PolSAR-SFCGN: An End-to-End PolSAR Superpixel Fully Convolutional Generation Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
2.1. Superpixel Generation for PolSAR Images
2.2. Deep Learning-Based Superpixel Generation
3. Methodology
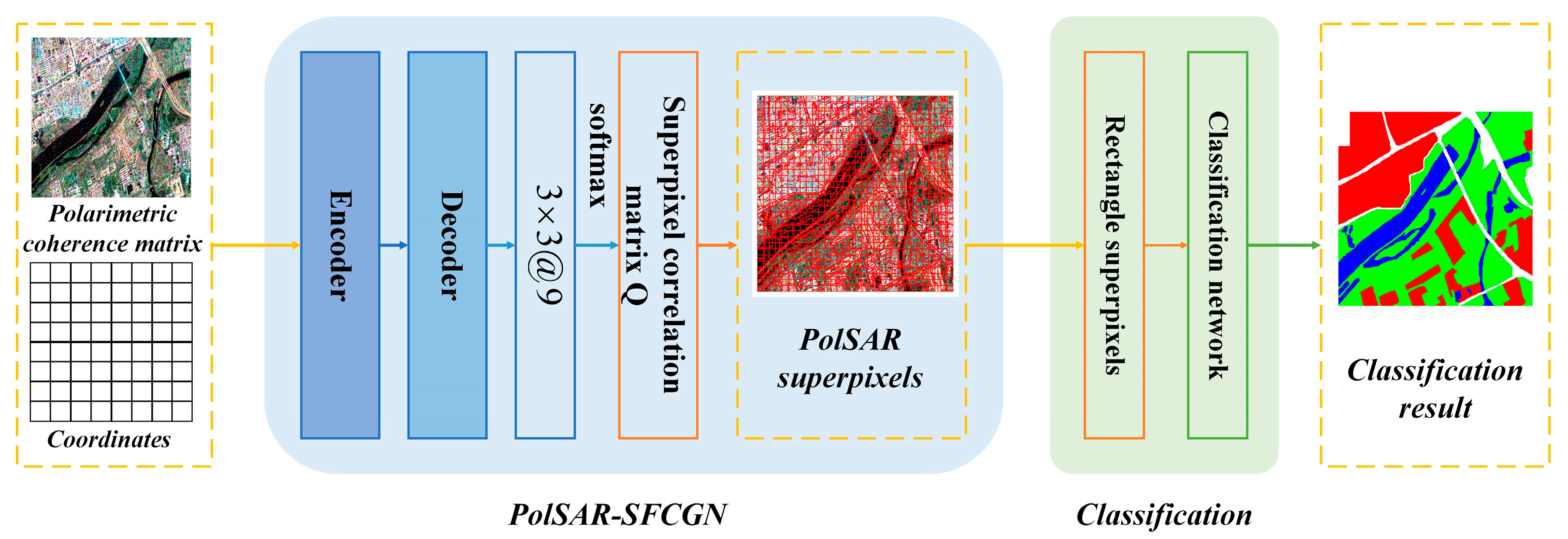
3.1. Overall Framework
3.2. Learning Superpixels on Regular Grids
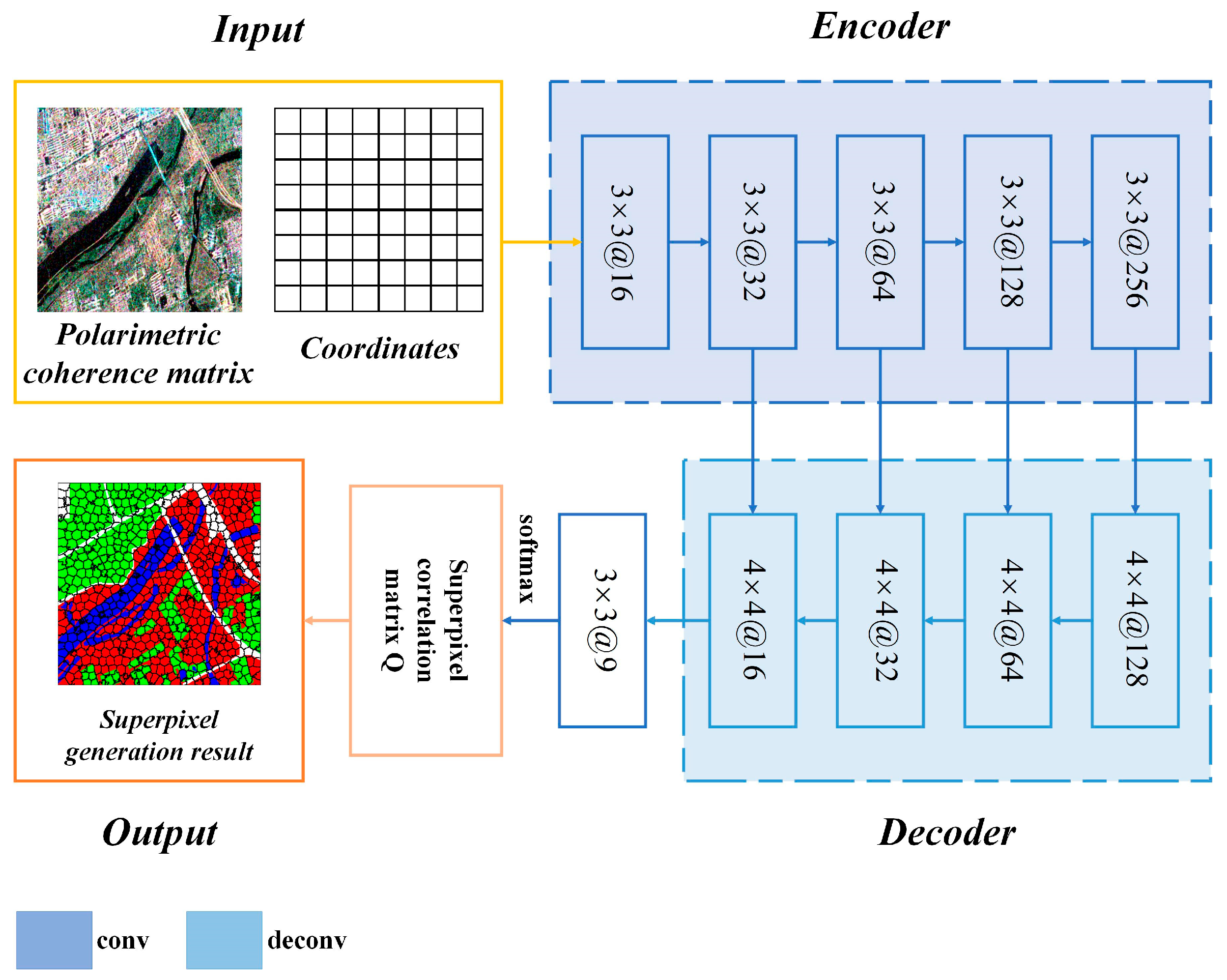
3.3. Network Structure of PolSAR-SFCGN
3.4. Loss Function of PolSAR-SFCGN
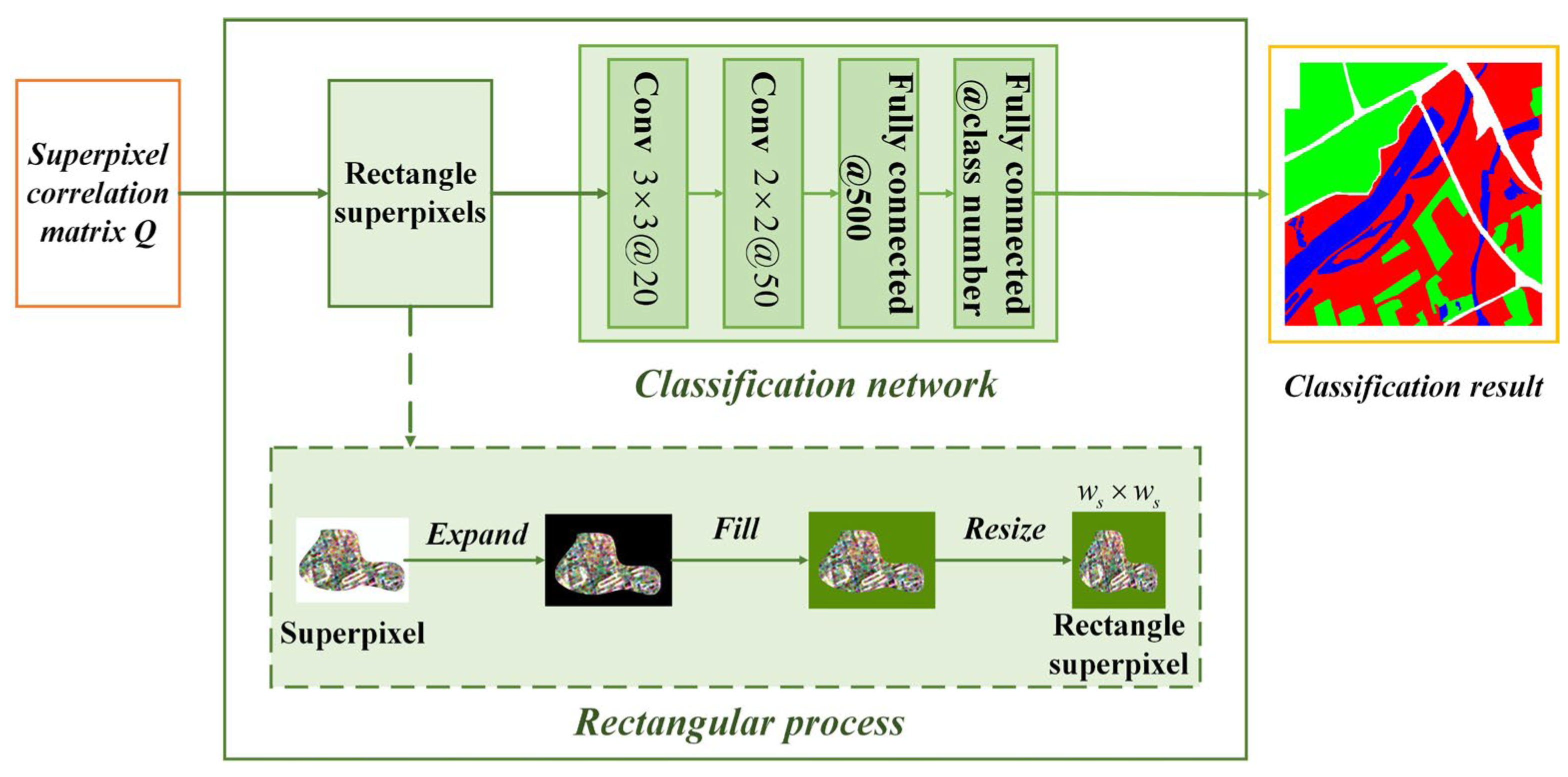
3.5. PolSAR Image Classification via PolSAR-SFCGN
4. Experimental Studies
4.1. Experimental Settings
- (1)
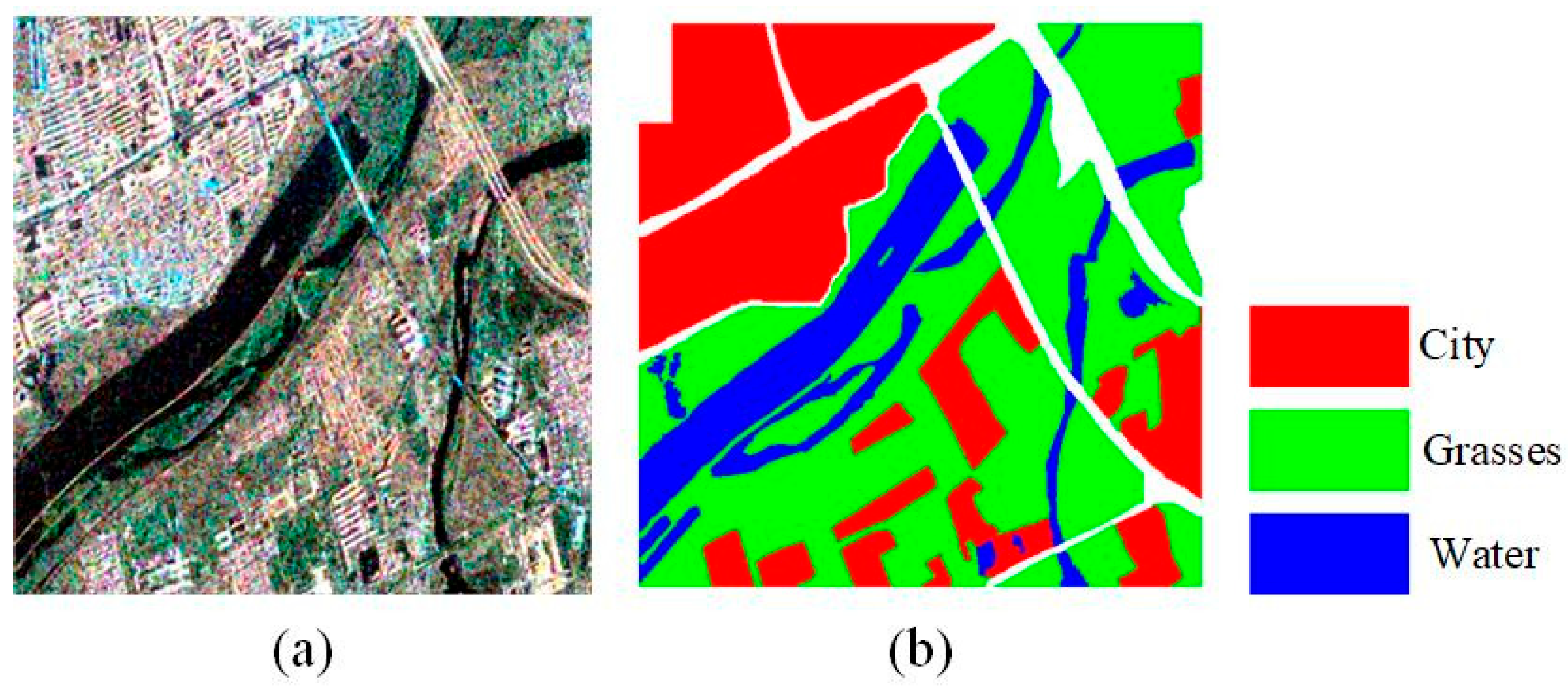
- PolSAR image datasets
- (2)
- Metrics
- (3)
- Comparison approaches and parameter settings
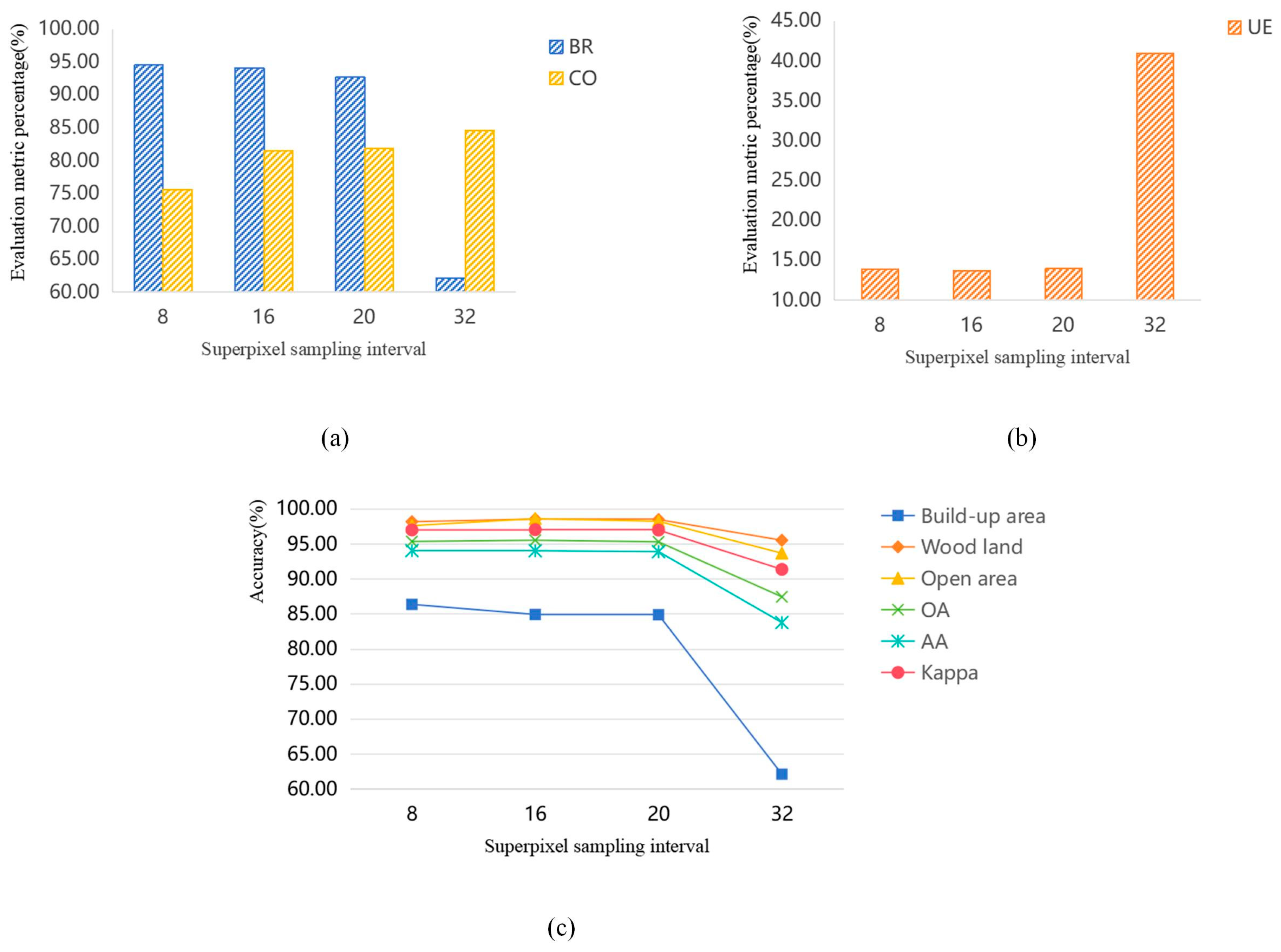
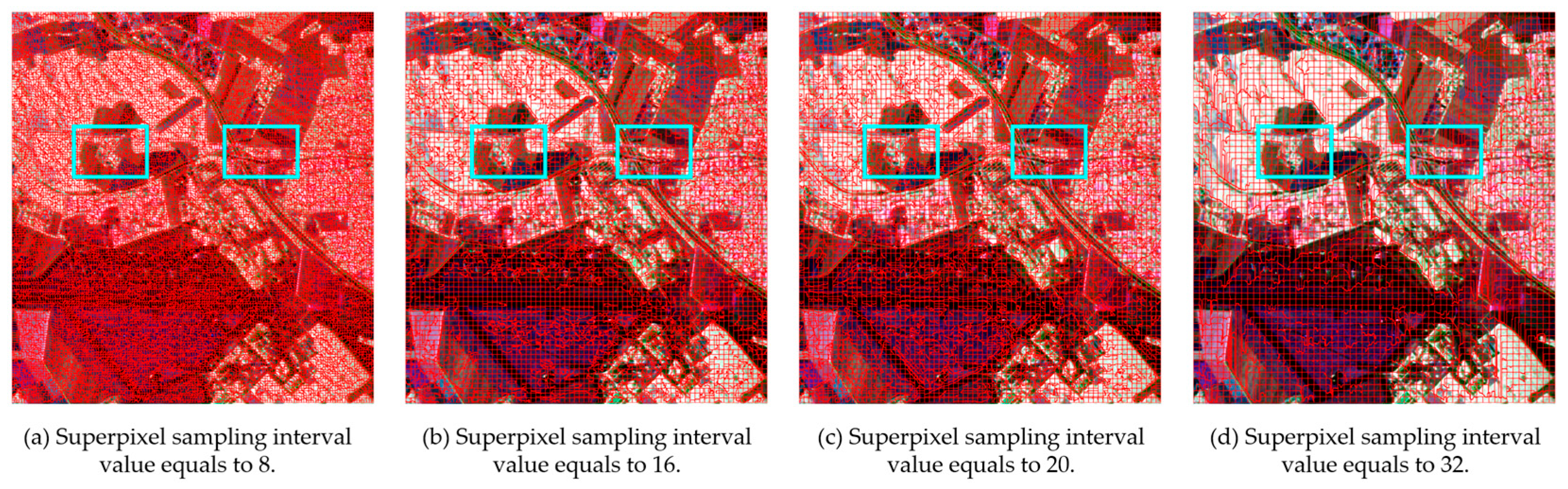
4.2. Analyses of Experiments on PolSAR Superpixel Generation
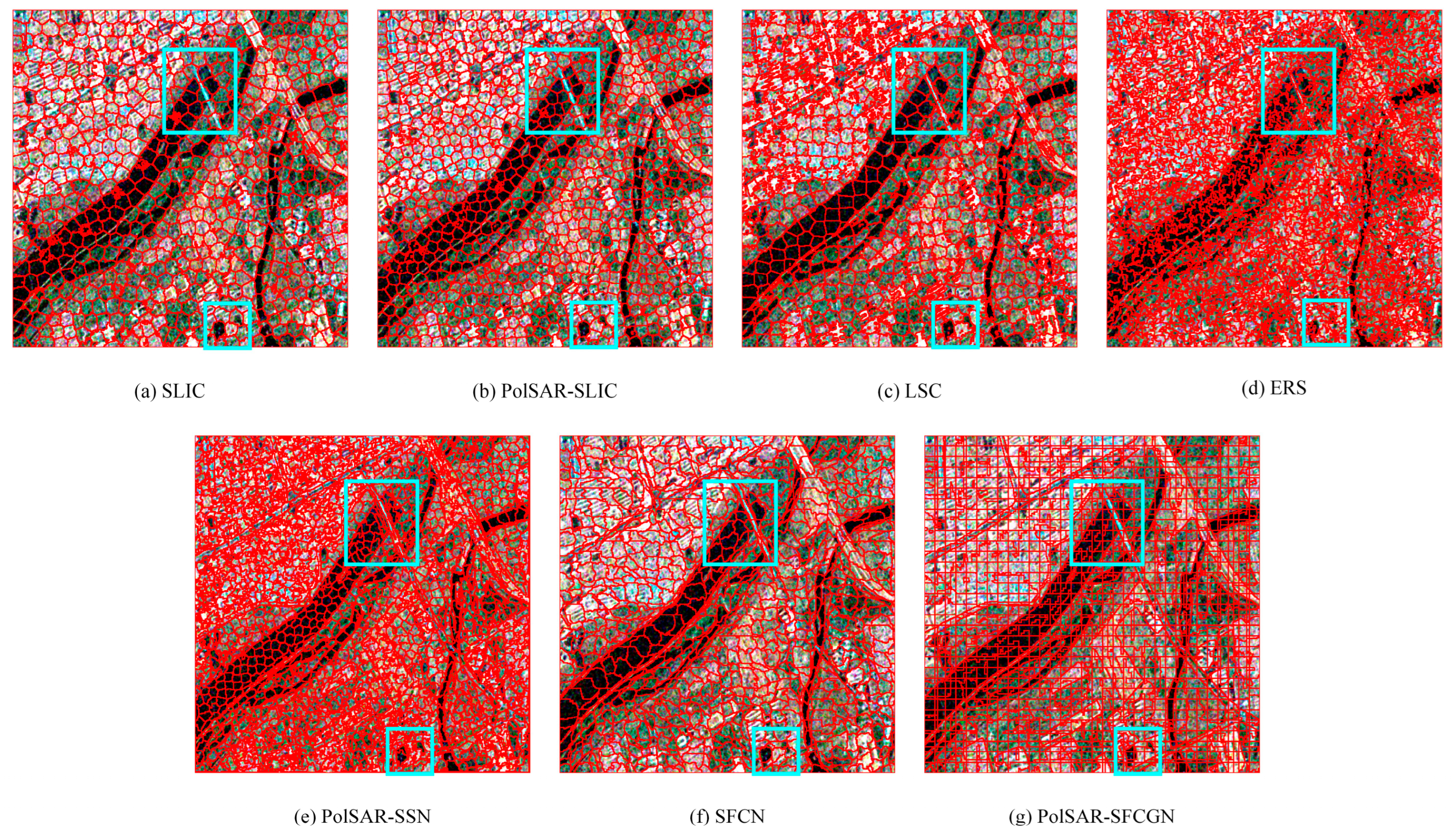
4.2.1. Superpixel Generation Results on the San Francisco Dataset
4.2.2. Superpixel Generation Results on the Oberpfaffenhofen Dataset
4.2.3. Superpixel Generation Results on the Xi’an Dataset
4.3. Analyses of Experiments on PolSAR Image Classification
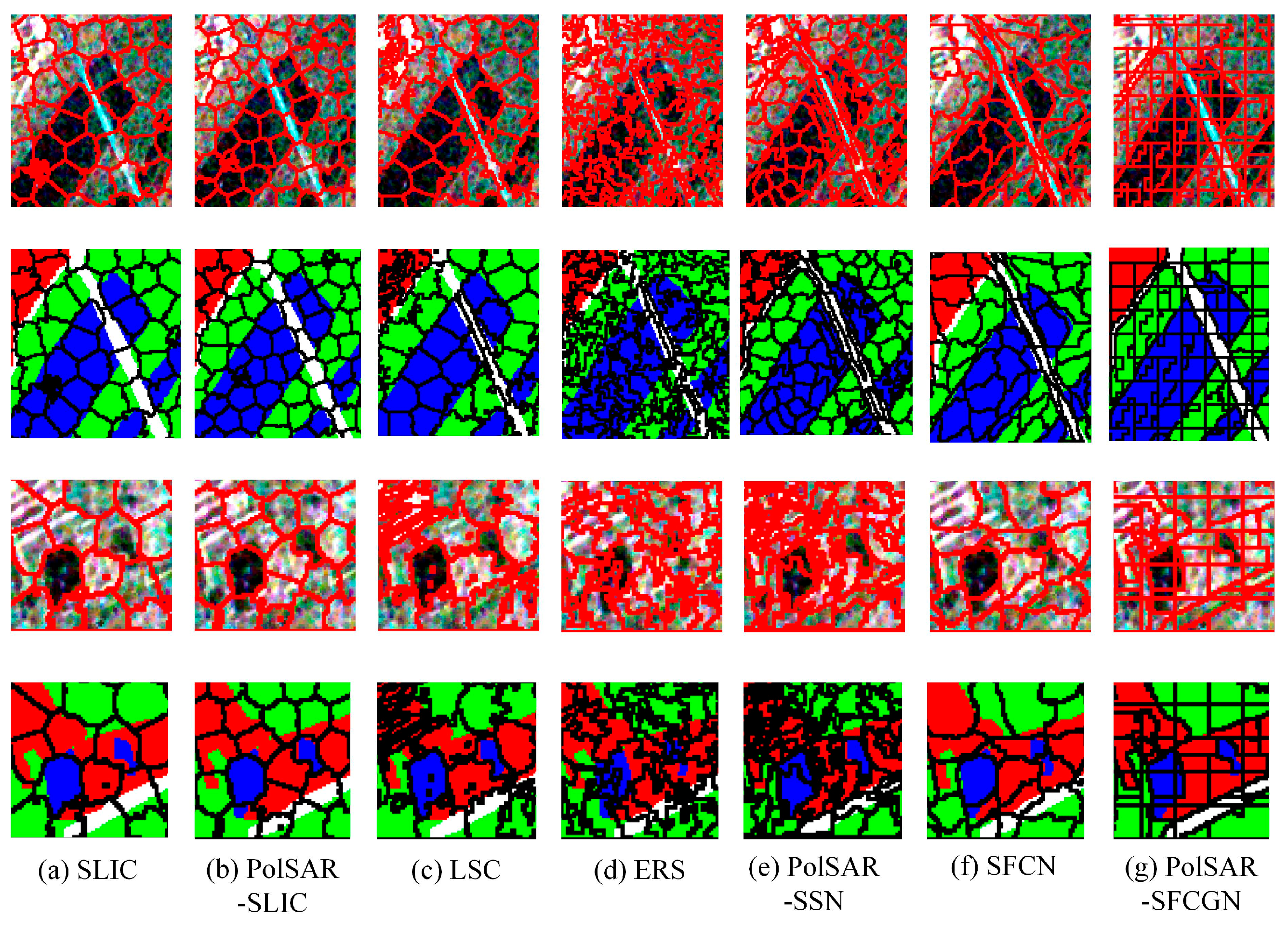
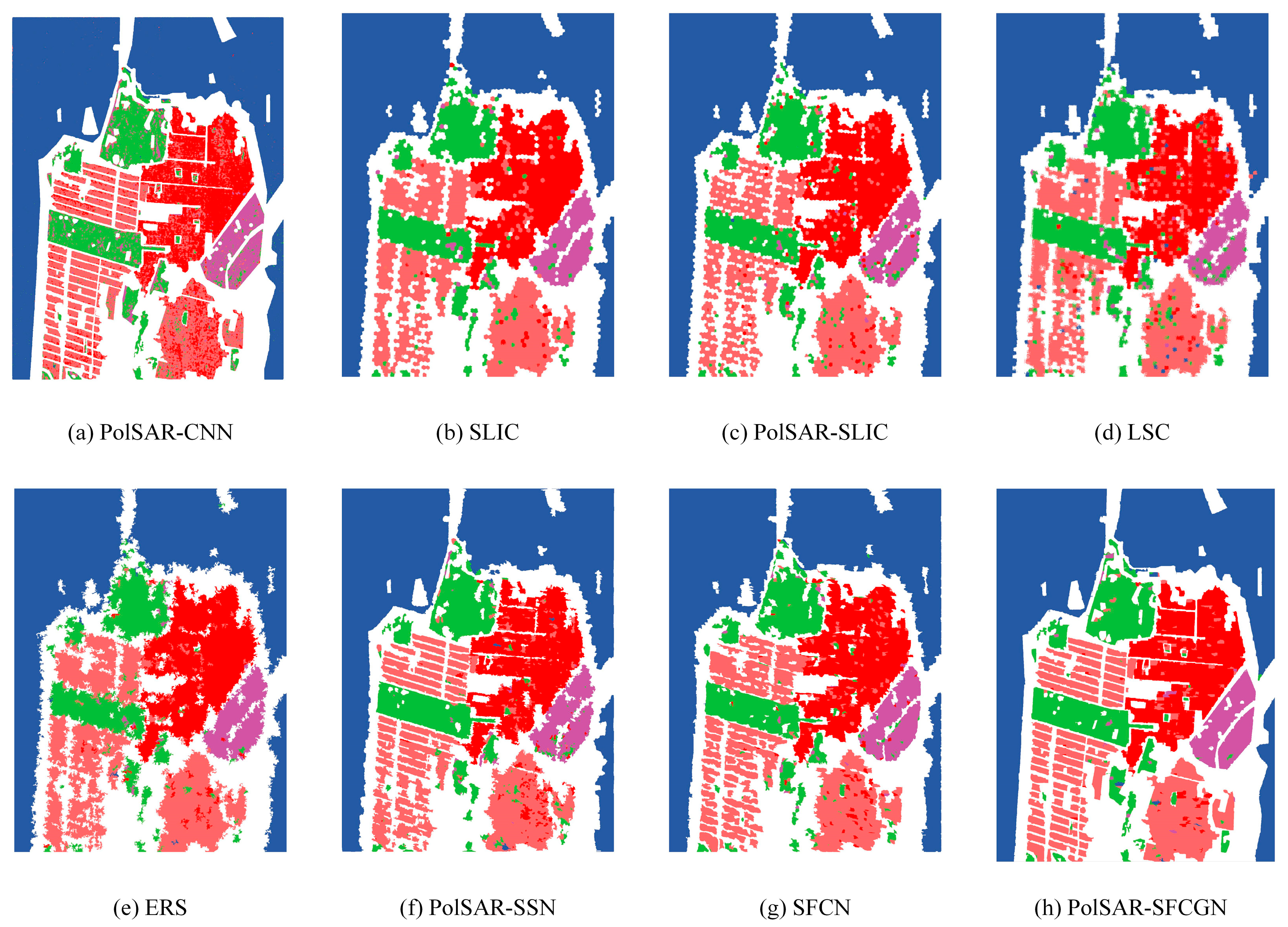
4.3.1. Classification Results on the San Francisco Dataset
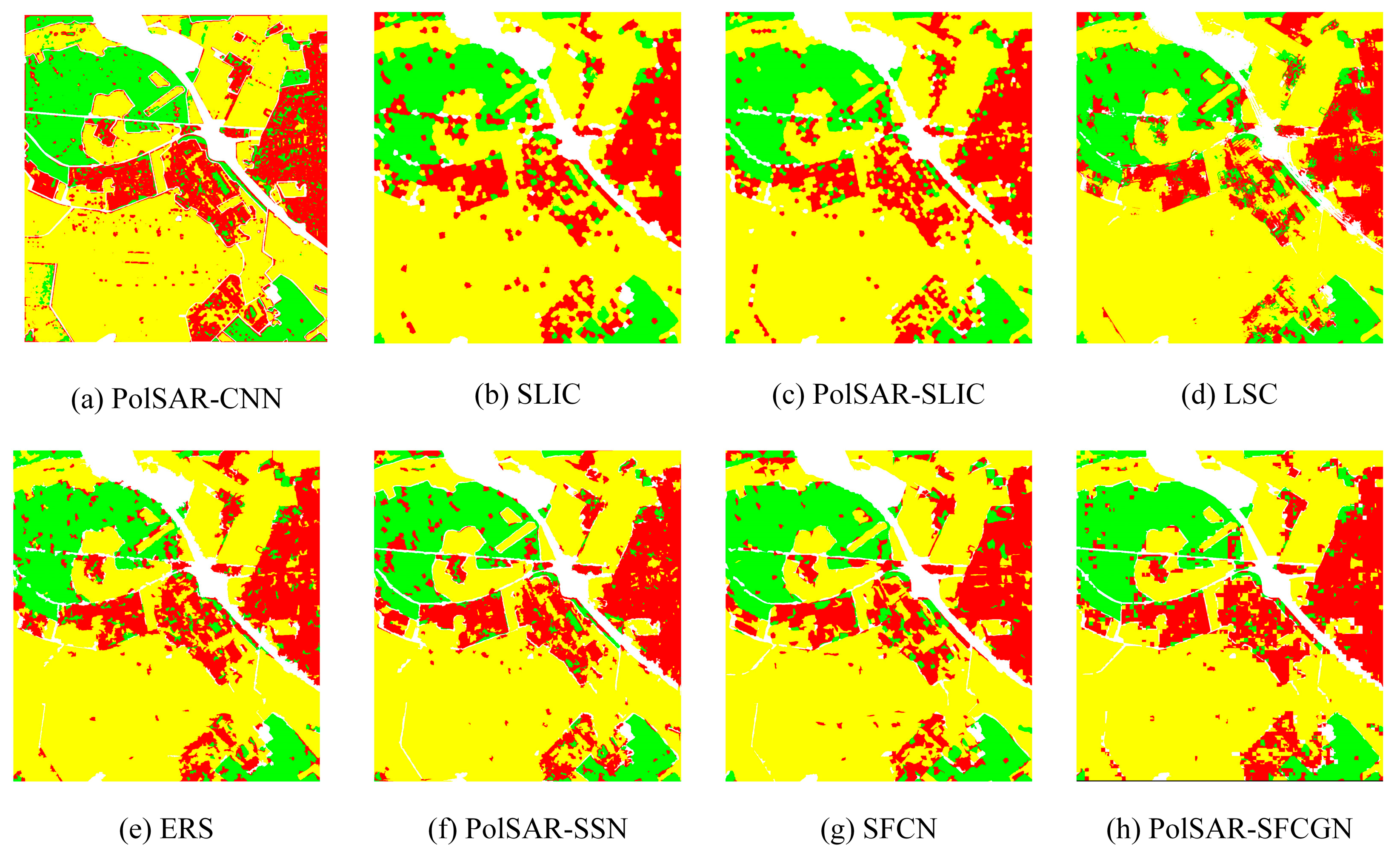
4.3.2. Classification Results on the Oberpfaffenhofen Dataset
4.3.3. Classification Results on the Xi’an Dataset
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, J.S.; Pottier, E. Polarimetric Radar Imaging: From Basics to Applications; M: CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; Zhou, F. Semi-supervised classification for PolSAR data with multi-scale evolving weighted graph convolutional network. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 2911–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paek, S.W.; Balasubramanian, S.; Kim, S.; Weck, O. Small-satellite synthetic aperture radar for continuous global biospheric monitoring: A review. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xu, X.; Dong, H.; Gui, R.; Yang, R.; Pu, F. Exploring convolutional lstm for polsar image classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Valencia, Spain, 22–27 July 2018; pp. 8452–8455. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, X.; Huang, W.; Gong, J. An unsupervised scattering mechanism classification method for PolSAR images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 1677–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hong, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Ma, L.; Zhu, Y. PolSAR-SSN: An end-to-end superpixel sampling network for PolSAR image Classification. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 4505305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Peng, D.; Chen, Z.; Guo, B. Superpixel-level CFAR detector based on truncated gamma distribution for SAR images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 18, 1421–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Jiao, L.; Qu, R.; Sun, Z.; Wang, S. Adaptive fuzzy learning superpixel representation for PolSAR image classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. 