Abstract
A reliable precipitation dataset with high spatial resolution is essential for climate research in the Tarim Basin. This study evaluated the performances of four models, namely a random forest (RF), a long short-term memory network (LSTM), a support vector machine (SVM), and a feedforward neural network (FNN). FNN, which was found to be superior to the other models, was used to integrate eight precipitation datasets spanning from 1990 to 2022 across the Tarim Basin, resulting in a new monthly high-resolution (0.1°) precipitation dataset named MoHiPr-TB. This dataset was subsequently bias-corrected by the China Land Data Assimilation System version 2.0 (CLDAS2.0). Validation results indicate that the corrected MoHiPr-TB not only accurately reflects the spatial distribution of precipitation but also effectively simulates its intensity and interannual and seasonal variations. Moreover, MoHiPr-TB is capable of detecting the precipitation–elevation relationship in the Pamir Plateau, where precipitation initially increases and then decreases with elevation, as well as the synchronous variation of precipitation and elevation in the Tianshan region. Collectively, this study delivers a high-accuracy precipitation dataset for the Tarim Basin, which is anticipated to have extensive applications in meteorological, hydrological, and ecological research.
1. Introduction
The Tarim Basin is one of the most arid regions in northwest China and characterized by scarcity of water all the year round [1]. Despite the continuous improvements in meteorological observation systems, long-term gauge-based observations are still characterized by low station density and spatial resolution, especially in mountainous areas and desert hinterlands [2,3,4]. This brings significant uncertainty to understand the climate change and mechanisms over the Tarim Basin [5]. Although a large number of satellites and precipitation reanalysis products can solve the problem of spatial resolution, their estimation of precipitation in the Tarim Basin is affected by algorithms and measurements, and has certain systematic and random errors. Therefore, a high-accuracy and long-term precipitation dataset is essential for investigating climate changes over the Tarim Basin, which significantly impact hydrology, agricultural production, and environmental management [2,6].
At present, the precipitation datasets utilized in the majority of climate studies encompass gauge-based datasets, reanalysis datasets, and satellite-based datasets. For example, various globally available satellite-derived precipitation products with appropriate resolutions have been reported [7,8]. These datasets include the Integrated Multisatellite Retrievals for Global Precipitation Measurement (IMERG) [9,10], the Precipitation Estimation from Remotely Sensed Information using Artificial Neural Networks–Climate Data Record (PERSIANN-CDR) [11], TRMM Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA), Climate Hazards Group InfraRed Precipitation with Station Data version 2.0 (CHIRPS) [12], and the NOAA Climate Prediction Center morphing method (CMORPH) [13]. However, not all satellite-based products possess long-term climate data records, and these products often exhibit systematic biases [14]. Additionally, various gauge-based precipitation datasets and reanalysis data are utilized to explore interannual and interdecadal variations of precipitation over the Tarim Basin, e.g., the Global Precipitation Climatology Project monthly precipitation dataset version 2.3 (GPCP) [15], the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts Reanalysis 5 (ERA5) [16], and the Climate Prediction Center (CPC) Unified Gauge-Based Analysis of Global Daily Precipitation [17,18]. Among these datasets, gauge-based datasets may exhibit significant bias in the Tarim Basin [19]. This is attributed to the region’s remote geographical location and sparse ground meteorological observations [20]. Reanalysis datasets such as ERA-Interim and the National Centers for Environmental Prediction–Department of Energy Reanalysis version 2 (NCEP2) have been found to produce the large errors and exhibit poor agreement with observations in western China, particularly in regions of higher elevation [21]. Various studies consistently show that ERA5 overestimates precipitation in areas with complex topography and during heavy precipitation [3,22]. Therefore, high-quality precipitation datasets are extremely necessary for the study of precipitation variation characteristics and mechanisms in the Tarim Basin. To obtain a high-accuracy precipitation dataset for the Tarim Basin, it is necessary to fully consider the gauge-based products, satellite-based data, and reanalysis data, and reasonably merge the multi-source precipitation datasets.
Integrating precipitation datasets from various sources helps reduce uncertainties in precipitation measurements. In addition, another widely used method to improve the quality of precipitation datasets is bias correction [23,24,25,26]. In recent years, machine learning has become a prevalent method for merging datasets or bias correction, owing to its capacity to address nonlinear problems. For example, Zhang et al. (2021) illustrated that machine learning is an effective tool for the fusion of satellite and gauge-based precipitation [27]. A random forest (RF) has been effectively utilized to combine gridded precipitation products in Chile [28]. Four distinct approaches, including a long short-term memory network (LSTM), an RF, a feedforward neural network (FNN), and multiple linear regression, have been employed to integrate different precipitation datasets and provide more precise precipitation estimations, including satellite and reanalysis data [29]. Previous studies have highlighted the significant advantages of machine learning models in merging multisource precipitation products. However, although machine learning has shown great potential in precipitation data fusion and bias correction, there are still relatively few studies in arid areas, especially in the Tarim Basin, that utilize machine learning to fuse multi-source precipitation datasets and combine them with high-precision data for bias correction.
The aim of this study is to obtain an accurate precipitation dataset for the Tarim Basin. First, eight different precipitation datasets with different spatial resolutions were evaluated against 58-gauge observations in the Tarim Basin. Subsequently, these eight precipitation datasets were merged using four machine learning methods, with the most effective method selected to create the final merged gridded dataset. Finally, the merged gridded dataset was corrected using the China Meteorological Administration Land Data Assimilation System version 2 (CLDAS2.0) dataset. The structure of this paper is as follows: the introduction is provided in Section 1. The data and methods employed in this study are detailed in Section 2. Section 3 presents the results. Section 4 and Section 5 contain the discussions and conclusions, respectively.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Precipitation Datasets
Given the varying temporal and spatial extents of different precipitation datasets, we carefully selected eight gridded precipitation datasets that encompass the period from 1990 to 2022 and specifically cover the Tarim Basin region. These eight commonly used gridded precipitation products served as input for different machine learning models in this study. These eight precipitation products include a reanalysis dataset (China Meteorological Administration Global Land Surface Reanalysis Interim (CRA40-Land) and European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts Reanalysis 5 (ERA5) [16]), gauge-based data (CPC [17,18], GPCP [15], and CN05.1 [30]), and a comprehensive dataset (CHIRPS [12], PERSIANN-CDR [11], and the Global Precipitation Climatology Centre (GPCC) [31]). Detailed information is provided in Table 1. All gridded precipitation datasets were resampled to a 0.1° resolution using linear interpolation.

Table 1.
