Feature Constraints Map Generation Models Integrating Generative Adversarial and Diffusion Denoising
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
2.1. GAN-Based Image Generation
2.2. Diffusion-Based Image Generation
2.3. Remote Sensing Map Generation
3. Method
3.1. Basement
3.1.1. GAN Framework
3.1.2. Diffusion Model
3.2. Overview
3.3. Diffusion-Fused Adversarial Generation
3.4. Geophysical Feature Attention Enhancement Mechanism
3.4.1. Channel Attention for Geophysical Feature Recognition
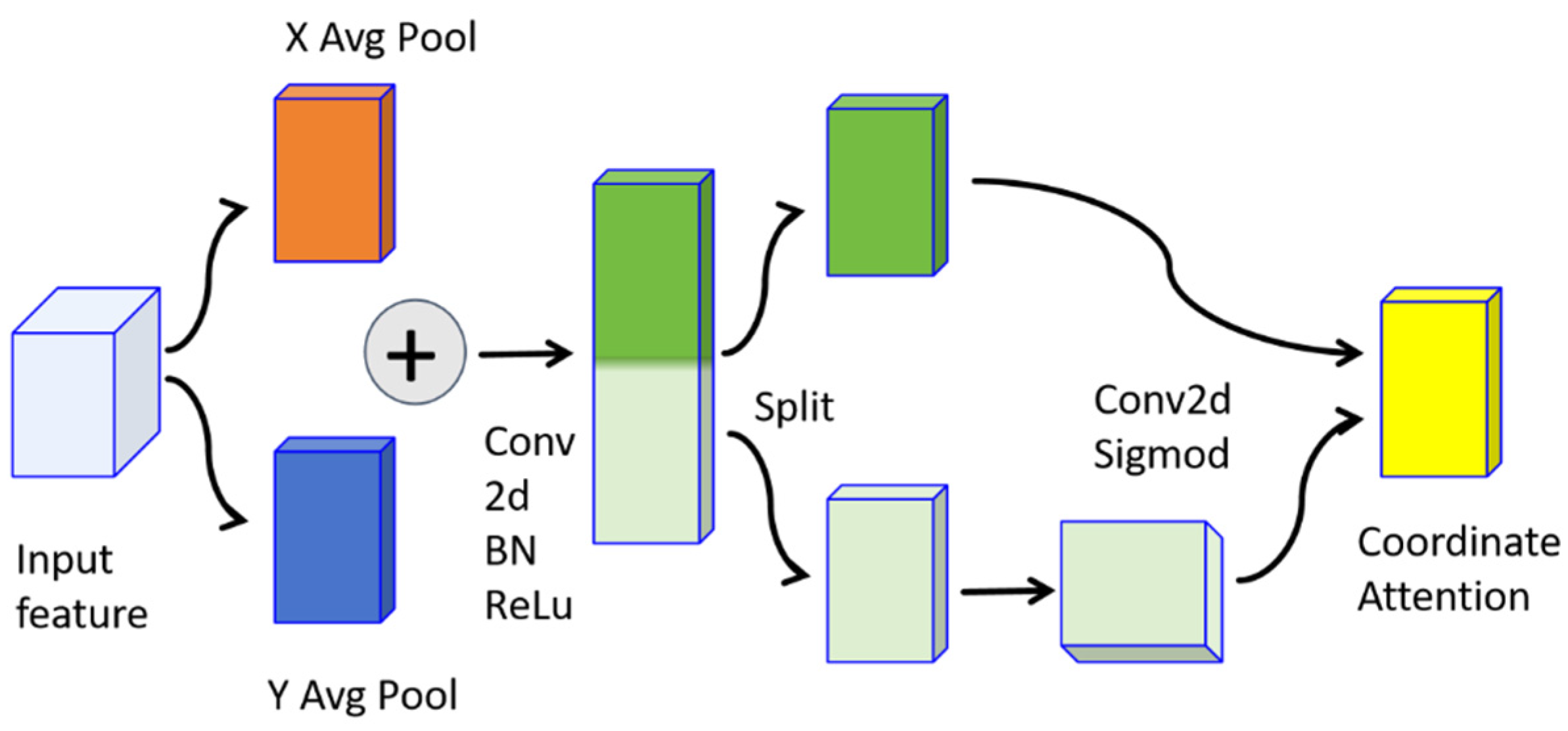
3.4.2. Coordinate Attention for Spatial Relationships
3.5. Loss Function
4. Experiment
4.1. Experimental Implementations
4.1.1. Datasets
4.1.2. Evaluation Metrics
4.1.3. Implementation Details
4.2. Evaluation Results