2022, 60, 5217818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, Y. A non-iterative clustering based soft segmentation approach for a class of fuzzy images. Appl. Soft Comput. 2017, 70, 988–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z. A new approach for robust segmentation of the noisy or textured images. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 2016, 9, 1409–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Malik, J. Learning a classification model for segmentation. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition CVPR, Nice, France, 13–16 October 2003; pp. 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, C.; Yu, M.; He, Y. Manifold slic: A fast method to compute content-sensitive superpixels. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition CVPR, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 651–659. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Chen, J. Superpixel segmentation using linear spectral clustering. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition CVPR, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1356–1363. [Google Scholar]
- Bergh, M.; Boix, X.; Gool, L. Seeds: Superpixels extracted via energy-driven sampling. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision ECCV, Florence, Italy, 7–13 October 2012; pp. 298–314. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.; Malik, J. Normalized cuts and image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2000, 22, 888–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.-Y.; Tuzel, O.; Ramalingam, S.; Chellappa, R. Entropy rate superpixel segmentation. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition CVPR, Colorado Springs, CO, USA, 20–25 June 2011; pp. 2097–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boix, X.; Gonfaus, J.; Van de Weijer, J. Harmony potentials: Fusing global and local scale for semantic image segmentation. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2012, 96, 83–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Du, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, X. Lazy random walks for superpixel segmentation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2014, 23, 1451–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadde, R.; Jampani, V.; Kiefel, M.; Kappler, D.; Gehler, P. Superpixel convolutional networks using bilateral inceptions. In Proceedings of the ECCV, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kwak, S.; Suha; Hong, S.; Han, B. Weakly supervised semantic segmentation using superpixel pooling network. In Proceedings of the AAAI, San Francisco, CA, USA, 4–9 February 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Jampani, V.; Sun, D.; Liu, M.Y.; Yang, M.H.; Kautz, J. Superpixel sampling networks. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision ECCV, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 352–368. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Sun, Q.; Jin, H.; Zhou, Z. Superpixel segmentation with fully convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF CVPR, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 13961–13970. [Google Scholar]
