An Improved Wavelet Soft-Threshold Function Integrated with SVMD Dual-Parameter Joint Denoising for Ancient Building Deformation Monitoring
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Related Theory
2.1. Successive Variational Mode Decomposition
2.2. Fuzzy Entropy
2.3. Dual Parameter Model
2.4. Wavelet Soft-Threshold Function
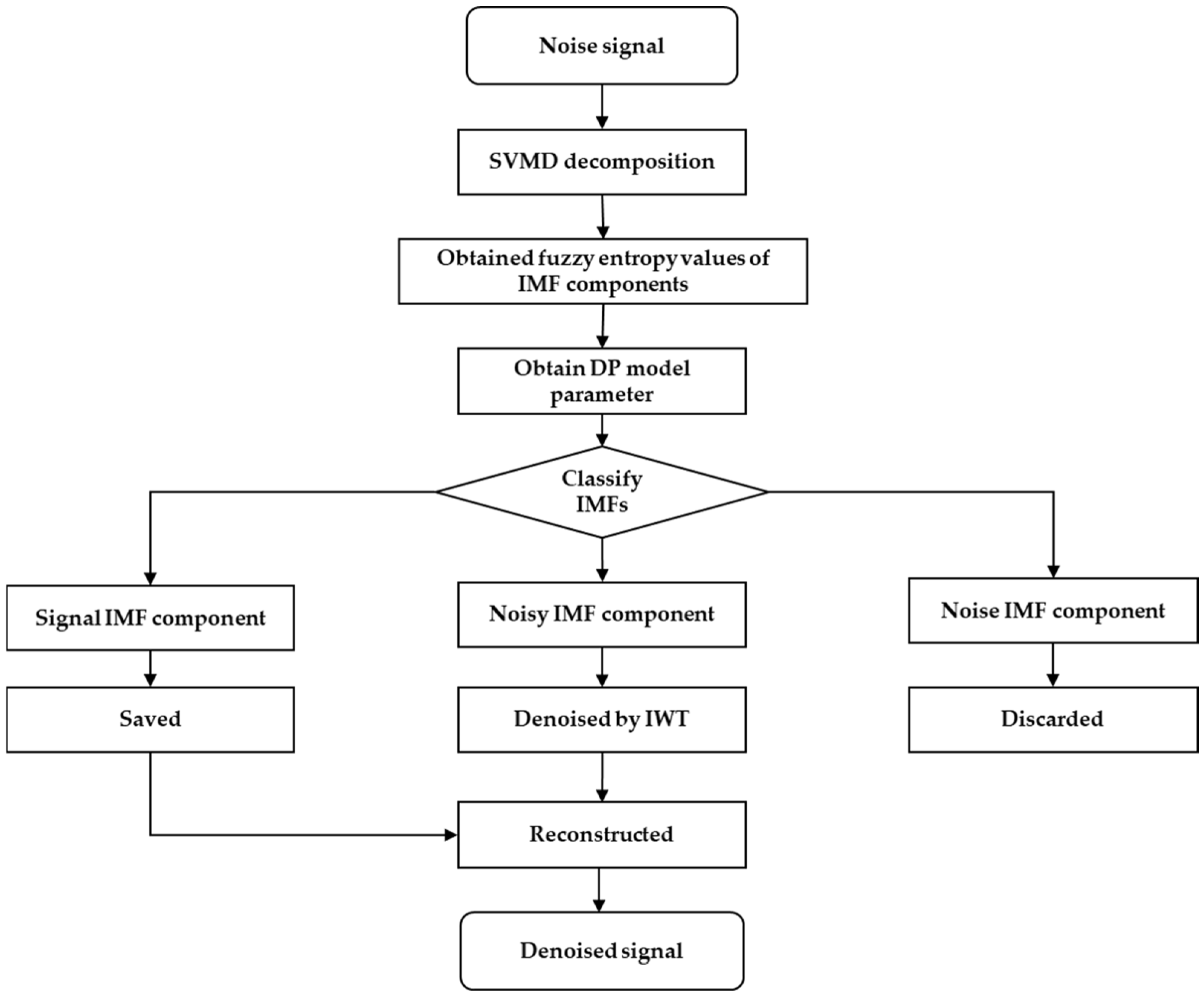
2.5. The SVMD-DP-IWT Method
2.6. Evaluation Index and Performance Comparison
3. Experiment Analysis
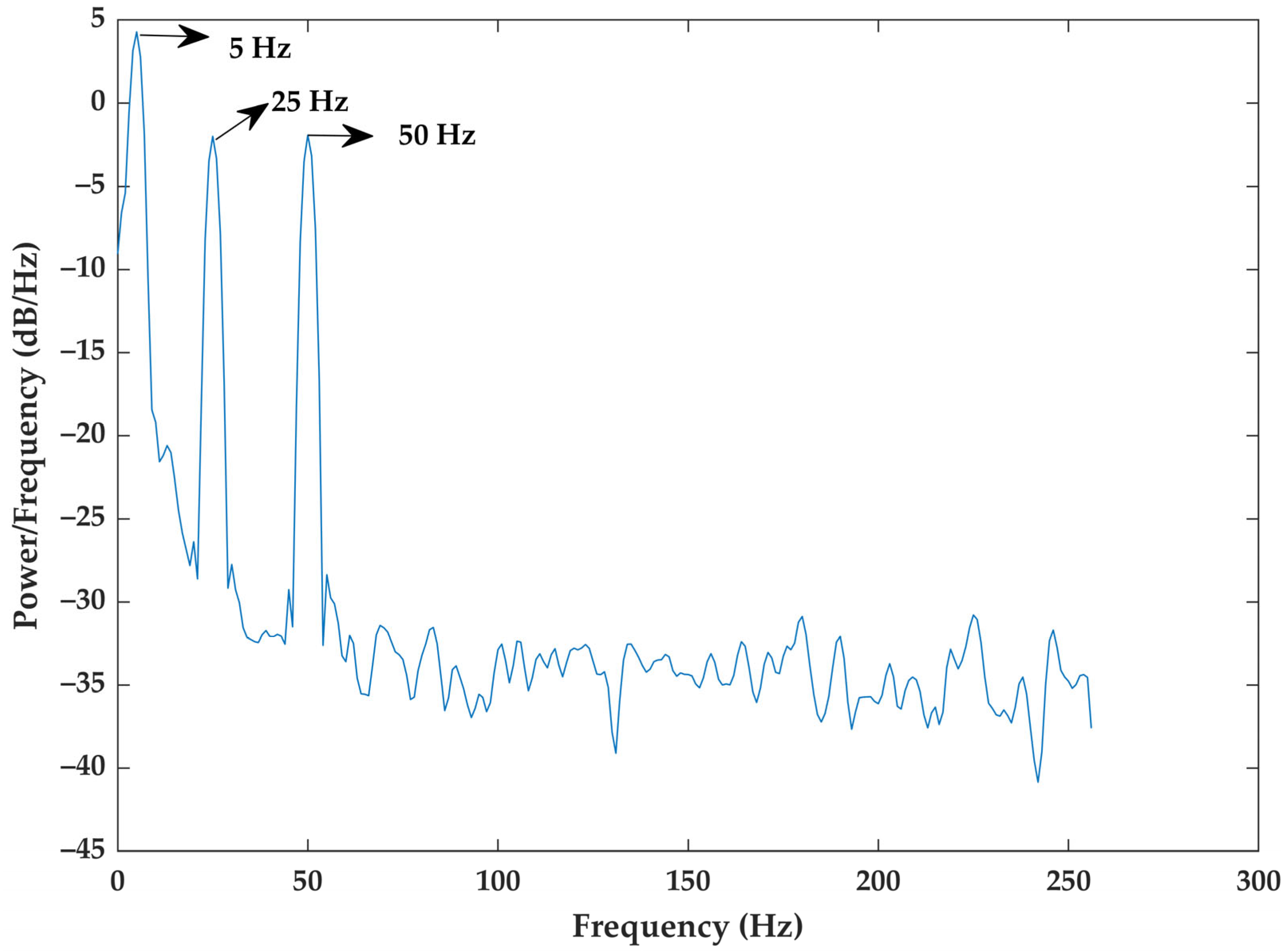
3.1. Simulated Signal
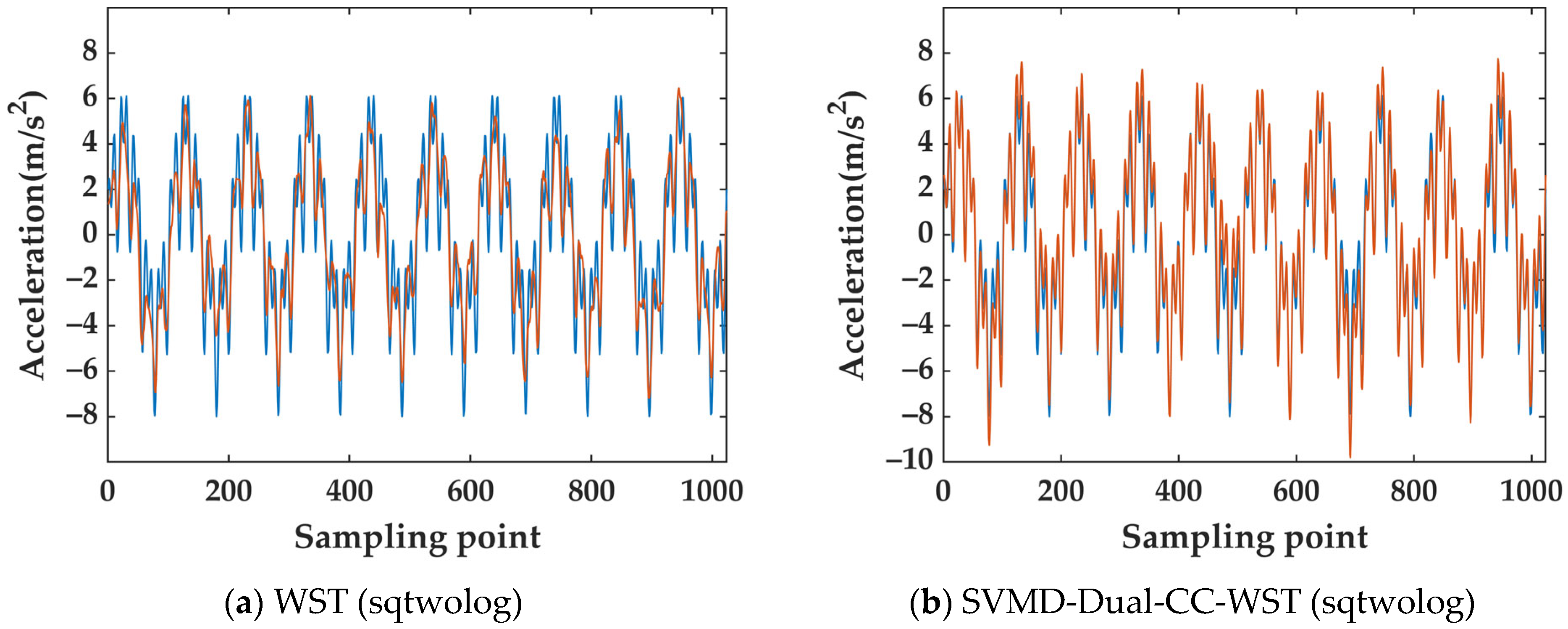
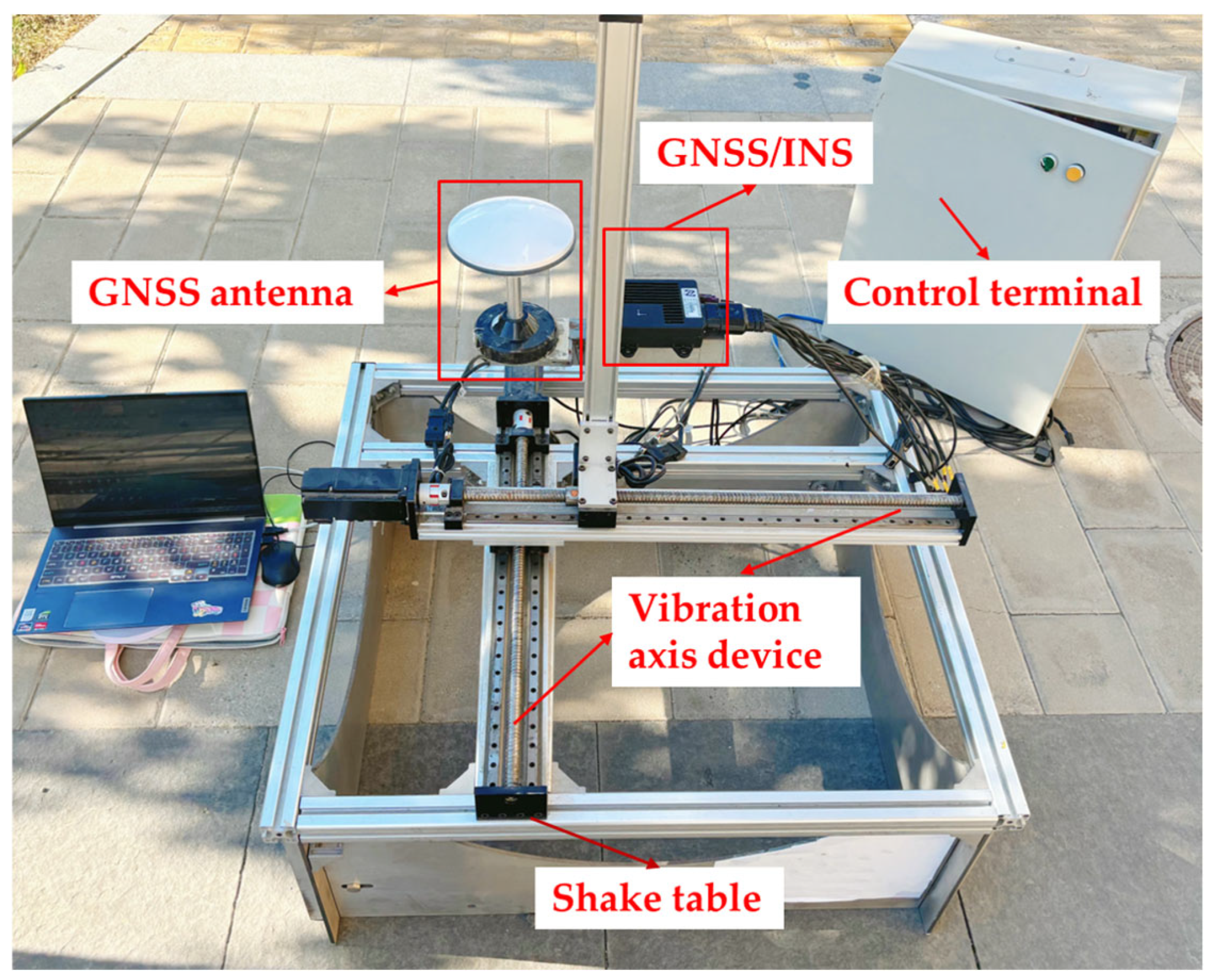
3.2. GNSS Vibration Monitoring Experiment
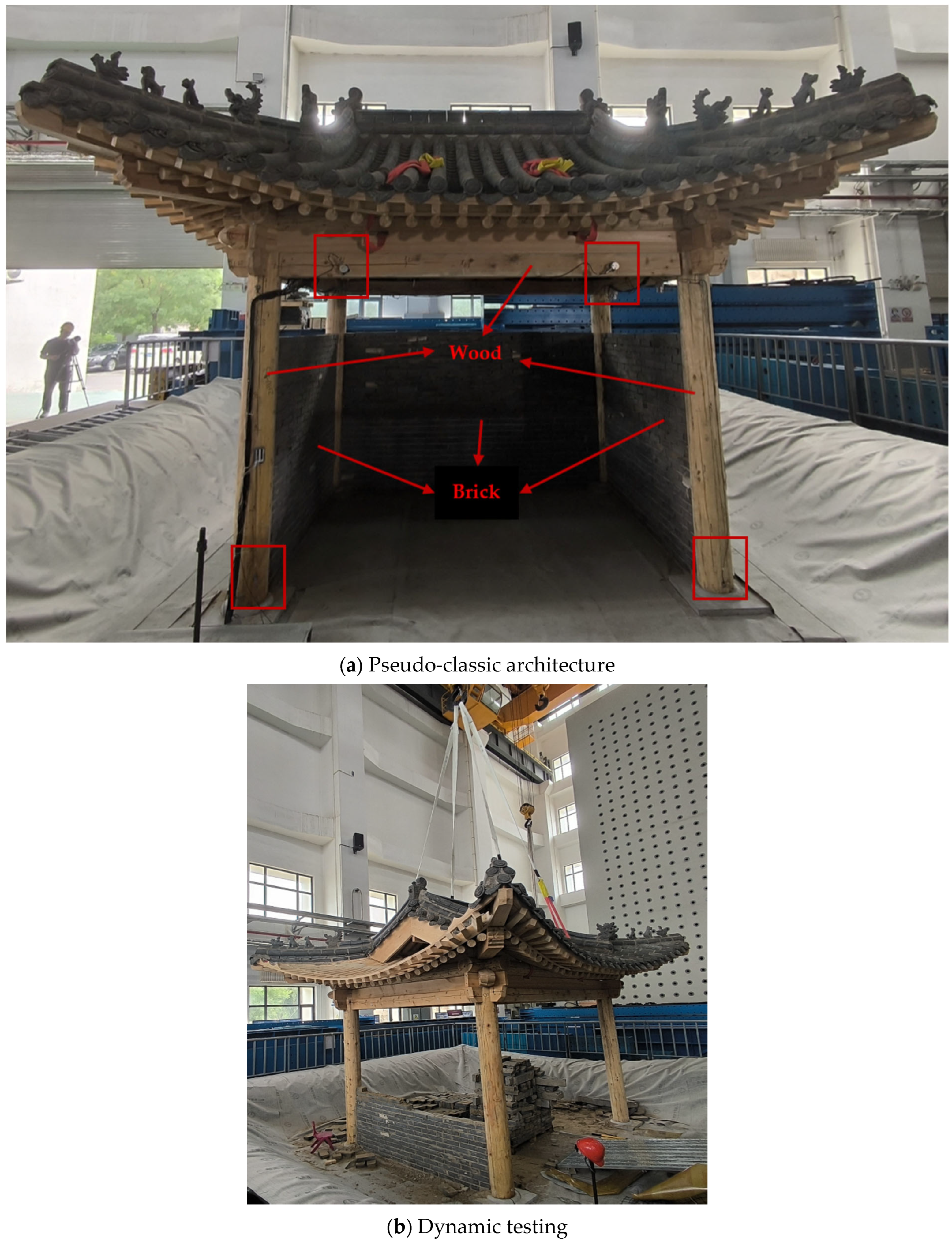
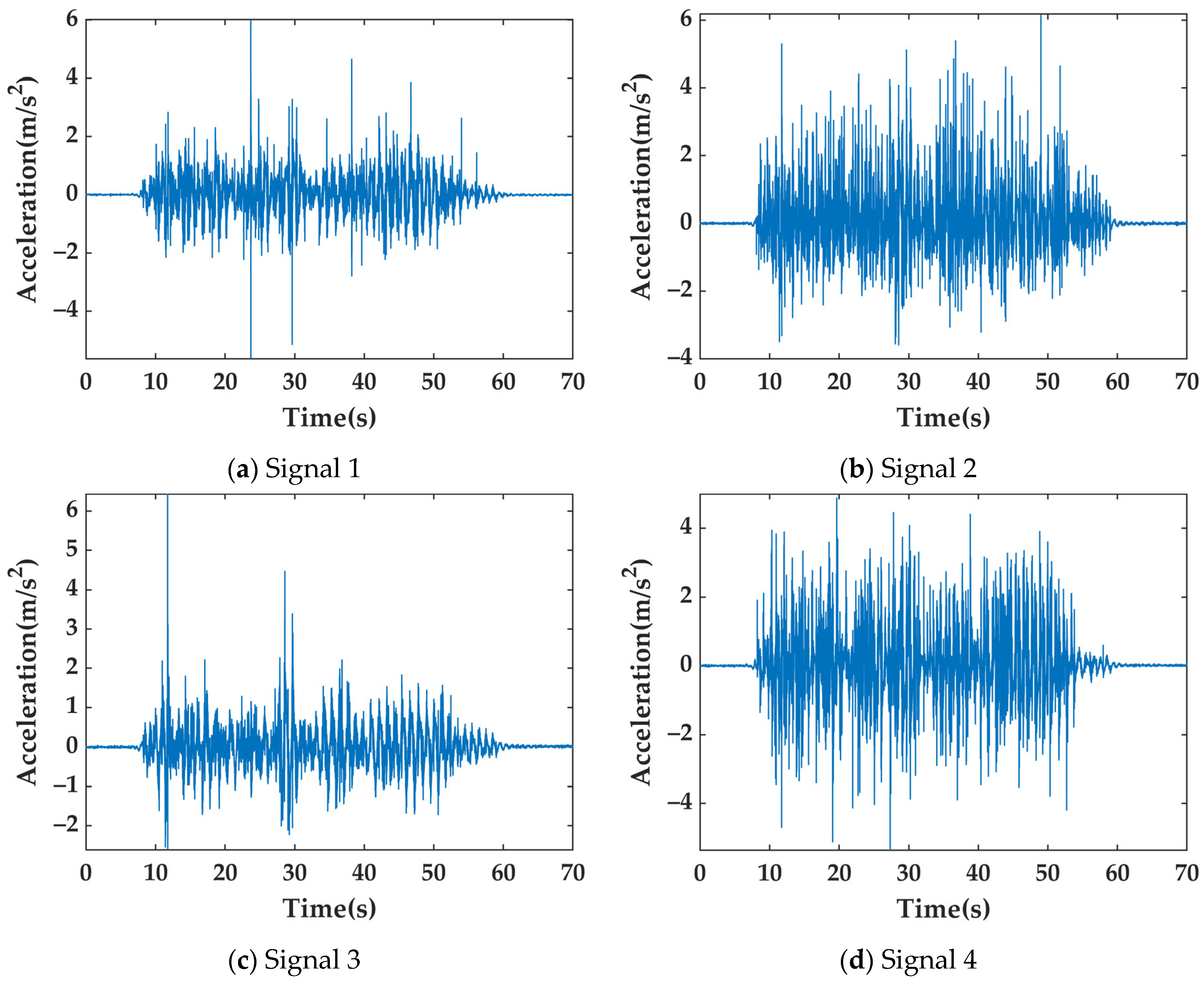
3.3. Engineering Measurement Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Information, V.F.A.; Uva, G.; Information, V.F.A.; Simeone, V.; Information, V.F.A.; Nettis, A.; Information, V.F.A.; Morga, M.; Information, V.F.A.; Doglioni, A. Probabilistic-based assessment of subsidence phenomena on the existing built heritage by combining MTInSAR data and UAV photogrammetry. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2024, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, G.R.; Zhao, L.; Liu, Z.C.; Wang, J.Y.; Huang, X.B.; Yuan, P. Research on loose bolt localization technology for transmission towers. Struct. Health Monit. 2024, 23, 3134–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, C.; Huang, G.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X.; Bai, Z.; Du, Y. GNSS/accelerometer adaptive coupled landslide deformation monitoring technology. