Twilight Near-Infrared Radiometry for Stratospheric Aerosol Layer Height
Abstract
1. Introduction
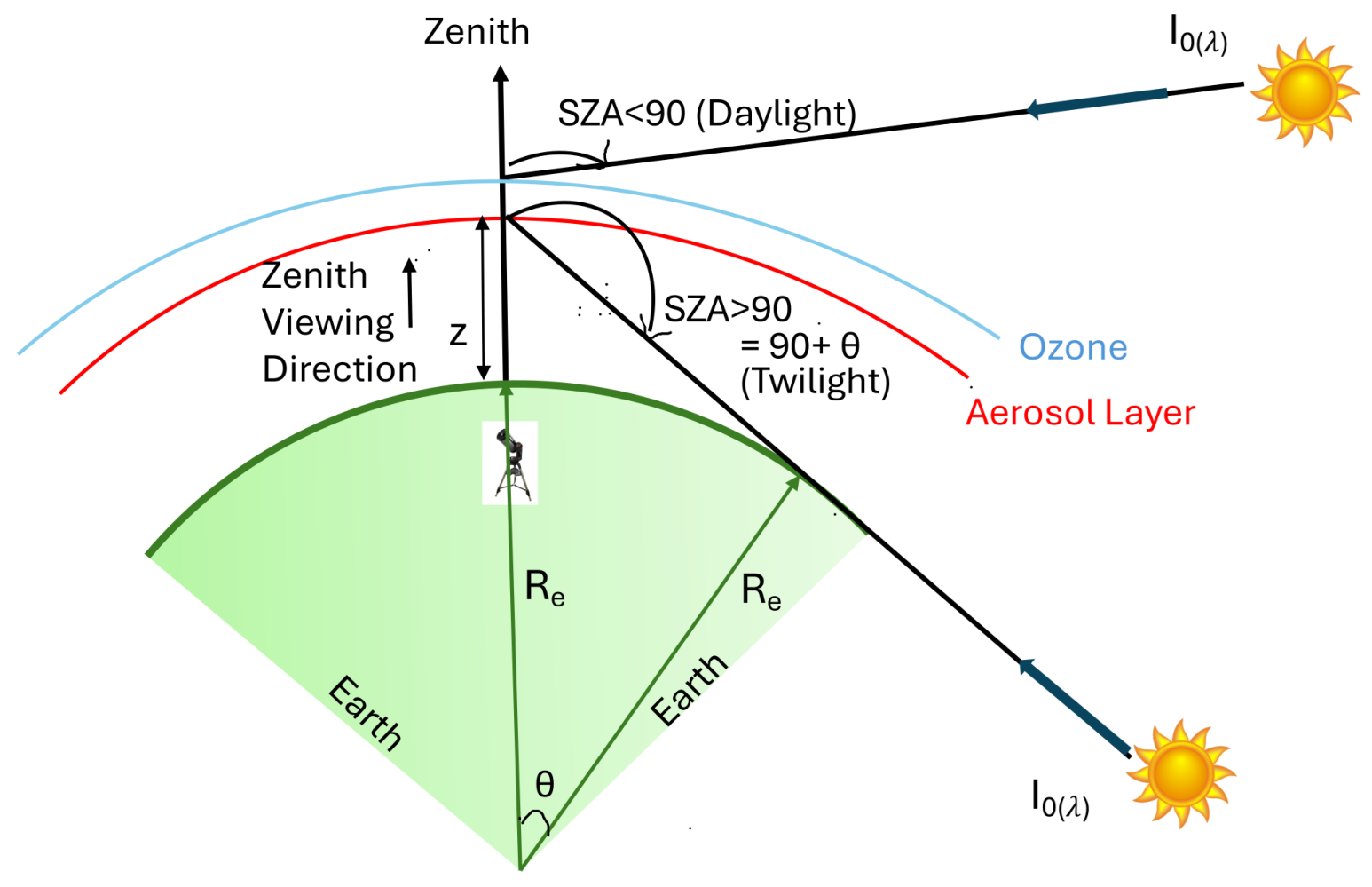
2. Twilight Radiometry
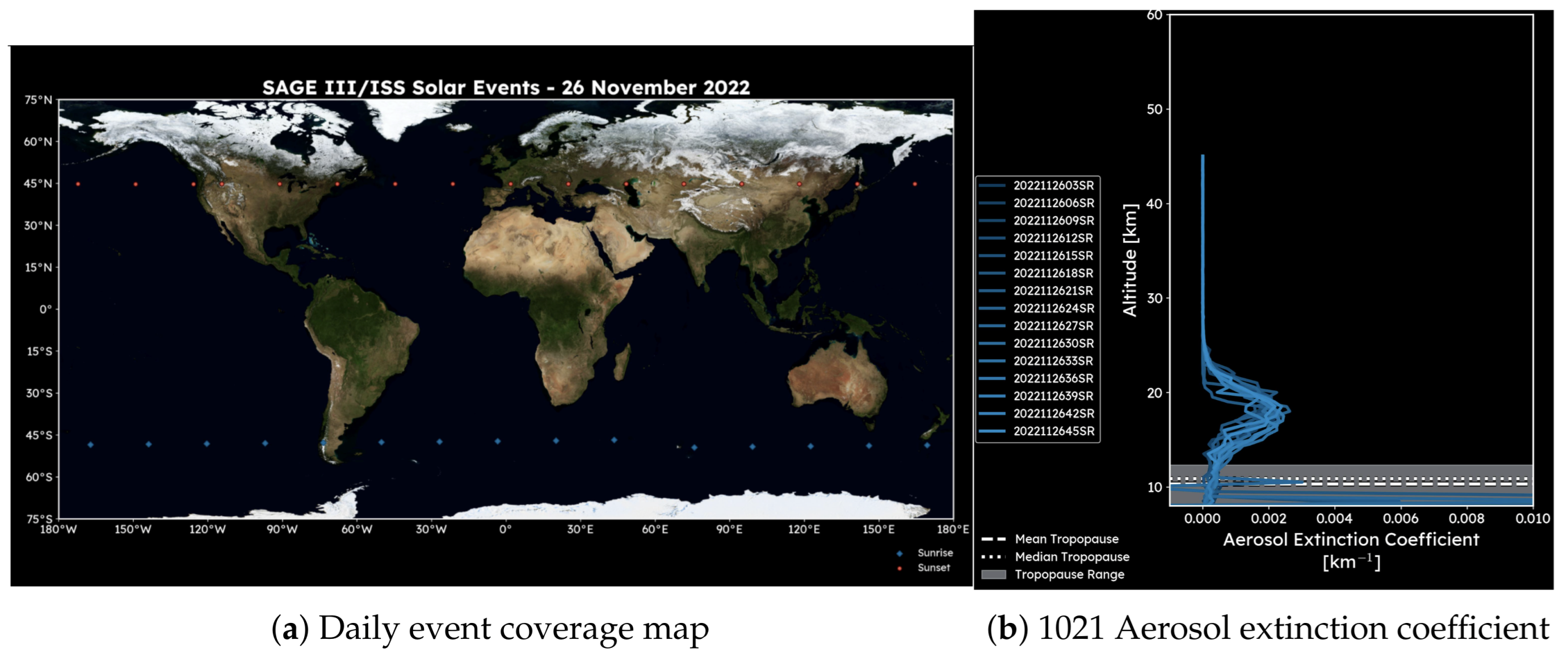
3. Data
4. Results
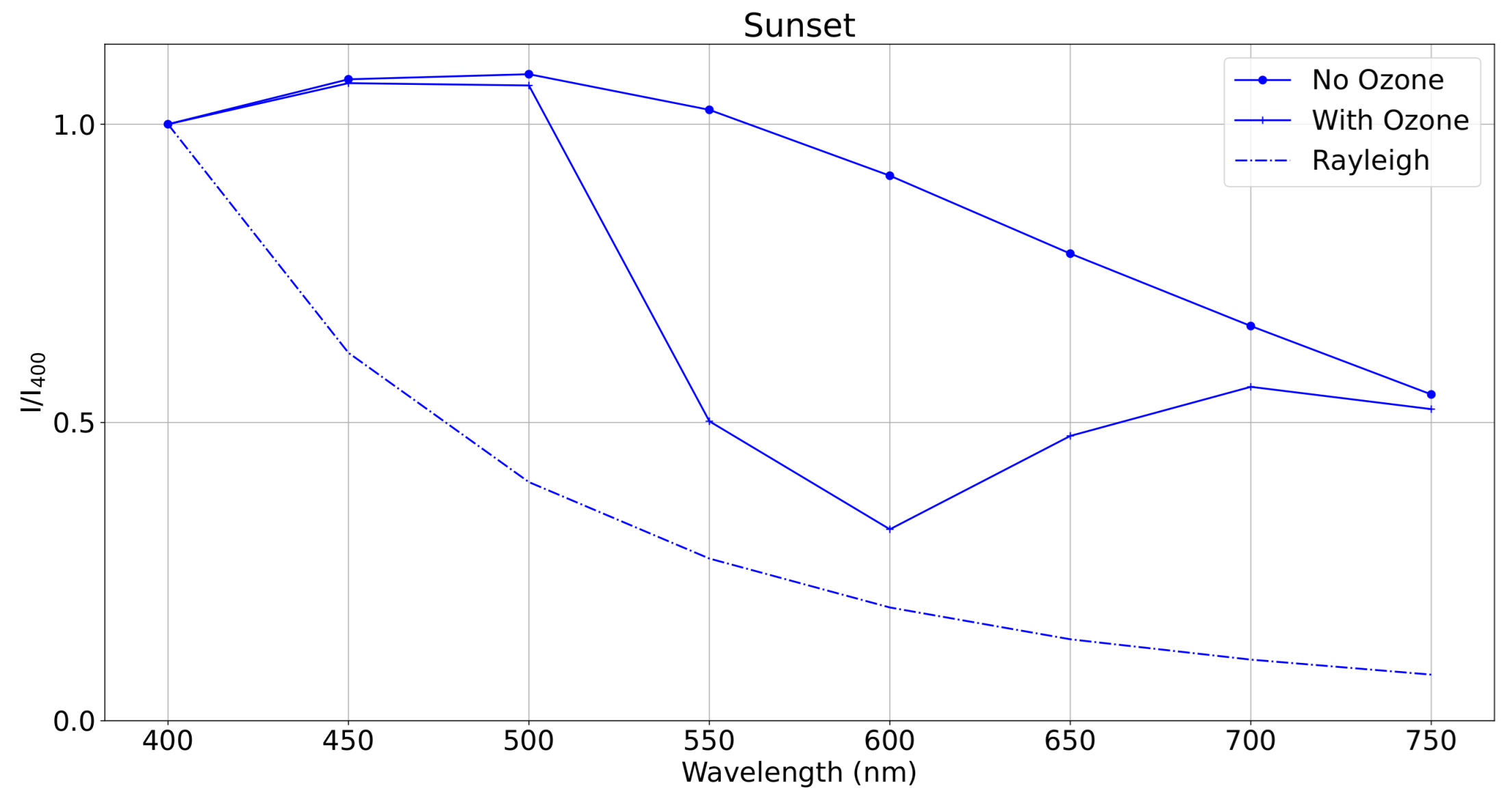
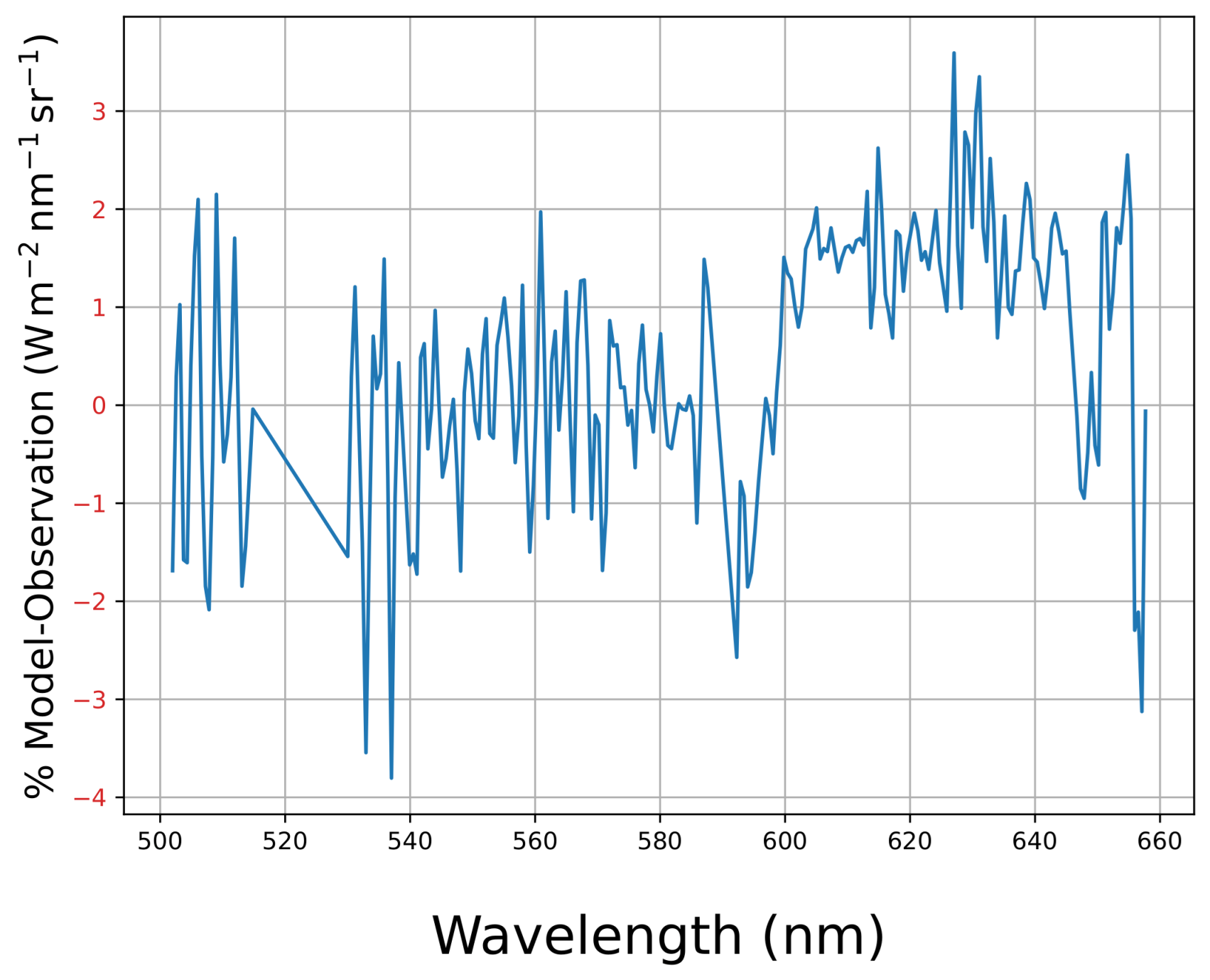
