Joint-Pixel Inversion for Ground Phase and Forest Height Estimation Using Spaceborne Polarimetric SAR Interferometry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials
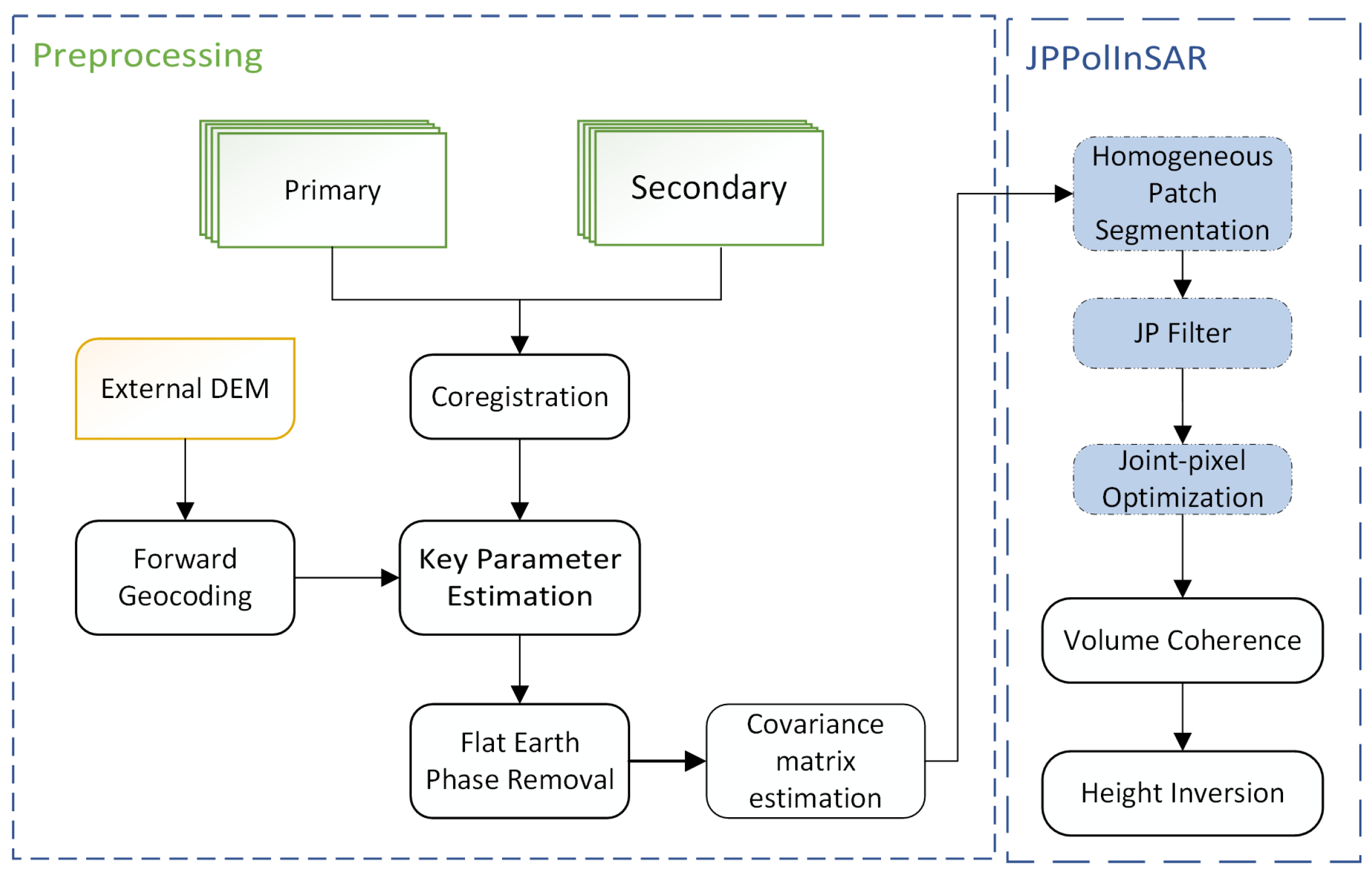
