Submarine Topography Classification Using ConDenseNet with Label Smoothing Regularization
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Marine Observations and Technology
1.2. Submarine Landform Classification Development
2. Materials and Methods
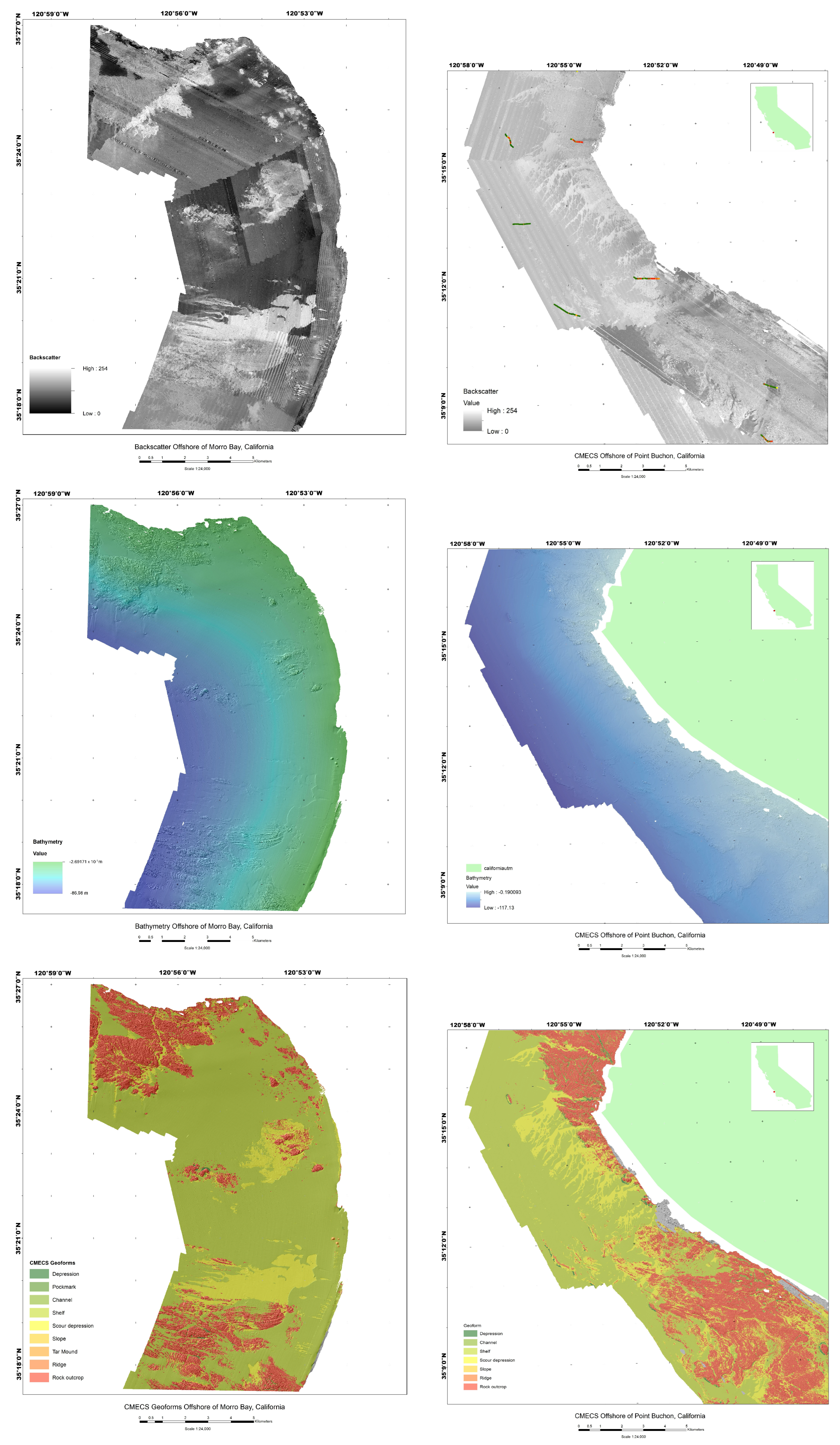
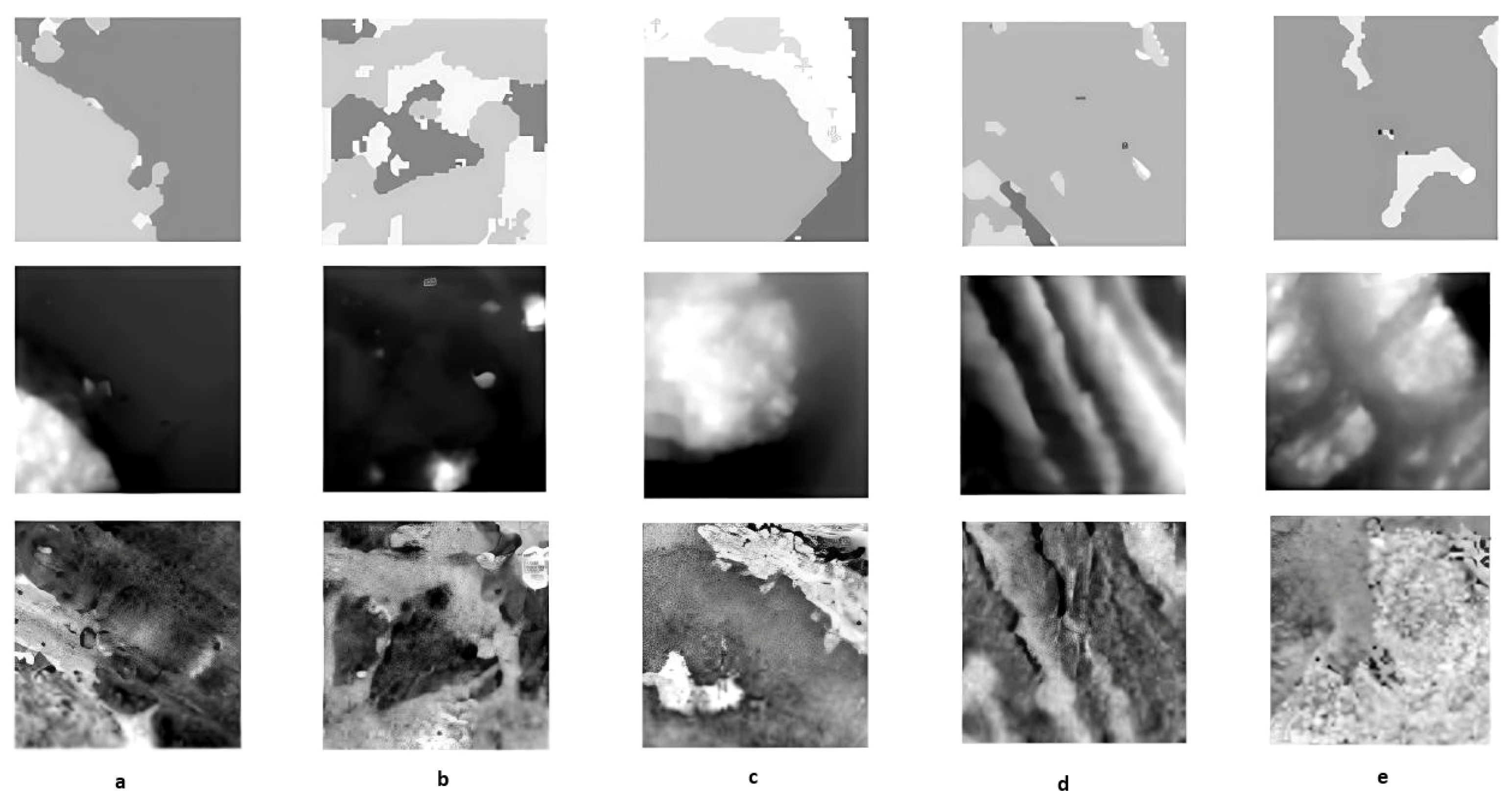
2.1. Dataset
2.2. Models and Methods
2.2.1. AlexNet, VGG and ResNet
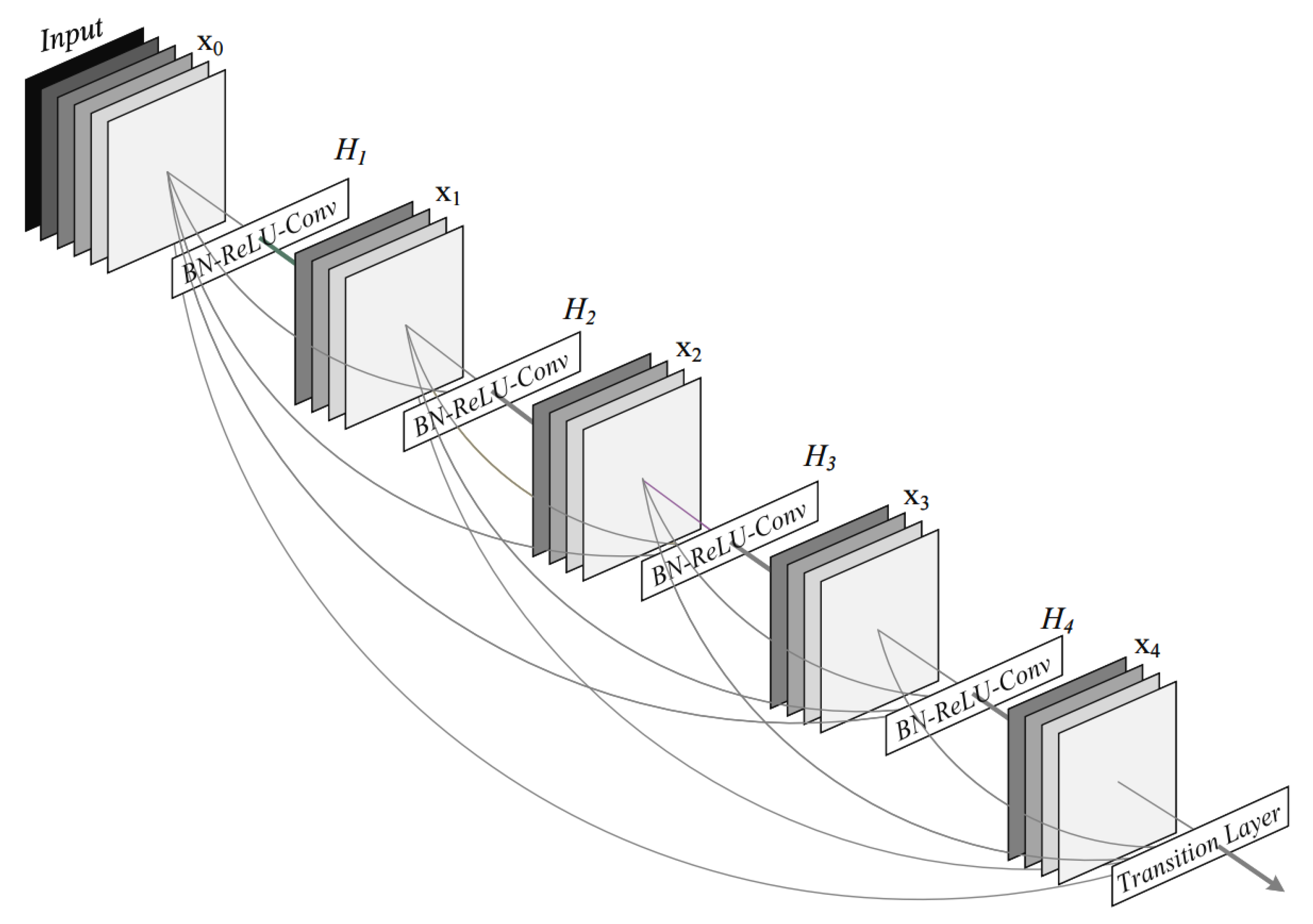
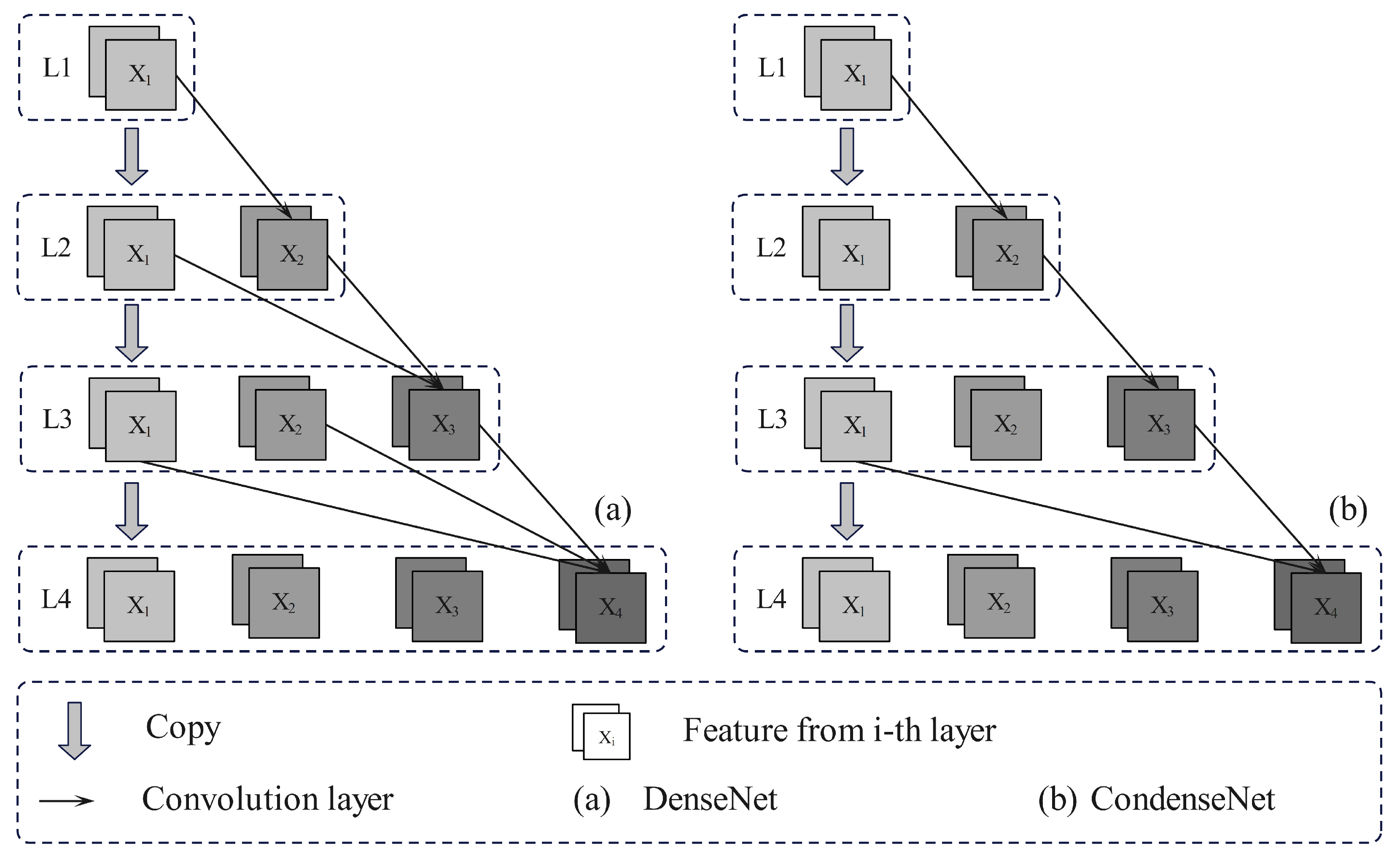
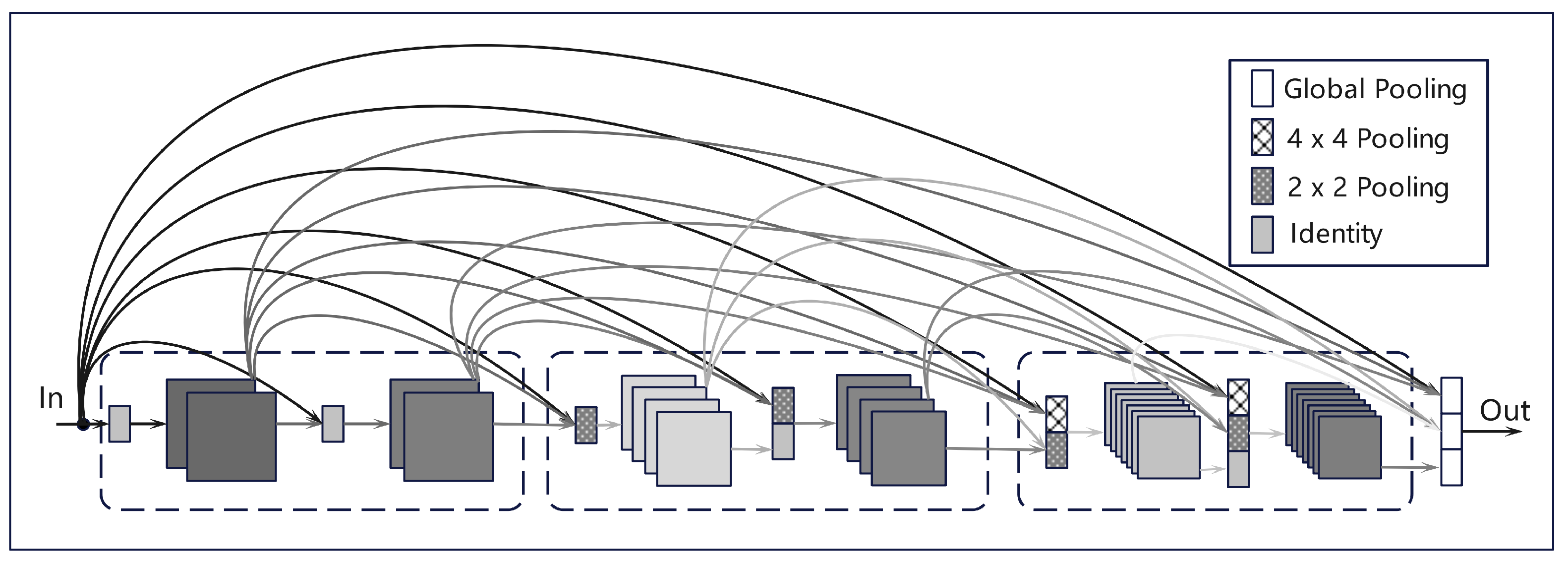
2.2.2. DenseNet and ConDenseNet
2.2.3. Cross-Entropy Loss Function and Label Smoothing Regularization
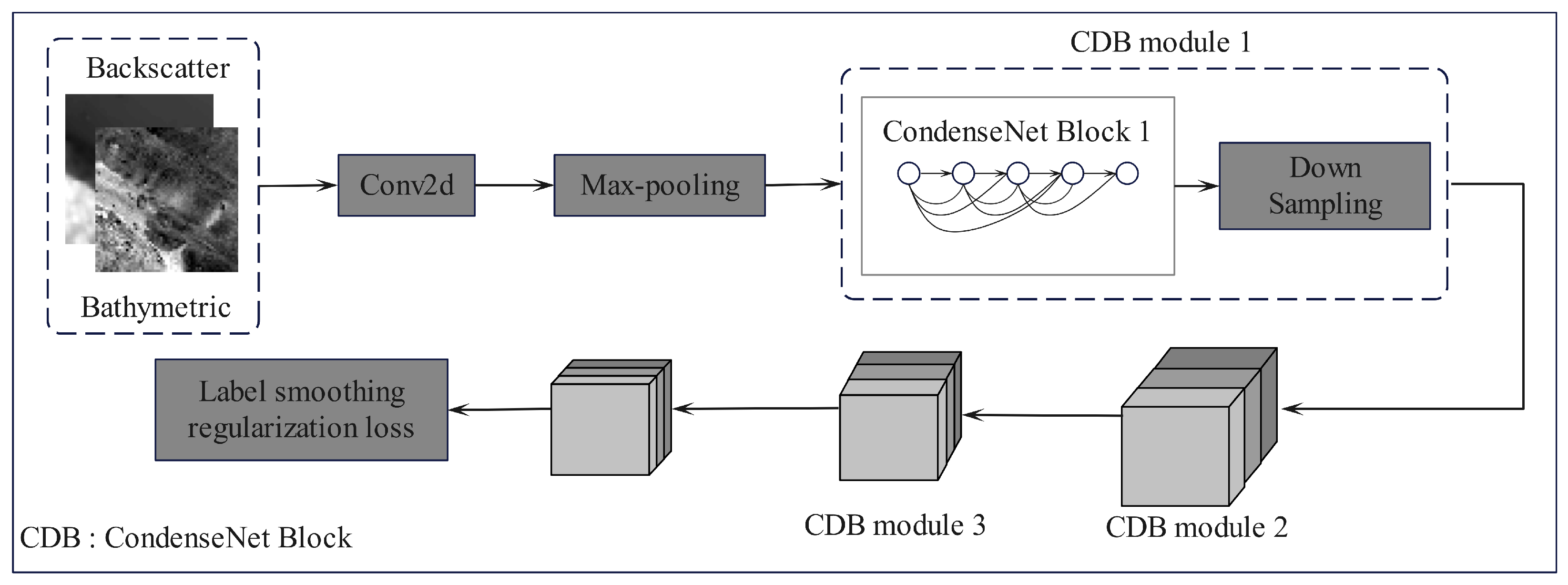
2.2.4. Our Methods: Fine-Tuning Pruned ConDenseNet with Label Smoothing Regulation
3. Results
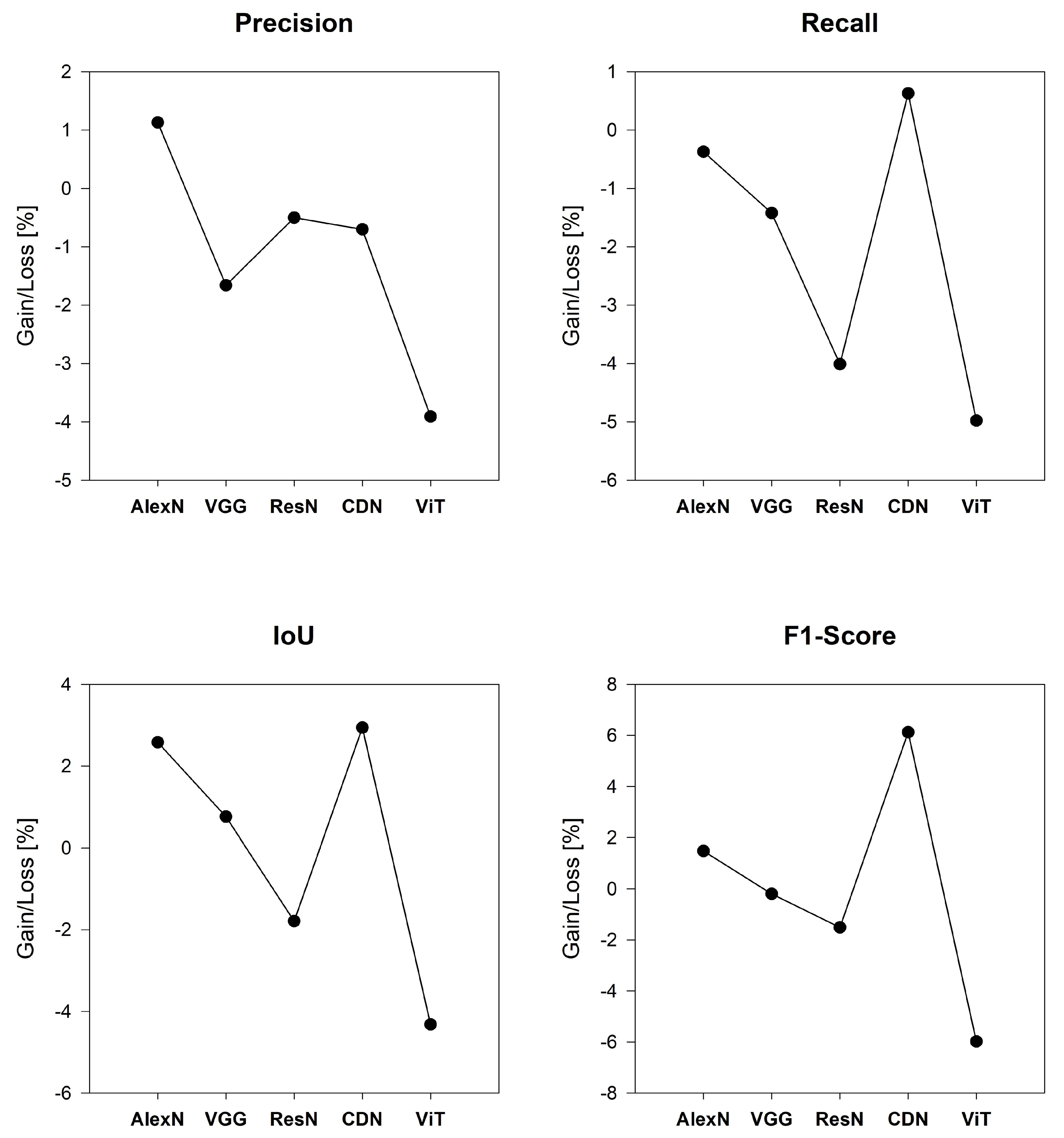
3.1. Comparison Results Across Models
3.2. Ablation Experiments
3.3. Different Models Adopt LSR
4. Discussion
4.1. The Benefit of Adopting Pruned ConDenseNet+LSR (Our Method)
4.2. LSR Impact
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mittal, S.; Srivastava, S.; Jayanth, J.P. A Survey of Deep Learning Techniques for Underwater Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2023, 34, 6968–6982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micallef, A.; Krastel, S.; Savini, A. Submarine Geomorphology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sowers, D.C.; Masetti, G.; Mayer, L.A.; Johnson, P.; Gardner, J.V. Standardized geomorphic classification of seafloor within the United States Atlantic canyons and continental margin. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witze, A. Diving deep: The centuries-long quest to explore the deepest ocean. Nature 2023, 616, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vesnaver, A.; Baradello, L. Sea Floor Characterization by Multiples’ Amplitudes in Monochannel Surveys. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikiforov, S.; Ananiev, R.; Jakobsson, M.; Moroz, E.; Sokolov, S.; Sorokhtin, N.; Dmitrevsky, N.; Sukhikh, E.; Chickiryov, I.; Zarayskaya, Y.; et al. The Extent of Glaciation in the Pechora Sea, Eurasian Arctic, Based on Submarine Glacial Landforms. Geosciences 2023, 13, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, K.; Mohrig, D. Signatures