Data used in this study.
The observed monthly precipitation data of 58 stations were obtained from the China Meteorological Climatological Data Service Centre (http://data.cma.cn/), and their distribution is shown in Figure 1. Additionally, precipitation data from CLDAS2.0 for the period of 1998–2022 were used to correct the final merged dataset, as CLDAS2.0 can provide more accurate precipitation estimates than other datasets [32,33]. Furthermore, ground-based automatic station-derived precipitation from 2016 to 2019 were used to evaluate the performance of the merged dataset at various elevations (Table 2).
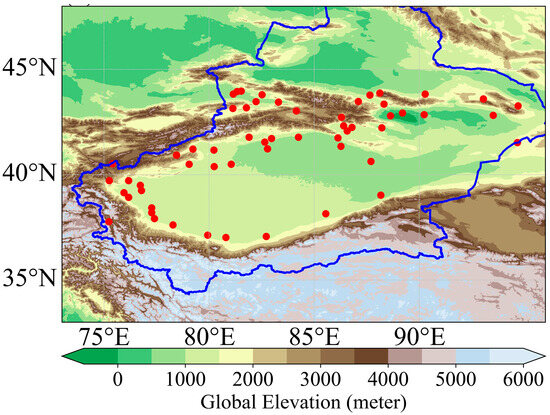
Figure 1.
Locations of the meteorological stations (red dots) in the Tarim Basin. The blue line represents the Xinjiang region.

Table 2.
Information of ground-based automatic stations.
2.2. Method
This study evaluated different precipitation datasets using two methods: correlation coefficient and root mean square error (RMSE). When conducting multi-source precipitation dataset fusion, the complexity of the dataset and the characteristics of the model were comprehensively considered. Ultimately, four models were selected: a random forest (RF), a support vector machine (SVM), an FNN, and LSTM.
RFs can handle nonlinear relationships very well and have strong robustness against noise in the data [34]. They learn from the data by constructing multiple decision trees, each of which uses different data subsets and feature subsets during the training process [35]. In our RF model, the number of decision trees was set to 50. LSTM is a model specifically designed for processing time series data, capable of capturing the long-term dependencies of data in the temporal dimension [36,37,38]. LSTM can effectively control the flow of information through its unique gating mechanism, enabling the model to remember important historical information [37]. In this study, a fully connected layer was added after the LSTM layer to produce the result [29]. Additionally, the Adam optimizer was employed, and the mean squared error was utilized as the loss function. An FNN is a model that can learn complex mapping relationships in data [29,39]. The multi-layer network structure of an FNN can extract multi-level features of the data. In this study, the FNN consisted of an input layer, a hidden layer with 20 neurons and an output layer. The output layer had one neuron with a linear activation function to directly produce the predicted value. Finally, SVMs perform well in handling small sample, nonlinear data classification and regression problems [40]. In some cases, the sample size of precipitation datasets may be limited. However, SVMs can find better decision boundaries within the limited samples by seeking the optimal segmentation hyperplane of the data [41,42]. For our SVM model, the regularization parameter was set to 100, and the kernel function parameter was set to 0.1.
Based on grid precipitation products and observation station data, a tenfold cross-validation method was adopted to generate a combined precipitation dataset from 1990 to 2022.
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation of Eight Gridded Precipitation Datasets
Spatial distribution of annual precipitation from observations and various gridded datasets are presented in Figure 2. In observations, the precipitation in the Tarim Basin is mainly concentrated in the Tianshan Mountains, with an annual precipitation of over 400 mm. However, the precipitation around the basin is relatively low, with an annual precipitation ranging from 0 to 150 mm (Figure 2a). By comparing the spatial characteristics of annual precipitation across eight datasets, it is evident while the spatial distribution patterns of these datasets align closely with observed data, substantial discrepancies exist in the magnitude of precipitation (Figure 2). The CHRIPS, CRA40, ERA5, and CN05.1 datasets show spatial consistency with the observed data. In the northern Tarim Basin, CPC and GPCC data have a similar spatial pattern to the observed data, but the values are lower. Meanwhile, the estimated values of the CDR and GPCP datasets are higher than the observed values at the western Tarim Basin. Compared with the other seven precipitation datasets, the ERA5 reanalysis dataset significantly overestimated precipitation, especially in the Tianshan Mountains and southern regions of the Tarim Basin (Figure 2h).
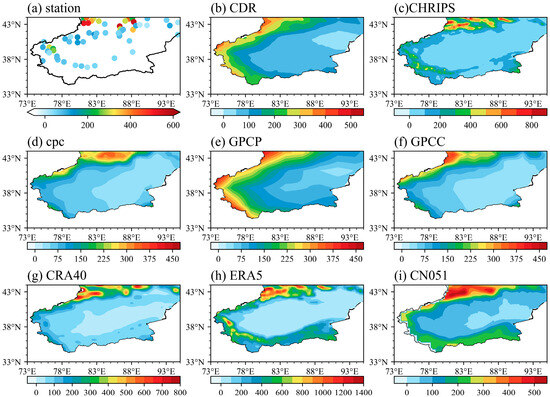
Figure 2.
Spatial patterns of the annual mean precipitation of (a) observations, (b) PERSIANN-CDR, (c) CHRIPS, (d) CPC, (e) GPCP, (f) GPCC, (g) CRA40, (h) ERA5, and (i) CN05.1 during the period from 1990 to 2022 over the Tarim Basin.
The temporal variation characteristics of precipitation were further compared between the observations and each gridded precipitation dataset. Here, the gridded precipitation dataset was interpolated to the stations using the nearest neighbor interpolation method. During 1990–2022, the annual precipitation in the Tarim Basin varied between 80 and 320 mm, as indicated by both observational data and eight precipitation datasets (Figure 3a). Observed precipitation has shown a slightly increasing trend in the past 30 years, and there are significant interannual variations, such as extreme less precipitation in 1997 and more precipitation in 1998 (Figure 3a). Precipitation estimated from eight different precipitation datasets shows consistent interannual variations and has similar intensity, except for ERA5 (Figure 3a). The ERA5 dataset tends to overestimate precipitation in the Tarim Basin, displaying significantly higher values before 2009 compared to observations (Figure 3a) [43]. The interannual variations of the CN05.1 and GPCP datasets are the most consistent with the observed values, while the CN05.1 dataset performs better (the correlation coefficient is 0.99 between the CN05.1 and observations). Figure 3b illustrates mean monthly precipitation averages across the Tarim Basin. It shows that, except for ERA5, the main differences between the other datasets and the observations occur during the rainy season (May to August), while the features of the dry winter season are captured relatively well. Overestimation of ERA5 exists throughout the year, with a greater deviation in summer than in winter (Figure 3b). Overall, the GPCP, CN05.1, and CRA40 datasets are generally in good agreement with the observed annual and monthly precipitation (Figure 3b).