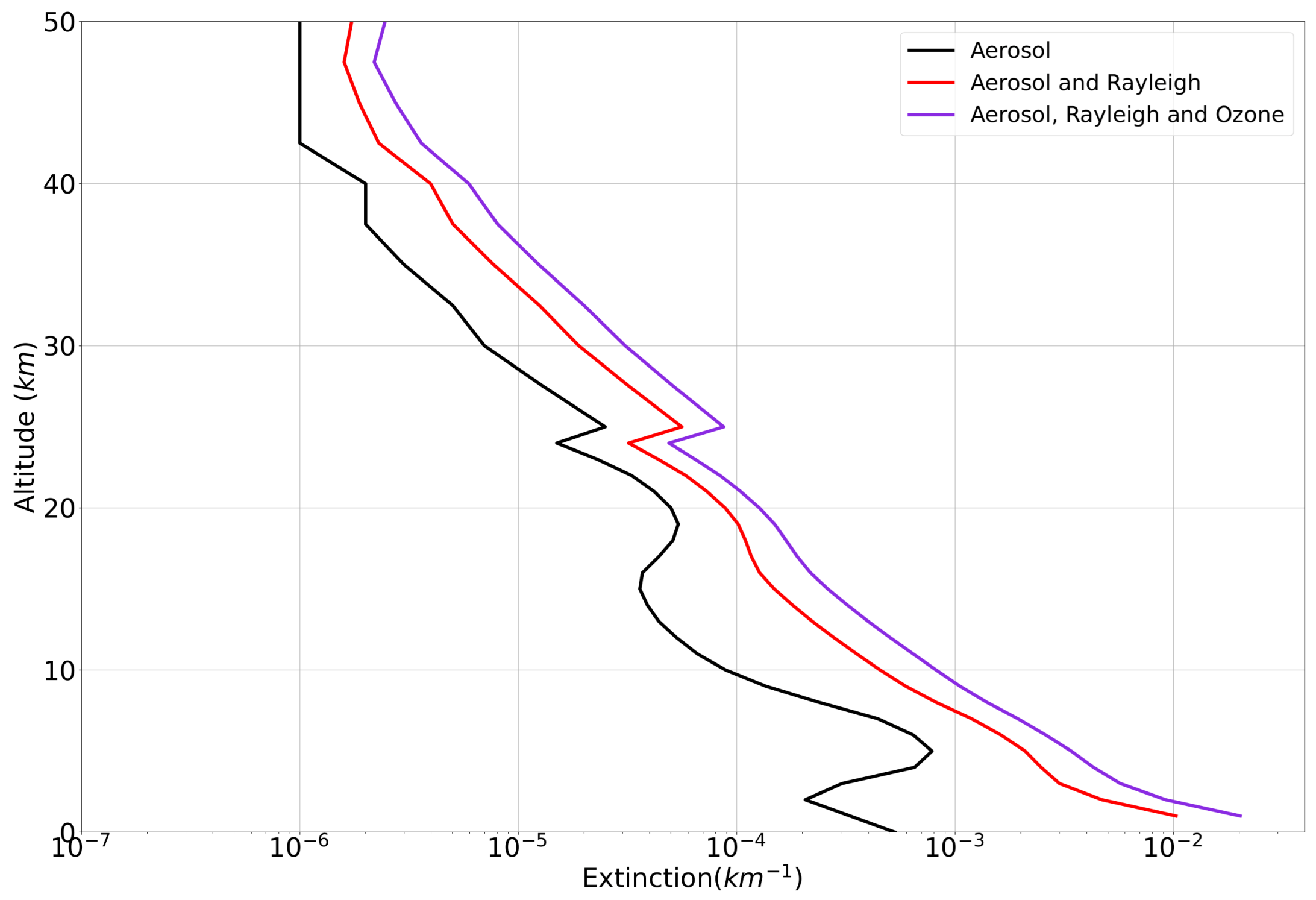
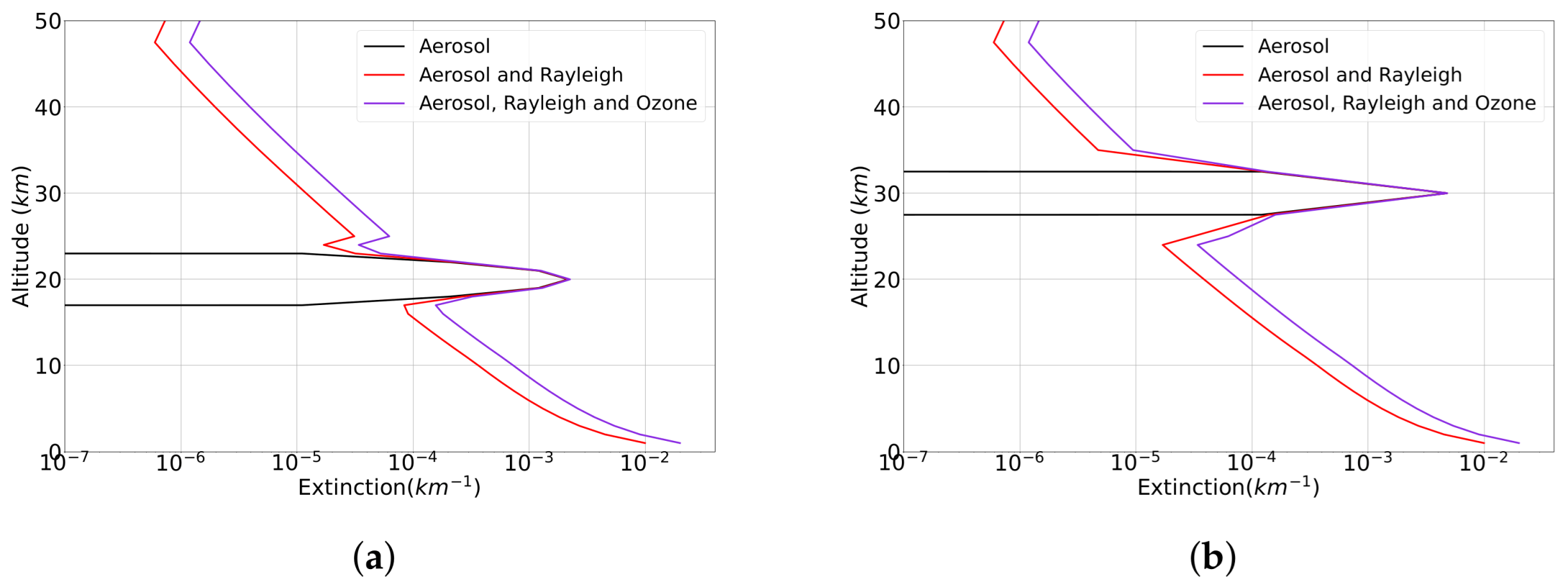
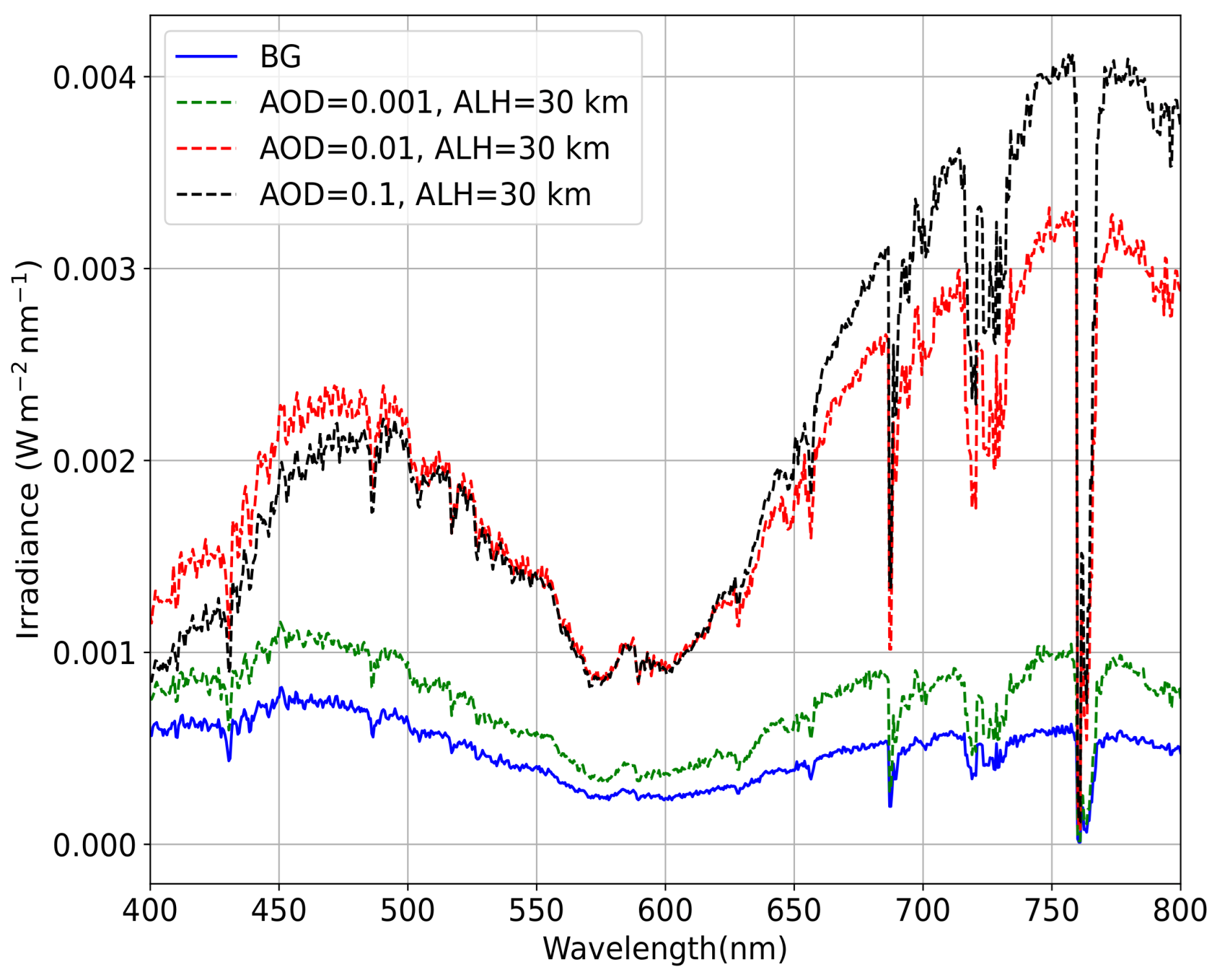
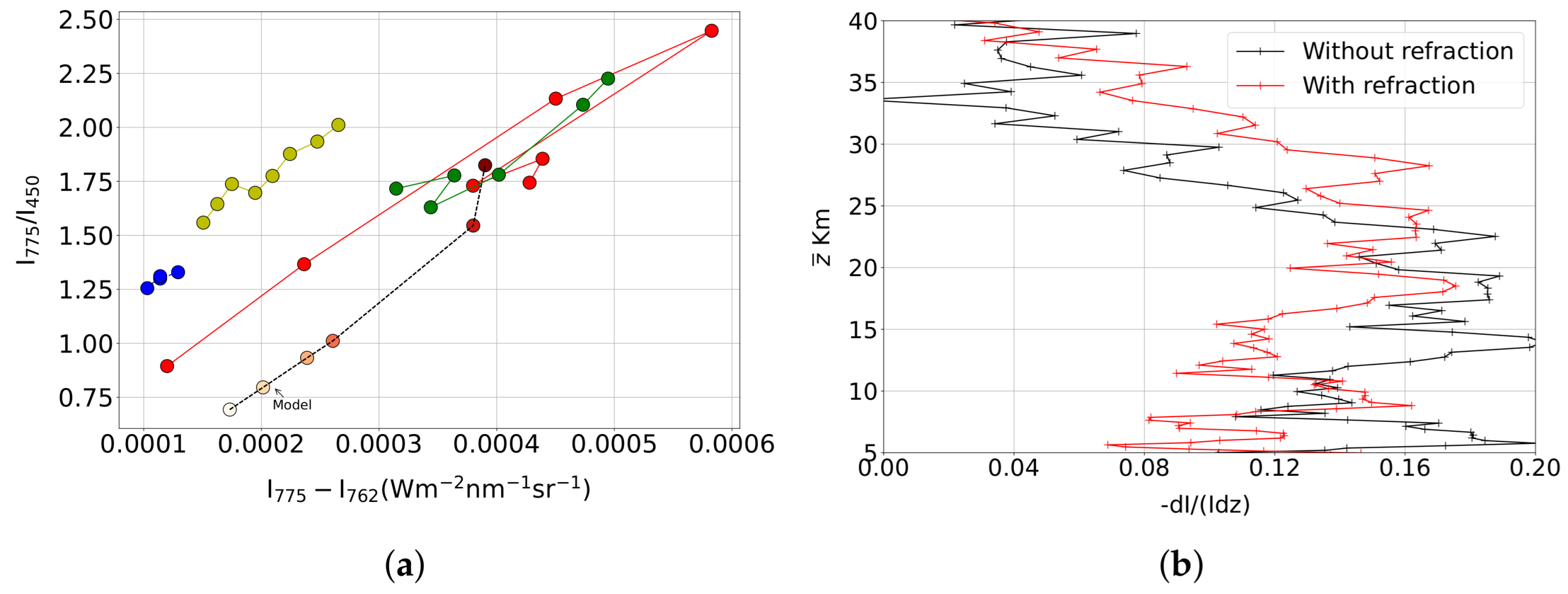
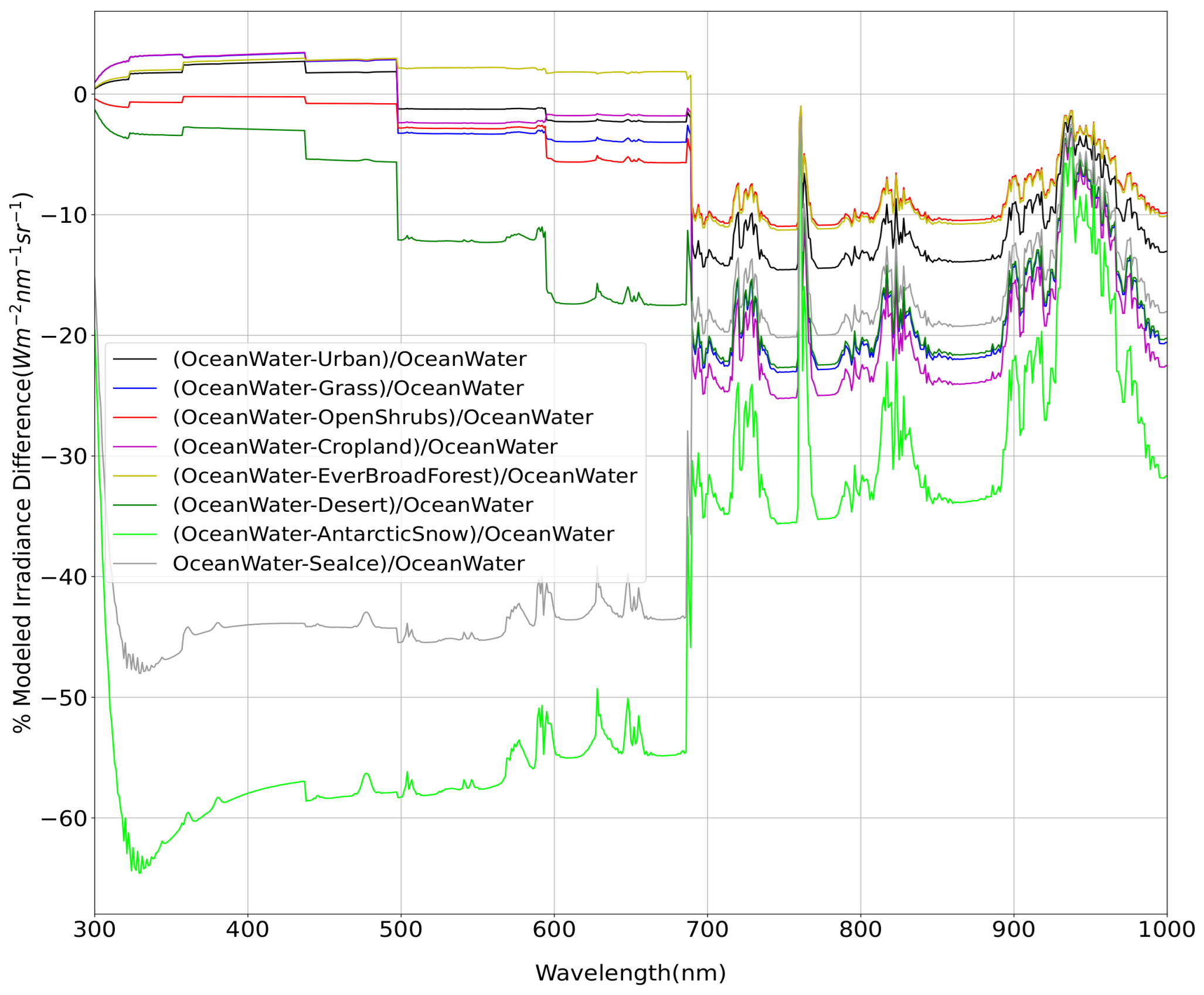
4.1. Model Simulation
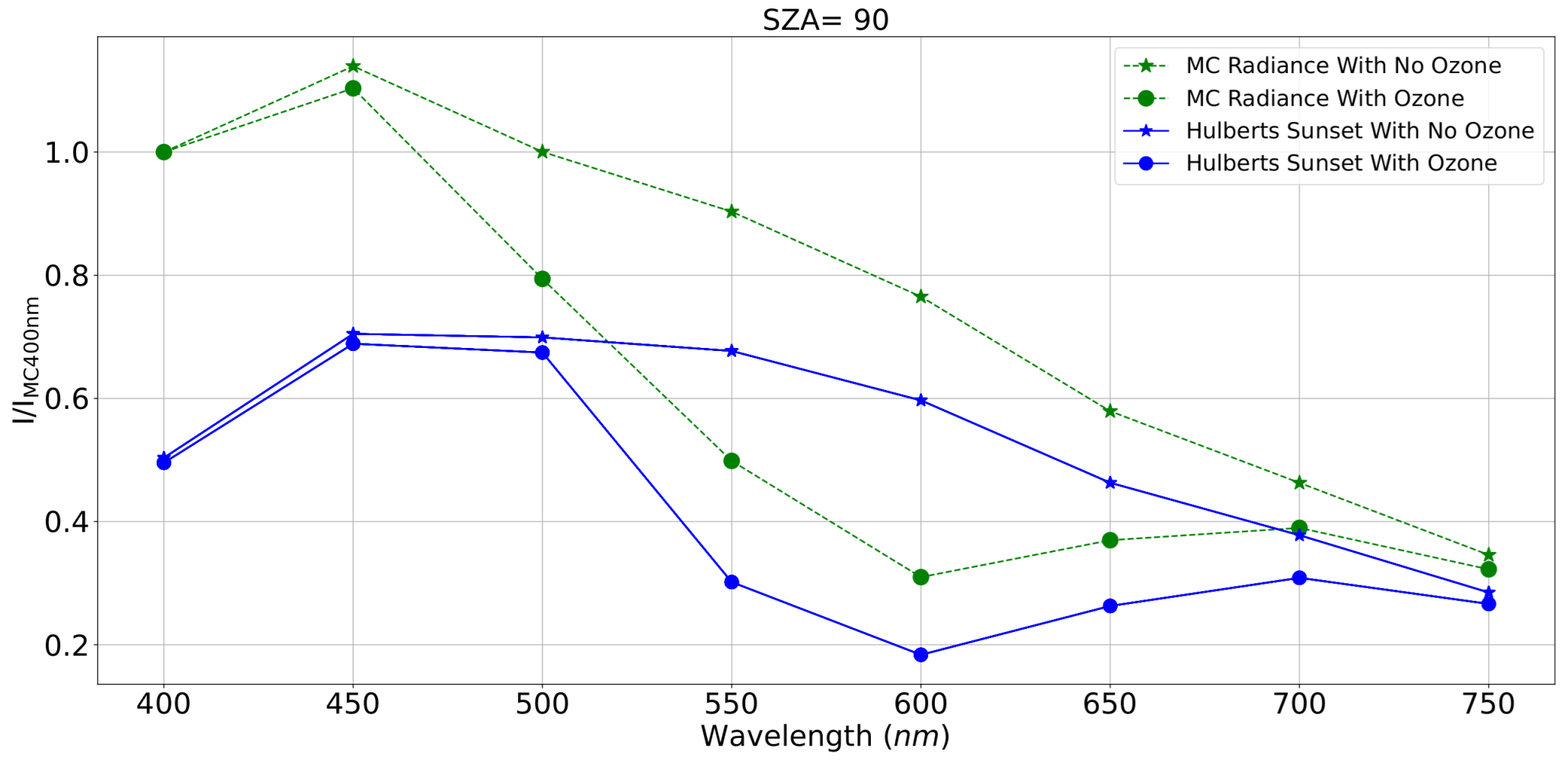
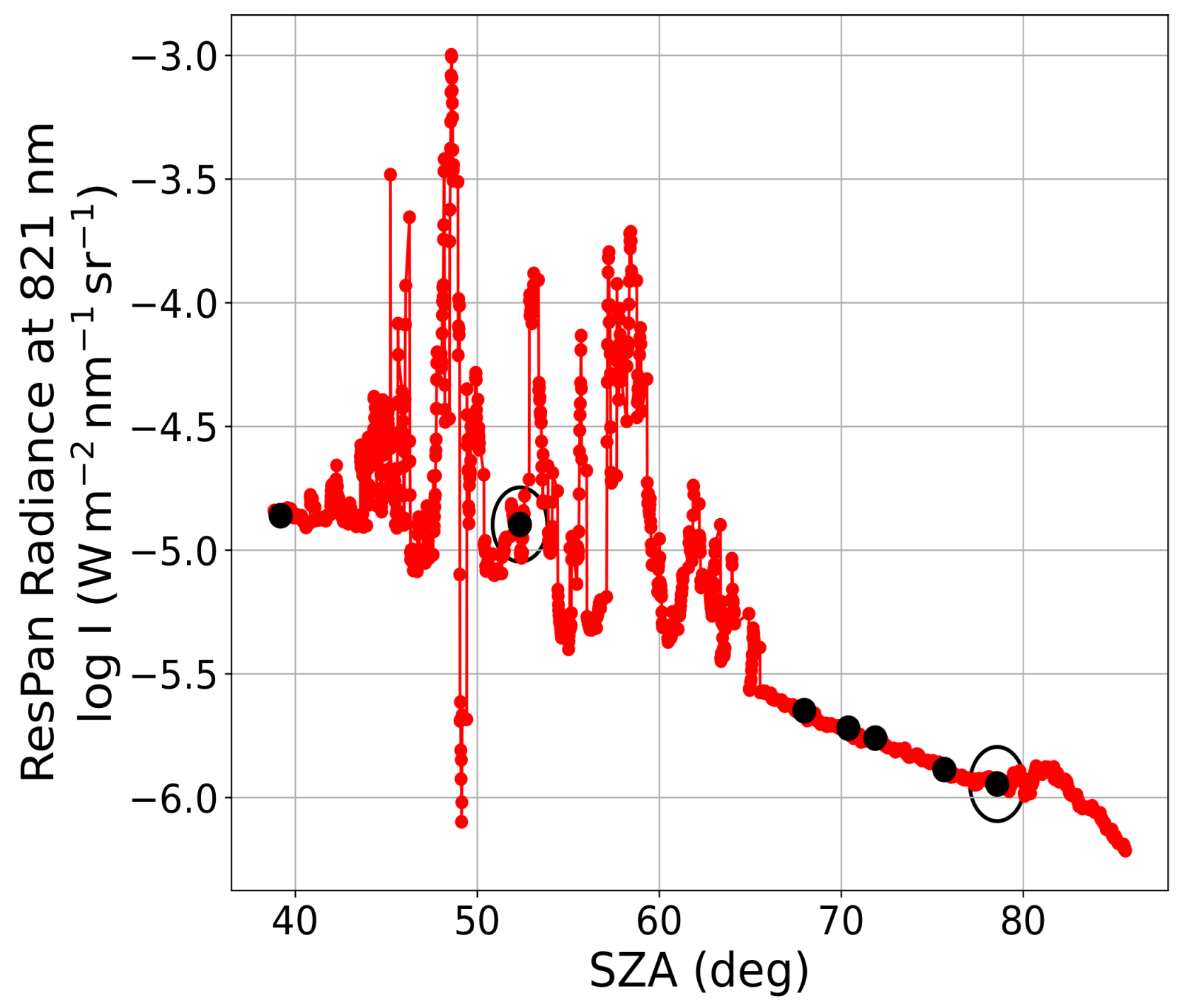
