The Dynamic Monitoring of River-Ice Thickness on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau: Four-Dimensional Structure-from-Motion Photogrammetry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
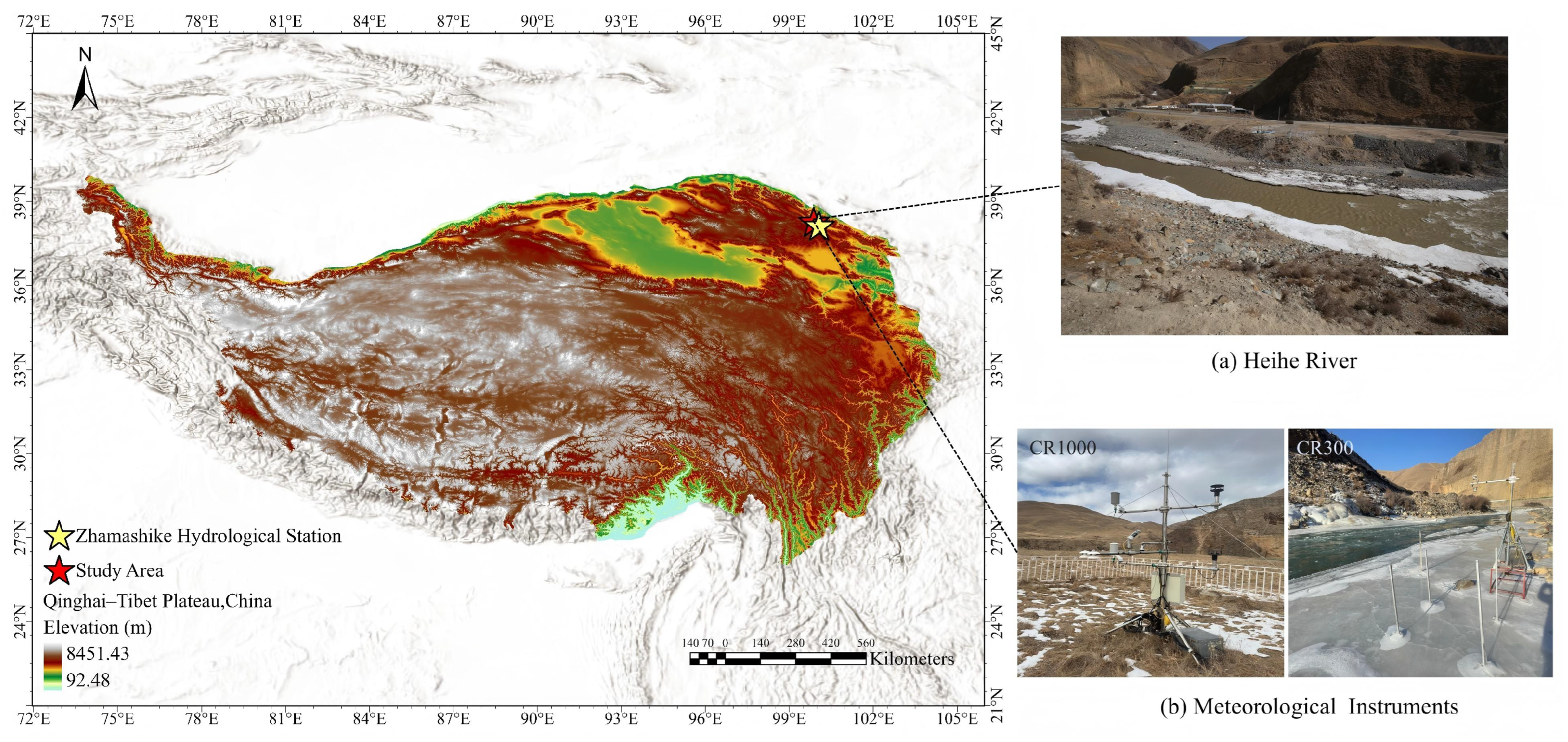
2.1. Study Area
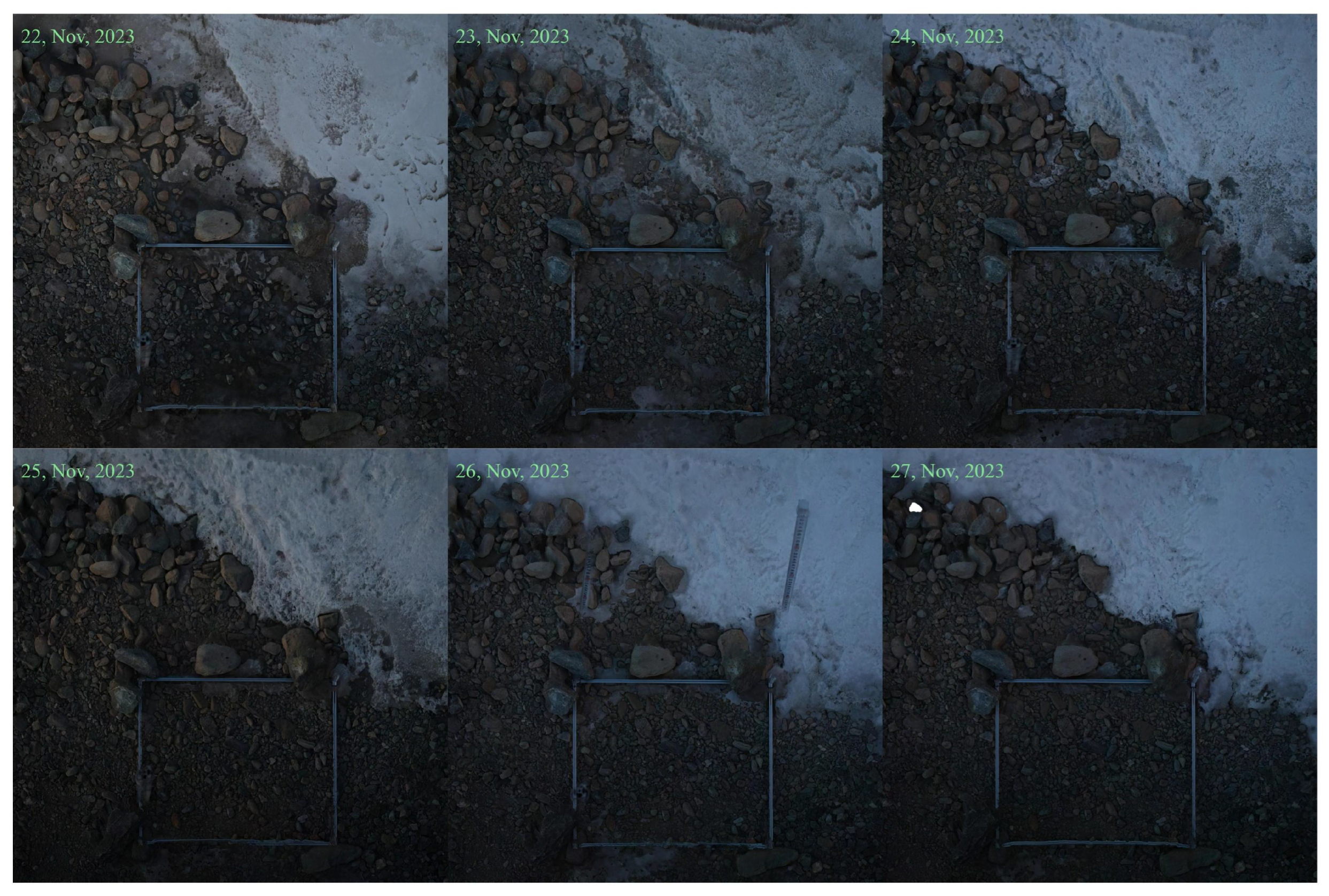
2.2. Shooting Strategies and Equipment
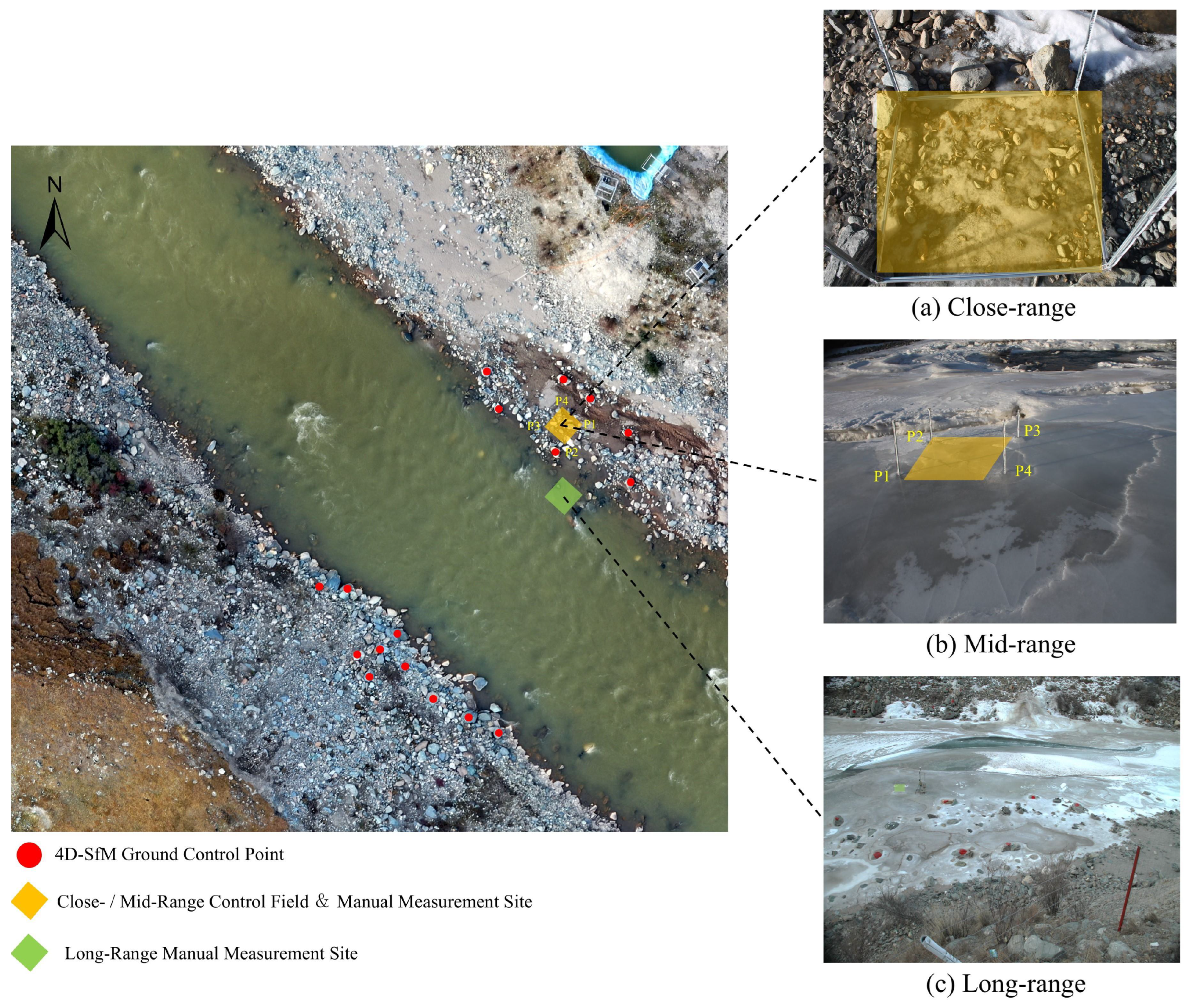
2.3. Selection of Control Points
2.4. Photo Processing
2.5. Manual Measurement Methods
2.6. Calculation of River-Ice Thickness
2.7. Image Brightness Value Calculation Method
2.8. Precision Evaluation
3. Results
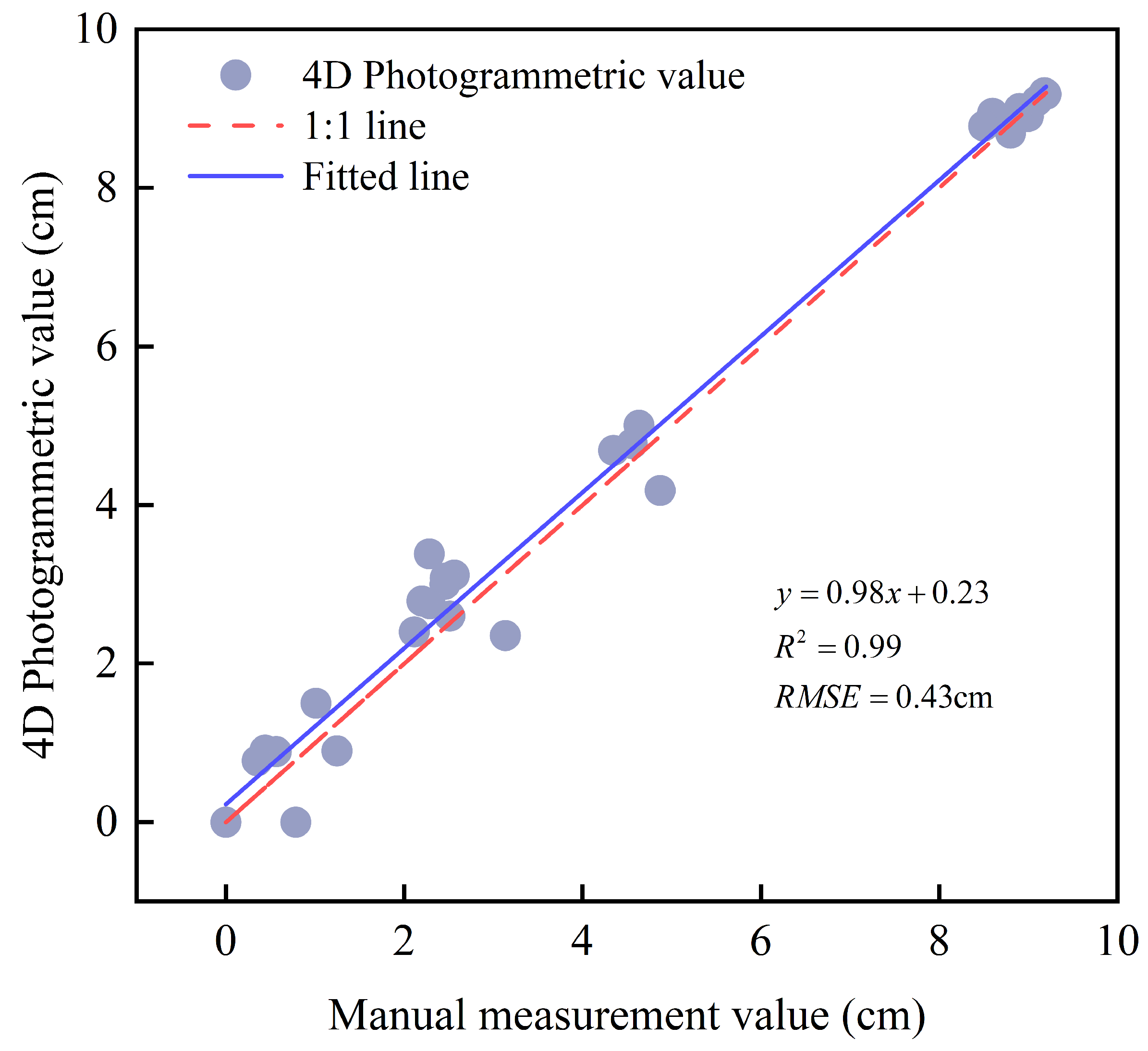
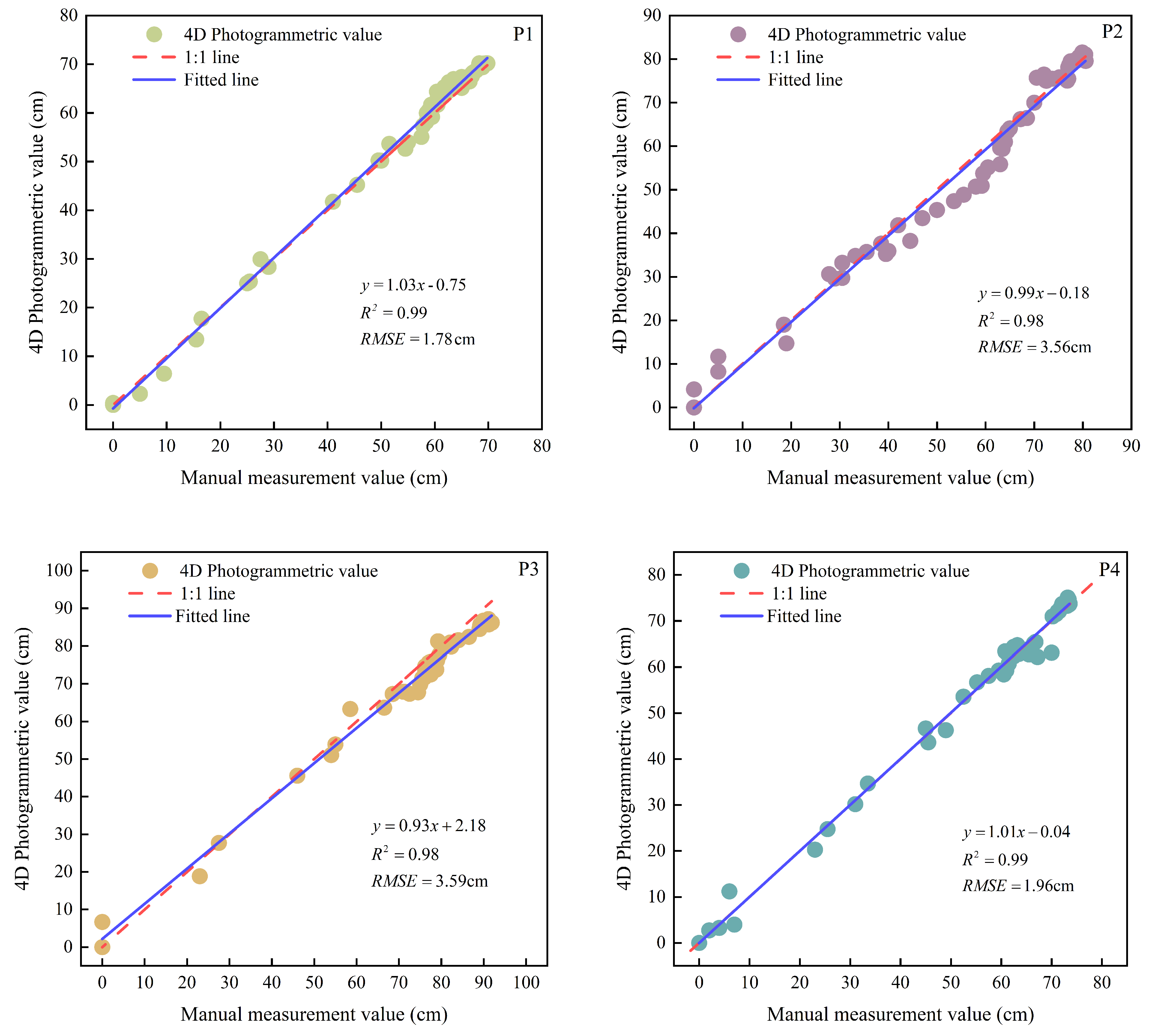
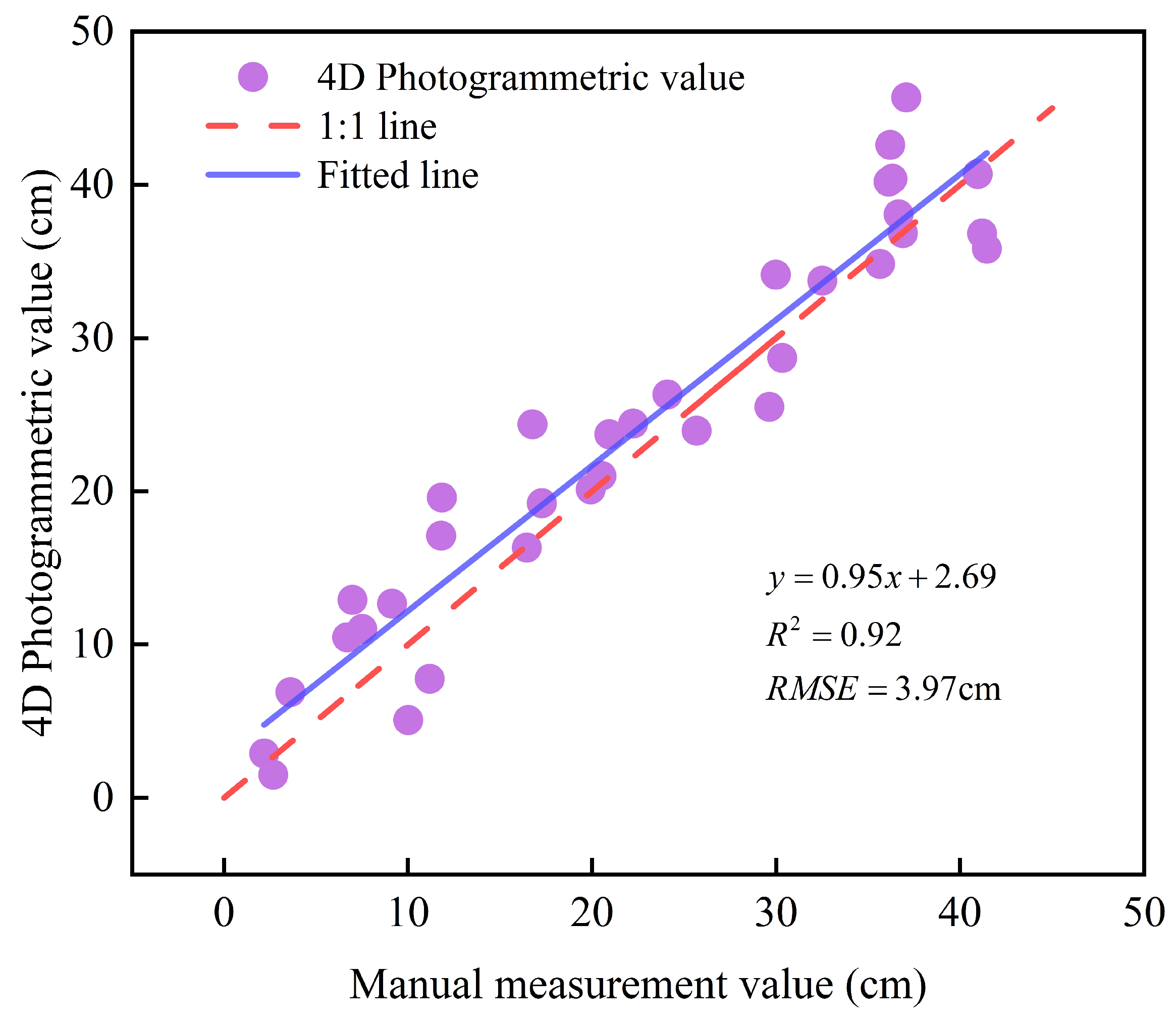
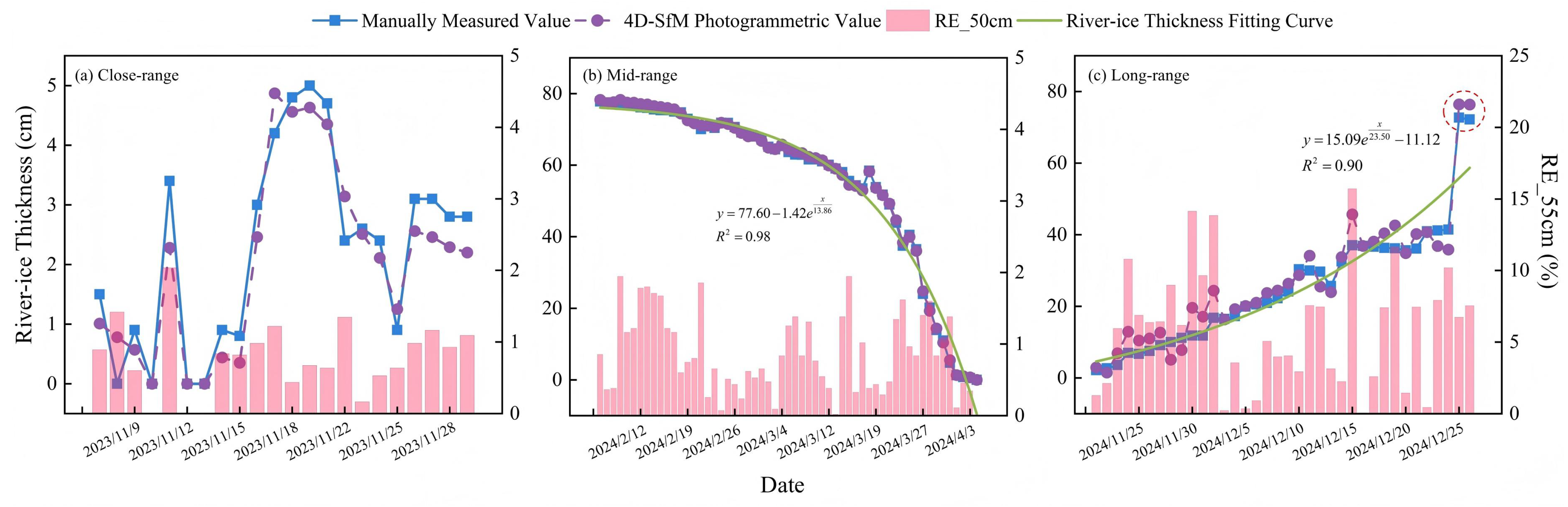
3.1. Assessment of River-Ice Thickness Accuracy Under Three Distance Modes
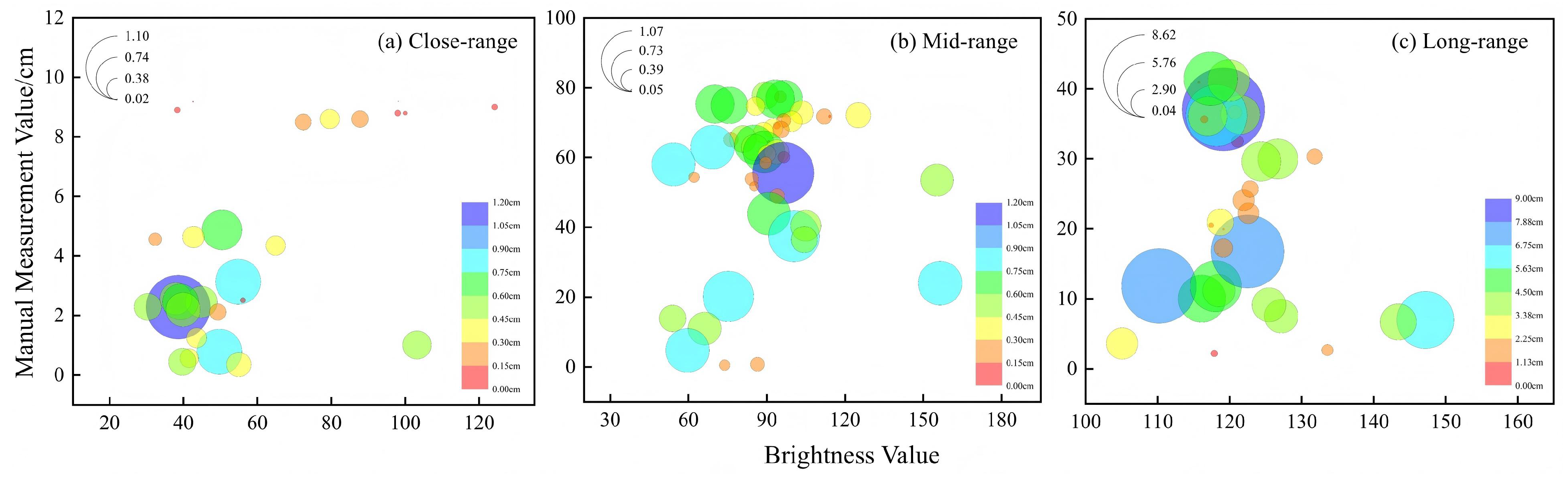
3.2. Analysis of Error Distribution and Influencing Factors