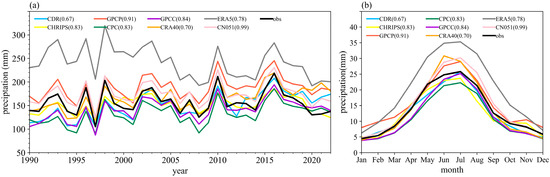
Figure 3.
(a) Annual precipitation and (b) mean monthly precipitation of observations and eight precipitation datasets for the period of 1990–2022 in the Tarim Basin.
Figure 4 depicts the relationships between the observations and eight different precipitation datasets. Overall, among the various gridded precipitation datasets, CN05.1 exhibits the highest accuracy, with an R2 of 0.47, with CHRIPS ranking second. When the precipitation is below 300 mm/year, the majority of the estimated precipitation from the eight dataset aligns closely with the 1:1 line (except for GPCP), whereas when the precipitation exceeds 300 mm, the performance of eight datasets varies significantly. For instance, a number of data points for CRA40 and ERA5 are concentrated in the region indicating overestimated precipitation. Furthermore, a number of data points for PERSLANN-CDR are concentrated in the region indicating underestimated precipitation.
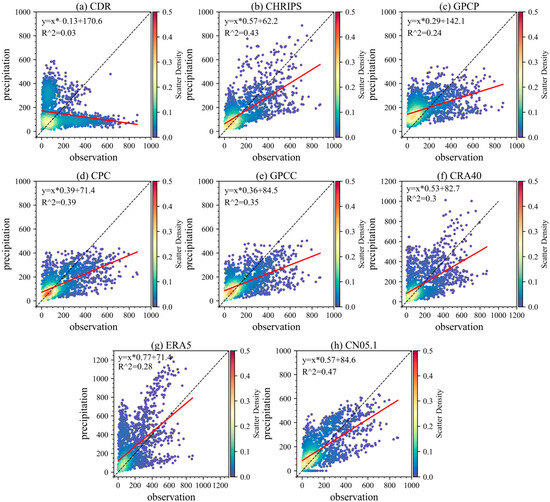
Figure 4.
Scatter density plots of the observed annual precipitation and eight precipitation datasets between 1990 and 2022. The grey line has a slope of 1 and the red line is a fit between different datasets and observations. R2 is the determination coefficient between different datasets and observations.
The evaluation results, illustrated in Figure 5, are based on the CC and RMSE calculated between the eight precipitation datasets and the observed precipitation. The CN05.1 dataset is highly consistent with the observations at corresponding stations (highest CC values), as it is derived through interpolation of gauge data (Figure 5a). In terms of CC values, GPCP, CPC, and GPCC exhibit relatively high quality with most CC values exceeding 0.5. In contrast, PERSIANN-CDR shows relatively poor quality, characterized by CC values below 0.2 across the Tarim Basin. As for the RMSE, except for ERA5 and CDR, the other six precipitation datasets were of similar quality, with averaged RMSE values mostly below 120 (Figure 5b). This may be due to overestimation of precipitation in ERA5.
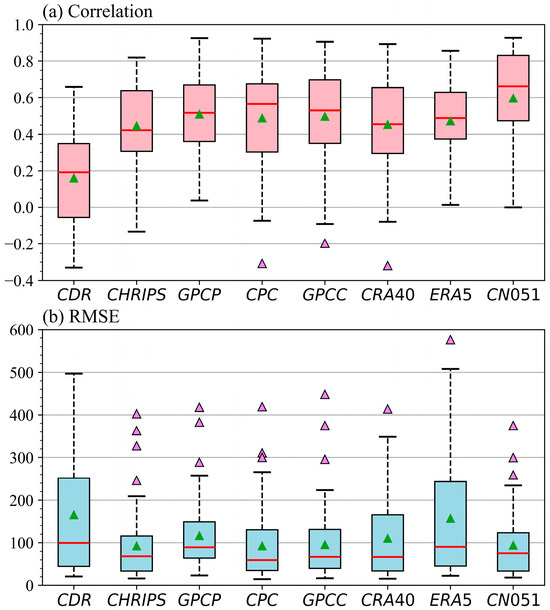
Figure 5.
Box plots of coefficient correlation and RMSE for eight precipitation datasets at independent weather stations. Red lines in boxes represent median values. Boxes indicate the inter-quantile range (25–75%). Green triangle in boxes indicate the averages of all anomaly values. The dots represent extreme outliers.
From the above results, it can be seen that different precipitation products have different advantages. The CHRIPS, CRA40, ERA5, and CN05.1 datasets simulate the spatial distribution more accurately, whereas CDR, GPCC, and GPCP better capture the magnitude, interannual variation, and seasonal characteristics of precipitation. The CPC and GPCC datasets perform particularly well for annual precipitation amounts of less than 250 mm/year. Subsequently, various machine learning models will be employed to integrate these eight precipitation datasets, aiming to derive a merged precipitation dataset with enhanced comprehensive performance.
3.2. Evaluation of the Four Merged Station Precipitation Datasets
In this section, the nearest neighbor interpolation method is first applied to eight gridded precipitation datasets to obtain the corresponding eight station precipitation datasets. Then, these datasets are utilized as inputs of the RF, LSTM, FNN, and SVM models to obtain the multi-source fused station precipitation datasets, which are respectively named M-RF, M-LSTM, M-FNN, and M-SVM.
Figure 6 shows the differences between the observed precipitation and the results of M-RF, M-LSTM, M-FNN, and M-SVM. These four models generally underestimate the actual precipitation in the mountainous areas and overestimate it in other regions. Among them, the SVM model has the most significant deviation in the Tianshan Mountains, with an annual precipitation deviation of up to 200 mm. However, in the southern Tarim Basin, its deviation is relatively small. In contrast, the results of M-RF, M-FNN, and M-LSTM are closer to the observations, with differences mainly occurring at a few stations with extreme precipitation in the Tianshan Mountains. The precipitation differences at other stations are within 100 mm. Overall, the performance of the four models is not significantly different, and all machine learning models have limitations in simulating extreme precipitation values.
