Remote Sensing of Particle Absorption Coefficient of Pigments Using a Two-Stage Framework Integrating Optical Classification and Machine Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Remote Sensing Inversion Methods for aph(λ)
1.1.1. Empirical and Semi-Analytical Approaches
1.1.2. Limitations of Existing Models
1.2. Water Optical Classification Techniques
1.2.1. Classification Based on Bio-Optical and Inherent Properties
1.2.2. Challenges in Classification Criteria
1.2.3. Subjectivity and Machine Learning Potential
1.3. Research Gaps and Objectives
2. Materials and Methods
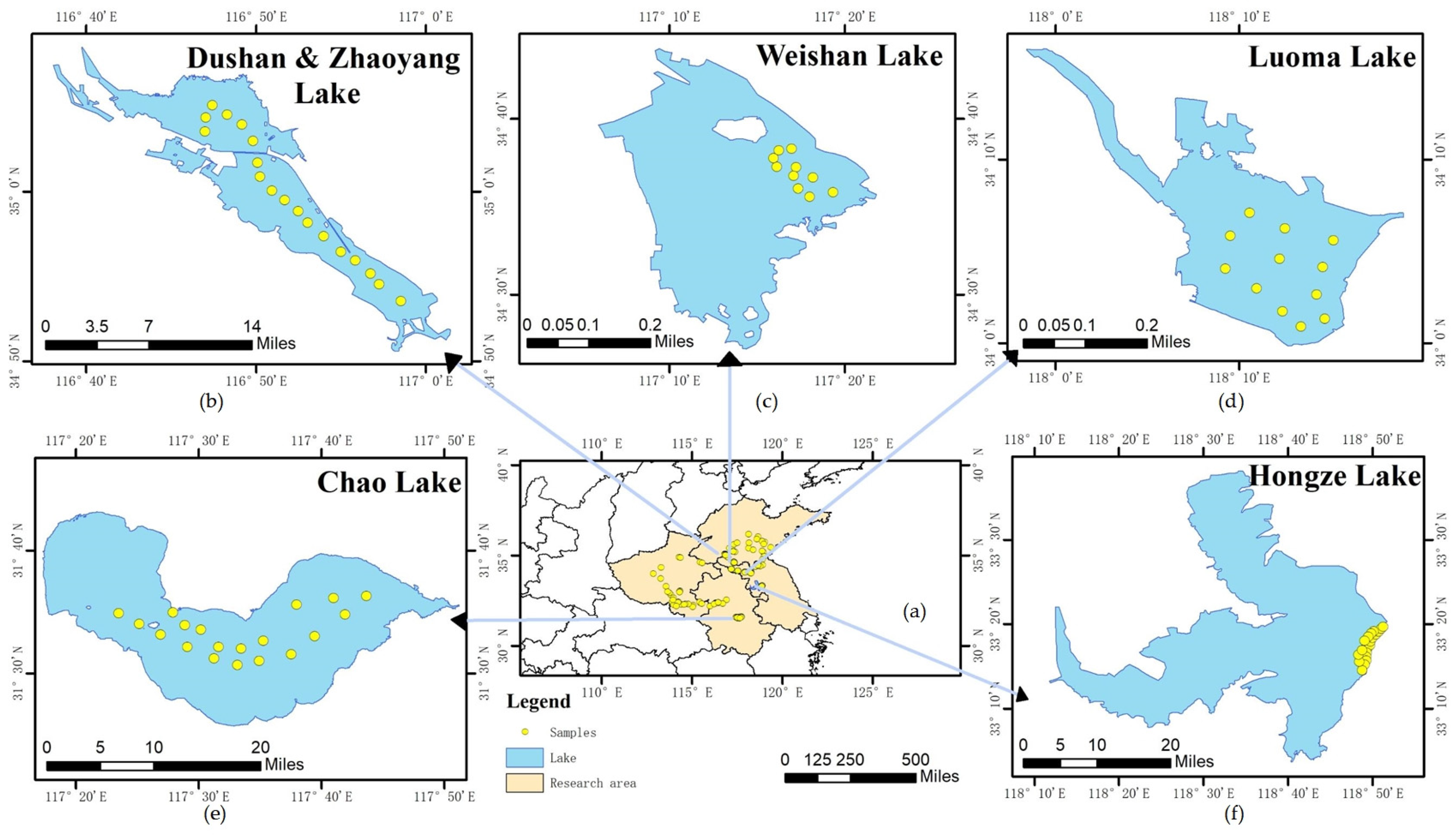