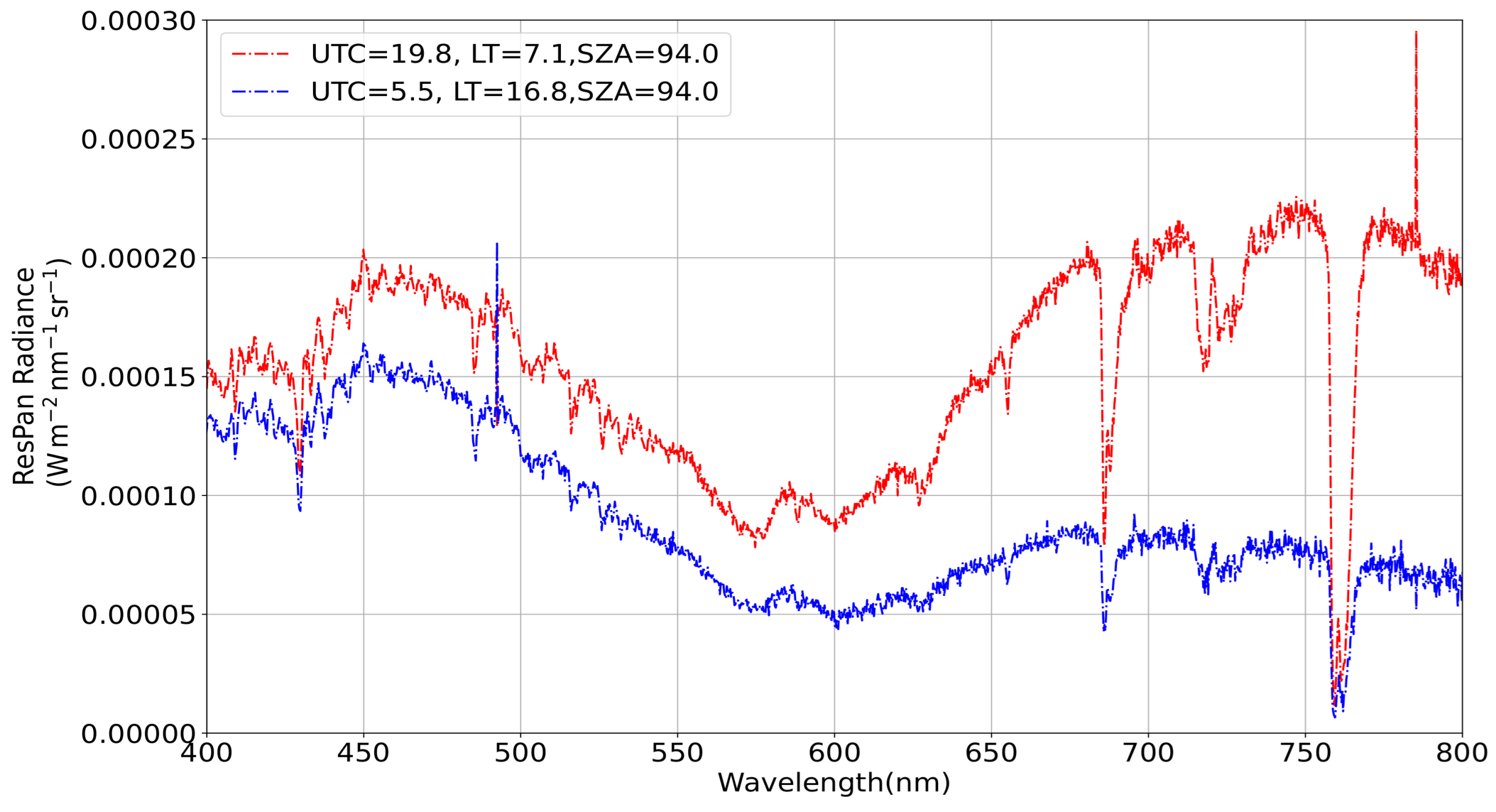
4.2. Daylight
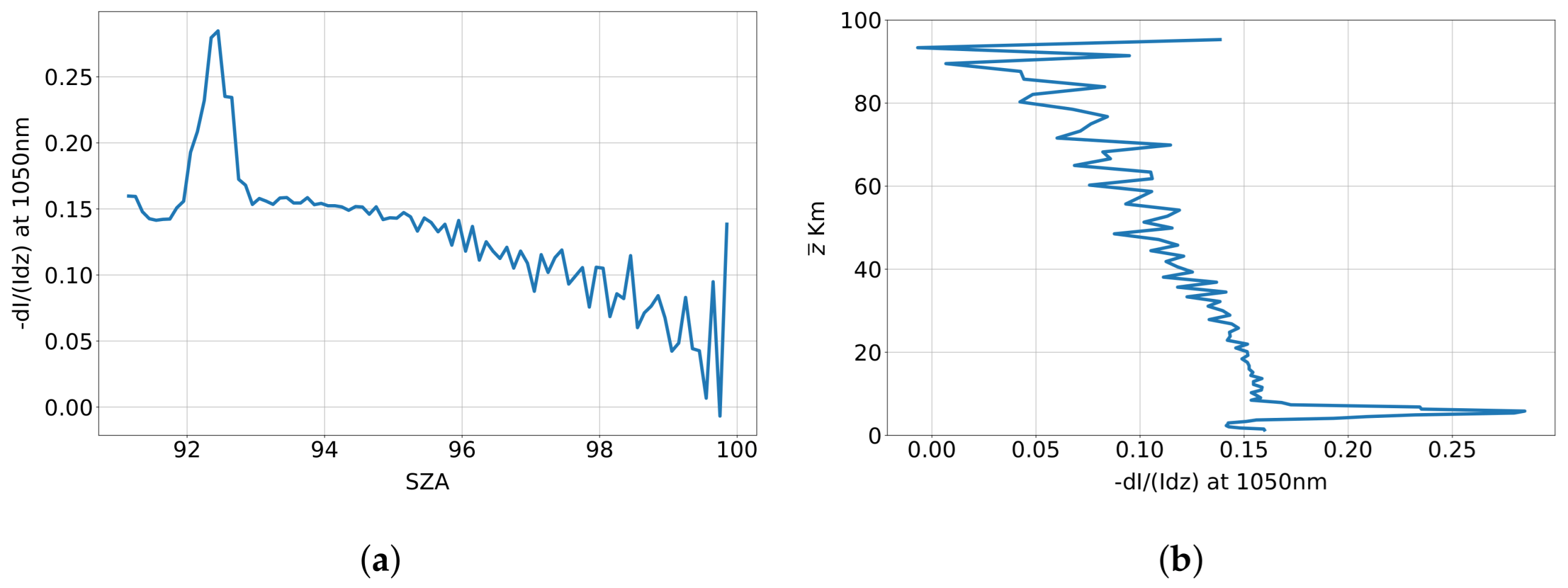
4.3. Twilight
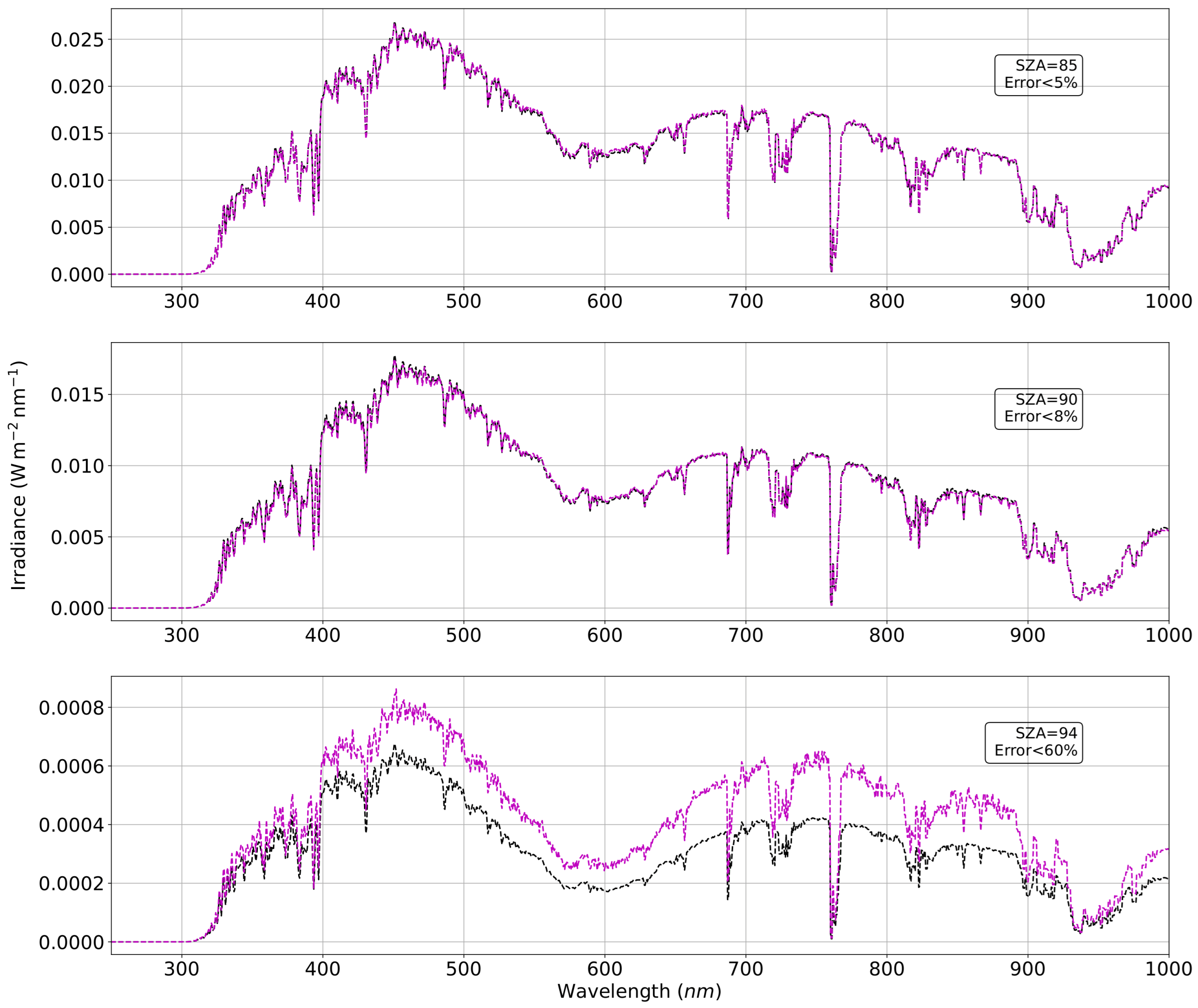
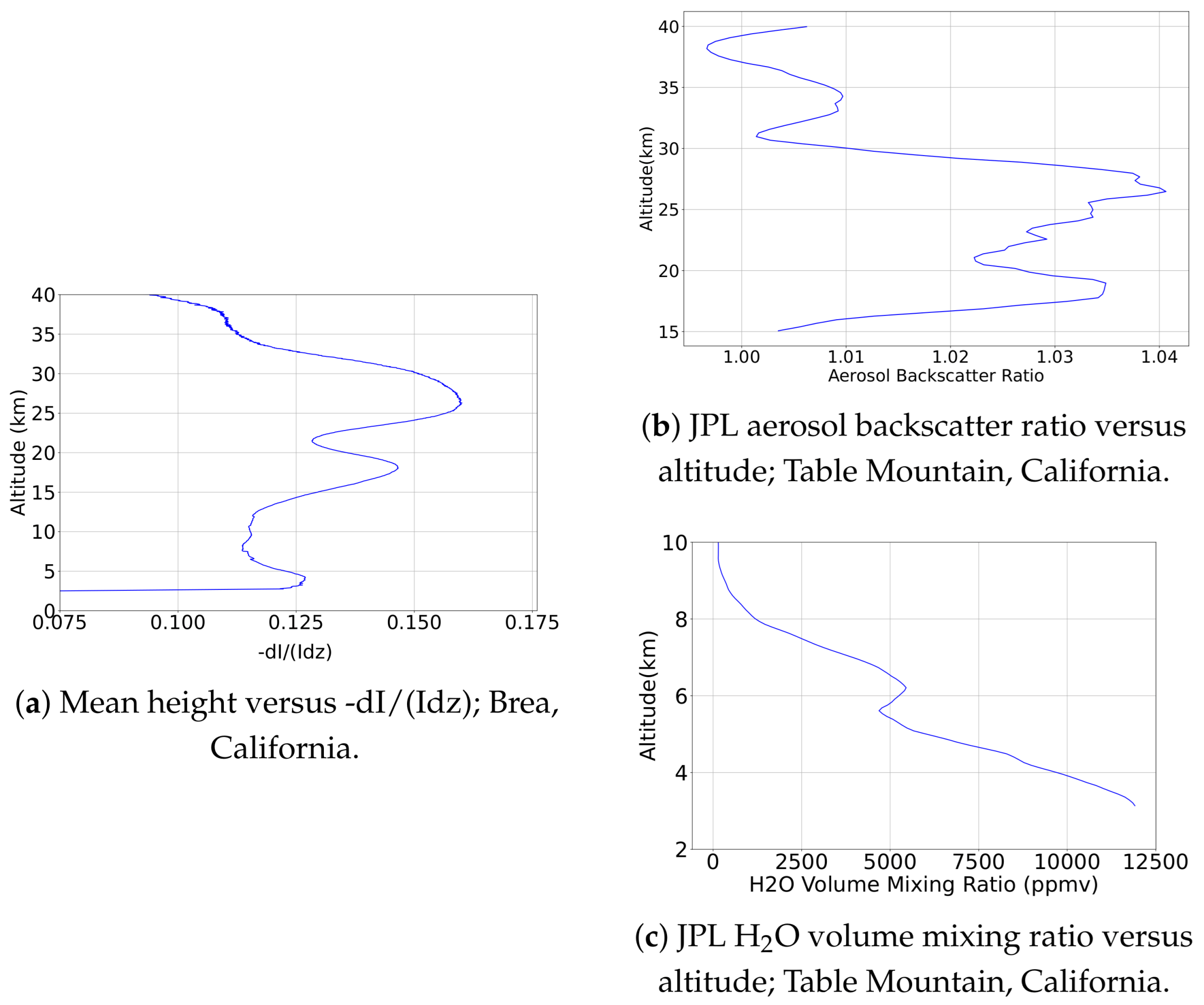
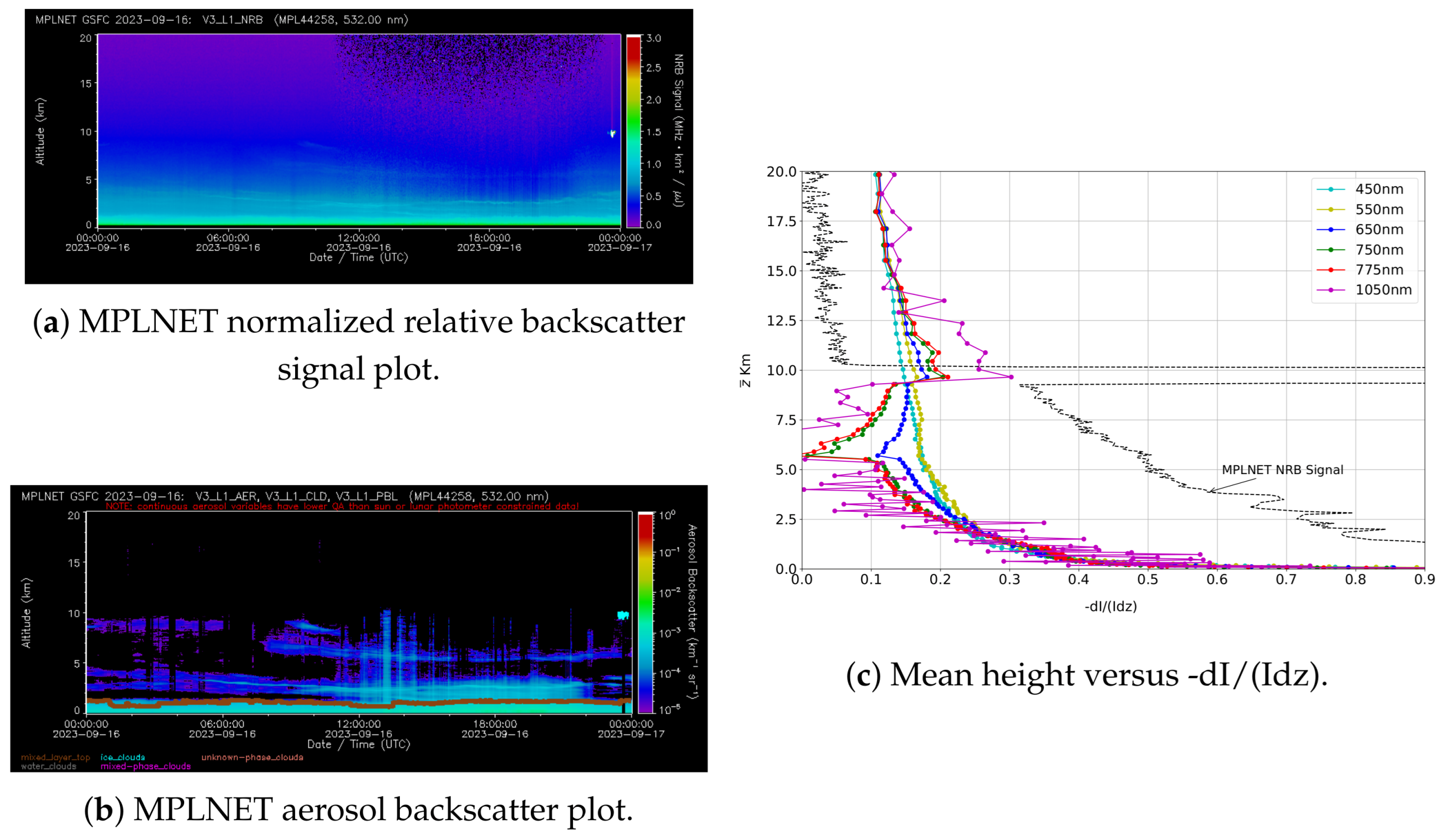
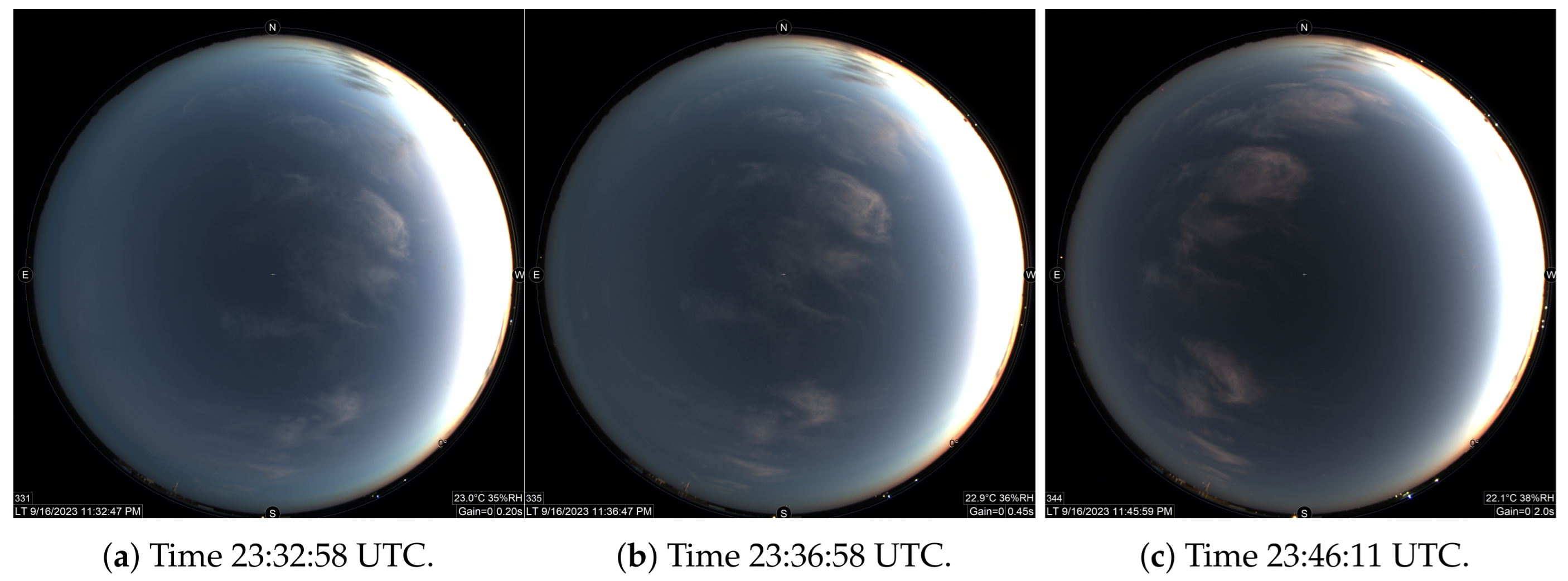
4.4. Twilight Photometer