3.3. Spatial Distribution of River-Ice Thickness
3.4. Temporal Variations in River-Ice Thickness and Distribution of Relative Percentage Accuracy
3.5. The Development Process of Different Types of River-Ice
4. Discussion
4.1. Analysis of Factors Affecting 4D-SfM Photogrammetric Accuracy
4.2. Analysis of Extreme River-Ice Events and Evaluation of the Capture Capability of 4D-SfM Photogrammetry
4.3. Comparison Between 4D-SfM Photogrammetric Techniques and Conventional River-Ice Thickness Measurement Methods
| Method | Accuracy | Coverage | Cost | Difficulty | Data Processing | Adaptability | Real Time | Temporal Resolution | Scalability | Complementarity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drilling [24] | ±1 cm | Point | Low (hand tools) | Low (manual) | Low (no) | High (not limited by visibility) | No | Single (on-site) | Low (labor-intensive) | Calibrate other methods |
| Ultrasonic [25] | ±2 cm | Point /Line | Medium (requires probe) | Low (probe setup below water) | Medium (auto logging, some filtering) | Medium (snow cover ) | Yes | Continuous (sec–min) | Medium (multiple transects) | Complement GPR/SfM |
| GPR [24] | ±6.2 cm | Continuous Transect | High (antenna, software) | Medium (stable platform needed) | Medium (signal processing) | Medium (ice–water effect) | Partial | Periodic | Medium (along track) | Combine with drilling, SAR |
| SAR [61] | RMSE 10.9–25.8 cm | Kilometer-scale reach | Low (open data) | None (automatic acquisition) | Medium (image backscatter) | Medium (terrain effects) | No | 6–12 days revisit | High (global) | Validate GPR, combine large -scale demand |
| UAV-SfM [36] | RMSE 3–9 cm | Hundred-meter reach | Medium (drone + GCP) | Medium (flight planning and calibration) | High (SfM reconstruction, large data) | Low (lighting, weather) | No | Episodic (flight-based) | Medium (multi-UAV) | LiDAR/GPR validation, high spatial detail |
| Airborne LiDAR [3] | ±10 cm (vertical) | Flightline | High (LiDAR, platform upkeep) | Medium (aircraft or rotorcraft) | Medium (point cloud registration) | Medium (snow–ground) | No | Episodic (flight) | Medium (extend via flightlines) | SfM/GPR fusion, enhance depth |
| Optical Satellite [62] | RMSE 7–18 cm | Kilometer-scale reach | Low (no build, license only) | None (auto acquisition) | Low (DSM generation only) | Low (cloud, low light) | No | 5–16 days revisit | High (multi-constellation) | Combine SAR/UAV for high resolution |
| 4D-SfM | RMSE 0.43–3.97 cm | River cross-section | Low (camera and rig) | Low (shore-based at fixed points) | High (4D-SfM reconstruction) | High (not limited by weather) | No | Continuous (daily) | Medium (adjust flight path) | SfM/GPR fusion, improve precision |
5. Conclusions
- 1.