2.1. Study Area
2.2. In Situ Data Collection
2.3. A Novel Two-Stage Framework for aph(λ) Inversion Combining Optical Classification and Regression
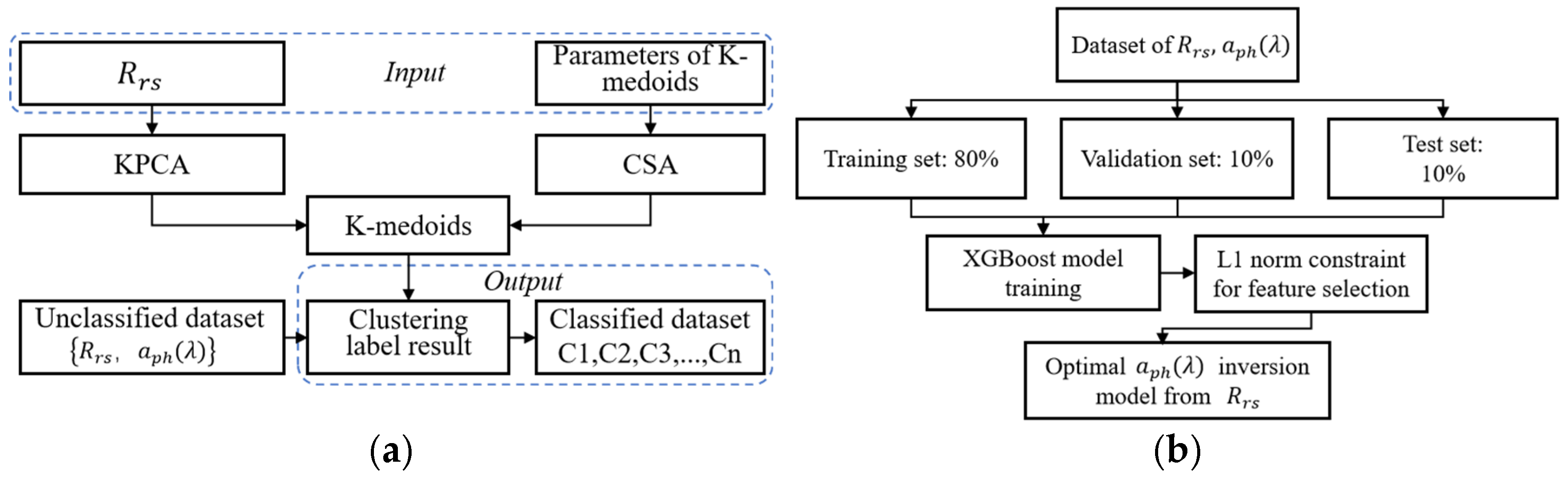
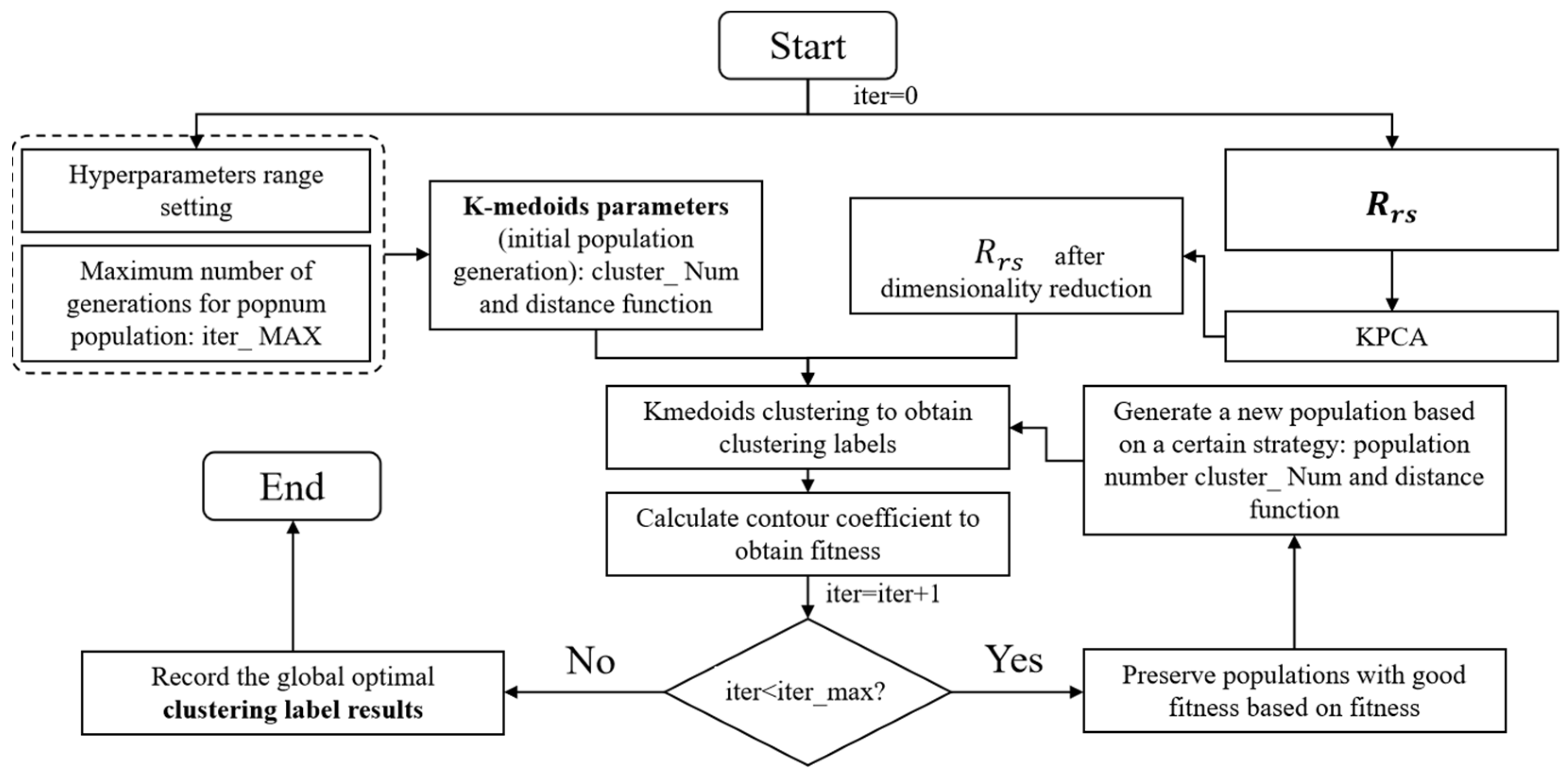
2.3.1. K-Medoid Optical Clustering Method Based on KPAC Dimensionality Reduction and CSA
- (1)
- KPAC Dimensionality Reduction:
- (2)
- CSA Optimization for k-medoids:
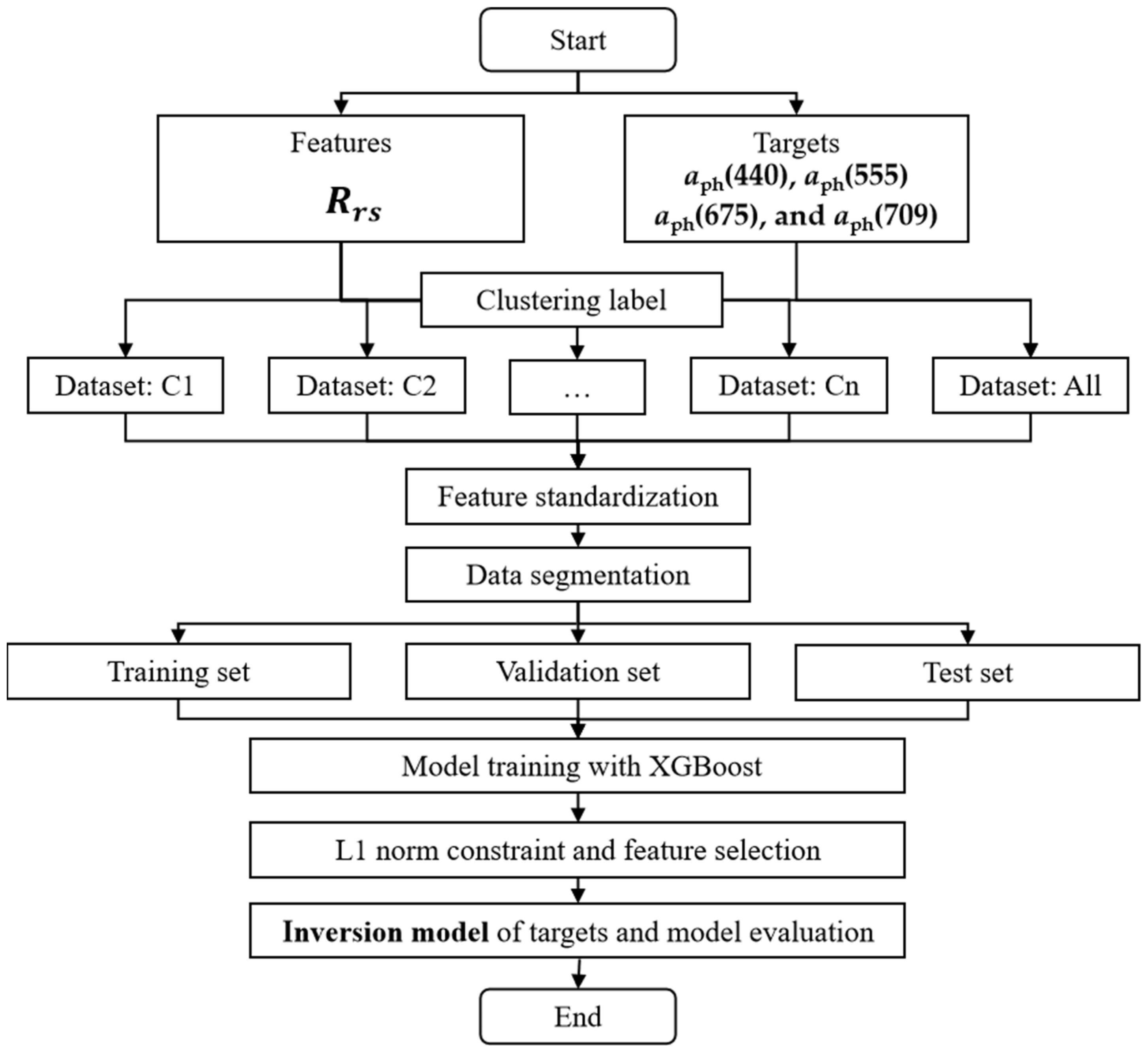
2.3.2. XGBoost Regression Method Based on L1-Norm Feature Selection
- (1)
- Data Preparation and Normalization: Construct datasets integrating full-band reflectance spectra with target parameters, followed by feature standardization to mitigate scale variance.
- (2)
- Regularized Model Training: Partition data into training (80%), validation (10%), and test sets (10%). Implement L1-norm constraints within the loss function to enforce feature sparsity during XGBoost training.
- (3)
- Spectral Band Selection: Eliminate non-informative bands exhibiting zero feature weights post-regularization, establishing a parsimonious inversion model.
- (4)
- Accuracy Validation: Quantify model performance using root mean square error (RMSE) and coefficient of determination (R2) metrics on independent test data.