3. Model-Based PolInSAR Inversion Processing
3.1. Model-Based PolInSAR Inversion
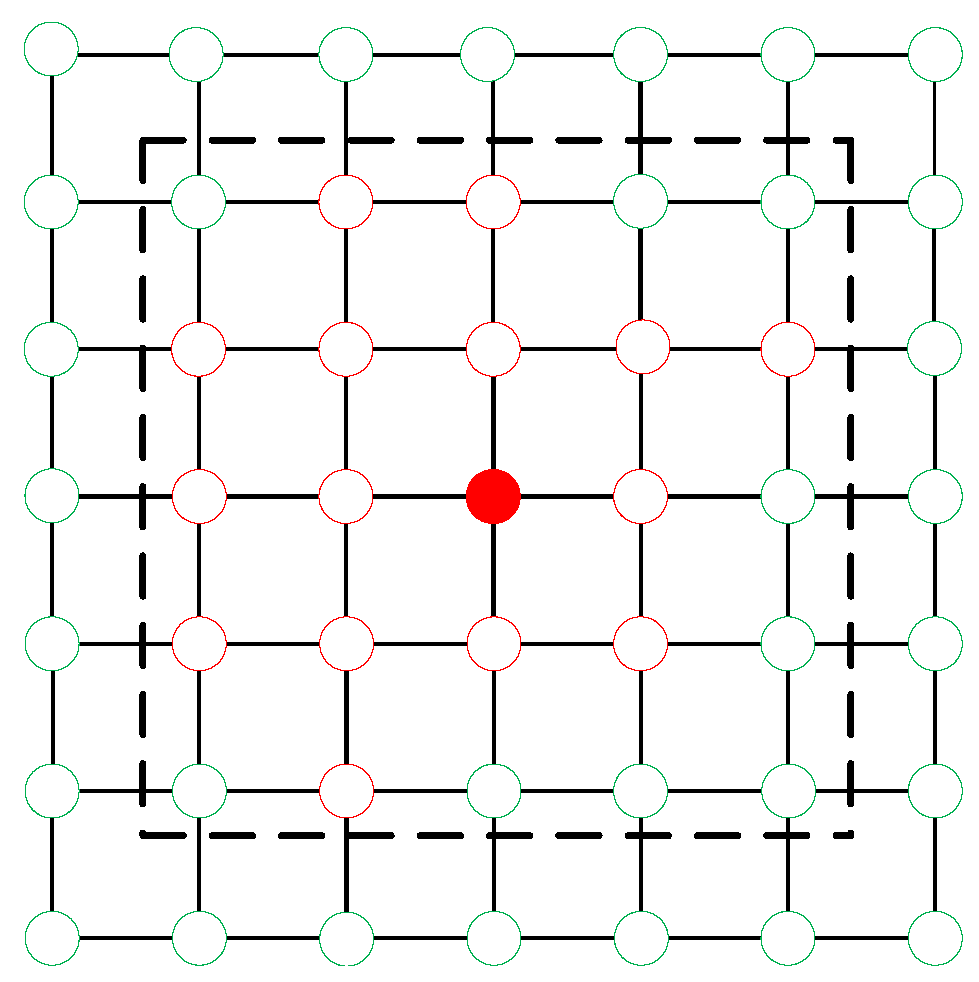