- Lang, F.; Yang, J.; Li, D.; Zhao, L.; Shi, L. Polarimetric SAR Image Segmentation Using Statistical Region Merging. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 509–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, H.; Xu, L.; Cao, X.; Xue, Y.; Xu, Z. Polarimetric SAR Image Semantic Segmentation With 3D Discrete Wavelet Transform and Markov Random Field. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 6601–6614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, S.; Xiang, D.; Wang, W.; Xiong, B.; Kuang, G. Scattering Feature-Driven Superpixel Segmentation for Polarimetric SAR Images. IEEE J. Stars 2021, 14, 2173–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Quan, S.; Xing, S.; Li, Y. PSO-based Fine Polarimetric Decomposition for Ship Scattering Characterization. ISPRS J. Photogramm. 2024, 220, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, D.; Tang, T.; Quan, S.; Guan, D.; Su, Y. Adaptive Superpixel Generation for SAR Images with Linear Feature Clustering and Edge Constraint. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 3873–3889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, G.; Dehghan, A.; Shah, M. Improving an object detector and extracting regions using superpixels. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition CVPR, Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013; pp. 3721–3727. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.; Yu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Lei, Z.; Li, S.Z. Object detection by labeling superpixels. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition CVPR, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 5107–5116. [Google Scholar]
- Gould, S.; Rodgers, J.; Cohen, D. Multi-class segmentation with relative location prior. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2008, 80, 300–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Tuzel, O.; Liu, M.Y. Recursive context propagation network for semantic scene labeling. In Proceedings of the Neural Information Processing Systems NIPS, Montreal, QC, Canada, 8–13 December 2014. [Google Scholar]
- He, S.; Lau, R.W.; Liu, W.; Huang, Z.; Yang, Q. SuperCNN: A superpixelwise convolutional neural network for salient object detection. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2015, 115, 330–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perazzi, F.; Kr, P.; Pritch, Y.; Hornung, A. Saliency filters: Contrast based filtering for salient region detection. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition CVPR, Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2012; pp. 733–740. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Zhang, L.; Lu, H.; Ruan, X.; Yang, M.H. Saliency detection via graph based manifold ranking. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition CVPR, Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, W.; Liang, S.; Wei, Y.; Sun, J. Saliency optimization from robust background detection. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition CVPR, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Song, R.; Li, Y.; Rao, P.; Wang, Y. Highly accurate optical flow estimation on superpixel tree. Image Vis. Comput. 2016, 52, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Yang, H.; Min, D.; Do, M.N. Patch match filter: Efficient edge-aware filtering meets randomized search for fast correspondence field estimation. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition CVPR, Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013; pp. 1854–1861. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, D.; Liu, C.; Pfister, H. Local layering for joint motion estimation and occlusion detection. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition CVPR, Columbus, OH, USA, 24–27 June 2014; pp. 1098–1105. [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi, K.; McAllester, D.; Urtasun, R. Robust monocular epipolar flow estimation. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition CVPR, Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013; pp. 1862–1869. [Google Scholar]
- Van den Bergh, M.; Carton, D.; Van Gool, L. Depth SEEDS: Recovering incomplete depth data using superpixels. In Proceedings of the WACV, Clearwater Beach, FL, USA, 15–17 January 2013; pp. 363–368. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Lu, H.; Yang, M.H. Robust superpixel tracking. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2014, 23, 1639–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Sun, Z.; Qu, R.; Jiao, L.; Liu, F.; Zhang, X. Fuzzy superpixels based semi-supervised similarity-constrained CNN for PolSAR image classification. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, F.; Guo, J.; Lang, F. Superpixel segmentation for polarimetric SAR imagery using local iterative clustering. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 13–17. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, J.; Ma, X.; Fan, J.; Wang, H. Semisupervised classification of polarimetric SAR image via superpixel restrained deep neural network. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 15, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Wu, Y.; Li, M.; Liang, W.; Zhang, P. PolSAR image classification using a superpixel-based composite kernel and elastic net. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadhiya, T.; Roy, A.K. Superpixel-driven optimized Wishart network for fast PolSAR image classification using global k-means algorithm. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Wang, T.; Du, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhou, L.; Yang, J. SLIC superpixel segmentation for polarimetric SAR images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 5201317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Shi, J.; Jiao, L.; Liu, H.; Yang, S.; Wu, J. Hierarchical semantic model and scattering mechanism based PolSAR image classification. Pattern Recognit. 