of Pleistocene Marine Transgression Preserved in Lithified Coastal Dune Morphology of The Bahamas. Geosciences 2023, 13, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xing, Q.; Tian, L.; Hou, Y.; Zheng, X.; Arif, M.; Li, L.; Jiang, S.; Cai, J.; Chen, J.; et al. An Improved UAV RGB Image Processing Method for Quantitative Remote Sensing of Marine Green Macroalgae. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 19864–19883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Principi, S.; Palma, F.; Bran, D.M.; Bozzano, G.; Isola, J.; Ormazabal, J.; Esteban, F.; Acosta, L.Y.; Tassone, A. Seafloor geomorphology of the northern Argentine continental slope at 40–41° S mapped from high-resolution bathymetry. J. S. Am. Earth Sci. 2023, 134, 104748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruss, A.; Rucinska, M.; Grzadziel, A.; Waz, M.; Pocwiardowski, P. Multi-band, calibrated backscatter from high frequency multibeam systems as an efficient tool for seabed monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE Underwater Technology (UT), Tokyo, Japan, 6–9 March 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhuge, J. Modeling and Solving of Seafloor Terrain Detection Based on Multibeam Bathymetr. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Electrical Engineering, Big Data and Algorithms (EEBDA), Changchun, China, 27–29 February 2024; pp. 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, D.; Mitchell, G.; Brumley, K. How Modern Multibeam Surveys Can Dramatically Increase Our Understanding of the Seafloor and Waters Above to Support the United Nations Decade of Ocean Science for Sustainable Development. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2019 MTS/IEEE SEATTLE, Seattle, WA, USA, 27–31 October 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dijk, T.A.G.P.; Roche, M.; Lurton, X.; Fezzani, R.; Simmons, S.M.; Gastauer, S.; Fietzek, P.; Mesdag, C.; Berger, L.; Klein Breteler, M.; et al. Bottom and Suspended Sediment Backscatter Measurements in a Flume—Towards Quantitative Bed and Water Column Properties. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anokye, M.; Cui, X.; Yang, F.; Wang, P.; Sun, Y.; Ma, H.; Amoako, E.O. Optimizing multi-classifier fusion for seabed sediment classification using machine learning. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2023, 17, 2295988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zhao, D.; Zhou, J.; Shang, J.; Wang, M.; Zhu, C.; Luo, X. Construction of High-Resolution Bathymetric Dataset for the Mariana Trench. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 142441–142450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tang, Y.; Jin, S.; Bian, G.; Zhao, X.; Peng, C. A Method for Multi-Beam Bathymetric Surveys in Unfamiliar Waters Based on the AUV Constant-Depth Mode. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Andrade Neto, W.P.; Paz, I.D.S.R.; Oliveira, R.A.A.C.E.; De Paulo, M.C.M. Comparison of the vertical accuracy of satellite-based correction service and the PPK GNSS method for obtaining sensor positions on a multibeam bathymetric survey. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 11104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.; Dong, L.; Zhao, J. Optimal Scale Determination for Object-Based Backscatter Image Analysis in Seafloor Substrate Classification Based on Classification Uncertainty. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2024, 21, 1501005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orange, D.L.; Teas, P.A.; Decker, J.; Gharib, J. Use of multibeam bathymetry and backscatter to improve seabed geochemical surveys—Part 1: Historical review, technical description, and best practices. Interpretation 2023, 11, T215–T247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grządziel, A. The Impact of Side-Scan Sonar Resolution and Acoustic Shadow Phenomenon on the Quality of Sonar Imagery and Data Interpretation Capabilities. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, M.; Ma, P.; Gao, W.; Liu, X. Automatic Detection of Subsidence Funnels in Large-Scale SAR Interferograms Based on an Improved-YOLOv8 Model. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 6200117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K. The Application Of Acoustic Detection Technology In The Investigation Of Submarine Pipelines. J. Appl. Sci. Eng. 2024, 27, 2981–2991. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Chen, G.; Chen, J.; Cheng, Q. Seismic data denoising using a self-supervised deep learning network. Math. Geosci. 