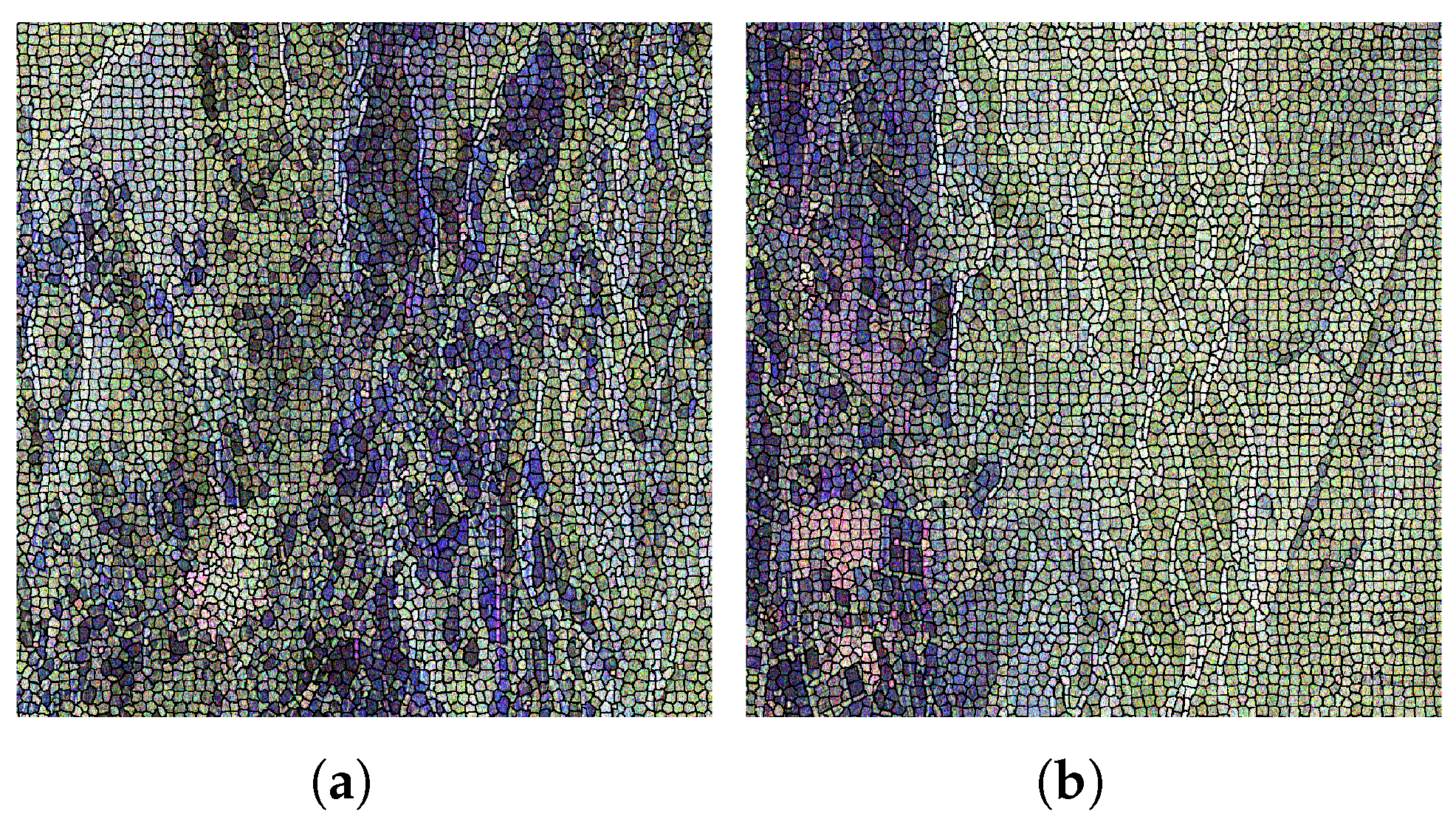
3.2. Homogeneous Patch Segmentation
3.3. Covariance Matrix Re-Estimation