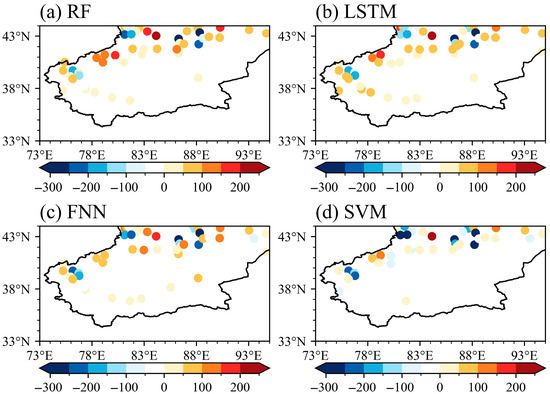
Figure 6.
The spatial pattern of the differences between (a) M-RF, (b) M-LSTM, (c) M-FNN, and (d) M-SVM annual precipitation and observations in the Tarim Basin from 1990 to 2022.
Precipitation estimates from three different merged precipitation datasets (M-RF, M-LSTM, M-FNN) exhibit consistent interannual variations and have similar precipitation intensity, except for M-SVM (Figure 7a). M-SVM underestimates precipitation in the Tarim Basin and its precipitation estimate is considerably lower in comparison to the other three merged datasets. Both M-LSTM and M-FNN show a similar trend with observations in the Tarim Basin, while M-FNN performs outstandingly (the correlation coefficient is 0.97 between M-FNN and observations). Figure 7b shows the mean annual cycle of observations and four merged precipitation datasets for Tarim Basin. The underestimation of M-SVM occurs throughout the year, with a more significant bias in summer compared to winter. Moreover, it is observed that M-RF overestimates precipitation during the summer months, while M-FNN generally provides estimates that are closely aligned with the observed values throughout all months (Figure 7b). Figure 7c,d depict the differences in annual and monthly precipitation between the observations and the four merged datasets. The results also indicate that the LSTM and FNN models perform better than the RF and SVM models. The bias of annual precipitation and seasonal precipitation obtained by M-LSTM and M-FNN are close to zero. However, M-RF significantly overestimates the annual and monthly precipitation, while M-SVM significantly underestimates the annual and monthly precipitation in the Tarim Basin.
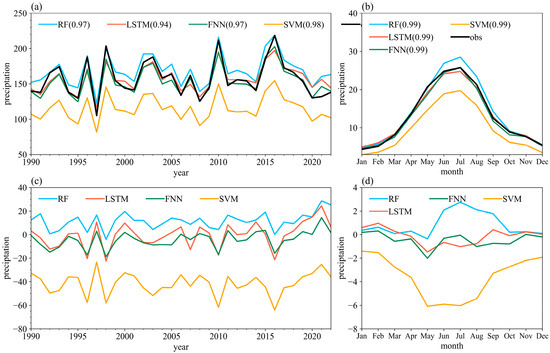
Figure 7.
(a) Annual precipitation and (b) mean annual cycle of observations and four merged precipitation datasets (M-RF, M-LSTM, M-FNN, M-SVM) in the Tarim Basin. Differences of (c) annual precipitation and (d) mean annual cycle between observations and four merged precipitation datasets (M-RF, M-LSTM, M-FNN, M-SVM) in the Tarim Basin.
Figure 8 demonstrates the relationships between observations and the four merged precipitation datasets. For precipitation of less than 300 mm/year, the M-FNN and M-SVM datasets are generally in close agreement with observations, with the majority of data points aligning near the 1:1 line (Figure 8c,d). For precipitation of more than 300 mm/year, M-SVM tends to underestimate precipitation, while the fitting slopes between the other three precipitation datasets and observations were close to 1.
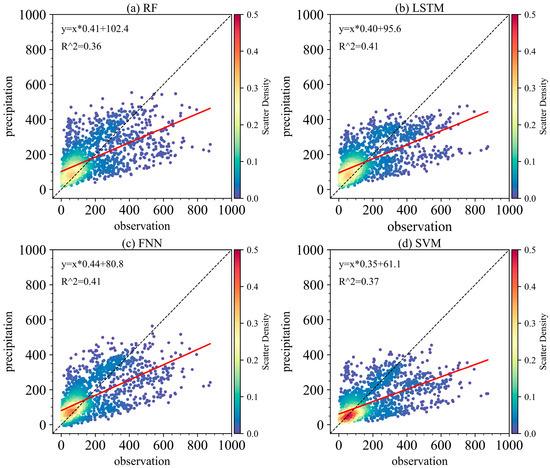
Figure 8.
Scatter density plots of the observed annual precipitation and four merged datasets (M-RF, M-LSTM, M-FNN, M-SVM) between 1990 and 2022. The dashed line has a slope of 1 and the red line is a fit between different datasets and observations. R2 is the determination coefficient between different datasets and observations.
The coefficient correlations and RMSEs between the four merged datasets and gauge observations are illustrated in Figure 9. The results indicate that the coefficient correlations between the observations and four merged datasets are greater than 0.5, with M-FNN and M-SVM performing better (Figure 9a). Similar results can also be seen in the box plot of RMSE, where the RMSEs of M-FNN and M-SVM are smaller than those of M-RF and M-LSTM. Combining the previous evaluation results, M-FNN can not only accurately grasp the intensity of annual precipitation in different regions but also accurately estimate the actual interannual and seasonal variations of precipitation. Therefore, by inputting the eight gridded multi-source precipitation datasets into the trained NN model, a fused gridded precipitation dataset is obtained.
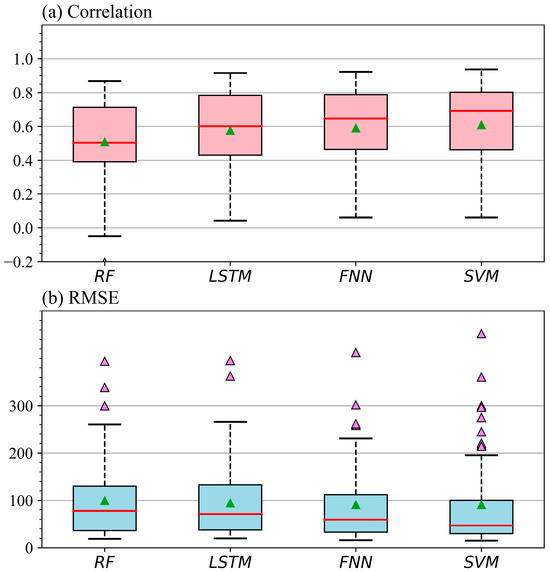
Figure 9.
Box plots of coefficient correlation and RMSE for four merged datasets at independent weather stations. Red lines in boxes represent median values. Boxes indicate the inter-quantile range (25–75%). Green triangle in boxes indicate the averages of all anomaly values. The dots represent extreme outliers.