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Siyuan, C.; Yangkang, C. Applications of variational mode decomposition in seismic time-frequency analysis. Geophysics 2016, 81, 365–378. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, L.L.; Xu, N.W.; Zhang, P.; Li, B.; Xiao, P.W.; Sun, Y.P. An ICEEMDAN-WPD based denoising method for MS signals and its engineering application. Nondestruct. Test. Eval. 2025, 40, 1946–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragomiretskiy, K.; Zosso, D. Variational Mode Decomposition. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2014, 62, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Peng, Y.X.; Lu, H.; Chang, X.D.; Chen, G.A. A novel fault diagnosis method of rotating machinery via VMD, CWT and improved CNN. Measurement 2022, 200, 111635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazari, M.; Sakhaei, S.M. Successive variational mode decomposition. Signal Process. 2020, 174, 107610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.X.; Xiao, L.Q.; Tang, B.Z.; Liang, L.L.; Lou, Y.L.; Guo, X.Y.; Xue, X.H. A Denoising Method for Ship-Radiated Noise Based on Optimized Variational Mode Decomposition with Snake Optimization and Dual-Threshold Criteria of Correlation Coefficient. Math. Probl. Eng. 2022, 2022, 8024753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jauhari, K.; Rahman, A.Z.; Al Huda, M.; Azka, M.; Widodo, A.; Prahasto, T. A feature extraction method for intelligent chatter detection in the milling process. J. Intell. Manuf. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.Y.; Li, Y.B.; Jiang, L.; Zhou, L. Fault feature extraction for rolling bearings based on parameter-adaptive variational mode decomposition and multi-point optimal minimum entropy deconvolution. Measurement 2021, 173, 108469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.F.; Li, H.K.; Ou, J.Y.; Wang, Z.D. Milling chatter identification by optimized variational mode decomposition and fuzzy entropy. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Tech. 2022, 121, 6111–6124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.J.; Yang, J.T.; Zhang, T.Y.; Li, K.; Zhang, K. Adaptive parameter selection variational mode decomposition based on a novel hybrid entropy and its applications in locomotive bearing diagnosis. Measurement 2023, 217, 113110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.M.; Xu, Y.F.; Wang, J.Y.; Song, M.M.; Zhang, S.L. SVMD coupled with dual-threshold criteria of correlation coefficient: A self-adaptive denoising method for ship-radiated noise signal. Ocean Eng. 2023, 281, 114931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.; Chen, J.T.; Bai, Y.L.; Ye, C.L. Train axlebox bearing composite fault denoising method based on SVMD and dual threshold classification criteria. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2025, 36, 026139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.Z.; Li, T.C.; Zhang, Y.M.; Pei, Z.M. Fault diagnosis method of rolling bearings based on adaptive modified CEEMD and 1DCNN model. ISA Trans. 2023, 140, 309–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.X.; Zhang, C.L.; Zhou, Y.H. A Novel Denoising Method for Ship-Radiated Noise. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wang, Z.; Xie, H.; Yu, W. Characterization of Surface EMG Signal Based on Fuzzy Entropy. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2007, 15, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donoho, D.L. De-noising by soft-thresholding. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1995, 41, 613–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, P.; Guo, B.P. Wavelet denoising based on modified threshold function optimization method. J. Signal Process. 2017, 33, 102–110. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; Su, H.Z.; Cai, D.; Zhou, R.L. RDTS Noise Reduction Method Based on ICEEMDAN-FE-WSTD. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 17854–17863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, X.W.; Liu, H.; Li, Y.F. Wind speed prediction model using singular spectrum analysis, empirical mode decomposition and convolutional support vector machine. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 180, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.Q.; Guo, J.; Yuan, F.; Shi, Y.J.; Li, Z.Y. Research on Denoising Method for Hydroelectric Unit Vibration Signal Based on ICEEMDAN-PE-SVD. Sensors 2023, 23, 6368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.W.; Du, S.; Wang, D. GNSS techniques for real-time monitoring of landslides: A review. Satell. Navig. 2023, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Huang, G.W.; Du, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Bai, Z.W.; Tian, J. Stability analysis of reference station and compensation for monitoring stations in GNSS landslide monitoring. Satell. Navig. 2023, 4, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sheimy, N.; Youssef, A. Inertial sensors technologies for navigation applications: State of the art and future trends. Satell. Navig. 2020, 1, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



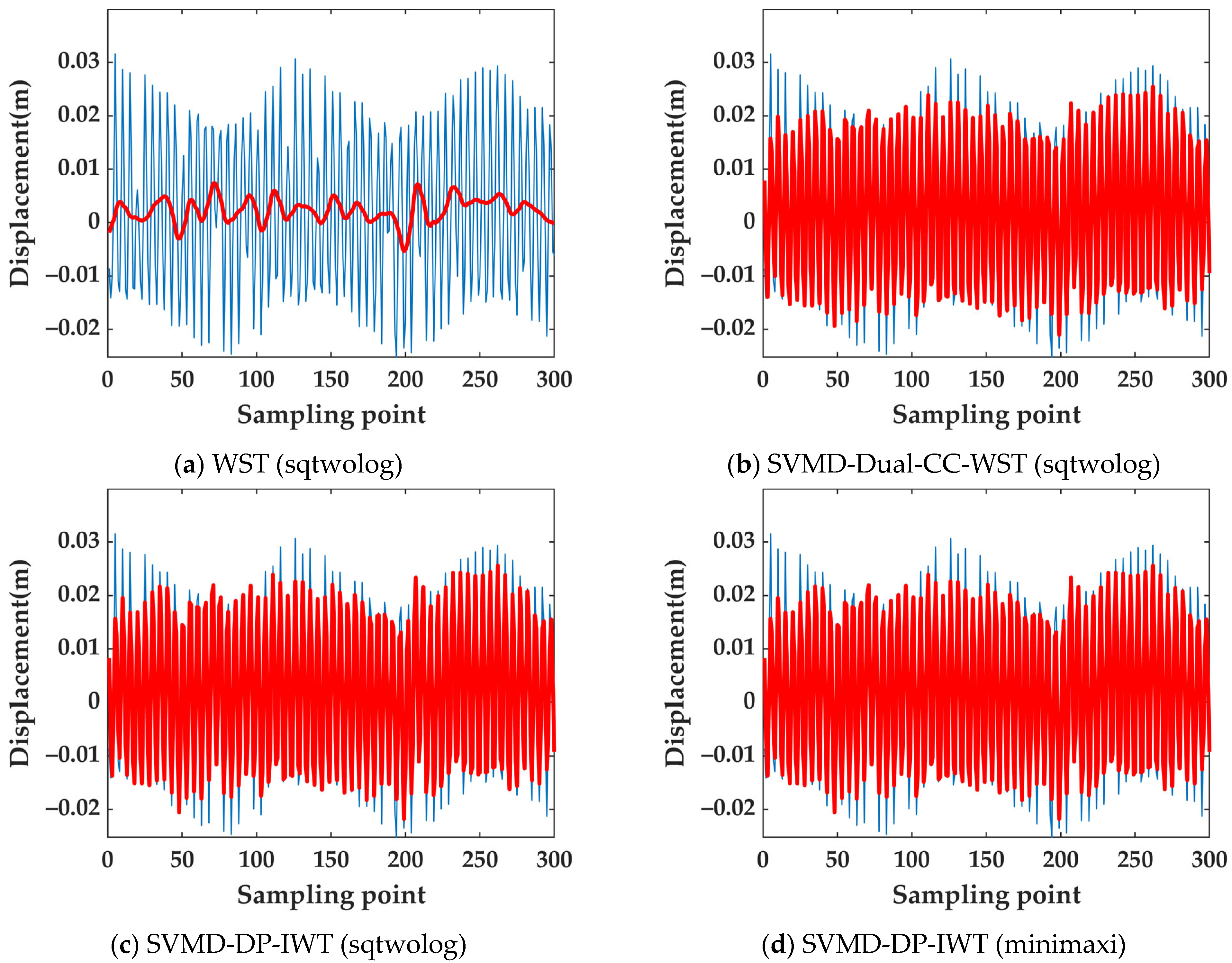
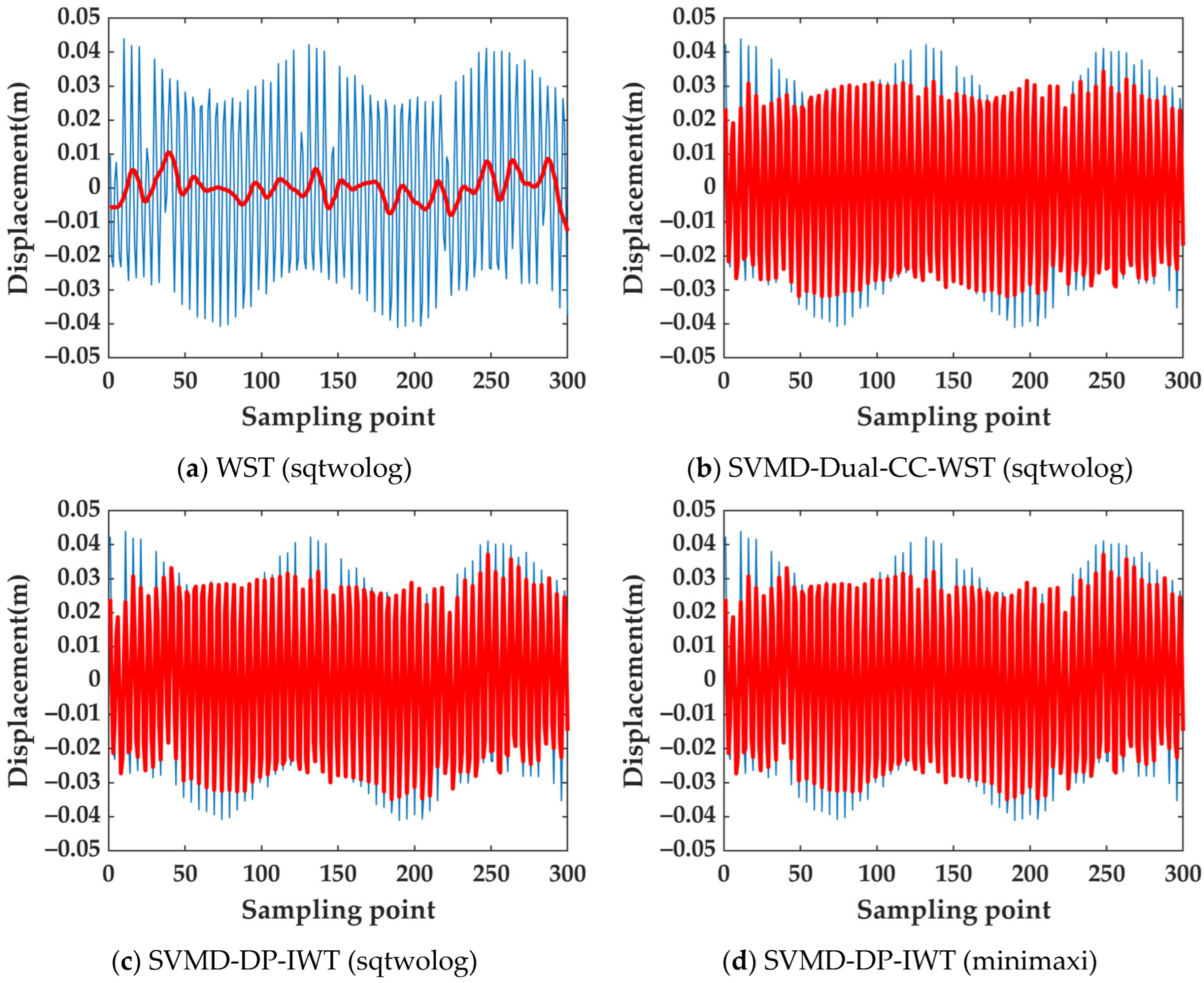

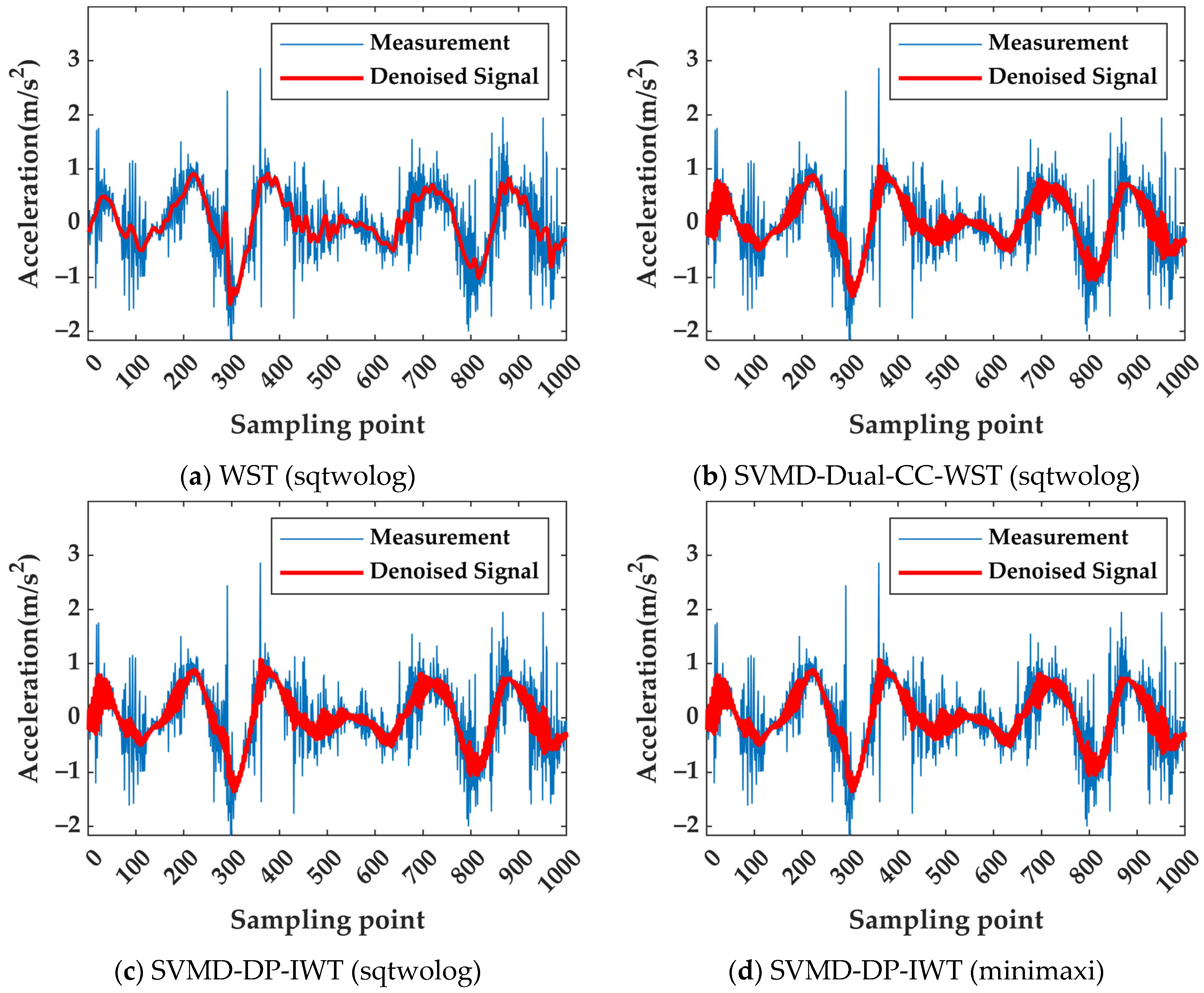
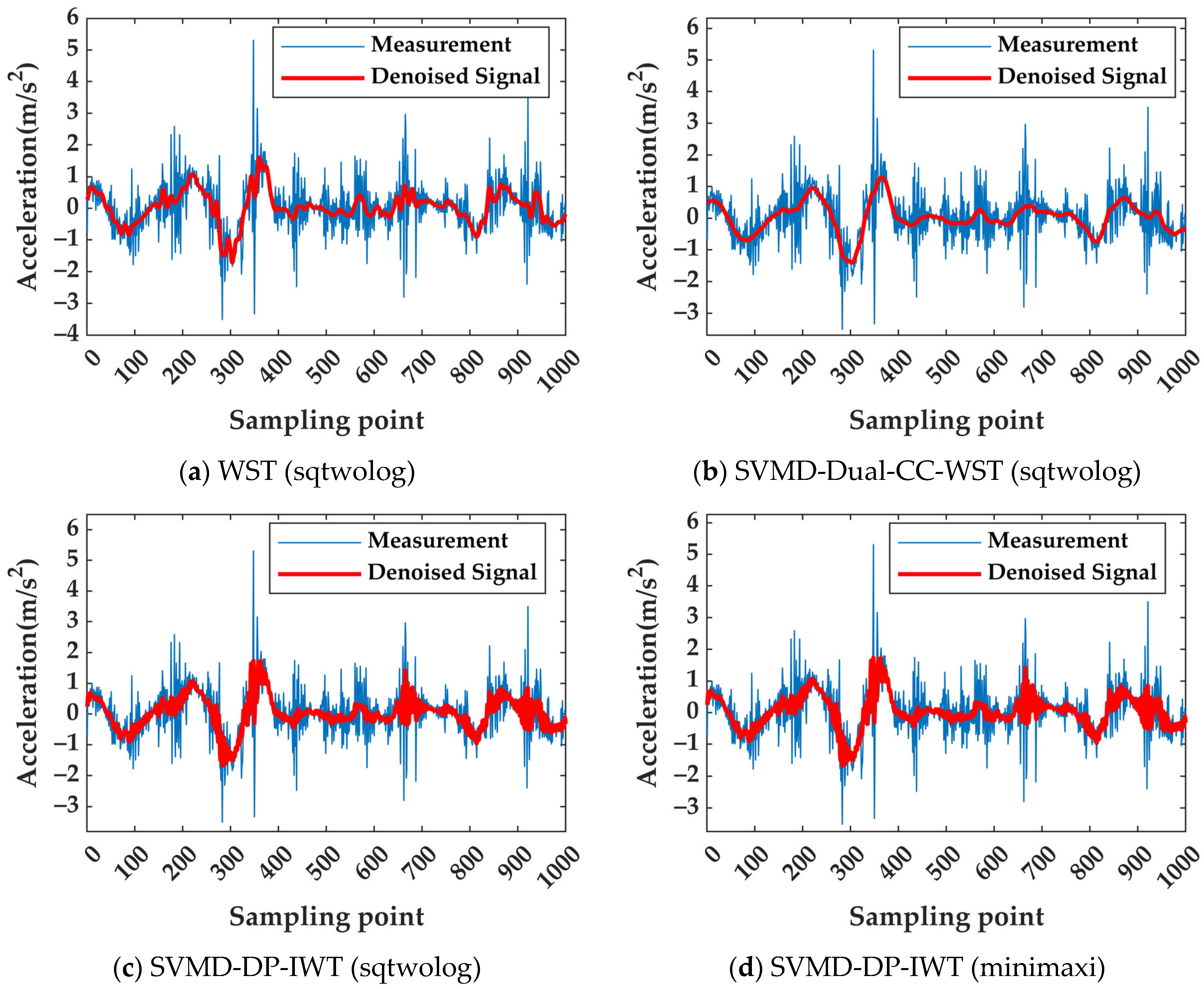
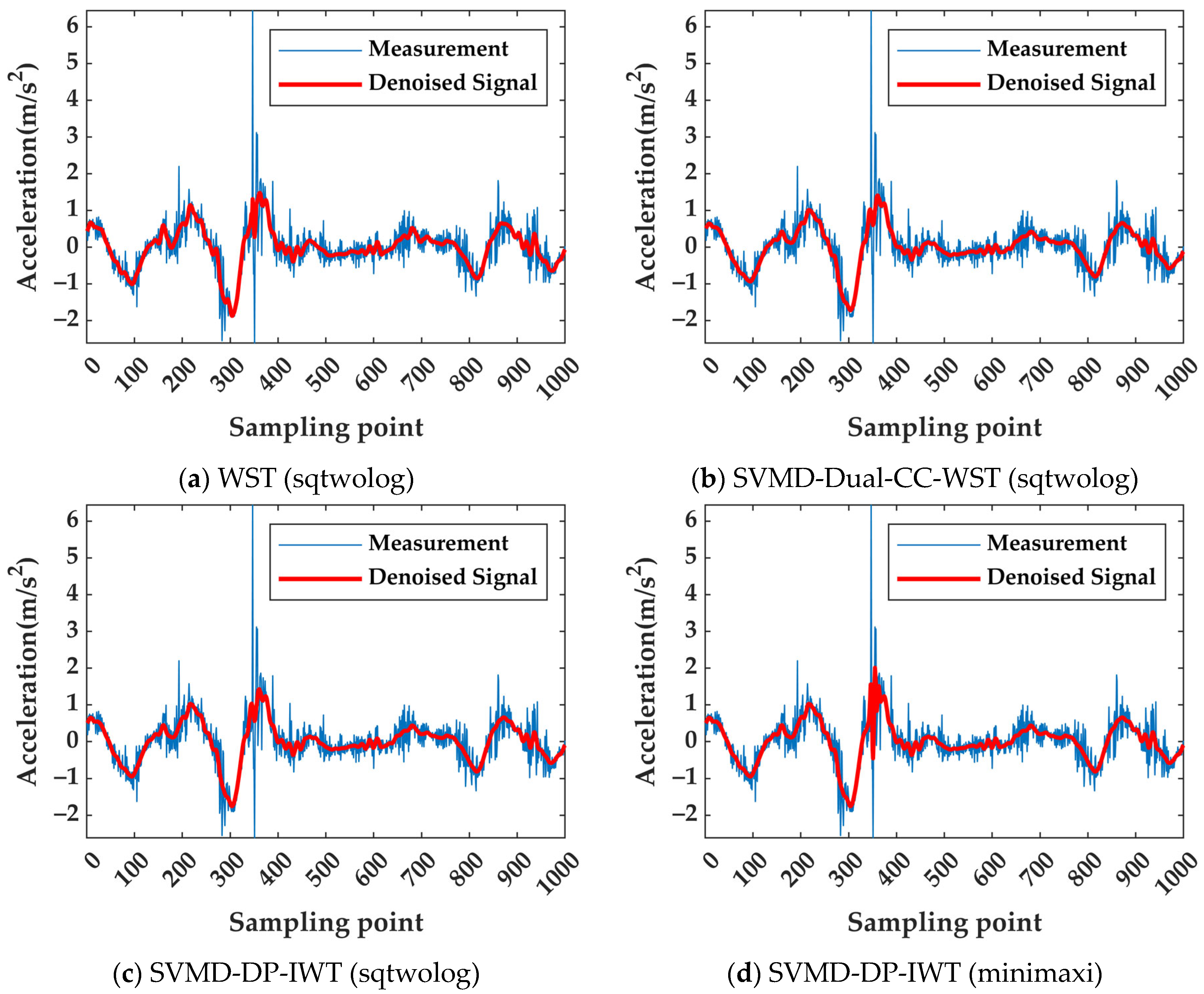
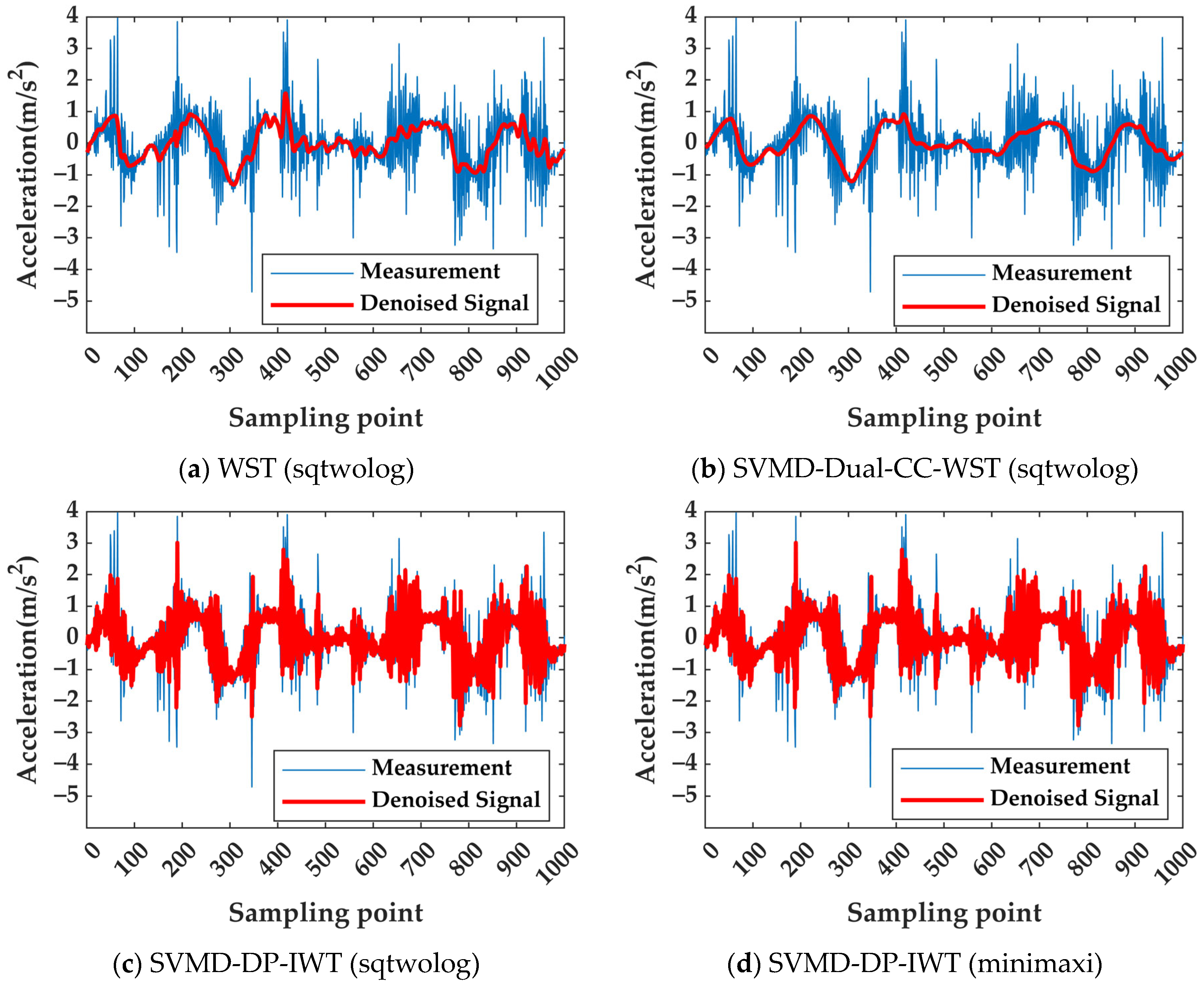
| Scheme | Noise IMF | Noisy IMF | Signal IMF |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | — | — | All |
| 2 | — | Part | Part |
| 3 | Part | Part | Part |
| 4 | Part | — | Part |
| 5 | — | All | — |
| 6 | Part | Part | — |
| 7 | All | — | — |
| WST (Sqtwolog) | SVMD-Dual-CC-WST (Sqtwolog) | SVMD-DP-IWT (Sqtwolog) | SVMD-DP-IWT (Minimaxi) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE (m/s2) | SNR | RMSE (m/s2) | SNR | RMSE (m/s2) | SNR | RMSE (m/s2) | SNR | |
| 1 | 1.3302 | 8.3108 | 0.7076 | 13.7937 | 0.5751 | 15.5941 | 0.5724 | 15.6352 |
| 2 | 1.5701 | 6.8705 | 0.6577 | 14.4287 | 0.6499 | 14.5321 | 0.9161 | 11.5503 |
| 3 | 1.3179 | 8.3912 | 0.7452 | 13.3435 | 0.6674 | 14.3014 | 0.6623 | 14.3683 |
| 4 | 1.4426 | 7.6062 | 0.6928 | 13.9774 | 0.6476 | 14.5633 | 0.7225 | 13.6119 |
| 5 | 1.4859 | 7.3495 | 0.5759 | 15.5826 | 0.6397 | 14.6688 | 0.6661 | 14.3179 |
| 6 | 1.4345 | 7.6547 | 0.7867 | 12.8728 | 0.7025 | 13.8561 | 0.6805 | 14.1318 |
| 7 | 1.4298 | 7.6836 | 0.6336 | 14.7529 | 0.7043 | 13.8344 | 0.5216 | 16.4422 |