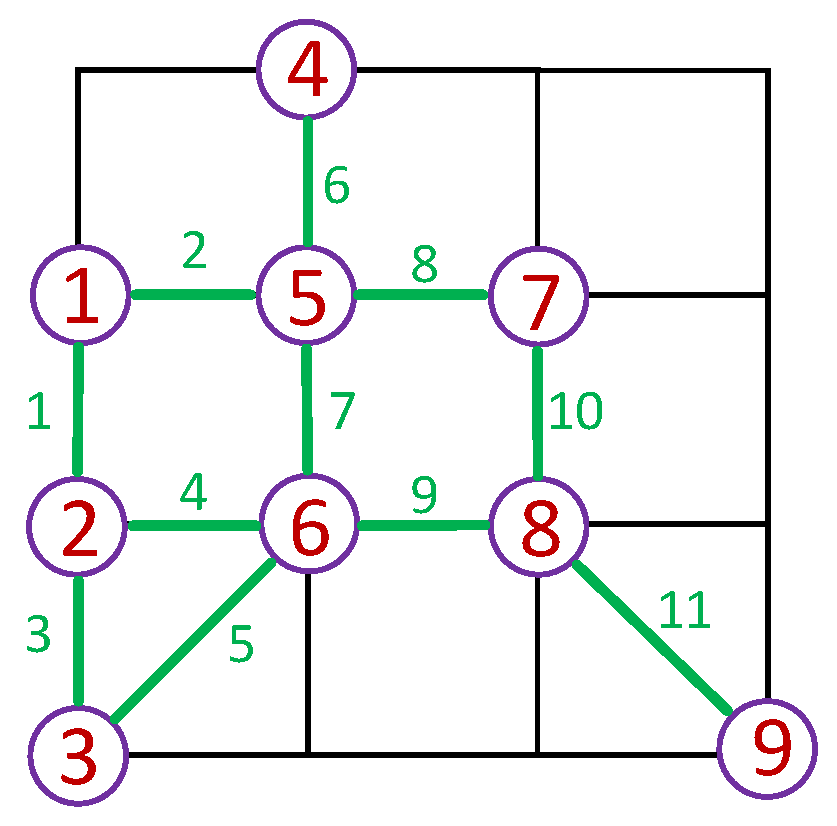
4. Joint-Pixel Optimization Inversion
| Algorithm 1 Joint-Pixel