A Re-Identification Framework for Visible and Thermal-Infrared Aerial Remote Sensing Images with Large Differences of Elevation Angles
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A VTI-ReID framework for aerial images with large elevation angle differences has been proposed.
- To alleviate large elevation angle differences, a method for identity-feature extraction based on global representation decomposition and local feature aggregation is proposed.
- To verify the effectiveness of the proposed framework, a dataset group consisting of aerial visible and thermal-infrared images was proposed. Extensive experiments have shown that the RIRE framework provides relatively reliable cross-modality identity correspondence, and our proposed framework has significantly improved the accuracy of aerial VTI-ReID.
2. Related Works
2.1. Image-Level Methods
2.2. Feature-Level Methods
3. Datasets
3.1. Beach Aerial Infrared Visible Person Dataset
- (1)
- (Lack of quantitative observation angle data: Due to the dependency of person imaging angles on UAV flight altitude, UAV-target distance, and other factors, the BA-VIP dataset currently fails to provide precise quantitative angular measurements. Consequently, it is challenging to analyze the specific impact of elevation angle variations on model performance, which restricts the design of optimization strategies tailored to angular discrepancies.
- (2)
- Limited scene diversity: Constrained by its acquisition environment, the dataset only covers beach and sidewalk scenarios, lacking data from complex urban environments, nighttime conditions, or other geographic regions.
- (3)
- Data scale and imbalance issues: With only 205 identities and an imbalanced distribution between visible (43,843 images) and thermal-infrared (26,795 images) modalities, certain identities may suffer from insufficient samples. This imbalance limits the depth of model training and may lead to inadequate feature learning for low-frequency identities.
3.2. Airborne Vessel Cross-Modality Re-Identification Dataset
4. Methodology
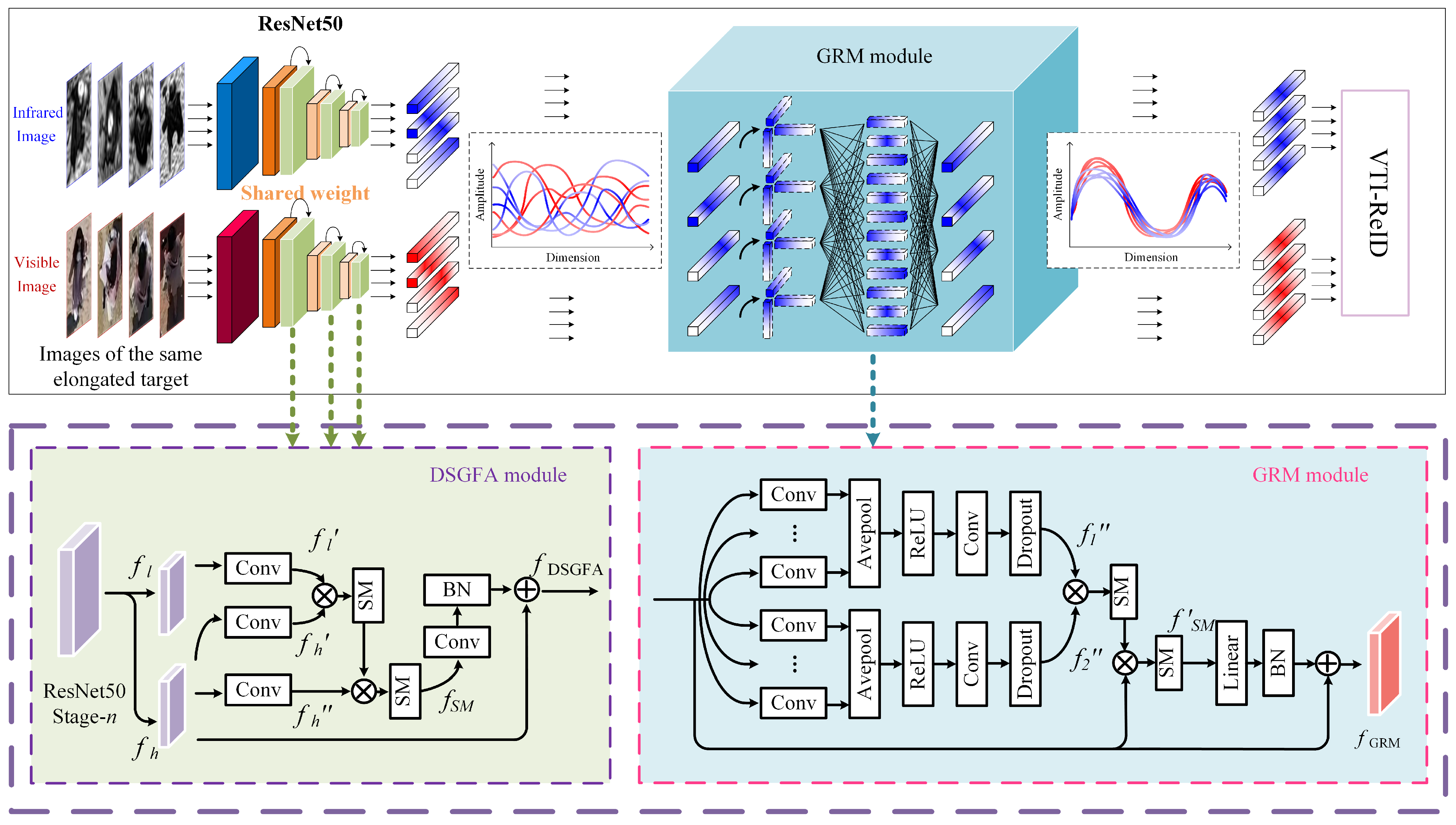
4.1. Aggregation of Deep and Shallow Global Features Module (DSGFA)
4.2. Global Representation Mapping Module (GRM)
5. Results
5.1. Implementation Details
5.2. Comparison with State-of-the-Art Methods
5.3. Ablation Studies
5.4. Visualization
5.4.1. Retrieval Results
5.4.2. Feature Distribution
5.5. Experiments on Public Datasets
6. Discussion
6.1. Analysis of the Effectiveness of Robust Identity Representation Extraction Framework
6.2. Limitations Analysis of Robust Identity Representation Extraction Framework
6.3. Future Research Trends
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, W.; Liu, J.; Qi, G.-J.; Tian, Q.; Li, H. An End-to-End Foreground-Aware Network for Person Re-Identification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 2060–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Z.; Zheng, L.; Luo, Z.; Li, S.; Yang, Y. Learning to Adapt Invariance in Memory for Person Re-Identification. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 43, 2723–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Wang, P.; Ding, C.; Tao, D. Batch Coherence-Driven Network for Part-Aware Person Re-Identification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 3405–3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Liu, M.; Wang, F.; Dai, J.; Liu, A.-A.; Wang, Y. Relation-Preserving Feature Embedding for Unsupervised Person Re-Identification. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2024, 26, 714–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Lu, J.; Yang, M.; Zhou, J. Spatial-Temporal Attention-Aware Learning for Video-Based Person Re-Identification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 28, 4192–4205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, S.; Tian, Q.; Wang, M.; Gao, W. Pose-Guided Representation Learning for Person Re-Identification. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 44, 622–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdous, S.N.; Li, X.; Lyu, S. Uncertainty Aware Multitask Pyramid Vision Transformer for UAV-Based Object Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Bordeaux, France, 16–19 October 2022; pp. 2381–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, A.; Qi, J.; Zhong, P. Self-Aligned Spatial Feature Extraction Network for UAV Vehicle Reidentification. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 20, 6002305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, M.; Yang, X.; Chen, H.; Aly, W.H.; AlTameem, A.; Saudagar, A.K.; Mumtaz, S.; Muhammad, K. Cloth-Changing Person Re-Identification with Invariant Feature Parsing for UAVs Applications. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2024, 73, 12448–12457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Wang, F.; Wang, X.; Li, H.; Sun, F.; Zhou, H. Temporal Context and Environment-Aware Correlation Filter for UAV Object Tracking. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5630915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Wu, C.; Wang, X.; Zhou, F.; Chang, Y.; Yan, L. Online Infrared UAV Target Tracking with Enhanced Context-Awareness and Pixel-Wise Attention Modulation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5005417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Huang, Y.; Lu, H.; Yang, Y. Pose-Invariant Embedding for Deep Person Re-Identification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 28, 4500–4509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Li, W.; Liang, B.; Zhang, J. Spatiotemporal Interaction Transformer Network for Video-Based Person Reidentification in Internet of Things. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023, 10, 12537–12547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Pan, C.; He, S.; Wang, G.; Yang, Y.; Shen, H.T. Towards Robust Person Re-Identification by Adversarial Training with Dynamic Attack Strategy. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2024, 26, 10367–10380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Cui, K.; Wang, C.; Qi, M.; Ma, H. Mutual Distillation Learning for Person Re-Identification. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2024, 26, 8981–8995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Liu, Y. Person Reidentification Based on Automotive Radar Point Clouds. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5101913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhu, M.; Wei, X.; Wang, X.; Zhu, J.; Cheng, J.; Yang, Y. Deep learning-based person re-identification methods: A survey and outlook of recent works. Image Vis. Comput. 2022, 119, 104394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, R.; Chen, L.; Li, Z.; Chen, Z.; Wu, B. A Scene Graph Encoding and Matching Network for UAV Visual Localization. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 9890–9902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maboudi, M.; Homaei, M.; Song, S.; Malihi, S.; Saadatseresht, M.; Gerke, M. A Review on Viewpoints and Path Planning for UAV-Based 3-D Reconstruction. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2023, 16, 5026–5048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Quijano, K.; Crawford, M.M. YOLOv5-Tassel: Detecting Tassels in RGB UAV Imagery with Improved YOLOv5 Based on Transfer Learning. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 8085–8094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Qi, J.; Chen, C.; Bin, K.; Zhong, P. Relation-Aware Weight Sharing in Decoupling Feature Learning Network for UAV RGB-Infrared Vehicle Re-Identification. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2024, 26, 9839–9853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Cao, H.; Yang, X.; Deng, C.; Tao, D. Self-Training With Progressive Representation Enhancement for Unsupervised Cross-Domain Person Re-Identification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 5287–5298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Tian, M.; Li, M.; Wei, Z.; Yuan, L.; Wang, N.; Gao, X. SSRR: Structural Semantic Representation Reconstruction for Visible-Infrared Person Re-Identification. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2024, 26, 6273–6284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kansal, K.; Subramanyam, A.V.; Wang, Z.; Satoh, S. SDL: Spectrum-Disentangled Representation Learning for Visible-Infrared Person Re-Identification. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2020, 30, 3422–3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Liu, H.; Meng, F.; Li, X. Bi-Directional Exponential Angular Triplet Loss for RGB-Infrared Person Re-Identification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 1583–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Xu, J.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Z. Alleviating Modality Bias Training for Infrared-Visible Person Re-Identification. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2022, 24, 1570–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Lan, X.; Leng, Q.; Shen, J. Cross-Modality Person Re-Identification via Modality-Aware Collaborative Ensemble Learning. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 9387–9399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Chai, Y.; Chen, F.; Liu, H. A Fourier-Based Semantic Augmentation for Visible-Thermal Person Re-Identification. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2022, 29, 1684–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Yang, X.; Wang, N.; Gao, X. Flexible Body Partition-Based Adversarial Learning for Visible Infrared Person Re-Identification. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2022, 33, 4676–4687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Dong, W.; Li, M.; Wei, Z.; Wang, N.; Gao, X. Cooperative Separation of Modality Shared-Specific Features for Visible-Infrared Person Re-Identification. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2024, 26, 8172–8183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Chen, F.; Yu, J.; Ji, Y.; Wu, F.; Liu, T.; Liu, S.; Jing, X.Y.; Luo, J. Cross-Modality Spatial-Temporal Transformer for Video-Based Visible-Infrared Person Re-Identification. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2024, 26, 6582–6594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yan, Y.; Gao, L.; Xu, C.; Su, N.; Feng, S. A Third-Modality Collaborative Learning Approach for Visible-Infrared Vessel Reidentification. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 19035–19047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.; Zheng, W.-S.; Yu, H.-X.; Gong, S.; Lai, J. RGB-Infrared Cross-Modality Person Re-identification. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 5390–5399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, T.; Cheng, J.; Liu, S.; Yang, Y.; Hou, Z. RGB-Infrared Cross-Modality Person Re-Identification via Joint Pixel and Feature Alignment. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 3622–3631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Chuang, Y.-Y.; Satoh, S. Learning to Reduce Dual-Level Discrepancy for Infrared-Visible Person Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 618–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Zhao, S.; Ye, M.; Shen, J. Cross-Modality Person Re-Identification via Modality Confusion and Center Aggregation. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 16383–16392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Yang, X.; Wang, N.; Gao, X. Syncretic Modality Collaborative Learning for Visible Infrared Person Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Ruan, W.; Du, B.; Shou, M.Z. Channel Augmented Joint Learning for Visible-Infrared Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 13547–13556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wei, X.; Hong, X.; Gong, Y. Infrared-visible cross-modal person re-identification with an x modality. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2020, 34, 4610–4617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yan, Y.; Lu, Y.; Wang, H. Towards a unified middle modality learning for visible-infrared person re-identification. In Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Chengdu, China, 20–24 October 2021; pp. 788–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Kim, S.; Park, J.; Park, S.; Sohn, K. PartMix: Regularization Strategy to Learn Part Discovery for Visible-Infrared Person Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2023; pp. 18621–18632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Shen, J.; Crandall, D.J.; Shao, L.; Luo, J. Dynamic dual-attentive aggregation learning for visible-infrared person re-identification. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Proceedings, Part XVII 16; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 229–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Lee, S.; Kim, Y.; Kim, T.; Kim, C. Hi-CMD: Hierarchical Cross-Modality Disentanglement for Visible-Infrared Person Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 10254–10263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhang, T.; Li, B.; Chu, Q.; Yu, N. Cross-Modality Person Re-Identification with Shared-Specific Feature Transfer. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 13376–13386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Dai, P.; Chen, J.; Lin, C.W.; Wu, Y.; Huang, F.; Zhong, B.; Ji, R. Discover Cross-Modality Nuances for Visible-Infrared Person Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 4328–4337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, F.; Pei, H.; Yang, Y.; Li, W. Learning Memory-Augmented Unidirectional Metrics for Cross-modality Person Re-identification. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 19344–19353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, H. Diverse Embedding Expansion Network and Low-Light Cross-Modality Benchmark for Visible-Infrared Person Re-identification. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2023; pp. 2153–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Wu, A.; Zheng, W.-S. Shape-Erased Feature Learning for Visible-Infrared Person Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2023; pp. 22752–22761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Wang, Z.; Lan, X.; Yuen, P. Visible thermal person re-identification via dual-constrained top-ranking. IJCAI 2018, 1, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Wang, N.; Li, J.; Gao, X. HSME: Hypersphere manifold embedding for visible thermal person re-identification. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2019, 33, 8385–8392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Lai, J.; Xie, X. Learning Modality-Specific Representations for Visible-Infrared Person Re-Identification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Lan, X.; Wang, Z.; Yuen, P.C. Bi-Directional Center-Constrained Top-Ranking for Visible Thermal Person Re-Identification. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2020, 15, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, S.; Wang, Y.; Dai, P.; Lin, X.; Wu, Y.; Ji, R. Exploring invariant representation for visible-infrared person re-identification. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.00884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhong, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Liang, F.; Ma, L. Adaptive Sparse Pairwise Loss for Object Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2023; pp. 19691–19701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.T.; Hong, H.G.; Kim, K.W.; Park, K.R. Person recognition system based on a combination of body images from visible light and thermal cameras. Sensors 2017, 17, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://enterprise.dji.com/cn/matrice-300 (accessed on 1 November 2023).
