VAWIlog: A Log-Transformed LSWI–EVI Index for Improved Surface Water Mapping in Agricultural Environments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
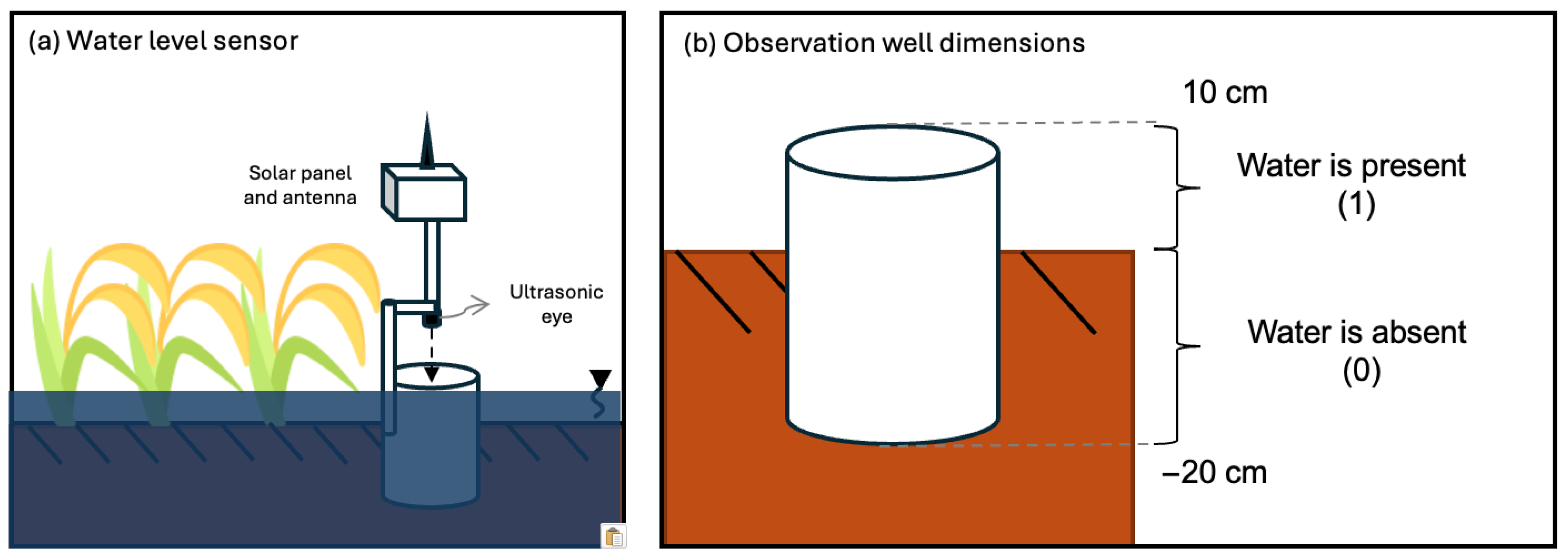
2.1. On-the-Ground Water Level Measurements
2.1.1. Sensor Installation
2.1.2. Time Series Smoothing and Dynamic Outlier Detection
2.2. Satellite Data
2.2.1. Data Pre-Processing
2.2.2. Temporal Alignment of Satellite and Water Level Data
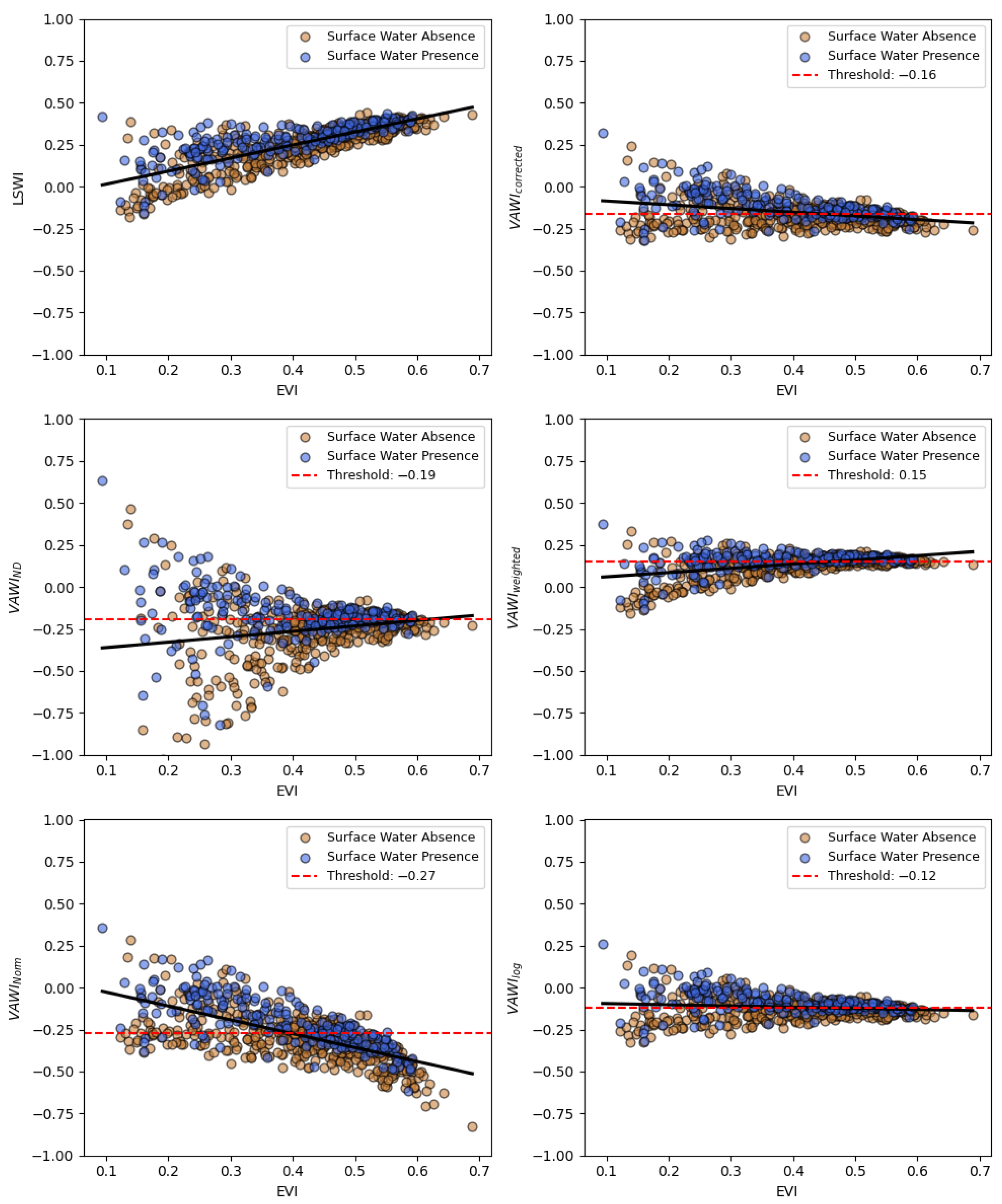
2.3. Vegetation-Adjusted Water Index Formulations and Their Interpretations
2.4. Comparative Analysis Against Established Water Indices and Dynamic World V1
3. Results
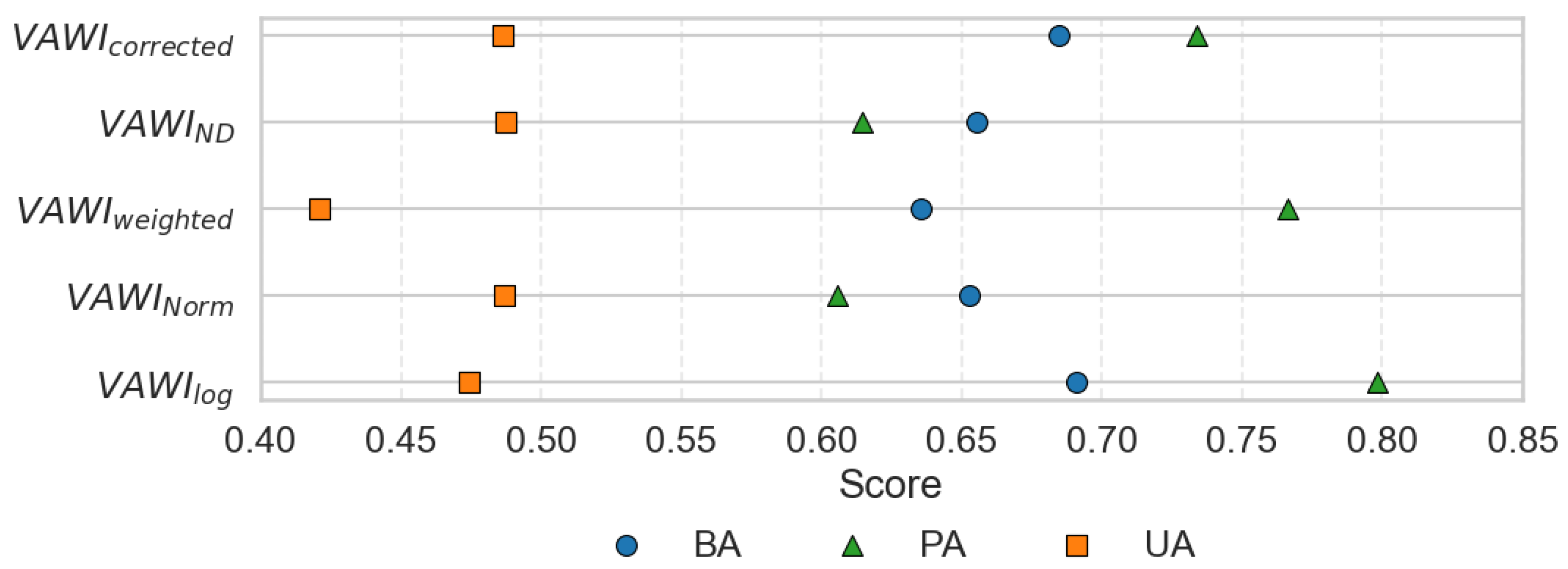
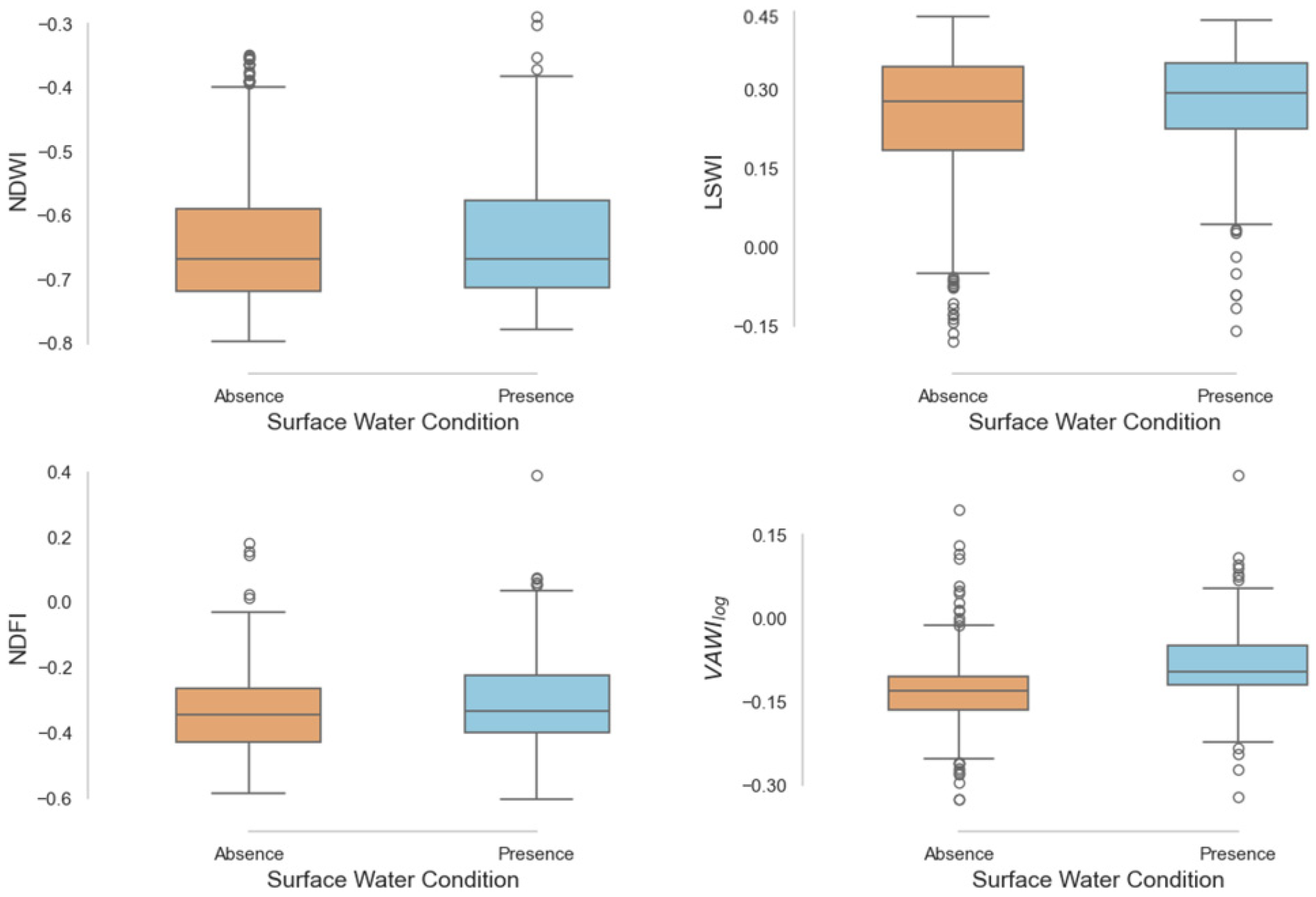
3.1. Vegetation Influence Reduction and Performance of LSWI–EVI Transformations
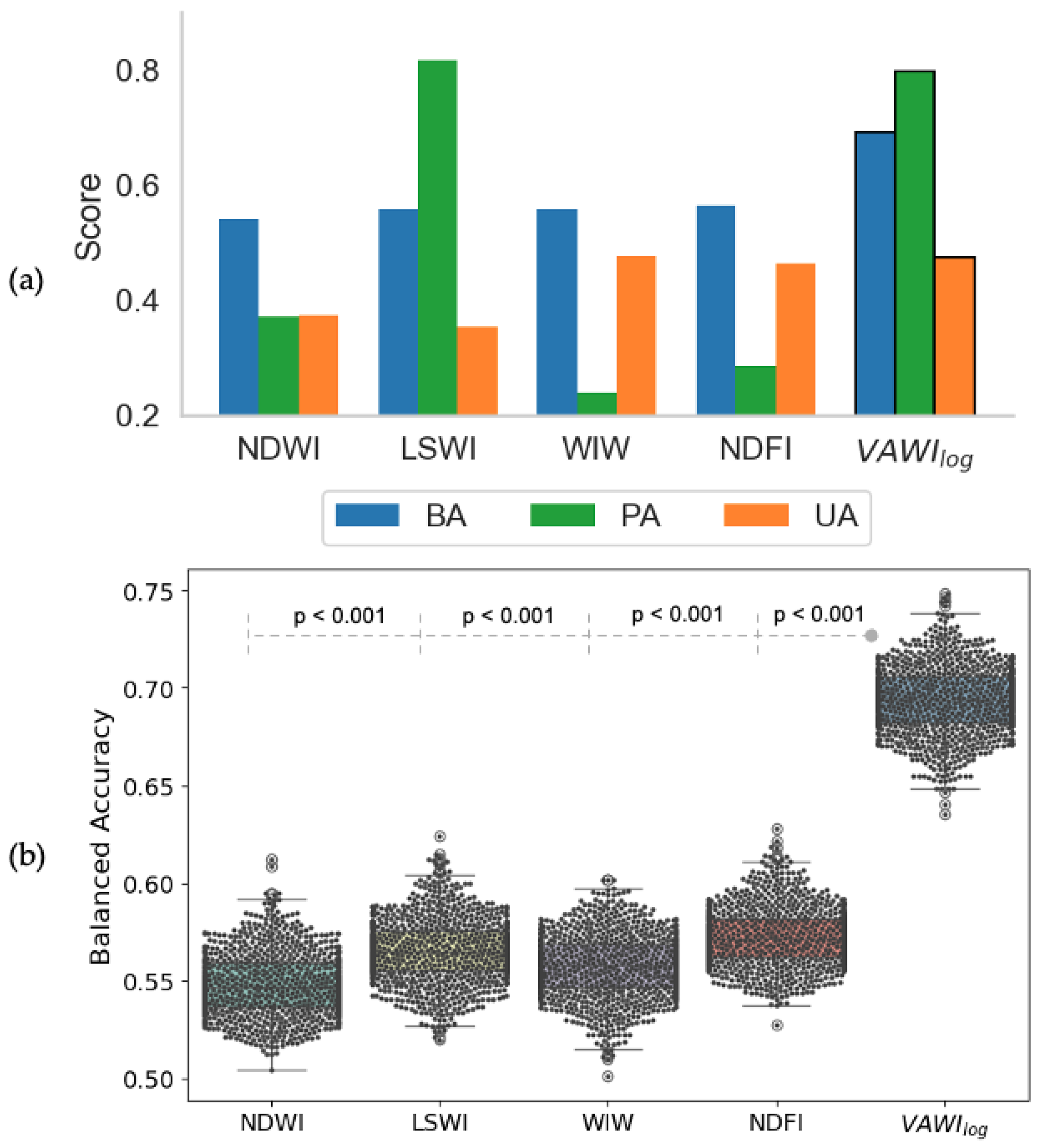
3.2. Benchmarking Against Established Water Indices
3.2.1. Overall Detection Performance
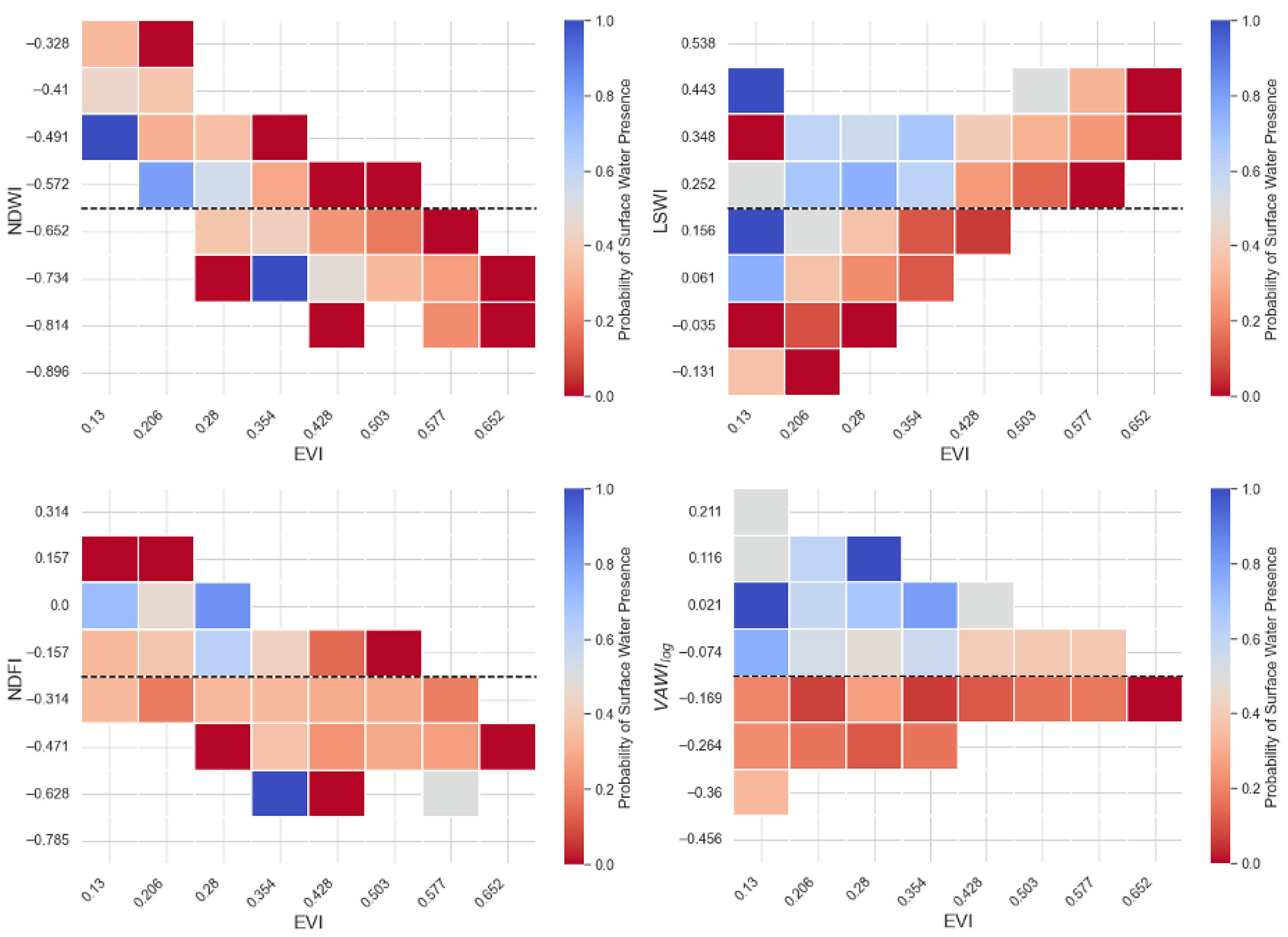
3.2.2. Detection Stability with Increasing EVI
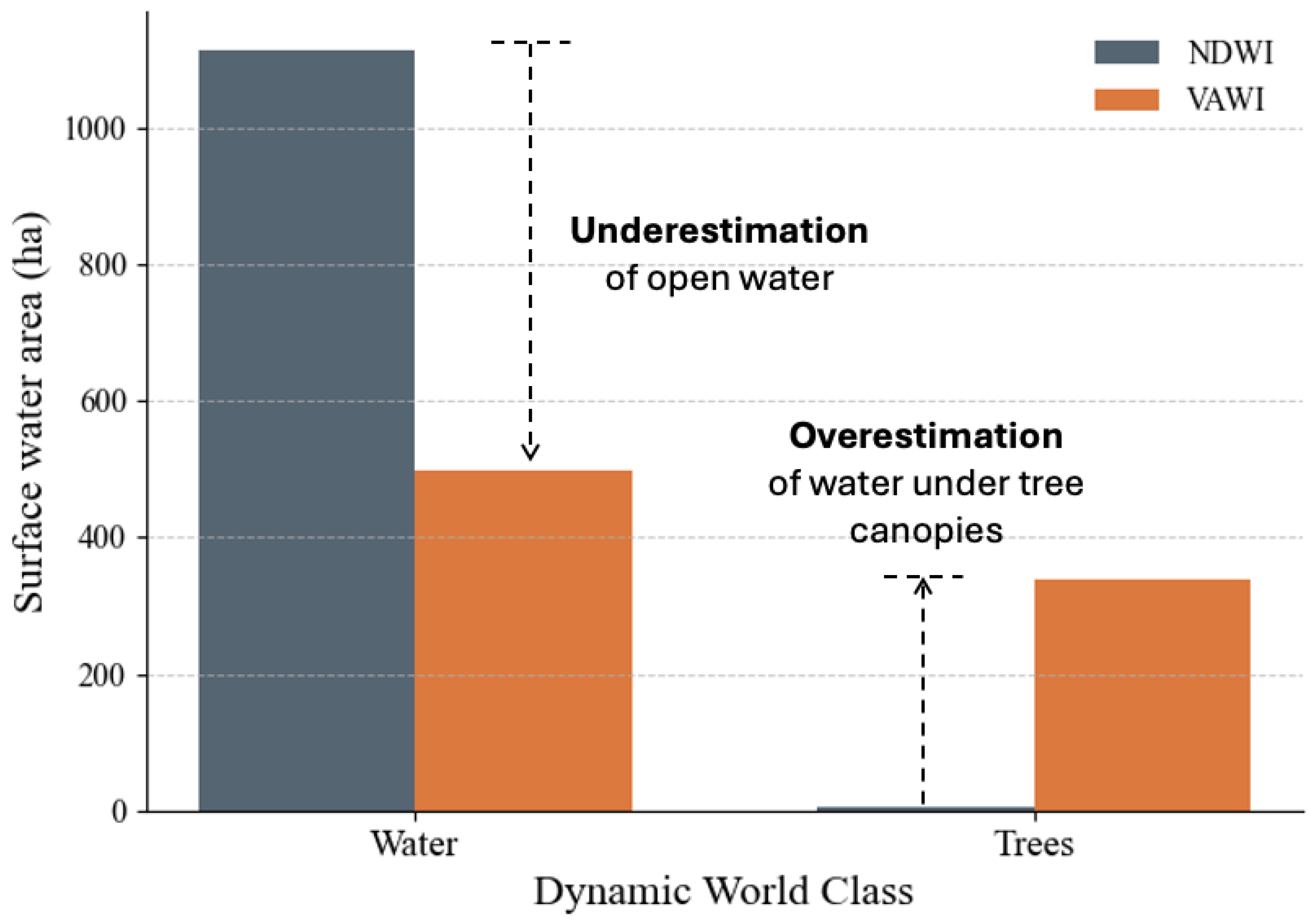
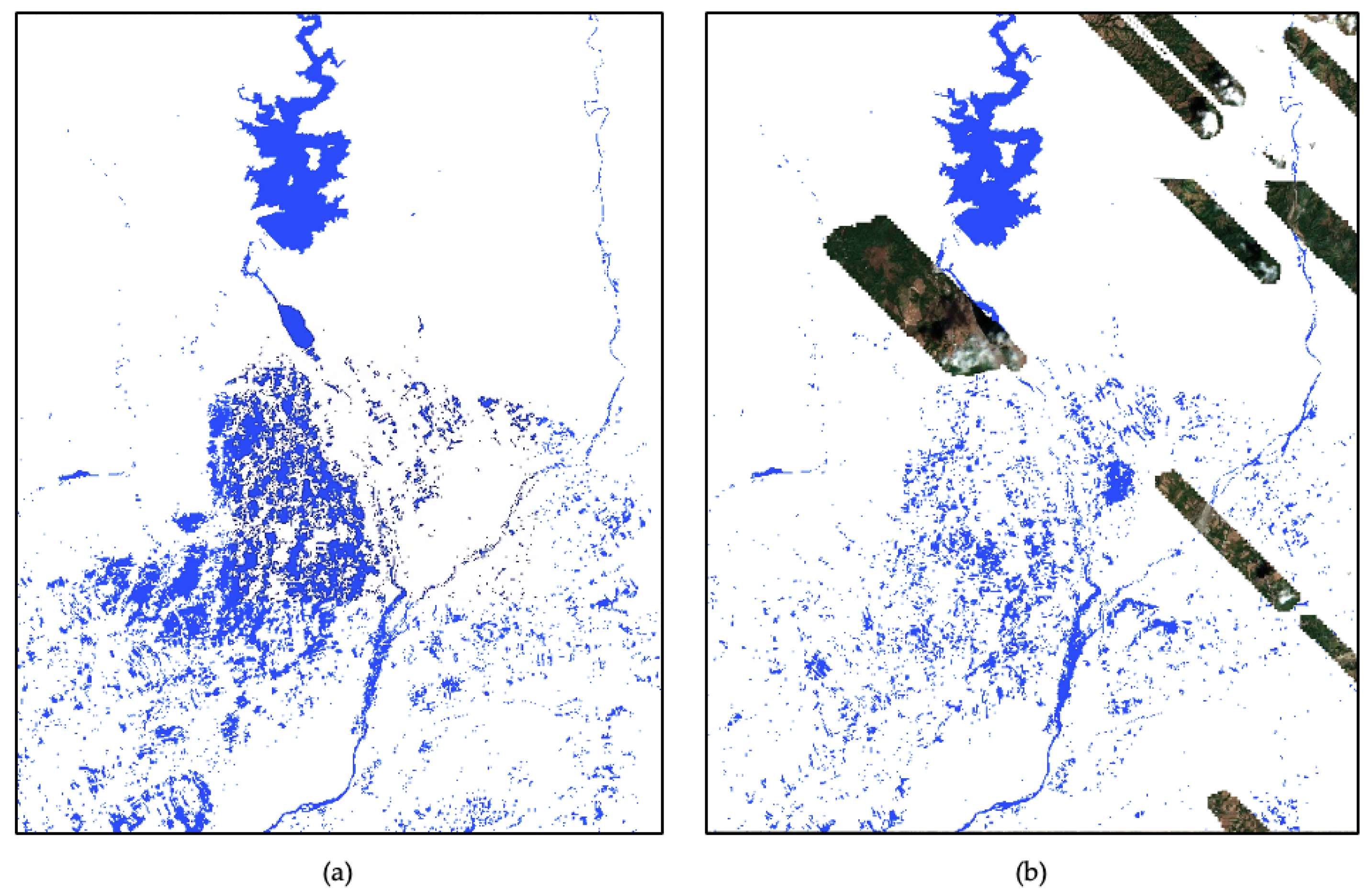
3.3. Benchmarking Against Dynamic World V1 Dataset
4. Discussion
In Developing Surface Water Maps
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Performance Metrics
- represents the instances where the water indices correctly predicted water presence (true positive).
- represents the instances where the water indices correctly predicted water absence (true negative).
- represents the instances where the water indices predicted water presence, but water was absent (false positive).
- represents the instances where the water indices predicted water absence, but water was present (false negative).
References