2024, 56, 487–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Li, X.; Zheng, J.; Li, X.; Kan, G.; Liu, B. Inversion of Sub-Bottom Profile Based on the Sediment Acoustic Empirical Relationship in the Northern South China Sea. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamieson, J.W.; Gini, C.; Brown, C.; Robert, K. Interferometric synthetic aperture sonar: A new tool for seafloor characterization. In Frontiers in Ocean Observing: Marine Protected Areas, Western Boundary Currents, and the Deep Sea; Kappel, E.S., Cullen, V., Coward, G., da Silveira, I.C.A., Edwards, C., Morris, T., Roughan, M., Eds.; Oceanography 38 (Supplement 1); The Oceanography Society: Rockville, MD, USA, 2025; pp. 86–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerg, I.D.; Cook, D.A.; Monga, V. Adaptive Phase Learning: Enhancing SyntheticAperture Sonar Imagery Through Learned Coherent Autofocus. IEEE J. Sel. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 9517–9532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, S.; Novellino, A.; Hussain, E.; Grebby, S.; Bateson, L.; Capsey, A.; Marsh, S. Coastal Sediment Grain Size Estimates on Gravel Beaches Using Satellite Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR). Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P. An imaging algorithm for high-resolution imaging sonar system. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 31957–31973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, P.; Hoefler, T.; Stevens, B.; Hazeleger, W. Digital twins of Earth and the computing challenge of human interaction. Nat. Comput. Sci. 2024, 4, 154–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vance, T.C.; Huang, T.; Butler, K.A. Big data in Earth science: Emerging practice and promise. Science 2024, 383, eadh9607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerhardinger, L.C.; Colonese, A.C.; Martini, R.G.; da Silveira, I.; Zivian, A.; Herbst, D.F.; Glavovic, G.B.; Calvo, S.T.; Christie, P. Networked media and information ocean literacy: A transformative approach for UN ocean decade. npj Ocean Sustain. 