- Available online: https://enterprise.dji.com/cn/zenmuse-h20-series (accessed on 1 November 2023).
- Luo, H.; Gu, Y.; Liao, X.; Lai, S.; Jiang, W. Bag of Tricks and a Strong Baseline for Deep Person Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 1487–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, T.; Yang, Y.; Cheng, J.; Chang, J.; Liang, X.; Hou, Z. Cross-modality paired-images generation for RGB-infrared person re-identification. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2020, 34, 12144–12151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Zheng, L.; Kang, G.; Li, S.; Yang, Y. Random erasing data augmentation. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2020, 34, 13001–13008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Shen, J.; Lin, G.; Xiang, T.; Shao, L.; Hoi, S.C.H. Deep Learning for Person Re-Identification: A Survey and Outlook. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 44, 2872–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, C.; Hu, Y.; Wu, X.; Shi, H.; Mei, T.; He, R. CM-NAS: Cross-Modality Neural Architecture Search for Visible-Infrared Person Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 11803–11812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Huang, Z.; Hu, P.; Li, T.; Lv, J.; Peng, X. Learning with Twin Noisy Labels for Visible-Infrared Person Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 14288–14297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Maaten, L.; Hinton, G.E. Visualizing Data using t-SNE. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2008, 9, 2579–2605. [Google Scholar]
- Xuan, H.; Stylianou, A.; Liu, X.; Pless, R. Hard negative examples are hard, but useful. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Proceedings, Part XIV 16; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 126–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
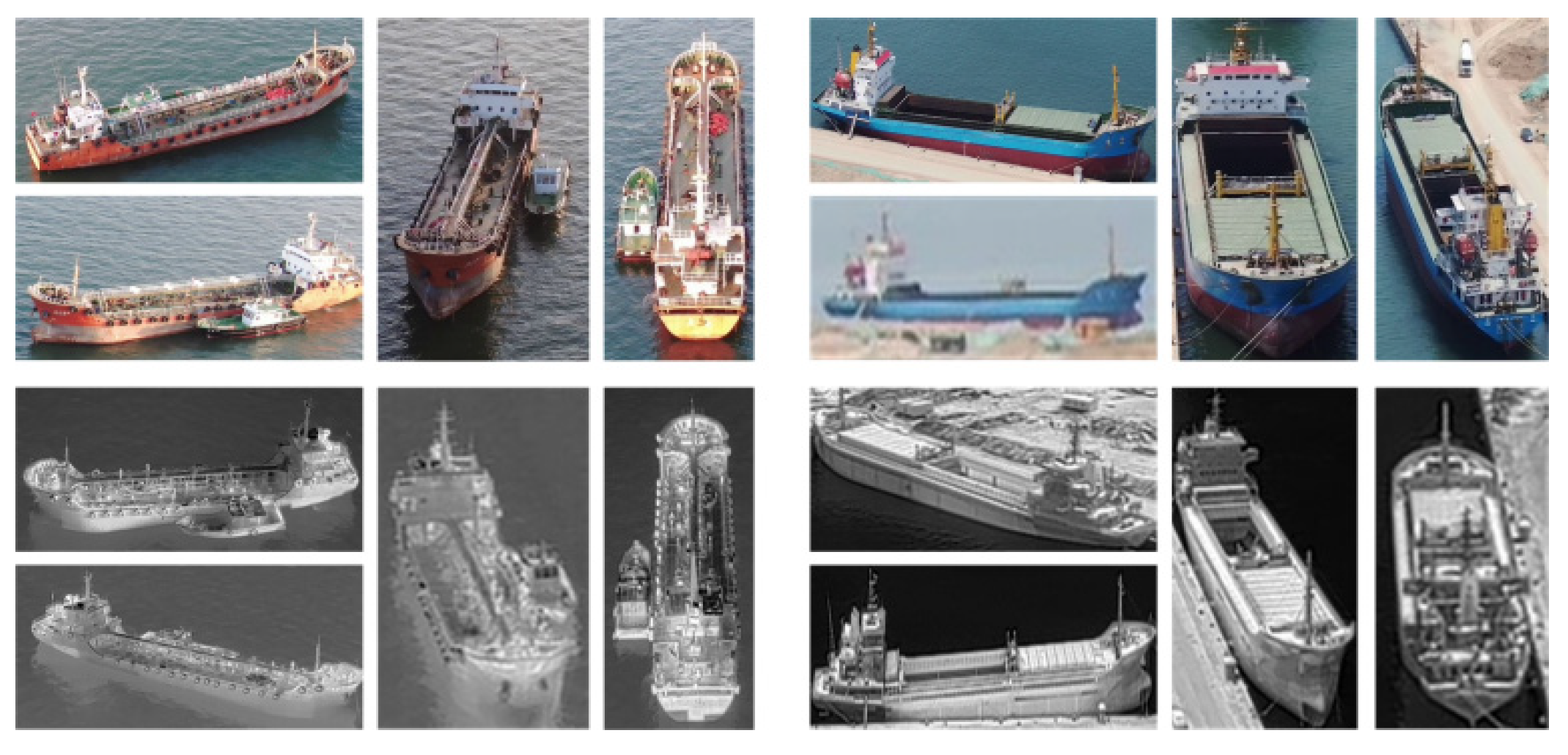






| Datasets | Types of Targets | Range of Elevation Angle | Modality | Identity | Visible | Infrared |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RegDB [55] | Person | 0–20/160–180 | Visible and Thermal-infrared | 412 | 4120 | 4120 |