- Measurement accuracy gradually decreases as the shooting distance increases. Specifically, the RMSE at close range (0.5–1.5 m) is 0.43 cm; the RMSE for mid-range (3–10 m) applications is 1.78–3.59 cm; and the RMSE for long-range (25–60 m) applications is 3.97 cm.
- 2.
- Although ice thickness, ice surface undulation, and image brightness influence the results of 4D-SfM photogrammetry to some extent, their impact is less significant than that of shooting distance on measurement accuracy.
- 3.
- The survey area increases with shooting distance—the area at close range is 11.38 m2; at mid range, it is 33.37 m2; and at long range, it is 2642 m2.
- 4.
- The 4D-SfM photogrammetry is capable of not only illustrating the developmental processes of shore ice and anchor ice, but also effectively capturing extreme events characterized by sudden changes in river-ice thickness, owing to its high spatiotemporal resolution.
- 5.
- All three shooting distances can effectively reflect the nonlinear variation trend in river-ice thickness.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, H.; Li, H.; Wang, J.; Hao, X. Advances in Remote Sensing of River Ice. Adv. Earth Sci. 2020, 35, 1041–1051. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, S.; Xu, Y.; You, Q.; Pepin, N.; Flügel, W.-A.; Yao, T. Review of Climate and Cryospheric Change in the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Environ. Res. Lett. 2010, 5, 015101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharova, E.; Frolova, N.; Kouraev, A.; Agafonova, S.; Duguay, C. River ice Phenology and Thickness from Satellite Altimetry: Potential for Ice Bridge Road Operation and Climate Studies. Cryosphere 2021, 15, 5387–5407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallerbäck, S.; Aghakouchak, A.; Love, C.; Persson, M.; Stensen, K.; Huning, L.S.; Gustafsson, D. Climate Warming Shortens Ice Durations and Alters Freeze and Break-up Patterns in Swedish Water Bodies. Cryosphere 2022, 16, 2493–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Pavelsky, T.M.; Allen, G.H. The Past and Future of Global River Ice. Nature 2020, 577, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesack, L.F.W.; Hicks, F.E.; Forbes, D.L.; Marsh, P. Local Spring Warming Drives Earlier River-ice Breakup in a Large Arctic Delta. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 1560–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrell, B.C.; Beltaos, S.; Turcotte, B. Effects of Climate Change on River Ice Processes and Ice Jams. Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2021, 21, 421–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Wu, P.; Zhou, S.; Sun, J.; Han, Z. Tracing the Origin and Geochemical Processes of Dissolved Sulphate in a Karst-Dominated Wetland Catchment Using Stable Isotope Indicators. J. Hydrol. 2018, 562, 210–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Cao, G.; Cheng, T.; Wang, J. Accumulation and Evolution of Ice Jams Influenced by Different Ice Discharge: An Experimental Analysis. Front. Earth Sci. 2023, 10, 1054040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.-X.; Szydlowski, M.; Li, C.; Li, W.; Kolerski, T.; Wu, Y.-J.; Shi, X.-H.; Quan, Q.; Wang, W.-J.; Zhao, S.-N. Freeze-Up Ice Jam Formation in the River Bend, a Case Study on the Inner Mongolia Reach of Yellow River. Crystals 2021, 11, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoreishi, M.; Das, A.; Lindenschmidt, K.-E. Advancement in Ice-Jam Flood Risk Management: Integrating Dynamic Adaptive Behavior by an Agent-Based Modeling in Fort McMurray, Canada. J. Hydrol. 2024, 635, 131236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Reed, M.; Lindenschmidt, K.-E. Sustainable Ice-Jam Flood Management for Socio-Economic and Socio-Ecological Systems. Water 2018, 10, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chave, R.A.J.; Dupuis, L.; Fissel, D.B.; Dumont, S.; Lemon, D.D. Real-Time Measurements of Ice Draft and Velocity in the St. Lawrence River. Inst. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2004, 3, 1629–1633. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.-G.; Jin, J.-L.; Zhou, Y.-L.; Wei, Y.-M.; Huang, Q.; Liu, L. Comprehensive Evaluation of Ice Disaster Risk of the Ningxia–Inner Mongolia Reach in the Upper Yellow River. Nat. Hazards 2014, 75, 179–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.; Huang, H.Q.; Zhou, Y.Y. Effect of Hydrological Processes, Water Temperature and River Channel Geometry Changes on Ice Floods in the Ningxia-Inner Mongolia Reach of the Yellow River. Resour. Sci. 2016, 38, 948–955. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, H.; Ding, Y.; Duan, Z.; Wang, J.; Pan, X.; Yang, Y. Permafrost Hydrology of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau: A Review of Processes and Modeling. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 8, 576838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Hou, J.; Huang, C.; Duan, H.; Gu, J. Lake Phenology of Freeze-Thaw Cycles Using Random Forest: A Case Study of Qinghai Lake. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Ren, W.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, Y. Predicting Gross Primary Productivity under Future Climate Change for the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau Based on Convolutional Neural Networks. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Ma, Y.; Xue, Y.; Piao, S. Climate Change Trends and Impacts on Vegetation Greening Over the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 7540–7552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, H.; Wang, J.; Hao, X. Monitoring High-Altitude River Ice Distribution at the Basin Scale in the Northeastern Qinghai–Tibet Plateau from a Landsat Time-Series Spanning 1999–2018. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 247, 111915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; Li, H.; Ren, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, Y.; Hao, X.; Niu, L. Machine Learning-Enhanced River Ice Identification in the Complex Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharov, I.; Puestow, T.; Khan, A.A.; Briggs, R.; Barrette, P. Review of River Ice Observation and Data Analysis Technologies. Hydrology 2024, 11, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Chen, J.; Wei, Q.; Yao, X.; Yu, Z.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, Y. Ice Thickness Assessment of Non-Freshwater Lakes in the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau Based on Unmanned Aerial Vehicle-Borne Ice-Penetrating Radar: A Case Study of Qinghai Lake and Gahai Lake. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, M.; Briggs, R.; English, J.; Khan, A.A.; Khan, H.; Puestow, T. Operational Monitoring of River Ice on the Churchill River, Labrador. In Proceedings of the 21st Workshop on the Hydraulics of Ice Covered Rivers, Saskatoon, SK, Canada, 29 August–1 September 2021; Volume 29. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Li, H. Monitoring the Ice Thickness in High-Order Rivers on the Tibetan Plateau with Dual-Polarized C-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mermoz, S.; Van Der Sanden, J.J.; Chokmani, K.; Bernier, M.; Pottier, E.; Allain-Bailhache, S. Retrieval of River Ice Thickness From C-Band PolSAR Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 3052–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, R.; Ding, Y.; Han, C.; Ma, S. Snow Process Monitoring Using Time-Lapse Structure-from-Motion Photogrammetry with a Single Camera. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2021, 190, 103355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piermattei, L.; Carturan, L.; Tarolli, P.; Vettore, A.; Pfeifer, N.; Dalla Fontana, G.; De Blasi, F. Suitability of Ground-Based SfM–MVS for Monitoring Glacial and Periglacial Processes. Earth Surf. Dyn. 2016, 4, 425–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioli, F.; Gaspari, F.; Pinto, L.; Nex, F.; Barbieri, F. ICEPY4D: A Python Toolkit for Advanced Multi-Epoch Glacier Monitoring with Deep-Learning Photogrammetry. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2023, XLVIII-1/W2-2023, 1037–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filhol, S.; Sutter, G.; Burkhart, J.F.; Perret, A.; Girod, L.; Schuler, T.V. Time-Lapse Photogrammetry of Distributed Snow Depth During Snowmelt. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 7916–7926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, R.; Ma, S.; Han, C.; Ding, Y.; Guo, S.; Wang, X. The Challenge of Monitoring Snow Surface Sublimation in Winter Could Be Resolved with Structure-from-Motion Photogrammetry. J. Hydrol. 2024, 630, 130733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo, D.; Kachamba, D.; Næsset, E.; Ørka, H.O.; Gobakken, T. Effects of UAV Image Resolution, Camera Type, and Image Overlap on Accuracy of Biomass Predictions in a Tropical Woodland. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifert, E.; Van Aardt, J.; Vogt, H.; Seifert, T.; Seifert, S.; Kunneke, A.; Drew, D. Influence of Drone Altitude, Image Overlap, and Optical Sensor Resolution on Multi-View Reconstruction of Forest Images. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quoc Long, N.; Goyal, R.; Van Chung, P.; Van Canh, L.; Bui, X.-N.; Xuan Cuong, C.; Ngoc Quy, B.; Khac Luyen, B. Influence of Flight Height on the Accuracy of UAV-Derived Digital Elevation Model at Complex Terrain. Inżynieria Miner. 2020, 45, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ma, S.; Chen, R. Exploring the Optimal 4D-SfM Photogrammetric Models at Plot Scale. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rødtang, E.; Alfredsen, K.; Juárez, A. Drone Surveying of Volumetric Ice Growth in a Steep River. Front. Remote Sens. 2021, 2, 767073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezryadin, S.; Bourov, P.; Ilinih, D. Brightness Calculation in Digital Image Processing. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Technologies for Digital Photo Fulfillment, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 5 March 2007; pp. 10–15. [Google Scholar]
- Rangelov, D.; Waanders, S.; Waanders, K.; Van Keulen, M.; Miltchev, R. Impact of Camera Settings on 3D Reconstruction Quality: Insights from NeRF and Gaussian Splatting. Sensors 2024, 24, 7594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debevec, P.E.; Malik, J. Recovering High Dynamic Range Radiance Maps from Photographs. In Proceedings of the Association for Computing Machinery; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 643–652, ISBN 9798400708978. [Google Scholar]
- Fukś, M. Changes in River Ice Cover in the Context of Climate Change and Dam Impacts: A Review. Aquat. Sci. 2023, 85, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rham, L.; Prowse, T.; Beltaos, S.; Dibike, Y.; Peters, D.; Bonsal, B. A Canadian River Ice Database from the National Hydrometric Program Archives. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2020, 12, 1835–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Rokaya, P.; Lindenschmidt, K.-E. Modelling Climatic Impacts on Ice-Jam Floods: A Review of Current Models, Modelling Capabilities, Challenges and Future Prospects. Environ. Rev. 2021, 29, 378–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolerski, T. Assessment of the Ice Jam Potential on Regulated Rivers and Reservoirs with the Use of Numerical Model Results. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2021, 191, 103372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, B.T.; Congalton, R.G. Issues in Unmanned Aerial Systems (UAS) Data Collection of Complex Forest Environments. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.W.; Carrivick, J.L.; Quincey, D.J. Structure from Motion Photogrammetry in Physical Geography. Prog. Phys. Geogr. Earth Environ. 2015, 40, 247–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javadnejad, F.; Olsen, M.J.; Slocum, R.K.; Gillins, D.T.; Parrish, C.E. Dense Point Cloud Quality Factor as Proxy for Accuracy Assessment of Image-Based 3D Reconstruction. J. Surv. Eng. 2020, 147, 04020021-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazur, A.; Kacprzak, M.; Kotlarz, J.; Kubiak, K.; Skocki, K. The Influence of Atmospheric Light Scattering on Reflectance Measurements during Photogrammetric Survey Flights at Low Altitudes over Forest Areas. For. Res. Pap. 2018, 79, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Omali, T.U. Impacts of Sensor Spatial Resolution on Remote Sensing Image Classification. Glob. Sci. J. 2018, 6, 63–68. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Li, L.; Nearing, M.A.; Nichols, M.H.; Polyakov, V.O.; Guertin, D.P.; Cavanaugh, M.L. The Effects of DEM Interpolation on Quantifying Soil Surface Roughness Using Terrestrial LiDAR. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 198, 104520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, M. Evaluation of DEM Interpolation Techniques for Characterizing Terrain Roughness. CATENA 2020, 198, 105072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulverhill, C.; Coops, N.C.; Tompalski, P.; Bater, C.W.; Dick, A.R. The utility of terrestrial photogrammetry for assessment of tree volume and taper in boreal mixedwood forests. Ann. For. Sci. 2019, 76, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Wackrow, R.; Meng, F.