3. Results
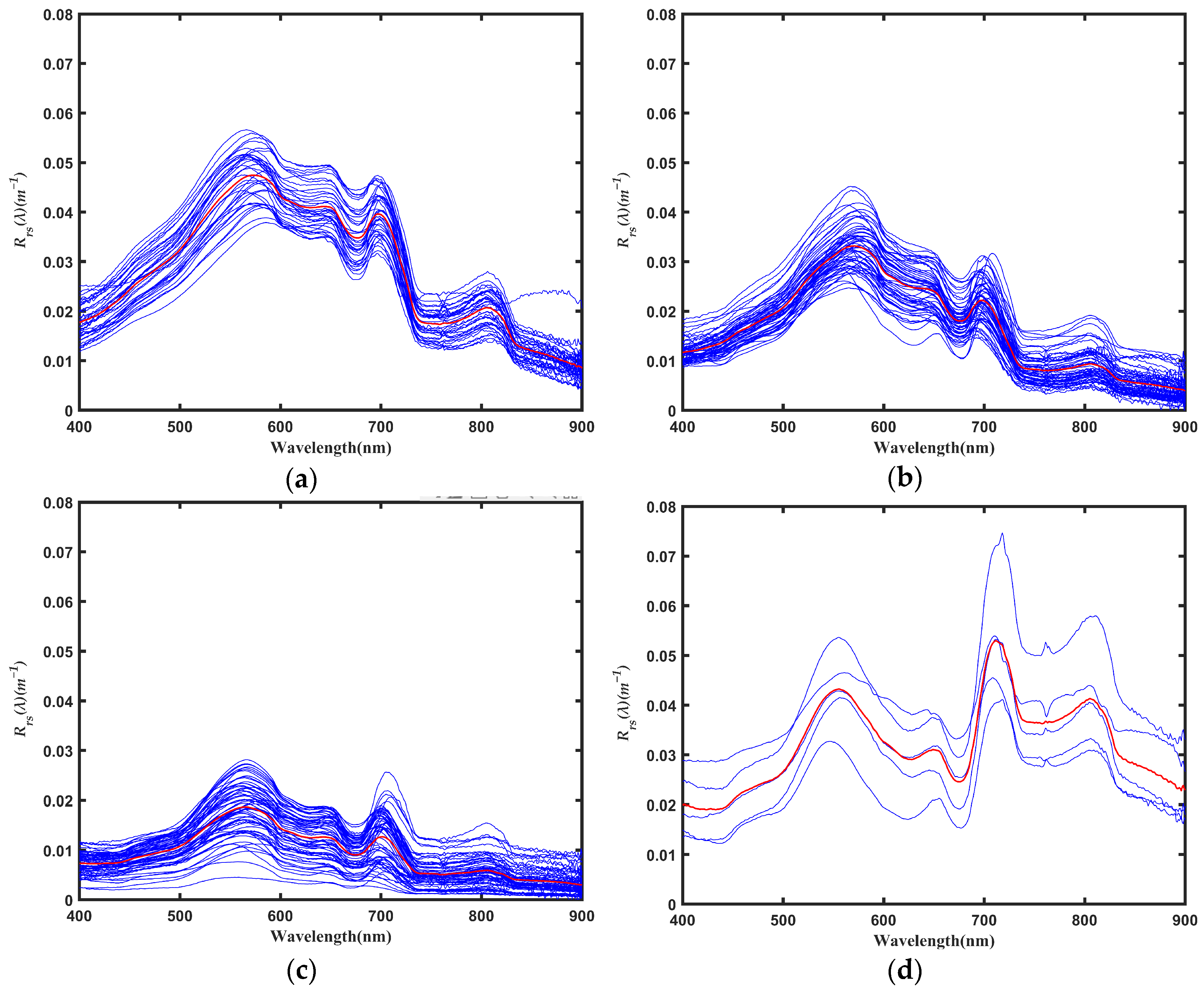
3.1. Spectrum of Remote Sensing Reflectance and Pigment Particle Absorption Coefficient
3.2. Result of Classification
3.3. Result of Regression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Optical classification significantly improved inversion accuracy, with R2 > 0.9 for aph(440), aph(675), and aph(709) across water types.
- (2)
- The method effectively addresses current limitations in remote monitoring of pigment absorption, particularly in complex inland waters.