| SYSU-MM01 [34] | Person | 0–10/170–180 | Visible and Near-infrared | 491 | 26,061 | 12,210 |
| LLCM [47] | Person | 0–20/160–180 | Visible and Near-infrared | 1064 | 25,626 | 21,141 |
| AVC-ReID [32] | Vessel | 10–170 | Visible and Thermal-infrared | 138 | 3071 | 2530 |
| BA-VIP (Ours) | Person | 60–120 | Visible and Thermal-infrared | 205 | 43,843 | 26,795 |
| Settings | BA-VIP (VIS to IR) | BA-VIP (IR to VIS) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | Year | Rank-1 | Rank-10 | Rank-20 | mAP | mINP | Rank-1 | Rank-10 | Rank-20 | mAP | mINP |
| DDAG [42] | 2020 | 55.85% | 76.96% | 81.85% | 41.88% | 15.13% | 56.58% | 73.96% | 78.90% | 42.20% | 14.80% |
| CM-NAS [62] | 2021 | 56.25% | 76.35% | 81.48% | 44.94% | 17.09% | 61.45% | 77.16% | 81.70% | 49.89% | 21.23% |
| CAJ [38] | 2021 | 58.71% | 75.77% | 81.36% | 42.55% | 14.97% | 62.01% | 78.10% | 82.62% | 50.22% | 20.76% |
| DEEN [47] | 2023 | 63.54% | 81.79% | 86.34% | 49.96% | 21.11% | 72.19% | 86.84% | 90.22% | 56.15% | 23.48% |
| SGIEL [48] | 2023 | 67.05% | 82.16% | 86.41% | 53.70% | 22.08% | 69.15% | 83.24% | 86.47% | 57.14% | 25.78% |
| RIRE (Ours) | 69.07% | 84.01% | 88.55% | 59.54% | 33.23% | 76.62% | 86.41% | 88.91% | 66.40% | 37.52% | |
| Settings | AVC-ReID (VIS to IR) | AVC-ReID (IR to VIS) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | Year | Rank-1 | Rank-10 | Rank-20 | mAP | Rank-1 | Rank-10 | Rank-20 | mAP |
| DDAG [42] | 2020 | 28.10% | 74.39% | 90.02% | 42.70% | 25.26% | 72.54% | 89.33% | 39.98% |
| CAJ [38] | 2021 | 29.58% | 72.50% | 87.49% | 43.44% | 31.13% | 75.87% | 90.09% | 45.44% |
| AGW [61] | 2022 | 31.41% | 78.79% | 92.73% | 46.54% | 33.79% | 80.61% | 92.72% | 49.04% |
| DART [63] | 2022 | 43.73% | 87.46% | 96.48% | 58.35% | 45.30% | 87.94% | 96.32% | 59.73% |
| DEEN [47] | 2023 | 47.47% | 92.07% | 98.50% | 62.58% | 46.55% | 89.36% | 96.88% | 61.00% |
| TMCN [32] | 2024 | 50.40% | 94.53% | 99.00% | 65.61% | 53.09% | 94.67% | 99.06% | 67.76% |
| RIRE (Ours) | 52.91% | 94.65% | 99.30% | 66.99% | 59.69% | 90.74% | 95.87% | 69.99% | |
| Settings (IR to VIS) | BA-VIP (VIS to IR) | BA-VIP (IR to VIS) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DSGFA | GRM | Rank-1 | Rank-10 | Rank-20 | mAP | mINP | Rank-1 | Rank-10 | Rank-20 | mAP | mINP |
