quality Management
5.1. Insights into the Mechanisms Underlying Integrated Modeling Approaches
5.2. Innovative Applications of Integrated Methods in Water Quality Monitoring and Cross-Domain Research
6. Summary and Perspectives
- (1)
- Standardization and Integration of Multi-Source Data: Efforts will focus on the standardization and efficient fusion of multi-source, heterogeneous datasets to build comprehensive spatiotemporal water environment databases.
- (2)
- Deep Learning–Mechanism Integration: The coupling of deep learning with physical process modeling will be further developed to enhance model interpretability and strengthen decision-support capabilities.
- (3)
- Lightweight, High-Performance Model Structures: The design of streamlined, high-efficiency models will enable deployment on edge-computing platforms and support real-time monitoring and early warning applications.
- (4)
- Evaluation and Adaptation Frameworks: A robust evaluation and adaptation system will be established to facilitate the cross-regional and cross-seasonal scalability of integrated models.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LUCC | Land Use and Land Cover Changes |
| RS | Remote Sensing |
| PBMs | Process-Based Models |
| UAV | Unmanned Aerial Vehicle |
| SDGSAT-1 | Sustainable Development Goals Science Satellite 1 |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| ANN | Artificial Neural Network |
| SVM | Support Vector Machine |
| RF | Random Forest |
| DO | Dissolved Oxygen |
| BOD | Biochemical Oxygen Demand |
| WQI | Water Quality Index |
| PCA | Principal Component Analysis |
| IoT | Internet of Things |
| GNN | Graph Neural Network |
| CE-QUAL-W2 | Corps of Engineers Water Quality-2D model |
| EFDC | Environmental Fluid Dynamics Code |
| Chl-a | Chlorophyll-a |
| CDOM | Colored Dissolved Organic Matter |
| HJ-1A HSI | HuanJing-1A Hyperspectral Imager |
| OACs | Optically Active Constituents |
| TSS | Total Suspended Solids |
| SDD | Secchi Disk Depth |
| NOACs | Non-Optically Active Constituents |
| TN | Total Nitrogen |
| TP | Total Phosphorus |
| COD | Chemical Oxygen Demand |
| SPM | Suspended Particulate Matter |
| Rrs | Remote Sensing Reflectance |
| NDWI | Normalized Difference Water Index |
| MNDWI | Modified Normalized Difference Water Index |
| NDMI | Normalized Difference Moisture Index |
| AWEI | Automated Water Extraction Index |
| WI | Water Index |
| XGBoost | Extreme Gradient Boosting |
| LSTM | Long Short-Term Memory |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| SWAT | Soil and Water Assessment Tool |
| RFE | Recursive Feature Elimination |
| DL | Deep Learning |
| RMSE | Root Mean Square Error |
| U-Net | Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation |
| SAR | Synthetic Aperture Radar |
| GWR | Geographically Weighted Regression |
| EC | Electrical Conductivity |
| WASP | Water Quality Analysis Simulation Program |
| PPCPs | Pharmaceutical and Personal Care Products |
| PFASs | Per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances |
| EDCs | Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals |
| SELDM | Stochastic Empirical Loading and Dilution Model |
| ECOMSED | Estuarine, Coastal Ocean Model with Sediment Transport |
| COHERENS | Coupled Hydrodynamical Ecological model for Regional Shelf seas |
| DSSAT | Decision Support System for Agrotechnology Transfer |
References
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Climate Change 2021—The Physical Science Basis: Working Group I Contribution to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, 1st ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2023; ISBN 978-1-009-15789-6. [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead, P.G.; Wilby, R.L.; Battarbee, R.W.; Kernan, M.; Wade, A.J. A Review of the Potential Impacts of Climate Change on Surface Water Quality. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2009, 54, 101–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Hall, N.S.; Calandrino, E.S. Controlling Harmful Cyanobacterial Blooms in a World Experiencing Anthropogenic and Climatic-Induced Change. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 1739–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.C.; Michalak, A.M.; Pahlevan, N. Widespread global increase in intense lake phytoplankton blooms since the 1980s. Nature 2019, 574, 667–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulder, M.A.; Loveland, T.R.; Roy, D.P.; Crawford, C.J.; Masek, J.G.; Woodcock, C.E.; Allen, R.G.; Anderson, M.C.; Belward, A.S.; Cohen, W.B.; et al. Current Status of Landsat Program, Science, and Applications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 225, 127–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drusch, M.; Del Bello, U.; Carlier, S.; Colin, O.; Fernandez, V.; Gascon, F.; Hoersch, B.; Isola, C.; Laberinti, P.; Martimort, P.; et al. Sentinel-2: ESA’s Optical High-Resolution Mission for GMES Operational Services. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Kong, J.; Hu, H.; Du, Y.; Gao, M.; Chen, F. A Review of Remote Sensing for Water Quality Retrieval: Progress and Challenges. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholizadeh, M.; Melesse, A.; Reddi, L. A Comprehensive Review on Water Quality Parameters Estimation Using Remote Sensing Techniques. Sensors 2016, 16, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, S.C.J.; Kutser, T.; Hunter, P.D. Remote Sensing of Inland Waters: Challenges, Progress and Future Directions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 157, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, M.A.; Simis, S.G.H.; Martinez-Vicente, V.; Poser, K.; Bresciani, M.; Alikas, K.; Spyrakos, E.; Giardino, C.; Ansper, A. Assessment of Atmospheric Correction Algorithms for the Sentinel-2A MultiSpectral Imager over Coastal and Inland Waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 225, 267–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Du, J.; Yu, W.; Zhuo, K.; Shao, K.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, C.; Qin, J.; Han, Y.; Sui, B.; et al. Evaluating Maize Residue Cover Using Machine Learning and Remote Sensing in the Meadow Soil Region of Northeast China. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Du, J. Improving Maize Residue Cover Estimation with the Combined Use of Optical and SAR Remote Sensing Images. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2024, 12, 578–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Li, X.; Zuo, L.; Zou, B.; Wang, B.; Wang, W.J. Unveiling Soil Salinity Patterns in Soda Saline-Alkali Regions Using Sentinel-2 and SDGSAT-1 Thermal Infrared Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2025, 322, 114708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Wang, J.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ren, H.; Wu, B.; Ye, L. A Review of the Application of Machine Learning in Water Quality Evaluation. Eco-Environ. Health 2022, 1, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essamlali, I.; Nhaila, H.; El Khaili, M. Advances in Machine Learning and IoT for Water Quality Monitoring: A Comprehensive Review. Heliyon 2024, 10, e27920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Ma, W.; Zhong, D.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Zou, K. Applications of Machine Learning in Drinking Water Quality Management: A Critical Review on Water Distribution System. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 481, 144171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Tian, Z. Assessment and a Review of Research on Surface Water Quality Modeling. Ecol. Model. 2022, 466, 109888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooij, W.M.; Van Wijk, D.; Beusen, A.H.; Brederveld, R.J.; Chang, M.; Cobben, M.M.; DeAngelis, D.L.; Downing, A.S.; Green, P.; Gsell, A.S.; et al. Modeling Water Quality in the Anthropocene: Directions for the next-Generation Aquatic Ecosystem Models. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2019, 36, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatichi, S.; Vivoni, E.R.; Ogden, F.L.; Ivanov, V.Y.; Mirus, B.; Gochis, D.; Downer, C.W.; Camporese, M.; Davison, J.H.; Ebel, B.; et al. An Overview of Current Applications, Challenges, and Future Trends in Distributed Process-Based Models in Hydrology. J. Hydrol. 2016, 537, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, S.; Kumar, B.; Nejadhashemi, A.P. Integration of Machine Learning and Remote Sensing for Water Quality Monitoring and Prediction: A Review. Sustainability 2025, 17, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, D.; Yang, S.X.; Gharabaghi, B. Review of Recent Advances in Remote Sensing and Machine Learning Methods for Lake Water Quality Management. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, D.; Li, L.; Ning, R.; Yu, S.; Gao, N. Application of Remote Sensing Technology in Water Quality Monitoring: From Traditional Approaches to Artificial Intelligence. Water Res. 2024, 267, 122546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Yu, H.; Lee, H.; Beighley, E.; Durand, M.; Alsdorf, D.E.; Hwang, E. Ensemble Learning Regression for Estimating River Discharges Using Satellite Altimetry Data: Central Congo River as a Test-Bed. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 221, 741–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaelani, L.M.; Limehuwey, R.; Kurniadin, N.; Pamungkas, A.; Koenhardono, E.S.; Sulisetyono, A. Estimation of TSS and Chl-a Concentration from Landsat 8-OLI: The Effect of Atmosphere and Retrieval Algorithm. IPTEK J. Technol. Sci. 2016, 27, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, Z.-L.; Yao, H.-M.; Chen, H.-Q.; Wei, Y.-M.; Wen, K.; Huang, Y.; Liao, P.