Comprehensive Validation of MODIS-MAIAC Aerosol Products and Long-Term Aerosol Detection over an Urban–Rural Area Around Rome in Central Italy
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Validate MAIAC AOD over 20 years using AERONET ground-based observations, to assess retrieval accuracy and biases related to the MODIS geometrical configuration of acquisition and the size and loading of aerosols.
- Analyze AOD variation over two decades (2001–2022) in Rome and its surroundings to evaluate changes in aerosol levels and their potential drivers.
- Assess local emission sources in selected sub-areas on the aerosol loads through the satellite-based Local-to-Regional Ratio.
2. Materials and Methods
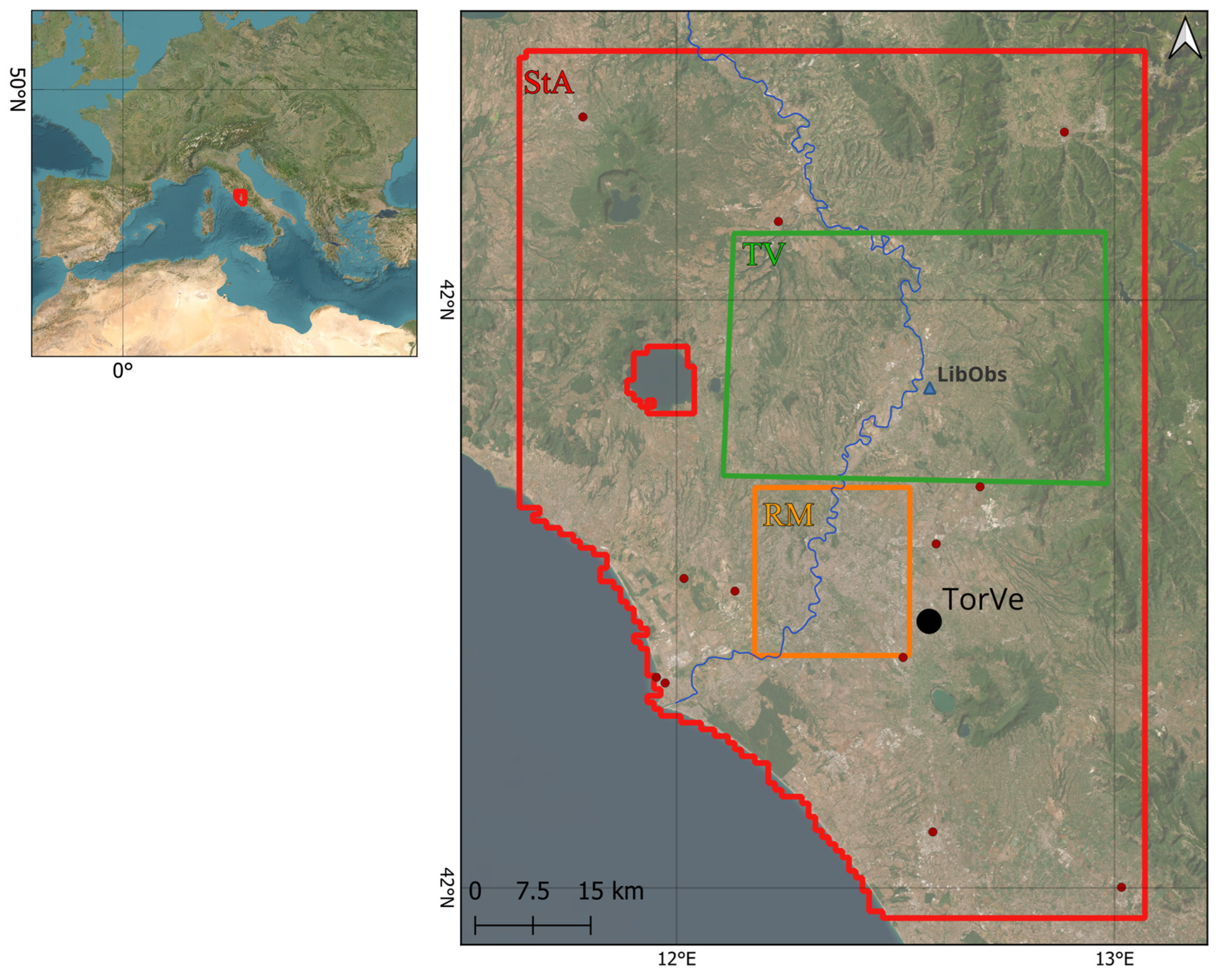
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Ground-Based Remote Sensing with AERONET
2.3. Satellite-Based Remote Sensing with MODIS-MAIAC (AOD) Data
2.4. Meteorological Data
2.5. Data Processing and Validation
2.6. Spatial–Temporal Analysis in Tiber Valley
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Validation with Ground AOD Observations
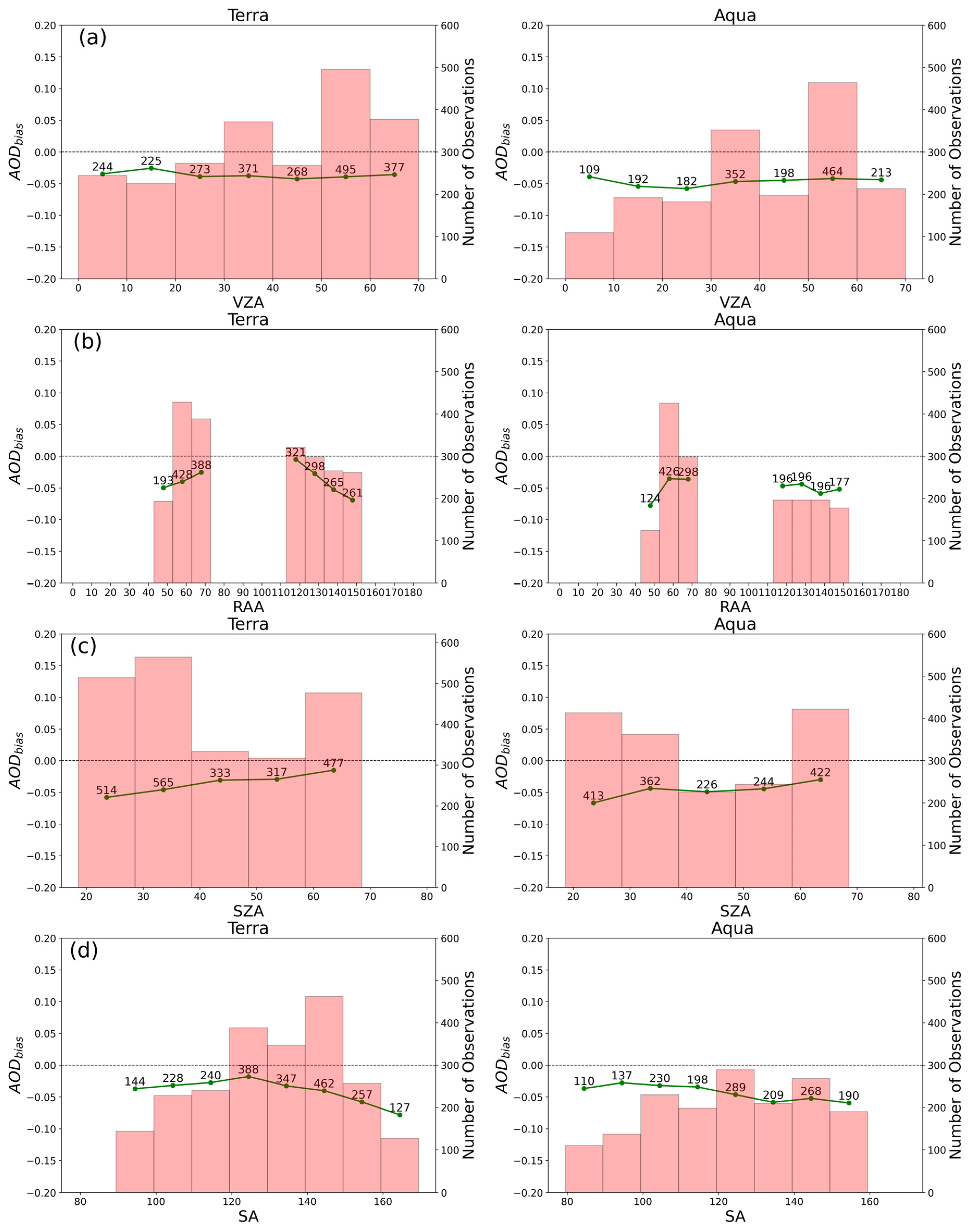
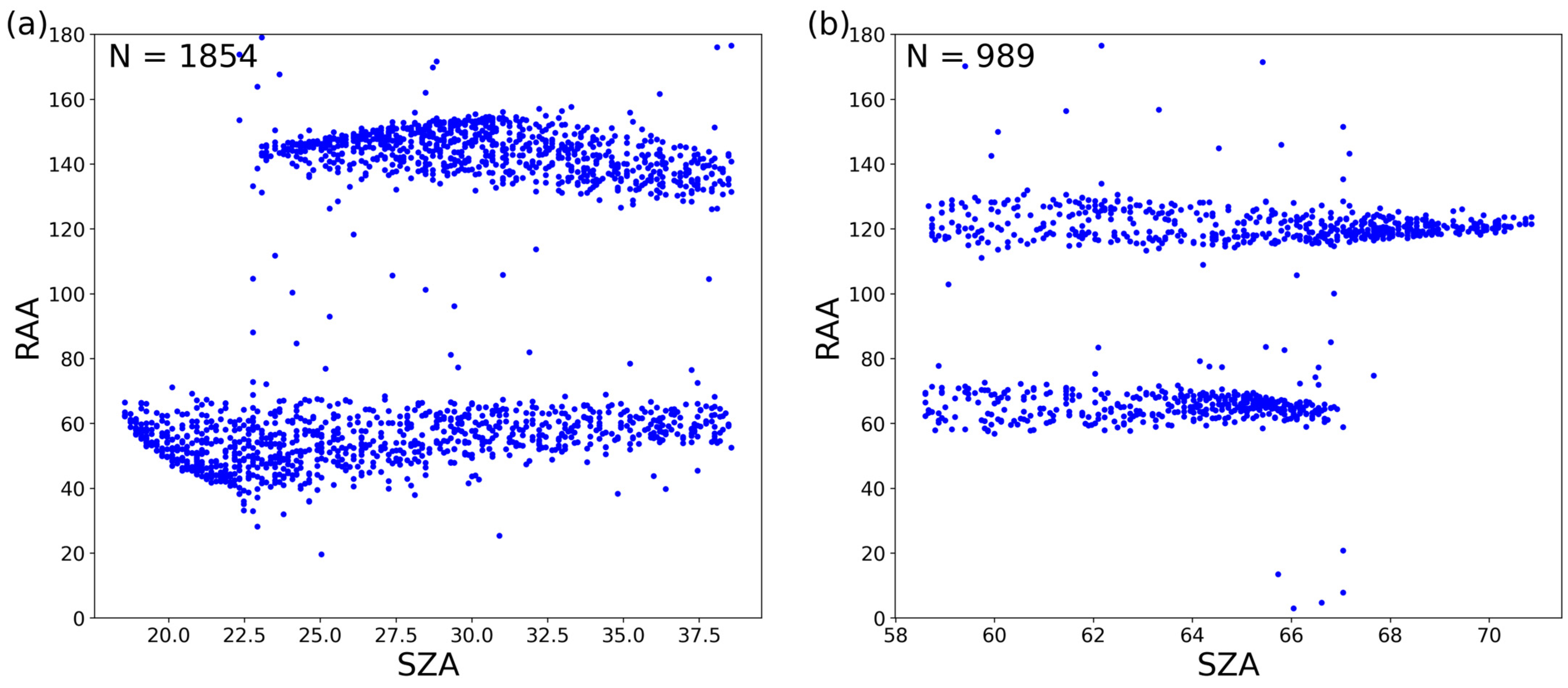
3.2. Geometry Dependence of AOD Retrieval
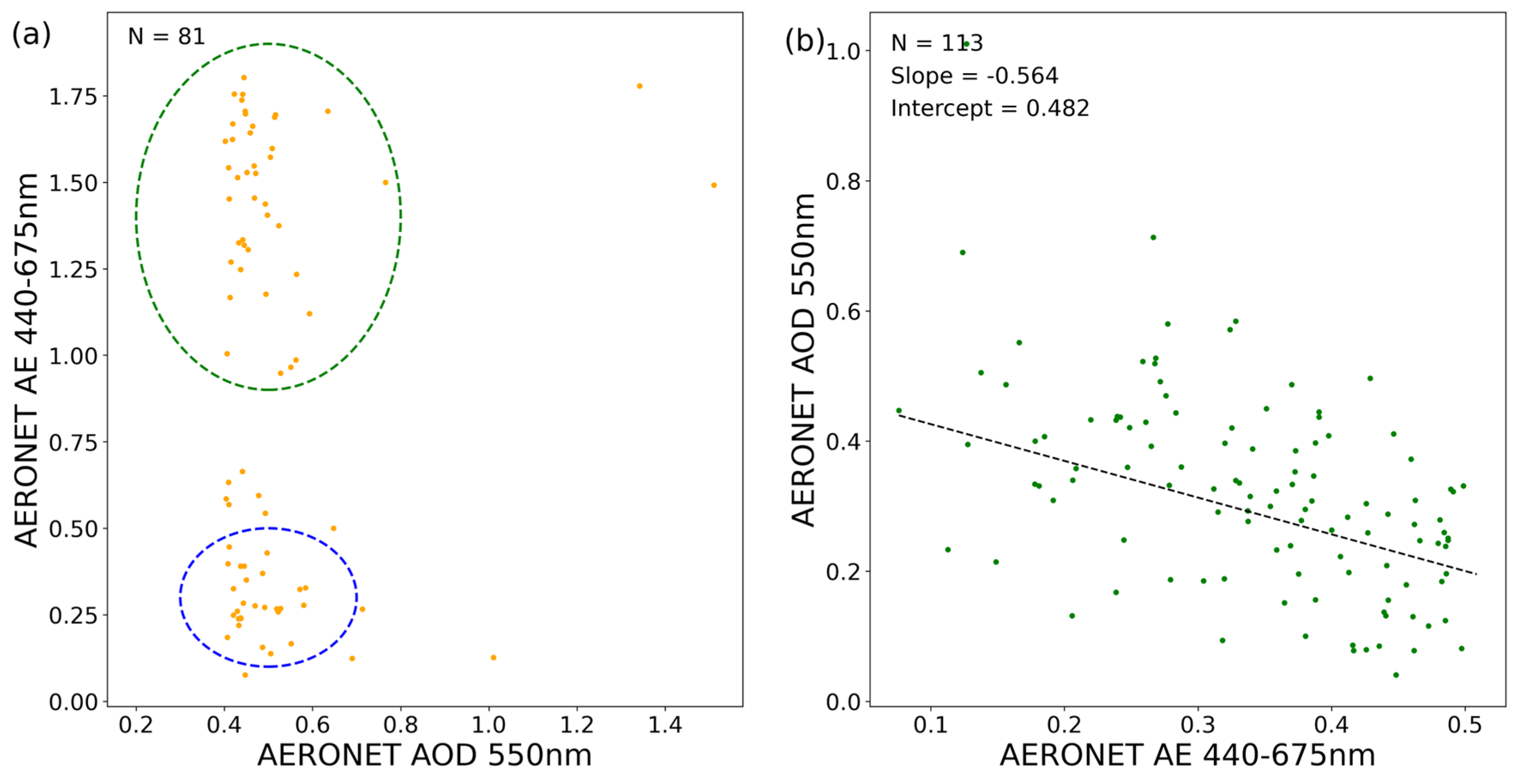
3.3. Aerosol Size and Loading Dependence of AOD Retrieval
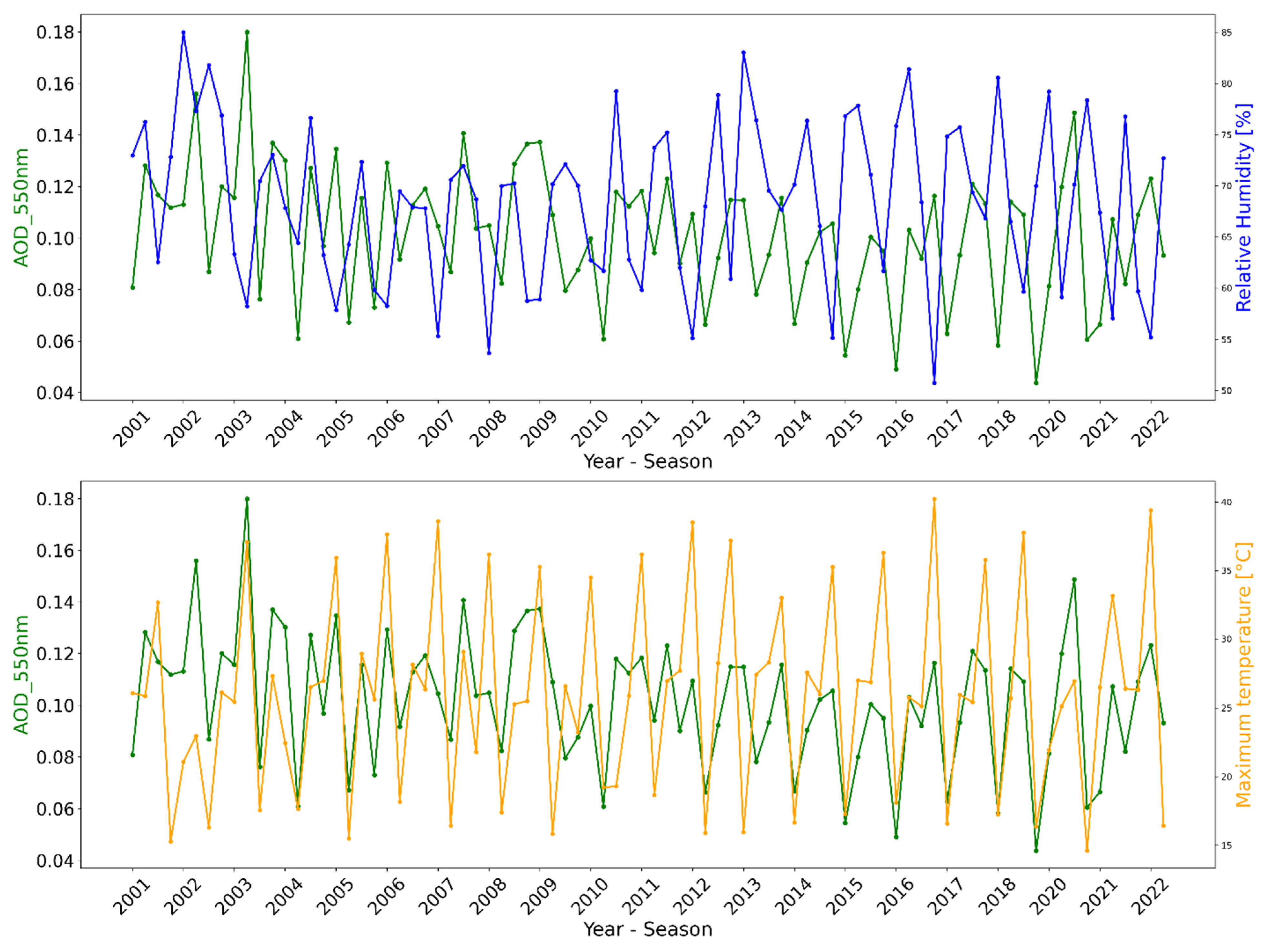
3.4. Meteorological Analysis
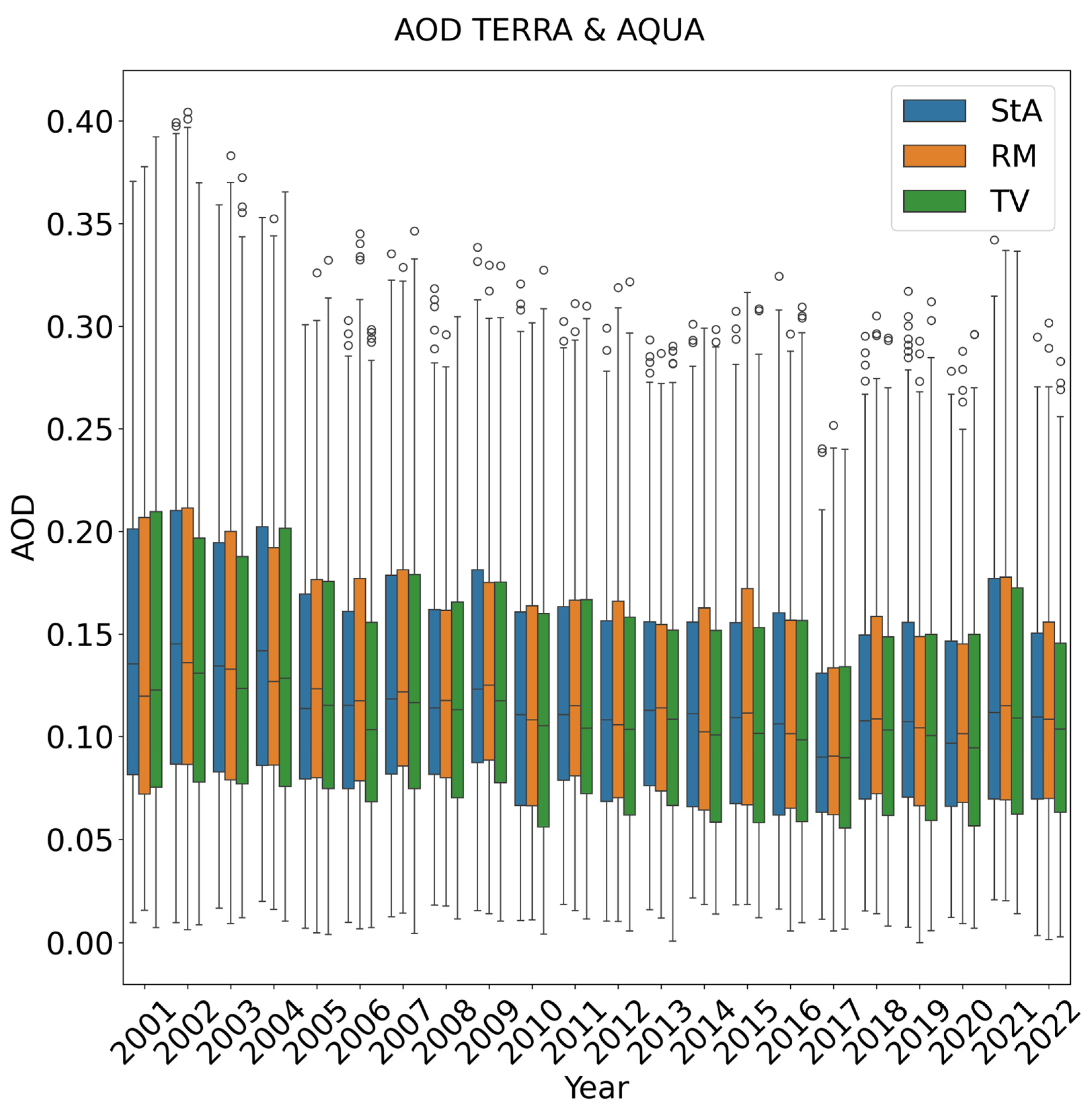
3.5. Spatial–Temporal Analysis in Tiber Valley
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AE | Angstrom Exponent |
| AERONET | Aerosol Robotic Network |
| AOD | Aerosol Optical Depth |
| CNES | Centre National D’Études Spatiales |
| CNRS—INSU | Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique —Institut National des Sciences de l’Univers |
| CR | Cumulative Rainfall |
| EE | Expected Error |
| LTRR | Local-to-Regional Ratio |
| MAIAC | Multi-Angle Implementation of Atmospheric Correction |
| MAE | Mean Absolute Error |
| MODIS | Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer |
| NASA | National Aeronautics and Space Administration |
| PHOTONS | PHOtométrie pour le Traitement Opérationnel de Normalisation Satellitaire |
| RAA | Relative Azimuth Angle |
| RH | Relative Humidity |
| RM | Rome |
| RMB | Root Mean Bias |
| RMSE | Root Mean Square Error |
| SA | Scattering Angle |
| SD | Surface Downwelling Shortwave Radiation |
| StA | Study Area |
| SZA | Solar Zenith Angle |
| Tmax | Temperature Maximum |
| TorVe | AERONET Rome_Tor_Vergata Site |
| TV | Tiber River Valley |
| VZA | View Zenith Angle |
| WS | Wind Speed |
References
- European Environment Agency. Air Pollution in Europe: 2024 Reporting Status Under the National Emission Reduction Commitments Directive; Publications Office: Luxembourg, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- European Parliament. Council of the European Union. Direttiva (UE) 2024/2881 del Parlamento Europeo e del Consiglio, del 23 Ottobre 2024, Relativa alla Qualità dell’aria Ambiente e per Un’aria Più Pulita in Europa; Publications Office: Luxembourg, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. WHO Global Air Quality Guidelines: Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM10), Ozone, Nitrogen Dioxide, Sulfur Dioxide and Carbon Monoxide, 1st ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021; ISBN 978-92-4-003422-8. [Google Scholar]