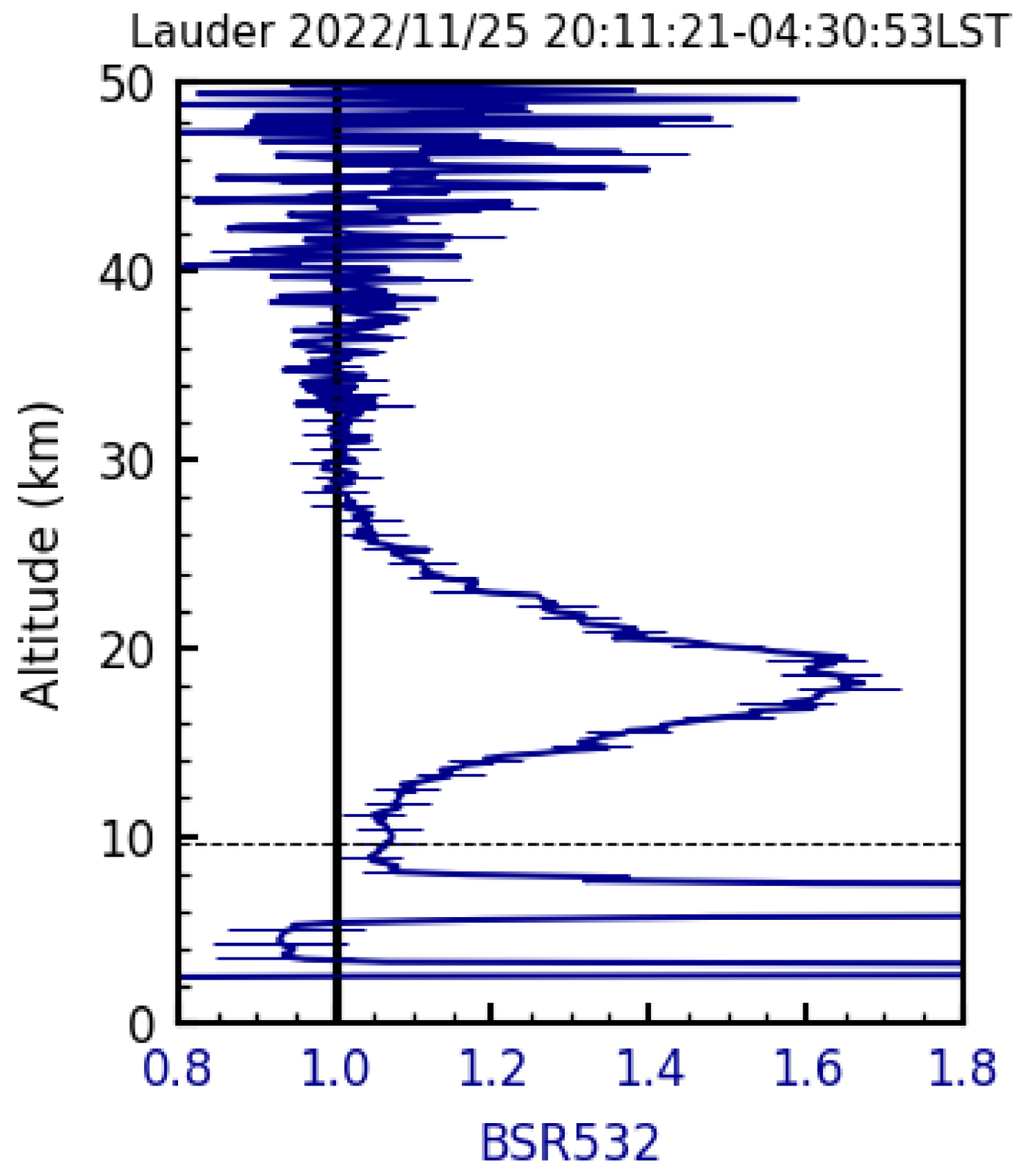
4.5. Ground Surface
5. Discussions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

Appendix B
Appendix C
References
- Mehta, D.; Scandola, S.; Kennedy, C.; Lummer, C.; Gallo, M.; Grubb, L.; Tan, M.; Scarpella, E.; Uhrig, R. Twilight length alters growth and flowering time in Arabidopsis via LHY/CCA1. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eadl3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, A.D. Power Hours: The Magic Of Twilight. 2020. Available online: https://www.thefisherman.com/article/power-hours-the-magic-of-twilight/ (accessed on 31 December 2024).