-R. Retrieval and Evaluation of Chlorophyll-a Spatiotemporal Variability Using GF-1 Imagery: Case Study of Qinzhou Bay, China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmanson, L.G.; Brezonik, P.L.; Finlay, J.C.; Bauer, M.E. Comparison of Landsat 8 and Landsat 7 for Regional Measurements of CDOM and Water Clarity in Lakes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 185, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courville, B.C.; Jensen, J.L.R.; Dixon, R.W.; Fonstad, M.A. A Landsat-Based Evaluation of Lake Water Clarity in Maine Lakes. Phys. Geogr. 2014, 35, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekel, J.-F.; Cottam, A.; Gorelick, N.; Belward, A.S. High-Resolution Mapping of Global Surface Water and Its Long-Term Changes. Nature 2016, 540, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, I.; Karthikeyan, L.; Mishra, A.K. A Review of Remote Sensing Applications for Water Security: Quantity, Quality, and Extremes. J. Hydrol. 2020, 585, 124826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahlevan, N.; Smith, B.; Schalles, J.; Binding, C.; Cao, Z.; Ma, R.; Alikas, K.; Kangro, K.; Gurlin, D.; Hà, N.; et al. Seamless Retrievals of Chlorophyll-a from Sentinel-2 (MSI) and Sentinel-3 (OLCI) in Inland and Coastal Waters: A Machine-Learning Approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 240, 111604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, K.; Zhang, Y.; Li, N.; Wang, W.; Huang, X.; Qin, B. Monitoring Water Quality Using Proximal Remote Sensing Technology. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 803, 149805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si-meng, W.; Bo-qiang, Q. Research Progress on Remote Sensing Monitoring of Lake Water Quality Parameters. Huanjing Kexue 2023, 44, 1228–1243. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Wei, X.; Huang, Z.; Liu, H.; Ma, R.; Wang, M.; Hu, M.; Jiang, L.; Xue, K. Monitoring the Vertical Variations in Chlorophyll-a Concentration in Lake Chaohu Using the Geostationary Ocean Color Imager. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cillero Castro, C.; Domínguez Gómez, J.A.; Delgado Martín, J.; Hinojo Sánchez, B.A.; Cereijo Arango, J.L.; Cheda Tuya, F.A.; Díaz-Varela, R. An UAV and Satellite Multispectral Data Approach to Monitor Water Quality in Small Reservoirs. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Guo, H.; Xu, W.; Zhu, X.; Wang, B.; Zeng, Q.; Mai, Y.; Huang, J.J. Remote Sensing Retrieval of Inland Water Quality Parameters Using Sentinel-2 and Multiple Machine Learning Algorithms. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 30, 18617–18630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liu, L.; Liu, S.; Shi, Z.; Shi, C. The Application of Remote Sensing Technology in Inland Water Quality Monitoring and Water Environment Science: Recent Progress and Perspectives. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, Q.; Shi, T.; Hu, S.; Wu, G.; Zhou, Q. Application of Sentinel 2 MSI Images to Retrieve Suspended Particulate Matter Concentrations in Poyang Lake. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, J.; Tian, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Tao, J.; Lin, J. Remote Sensing Inversion of Suspended Particulate Matter in the Estuary of the Pinglu Canal in China Based on Machine Learning Algorithms. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1473104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, D. Long-Term Changes in Water Clarity in Lake Liangzi Determined by Remote Sensing. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmanson, L.G.; Bauer, M.E.; Brezonik, P.L. A 20-Year Landsat Water Clarity Census of Minnesota’s 10,000 Lakes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 4086–4097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josef, C. Hyperspectral Sensing from Unmanned Aerial Systems for Water Quality and Quantity in Terrestrial and Aquatic Systems. Ph.D. Thesis, Technical University of Denmark, Lyngby, Denmark, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Q.; Tang, Z.; Zhou, L.; Hu, G.; Deng, G.; Xu, M.; Sang, G. Mapping Paddy Rice Planting Area in Dongting Lake Area Combining Time Series Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 Images. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Shu, G.; Xiping, Y.; Yan, L.; Guokun, C.; Sha, G. Spatial Differentiation Analysis of Water Quality in Dianchi Lake Based on GF-5 NDVI Characteristic Optimization. J. Spectrosc. 2021, 2021, 5542126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutser, T.; Pierson, D.C.; Tranvik, L.; Reinart, A.; Sobek, S.; Kallio, K. Using Satellite Remote Sensing to Estimate the Colored Dissolved Organic Matter Absorption Coefficient in Lakes. Ecosystems 2005, 8, 709–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Shangguan, Y.; Sun, Z.; Shen, Q.; Shi, Z. Estimation of Non-Optically Active Water Quality Parameters in Zhejiang Province Based on Machine Learning. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Wen, Y.; Li, X.; Yan, F.; Zhao, S. Remote Sensing Inversion of Typical Water Quality Parameters of a Complex River Network: A Case Study of Qidong’s Rivers. Sustainability 2023, 15, 6948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jin, S.; Wang, N.; Zhao, J.; Guo, H.; Pellikka, P. Total Phosphorus and Nitrogen Dynamics and Influencing Factors in Dongting Lake Using Landsat Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feyisa, G.L.; Meilby, H.; Fensholt, R.; Proud, S.R. Automated Water Extraction Index: A New Technique for Surface Water Mapping Using Landsat Imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, A.; Flood, N.; Danaher, T. Comparing Landsat Water Index Methods for Automated Water Classification in Eastern Australia. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 175, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Hu, H.; Luo, Y.; Lei, X.; Wu, D.; Jiang, J. Monitoring of Urban Black-Odor Water Using UAV Multispectral Data Based on Extreme Gradient Boosting. Water 2022, 14, 3354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Liu, Y. Assessment of the Hydro-Ecological Impacts of the Three Gorges Dam on China’s Largest Freshwater Lake. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giardino, C.; Bresciani, M.; Valentini, E.; Gasperini, L.; Bolpagni, R.; Brando, V.E. Airborne Hyperspectral Data to Assess Suspended Particulate Matter and Aquatic Vegetation in a Shallow and Turbid Lake. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 157, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashok, A.; Rani, H.P.; Jayakumar, K.V. Monitoring of Dynamic Wetland Changes Using NDVI and NDWI Based Landsat Imagery. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2021, 23, 100547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.; Qiu, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, Y. Evaluating Water Turbidity in Small Lakes within the Taihu Lake Basin, Eastern China, Using Consumer-Grade UAV RGB Cameras. Drones 2024, 8, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, F.L.; Costa, M.P.F.; Novo, E.M.L.M. Time-Series Analysis of Landsat-MSS/TM/OLI Images over Amazonian Waters Impacted by Gold Mining Activities. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 157, 170–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, K.B.; Cardall, A.C.; Williams, G.P. A Spatial Long-Term Trend Analysis of Estimated Chlorophyll-a Concentrations in Utah Lake Using Earth Observation Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Major, R.; Floerl, L. Trend Analysis of Chlorophyll-a in Hawke’s Bay Using Remote-Sensing Data: 2018–2023; Cawthron Institute: Nelson, New Zealand, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ma, Y.; Li, Z.; Jiang, Z. Identification of Marine Oil Spill Pollution Using Hyperspectral Combined with Thermal Infrared Remote Sensing. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1135356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, P.; Kang, X.; Ghamisi, P. Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Benchmark Database for Oil Spill Detection with an Isolation Forest-Guided Unsupervised Detector. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Song, K.; Wen, Z.; Liu, G.; Shang, Y.; Lyu, L.; Du, J.; Yang, Q.; Li, S.; Tao, H.; et al. Remote Sensing of Turbidity for Lakes in Northeast China Using Sentinel-2 Images with Machine Learning Algorithms. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 9132–9146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Yang, X.; Chen, C.; Wang, J. River Water Quality Parameters Prediction Method Based on LSTM-RNN Model. In Proceedings of the 2019 Chinese Control and Decision Conference (CCDC), Nanchang, China, 3–5 June 2019; pp. 3024–3028. [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie, J.C.; Zimba, P.V.; Everitt, J.H. Remote Sensing Techniques to Assess Water Quality. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2003, 69, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, F.; Cai, Z.; Shoaib, M.; Iqbal, J.; Ismail, M.; Arifullah; Alrefaei, A.F.; Albeshr, M.F. Machine Learning Models for Water Quality Prediction: A Comprehensive Analysis and Uncertainty Assessment in Mirpurkhas, Sindh, Pakistan. Water 2024, 16, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, B.; Li, A.; Jia, X.; Gao, L.; Peng, M. Hyperspectral Imagery Clustering with Neighborhood Constraints. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 10, 588–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Q.; Ni, L.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Q. Deep Learning Based Feature Selection for Remote Sensing Scene Classification. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 2321–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Driscol, J.; Sarigai, S.; Wu, Q.; Lippitt, C.D.; Morgan, M. Towards Synoptic Water Monitoring Systems: A Review of AI Methods for Automating Water Body Detection and Water Quality Monitoring Using Remote Sensing. Sensors 2022, 22, 2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.; Das, K.; Thakur, M.; Padmanaban, M.; Hazra, J. Improved Dissolved Organic Carbon Prediction in Diverse Inland Water Bodies: Utilizing Machine Learning and Remote Sensing. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2024—2024 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Athens, Greece, 7–12 July 2024; pp. 5079–5083. [Google Scholar]