2016, 59, 325–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, B.; Yang, C.; Ren, B.; Jiao, L. Decomposition-feature-iterative-clustering-based superpixel segmentation for PolSAR image classification. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 15, 1239–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Cao, Z.; Pi, Y. Polarimetric contextual classification of PolSAR images using sparse representation and superpixels. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 7158–7181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, B.; Kou, H.; Jiao, L. Classification of polarimetric SAR images using multilayer autoencoders and superpixels. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 3072–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, B.; Zhang, M.; Ma, K.; Liu, L.; Wan, J.; Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Zeng, H. Multiobjective Evolutionary Superpixel Segmentation for PolSAR Image Classification. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloude, S.R.; Pottier, E. A review of target decomposition theorems in radar polarimetry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1996, 34, 498–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, H.; Xu, F.; Jin, Y. Polarimetric SAR image classification using deep convolutional neural networks. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 13, 1935–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Jiao, L.; Liu, F.; Zhang, D.; Tang, X. PolSF: PolSAR image datasets on San Francisco. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information Systems ICIS, Xi’an, China, 28–31 October 2022; pp. 214–219. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Hu, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, K. Superpixel-based classification with an adaptive number of classes for polarimetric SAR images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 907–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Jiao, L.; Biao, H.; Ma, W.; Zhao, J. POLSAR Image Classification via Wishart-AE Model or Wishart-CAE Model. IEEE J. STARS 2017, 10, 3604–3615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, R.; He, J.; Wang, J.; Xu, K.; Jiao, L.; Stolkin, R. Dense connection and depthwise separable convolution based CNN for polarimetric SAR image classification. Knowl. Based Syst. 2020, 194, 105542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Zou, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, S. Automatic design of CNNs via differentiable neural architecture search for PolSAR image classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 6362–6375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Types of Methods | Features | Main Ideas | Advantages and Disadvantages | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Improved traditional approaches | [43] | Average Coherence matrix | Replace the nearest distance in SLIC with a Wishart hypothesis test distance. | Introduce polarimetric information into superpixel segmentation but do have not good enough performances. |