3.3. Evaluation and Bias Correction of the Merged Gridded Precipitation Datasets
The merged precipitation dataset (M-FNN) performed well in spatial distribution and can basically simulate the rain belt in the Tianshan Mountains, but the precipitation intensity was seriously underestimated in some mountainous areas (Figure 10b). Therefore, a linear regression method is used to correct the precipitation from the M-FNN dataset. The CLDAS dataset spans the period from 1998 to 2022, whereas the M-FNN dataset covers the period from 1990 to 2022. To construct the linear regression model, we extracted the corresponding precipitation data from both datasets for the period of 1998–2022, using the CLDAS data as the dependent variable and the M-FNN data as the independent variable. For each grid, a separate linear regression model was established. The regression coefficients obtained were then applied to correct the entire M-FNN dataset’s precipitation data for the period of 1990–2022. The performances of M-FNN and the corrected M-FNN monthly precipitation estimates were evaluated against observations in Figure 10. The spatial distributions of annual precipitation show that the corrected M-FNN dataset shares similar spatial distributions and intensity of precipitation with observations (Figure 10c). For example, the large precipitation of Ayakkum Lake (37°N, 89°E; [44]) is well simulated in the corrected M-FNN dataset. Compared with CN05.1 (Figure 2i), the most commonly used dataset in China, the corrected M-FNN is capable of simulating the precipitation belt in the Kunlun and Tianshan mountain region.
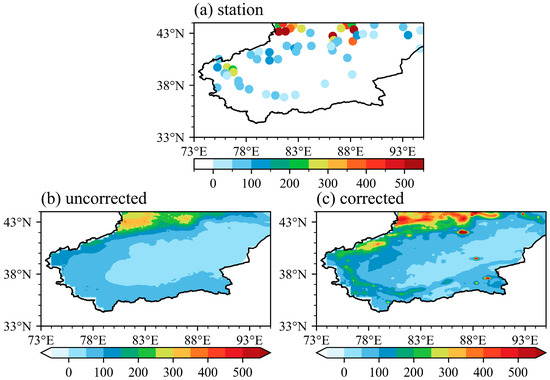
Figure 10.
Spatial patterns of the mean annual precipitation of (a) observations, (b) M-FNN, and (c) the corrected M-FNN dataset during the period from 1990 to 2022 over the Tarim Basin.
Precipitation estimated from corrected M-FNN dataset shows consistent interannual variations and has a similar magnitude with observations (Figure 11a,b). Except for the underestimation of the extreme values in a few months, such as the summer of 2021, the precipitation in other months is basically consistent with observations. Uncorrected M-FNN dataset underestimate precipitation over the Tarim Basin and shows much lower values compared with observations, which may be due to underestimation near mountainous areas (Figure 11a). From the perspective of annual precipitation, the correlation coefficients between the corrected M-FNN and the uncorrected M-FNN and the observations both reach above 0.9. However, the corrected M-FNN is closer to the observed precipitation intensity (Figure 11b). Figure 11c shows mean annual cycle of precipitation in the Tarim Basin. The underestimation of uncorrected M-FNN dataset occurs throughout the year, but the corrected M-FNN dataset is better at simulating the seasonal cycle of precipitation (Figure 11c).
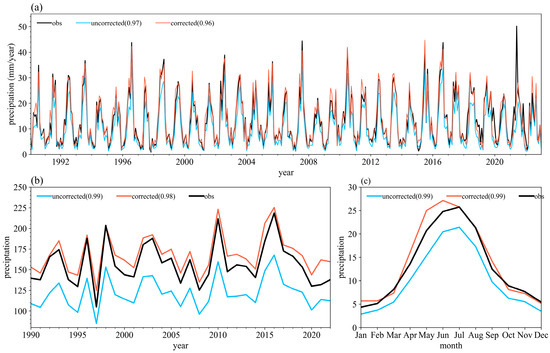
Figure 11.
(a) Monthly precipitation, (b) annual precipitation, and (c) mean annual cycle of observations incorporating the M-FNN and corrected M-FNN datasets in the Tarim Basin.
To access the accuracy of the precipitation–elevation relationship in the corrected M-FNN dataset, two lines around the Tarim Basin with significant elevation gradients were selected (Figure 12). The first line is located in the southwestern Tarim Basin–Pamir Plateau region and includes precipitation data from 14 automatic meteorological stations. These 14 stations are distributed from north to south, with elevations rising from 1200 m to 3700 m, showing a large gradient change. The second line is in the northern Tarim Basin–Tianshan region and comprises 23 automatic meteorological stations. These stations are distributed from west to east, with elevations rising from 1000 m to 3400 m and then falling to 800 m.
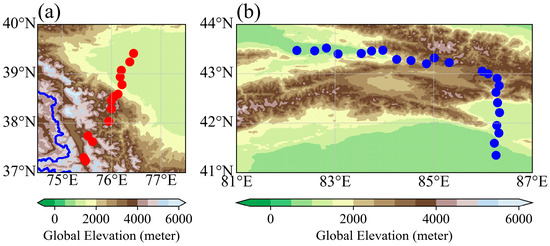
Figure 12.
Test lines (a) in the Pamir Plateau area and (b) Tianshan area with a large elevation gradient around the Tarim Basin. Red (blue) dots represent ground-based automatic stations in the Pamir Plateau area (Tianshan area).
Given that CN05.1 exhibits the best performance among the eight precipitation datasets, its simulation is superior in both spatial distribution and temporal variation. Therefore, a comparison between CN05.1 and the corrected merged precipitation dataset (monthly high-resolution precipitation dataset for the Tarim Basin, MoHiPr-TB) was conducted to see how they perform in a simulation of the precipitation–elevation relationship. In different years, the precipitation initially increases with elevation and then decreases when the elevation exceeds 3000 m (Figure 13). The MoHiPr-TB can simulate part of this relationship between precipitation and elevation. Although the precipitation intensity is underestimated in some stations (Y8963), the overall trend of precipitation increasing and then decreasing with elevation is generally captured. In contrast, CN05.1 performs poorly in simulating the precipitation–elevation relationship. The precipitation of CN05.1 shows a trend of continuous increase with the rise of elevation. When the elevation is below 2000 m, its simulation of the precipitation intensity is relatively accurate. However, there is a certain bias when the elevation exceeds 2000 m (Figure 13). Similar results can also be obtained in the Tianshan Mountains (Figure 14). MoHiPr-TB can roughly simulate the relationship between precipitation and elevation during 2016–2019 (Figure 14). However, unlike the characteristic of precipitation in the Pamir Plateau that first increases and then decreases with elevation, the elevation in the Tianshan region first increases and then decreases, and precipitation also shows a trend of first increasing and then decreasing. This synchronous change of precipitation and elevation can be well captured in MoHiPr-TB, and the intensity of precipitation is also basically close to the observations. In contrast, CN05.1 fails to simulate this synchronous change between precipitation and elevation and overestimates the intensity of precipitation in most stations.