- Do, T.-N.; Nguyen, D.-M.T.; Ghimire, J.; Vu, K.-C.; Do Dang, L.-P.; Pham, S.-L.; Pham, V.-M. Assessing Surface Water Pollution in Hanoi, Vietnam, Using Remote Sensing and Machine Learning Algorithms. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 82230–82247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira Kupssinskü, L.; Thomassim Guimarães, T.; Menezes De Souza, E.; Zanotta, D.C.; Roberto Veronez, M.; Gonzaga, L.; Mauad, F.F. A Method for Chlorophyll-a and Suspended Solids Prediction through Remote Sensing and Machine Learning. Sensors 2020, 20, 2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.; Fan, M.; Qin, G.; Xu, Y.; Wang, H. Comparative Analysis of Machine Learning Algorithms in Automatic Identification and Extraction of Water Boundaries. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leggesse, E.S.; Zimale, F.A.; Sultan, D.; Enku, T.; Tilahun, S.A. Advancing Non-Optical Water Quality Monitoring in Lake Tana, Ethiopia: Insights from Machine Learning and Remote Sensing Techniques. Front. Water 2024, 6, 1432280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, B.; Lee, S.; Heo, J.; Lee, J.; Lee, M.-J. Deep Learning-Based Retrieval of Chlorophyll-a in Lakes Using Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 Satellite Imagery. Water 2025, 17, 1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Wu, M.; Xue, M.; Wu, H.; Liang, F.; Li, X.; Hou, S.; Liu, J. Power of SAR Imagery and Machine Learning in Monitoring Ulva Prolifera: A Case Study of Sentinel-1 and Random Forest. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2024, 34, 1134–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnann, N.; Baschek, B.; Ternes, T.A. Close-Range Remote Sensing-Based Detection and Identification of Macroplastics on Water Assisted by Artificial Intelligence: A Review. Water Res. 2022, 222, 118902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wu, Z.; Shen, W. Addressing Challenges in Port Depth Analysis: Integrating Machine Learning and Spatial Information for Accurate Remote Sensing of Turbid Waters. Sensors 2024, 24, 3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Mei, K.; Dahlgren, R.; Zhang, M. Monitoring and Modeling Dissolved Oxygen Dynamics through Continuous Longitudinal Sampling: A Case Study in Wen-rui Tang River, Wenzhou, China. Hydrol. Process. 2013, 27, 3502–3510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemaire, G.; Carnohan, S.; Grand, S.; Mazel, V.; Bjerg, P.; McKnight, U. Data-Driven System Dynamics Model for Simulating Water Quantity and Quality in Peri-Urban Streams. Water 2021, 13, 3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, G.; Xu, Y.J.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Y.; Ju, H. Determining Water Allocation Scheme to Attain Nutrient Management Objective for a Large Lake Receiving Irrigation Discharge. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 126900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; He, Y. Rapid Detection Methods and Modelling Simulations Provide New Insights into Cyanobacteria Detection and Bloom Management in a Tropical Reservoir. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 326, 116730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; You, L.; Zhang, J.; He, Y.; Gin, K.Y.-H. Advancing Prediction of Emerging Contaminants in a Tropical Reservoir with General Water Quality Indicators Based on a Hybrid Process and Data-Driven Approach. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 430, 128492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Mohapatra, S.; Zhang, J.; Tran, N.H.; You, L.; He, Y.; Gin, K.Y.-H. Source, Fate, Transport and Modelling of Selected Emerging Contaminants in the Aquatic Environment: Current Status and Future Perspectives. Water Res. 2022, 217, 118418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stonewall, A.J.; Granato, G.E.; Kira, M. Glover-Cutter Assessing Potential Effects of Highway and Urban Runoff on Receiving Streams in Total Maximum Daily Load Watersheds in Oregon Using the Stochastic Empirical Loading and Dilution Model; Scientific Investigations Report; USA Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2019.