| 8 | 1.4227 | 7.7265 | 0.5793 | 15.5313 | 0.8403 | 12.3005 | 0.6476 | 14.5626 |
| 9 | 1.3453 | 8.2125 | 0.731 | 13.5105 | 0.7251 | 13.5806 | 0.7361 | 13.4501 |
| 10 | 1.3841 | 7.9658 | 0.7688 | 13.0727 | 0.6279 | 14.8316 | 0.6036 | 15.174 |
| Method | RMSE (m/s2) | SNR |
|---|---|---|
| WST (sqtwolog) | 1.4163 | 7.7771 |
| SVMD-Dual-CC-WST (sqtwolog) | 0.6878 | 14.0866 |
| SVMD-DP-IWT (sqtwolog) | 0.6780 | 14.2063 |
| SVMD-DP-IWT (minimaxi) | 0.6729 | 14.3244 |
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Supported Constellations | BDS: B1/B2; GPS: L1/L2; GLONASS: L1/L2; GALILEO: E1/E5b |
| Positioning Accuracy | - RTK (RMS): Horizontal 1 cm + 1 ppm, Vertical 1.5 cm + 1 ppm - DGPS: Horizontal 0.5 m, Vertical 1 m |
| Update Rate | - GNSS: 5 Hz, 10 Hz - Integrated Navigation: 100 Hz, 200 Hz |
| INS Performance | - Position Hold: 3.75 m (1σ) for 1 km/2 min - Heading Drift: 0.15°/min - Odometer—Fused Position: 2‰ |
| Method | Mean (mm) | Variance (mm2) | Skewness | Kurtosis | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GNSS Signal 1 | Before denoising | 2.2958 | 0.2061 | 0.0691 | 2.0554 |
| WST (sqtwolog) | 2.2951 | 0.0049 | −0.3565 | 3.5635 | |
| SVMD-Dual-CC-WST (sqtwolog) | 2.3071 | 0.1763 | 0.0140 | 1.5714 | |
| SVMD-DP-IWT (sqtwolog) | 2.3178 | 0.1772 | 0.0141 | 1.5853 | |
| SVMD-DP-IWT (minimaxi) | 2.3178 | 0.1772 | 0.0141 | 1.5853 | |
| GNSS Signal 2 | Before denoising | −0.0352 | 0.4966 | 0.0385 | 2.0513 |
| WST (sqtwolog) | −0.0903 | 0.0156 | 0.1151 | 3.2631 | |
| SVMD-Dual-CC-WST (sqtwolog) | −0.0009 | 0.4349 | −0.0001 | 1.5507 | |
| SVMD-DP-IWT (sqtwolog) | −0.0318 | 0.4419 | 0.0005 | 1.5861 | |