- (3)
- While performance for aph(555) was comparatively lower (R2 = 0.877–0.998), the overall framework shows strong potential for water quality monitoring applications.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smetacek, V.; Zingone, A. Green and golden seaweed tides on the rise. Nature 2013, 504, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Field, C.B.; Behrenfeld, M.J.; Randerson, J.T.; Falkowski, P. Primary production of the biosphere: Integrating terrestrial and oceanic components. Science 1998, 281, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosik, H.M.; Mitchell, B.G. Light absorption by phytoplankton, photosynthetic pigments and detritus in the california current system. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 1995, 42, 1717–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woźniak, S.B.; Litwicka, D.; Stoń-Egiert, J. Variability and relationships between particle sizes, composition and optical properties of suspended particulate matter in the coastal waters of western spitsbergen, assessed through measurements of size-fractionated seawater samples. Oceanologia 2024, 66, 66403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lednicka, B.; Kubacka, M.; Freda, W.; Haule, K.; Ficek, D.; Sokólski, M. Multi-parameter algorithms of remote sensing reflectance, absorption and backscattering for coastal waters of the southern baltic sea applied to pomeranian lakes. Water 2023, 15, 2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, C.; Tan, K.; Wang, X.; Du, P.; Pan, C. A semi-analytical approach for estimating inland water inherent optical properties and chlorophyll a using airborne hyperspectral imagery. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2024, 128, 103774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Chicote, J.; Armengol, X.; Rojo, C. Zooplankton abundance: A neglected key element in the evaluation of reservoir water quality. Limnologica 2018, 69, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efimova, T.; Churilova, T.; Skorokhod, E.; Suslin, V.; Buchelnikov, A.S.; Glukhovets, D.; Khrapko, A.; Moiseeva, N. Light absorption by optically active components in the arctic region (august 2020) and the possibility of application to satellite products for water quality assessment. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Duan, G.; Huang, Z.; Cai, W.; Lu, C.; Su, W.; Yang, J.; Zhang, C. Remote sensing classification of the dominant optically active components and its variations in the pearl river estuary. Haiyang Xuebao 2016, 38, 64–75. [Google Scholar]
- Matsushita, B.; Yang, W.; Yu, G.; Oyama, Y.; Yoshimura, K.; Fukushima, T. A hybrid algorithm for estimating the chlorophyll-a concentration across different trophic states in asian inland waters. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 102, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Loiselle, S.A.; Yang, D.; Ma, R.; Su, W.; Gao, C. Remote estimation of chlorophyll a concentrations over a wide range of optical conditions based on water classification from viirs observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 241, 111735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bricaud, A.; Babin, M.; Morel, A.; Claustre, H. Variability in the chlorophyll-specific absorption coefficients of natural phytoplankton: Analysis and parameterization. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1995, 100, 13321–13332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Lei, S.; Bi, S.; Li, Y.; Lyu, H.; Xu, J.; Xu, X.; Mu, M.; Miao, S.; Zeng, S.; et al. Tracking spatio-temporal dynamics of poc sources in eutrophic lakes by remote sensing. Water Res. 2020, 168, 115162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Liu, Z. Deriving absorption coefficients from remote sensing reflectance using the quasi analytical algorithm (qaa) in the yellow sea. Period. Ocean. Univ. China 2007, S2, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Z.; Carder, K.L.; Arnone, R.A. Deriving inherent optical properties from water color: A multiband quasi-analytical algorithm for optically deep waters. Appl. Opt. 2002, 41, 5755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Matsushita, B.; Chen, J.; Yoshimura, K.; Fukushima, T. Application of a semianalytical algorithm to remotely estimate diffuse attenuation coefficient in turbid inland waters. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 1046–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, J.; Zhang, D.J.; Zhang, G.Y.; Wang, C.X.; Zhou, G.Q. Estimation of optical properties using qaa-v6 model based on modis data. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2020, XLII-3/W10, 937–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.; Weidemann, A.; Kindle, J.; Arnone, R.; Carder, K.L.; Davis, C. Euphotic zone depth: Its derivation and implication to ocean-color remote sensing. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2007, 112, 2006JC003802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Matsushita, B.; Chen, J.; Yoshimura, K.; Fukushima, T. Retrieval of inherent optical properties for turbid inland waters from remote-sensing reflectance. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 3761–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert Chen, F.; Lee, Z.; Carder, K.L. An bathymetric algorithm of water-leaving radiances in aviris imagery: Use of a reflectance model. In Space Remote Sensing of Subtropical Oceans (SRSSO); COSPAR Colloquia Series; COSPAR: Paris, France, 1997; pp. 221–228. Available online: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0964274997800261 (accessed on 31 January 2024). [CrossRef]
- Zibordi, G.; Berthon, J.F.; Talone, M.; Gossn, J.I.; Dessailly, D.; Kwiatkowska, E. Assessment of olci-a derived aquatic optical properties across european seas. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 20, 1502605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shen, F.; Zhao, H.; Sun, X.; Zhu, Q.; Li, M. Optical distinguishability of phytoplankton species and its implications for hyperspectral remote sensing discrimination potential. J. Sea Res. 2024, 202, 102540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, H.; Bi, S.; Lyu, H. Research progress of remote sensing monitoring of case ii water environmental parameters based on water optical classification. Natl. Remote Sens. Bull. 2021, 26, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, C.; Li, Y.; Zha, Y.; Sun, D. Specific absorption coefficient and the phytoplankton package effect in lake taihu, china. Hydrobiologia 2009, 619, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spyrakos, E.; O’donnell, R.; Hunter, P.D.; Miller, C.; Scott, M.; Simis, S.G.; Neil, C.; Barbosa, C.C.; Binding, C.E.; Bradt, S.; et al. Optical types of inland and coastal waters. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2018, 63, 846–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arst, H.; Reinart, A. Application of optical classifications to north european lakes. Aquat. Ecol. 2009, 43, 789–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alimonte, D.; Zibordi, G.; Berthon, J.-F. A statistical index of bio-optical seawater types. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 2644–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenings, J.P.; Edmundson, J.A. Secchi disk and photometer estimates of light regimes in alaskan lakes: Effects of yellow color and turbidity. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1991, 36, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koponen, S. Lake water quality classification with airborne hyperspectral spectrometer and simulated meris data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 79, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinart, A.; Herlevi, A.; Arst, H.; Sipelgas, L. Preliminary optical classification of lakes and coastal waters in estonia and south finland. J. Sea Res. 2003, 49, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Ma, R.; Feng, S.; Le, C. Optically active substances and their contributions to the underwater light climate in lake taihu, a large shallow lake in china. Fundam. Appl. Limnol. 2007, 170, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wu, C.; Zhao, S.; Xu, X.; Wang, Y.; Huang, C. Estimation of chlorophyll a concentration using nir/red bands of meris and classification procedure in inland turbid water. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 988–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, H.; Hieronymi, M.; Röttgers, R.; Krasemann, H.; Qiu, Z. Hyperspectral differentiation of phytoplankton taxonomic groups: A comparison between using remote sensing reflectance and absorption spectra. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 14781–14805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieur, L.; Sathyendranath, S. An optical classification of coastal and oceanic waters based on the specific spectral absorption curves of phytoplankton pigments, dissolved organic matter, and other particulate materials1. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1981, 26, 671–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, K. Research progress on remote sensing assessment of lake nutrient status and retrieval algorithms of characteristic parameters. Natl. Remote Sens. Bull. 2022, 26, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welschmeyer, N.A. Fluorometric analysis of chlorophyll a in the presence of chlorophyll b and pheopigments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1994, 39, 1985–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Feng, S.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, M.; Qin, B. A study of absorption characteristics of chromophoric dissolved organic matter and particles in lake taihu, china. Hydrobiologia 2007, 592, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, Y.