- Calvin, K.; Dasgupta, D.; Krinner, G.; Mukherji, A.; Thorne, P.W.; Trisos, C.; Romero, J.; Aldunce, P.; Barrett, K.; Blanco, G.; et al. IPCC, 2023: Climate Change 2023: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, 1st ed.; Core Writing Team, Lee, H., Romero, J., Eds.; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Sicard, P.; Agathokleous, E.; De Marco, A.; Paoletti, E.; Calatayud, V. Urban Population Exposure to Air Pollution in Europe over the Last Decades. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2021, 33, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Environment Agency. Europe’s Air Quality Status 2024; EEA Briefing; Publications Office: Luxembourg, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Diapouli, E.; Manousakas, M.I.; Vratolis, S.; Vasilatou, V.; Pateraki, S.; Bairachtari, K.A.; Querol, X.; Amato, F.; Alastuey, A.; Karanasiou, A.A.; et al. AIRUSE-LIFE +: Estimation of Natural Source Contributions to Urban Ambient Air PM10 and PM2. 5 Concentrations in Southern Europe—Implications to Compliance with Limit Values. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 3673–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diner, D.J.; Boland, S.W.; Brauer, M.; Bruegge, C.; Burke, K.A.; Chipman, R.; Di Girolamo, L.; Garay, M.J.; Hasheminassab, S.; Hyer, E. Advances in Multiangle Satellite Remote Sensing of Speciated Airborne Particulate Matter and Association with Adverse Health Effects: From MISR to MAIA. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2018, 12, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollmann, R.; Merchant, C.J.; Saunders, R.; Downy, C.; Buchwitz, M.; Cazenave, A.; Chuvieco, E.; Defourny, P.; De Leeuw, G.; Forsberg, R.; et al. The ESA Climate Change Initiative: Satellite Data Records for Essential Climate Variables. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 94, 1541–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, R.; Xue, Y.; Jiang, X.; Jin, C.; Sun, Y. Retrieval of High-Resolution Aerosol Optical Depth for Urban Air Pollution Monitoring. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnaba, F.; Gobbi, G.P. Aerosol Seasonal Variability over the Mediterranean Region and Relative Impact of Maritime, Continental and Saharan Dust Particles over the Basin from MODIS Data in the Year 2001. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2004, 4, 2367–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faisal, A.-A.-; Kafy, A.-A.; Fattah, M.A.; Jahir, D.M.A.; Al Rakib, A.; Rahaman, Z.A.; Ferdousi, J.; Huang, X. Assessment of Temporal Shifting of PM2.5, Lockdown Effect, and Influences of Seasonal Meteorological Factors over the Fastest-Growing Megacity, Dhaka. Spat. Inf. Res. 2022, 30, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Just, A.C.; Wright, R.O.; Schwartz, J.; Coull, B.A.; Baccarelli, A.A.; Tellez-Rojo, M.M.; Moody, E.; Wang, Y.; Lyapustin, A.; Kloog, I. Using High-Resolution Satellite Aerosol Optical Depth to Estimate Daily PM2.5 Geographical Distribution in Mexico City. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 8576–8584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raptis, I.-P.; Kazadzis, S.; Amiridis, V.; Gkikas, A.; Gerasopoulos, E.; Mihalopoulos, N. A Decade of Aerosol Optical Properties Measurements over Athens, Greece. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnov, A.; Holben, B.N.; Giles, D.M.; Slutsker, I.; O’Neill, N.T.; Eck, T.F.; Macke, A.; Croot, P.; Courcoux, Y.; Sakerin, S.M.; et al. Maritime Aerosol Network as a Component of AERONET—First Results and Comparison with Global Aerosol Models and Satellite Retrievals. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2011, 4, 583–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, E.; Xu, X.; Che, H.; Tang, Z.; Gui, K.; An, L.; Lu, C.; Shi, G. Variation in MERRA-2 Aerosol Optical Depth and Absorption Aerosol Optical Depth over China from 1980 to 2017. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2019, 186, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.C.; Mattoo, S.; Munchak, L.A.; Remer, L.A.; Sayer, A.M.; Patadia, F.; Hsu, N.C. The Collection 6 MODIS Aerosol Products over Land and Ocean. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 2989–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanré, D.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Herman, M.; Mattoo, S. Remote Sensing of Aerosol Properties over Oceans Using the MODIS/EOS Spectral Radiances. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 16971–16988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, N.C.; Jeong, M.-J.; Bettenhausen, C.; Sayer, A.M.; Hansell, R.; Seftor, C.S.; Huang, J.; Tsay, S.-C. Enhanced Deep Blue Aerosol Retrieval Algorithm: The Second Generation. JGR Atmos. 2013, 118, 9296–9315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyapustin, A.; Martonchik, J.; Wang, Y.; Laszlo, I.; Korkin, S. Multiangle Implementation of Atmospheric Correction (MAIAC): 1. Radiative Transfer Basis and Look-up Tables. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, D03210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyapustin, A.; Wang, Y.; Laszlo, I.; Kahn, R.; Korkin, S.; Remer, L.; Levy, R.; Reid, J.S. Multiangle Implementation of Atmospheric Correction (MAIAC): 2. Aerosol Algorithm. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, D03211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyapustin, A.; Wang, Y.; Korkin, S.; Huang, D. MODIS Collection 6 MAIAC Algorithm. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 5741–5765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ding, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Ge, X.; Wang, R.; Zuo, H. Validation and Comparison of High-Resolution MAIAC Aerosol Products over Central Asia. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 251, 118273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, X.; Spurr, R.; Wang, Y.; Drury, E. Improved Algorithm for MODIS Satellite Retrievals of Aerosol Optical Thickness over Land in Dusty Atmosphere: Implications for Air Quality Monitoring in China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2575–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhawish, A.; Banerjee, T.; Sorek-Hamer, M.; Lyapustin, A.; Broday, D.M.; Chatfield, R. Comparison and Evaluation of MODIS Multi-Angle Implementation of Atmospheric Correction (MAIAC) Aerosol Product over South Asia. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 224, 12–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Antonio, L.; Di Biagio, C.; Foret, G.; Formenti, P.; Siour, G.; Doussin, J.-F.; Beekmann, M. Aerosol Optical Depth Climatology from the High-Resolution MAIAC Product over Europe: Differences between Major European Cities and Their Surrounding Environments. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2023, 23, 12455–12475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhdanova, E.Y.; Chubarova, N.Y.; Lyapustin, A.I. Assessment of Urban Aerosol Pollution over the Moscow Megacity by the MAIAC Aerosol Product. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 877–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Águila, A.; Alcaraz-Segura, D.; Martínez-López, J.; Postma, T.; Alados-Arboledas, L.; Zamora, R.; Navas-Guzmán, F. Two Decades of High-Resolution Aerosol Product over the Sierra Nevada Mountain Region (SE Spain): Spatio-Temporal Distribution and Impact on Ecosystems. Atmos. Res. 2024, 308, 107515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Ceca, L.S.; García Ferreyra, M.F.; Lyapustin, A.; Chudnovsky, A.; Otero, L.; Carreras, H.; Barnaba, F. Satellite-Based View of the Aerosol Spatial and Temporal Variability in the Córdoba Region (Argentina) Using over Ten Years of High-Resolution Data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 145, 250–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.; Aditi, K.; Baranwal, H.; Siddiqui, A.; Banerjee, T. Contrasting Nature of Aerosols over South Asian Cities and Its Surrounding Environment. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 360, 124622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I.; Tanré, D.; Buis, J.P.; Setzer, A.; Vermote, E.; Reagan, J.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Nakajima, T.; et al. AERONET—A Federated Instrument Network and Data Archive for Aerosol Characterization. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 66, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassani, C.; Vichi, F.; Esposito, G.; Falasca, S.; Di Bernardino, A.; Battistelli, F.; Casadio, S.; Iannarelli, A.M.; Ianniello, A. Characterization of Nitrogen Dioxide Variability Using Ground-Based and Satellite Remote Sensing and In Situ Measurements in the Tiber Valley (Lazio, Italy). Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanelli, M.; Diémoz, H.; Siani, A.M.; Di Sarra, A.; Iannarelli, A.M.; Kudo, R.; Fasano, G.; Casasanta, G.; Tofful, L.; Cacciani, M.; et al. Aerosol Optical Characteristics in the Urban Area of Rome, Italy, and Their Impact on the UV Index. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2022, 15, 1171–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Bernardino, A.; Iannarelli, A.M.; Casadio, S.; Perrino, C.; Barnaba, F.; Tofful, L.; Campanelli, M.; Di Liberto, L.; Mevi, G.; Siani, A.M.; et al. Impact of Synoptic Meteorological Conditions on Air Quality in Three Different Case Studies in Rome, Italy. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2021, 12, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Struckmeier, C.; Drewnick, F.; Fachinger, F.; Gobbi, G.P.; Borrmann, S. Atmospheric Aerosols in Rome, Italy: Sources, Dynamics and Spatial Variations during Two Seasons. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 15277–15299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yttri, K.E.; Simpson, D.; Bergström, R.; Kiss, G.; Szidat, S.; Ceburnis, D.; Eckhardt, S.; Hueglin, C.; Nøjgaard, J.K.; Perrino, C.; et al. The EMEP Intensive Measurement Period Campaign, 2008–2009: Characterizing Carbonaceous Aerosol at Nine Rural Sites in Europe. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 4211–4233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, D.M.; Sinyuk, A.; Sorokin, M.G.; Schafer, J.S.; Smirnov, A.; Slutsker, I.; Eck, T.F.; Holben, B.N.; Lewis, J.R.; Campbell, J.R.; et al. Advancements in the Aerosol Robotic Network (AERONET) Version 3 Database—Automated near-Real-Time Quality Control Algorithm with Improved Cloud Screening for Sun Photometer Aerosol Optical Depth (AOD) Measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 169–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copernicus Climate Change Service. E-OBS Daily Gridded Meteorological Data for Europe from 1950 to Present Derived from in-Situ Observations; Copernicus Climate Change Service: Reading, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Falah, S.; Mhawish, A.; Sorek-Hamer, M.; Lyapustin, A.I.; Kloog, I.; Banerjee, T.; Kizel, F.; Broday, D.M. Impact of Environmental Attributes on the Uncertainty in MAIAC/MODIS AOD Retrievals: A Comparative Analysis. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 262, 118659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, V.S.; Lyapustin, A.; De Carvalho, L.A.S.; Barbosa, C.C.F.; Novo, E.M.L.M. Validation of High-resolution MAIAC Aerosol Product over South America. JGR Atmos. 2017, 122, 7537–7559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.; Yang, L.; Tian, X.; Bilal, M.; Pei, X.; Zheng, Y.; Lu, X.; Cheng, X. Long-Term Validation and Error Analysis of DB and MAIAC Aerosol Products over Bright Surface of China. Atmos. Res. 2024, 297, 107106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Su, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Cao, M.; Wang, L.; Ma, X.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, L. Evaluation and Analysis of Long-Term MODIS MAIAC Aerosol Products in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 948, 174983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Gui, K.; Che, H.; Li, L.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, X. Changes in Aerosol Loading before, during and after the COVID-19 Pandemic Outbreak in China: Effects of Anthropogenic and Natural Aerosol. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deaconu, L.-T.; Mereuță, A.; Radovici, A.; Ștefănie, H.I.; Botezan, C.; Ajtai, N. Consistency of Aerosol Optical Properties between MODIS Satellite Retrievals and AERONET over a 14-Year Period in Central–East Europe. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizza, U.; Mancinelli, E.; Morichetti, M.; Passerini, G.; Virgili, S. Aerosol Optical Depth of the Main Aerosol Species over Italian Cities Based on the NASA/MERRA-2 Model Reanalysis. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Fang, H.; Wang, L.; Wei, J.; Zhang, M.; Su, X.; Bilal, M.; Liang, X. MODIS High-Resolution MAIAC Aerosol Product: Global Validation and Analysis. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 264, 118684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Zou, B.; Feng, H.; Tang, Y.; Liang, Y. Evaluation and Comparison of MAIAC, DT and DB Aerosol Productsover China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss 2019, 19, 8243–8268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Hoff, R.M.; Kondragunta, S.; Laszlo, I.; Lyapustin, A. Aerosol Optical Depth (AOD) Retrieval Using Simultaneous GOES-East and GOES-West Reflected Radiances over the Western United States. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 471–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolmonen, P.; Virtanen, T. EUMETSAT—Atmospheric Aerosol Optical Depth Retrieval Performance from Sentinel-3 SLSTR SARP; EUMETSAT: Darmstadt, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kokhanovsky, A.A.; Breon, F.-M. Validation of an Analytical Snow BRDF Model Using PARASOL Multi-Angular and Multispectral Observations. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2012, 9, 928–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román, M.O.; Gatebe, C.K.; Schaaf, C.B.; Poudyal, R.; Wang, Z.; King, M.D. Variability in Surface BRDF at Different Spatial Scales (30m–500m) over a Mixed Agricultural Landscape as Retrieved from Airborne and Satellite Spectral Measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2184–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.; Wu, Y.; Levy, R.; Ting, M. The Solar Zenith Angle Impacts MODIS versus CALIPSO AOD Retrieval Biases, with Implications for Arctic Aerosol Seasonality. EGUsphere 2025, 2025, 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Chylek, P.; Henderson, B.; Mishchenko, M. Satellite Based Retrieval of Aerosol Optical Thickness: The Effect of Sun and Satellite Geometry. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, 2003GL016917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutgens, N.; Sayer, A.M.; Heckel, A.; Hsu, C.; Jethva, H.; De Leeuw, G.; Leonard, P.J.T.; Levy, R.C.; Lipponen, A.; Lyapustin, A.; et al. An AeroCom–AeroSat Study: Intercomparison of Satellite AOD Datasets for Aerosol Model Evaluation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 12431–12457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Ianni, A.; Costabile, F.; Barnaba, F.; Di Liberto, L.; Weinhold, K.; Wiedensohler, A.; Struckmeier, C.; Drewnick, F.; Gobbi, G. Black Carbon Aerosol in Rome (Italy): Inference of a Long-Term (2001–2017) Record and Related Trends from AERONET Sun-Photometry Data. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogozovsky, I.; Ohneiser, K.; Lyapustin, A.; Ansmann, A.; Chudnovsky, A. The Impact of Different Aerosol Layering Conditions on the High-Resolution MODIS/MAIAC AOD Retrieval Bias: The Uncertainty Analysis. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 309, 119930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calidonna, C.R.; Avolio, E.; Gullì, D.; Ammoscato, I.; De Pino, M.; Donateo, A.; Lo Feudo, T. Five Years of Dust Episodes at the Southern Italy GAW Regional Coastal Mediterranean Observatory: Multisensors and Modeling Analysis. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas-Agulló, E.; Barriopedro, D.; García, R.D.; Alonso-Pérez, S.; González-Alemán, J.J.; Werner, E.; Suárez, D.; Bustos, J.J.; García-Castrillo, G.; García, O.; et al. Sharp Increase in Saharan Dust Intrusions over the Western Euro-Mediterranean in February–March 2020–2022 and Associated Atmospheric Circulation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2024, 24, 4083–4104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnaba, F.; Bolignano, A.; Di Liberto, L.; Morelli, M.; Lucarelli, F.; Nava, S.; Perrino, C.; Canepari, S.; Basart, S.; Costabile, F.; et al. Desert Dust Contribution to PM10 Loads in Italy: Methods and Recommendations Addressing the Relevant European Commission Guidelines in Support to the Air Quality Directive 2008/50. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 161, 288–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobbi, G.P.; Barnaba, F.; Di Liberto, L.; Bolignano, A.; Lucarelli, F.; Nava, S.; Perrino, C.; Pietrodangelo, A.; Basart, S.; Costabile, F.; et al. An Inclusive View of Saharan Dust Advections to Italy and the Central Mediterranean. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 201, 242–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallone, S.; Stafoggia, M.; Faustini, A.; Gobbi, G.P.; Marconi, A.; Forastiere, F. Saharan Dust and Associations between Particulate Matter and Daily Mortality in Rome, Italy. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 1409–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Martin, R.V.; Van Donkelaar, A.; Hammer, M.S.; Li, C.; Meng, J.; Oxford, C.R.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, D.; et al. Importance of Aerosol Composition and Aerosol Vertical Profiles in Global Spatial Variation in the Relationship between PM2.5 and Aerosol Optical Depth. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2024, 24, 11565–11584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, D.; Tian, P.; Sheng, J.; Liu, Q.; Li, R.; Hu, K.; Jiang, X.; Li, S.; Bi, K.; et al. Tracing the Formation of Secondary Aerosols Influenced by Solar Radiation and Relative Humidity in Suburban Environment. JGR Atmos. 