- Wang, L.; Xu, B.; Zhang, C.; Fu, G.; Chen, X.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, J. Surface Water Temperature Prediction in Large-Deep Reservoirs Using a Long Short-Term Memory Model. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 134, 108491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Te, S.H.; Gin, K.Y.-H.; Fan, Y.V.; Klemeš, J.J.; Shoemaker, C.A. Cyanobacterial Risk Prevention under Global Warming Using an Extended Bayesian Network. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 312, 127729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, S.; Fu, R.; Li, D.; Jiang, H.; Wang, C.; Peng, Y.; Jia, K.; Hicks, B.J. Remote Sensing Big Data for Water Environment Monitoring: Current Status, Challenges, and Future Prospects. Earth’s Future 2022, 10, e2021EF002289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mano, A.; Malve, O.; Koponen, S.; Kallio, K.; Taskinen, A.; Ropponen, J.; Juntunen, J.; Liukko, N. Assimilation of Satellite Data to 3D Hydrodynamic Model of Lake Säkylän Pyhäjärvi. Water Sci. Technol. 2015, 71, 1033–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleskachevsky, A.; Gayer, G.; Horstmann, J.; Rosenthal, W. Synergy of Satellite Remote Sensing and Numerical Modeling for Monitoring of Suspended Particulate Matter. Ocean Dyn. 2005, 55, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouts, T.; Sipelgas, L.; Savinits, N.; Raudsepp, U. Environmental Monitoring of Water Quality in Coastal Sea Area Using Remote Sensing and Modeling. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE US/EU Baltic International Symposium, Klaipeda, Lithuania, 23–26 May 2006; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Dekker, A.G.; Peters, S.W.M. The Use of the Thematic Mapper for the Analysis of Eutrophic Lakes: A Case Study in the Netherlands. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1993, 14, 799–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia, A.; Govind, A.; Qureshi, A.S.; Feike, T.; Rizk, M.S.; Shabana, M.M.A.; Kheir, A.M.S. Coupling Process-Based Models and Machine Learning Algorithms for Predicting Yield and Evapotranspiration of Maize in Arid Environments. Water 2022, 14, 3647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Zhang, L. Coupling Model-Driven and Data-Driven Methods for Remote Sensing Image Restoration and Fusion. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2022, 10, 231–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, X.; Song, D.; Nie, J.; Liang, S. Prediction on Daily Spatial Distribution of Chlorophyll-a in Coastal Seas Using a Synthetic Method of Remote Sensing, Machine Learning and Numerical Modeling. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 910, 168642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Jiang, M.; Shen, H.; Li, H.; Zeng, C.; Ma, J.; Zhang, L. A Mechanism-Learning Deeply Coupled Model for Remote Sensing Retrieval of Global Land Surface Temperature. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2504.07481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagan, V.; Peterson, K.T.; Maimaitijiang, M.; Sidike, P.; Sloan, J.; Greeling, B.A.; Maalouf, S.; Adams, C. Monitoring Inland Water Quality Using Remote Sensing: Potential and Limitations of Spectral Indices, Bio-Optical Simulations, Machine Learning, and Cloud Computing. Earth Sci. Rev. 2020, 205, 103187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Carpena, R.; Carmona-Cabrero, A.; Yu, Z.; Fox, G.; Batelaan, O. Convergence of Mechanistic Modeling and Artificial Intelligence in Hydrologic Science and Engineering. PLoS Water 2023, 2, e0000059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccolroaz, S.; Zhu, S.; Ladwig, R.; Carrea, L.; Oliver, S.; Piotrowski, A.P.; Ptak, M.; Shinohara, R.; Sojka, M.; Woolway, R.I.; et al. Lake Water Temperature Modeling in an Era of Climate Change: Data Sources, Models, and Future Prospects. Rev. Geophys. 2024, 62, e2023RG000816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhou, W.; Guan, K.; Peng, B.; Xu, S.; Tang, J.; Zhu, Q.; Till, J.; Jia, X.; Jiang, C.; et al. Knowledge-Guided Machine Learning Can Improve Carbon Cycle Quantification in Agroecosystems. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Babovic, V. Improving Real-Time Forecasting of Water Quality Indicators with Combination of Process-Based Models and Data Assimilation Technique. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 66, 428–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Babovic, V.; Gin, K.Y.H. A Comprehensive Integrated Catchment-Scale Monitoring and Modelling Approach for Facilitating Management of Water Quality. Environ. Model. Softw. 2019, 120, 104489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyoum, W.M.; Kwon, D. Suitability of Satellite-Based Hydro-Climate Variables and Machine Learning for Streamflow Modeling at Various Scale Watersheds. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2020, 65, 2233–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xue, F.; Ding, J.; Xu, T.; Song, L.; Pang, Z.; Wang, J.; Xu, Z.; Ma, Y.; Lu, Z.; et al. A Hybrid Model Coupling Physical Constraints and Machine Learning to Estimate Daily Evapotranspiration in the Heihe River Basin. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
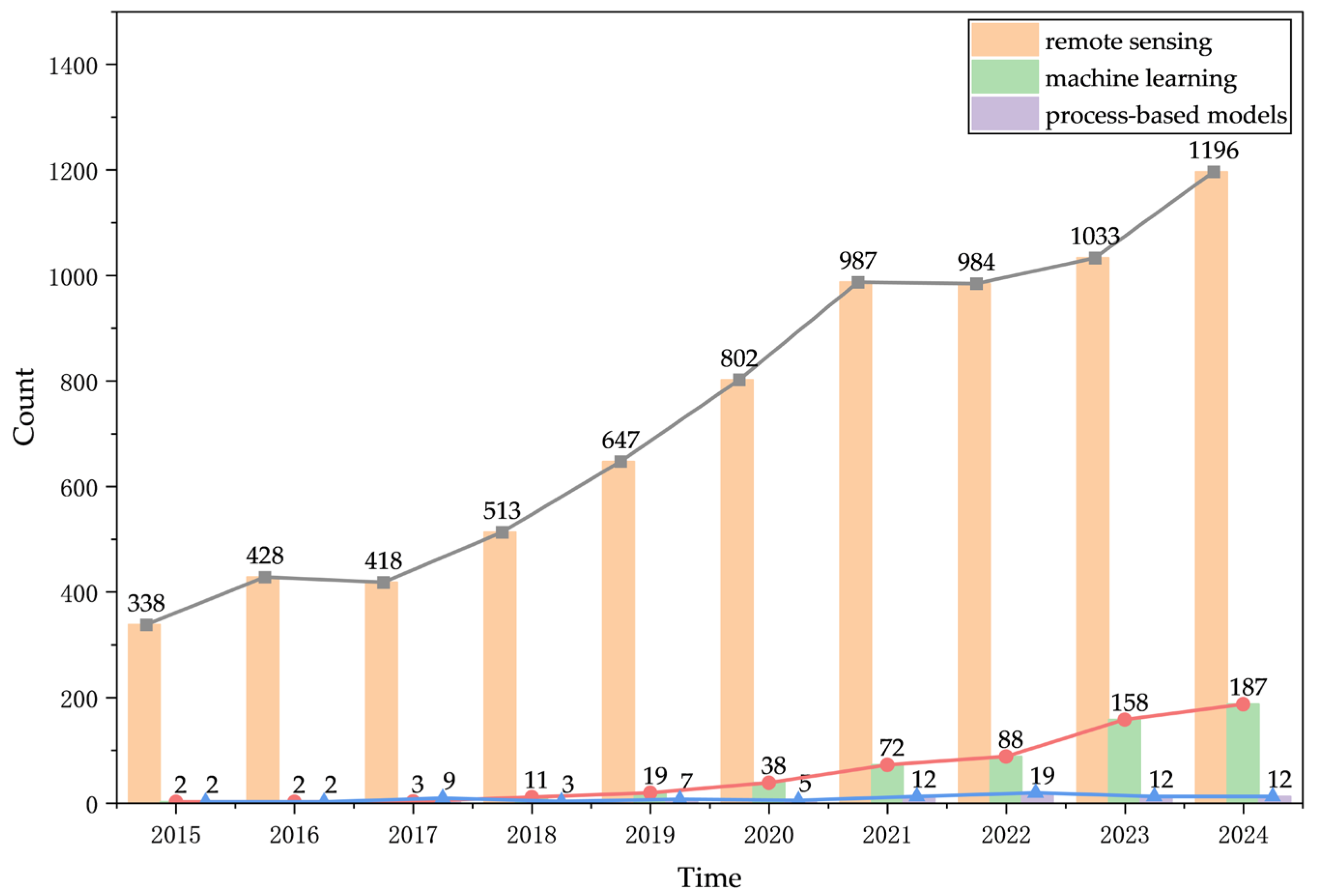
| Keywords Category | Search Strategy | Time Interval | Number of Papers Reviewed |
|---|---|---|---|
| Remote sensing Water quality | Remote sensing OR Remote sensing data AND Water quality monitoring | 2015–2024 | 7346 |
| Artificial intelligence Water quality | Artificial intelligence AND Water quality | 2015–2024 | 568 |
| Machine learning Water quality | machine learning AND Water quality | 2015–2024 | 580 |
| Machine learning Remote sensing Water quality | Machine learning AND Remote sensing AND Water quality | 2015–2024 | 119 |