-H.; Bricaud, A.; Morel, A. Light backscattering efficiency and related properties of some phytoplankters. Deep Sea Res. Part A Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 1992, 39, 1835–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutser, T. Quantitative detection of chlorophyll in cyanobacterial blooms by satellite remote sensing. Limnol. Ocean. 2004, 49, 2179–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, S.; Li, Y.; Xu, J.; Liu, G.; Song, K.; Mu, M.; Lyu, H.; Miao, S.; Xu, J. Optical classification of inland waters based on an improved Fuzzy C-Means method. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 34838–34856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameters | Clusters | RMSE | R2 | λ (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
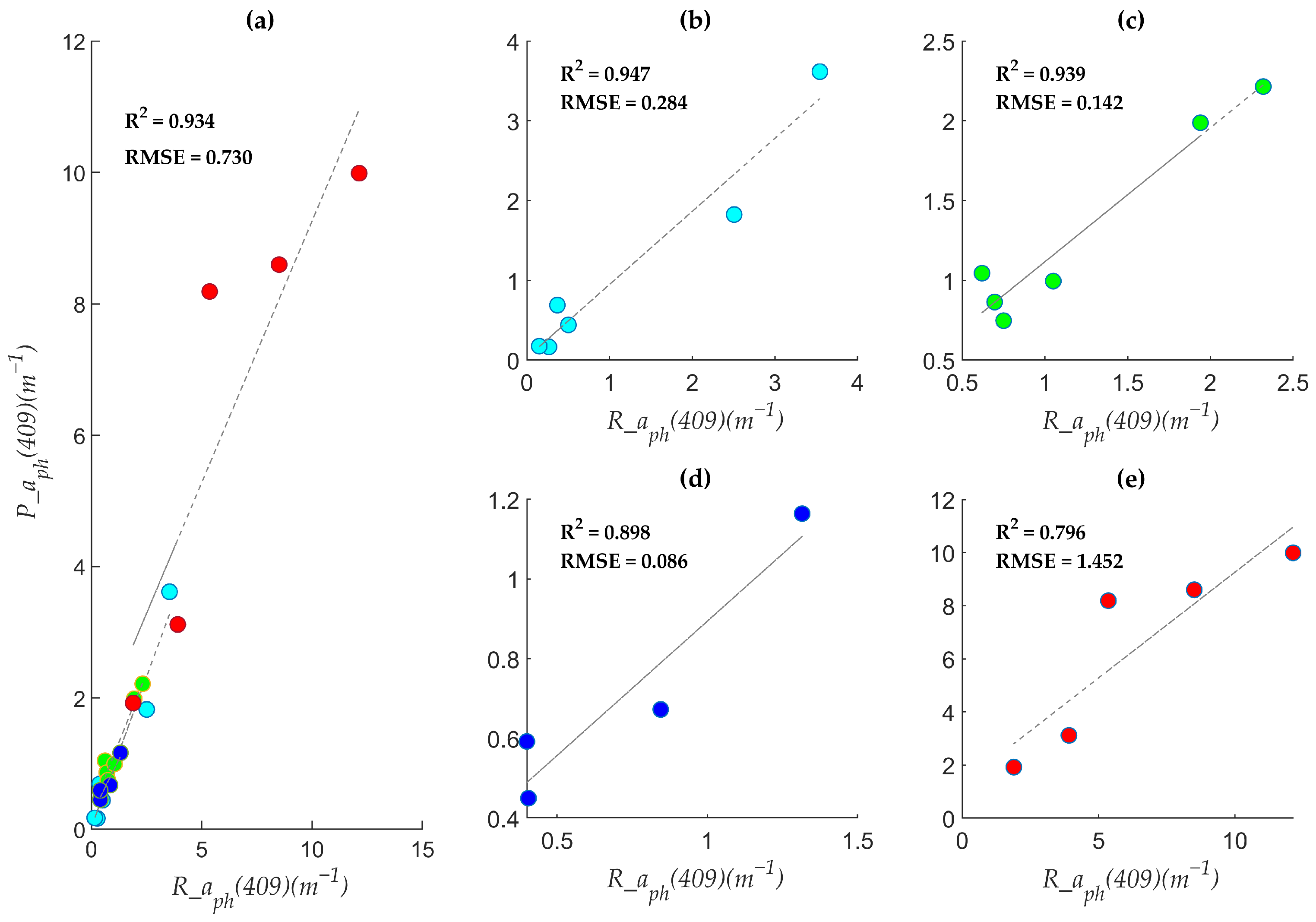
| aph(440) | Unclassified dataset | 2.07 | 0.457 | 761,762,899 |
| C1 | 0.284 | 0.947 | 677,711,734 | |
| C2 | 0.142 | 0.939 | 443,719,729 | |
| C3 | 0.086 | 0.898 | 438,677,714 | |
| C4 | 1.452 | 0.796 | ||
| Pooled C1–C4 | 0.730 | 0.934 | / | |
| aph(555) | Unclassified dataset | 0.09 | 0.822 | 441,676,677,714,715,735 |
| C1 | 0.007 | 0.998 | 500,730,734 | |
| C2 | 0.042 | 0.948 | 441,628,728,729 | |
| C3 | 0.017 | 0.891 | 415,717,721 | |
| C4 | 0.183 | 0.877 | ||
| Pooled C1–C4 | 0.092 | 0.961 | / | |
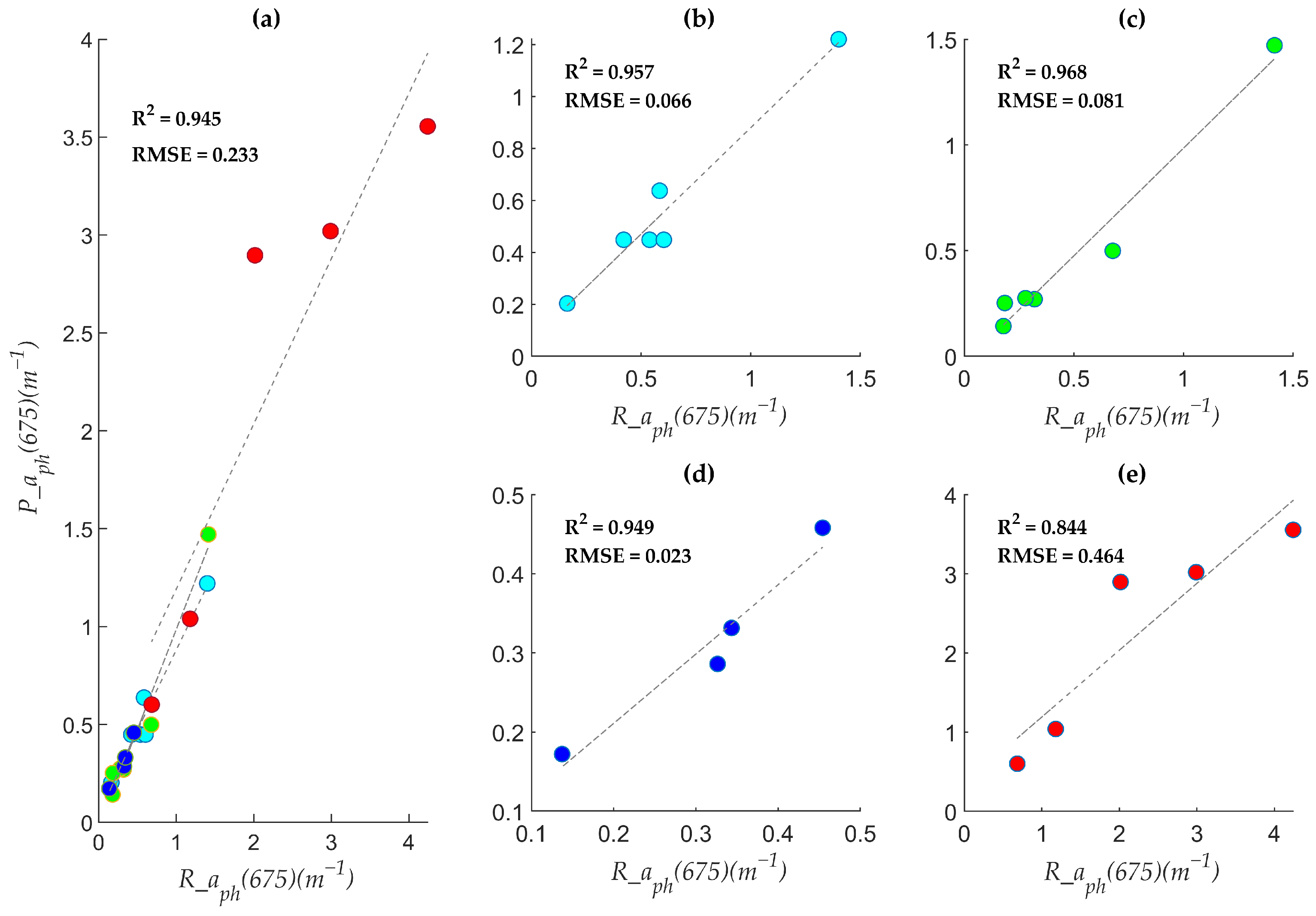
| aph(675) | Unclassified dataset | 0.40 | 0.714 | 441,677,735,739,748 |
| C1 | 0.066 | 0.957 | 727,730 | |
| C2 | 0.081 | 0.968 | 441,548,627,681,715 | |
| C3 | 0.023 | 0.949 | 549,679,721 | |
| C4 | 0.464 | 0.844 | ||
| Pooled C1–C4 | 0.233 | 0.945 | / | |
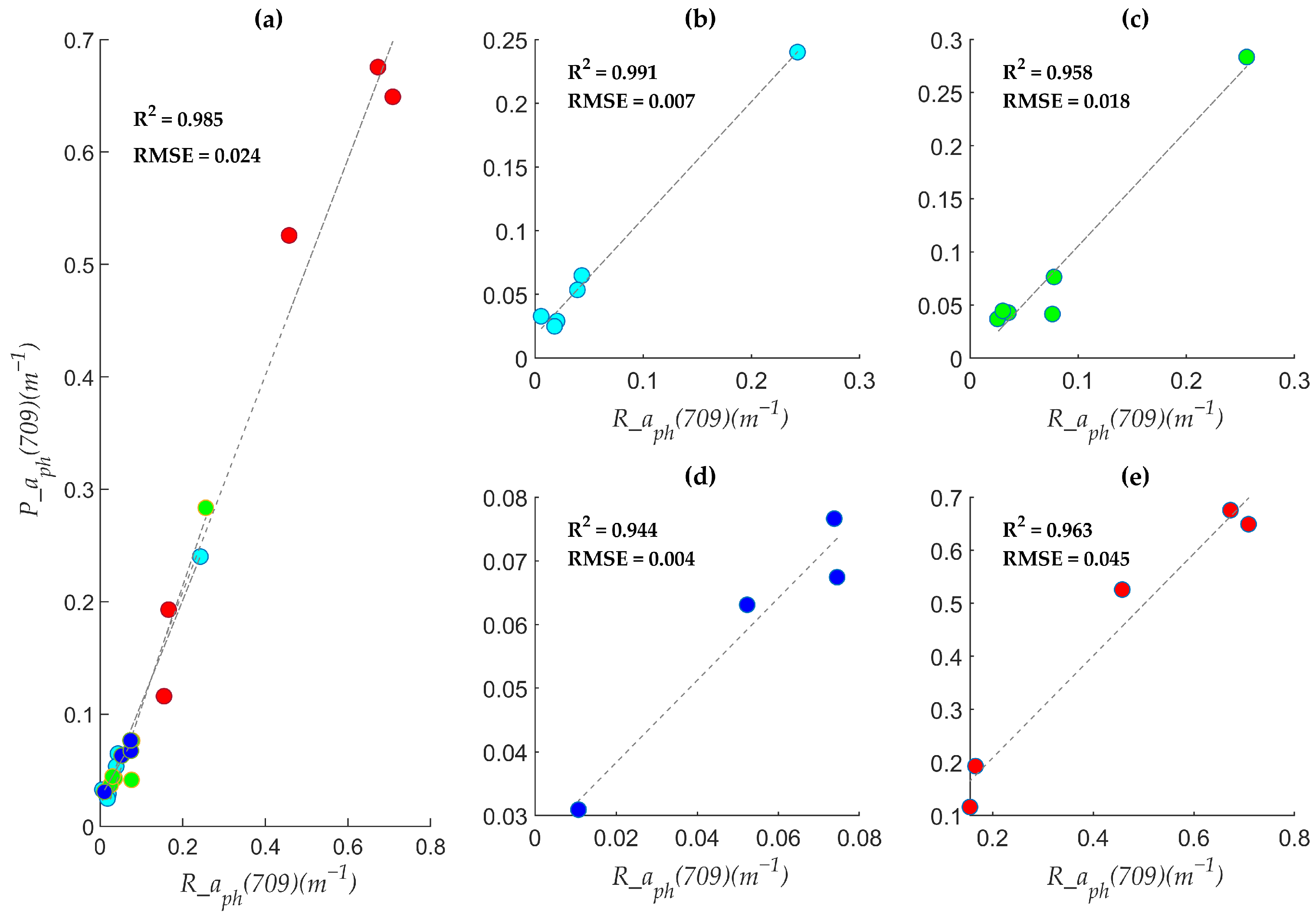
| aph(709) | Unclassified dataset | 0.35 | 0.749 | 441,677,714,715,748 |
| C1 | 0.007 | 0.991 | 494,729,734 | |
| C2 | 0.018 | 0.958 | 441,680,681,719,728 | |
| C3 | 0.004 | 0.944 | 720 | |
| C4 | 0.045 | 0.963 | ||
| Pooled C1–C4 | 0.024 | 0.985 | / |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xia, X.; Lei, S.; Lu, H.; Xu, Z.; Li, X.; Chen, X.; Hong, N.; Xu, J.; Shi, K.; Huang, J. Remote Sensing of Particle Absorption Coefficient of Pigments Using a Two-Stage Framework Integrating Optical Classification and Machine Learning. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1756. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17101756
Xia X, Lei S, Lu H, Xu Z, Li X, Chen X, Hong N, Xu J, Shi K, Huang J. Remote Sensing of Particle Absorption Coefficient of Pigments Using a Two-Stage Framework Integrating Optical Classification and Machine Learning. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(10):1756. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17101756
Chicago/Turabian StyleXia, Xietian, Shaohua Lei, Hui Lu, Zenghui Xu, Xiang Li, Xing Chen, Niancheng Hong, Jie Xu, Kun Shi, and Jiacong Huang. 2025. "Remote Sensing of Particle Absorption Coefficient of Pigments Using a Two-Stage Framework Integrating Optical Classification and Machine Learning" Remote Sensing 17, no. 10: 1756. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17101756
APA StyleXia, X., Lei, S., Lu, H., Xu, Z., Li, X., Chen, X., Hong, N., Xu, J., Shi, K., & Huang, J. (2025). Remote Sensing of Particle Absorption Coefficient of Pigments Using a Two-Stage Framework Integrating Optical Classification and Machine Learning. Remote Sensing, 17(10), 1756. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17101756