Optimization for PolInSAR |
|
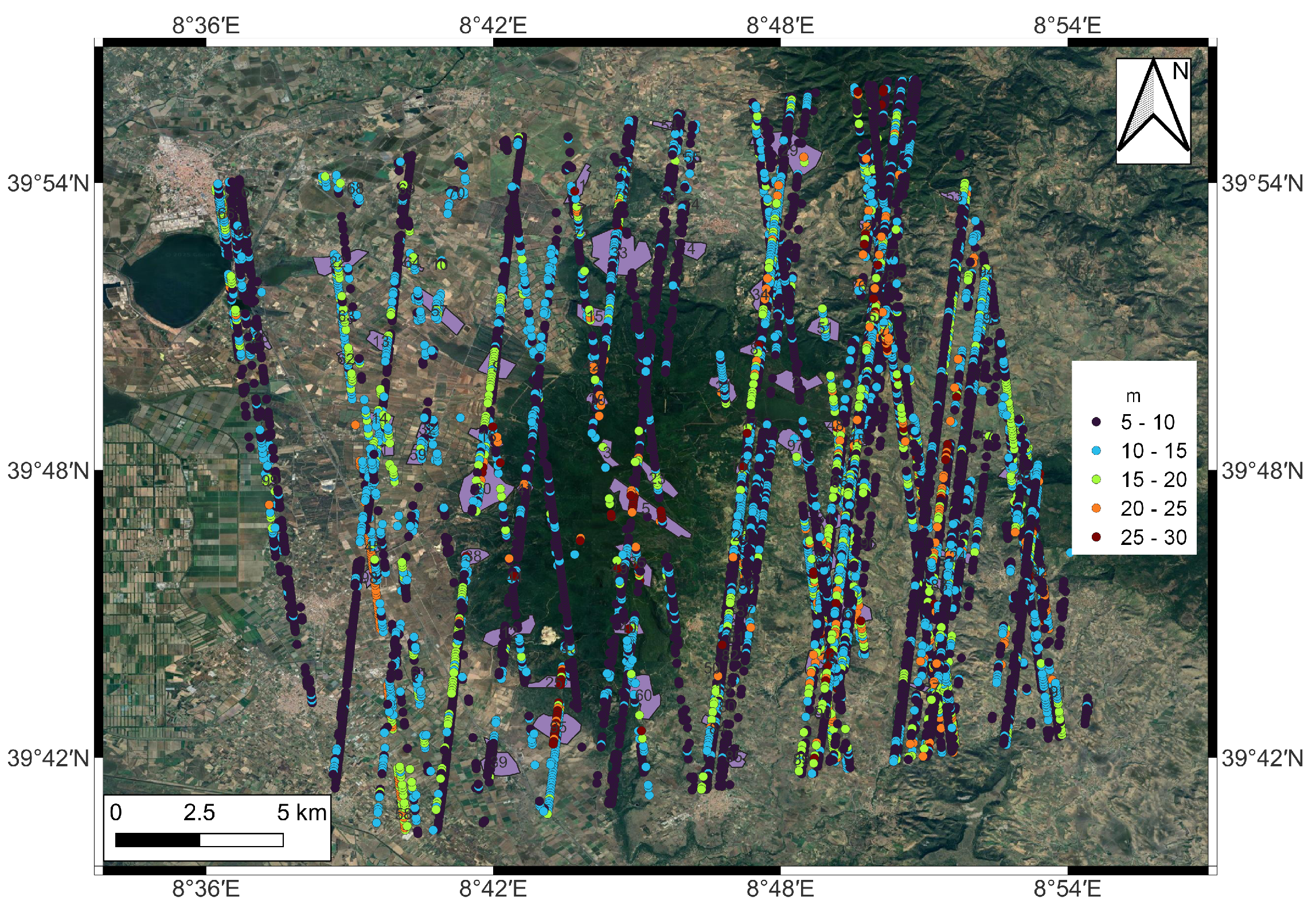
5. Experiments and Discussion