| SVMD-DP-IWT (minimaxi) | −0.0318 | 0.4419 | 0.0005 | 1.5861 |
| Main Oscillator Y Direction (m/s2) | Main Oscillator X Direction (m/s2) | |
|---|---|---|
| 8-degree earthquake intensity | 4 | 3.4 |
| Main Technical Indicators | Parameters |
|---|---|
| Sensitivity | 300 mV/g |
| Range | ±5 g |
| Resolving power | 0.05 g |
| Frequency response range | DC-2500 Hz (−3 dB) |
| Weight | 35 gm |
| Method | Mean (m/s2) | Variance (m2/s4) | Skewness | Kurtosis | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal 1 | Before denoising | 0.0232 | 0.4341 | −0.2005 | 3.5368 |
| WST (sqtwolog) | 0.0233 | 0.2241 | −0.3486 | 3.0688 | |
| SVMD-Dual-CC-WST (sqtwolog) | 0.0204 | 0.2219 | −0.1984 | 2.7202 | |
| SVMD-DP-IWT (sqtwolog) | 0.0205 | 0.2221 | −0.1991 | 2.7246 | |
| SVMD-DP-IWT (minimaxi) | 0.0205 | 0.2221 | −0.1991 | 2.7246 | |
| Signal 2 | Before denoising | 0.0285 | 0.6442 | 0.2516 | 6.2358 |
| WST (sqtwolog) | 0.0287 | 0.2564 | −0.2438 | 4.2555 | |
| SVMD-Dual-CC-WST (sqtwolog) | 0.0241 | 0.2248 | −0.2955 | 4.0302 | |
| SVMD-DP-IWT (sqtwolog) | 0.0247 | 0.2602 | −0.1103 | 4.2131 | |
| SVMD-DP-IWT (minimaxi) | 0.0247 | 0.2602 | −0.1103 | 4.2132 | |
| Signal 3 | Before denoising | 0.0015 | 0.4380 | 0.8008 | 13.5810 |
| WST (sqtwolog) | 0.0017 | 0.2842 | −0.5408 | 4.5606 | |
| SVMD-Dual-CC-WST (sqtwolog) | 0.0014 | 0.2664 | −0.5135 | 4.3759 | |
| SVMD-DP-IWT (sqtwolog) | 0.0015 | 0.2680 | −0.5138 | 4.4176 | |
| SVMD-DP-IWT (minimaxi) | 0.0015 | 0.2749 | −0.3765 | 4.6807 | |
| Signal 4 | Before denoising | 0.0007 | 0.9585 | −0.0722 | 5.1131 |
| WST (sqtwolog) | 0.0011 | 0.2786 | −0.0491 | 2.4973 | |