- Svetlana, R.; Genin, A. Twilight transitions in coral reef fish: The input of light-induced changes in foraging behaviour. Anim. Behav. 2005, 70, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tom, B. Can You Photograph Northern Lights in Nautical Twilight? 2022. Available online: https://www.tombolphoto.com/can-you-photograph-northern-lights-in-nautical-twilight/ (accessed on 31 December 2024).
- Kimball, H.H. Photometric measurements of daylight illumination on a horizontal surface at mount weather, VA. Mon. Weather Rev. 1914, 42, 650–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ljunghall, A. The intensity of twilight and its connection with the density of the atmosphere. Medd. Fran Lunds Astron. Obs. Ser. 1949, 125, 5–171. [Google Scholar]
- Bigg, E.K. The detection of atmospheric dust and temperature inversions by twilight scattering. J. Atmos. Sci. 1956, 13, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigg, E.K. Atmospheric stratification revealed by twilight scattering. Tellus 1964, 16, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, G. Radiance and color of the sky at twilight - Perturbations caused by stratospheric haze. Pure Appl. Geophys. 1981, 119, 231–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateshvili, I.; Mateshvili, G.; Mateshvili, N. Measurement of the vertical aerosol distribution in the middle atmosphere by the twilight sounding method. J. Aerosol Sci. 1998, 29, 1189–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateshvili, N.; Rietmeijer, F. Stratospheric dust loading from early 1981 to September 1985 based on the twilight sounding method and stratospheric dust collections. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2003, 120, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateshvili, N.; Fussen, D.; Vanhellemont, F.; Bingen, C.; Kyrölä, E.; Mateshvili, I.; Mateshvili, G. Twilight sky brightness measurements as a useful tool for stratospheric aerosol investigations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2005, 110, D09209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateshvili, N.; Fussen, D.; Mateshvili, G.; Mateshvili, I.; Vanhellemont, F.; Kyrölä, E.; Tukiainen, S.; Kujanpää, J.; Bingen, C.; Robert, C.; et al. Nabro volcano aerosol in the stratosphere over Georgia, South Caucasus from ground-based spectrometry of twilight sky brightness. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 2563–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutton, E.G.; Christy, J. Solar radiative forcing at selected locations and evidence for global lower tropospheric cooling following the eruptions of El Chichón and Pinatubo. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1992, 19, 2313–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitari, G.; Di Genova, G.; Mancini, E.; Visioni, D.; Gandolfi, I.; Cionni, I. Stratospheric Aerosols from Major Volcanic Eruptions: A Composition-Climate Model Study of the Aerosol Cloud Dispersal and e-folding Time. Atmosphere 2016, 7, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, M.; Langford, A.; O’Leary, T.; Arpag, K.; Miller, H.; Proffitt, M.; Sanders, R.; Solomon, S. On the relationship between stratospheric aerosols and nitrogen dioxide. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1993, 20, 1187–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krueger, A.J. Sighting of El Chichon sulfur dioxide clouds with the Nimbus 7 total ozone mapping spectrometer. Science 1983, 220, 1377–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, G.S.; Farrukh, U.O.; Wang, P.H.; Deepak, A. SAGE I and SAM II Measurements of 1 μm Aerosol Extinction in the Free Troposphere. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 1988, 27, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, G.S.; McCormick, M.; Wang, P. Validation of Stratospheric Aerosol and Gas Experiments I and II satellite aerosol optical depth measurements using surface radiometer data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1994, 99, 10333–10339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remsberg, E.; Lingenfelser, G. Analysis of SAGE II ozone of the middle and upper stratosphere for its response to a decadal-scale forcing. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 11779–11790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damadeo, R.; Sofieva, V.; Rozanov, A.; Thomason, L. An empirical characterization of the aerosol Ångström exponent interpolation bias using SAGE III/ISS data. Atmos. Meas. Tech. Discuss. 2023, 2023, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackerman, S. Using the radiative temperature difference at 3.7 and 11 μm to tract dust outbreaks. Remote Sens. Environ. 1989, 27, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Griffin, D.; Fioletov, V.; McLinden, C.; Davies, J.; Ogyu, A.; Lee, S.C.; Lupu, A.; Moran, M.; Cede, A.; et al. Retrieval of total column and surface NO 2 from Pandora zenith-sky measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 10619–10642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, B.; Kylling, A. The libRadtran software package for radiative transfer calculations-description and examples of use. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2005, 5, 1855–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, U.; Tsay, S.C.; Hsu, N.C.; Giles, D.M.; Cooper, J.W.; Lee, J.; Swap, R.J.; Holben, B.N.; Butler, J.J.; Wang, S.H.; et al. Simultaneous retrievals of biomass burning aerosols and trace gases from the ultraviolet to near-infrared over northern Thailand during the 2019 pre-monsoon season. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 11957–11986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laxmi, S.U.; Chandralingam, S.; Nagamani, P.V.; Bhavani, I.V.G.; Rao, Y.U. Importance of Aerosol Optical Depth in the Atmospheric Correction of Ocean Colour Remote Sensing Data. Open J. Mar. Sci. 2017, 7, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, D.; Sherwood, S.; Wood, R.; Donner, L. Climate effects of aerosol-cloud interactions. Science 2014, 343, 379–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, E.M. Direct and semi-direct radiative forcing of smoke aerosols over clouds. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kylling, A.; Vandenbussche, S.; Capelle, V.; Cuesta, J.; Klüser, L.; Lelli, L.; Popp, T.; Stebel, K.; Veefkind, P. Comparison of dust-layer heights from active and passive satellite sensors. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 2911–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachauri, R.K.; Allen, M.R.; Barros, V.R.; Broome, J.; Cramer, W.; Christ, R.; Church, J.A.; Clarke, L.; Dahe, Q.; Dasgupta, P.; et al. Climate Change 2014: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014.
- Jänicke, L.K.; Preusker, R.; Docter, N.; Fischer, J. Estimation of Aerosol Layer Height from OLCI Measurements in the O 2A-Absorption Band over Oceans. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Rascado, J.; Ruiz, B.; Alados-Arboledas, L. Multi-spectral Lidar characterization of the vertical structure of Saharan dust aerosol over southern Spain. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 2668–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulburt, E. Explanation of the brightness and color of the sky, particularly the twilight sky. JOSA 1953, 43, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emde, C.; Buras-Schnell, R.; Kylling, A.; Mayer, B.; Gasteiger, J.; Hamann, U.; Kylling, J.; Richter, B.; Pause, C.; Dowling, T.; et al. The libRadtran software package for radiative transfer calculations (version 2.0.1). Geosci. Model Dev. 2016, 9, 1647–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emde, C.; Mayer, B. Simulation of solar radiation during a total eclipse: A challenge for radiative transfer. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2007, 7, 2259–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randles, C.A.; da Silva, A.M.; Buchard, V.; Colarco, P.R.; Darmenov, A.; Govindaraju, R.; Smirnov, A.; Holben, B.; Ferrare, R.; Hair, J.; et al. The MERRA-2 Aerosol Reanalysis, 1980 Onward. Part I: System Description and Data Assimilation Evaluation. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 6823–6850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zerefos, C.; Gerogiannis, V.; Balis, D.; Zerefos, S.; Kazantzidis, A. Atmospheric effects of volcanic eruptions as seen by famous artists and depicted in their paintings. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2007, 7, 4027–4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Savigny, C.; Lange, A.; Hemkendreis, A.; Hoffmann, C.; Rozanov, A. Is it possible to estimate aerosol optical depth from historic colour paintings? Clim. Past Discuss. 2022, 2022, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, K. Calculation of the effective height of the Earth’s shadow. Planet. Space Sci. 1968, 16, 1071–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozenberg, G.V. Twilight; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Corradini, S.; Cervino, M. Aerosol extinction coefficient profile retrieval in the oxygen A-band considering multiple scattering atmosphere. Test case: SCIAMACHY nadir simulated measurements. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2006, 97, 354–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokhanovsky, A.A.; Rozanov, V.V. The determination of dust cloud altitudes from a satellite using hyperspectral measurements in the gaseous absorption band. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 31, 2729–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, A.F.; De Haan, J.F.; Veefkind, J.P. Retrieval of aerosol height from the oxygen A band with TROPOMI. In Proceedings of the Advances in Atmospheric Science and Applications, Bruges, Belgium, 18–22 June 2012; pp. 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Sanghavi, S.; Martonchik, J.; Landgraf, J.; Platt, U. Retrieval of the optical depth and vertical distribution of particulate scatterers in the atmosphere using O 2 A-and B-band SCIAMACHY observations over Kanpur: A case study. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2012, 5, 1099–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, Q.; Yin, B.; Li, S.; Berndt, J.; Harrison, L.; Joseph, E.; Duan, M.; Kiedron, P. A high-resolution oxygen A-band spectrometer (HABS) and its radiation closure. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 1711–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, L.; Min, Q. Photon pathlength distributions from O2 A-band absorption. In Proceedings of the International Radiation Symposium, Vienna, Austria, 14 August 1996; pp. 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Floutsi, A.A.; Korras-Carraca, M.B.; Matsoukas, C.; Hatzianastassiou, N.; Biskos, G. Climatology and trends of aerosol optical depth over the Mediterranean basin during the last 12 years (2002–2014) based on Collection 006 MODIS-Aqua data. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 551, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coddington, O.M.; Richard, E.C.; Harber, D.; Pilewskie, P.; Woods, T.N.; Snow, M.; Chance, K.; Liu, X.; Sun, K. Version 2 of the TSIS-1 Hybrid Solar Reference Spectrum and Extension to the Full Spectrum. Earth Space Sci. 2023, 10, e2022EA002637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, B. Radiative transfer in the cloudy atmosphere. Eur. Phys. J. Conf. 2009, 1, 75–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamnes, K.; Tsay, S.; Wiscombe, W.; Jayaweera, K. A numerically stable algorithm for discrete-ordinate-method radiative transfer in multiple scattering and emitting layered media. Appl. Opt. 1988, 27, 2502–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahalan, R.F.; Oreopoulos, L.; Marshak, A.; Evans, K.F.; Davis, A.B.; Pincus, R.; Yetzer, K.H.; Mayer, B.; Davies, R.; Ackerman, T.P.; et al. THE I3RC: Bringing Together the Most Advanced Radiative Transfer Tools for Cloudy Atmospheres. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2005, 86, 1275–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. US Standard Atmosphere, 1976; National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 1976.
- Herman, J.; Cede, A.; Spinei, E.; Mount, G.; Tzortziou, M.; Abuhassan, N. NO2 column amounts from ground-based Pandora and MFDOAS spectrometers using the direct-sun DOAS technique: Intercomparisons and application to OMI validation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, J.; Evans, R.; Cede, A.; Abuhassan, N.; Petropavlovskikh, I.; McConville, G. Comparison of ozone retrievals from the Pandora spectrometer system and Dobson spectrophotometer in Boulder, Colorado. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2015, 8, 3407–3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holben, B.; Eck, T.; Slutsker, I.; Tanré, D.; Buis, J.; Setzer, A.; Vermote, E.; Reagan, J.; Kaufman, Y.; Nakajima, T.; et al. AERONET—A Federated Instrument Network and Data Archive for Aerosol Characterization. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 66, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinyuk, A.; Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Giles, D.M.; Slutsker, I.; Korkin, S.; Schafer, J.S.; Smirnov, A.; Sorokin, M.; Lyapustin, A. The AERONET Version 3 aerosol retrieval algorithm, associated uncertainties and comparisons to Version 2. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 3375–3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NASA GES DISC. Giovanni: NASA Goddard Earth Sciences Data and Information Services Center. 2016. Available online: http://giovanni.gsfc.nasa.gov/ (accessed on 31 December 2024).
- Mims, F.M., III. An inexpensive and stable LED Sun photometer for measuring the water vapor column over South Texas from 1990 to 2001. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 20-1–20-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mims, F.M., III. Build a Twilight Photometer to Detect Stratospheric Particles. Make 2015, 44–45, 84–85. Available online: https://makezine.com/projects/twilight-photometer/ (accessed on 31 December 2024).
- Leblanc, T. Lidar 101: Introduction to the JPL Lidars. 2024. Available online: https://tmf.jpl.nasa.gov/tmf-lidar/instruments/instruments_intro.htm/ (accessed on 31 December 2024).