| [45] | Coherency matrix | Introduce a coherency matrix into SLIC. | ||
| [46] | Pauli decomposition | Use a Wishart distance and design a global K-means superpixel segmentation. | ||
| [47] | Coherency matrix | Introduce four classical dissimilarity statistical distances of PolSAR images. | ||
| Fuzzy superpixels-based approaches | [8] | Pauli decomposition and H/A/Alpha decomposition | Consider the correlation among pixels’ polarimetric scattering information through fuzzy rough set theory to generate superpixels. Update the ratio of undetermined pixels dynamically and adaptively. | Generate the improved fuzzy superpixels to yield pure superpixels but need to manually design the features and still use the traditional generation strategies. |
| [42] | Average Coherence matrix | Propose fuzzy superpixels to forcefully reduce the generated mixed superpixels. | ||
| Mult objective evolution based approach | [52] | Coherency matrix | Optimize the similarity information within the superpixels and the differences among the superpixels simultaneously. Improve the qualities of superpixels by fully using the boundary information of good-quality superpixels. | Determine the suitable number of superpixels automatically and generate high-quality superpixels but the evolution process is time-consuming. |
| Deep Learning-based approach | [6] | Coherency matrix | Deep neural networks are used to extract deep features, and the superpixels are generated by using soft K-means clustering. | Still use the clustering technique to generate superpixels. |
| Metric (%) | SLIC | PolSAR- SLIC | LSC | ERS | PolSAR- SSN | SFCN | PolSAR- SFCGN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BR↑ | 67.73 | 62.23 | 85.36 | 85.80 | 80.78 | 71.51 | 97.83 |
| UE↓ | 33.99 | 26.83 | 34.94 | 39.25 | 25.30 | 28.06 | 7.50 |
| CO↑ | 57.97 | 66.13 | 16.89 | 17.47 | 54.81 | 57.51 | 53.01 |
| Bare soil | 91.24 | 87.63 | 81.74 | 81.03 | 96.93 | 86.65 | 98.50 |
| Ocean | 98.29 | 94.84 | 91.81 | 91.90 | 98.11 | 95.68 | 99.81 |
| Urban | 94.76 | 98.59 | 98.37 | 97.90 | 95.86 | 98.54 | 99.01 |
| Buildings | 88.54 | 94.44 | 93.97 | 93.41 | 97.19 | 95.44 | 98.04 |
| Vegetation | 88.36 | 88.30 | 89.02 | 88.52 | 96.97 | 90.71 | 98.57 |
| OA↑ | 94.37 | 92.90 | 90.84 | 90.30 | 96.19 | 93.06 | 99.13 |
| AA↑ | 92.24 | 92.76 | 90.98 | 90.55 | 97.57 | 93.40 | 98.79 |
| Kappa↑ | 89.30 | 91.58 | 89.06 | 87.96 | 96.97 | 90.93 | 98.63 |
| Metric (%) | SLIC | PolSAR- SLIC | LSC | ERS | PolSAR- SSN | SFCN | PolSAR- SFCGN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BR↑ | 65.07 | 71.05 | 88.41 | 89.54 | 93.85 | 80.69 | 94.10 |
| UE↓ | 31.20 | 26.01 | 29.21 | 24.63 | 16.74 | 23.74 | 13.69 |
| CO↑ | 71.26 | 78.65 | 67.52 | 41.59 | 61.41 | 57.04 | 81.49 |
| Build-up area | 61.67 | 64.48 | 65.16 | 69.65 | 83.23 | 71.94 | 84.90 |
| Woodland | 97.16 | 97.51 | 96.96 | 97.34 | 97.44 | 96.58 | 98.52 |
| Open area | 97.19 | 97.45 | 97.79 | 97.21 | 97.72 | 97.07 | 98.58 |
| OA↑ | 89.24 | 90.11 | 90.14 | 91.11 | 94.36 | 91.24 | 95.50 |