2024, 3, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Liu, R.; Fan, X.; Chen, P.; Fu, H.; Yuan, W.; Zhu, M.; Luo, Z. Rethinking general underwater object detection: Datasets, challenges, and solutions. Neurocomputing 2023, 517, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, M.; Xu, H.; Jiang, G.; Yu, M.; Chen, Y.; Luo, T.; Zhang, X. DiffWater: Underwater Image Enhancement Based on Conditional Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Model. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 2319–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Tang, S.; Chang, S.; Zhang, H.; Liu, D.; Wang, W. A Novel Scheme for Range Ambiguity Suppression of Spaceborne SAR Based on Underdetermined Blind Source Separation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2025, 63, 5207915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, S. Segmentation of sonar image on seafloor sediments based on multiclass SVM. J. Coast. Res. 2018, 83, 597–602. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/26543022 (accessed on 27 July 2025). [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xu, K.; Li, B.; Han, Y.; Li, G. Sediment Identification Using Machine Learning Classifiers in a Mixed-Texture Dredge Pit of Louisiana Shelf for Coastal Restoration. Water 2019, 11, 1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Yang, B.; Tang, Q. Seabed sediment classification using multibeam backscatter data based on the selecting optimal random forest model. Appl. Acoust. 2020, 167, 107387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheykhmousa, M.; Mahdianpari, M.; Ghanbari, H. Support Vector Machine Versus Random Forest for Remote Sensing Image Classification: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 6308–6325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, S.; Xu, J.; Chen, W.; Dong, Y.; Li, X.; Li, J. A Fine-Grained Genetic Landform Classification Network Based on Multimodal Feature Extraction and Regional Geological Context. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 4511914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.T.T.; Nguyen, Q.H.; Pham, T.H.; Ngo, G.T.H.; Pham, N.T.D.; Pham, T.G.; Tran, C.T.M.; Ha, T.N. Novel Learning of Bathymetry from Landsat 9 Imagery Using Machine Learning, Feature Extraction and Meta-Heuristic Optimization in a Shallow Turbid Lagoon. Geosciences 2024, 14, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Kusky, T.; Luo, L.; Li, Q.; Cheng, Q. Hadean tectonics: Insights from machine learning. Geology 2023, 51, 718–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Yang, F.; Wang, X.; Ai, B.; Luo, Y.; Ma, D. Deep learning model for seabed sediment classification based on fuzzy ranking feature optimization. Mar. Geol. 2020, 432, 106390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Fu, X.; Hu, Y. A Sonar image recognition method using transfer learning to train Convolutional neural networks. J. Unmanned Underw. Syst. 2020, 28, 89–96. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Qin, Z.; Cui, X.; Yang, F.; Yasir, M.; Ma, B.; Liu, X. MBES Seabed Sediment Classification Based on a Decision Fusion Method Using Deep Learning Model. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Liang, H.; Duan, T. Small-Sample Sonar Image Classification Based on Deep Learning. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Luo, Z.; Wu, J.; Shang, J.; Zhao, D. Deep Learning-Based High Accuracy Bottom Tracking on 1-D Side-Scan Sonar Data. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 8011005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, W.; Zhang, J. Sonar Images Classification While Facing Long-Tail and Few-Shot. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arosio, R.; Hobley, B.; Wheeler, A.J.; Sacchetti, F.; Conti, L. A,; Furey, T.; Lim, A. Fully convolutional neural networks applied to large-scale marine morphology mapping. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1228867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Sun, Y.; Song, Y.; Dong, L.; Zhao, X. Revealing the Potential of Deep Learning for Detecting Submarine Pipelines in Side-Scan Sonar Images: An Investigation of Pre-Training Datasets. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anokye, M.; Cui, X.; Yang, F.; Fan, M.; Luo, Y.; Liu, H. CNN multibeam seabed sediment classification combined with a novel feature optimization method. Math. Geosci. 2024, 56, 279–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Song, W.; Liu, T.; Cui, X.; Yan, J.; Wang, X. Submarine Landslide Identification Based on Improved DeepLabv3 with Spatial and Channel Attention. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Chen, P.; Zhang, S.; Huang, H. Nearshore Bathymetry from ICESat-2 LiDAR and Sentinel-2 Imagery Datasets Using Physics-Informed CNN. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Zhu, C.; Guo, J.; Yang, L.; Li, W. Enhanced Deep-Learning Method for Marine Gravity Recovery From Altimetry and Bathymetry Data. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2024, 21, 1501805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisz, J.K.; Wernette, P.A.; Esselman, P.C. Classification of Lakebed Geologic Substrate in Autonomously Collected Benthic Imagery Using Machine Learning. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Yan, J.; Zhang, Q. Anti-Interference Bottom Detection Method of Multibeam Echosounders Based on Deep Learning Models. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Wu, Z.; Wang, M.; Shang, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, D.; Luo, X. Accurate Identification Method of Small-Size Polymetallic Nodules Based on Seafloor Hyperspectral Data. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, B.; Shuai, H.; Cheng, W. Vision Transformers: State of the Art and Research Challenges, Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. arXiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, X. DeepBlue: Advanced convolutional neural network applications for ocean remote sensing. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2024, 12, 138–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavala-Romero, O.; Bozec, A.; Chassignet, E.P.; Miranda, J.R. Convolutional neural networks for sea surface data assimilation in operational ocean models: Test case in the Gulf of Mexico. Ocean Sci. 2025, 21, 113–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Wang, A.Y.; Joo, M. Review on deep learning techniques for marine object recognition: Architectures and algorithms. Control Eng. Pract. 2022, 118, 104458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochrane, G.R.; Cole, A.; Sherrier, M.; Roca-Lezra, A. Bathymetry, Backscatter Intensity, and Benthic Habitat Offshore of Morro Bay, California (ver. 1.1, January 2024): U.S. Geological Survey Data Release. 2022. Available online: https://cmgds.marine.usgs.gov/data-releases/datarelease/10.5066-P9HEZNRO/ (accessed on 27 July 2025).