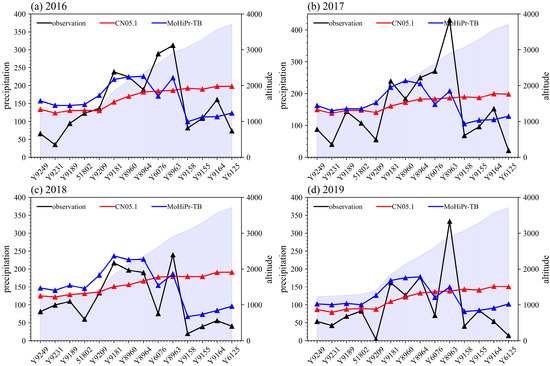
Figure 13.
The precipitation characteristics in topographic profiles of the Pamir Plateau in (a) 2016, (b) 2017, (c) 2018, and (d) 2019 based on observations, CN05.1, and MoHiPr-TB. Marked lines represent precipitation, blue shading indicates the elevation.
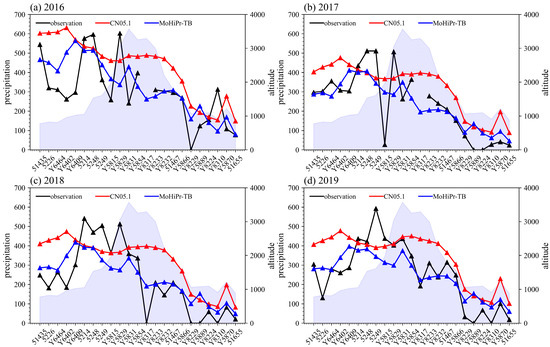
Figure 14.
The precipitation characteristics in topographic profiles of the Tianshan area in (a) 2016, (b) 2017, (c) 2018, and (d) 2019 based on observations, CN05.1, and MoHiPr-TB. Marked lines represent precipitation, blue shading indicates the elevation.
The excellent performance of MoHiPr-TB can also be seen from the absolute error of precipitation in the Pamir Plateau (Figure 15a) and the Tianshan region (Figure 15b). During 2016–2019, the average absolute error of precipitation between observations and MoHiPr-TB is not much different from that of CN05.1 in the Pamir Plateau (Figure 15a). However, in the Tianshan region, MoHiPr-TB outperforms CN05.1 significantly. Specifically, in 2016, 2017, 2018, and 2019, the average absolute error between observed precipitation and MoHiPr-TB is significantly lower than that of CN05.1, and the 25th, 50th, and 75th percentiles of precipitation absolute error are also lower than those of CN05.1 (Figure 15b). This indicates that MoHiPr-TB not only outperforms CN05.1 in simulating the relationship between precipitation and elevation, but also its bias is smaller than that of CN05.1.
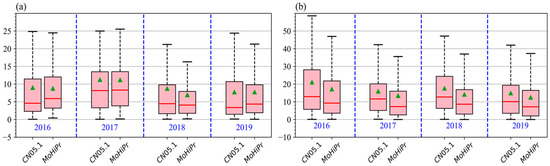
Figure 15.
Box plots of absolute error of precipitation for CN05.1 and MoHiPr-TB at independent automatic meteorological stations in the (a) Pamir Plateau and (b) Tianshan area. Red lines in boxes show median values. Boxes indicate the inter-quantile range (25–75%). Green triangle in boxes indicate the averages of all anomaly values.
4. Discussions
This study focuses on the fusion of multi-source precipitation datasets within the Tarim Basin, a typical arid region, thereby offering novel perspectives and robust data support for precipitation-related research. Prior investigations into the precipitation characteristics of the Tarim Basin were predominantly based on single-source data or relied on more conventional statistical methodologies. In contrast, this study explores data fusion methods by comparing the performance of four distinct models—RF, LSTM, FNN, and SVM—when applied to the fusion of multi-source precipitation datasets. The results demonstrate that when the sample size is limited, a more complex model does not outperform a simpler one. For instance, the relatively simpler FNN model exhibits superior performance compared to the LSTM model. This phenomenon may be attributed to the fact that simpler models are less prone to overfitting, especially when dealing with smaller sample sizes. This significant finding holds substantial implications for precipitation data fusion in arid regions and serves as a valuable source of references for future studies when selecting appropriate data fusion models. This study also obtained a more accurate precipitation–elevation relationship. In arid regions, precipitation is one of the key driving factors of the water cycle, and its spatial distribution is closely related to elevation. A more precise precipitation–elevation relationship can provide more reasonable precipitation inputs for hydrological models, thereby improving the accuracy of these models in simulating runoff, groundwater recharge, and other processes. This advancement carries practical significance for the rational development, utilization, and protection of water resources in arid regions.
Despite the achievements made in precipitation data fusion in this study, there are still some limitations. First, the observation stations in the Tarim Basin are relatively sparse, which limits the spatial resolution of the data. Second, there is inherent uncertainty in the CLDAS2.0 data, and its intrinsic errors may have been transferred to the fused data, thereby affecting the quality of the final precipitation data. In addition, the dataset obtained in this study is on a monthly scale, and this relatively low temporal resolution restricts its application in extreme event analysis. Future research can be expanded in the following directions. First, the development of a daily-scale dataset is of utmost urgency. Data with higher temporal resolution can better capture the characteristics of extreme precipitation events, which is crucial for improving the ability to predict extreme events. Secondly, exploring the application of more advanced deep learning models in data fusion is also an important direction for future research.
5. Conclusions
This study collected eight multi-source gridded precipitation datasets and merged them to generate a comprehensive precipitation dataset covering the period from 1990 to 2022, which was subsequently bias-corrected using CLDAS2.0. First, the RF, LSTM, FNN, and SVM models were employed to generate four station datasets: M-RF, M-LSTM, M-FNN, and M-SVM. Second, the precipitation estimates of the four merged datasets were evaluated based on gauge observations. The evaluation results indicate that, compared with M-RF, M-LSTM, and M-SVM, M-FNN outperforms the others in simulating the spatial distribution of precipitation, interannual and seasonal variations, and precipitation intensity. Consequently, a monthly high-resolution (0.1°) precipitation dataset for the Tarim Basin (MoHiPr-TB) was produced by merging eight gridded multi-source precipitation datasets using the trained FNN model. The MoHiPr-TB dataset was bias-corrected using the CLDAS2.0, which provides more realistic precipitation estimates compared to other datasets.