2022, 127, e2022JD036913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerez, S.; Palacios-Peña, L.; Gutiérrez, C.; Jiménez-Guerrero, P.; López-Romero, J.M.; Pravia-Sarabia, E.; Montávez, J.P. Sensitivity of Surface Solar Radiation to Aerosol–Radiation and Aerosol–Cloud Interactions over Europe in WRFv3.6.1 Climatic Runs with Fully Interactive Aerosols. Geosci. Model. Dev. 2021, 14, 1533–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindfors, A.V.; Kouremeti, N.; Arola, A.; Kazadzis, S.; Bais, A.F.; Laaksonen, A. Effective Aerosol Optical Depth from Pyranometer Measurements of Surface Solar Radiation (Global Radiation) at Thessaloniki, Greece. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 3733–3741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, H.; Xia, X.; Zhu, J.; Li, Z.; Dubovik, O.; Holben, B.; Goloub, P.; Chen, H.; Estelles, V.; Cuevas-Agulló, E.; et al. Column Aerosol Optical Properties and Aerosol Radiative Forcing during a Serious Haze-Fog Month over North China Plain in 2013 Based on Ground-Based Sunphotometer Measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 2125–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomassetti, L.; Torre, M.; Tratzi, P.; Paolini, V.; Rizza, V.; Segreto, M.; Petracchini, F. Evaluation of Air Quality and Mobility Policies in 14 Large Italian Cities from 2006 to 2016. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2020, 55, 886–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, F.; Hina, S.; Ullah, I.; Habib, A.; Hina, A.; Ilyas, S.; Hamid, M. Impacts of Irregular and Strategic Lockdown on Air Quality over Indo-Pak Subcontinent: Pre-to-Post COVID-19 Analysis. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2024, 178, 114255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battista, G.; De Lieto Vollaro, E.; De Lieto Vollaro, R. Analysis of the Main Anthropogenic Sources’ Contribution to Pollutant Emissions in the Lazio Region, Italy. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassani, C.; Vichi, F.; Esposito, G.; Montagnoli, M.; Giusto, M.; Ianniello, A. Nitrogen Dioxide Reductions from Satellite and Surface Observations during COVID-19 Mitigation in Rome (Italy). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 22981–23004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garofalide, S.; Postolachi, C.; Cocean, A.; Cocean, G.; Motrescu, I.; Cocean, I.; Munteanu, B.S.; Prelipceanu, M.; Gurlui, S.; Leontie, L. Saharan Dust Storm Aerosol Characterization of the Event (9 to 13 May 2020) over European AERONET Sites. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tositti, L.; Brattich, E.; Cassardo, C.; Morozzi, P.; Bracci, A.; Marinoni, A.; Di Sabatino, S.; Porcù, F.; Zappi, A. Development and Evolution of an Anomalous Asian Dust Event across Europe in March 2020. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 4047–4073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentini, S.; Barnaba, F.; Bernardoni, V.; Calzolai, G.; Costabile, F.; Di Liberto, L.; Forello, A.C.; Gobbi, G.P.; Gualtieri, M.; Lucarelli, F.; et al. Classifying Aerosol Particles through the Combination of Optical and Physical-Chemical Properties: Results from a Wintertime Campaign in Rome (Italy). Atmos. Res. 2020, 235, 104799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| N | K | p-Value | R | RMSE | MAE | RMB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4211 | 0.56 | 0.00 | 0.80 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.20 |