-R.; Lobb, D.; Li, S. Assessing the Accuracy and Feasibility of Using Close-Range Photogrammetry to Measure Channelized Erosion with a Consumer-Grade Camera. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashton, G.D. River and Lake Ice Thickening, Thinning, and Snow Ice Formation. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2011, 68, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thellman, A.; Jankowski, K.; Hayden, B.; O’Sullivan, A. The Ecology of River Ice. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2021, 126, e2021JG006275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, R. Estimation of the Dependence of Ice Phenomena Trends on Air and Water Temperature in Rivers. Water 2020, 12, 3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokaya, P.; Lindenschmidt, K.-E.; Pietroniro, A.; Clark, M. Modelling of Ice Jam Floods under Past and Future Climates: A Review. J. Hydrol. X 2022, 15, 100120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turcotte, B.; Dubnick, A.; McKillop, R.; Ensom, T. Icing and aufeis in cold regions I: The origin of overflow. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 2024, 51, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallalieu, J.; Carrivick, J.L.; Quincey, D.J.; Smith, M.W.; James, W.H.M. An integrated Structure-from-Motion and time-lapse technique for quantifying ice-margin dynamics. J. Glaciol. 2017, 63, 937–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfredsen, K.; Haas, C.; Tuhtan, J.A.; Zinke, P. Brief Communication: Mapping River Ice Using Drones and Structure from Motion. Cryosphere 2018, 12, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gindraux, S.; Boesch, R.; Farinotti, D. Accuracy Assessment of Digital Surface Models from Unmanned Aerial Vehicles’ Imagery on Glaciers. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royer, A.; Langlois, A.; Jutras, S.; Roy, A. Review Article: Performance Assessment of Radiation-Based Field Sensors for Monitoring the Water Equivalent of Snow Cover (SWE). Cryosphere 2021, 15, 5079–5098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandlburger, G.; Hauer, C.; Pfeifer, N.; Wieser, M. Topo-Bathymetric LiDAR for Monitoring River Morphodynamics and Instream Habitats—A Case Study at the Pielach River. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 6160–6195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
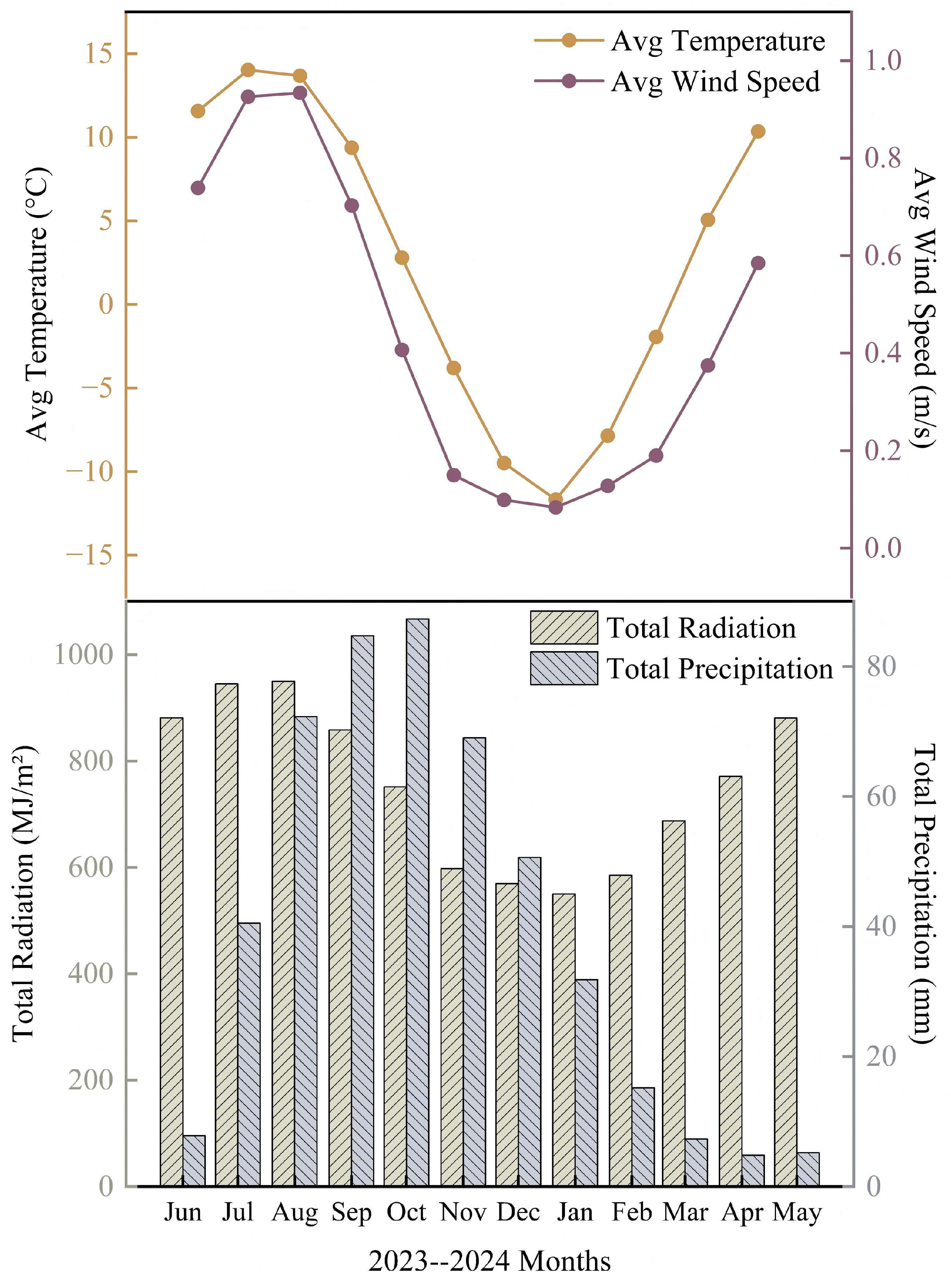
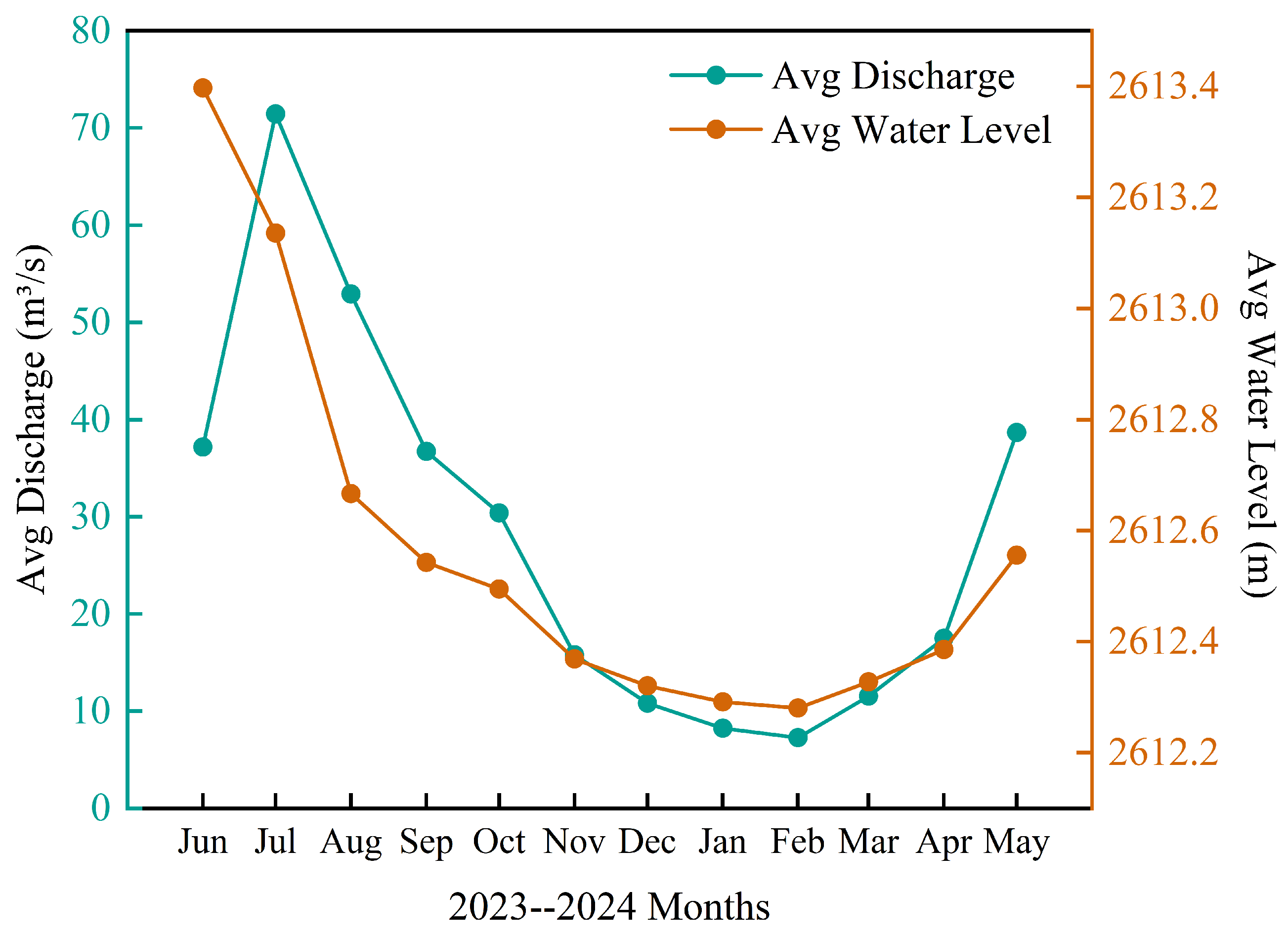




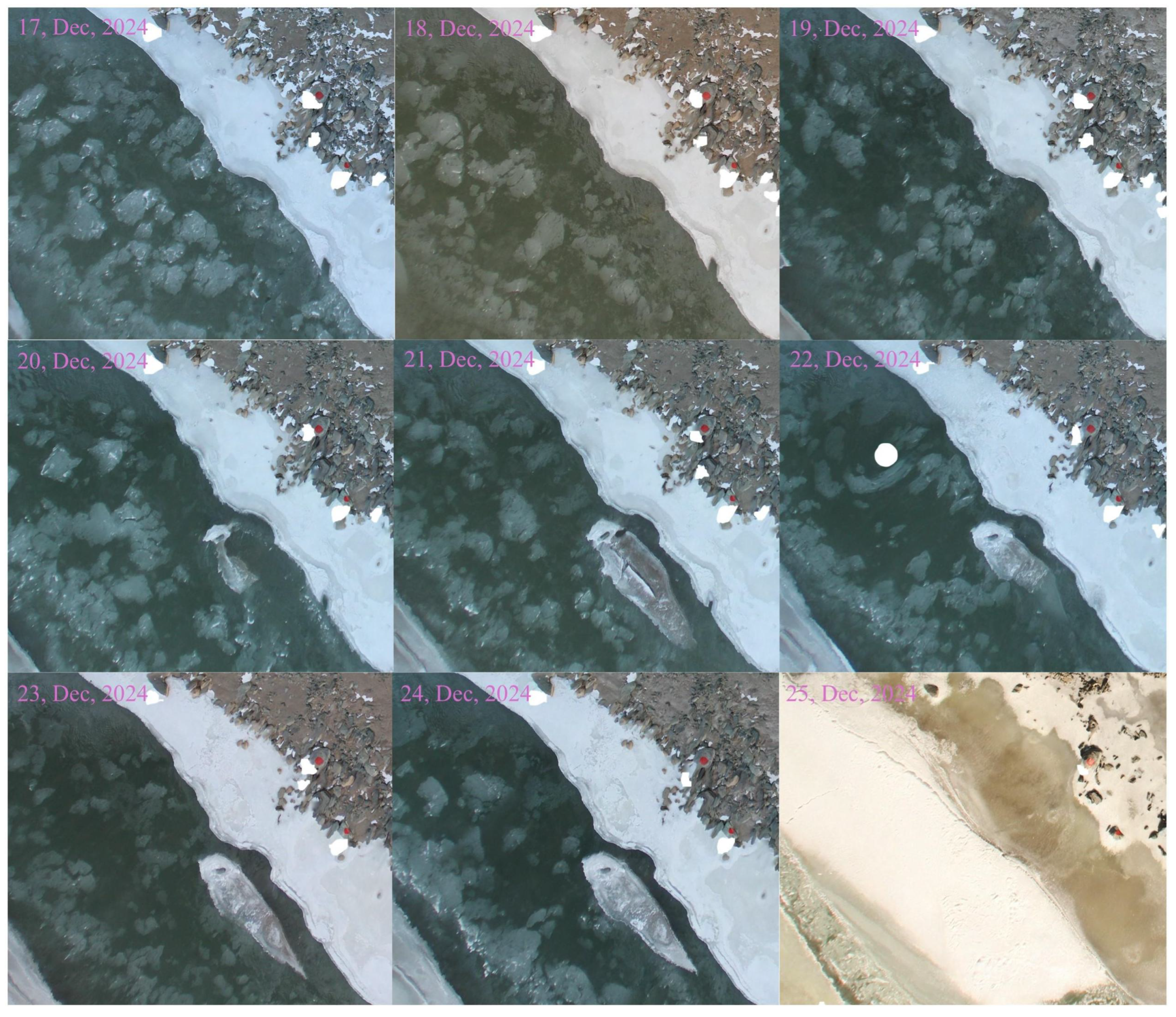
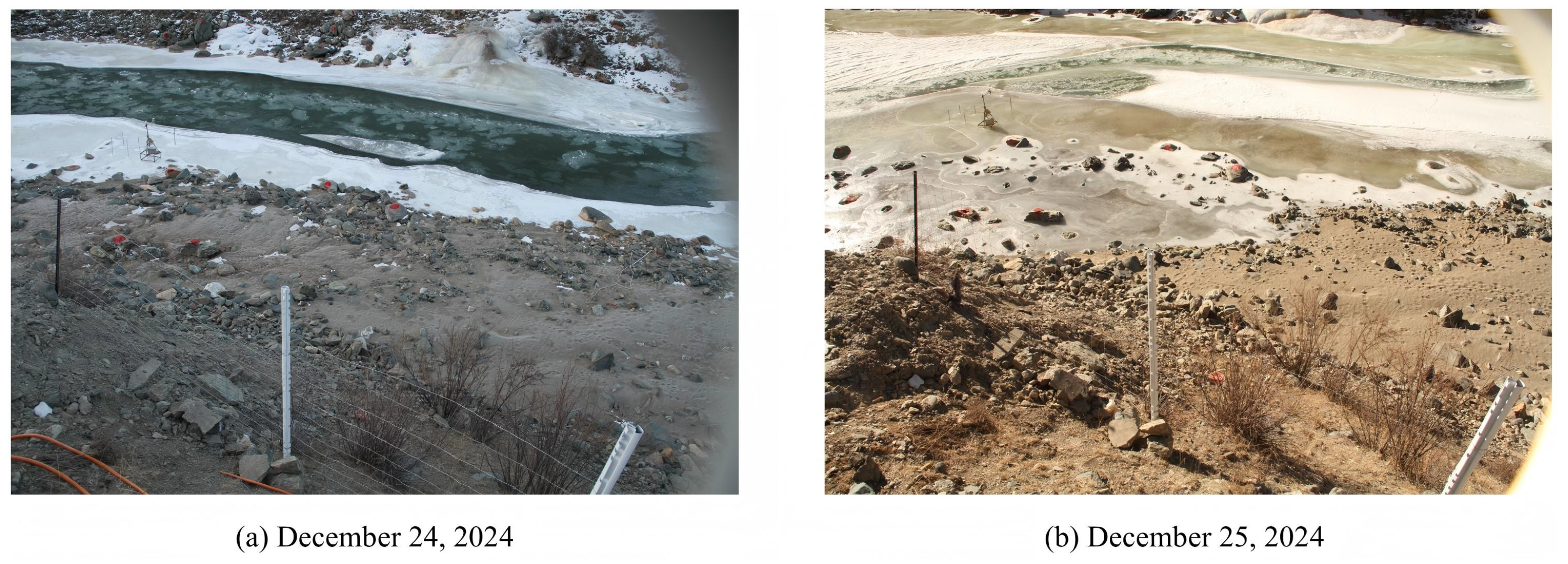
| Data | Temperature ℃ | Wind Speed m/s | River Discharge m3/s | River Stage m |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 21 December 2024 | −14.24 | 1.41 | 12.3 | 2613.34 |
| 22 December 2024 | −13.02 | 1.29 | 12.3 | 2613.34 |
| 23 December 2024 | −13.40 | 1.60 | 12.3 | 2613.34 |
| 24 December 2024 | −14.10 | 1.59 | 12.3 | 2613.34 |
| 25 December 2024 | −11.79 | 2.20 | 12.1 | 2613.31 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Chen, R.; Lyu, Z.; Wang, L.; Ao, X. The Dynamic Monitoring of River-Ice Thickness on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau: Four-Dimensional Structure-from-Motion Photogrammetry. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2887. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17162887
Fan Y, Zhang Y, Liu J, Chen R, Lyu Z, Wang L, Ao X. The Dynamic Monitoring of River-Ice Thickness on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau: Four-Dimensional Structure-from-Motion Photogrammetry. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(16):2887. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17162887
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Yanwei, Yao Zhang, Junfeng Liu, Rensheng Chen, Zijie Lyu, Lei Wang, and Xinmao Ao. 2025. "The Dynamic Monitoring of River-Ice Thickness on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau: Four-Dimensional Structure-from-Motion Photogrammetry" Remote Sensing 17, no. 16: 2887. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17162887
APA StyleFan, Y., Zhang, Y., Liu, J., Chen, R., Lyu, Z., Wang, L., & Ao, X. (2025). The Dynamic Monitoring of River-Ice Thickness on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau: Four-Dimensional Structure-from-Motion Photogrammetry. Remote Sensing, 17(16), 2887. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17162887