The validation indicates that MoHiPr-TB not only accurately captures the spatial distribution of precipitation but also efficiently simulates interannual and seasonal variations and precipitation intensity. Furthermore, compared with the CN05.1 dataset, MoHiPr-TB demonstrates higher accuracy in detecting the relationship between precipitation and elevation. Although there is a certain underestimation of precipitation intensity at some stations in MoHiPr-TB, it successfully captures the overall trend of precipitation increasing and then decreasing with elevation in the Pamir Plateau region, as well as the synchronous change trend with elevation in the Tianshan region. The average absolute error of precipitation simulated by M-FNN is also significantly lower than that of CN05.1. The MoHiPr-TB dataset will provide strong support for determining climate change in the Tarim Basin and can also be used to improve numerical models in meteorological, hydrological, and ecological studies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.C. and J.Y.; methodology, P.C.; software, J.C.; validation, J.C.; formal analysis, P.C.; investigation, P.C.; resources, M.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, P.C.; writing—review and editing, W.M.; supervision, L.M. and B.S.; funding acquisition, P.C. and J.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (2022D01B232), the Science and Technology Youth Top-notch Talent Support Program (Tianshan Talents) of Xinjiang (2022TSYCCX0005), the Third Xinjiang Scientific Expedition Program (2022xjkk0101), the Grassland Ecological Restoration and Management Technology Support Project (XJCYZZXZ202401).
Data Availability Statement
The PERSIANN-CDR data is available at https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/data/precipitation-persiann/access/ (accessed on 15 January 2024). The CHIRPS data is available at https://data.chc.ucsb.edu/products/CHIRPS-2.0/global_monthly/netcdf/byYear/ (accessed on 12 January 2024). The GPCP data is available at https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/data/global-precipitation-climatology-project-gpcp-monthly/access/ (accessed on 2 February 2024). The CRA40-Land data is available at http://data.cma.cn/analysis/cra40 (accessed on 13 January 2024). The ERA5 data is available at https://cds.climate.copernicus.eu/cdsapp#!/dataset/reanalysis-era5-single-levels-monthly-means?tab=form (accessed on 27 June 2023). The CPC data is available at https://ftp.cpc.ncep.noaa.gov/precip/CPC_UNI_PRCP/GAUGE_GLB/V1.0/ (accessed on 22 January 2024). The GPCC data is available at https://opendata.dwd.de/climate_environment/GPCC/monitoring_v2022/ (accessed on 19 February 2024).
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region Meteorological Service (http://xj.cma.gov.cn/) for providing the observed climate data (CLDAS2.0 and ground automatic station data).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Huang, W.; Feng, S.; Chen, J.; Chen, F. Physical Mechanisms of Summer Precipitation Variations in the Tarim Basin in Northwestern China. J. Clim. 2015, 28, 3579–3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Ding, Y.; Liu, W.; Li, Z. 1 Km Monthly Temperature and Precipitation Dataset for China from 1901 to 2017. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2019, 11, 1931–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, C.; Huang, D.; Xu, H.; Xu, Z. Evaluation of ERA5 Reanalysis over the Deserts in Northern China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2023, 151, 801–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, M.; Kang, S.; Li, X.; Han, H.; Li, X. Comprehensive Applicability Evaluation of Four Precipitation Products at Multiple Spatiotemporal Scales in Northwest China. J. Arid Land 2024, 16, 1232–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Shang, K.; Kang, Y.; Jia, X.; Wu, Z. Preliminary analysis of precipitation characteristics in the Badain Jaran and Tengger Desert. J. Arid Meteorol. 2016, 34, 261–268. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, G.; Luo, M.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, S.; Liu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wu, S.; Zeng, Z. Understanding the Mechanisms of Summer Extreme Precipitation Events in Xinjiang of Arid Northwest China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2021, 126, e2020JD034111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, S.; Wang, J.; Jin, J.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Song, F.; Zhang, L. Comprehensive Evaluation of Satellite-Derived Precipitation Products Considering Spatial Distribution Difference of Daily Precipitation over Eastern China. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2022, 44, 101242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Shao, H.; Yang, X.; Liu, G.; Xin, Q.; Gu, J. Optimization and Simulation of Flat Area Sites Based on Probability Matching and Transfer Intensity Using Remote Sensing Precipitation. Water Resour. Res. 2025, 61, e2024WR038622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Braithwaite, D.; Hsu, K.; Kidd, R.J.C.; Nelkin, E.J.; Sorooshian, S.; Tan, J.; Xie, P. NASA Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Integrated Multi-satellitE Retrievals for GPM (IMERG). In Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document (ATBD) Version 06; NASA/GSFC: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2019; 38p. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Li, Z.; Song, Y.; Duan, Z.; Mo, K.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Q. Performance of Multiple Satellite Precipitation Estimates over a Typical Arid Mountainous Area of China: Spatiotemporal Patterns and Extremes. J. Hydrometeorol. 2020, 21, 533–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashouri, H.; Hsu, K.-L.; Sorooshian, S.; Braithwaite, D.K.; Knapp, K.R.; Cecil, L.D.; Nelson, B.R.; Prat, O.P. PERSIANN-CDR: Daily Precipitation Climate Data Record from Multisatellite Observations for Hydrological and Climate Studies. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funk, C.; Peterson, P.; Landsfeld, M.; Pedreros, D.; Verdin, J.; Shukla, S.; Husak, G.; Rowland, J.; Harrison, L.; Hoell, A.; et al. The Climate Hazards Infrared Precipitation with Stations—A New Environmental Record for Monitoring Extremes. Sci. Data 2015, 2, 150066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, R.J.; Janowiak, J.E.; Arkin, P.A.; Xie, P. CMORPH: A Method That Produces Global Precipitation Estimates from Passive Microwave and Infrared Data at High Spatial and Temporal Resolution. J. Hydrometeorol. 2004, 5, 487–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, W. Evaluation of Satellite and Reanalysis Precipitable Water Vapor Data Sets Against Radiosonde Observations in Central Asia. Earth Space Sci. 2019, 6, 1129–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, R.; Sapiano, M.; Huffman, G.; Wang, J.-J.; Gu, G.; Bolvin, D.; Chiu, L.; Schneider, U.; Becker, A.; Nelkin, E.; et al. The Global Precipitation Climatology Project (GPCP) Monthly Analysis (New Version 2.3) and a Review of 2017 Global Precipitation. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 Global Reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Chen, M.; Yang, S.; Yatagai, A.; Hayasaka, T.; Fukushima, Y.; Liu, C. A Gauge-Based Analysis of Daily Precipitation over East Asia. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 607–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Shi, W.; Xie, P.; Silva, V.B.S.; Kousky, V.E.; Wayne Higgins, R.; Janowiak, J.E. Assessing Objective Techniques for Gauge-based Analyses of Global Daily Precipitation. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, 2007JD009132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilinuer, T.; Yao, J.; Chen, J.; Zhao, Y.; Mao, W.; Li, J.; Yang, L. Systematical Evaluation of Three Gridded Daily Precipitation Products Against Rain Gauge Observations Over Central Asia. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 9, 699628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Jin, L. Summary of meteorological field experiments in the Taklimakan Desert, China. J. Xinjiang Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed. Chin. Eng.) 2021, 38, 334–354. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Yang, X.; Wang, L.; Baig, M.H.A.; Chi, W.; Wang, Z. Evaluation of Spatial and Temporal Performances of ERA-Interim Precipitation and Temperature in Mainland China. J. Clim. 2018, 31, 4347–4365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, N. Evaluation of Eight High-Resolution Gridded Precipitation Products in the Heihe River Basin. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Z.; Han, Z.; Li, X.; Long, D.; Tang, G.; Wang, J. Generation of an Improved Precipitation Data Set from Multisource Information over the Tibetan Plateau. J. Hydrometeorol. 2021, 22, 1275–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Xu, J.; Ma, Y.; Zhu, S.; He, K.; Zhang, S.; Ma, W.; Xu, X. AERA5-Asia: A Long-Term Asian Precipitation Dataset (0.1°, 1-Hourly, 1951–2015, Asia) Anchoring the ERA5-Land under the Total Volume Control by APHRODITE. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2022, 103, E1146–E1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Yang, K.; Qi, Y.; Zhou, X.; He, J.; Lu, H.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Zhou, B.; et al. TPHiPr: A Long-Term (1979–2020) High-Accuracy Precipitation Dataset (1∕30°, Daily) for the Third Pole Region Based on High-Resolution Atmospheric Modeling and Dense Observations. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2023, 15, 621–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Miao, C.; Gou, J.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, X. A New Daily Gridded Precipitation Dataset for the Chinese Mainland Based on Gauge Observations. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2023, 15, 3147–3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Zheng, D.; Zhang, K.; Ma, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Ge, Y. Merging Multiple Satellite-Based Precipitation Products and Gauge Observations Using a Novel Double Machine Learning Approach. J. Hydrol. 2021, 594, 125969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baez-Villanueva, O.M.; Zambrano-Bigiarini, M.; Beck, H.E.; McNamara, I.; Ribbe, L.; Nauditt, A.; Birkel, C.; Verbist, K.; Giraldo-Osorio, J.D.; Xuan Thinh, N. RF-MEP: A Novel Random Forest Method for Merging Gridded Precipitation Products and Ground-Based Measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 239, 111606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Li, W.; Jiang, Q.; Sun, W.; Wen, J.; Gao, J. A Comparative Study of Four Merging Approaches for Regional Precipitation Estimation. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 33625–33637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Gao, X.J. A gridded daily observation dataset over China region and comparison with the other datasets. Chin. J. Geophys. 2013, 56, 1102–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, U.; Hänsel, S.; Finger, P.; Rustemeier, E.; Ziese, M. GPCC Full Data Monthly Version 2022 at 1.0°: Monthly Land-Surface Precipitation from Rain-Gauges Built on GTS-Based and Historic Data: Globally Gridded Monthly Totals 2022, min. 20 MB-max. 300 MB Per Gzip Archive (10 Years Per Archive); Global Precipitation Climatology Centre (GPCC): Offenbach/Main, Germany, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Lu, H.; Yang, K.; He, J.; Wang, W.; Wright, J.S.; Li, C.; Han, M.; Li, Y. Evaluation of Multiple Forcing Data Sets for Precipitation and Shortwave Radiation over Major Land Areas of China. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 5805–5821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Qian, L.; Wang, W.; Huo, X.; Hu, X.; Wang, Y. Assessing and Comparing Reference Evapotranspiration across Different Climatic Regions of China Using Reanalysis Products. Water 2023, 15, 2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Shi, G.; Shangguan, W.; Nourani, V.; Li, J.; Li, L.; Huang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, D.; et al. A 1 Km Daily Soil Moisture Dataset over China Using in Situ Measurement and Machine Learning. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2022, 14, 5267–5286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari Asanjan, A.; Yang, T.; Hsu, K.; Sorooshian, S.; Lin, J.; Peng, Q. Short-Term Precipitation Forecast Based on the PERSIANN System and LSTM Recurrent Neural Networks. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 12543–12563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Yang, L.; Fu, Z. Reconstructing Coupled Time Series in Climate Systems Using Three Kinds of Machine-Learning Methods. Earth Syst. Dynam. 2020, 11, 835–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Liu, Y.; Xue, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Jiang, L.; Cheng, Z. Time-Series Well Performance Prediction Based on Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) Neural Network Model. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2020, 186, 106682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran Anh, D.; Van, S.P.; Dang, T.D.; Hoang, L.P. Downscaling rainfall using deep learning long short-term memory and feedforward neural network. Int. J. Climatol. 2019, 39, 4170–4188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, R.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, J.; Ye, J.-S.; Li, F.-M.; Zhang, F. HRLT: A High-Resolution (1 d, 1 Km) and Long-Term (1961–2019) Gridded Dataset for Surface Temperature and Precipitation across China. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2022, 14, 4793–4810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellit, A.; Pavan, A.M.; Benghanem, M. Least Squares Support Vector Machine for Short-Term Prediction of Meteorological Time Series. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2013, 111, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochenek, B.; Ustrnul, Z. Machine Learning in Weather Prediction and Climate Analyses—Applications and Perspectives. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, K.; Su, F.; Yang, D.; Hao, Z. Evaluation of Satellite Precipitation Retrievals and Their Potential Utilities in Hydrologic Modeling over the Tibetan Plateau. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 423–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Bai, J.; Wang, Y. Time series area of the Ayakkum Lake and its response to climate change. Arid Zone Res. 2018, 35, 85–95. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).