| SVMD-Dual-CC-WST (sqtwolog) | 0.0008 | 0.2459 | −0.1795 | 2.2451 | |
| SVMD-DP-IWT (sqtwolog) | 0.0007 | 0.6101 | 0.0747 | 3.3963 | |
| SVMD-DP-IWT (minimaxi) | 0.0007 | 0.6101 | 0.0747 | 3.3963 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, J.; Han, H.; Deng, Y.; Dong, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, W. An Improved Wavelet Soft-Threshold Function Integrated with SVMD Dual-Parameter Joint Denoising for Ancient Building Deformation Monitoring. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2057. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17122057
Zhao J, Han H, Deng Y, Dong Y, Wang J, Chen W. An Improved Wavelet Soft-Threshold Function Integrated with SVMD Dual-Parameter Joint Denoising for Ancient Building Deformation Monitoring. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(12):2057. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17122057
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Jiaxing, Houzeng Han, Yang Deng, Youqiang Dong, Jian Wang, and Wenjin Chen. 2025. "An Improved Wavelet Soft-Threshold Function Integrated with SVMD Dual-Parameter Joint Denoising for Ancient Building Deformation Monitoring" Remote Sensing 17, no. 12: 2057. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17122057
APA StyleZhao, J., Han, H., Deng, Y., Dong, Y., Wang, J., & Chen, W. (2025). An Improved Wavelet Soft-Threshold Function Integrated with SVMD Dual-Parameter Joint Denoising for Ancient Building Deformation Monitoring. Remote Sensing, 17(12), 2057. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17122057