| Hydrology Water quality | Hydrology OR Hydrological processes AND Water quality OR Water pollution | 2015–2024 | 40,897 |
| Aquatic environment monitoring | Aquatic environment AND Remote sensing OR Machine learning | 2015–2024 | 35,315 |
| Process-based models Water quality | Water quality AND Process-based models | 2015–2024 | 83 |
| Process-based models Remote sensing Water quality | Process-based models AND Remote sensing AND Water quality | 2015–2024 | 9 |
| Satellite Sensor | Launch Date | Spatial Resolution (m) | Spectral Resolution Band | Temporal Resolution (Day) | Spectrum Ranges (nm) | Country | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NIMBUS-7 CZCS | 24 October 1978 | 825 | 6 bands | 6 | 443–12,500 | US | |
| Landsat7 ETM+ | 15 April 1999 | 15–60 | 8 bands | 16 | 450–1250 | US | |
| SeaWiFS | 1 August 1999 | 500–1100 | 8 bands | 1–2 | 412–905 | US | |
| AVHRR | 13 October 1978 | 1100 | 6 bands | 1–2 | 580–12,500 | US | |
| EO-1 ALI | 21 November 2000 | 10–30 | 10 bands | 16 | 433–2350 | US | |
| Multi-spectral | WorldView-2 | 8 October 2009 | 0.46–0.52 | 9 bands | 1.1 | 400–1040 | US |
| MERIS | March 2002 | 300 | 15 bands | 1–3 | 407.5–905 | EU | |
| MODIS | 18 December 1999 | 250–1000 | 36 bands | 1 | 405–14,385 | US | |
| Landsat-8 OLI | 11 February 2013 | 15–30 | 9 bands | 16 | 435–2294 | US | |
| Hyper-spectral | Hyperion | 21 November 2000 | 30 | 242 bands | 16 | 349.896–2582.28 | US |
| HJ-1A HSI | 6 September 2008 | 100 | 115 bands | 4 | 450–950 | CN | |
| Sensor for UAV | GaiaSky-mini | - | 0.04 | 176 bands | / | 400–1000 | CN |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, P.; Zou, S.; Li, J.; Ju, H.; Zhang, J. Advancing Water Quality Management: Harnessing the Synergy of Remote Sensing, Process-Based Models, and Machine Learning to Enhance Monitoring and Prediction. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 3157. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17183157
Wang P, Zou S, Li J, Ju H, Zhang J. Advancing Water Quality Management: Harnessing the Synergy of Remote Sensing, Process-Based Models, and Machine Learning to Enhance Monitoring and Prediction. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(18):3157. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17183157
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Peixin, Shubin Zou, Jie Li, Hanyu Ju, and Jingjie Zhang. 2025. "Advancing Water Quality Management: Harnessing the Synergy of Remote Sensing, Process-Based Models, and Machine Learning to Enhance Monitoring and Prediction" Remote Sensing 17, no. 18: 3157. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17183157
APA StyleWang, P., Zou, S., Li, J., Ju, H., & Zhang, J. (2025). Advancing Water Quality Management: Harnessing the Synergy of Remote Sensing, Process-Based Models, and Machine Learning to Enhance Monitoring and Prediction. Remote Sensing, 17(18), 3157. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17183157