| 63.54% | 81.79% | 86.34% | 49.96% | 21.11% | 72.19% | 86.84% | 90.22% | 56.15% | 23.48% | ||
| √ | 64.33% | 81.75% | 86.73% | 50.54% | 21.02% | 72.59% | 87.26% | 91.07% | 56.61% | 24.20% | |
| √ | 66.86% | 81.45% | 85.86% | 58.52% | 31.78% | 75.96% | 87.82% | 90.72% | 65.54% | 35.46% | |
| √ | √ | 69.07% | 84.01% | 88.55% | 59.54% | 33.23% | 76.62% | 86.41% | 88.91% | 66.40% | 37.52% |
| Settings (IR to VIS) | AVC-ReID (VIS to IR) | AVC-ReID (IR to VIS) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DSGFA | GRM | Rank-1 | Rank-10 | Rank-20 | mAP | Rank-1 | Rank-10 | Rank-20 | mAP |
| 40.00% | 87.67% | 95.47% | 55.47% | 45.01% | 86.18% | 94.02% | 58.70% | ||
| √ | 41.05% | 89.19% | 96.98% | 56.86% | 46.30% | 87.18% | 95.01% | 59.66% | |
| √ | 48.72% | 91.98% | 98.02% | 63.01% | 58.12% | 89.17% | 97.44% | 68.90% | |
| √ | √ | 52.91% | 94.65% | 99.30% | 66.99% | 59.69% | 90.74% | 95.87% | 69.99% |
| Methods | SYSU-MM01 | RegDB | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Search | Indoor Search | VIS to IR | IR to VIS | |||||||||||||
| R-1 | R-10 | R-20 | mAP | R-1 | R-10 | R-20 | mAP | R-1 | R-10 | R-20 | mAP | R-1 | R-10 | R-20 | mAP | |
| BDTR [49] | 17.0 | 55.4 | 72.0 | 19.7 | - | - | - | - | 33.6 | 58.6 | 67.4 | 32.8 | 32.9 | 58.5 | 68.4 | 32.0 |
| D2RL [35] | 28.9 | 70.6 | 82.4 | 29.2 | - | - | - | - | 43.4 | 66.1 | 76.3 | 44.1 | - | - | - | - |
| Hi-CMD [43] | 34.9 | 77.6 | - | 35.9 | - | - | - | - | 70.9 | 86.4 | - | 66.0 | - | - | - | - |
| JSIA-ReID [59] | 38.1 | 80.7 | 89.9 | 36.9 | 43.8 | 86.2 | 94.2 | 52.9 | 48.1 | - | - | 48.9 | 48.5 | - | - | 49.3 |
| AlignGAN [34] | 42.4 | 85.0 | 93.7 | 40.7 | 45.9 | 87.6 | 94.4 | 54.3 | 57.9 | - | - | 53.6 | 56.3 | - | - | 53.4 |
| X-Modality [39] | 49.9 | 89.8 | 96.0 | 50.7 | - | - | - | - | 62.2 | 83.1 | 91.7 | 60.2 | - | - | - | - |
| DDAG [42] | 54.8 | 90.4 | 95.8 | 53.0 | 61.0 | 94.1 | 98.4 | 68.0 | 69.3 | 86.2 | 91.5 | 63.5 | 68.1 | 85.2 | 90.3 | 61.8 |
| CM-NAS [62] | 60.8 | 92.1 | 96.8 | 58.9 | 68.0 | 94.8 | 97.9 | 52.4 | 82.8 | 95.1 | 97.7 | 79.3 | 81.7 | 94.1 | 96.9 | 77.6 |
| MCLNet [36] | 65.4 | 93.3 | 97.1 | 62.0 | 72.6 | 97.0 | 99.2 | 76.6 | 80.3 | 92.7 | 96.0 | 73.1 | 75.9 | 90.9 | 94.6 | 69.5 |