5.1. Data Preprocessing
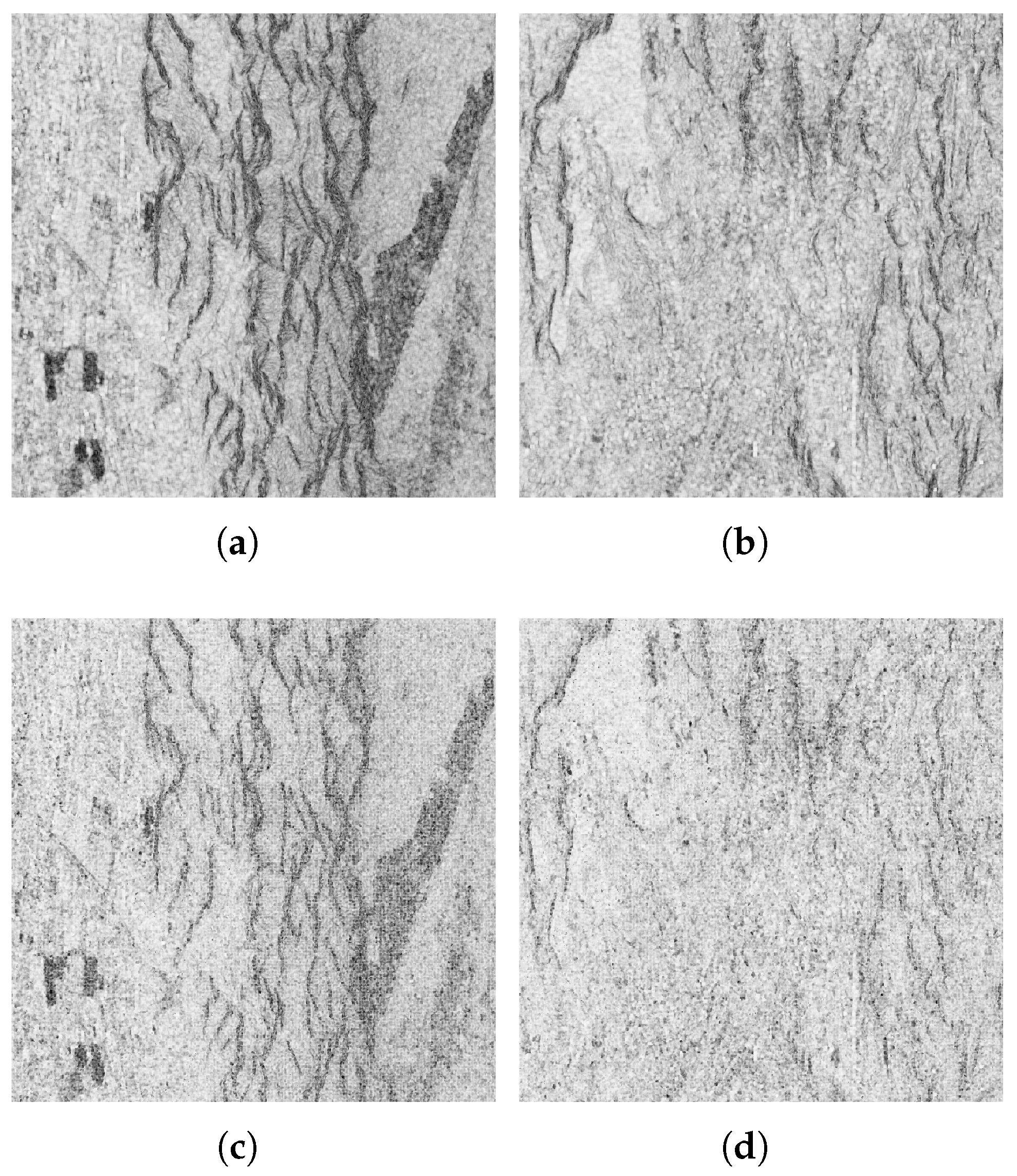
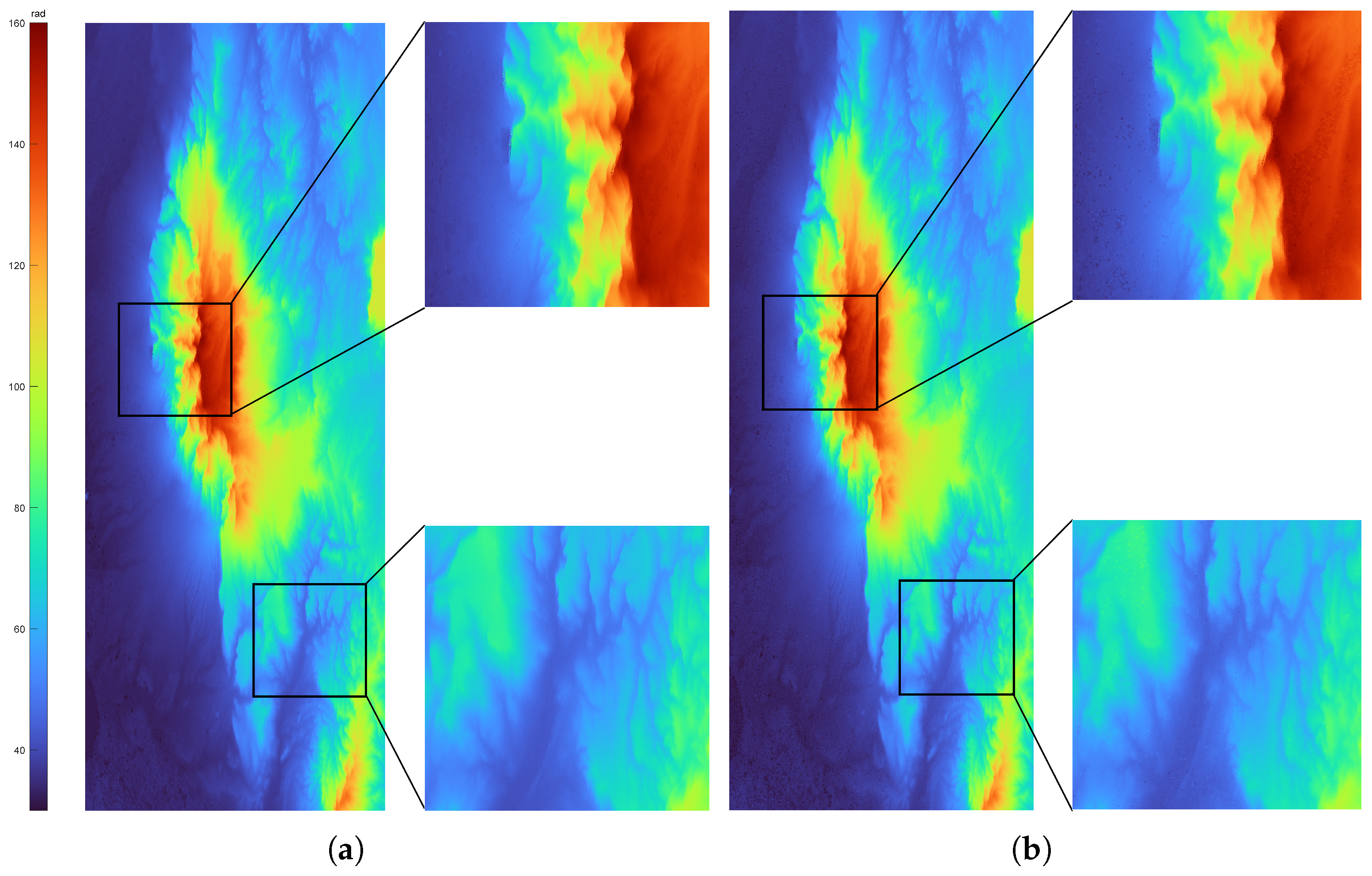