- Jiang, W.; Ni, Y.; Pang, Z.; Li, X.; Ju, H.; He, G.; Lv, J.; Yang, K.; Fu, J.; Qin, X. An Effective Water Body Extraction Method with New Water Index for Sentinel-2 Imagery. Water 2021, 13, 1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwang, C.; Jnr, E.M.O.; Amoah, A.S. Comparing of Landsat 8 and Sentinel 2A using Water Extraction Indexes over Volta River. J. Geogr. Geol. 2017, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nsubuga, F.W.N.; Botai, J.O.; Olwoch, J.M.; Rautenbach, C.; Kalumba, A.M.; Tsela, P.; Adeola, A.M.; Sentongo, A.A.; Mearns, K.F. Detecting changes in surface water area of Lake Kyoga sub-basin using remotely sensed imagery in a changing climate. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2017, 127, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFEETERS, S.K. The use of the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) in the delineation of open water features. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. Modification of normalised difference water index (NDWI) to enhance open water features in remotely sensed imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 3025–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kareem, H.; Attaee, M.; Omran, A. Estimation the Water Ratio Index (WRI) and Automated Water Extraction Index (AWEI) of Bath in The United Kingdom Using Remote Sensing Technology of The Multispectral Data of Landsat 8-Oli. Water Conserv. Manag. 2024, 8, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokni, K.; Ahmad, A.; Selamat, A.; Hazini, S. Water Feature Extraction and Change Detection Using Multitemporal Landsat Imagery. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 4173–4189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Li, C. Water body extraction from Landsat ETM+ imagery using adaboost algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2010 18th International Conference on Geoinformatics, Beijing, China, 18–20 June 2010; IEEE: Beijing, China, 2010; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Declaro, A.; Kanae, S. Enhancing Surface Water Monitoring through Multi-Satellite Data-Fusion of Landsat-8/9, Sentinel-2, and Sentinel-1 SAR. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, Y.; Yao, F.; Wang, P.; Guo, W.; Li, L.; Yang, L. Advances in estimation methods of vegetation water content based on optical remote sensing techniques. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2010, 53, 1159–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhou, G. Estimation of vegetation water content using hyperspectral vegetation indices: A comparison of crop water indicators in response to water stress treatments for summer maize. BMC Ecol. 2019, 19, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Qu, J.J. NMDI: A normalized multi-band drought index for monitoring soil and vegetation moisture with satellite remote sensing. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L20405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, G.M.; Parthiban, S.; Thummalu, N.; Christy, A. Ndvi: Vegetation Change Detection Using Remote Sensing and Gis—A Case Study of Vellore District. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015, 57, 1199–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huete, A.; Didan, K.; Miura, T.; Rodriguez, E.; Gao, X.; Ferreira, L. Overview of the radiometric and biophysical performance of the MODIS vegetation indices. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouman, B.A.M.; Humphreys, E.; Tuong, T.P.; Barker, R. Rice and water. Adv. Agron. 2007, 92, 187–237. [Google Scholar]
- Datta, A.; Ullah, H.; Ferdous, Z. Water management in rice. In Rice Production Worldwide; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 255–277. [Google Scholar]
- Carrijo, D.R.; Lundy, M.E.; Linquist, B.A. Rice yields and water use under alternate wetting and drying irrigation: A meta-analysis. Field Crop. Res. 2017, 203, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishfaq, M.; Farooq, M.; Zulfiqar, U.; Hussain, S.; Akbar, N.; Nawaz, A.; Anjum, S.A. Alternate wetting and drying: A water-saving and ecofriendly rice production system. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 241, 106363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siopongco, J.D.L.C.; Wassmann, R.; Sander, B.O. Alternate Wetting and Drying in Philippine Rice Production: Feasibility Study for a Clean Development Mechanism; International Rice Research Institute: Los Baños, Philippines, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Christian, J.I.; Basara, J.B.; Lowman, L.E.; Xiao, X.; Mesheske, D.; Zhou, Y. Flash drought identification from satellite-based land surface water index. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2022, 26, 100770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Wang, Z.; Liu, D.; Song, K.; Li, L.; Jia, M.; Ding, Z. Mapping Wetland Areas Using Landsat-Derived NDVI and LSWI: A Case Study of West Songnen Plain, Northeast China. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2014, 42, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, K.; Yuan, W.; Wang, L.; Deng, Y. An LSWI-Based Method for Mapping Irrigated Areas in China Using Moderate-Resolution Satellite Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 4181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.T.; Jang, K.C.; Hong, S.Y.; Kang, S.K. Detection of Irrigation Timing and the Mapping of Paddy Cover in Korea Using MODIS Images Data. Korean J. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2011, 13, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.; Kang, S.; Jang, K.; Lee, H.; Hong, S.; Ko, D. Development of Variable Threshold Models for detection of irrigated paddy rice fields and irrigation timing in heterogeneous land cover. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 115, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, Y.; Arifuzzanman, B.; Iwami, Y. Prompt Proxy Mapping of Flood Damaged Rice Fields Using MODIS-Derived Indices. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 15969–15988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkhoff, J.; Houborg, R.; Dunn, B.W. Rice ponding date detection in Australia using Sentinel-2 and Planet Fusion imagery. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 273, 107907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, P.; Liou, Y.A. Object-Based Flood Mapping and Affected Rice Field Estimation with Landsat 8 OLI and MODIS Data. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 5077–5097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tornos, L.; Huesca, M.; Dominguez, J.A.; Moyano, M.C.; Cicuendez, V.; Recuero, L.; Palacios-Orueta, A. Assessment of MODIS spectral indices for determining rice paddy agricultural practices and hydroperiod. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 101, 110–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranghetti, L.; Busetto, L.; Crema, A.; Fasola, M.; Cardarelli, E.; Boschetti, M. Testing estimation of water surface in Italian rice district from MODIS satellite data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 52, 284–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, G.; Davranche, A.; Willm, L.; Campagna, J.; Redmond, L.; Merle, C.; Guelmami, A.; Poulin, B. Introducing WIW for detecting the presence of water in wetlands with landsat and sentinel satellites. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Hunt, E.; Wardlow, B.; Basara, J.B.; Brown, J.F.; Verdin, J.P. Evaluation of MODIS NDVI and NDWI for vegetation drought monitoring using Oklahoma Mesonet soil moisture data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L22401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, J.; Shahidian, S.; da Silva, J.M. Evaluation of Normalized Difference Water Index as a Tool for Monitoring Pasture Seasonal and Inter-Annual Variability in a Mediterranean Agro-Silvo-Pastoral System. Water 2019, 11, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marusig, D.; Petruzzellis, F.; Tomasella, M.; Napolitano, R.; Altobelli, A.; Nardini, A. Correlation of Field-Measured and Remotely Sensed Plant Water Status as a Tool to Monitor the Risk of Drought-Induced Forest Decline. Forests 2020, 11, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.F.; Brumby, S.P.; Guzder-Williams, B.; Birch, T.; Hyde, S.B.; Mazzariello, J.; Czerwinski, W.; Pasquarella, V.J.; Haertel, R.; Ilyushchenko, S.; et