- Steinbrecht, W.; Leblanc, T. Lidars in the network for detection of atmospheric composition change (NDACC) and the tropospheric ozone lidar network (TOLNet). In Handbook of Air Quality and Climate Change; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Leblanc, T.; McDermid, I.; Walsh, T. Ground-based water vapor Raman lidar measurements up to the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere for long-term monitoring. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2012, 5, 17–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welton, E.J.; Campbell, J.R.; Spinhirne, J.D.; Scott, V.S., III. Global monitoring of clouds and aerosols using a network of micropulse lidar systems. In Proceedings of the Lidar Remote Sensing for Industry and Environment Monitoring, Sendai, Japan, 9–12 October 2000; Volume 4153, pp. 151–158. [Google Scholar]
- Welton, E.J.; Stewart, S.A.; Lewis, J.R.; Belcher, L.R.; Campbell, J.R.; Lolli, S. Status of the NASA Micro Pulse Lidar Network (MPLNET): Overview of the network and future plans, new version 3 data products, and the polarized MPL. In Proceedings of the EPJ Web of Conferences, EDP Sciences, Utrecht, The Netherlands, 10 July 2018; Volume 176, p. 09003. [Google Scholar]
- Smirnov, A.; Holben, B.; Eck, T.; Dubovik, O.; Slutsker, I. Cloud-screening and quality control algorithms for the AERONET database. Remote Sens. Environ. 2000, 73, 337–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, Y.; Yu, B.; Parsons, K.; Desha, C.; Ramezani, M. Evaluation and comparison of MERRA-2 AOD and DAOD with MODIS DeepBlue and AERONET data in Australia. Atmos. Environ. 2022, 277, 119054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, G. The calculation of astronomical refraction in marine navigation. J. Navig. 1982, 35, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, T.; Uchino, O.; Nagai, T.; Liley, B.; Morino, I.; Fujimoto, T. Long-term variation of stratospheric aerosols observed with lidars over Tsukuba, Japan, from 1982 and Lauder, New Zealand, from 1992 to 2015. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 10–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, T.; Shibata, T.; Iwasaka, Y. Relative humidity, backscattering ratio and depolarization ratio as derived from Raman lidar observations. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. Ser. II 1997, 75, 1179–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parajuli, S.P.; Stenchikov, G.L.; Ukhov, A.; Shevchenko, I.; Dubovik, O.; Lopatin, A. Aerosol vertical distribution and interactions with land/sea breezes over the eastern coast of the Red Sea from lidar data and high-resolution WRF-Chem simulations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 16089–16116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatebe, C.K.; Butler, J.J.; Cooper, J.W.; Kowalewski, M.; King, M.D. Characterization of errors in the use of integrating-sphere systems in the calibration of scanning radiometers. Appl. Opt. 2007, 46, 7640–7651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
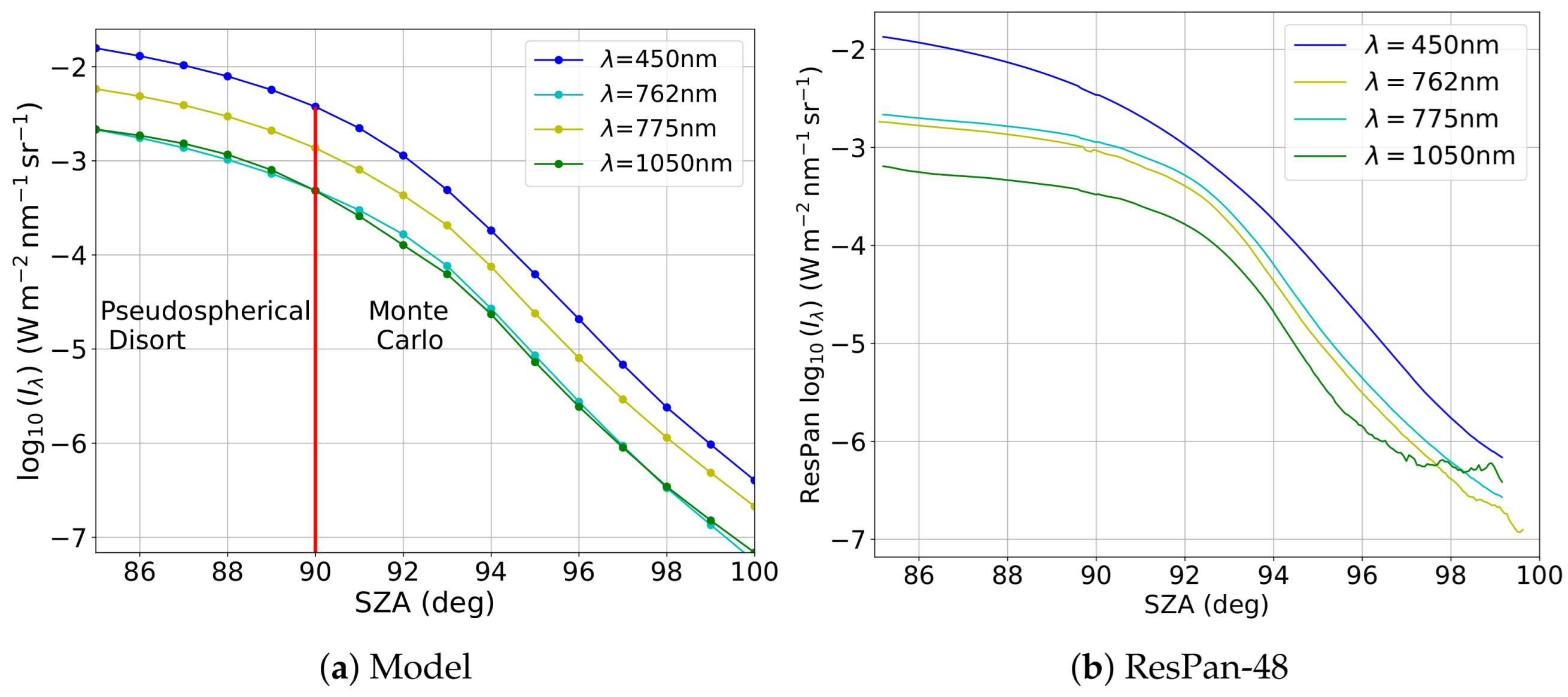
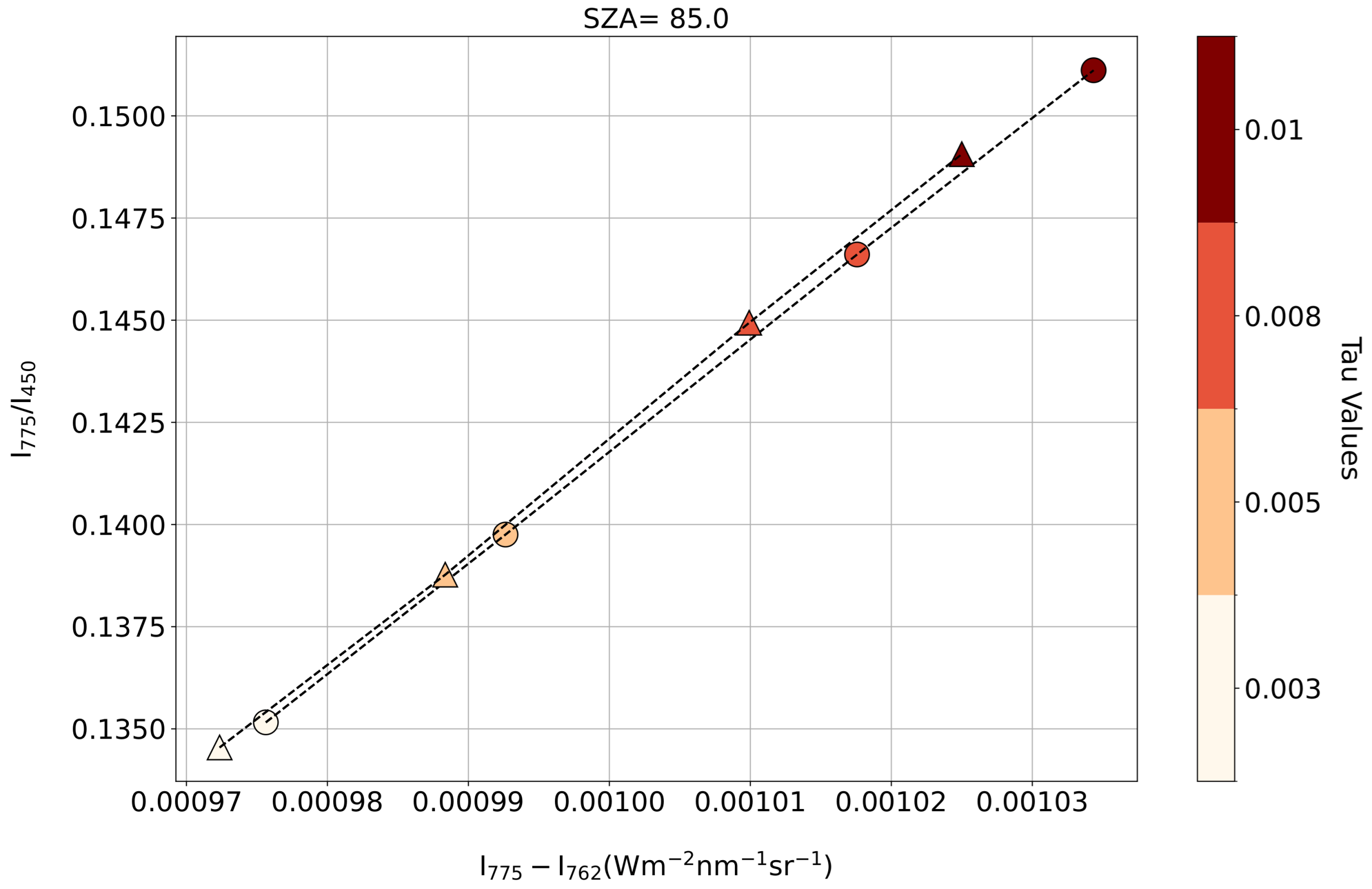
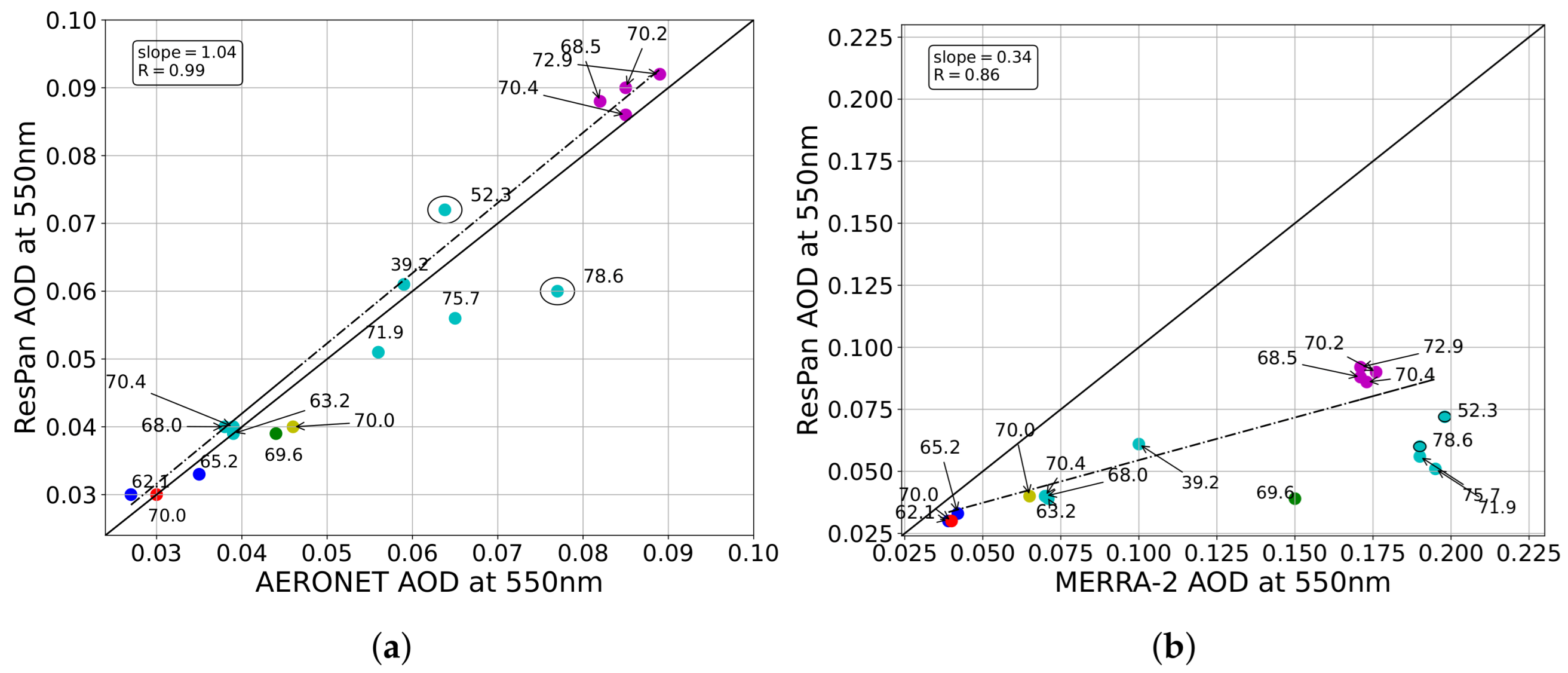
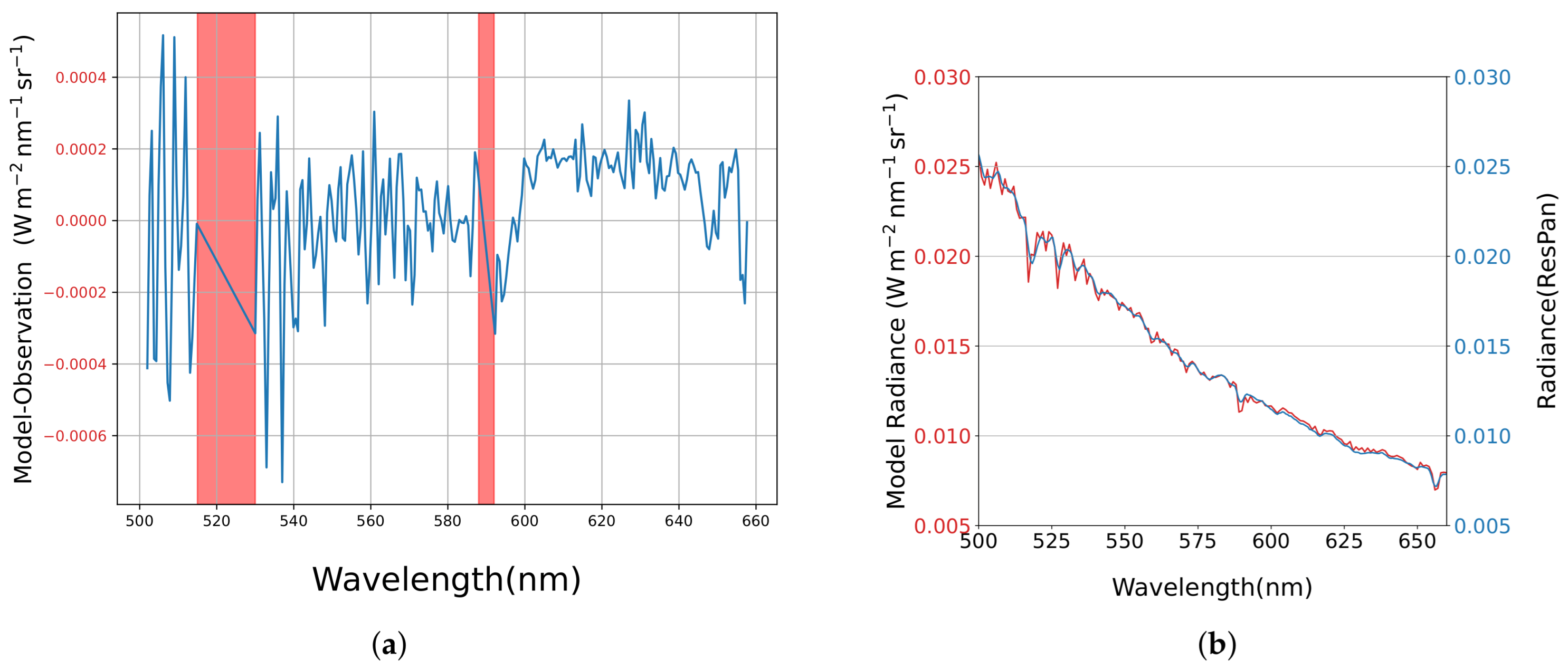

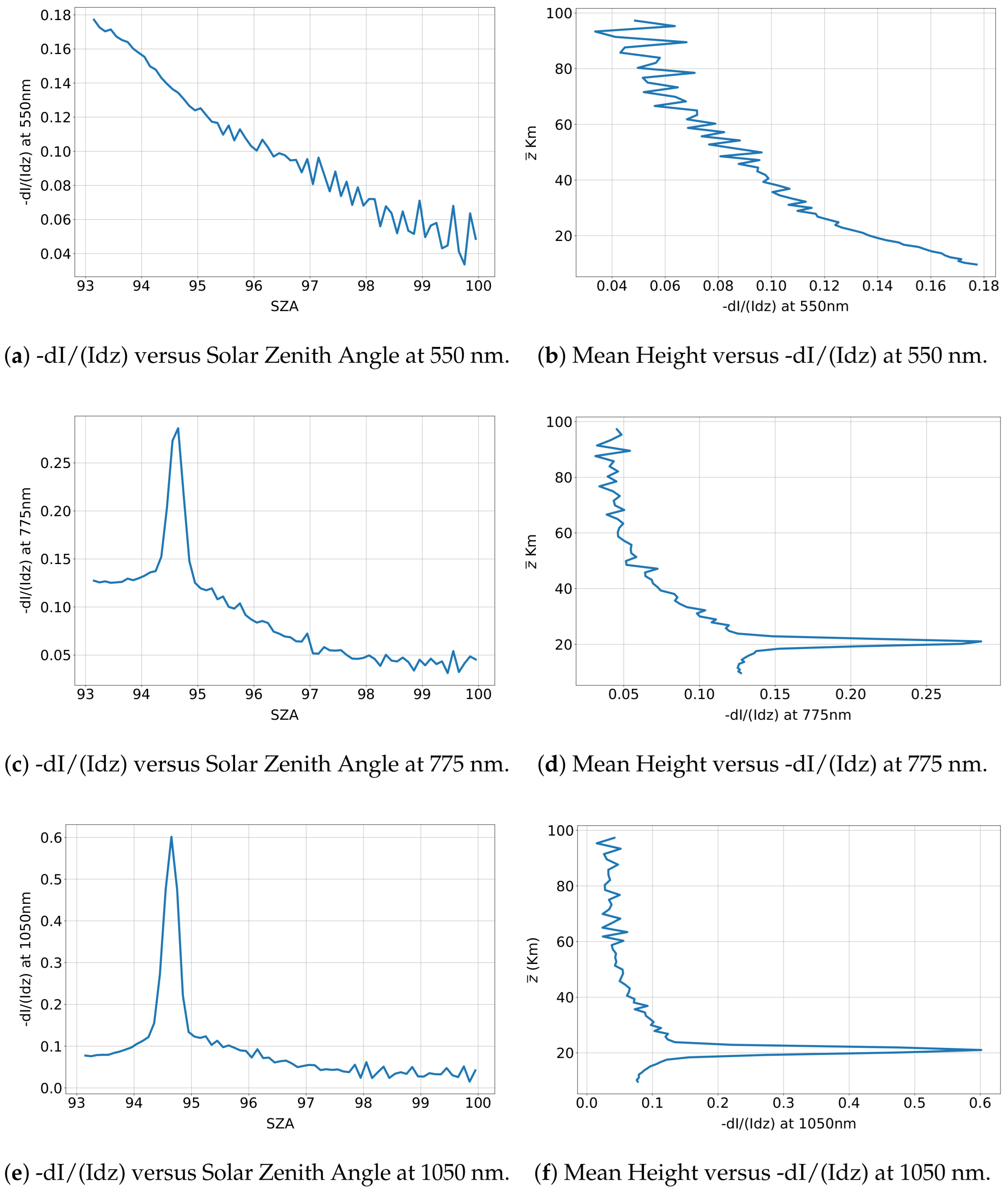
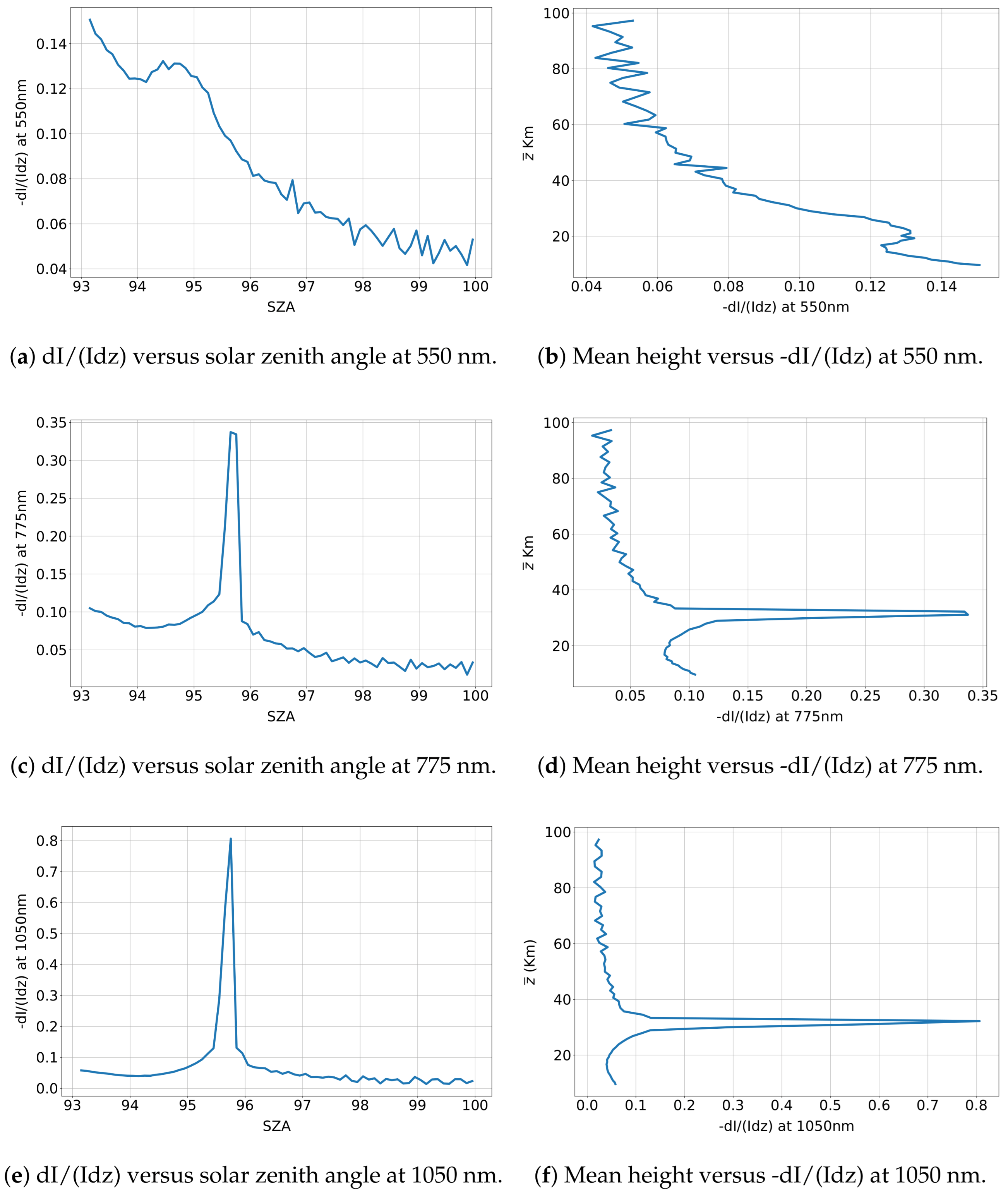
| Aerosol Peak Height (km) | TRM Height Prediction at Wavelengths (nm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 550 | 775 | 1050 | |
| 5.0 | - | - | 5.5 |
| 10.0 | - | - | 11.0 |
| 15.0 | - | - | 17.42 |
| 20.0 | - | 21.03 | 21.03 |
| 30.0 | 20.0 | 29.34 | 30.30 |
| 40.0 | 32.0 | 39.86 | 40.57 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mukherjee, L.; Wu, D.L.; Abuhassan, N.; Hanisco, T.F.; Jeong, U.; Jin, Y.; Leblanc, T.; Mayer, B.; Mims, F.M., III; Morino, I.; et al. Twilight Near-Infrared Radiometry for Stratospheric Aerosol Layer Height. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2071. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17122071
Mukherjee L, Wu DL, Abuhassan N, Hanisco TF, Jeong U, Jin Y, Leblanc T, Mayer B, Mims FM III, Morino I, et al. Twilight Near-Infrared Radiometry for Stratospheric Aerosol Layer Height. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(12):2071. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17122071
Chicago/Turabian StyleMukherjee, Lipi, Dong L. Wu, Nader Abuhassan, Thomas F. Hanisco, Ukkyo Jeong, Yoshitaka Jin, Thierry Leblanc, Bernhard Mayer, Forrest M. Mims, III, Isamu Morino, and et al. 2025. "Twilight Near-Infrared Radiometry for Stratospheric Aerosol Layer Height" Remote Sensing 17, no. 12: 2071. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17122071
APA StyleMukherjee, L., Wu, D. L., Abuhassan, N., Hanisco, T. F., Jeong, U., Jin, Y., Leblanc, T., Mayer, B., Mims, F. M., III, Morino, I., Nagai, T., Nicholls, S., Querel, R., Sakai, T., Welton, E. J., Windle, S., Pantina, P., & Uchino, O. (2025). Twilight Near-Infrared Radiometry for Stratospheric Aerosol Layer Height. Remote Sensing, 17(12), 2071. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17122071