| SMCL [37] | 67.4 | 92.9 | 96.8 | 61.8 | 68.8 | 96.6 | 98.8 | 75.6 | 83.9 | - | - | 79.8 | 83.1 | - | - | 78.6 |
| CAJ [38] | 69.9 | 95.7 | 98.5 | 66.9 | 76.3 | 97.9 | 99.5 | 80.4 | 85.0 | 95.5 | 97.5 | 79.1 | 84.8 | 95.3 | 97.5 | 77.8 |
| MPANet [45] | 70.6 | 96.2 | 98.8 | 68.2 | 76.7 | 98.2 | 99.6 | 81.0 | 82.8 | - | - | 80.7 | 83.7 | - | - | 80.9 |
| MMN [40] | 70.6 | 96.2 | 99.0 | 66.9 | 76.2 | 97.2 | 99.3 | 79.6 | 91.6 | 97.7 | 98.9 | 84.1 | 87.5 | 96.0 | 98.1 | 80.5 |
| DEEN [47] | 74.7 | 97.6 | 99.2 | 71.8 | 80.3 | 99.0 | 99.8 | 83.3 | 91.1 | 97.8 | 98.9 | 85.1 | 89.5 | 96.8 | 98.4 | 83.4 |
| PartMix [41] | 77.8 | - | - | 74.6 | 81.5 | - | - | 84.4 | 84.9 | - | - | 82.5 | 85.7 | - | - | 82.3 |
| RIRE (ours) | 80.9 | 98.1 | 99.8 | 79.1 | 86.2 | 99.1 | 100.0 | 88.9 | 92.6 | 98.5 | 99.2 | 84.3 | 89.8 | 97.7 | 98.9 | 83.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, C.; Wang, W.; Yan, Y.; Ge, B.; Hou, W.; Gao, F. A Re-Identification Framework for Visible and Thermal-Infrared Aerial Remote Sensing Images with Large Differences of Elevation Angles. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1956. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17111956
Zhao C, Wang W, Yan Y, Ge B, Hou W, Gao F. A Re-Identification Framework for Visible and Thermal-Infrared Aerial Remote Sensing Images with Large Differences of Elevation Angles. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(11):1956. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17111956
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Chunhui, Wenxuan Wang, Yiming Yan, Baoyu Ge, Wei Hou, and Fengjiao Gao. 2025. "A Re-Identification Framework for Visible and Thermal-Infrared Aerial Remote Sensing Images with Large Differences of Elevation Angles" Remote Sensing 17, no. 11: 1956. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17111956
APA StyleZhao, C., Wang, W., Yan, Y., Ge, B., Hou, W., & Gao, F. (2025). A Re-Identification Framework for Visible and Thermal-Infrared Aerial Remote Sensing Images with Large Differences of Elevation Angles. Remote Sensing, 17(11), 1956. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17111956