4.2.1. Quantitative Evaluation
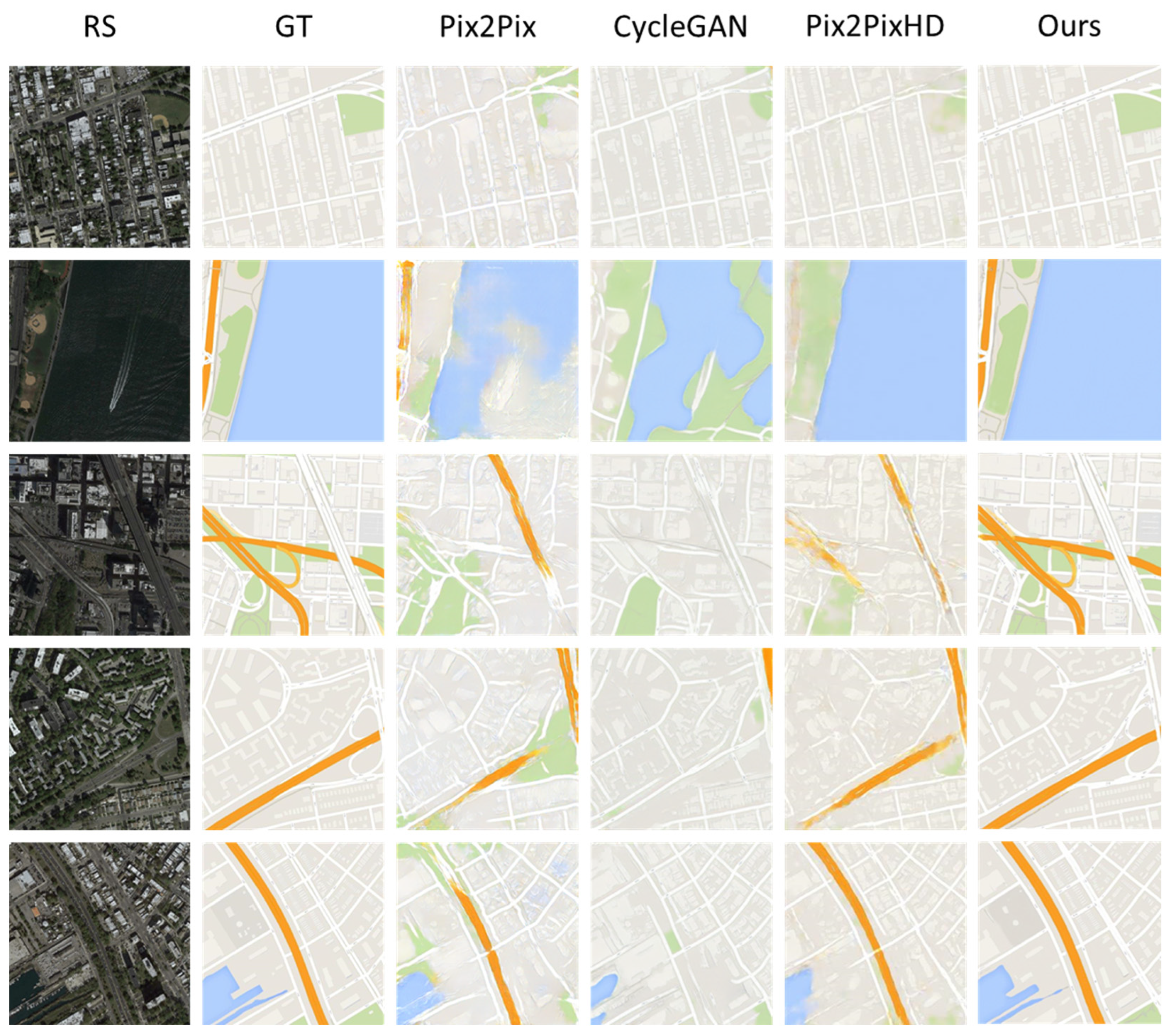
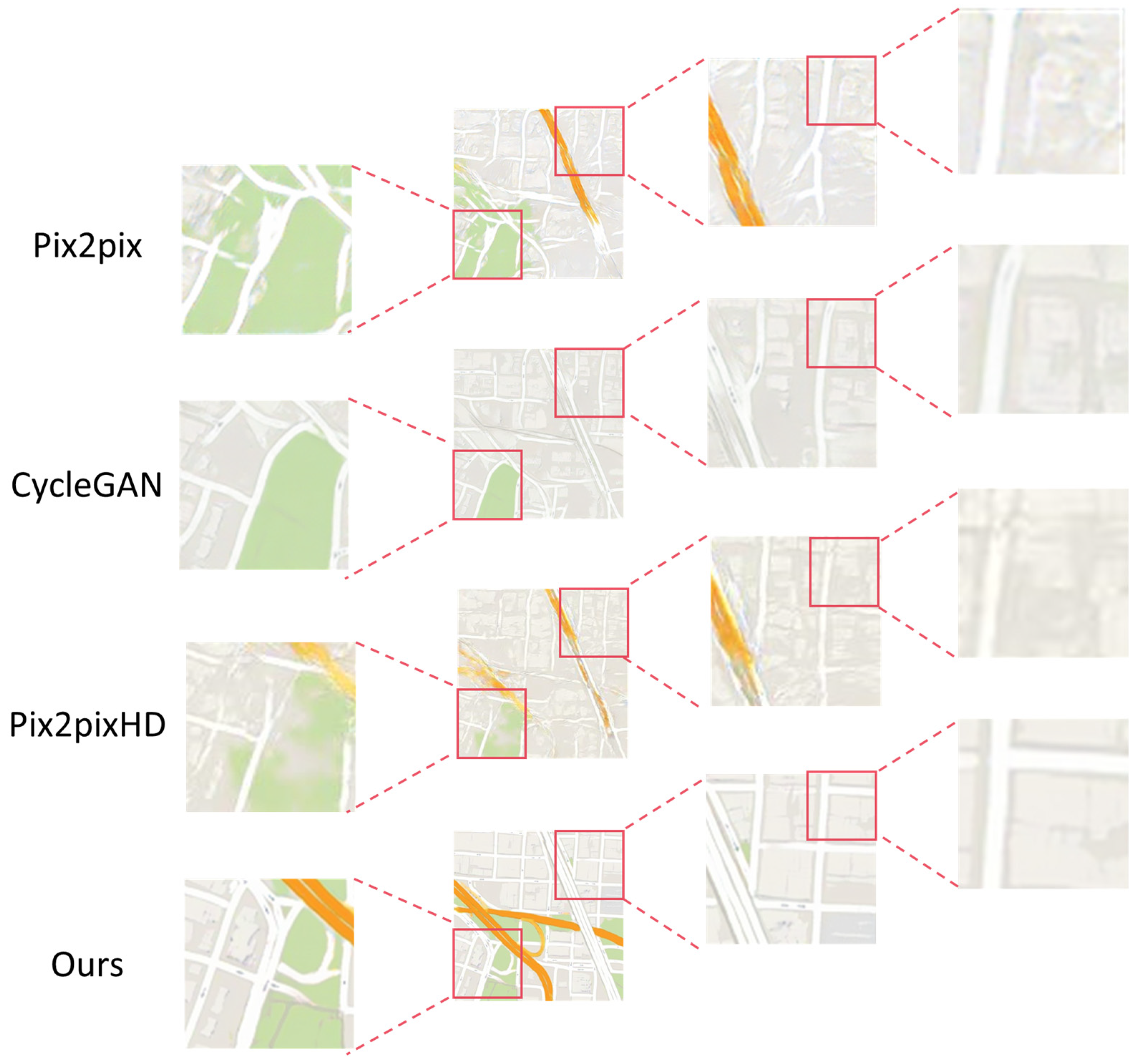
4.2.2. Qualitative Evaluation
4.3. Ablation Study
4.3.1. Effects of Diffusion and Attention
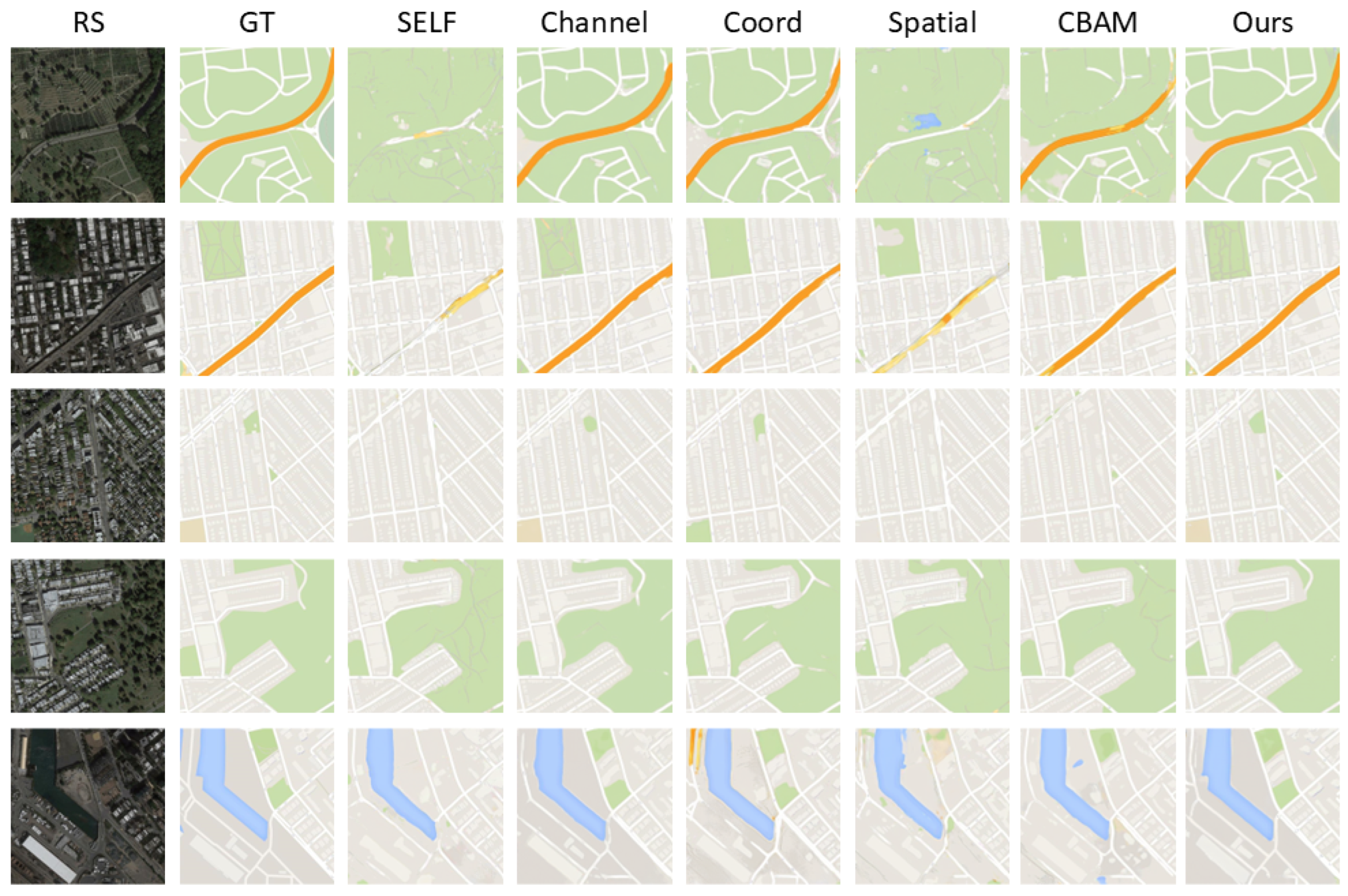
4.3.2. Analysis of Feature Enhancement Attention Effectiveness
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Skidmore, A.K.; Bijker, W.; Schmidt, K.; Kumar, L. Use of Remote Sensing and GIS for Sustainable Land Management. ITC-J. 1997, 3, 302–315. [Google Scholar]
- Ezequiel, C.A.F.; Cua, M.; Libatique, N.C.; Tangonan, G.L.; Alampay, R.; Labuguen, R.T.; Favila, C.M.; Honrado, J.L.E.; Canos, V.; Devaney, C. UAV Aerial Imaging Applications for Post-Disaster Assessment, Environmental Management and Infrastructure Development. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Unmanned Aircraft Systems (ICUAS), Orlando, FL, USA, 20–30 May 2014; pp. 274–283. [Google Scholar]
- Tasar, O.; Happy, S.L.; Tarabalka, Y.; Alliez, P. ColorMapGAN: Unsupervised Domain Adaptation for Semantic Segmentation Using Color Mapping Generative Adversarial Networks. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 7178–7193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanakis, E. Web Mercator and Raster Tile Maps: Two Cornerstones of Online Map Service Providers. Geomatica 2017, 71, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OGC 07-057r7; OpenGIS® Web Map Tile Service Implementation Standard. Open Geospatial Consortium Inc.: Arlington, TX, USA, 2010.