| Within EE (%) | <EE (%) | >EE (%) | ||||
| EE = ±(0.05 + 0.10 × AOD) | 72.31 | 25.72 | 1.97 | |||
| EE = ±(0.05 + 0.15 × AOD) | 77.77 | 20.59 | 1.64 | |||
| AOD Loading | Number | Percentage | R | Within EE (%) | <EE (%) | >EE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AOD ≤ 0.2 | 3342 | 79% | 0.6 | 85.49% | 12.57% | 1.94% |
| AOD > 0.2 | 869 | 21% | 0.7 | 48.10% | 51.44% | 0.46% |
| Year | LTRRRM/StA | Std | LTRRTV/StA | Std |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2001 | 0.093 | ±0.232 | −0.001 | ±0.107 |
| 2002 | 0.133 | ±0.217 | 0.004 | ±0.117 |
| 2003 | 0.070 | ±0.179 | −0.017 | ±0.106 |
| 2004 | 0.084 | ±0.182 | −0.001 | ±0.115 |
| 2005 | 0.106 | ±0.216 | 0.004 | ±0.111 |
| 2006 | 0.115 | ±0.212 | −0.014 | ±0.11 |
| 2007 | 0.092 | ±0.218 | −0.007 | ±0.113 |
| 2008 | 0.098 | ±0.203 | −0.013 | ±0.101 |
| 2009 | 0.097 | ±0.186 | −0.01 | ±0.103 |
| 2010 | 0.109 | ±0.206 | −0.029 | ±0.120 |
| 2011 | 0.087 | ±0.187 | −0.022 | ±0.102 |
| 2012 | 0.084 | ±0.211 | −0.011 | ±0.1 |
| 2013 | 0.106 | ±0.212 | −0.005 | ±0.113 |
| 2014 | 0.076 | ±0.217 | −0.03 | ±0.114 |
| 2015 | 0.102 | ±0.202 | −0.013 | ±0.111 |
| 2016 | 0.110 | ±0.219 | −0.002 | ±0.117 |
| 2017 | 0.072 | ±0.185 | −0.009 | ±0.1 |
| 2018 | 0.110 | ±0.214 | −0.014 | ±0.121 |
| 2019 | 0.116 | ±0.331 | −0.02 | ±0.109 |
| 2020 | 0.164 | ±0.305 | −0.02 | ±0.107 |
| 2021 | 0.109 | ±0.341 | −0.01 | ±0.116 |
| 2022 | 0.114 | ±0.334 | −0.007 | ±0.104 |
| Month | LTRRRM/StA | Std | LTRRTV/StA | Std |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| January | 0.129 | ±0.212 | −0.044 | ±0.107 |
| February | 0.051 | ±0.236 | −0.013 | ±0.110 |
| March | 0.049 | ±0.236 | 0.024 | ±0.109 |
| April | 0.045 | ±0.214 | 0.040 | ±0.105 |
| May | 0.038 | ±0.207 | 0.020 | ±0.117 |
| June | 0.041 | ±0.219 | −0.018 | ±0.112 |
| July | 0.053 | ±0.203 | −0.012 | ±0.111 |
| August | 0.124 | ±0.204 | −0.008 | ±0.095 |
| September | 0.163 | ±0.222 | −0.010 | ±0.104 |
| October | 0.207 | ±0.227 | −0.020 | ±0.109 |
| November | 0.166 | ±0.210 | −0.040 | ±0.101 |
| December | 0.130 | ±0.212 | −0.058 | ±0.108 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Terenzi, V.; Tratzi, P.; Paolini, V.; Ianniello, A.; Barnaba, F.; Bassani, C. Comprehensive Validation of MODIS-MAIAC Aerosol Products and Long-Term Aerosol Detection over an Urban–Rural Area Around Rome in Central Italy. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2051. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17122051
Terenzi V, Tratzi P, Paolini V, Ianniello A, Barnaba F, Bassani C. Comprehensive Validation of MODIS-MAIAC Aerosol Products and Long-Term Aerosol Detection over an Urban–Rural Area Around Rome in Central Italy. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(12):2051. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17122051
Chicago/Turabian StyleTerenzi, Valentina, Patrizio Tratzi, Valerio Paolini, Antonietta Ianniello, Francesca Barnaba, and Cristiana Bassani. 2025. "Comprehensive Validation of MODIS-MAIAC Aerosol Products and Long-Term Aerosol Detection over an Urban–Rural Area Around Rome in Central Italy" Remote Sensing 17, no. 12: 2051. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17122051
APA StyleTerenzi, V., Tratzi, P., Paolini, V., Ianniello, A., Barnaba, F., & Bassani, C. (2025). Comprehensive Validation of MODIS-MAIAC Aerosol Products and Long-Term Aerosol Detection over an Urban–Rural Area Around Rome in Central Italy. Remote Sensing, 17(12), 2051. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17122051