- Zhao, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Han, X.; Deveci, M.; Parmar, M. A review of convolutional neural networks in computer vision. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2024, 57, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 25 (NIPS 2012), Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 3–6 December 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1512.03385. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Vanhoucke, V.; Ioffe, S.; Shlens, J.; Wojna, Z. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2818–2826. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Ioffe, S.; Vanhoucke, V.; Alemi, A. Inception-v4, inception ResNet and the impact of residual connections on learning. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, San Francisco, CA, USA, 4–9 February 2017; Volume 31. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.G.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Weyand, T.; Andreetto, M.; Adam, H. MobileNets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision application. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.04861. [Google Scholar]
- Iandola, F.N.; Han, S.; Moskewicz, M.W.; Ashraf, K.; Dally, W.J.; Keutzer, K. SqueezeNet: AlexNet-level accuracy with 50x fewer parameters and <0.5 MB model size. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1602.07360. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, X.; Lin, M.; Sun, J. ShuffleNet: An extremely efficient convolutional neural network for mobile devices. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 6848–6856. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4700–4708. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, S.; Van der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. CondenseNet: An Efficient DenseNet using Learned Group Convolutions. Group 2017, 3, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, R.; Kornblith, S.; Hinton, E.G. When Does Label Smoothing Help. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.02629. [Google Scholar]



| Method | Precision [%] | Recall [%] | F1-Score [%] | IoU |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AlexNet | 65.46 ± 0.62 | 39.05 ± 0.78 | 35.60 ± 0.59 | 33.28 ± 0.67 |
| VGG | 67.87 ± 0.74 | 38.27 ± 0.82 | 37.76 ± 0.81 | 34.43 ± 0.83 |
| ResNet | 70.13 ± 0.58 | 45.77 ± 0.67 | 45.18 ± 0.73 | 42.46 ± 0.76 |
| ConDenseNet | 71.83 ± 0.84 | 47.77 ± 0.63 | 48.62 ± 0.69 | 40.34 ± 0.68 |
| ViT | 61.92 ± 0.38 | 29.98 ± 0.64 | 28.60 ± 0.52 | 31.32 ± 0.42 |
| Our | 73.13 ± 0.69 | 48.40 ± 0.72 | 54.74 ± 0.63 | 43.28 ± 0.56 |
| Method | Precision [%] | Recall [%] | F1-Score [%] | IoU [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ConDenseNet without pruning | 71.34 ± 0.56 | 50.53 ± 0.47 | 53.28 ± 0.44 | 35.17 ± 0.35 |
| ConDenseNet without LSR | 70.45 ± 0.52 | 48.43 ± 0.37 | 52.61 ± 0.55 | 34.46 ± 0.48 |
| ConDenseNet+LSR | 71.74 ± 0.69 | 50.62 ± 0.72 | 53.34 ± 0.43 | 35.28 ± 0.56 |
| Method | Precision [%] | Recall [%] | F1-Score [%] | IoU [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AlexNet+LSR | 66.59 ± 0.56 | 38.68 ± 0.64 | 37.08 ± 0.58 | 35.86 ± 0.56 |
| VGG+LSR | 66.21 ± 0.85 | 36.85 ± 0.37 | 37.56 ± 0.72 | 35.19 ± 0.45 |
| ResNet+LSR | 69.63 ± 0.23 | 41.76 ± 0.57 | 43.67 ± 0.36 | 40.67 ± 0.38 |
| ViT+LSR | 58.92 ± 0.74 | 25.47 ± 0.43 | 23.62 ± 0.61 | 27.58 ± 0.51 |
| ConDenseNet+LSR | 73.13 ± 0.69 | 48.40 ± 0.72 | 54.74 ± 0.63 | 36.38 ± 0.56 |
| Method | Parameters | Computation Time | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pruned ConDenseNet | 1× (3 M) | 1× | ConDenseNet-121 |
| ConDenseNet | 1.6× (4.8 M) | 1.5× | ConDenseNet-121 |
| AlexNet | 12.7× (61 M) | 0.9× | |
| VGG | 28× (138 M) | 7× | VGG16 |
| ResNet | 5.3× (25.6 M) | 1.4× | ResNet50 |
| ViT | 18× (86 M) | 4× | patch = 16 |
| Our | 1× (3 M) | 1× | Benchmark + LSR |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Zhang, K.; Liu, J. Submarine Topography Classification Using ConDenseNet with Label Smoothing Regularization. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2686. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17152686
Zhang J, Zhang K, Liu J. Submarine Topography Classification Using ConDenseNet with Label Smoothing Regularization. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(15):2686. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17152686
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jingyan, Kongwen Zhang, and Jiangtao Liu. 2025. "Submarine Topography Classification Using ConDenseNet with Label Smoothing Regularization" Remote Sensing 17, no. 15: 2686. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17152686
APA StyleZhang, J., Zhang, K., & Liu, J. (2025). Submarine Topography Classification Using ConDenseNet with Label Smoothing Regularization. Remote Sensing, 17(15), 2686. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17152686