- Peterson, M.P. The Tile-Based Mapping Transition in Cartography. In Maps for the Future: Children, Education and Internet; Zentai, L., Reyes Nunez, J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 151–163. ISBN 978-3-642-19522-8. [Google Scholar]
- Haunold, P.; Kuhn, W. A Keystroke Level Analysis of Manual Map Digitizing. In Spatial Information Theory A Theoretical Basis for GIS; Frank, A.U., Campari, I., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1993; Volume 716, pp. 406–420. ISBN 978-3-540-57207-7. [Google Scholar]
- Park, W.; Yu, K. Hybrid Line Simplification for Cartographic Generalization. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2011, 32, 1267–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative Adversarial Nets. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 27; Ghahramani, Z., Welling, M., Cortes, C., Lawrence, N.D., Weinberger, K.Q., Eds.; Curran Associates, Inc.: Sydney, NSW, Australia, 2014; pp. 2672–2680. [Google Scholar]
- Isola, P.; Zhu, J.-Y.; Zhou, T.; Efros, A.A. Image-to-Image Translation with Conditional Adversarial Networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 5967–5976. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, X.; Shao, L. MapGAN: An Intelligent Generation Model for Network Tile Maps. Sensors 2020, 20, 3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, W.; Fang, F.; Zhou, L.; Sun, C.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, Z. CscGAN: Conditional Scale-Consistent Generation Network for Multi-Level Remote Sensing Image to Map Translation. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguli, S.; Garzon, P.; Glaser, N. GeoGAN: A Conditional GAN with Reconstruction and Style Loss to Generate Standard Layer of Maps from Satellite Images. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1902.05611. [Google Scholar]
- Wolters, P.; Bastani, F.; Kembhavi, A. Zooming Out on Zooming In: Advancing Super-Resolution for Remote Sensing. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2311.18082. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Chen, S.; Xu, T.; Yin, B.; Peng, J.; Mei, X.; Li, H. SMAPGAN: Generative Adversarial Network-Based Semisupervised Styled Map Tile Generation Method. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 4388–4406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Liang, S.; Chen, D.; Chen, Z. Translation of Aerial Image Into Digital Map via Discriminative Segmentation and Creative Generation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.-C.; Liu, M.-Y.; Zhu, J.-Y.; Tao, A.; Kautz, J.; Catanzaro, B. High-Resolution Image Synthesis and Semantic Manipulation with Conditional GANs. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 8798–8807. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, Y.; Lin, J.; Qin, T.; Chen, Z. Image-to-Image Translation: Methods and Applications. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2022, 24, 3859–3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solano-Carrillo, E.; Rodriguez, A.B.; Carrillo-Perez, B.; Steiniger, Y.; Stoppe, J. Look ATME: The Discriminator Mean Entropy Needs Attention. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 787–796. [Google Scholar]