| AA↑ | 85.34 | 86.48 | 86.64 | 88.06 | 92.80 | 88.53 | 94.00 |
| Kappa↑ | 91.88 | 92.65 | 92.69 | 93.90 | 96.89 | 94.14 | 97.01 |
| Metric (%) | SLIC | PolSAR- SLIC | LSC | ERS | PolSAR- SSN | SFCN | PolSAR- SFCGN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BR↑ | 74.94 | 73.20 | 83.92 | 90.11 | 99.57 | 83.75 | 99.68 |
| UE↓ | 58.53 | 45.24 | 54.32 | 61.12 | 15.58 | 42.39 | 8.61 |
| CO↑ | 61.67 | 73.12 | 39.04 | 23.95 | 56.90 | 58.07 | 83.37 |
| Grass | 88.79 | 69.88 | 59.31 | 57.43 | 96.93 | 74.45 | 98.41 |
| City | 92.96 | 90.99 | 89.73 | 89.36 | 98.11 | 91.73 | 99.03 |
| Water | 85.38 | 92.40 | 93.07 | 89.08 | 95.86 | 93.72 | 97.23 |
| OA↑ | 89.75 | 89.21 | 87.65 | 85.77 | 97.19 | 90.58 | 98.45 |
| AA↑ | 89.04 | 84.42 | 80.70 | 78.62 | 96.97 | 86.64 | 98.22 |
| Kappa↑ | 83.11 | 85.90 | 84.26 | 85.69 | 96.19 | 87.57 | 97.78 |
| Metric (%) | PolSAR-CNN | SLIC | PolSAR- SLIC | LSC | ERS | PolSAR- SSN | SFCN | PolSAR- SFCGN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bare soil | 87.02 | 89.74 | 85.06 | 83.53 | 89.77 | 85.60 | 91.12 | 97.67 |
| Ocean | 99.81 | 98.35 | 98.58 | 98.28 | 97.91 | 98.63 | 98.53 | 99.76 |
| Urban | 78.22 | 88.35 | 88.95 | 81.70 | 89.78 | 90.18 | 88.97 | 92.15 |
| Buildings | 79.30 | 85.40 | 84.10 | 81.58 | 84.87 | 86.07 | 86.79 | 94.73 |
| Vegetation | 83.78 | 83.10 | 84.20 | 82.64 | 78.84 | 87.79 | 86.85 | 93.64 |
| OA↑ | 90.11 | 92.12 | 92.01 | 90.02 | 89.49 | 93.06 | 93.04 | 96.77 |
| AA↑ | 85.63 | 88.99 | 88.18 | 85.55 | 88.23 | 89.65 | 90.45 | 95.59 |
| Kappa↑ | 92.27 | 86.18 | 87.64 | 83.74 | 84.61 | 89.41 | 88.27 | 96.27 |
| Metric (%) | PolSAR-CNN | SLIC | PolSAR- SLIC | LSC | ERS | PolSAR-SSN | SFCN | PolSAR-SFCGN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Build-up area | 79.46 | 72.08 | 72.16 | 64.81 | 75.83 | 77.73 | 73.87 | 82.81 |
| Woodland | 92.00 | 84.72 | 89.81 | 87.87 | 86.11 | 83.18 | 89.29 | 89.80 |
| Open area | 93.08 | 96.02 | 95.52 | 96.96 | 96.22 | 96.25 | 96.14 | 96.17 |
| OA↑ | 89.51 | 87.94 | 88.66 | 87.28 | 89.24 | 89.17 | 89.33 | 91.64 |
| AA↑ | 88.18 | 84.27 | 85.83 | 83.21 | 86.05 | 85.72 | 86.44 | 89.59 |
| Kappa↑ | 73.39 | 76.75 | 78.28 | 75.20 | 80.05 | 82.38 | 81.04 | 86.12 |
| Metric (%) | PoSAR-CNN | SLIC | PolSAR- SLIC | LSC | ERS | PolSAR- SSN | SFCN | PolSAR- SFCGN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grass | 83.74 | 69.39 | 80.83 | 25.37 | 81.23 | 90.29 | 81.88 | 90.77 |
| City | 91.90 | 80.79 | 78.60 | 70.35 | 79.78 | 91.71 | 79.48 | 94.14 |
| Water | 92.70 | 91.70 | 88.72 | 98.93 | 77.53 | 85.79 | 90.51 | 89.79 |
| OA↑ | 87.97 | 76.77 | 81.23 | 52.33 | 80.16 | 90.12 | 82.33 | 91.81 |
| AA↑ | 89.45 | 80.63 | 82.72 | 64.88 | 79.51 | 89.26 | 83.96 | 91.56 |
| Kappa↑ | 83.79 | 64.46 | 70.53 | 38.45 | 66.87 | 85.96 | 72.63 | 88.42 |
| Datasets | Time Cost | PolSAR-SSN | PolSAR-SFCGN |
|---|---|---|---|
| San Francisco | Train time (h) | 19.013 | 4.303 |
| Test time (s) | 8.838 | 0.830 | |
| Oberpfaffenhofen | Train time (h) | 18.209 | 2.361 |
| Test time (s) | 7.942 | 0.929 | |
| Xi’an | Train time (h) | 17.873 | 1.984 |