al. Dynamic World, Near real-time global 10 m land use land cover mapping. Sci. Data 2022, 9, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jombo, S.; Adelabu, S. Evaluating Landsat-8, Landsat-9 and Sentinel-2 imageries in land use and land cover (LULC) classification in a heterogeneous urban area. GeoJournal 2023, 88, 377–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, L.; Chen, X.; Gao, Y.; Xie, S.; Mi, J. GLC_FCS30: Global land-cover product with fine classification system at 30 m using time-series Landsat imagery. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 2753–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Beslity, J.O.; Rustad, L.; Shelby, L.J.; Manos, P.T.; Khanal, P.; Reinmann, A.B.; Khanal, C. Remote Sensing and GIS in Natural Resource Management: Comparing Tools and Emphasizing the Importance of In-Situ Data. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corporal-Lodangco, I.L.; Leslie, L.M. Defining Philippine Climate Zones Using Surface and High-Resolution Satellite Data. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2017, 114, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, M.A.; Paguirigan, N.M.; Raviz, J.; Mabalay, M.R.; Alosnos, E.; Villano, L.; Asilo, S.; Arocena, A.A., Jr.; Maloom, J.; Laborte, A. The rice planting window in the Philippines: An analysis using multi-temporal SAR imagery. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2019, XLII-4/W19, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inocencio, A.; Barker, R. Current challenges in agricultural water resource development and management in the Philippines. DLSU Bus. Econ. Rev. 2018, 28, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Bouman, B. Water Management in Irrigated Rice: Coping with Water Scarcity; International Rice Research Institute (IRRI): Los Baños, Philippines, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Claverie, M.; Ju, J.; Masek, J.G.; Dungan, J.L.; Vermote, E.F.; Roger, J.C.; Skakun, S.V.; Justice, C. The Harmonized Landsat and Sentinel-2 surface reflectance data set. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 219, 145–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermosilla, T.; Wulder, M.A.; White, J.C.; Coops, N.C.; Hobart, G.W. An integrated Landsat time series protocol for change detection and generation of annual gap-free surface reflectance composites. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 158, 220–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Liang, S.; Wang, J.; Xiang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Song, J. Long-Time-Series Global Land Surface Satellite Leaf Area Index Product Derived from MODIS and AVHRR Surface Reflectance. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 5301–5318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, R.; Tormos, T.; Danis, P.A. Retrieving water surface temperature from archive LANDSAT thermal infrared data: Application of the mono-channel atmospheric correction algorithm over two freshwater reservoirs. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2014, 30, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, J.A.; Aylward, F.O.; Eppley, J.M.; Karl, D.M.; Church, M.J.; DeLong, E.F. Wind and sunlight shape microbial diversity in surface waters of the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre. ISME J. 2016, 10, 1308–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, L.; Zhang, L.; Wylie, B. Analysis of Dynamic Thresholds for the Normalized Difference Water Index. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2009, 75, 1307–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venter, Z.S.; Barton, D.N.; Chakraborty, T.; Simensen, T.; Singh, G. Global 10 m Land Use Land Cover Datasets: A Comparison of Dynamic World, World Cover and Esri Land Cover. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katayanagi, N.; Fumoto, T.; Hayano, M.; Takata, Y.; Kuwagata, T.; Shirato, Y.; Sawano, S.; Kajiura, M.; Sudo, S.; Ishigooka, Y.; et al. Development of a method for estimating total CH4 emission from rice paddies in Japan using the DNDC-Rice model. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 547, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhang, G.; Abdalla, M.; Kuhnert, M.; Bao, H.; Xu, H.; Ma, J.; Begum, K.; Smith, P. Modelling methane emissions and grain yields for a double-rice system in Southern China with DAYCENT and DNDC models. Geoderma 2023, 431, 116364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| LSWI − EVI Transformation | Formula |
|---|---|
| Simple Correction | |
| Normalized Difference 1 | |
| Vegetation Weighted | |
| Vegetation Normalized | |
| Log Transformed 1 |
| Water Indices | Formula | Detection Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
| NDWI | Optimum thresholding | |
| LSWI | as in Equation (4) | Optimum thresholding |
| NDFI | Optimum thresholding | |
| WIW | Landsat: Sentinel-2: | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Declaro, A.; Brown, Z.; Kanae, S. VAWIlog: A Log-Transformed LSWI–EVI Index for Improved Surface Water Mapping in Agricultural Environments. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2771. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17162771
Declaro A, Brown Z, Kanae S. VAWIlog: A Log-Transformed LSWI–EVI Index for Improved Surface Water Mapping in Agricultural Environments. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(16):2771. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17162771
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeclaro, Alexis, Zachary Brown, and Shinjiro Kanae. 2025. "VAWIlog: A Log-Transformed LSWI–EVI Index for Improved Surface Water Mapping in Agricultural Environments" Remote Sensing 17, no. 16: 2771. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17162771
APA StyleDeclaro, A., Brown, Z., & Kanae, S. (2025). VAWIlog: A Log-Transformed LSWI–EVI Index for Improved Surface Water Mapping in Agricultural Environments. Remote Sensing, 17(16), 2771. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17162771