- Brock, A.; Donahue, J.; Simonyan, K. Large Scale GAN Training for High Fidelity Natural Image Synthesis. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, New Orleans, LA, USA, 6–9 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sauer, A.; Schwarz, K.; Geiger, A. StyleGAN-XL: Scaling StyleGAN to Large Diverse Datasets. In Proceedings of the SIGGRAPH ’22: Special Interest Group on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques Conference, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 7–11 August 2022; Nandigjav, M., Mitra, N.J., Hertzmann, A., Eds.; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 49:1–49:10. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, G.; Kim, H.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.; Ha, J.-W.; Choi, Y. Generator Knows What Discriminator Should Learn in Unconditional GANs. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2022—17th European Conference, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Proceedings, Part XVII. Avidan, S., Brostow, G.J., Cissé, M., Farinella, G.M., Hassner, T., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; Volume 13677, pp. 406–422. [Google Scholar]
- Van Den Oord, A.; Vinyals, O. Neural Discrete Representation Learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 6309–6318. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, J.; Jain, A.; Abbeel, P. Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 6840–6851. [Google Scholar]
- Dhariwal, P.; Nichol, A. Diffusion Models Beat Gans on Image Synthesis. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 8780–8794. [Google Scholar]
- Croitoru, F.-A.; Hondru, V.; Ionescu, R.T.; Shah, M. Diffusion Models in Vision: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 45, 10850–10869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, B.; Ouyang, H.; Chen, D.; Chen, Q.; Wen, F. Pretraining Is All You Need for Image-to-Image Translation. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.12952. [Google Scholar]
- Nichol, A.; Dhariwal, P. Improved Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2102.09672. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.; Meng, C.; Ermon, S. Denoising Diffusion Implicit Models. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2010.02502. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Metz, L.; Chintala, S. Unsupervised Representation Learning with Deep Convolutional Generative Adversarial Networks. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2016, San Juan, Puerto Rico, 2–4 May 2016; Conference Track Proceedings. Bengio, Y., LeCun, Y., Eds.; 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Arjovsky, M.; Chintala, S.; Bottou, L. Wasserstein Gan. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1701.07875. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.-Y.; Park, T.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A. Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation Using Cycle-Consistent Adversarial Networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2242–2251. [Google Scholar]