| Test time (s) | 4.790 | 0.558 |
| Datasets | Time Cost | PolSAR-CNN | PolSAR-SFCGN |
|---|---|---|---|
| San Francisco | Train time (s) | 44.14 | 28.57 |
| Test time (s) | 130.33 | 0.51 | |
| Oberpfaffenhofen | Train time (s) | 29.53 | 22.37 |
| Test time (s) | 84.27 | 0.29 | |
| Xi’an | Train time (s) | 14.52 | 12.36 |
| Test time (s) | 18.29 | 0.05 |
| Metrics | PolSAR-SSN | PolSAR-SFCGN | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| BR↑ | 93.16 ± 0.29 | 93.25 ± 0.41 | 0.8082 |
| UE↓ | 15.69 ± 0.53 | 13.96 ± 0.52 | 0.0054 * |
| CO↑ | 67.82 ± 14.72 | 84.42 ± 15.84 | 0.0002 * |
| Build-up area | 84.15 ± 0.46 | 84.77 ± 0.70 | 0.236 |
| Woodland | 97.36 ± 0.01 | 98.05 ± 0.08 | 0.0008 * |
| Open area | 97.43 ± 0.03 | 97.76 ± 0.23 | 0.1879 |
| OA↑ | 94.79 ± 0.06 | 94.99 ± 0.11 | 0.314 |
| AA↑ | 92.71 ± 0.02 | 93.53 ± 0.13 | 0.0015 * |
| Kappa↑ | 96.03 ± 0.24 | 96.54 ± 0.18 | 0.1166 |
| San Francisco | Bare Soil | Ocean | Urban | Buildings | Vegetation | OA↑ | AA↑ | Kappa↑ | Parameter Number↓ (M) |
| PolSAR-SFCGN | 97.67 | 99.76 | 92.15 | 94.73 | 93.64 | 96.77 | 95.59 | 96.27 | 0.13 |
| DSNet | 97.43 | 99.95 | 92.43 | 96.58 | 93.70 | 97.26 | 96.02 | 96.78 | 0.24 |
| PDAS | 97.22 | 99.76 | 89.82 | 94.83 | 91.04 | 96.10 | 94.54 | 95.64 | 1.01 |
| Oberpfa- ffenhofen | Build-up Area | Woodland | Open Area | - | - | OA↑ | AA↑ | Kappa↑ | Parameter number↓ (M) |
| PolSAR-SFCGN | 82.81 | 89.80 | 96.17 | - | - | 91.64 | 89.59 | 86.12 | 0.13 |
| DSNet | 79.72 | 85.25 | 95.91 | - | - | 89.86 | 86.96 | 83.70 | 0.24 |
| PDAS | 83.78 | 93.54 | 96.03 | - | - | 92.52 | 91.12 | 87.33 | 1.14 |
| Xi’an | Grass | City | Water | - | - | OA↑ | AA↑ | Kappa↑ | Parameter number↓ (M) |
| PolSAR-SFCGN | 90.77 | 94.14 | 89.79 | - | - | 91.81 | 91.56 | 88.42 | 0.13 |
| DSNet | 91.73 | 92.44 | 92.65 | - | - | 92.12 | 92.28 | 88.84 | 0.24 |
| PDAS | 89.37 | 94.86 | 91.29 | - | - | 91.57 | 91.82 | 88.13 | 1.95 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, M.; Shi, J.; Liu, L.; Zhang, W.; Feng, J.; Zhu, J.; Chu, B. PolSAR-SFCGN: An End-to-End PolSAR Superpixel Fully Convolutional Generation Network. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2723. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17152723
Zhang M, Shi J, Liu L, Zhang W, Feng J, Zhu J, Chu B. PolSAR-SFCGN: An End-to-End PolSAR Superpixel Fully Convolutional Generation Network. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(15):2723. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17152723
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Mengxuan, Jingyuan Shi, Long Liu, Wenbo Zhang, Jie Feng, Jin Zhu, and Boce Chu. 2025. "PolSAR-SFCGN: An End-to-End PolSAR Superpixel Fully Convolutional Generation Network" Remote Sensing 17, no. 15: 2723. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17152723
APA StyleZhang, M., Shi, J., Liu, L., Zhang, W., Feng, J., Zhu, J., & Chu, B. (2025). PolSAR-SFCGN: An End-to-End PolSAR Superpixel Fully Convolutional Generation Network. Remote Sensing, 17(15), 2723. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17152723