- Karras, T.; Aila, T.; Laine, S.; Lehtinen, J. Progressive Growing of GANs for Improved Quality, Stability, and Variation. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2018, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 30 April–3 May 2018. Conference Track Proceedings; 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, W.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xue, J.-H.; Zhou, B.; Yang, M.-H. GAN Inversion: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 45, 3121–3138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; She, Q.; Ward, T.E. Generative Adversarial Networks in Computer Vision: A Survey and Taxonomy. ACM Comput. Surv. 2021, 54, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, J.; Sun, Z.; Wen, Y.; Tao, D.; Ye, J. A Review on Generative Adversarial Networks: Algorithms, Theory, and Applications. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2023, 35, 3313–3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karras, T.; Laine, S.; Aila, T. A Style-Based Generator Architecture for Generative Adversarial Networks. In Proceedings of the CVPR 2019, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Karras, T.; Laine, S.; Aittala, M.; Hellsten, J.; Lehtinen, J.; Aila, T. Analyzing and Improving the Image Quality of StyleGAN. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 8107–8116. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Peng, X.; Wu, Z.; Yang, F.; He, X.; Li, Z. M3GAN: A Masking Strategy with a Mutable Filter for Multidimensional Anomaly Detection. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2023, 271, 110585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Shao, Y.; Li, C.-N. CNTS: Cooperative Network for Time Series. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 31941–31950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Q.; Zhou, D.; Feng, J. Coordinate Attention for Efficient Mobile Network Design. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 13713–13722. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Chen, K.; Zhao, R.; Zou, Z.; Shi, Z. Text2Earth: Unlocking Text-Driven Remote Sensing Image Generation with a Global-Scale Dataset and a Foundation Model. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2025, 2–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebaq, A.; ElHelw, M. RSDiff: Remote Sensing Image Generation from Text Using Diffusion Model. Neural Comput. Appl. 2024, 36, 23103–23111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Wu, J.; Chen, H.; Ma, M. MapGen-Diff: An End-to-End Remote Sensing Image to Map Generator via Denoising Diffusion Bridge Model. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kweon, I.S. CBAM: Convolutional Block Attention Module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.; Fang, Z.; Chen, L.; Song, T.; Lin, D. Level-Aware Consistent Multilevel Map Translation from Satellite Imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image Quality Assessment: From Error Visibility to Structural Similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heusel, M.; Ramsauer, H.; Unterthiner, T.; Nessler, B.; Hochreiter, S. Gans Trained by a Two Time-Scale Update Rule Converge to a Local Nash Equilibrium. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 September 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Park, T.; Liu, M.-Y.; Wang, T.-C.; Zhu, J.-Y. Semantic Image Synthesis with Spatially-Adaptive Normalization. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 2332–2341. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, H.; Xu, D.; Sebe, N.; Wang, Y.; Corso, J.J.; Yan, Y. Multi-Channel Attention Selection GAN with Cascaded Semantic Guidance for Cross-View Image Translation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and pattern recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 2417–2426. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.; Zhang, C.; Huang, M.; Liu, C.; Shi, J.; Loy, C.C. TSIT: A Simple and Versatile Framework for Image-to-Image Translation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; pp. 206–222. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, J.; Zeng, H.; Zhang, L. High-Resolution Photorealistic Image Translation in Real-Time: A Laplacian Pyramid Translation Network. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 9392–9400. [Google Scholar]

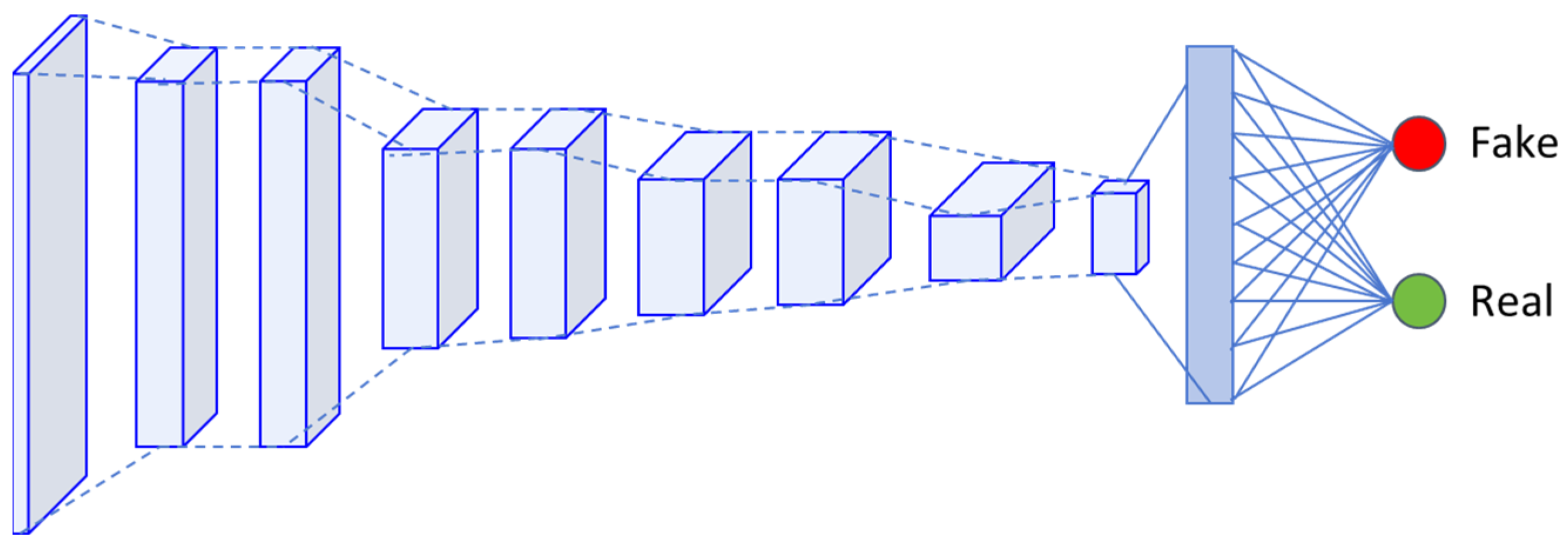
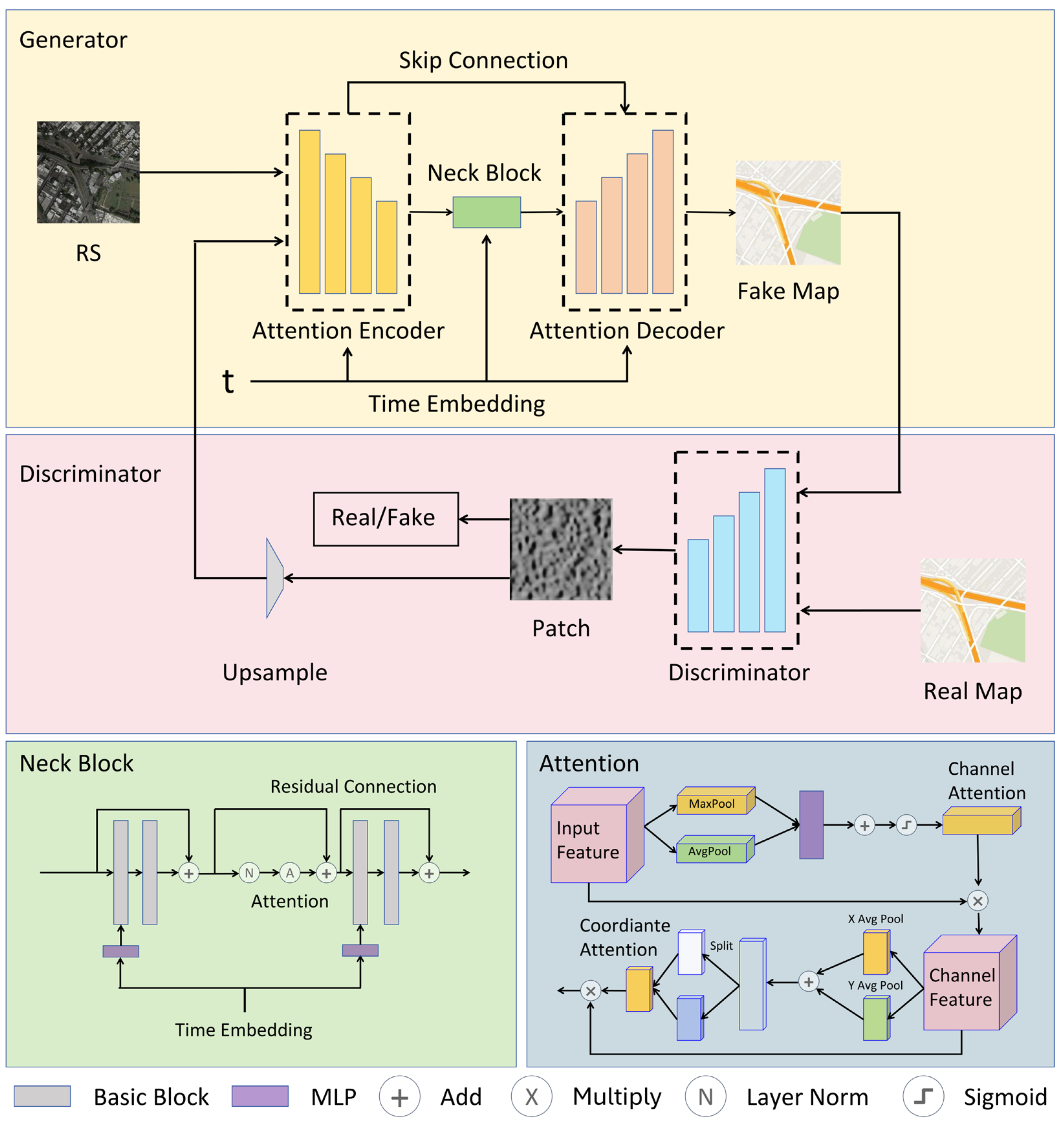

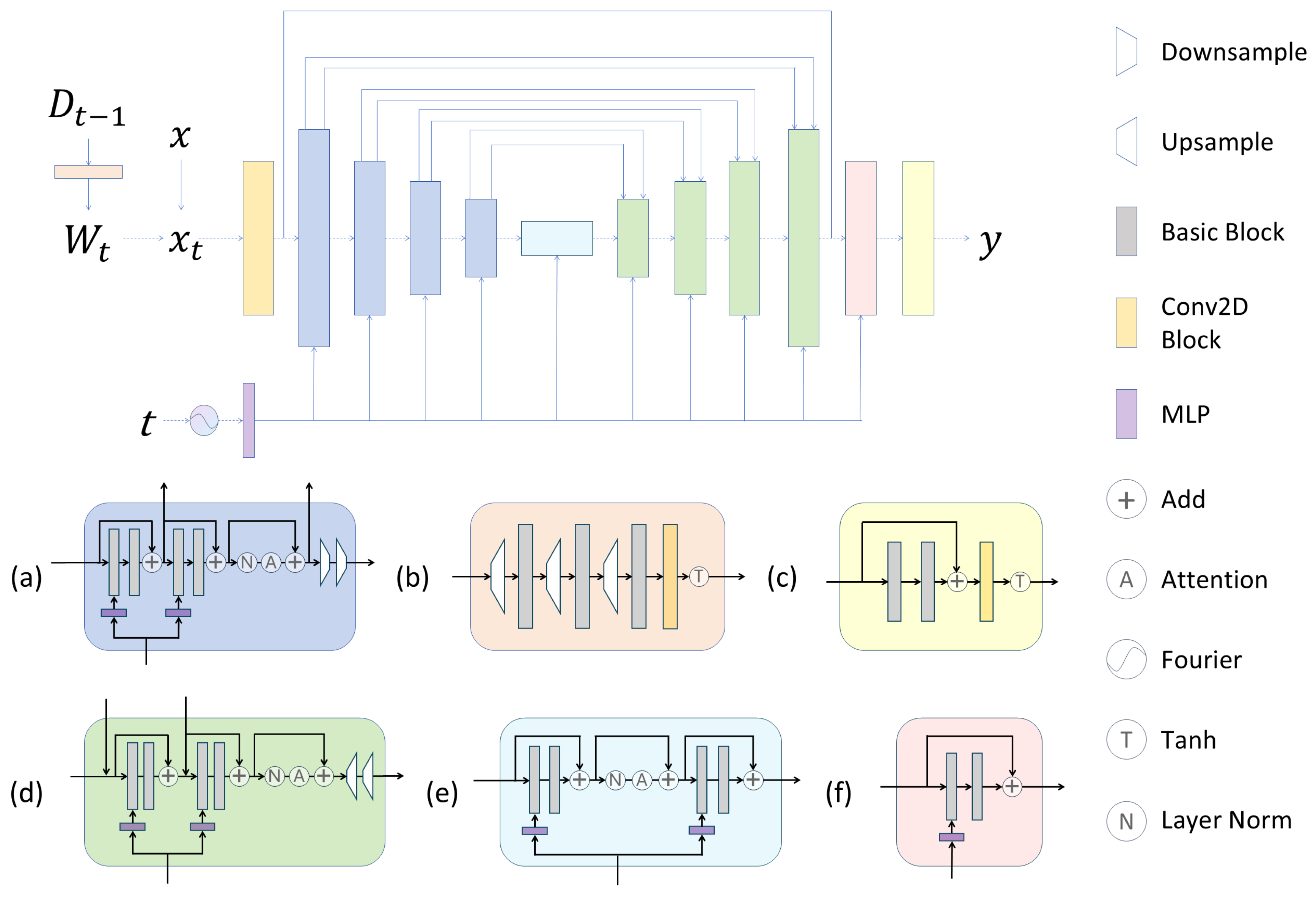

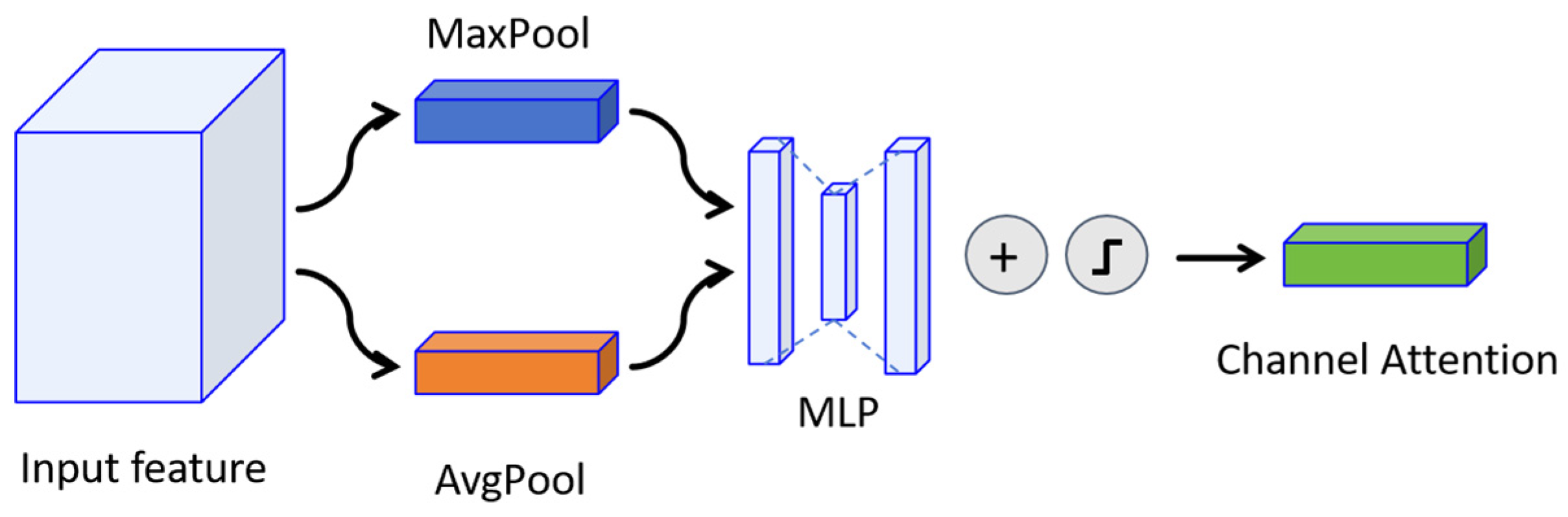
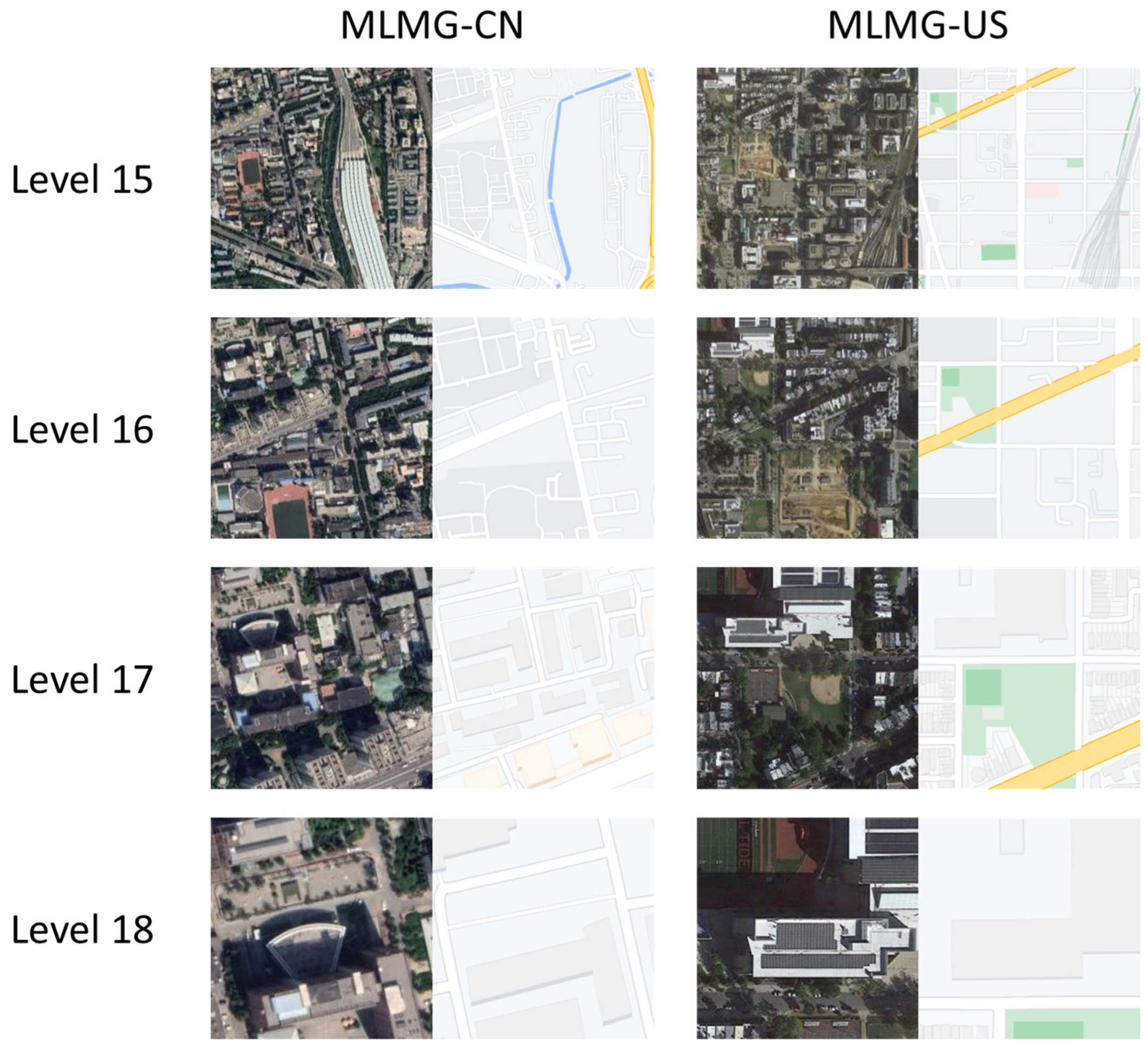


| Level | Train-US | Train-CN | Test-US | Test-CN | Pixel Zoom |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | 2000 | 2000 | 20 | 20 | 4.8 m/pixel |
| 16 | 2000 | 2000 | 80 | 80 | 2.4 m/pixel |
| 17 | 2000 | 2000 | 320 | 320 | 1.2 m/pixel |
| 18 | 2000 | 2000 | 1280 | 1280 | 0.6 m/pixel |
| Total | 8000 | 8000 | 1700 | 1700 | - |
| Method | Parameters (M) | Time/1k Tiles (s) | Throughput (Tiles/s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pix2Pix [10] | ~54 | ~98 | ~10.2 |
| BigGAN [20] | ~80 | ~125 | ~8.0 |
| StyleGAN2 [38] | ~150 | ~100 | ~10.0 |
| DDPM [24] (1000 step) | ~139 | ~1000 | ~1.0 |
| SD [17] (40 step) | ~900 | ~250 | ~4.0 |
| Ours (200 step) | ~35.8 | ~186 | ~5.4 |
| Method | SSIM↑ | FID↓ | PSNR↑ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pix2pix [10] | 0.631 | 216.557 | 24.535 |
| Pix2pixHD [17] | 0.726 | 129.901 | 21.243 |
| CycleGAN [32] | 0.724 | 123.618 | 25.929 |
| Ours | 0.817 | 39.832 | 27.912 |
| Level | Method | FID↓ | PSNR↑ | Level | Method | FID↓ | PSNR↑ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | CycleGAN [32] | 312.14 | 20.725 | 16 | CycleGAN [32] | 237.79 | 22.545 |
| Pix2pixHD [17] | 331.10 | 20.908 | Pix2pixHD [17] | 206.16 | 22.785 | ||
| SPADE [50] | 459.11 | 20.468 | SPADE [50] | 351.68 | 22.865 | ||
| SelectionGAN [51] | 337.83 | 20.617 | SelectionGAN [51] | 272.04 | 22.702 | ||
| TSIT [52] | 284.17 | 20.540 | TSIT [52] | 219.99 | 22.543 | ||
| LPTN [53] | 351.61 | 21.327 | LPTN [53] | 323.64 | 23.454 | ||
| SMAPGAN [15] | 336.35 | 22.506 | SMAPGAN [15] | 292.50 | 24.819 | ||
| CreativeGAN [16] | 267.37 | 21.428 | CreativeGAN [16] | 193.56 | 22.947 | ||
| LACM [47] | 195.64 | 21.532 | LACM [47] | 154.18 | 23.488 | ||
| Ours | 213.921 | 23.129 | Ours | 193.26 | 24.854 | ||
| 17 | CycleGAN [32] | 167.12 | 23.076 | 18 | CycleGAN [32] | 138.92 | 23.715 |
| Pix2pixHD [17] | 171.39 | 23.878 | Pix2pixHD [17] | 110.35 | 24.801 | ||
| SPADE [50] | 295.67 | 24.000 | SPADE [50] | 224.64 | 25.330 | ||
| SelectionGAN [51] | 239.45 | 23.914 | SelectionGAN [51] | 194.97 | 25.442 | ||
| TSIT [52] | 137.50 | 23.264 | TSIT [52] | 123.45 | 24.167 | ||
| LPTN [53] | 253.00 | 24.198 | LPTN [53] | 182.36 | 24.599 | ||
| SMAPGAN [15] | 286.87 | 25.304 | SMAPGAN [15] | 246.88 | 27.005 | ||
| CreativeGAN [16] | 129.51 | 23.640 | CreativeGAN [16] | 100.54 | 24.799 | ||
| LACM [47] | 107.95 | 24.514 | LACM [47] | 78.44 | 25.970 | ||
| Ours | 105.48 | 26.870 | Ours | 69.768 | 27.428 |
| Method | SSIM↑ | FID↓ | PSNR↑ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 0.631 | 216.557 | 24.535 |
| Only-Diffusion | 0.733 | 93.662 | 27.146 |
| Only-Attention | 0.759 | 56.944 | 27.741 |
| Ours | 0.817 | 39.832 | 28.700 |
| Attention | SSIM↑ | FID↓ | PSNR↑ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Self-Attention | 0.763 | 51.937 | 27.863 |
| Channel | 0.762 | 49.105 | 27.784 |
| Coord | 0.783 | 45.036 | 28.611 |
| Spatial | 0.767 | 52.381 | 27.846 |
| CBAM | 0.788 | 42.264 | 28.828 |
| Ours | 0.817 | 39.832 | 28.700 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, C.; Fan, X.; Lu, X.; Zhou, L.; Zhao, J.; Dong, Y.; Chen, Z. Feature Constraints Map Generation Models Integrating Generative Adversarial and Diffusion Denoising. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2683. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17152683
Sun C, Fan X, Lu X, Zhou L, Zhao J, Dong Y, Chen Z. Feature Constraints Map Generation Models Integrating Generative Adversarial and Diffusion Denoising. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(15):2683. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17152683
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Chenxing, Xixi Fan, Xiechun Lu, Laner Zhou, Junli Zhao, Yuxuan Dong, and Zhanlong Chen. 2025. "Feature Constraints Map Generation Models Integrating Generative Adversarial and Diffusion Denoising" Remote Sensing 17, no. 15: 2683. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17152683
APA StyleSun, C., Fan, X., Lu, X., Zhou, L., Zhao, J., Dong, Y., & Chen, Z. (2025). Feature Constraints Map Generation Models Integrating Generative Adversarial and Diffusion Denoising. Remote Sensing, 17(15), 2683. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17152683