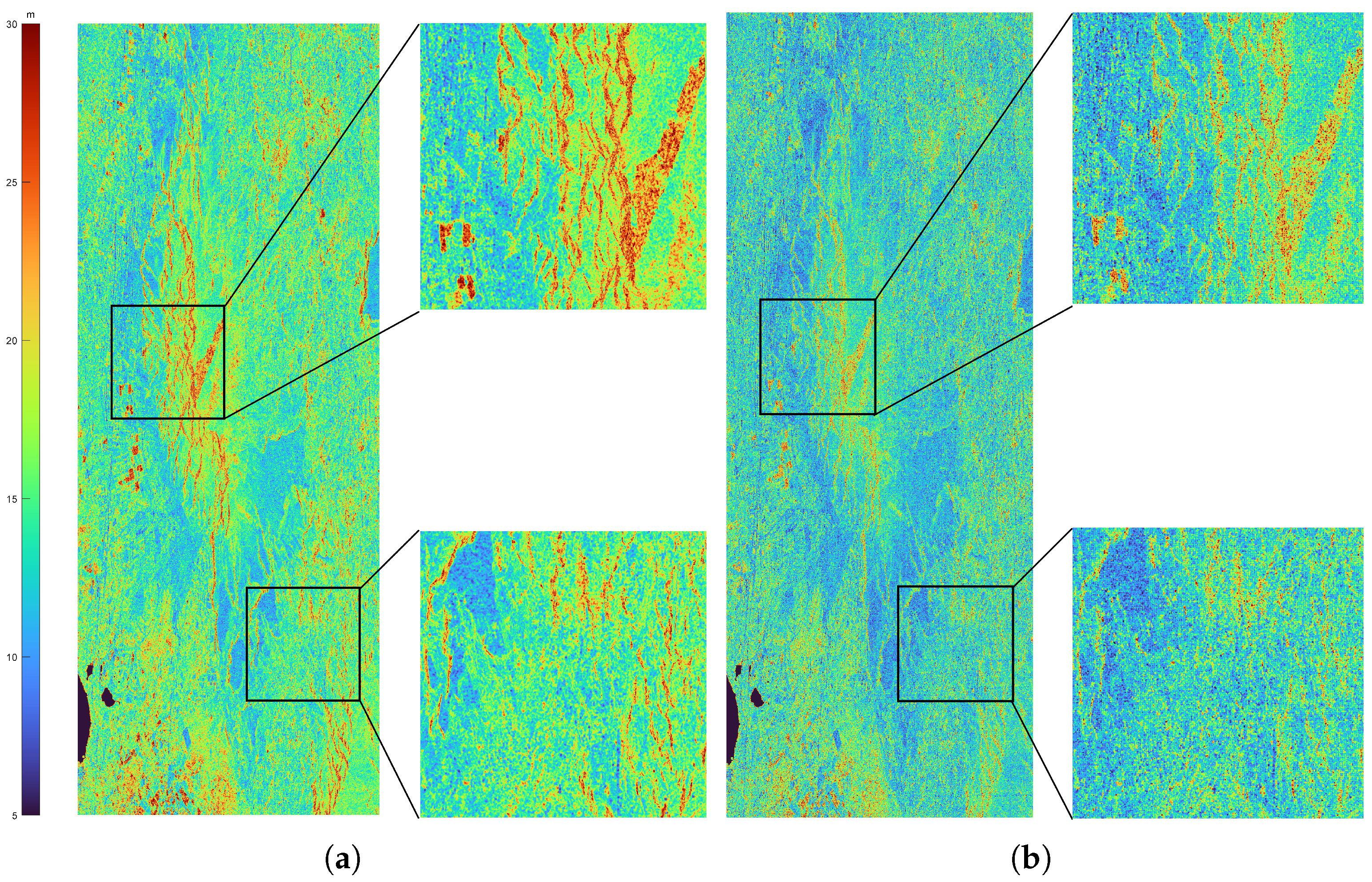
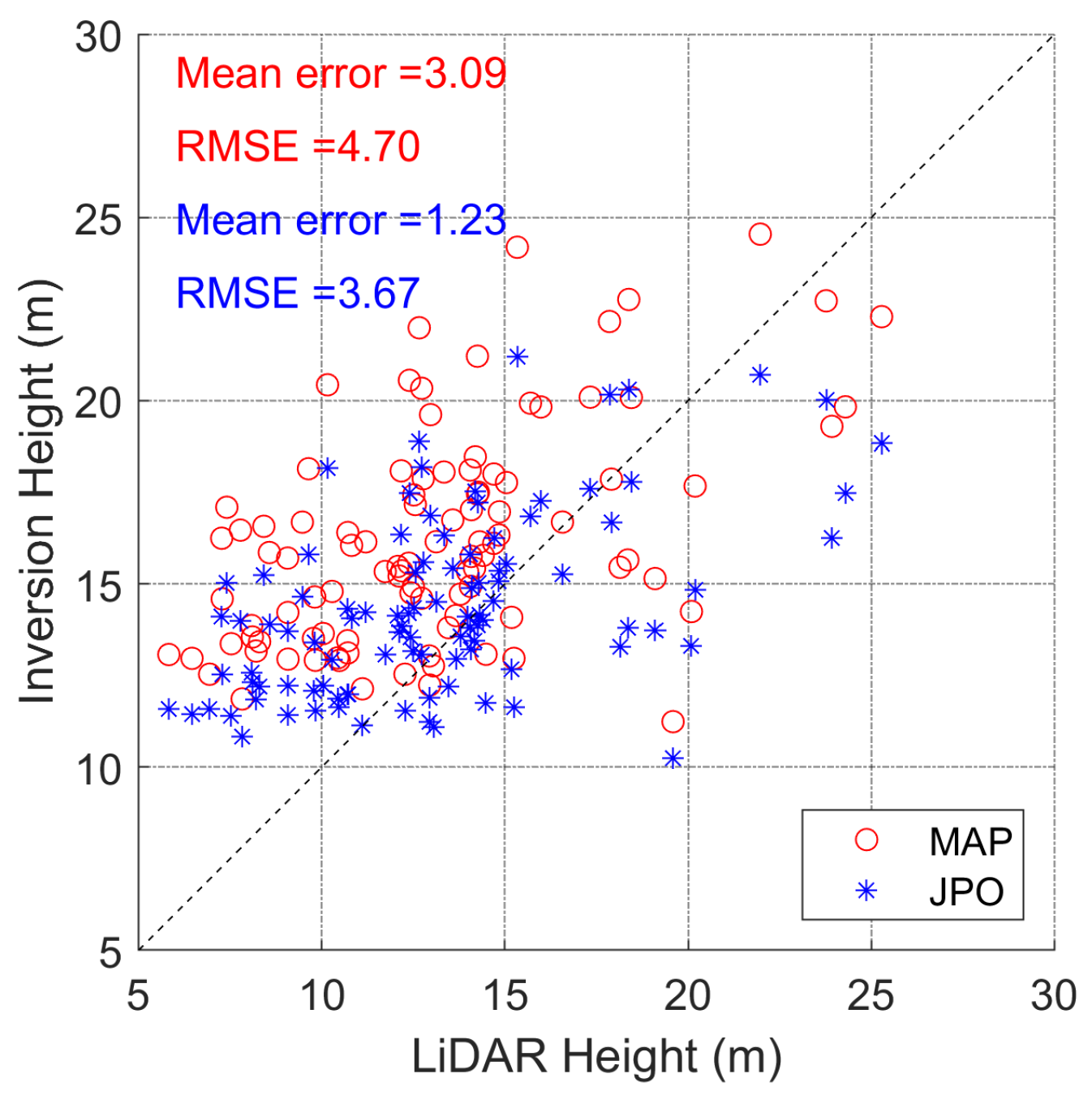
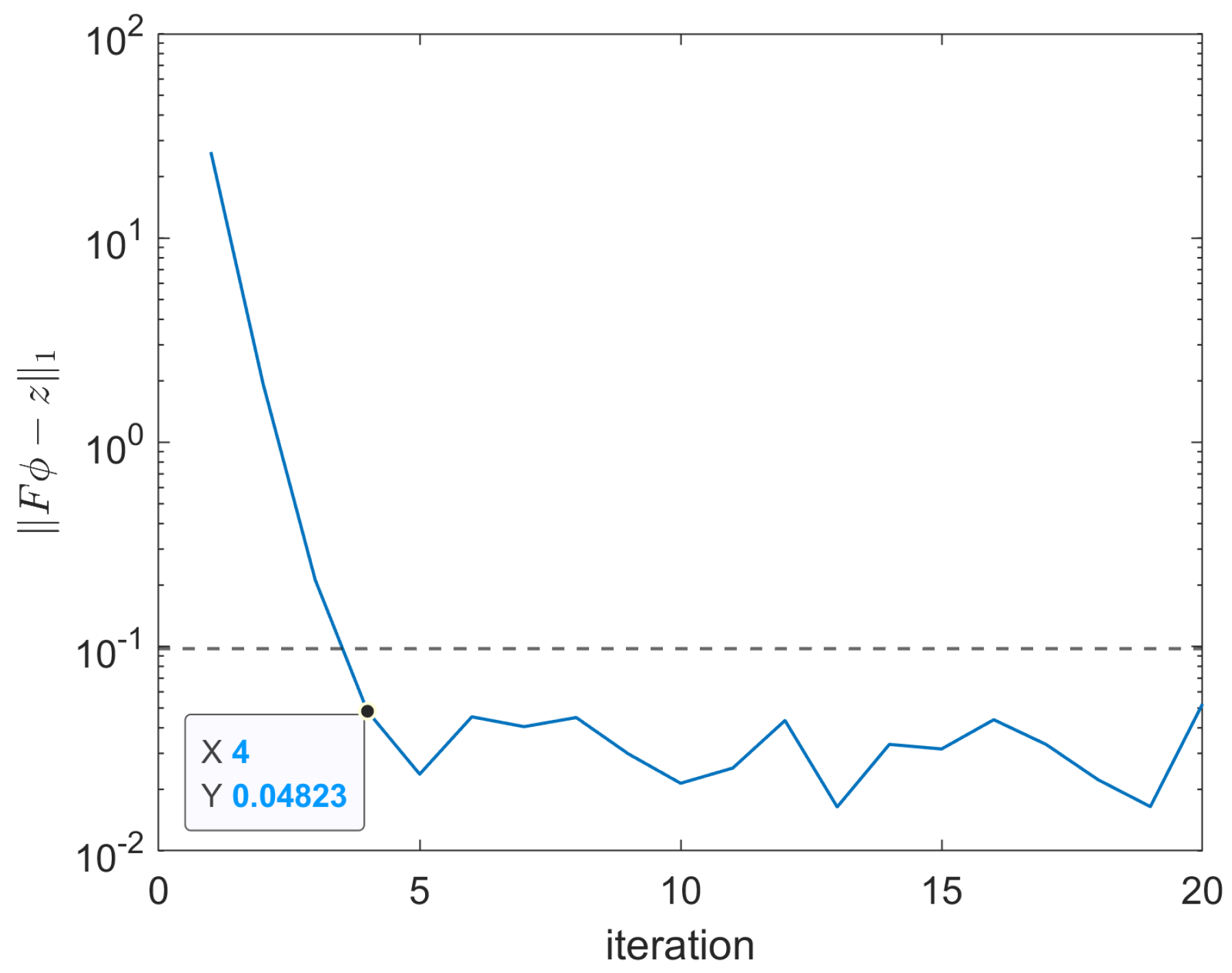
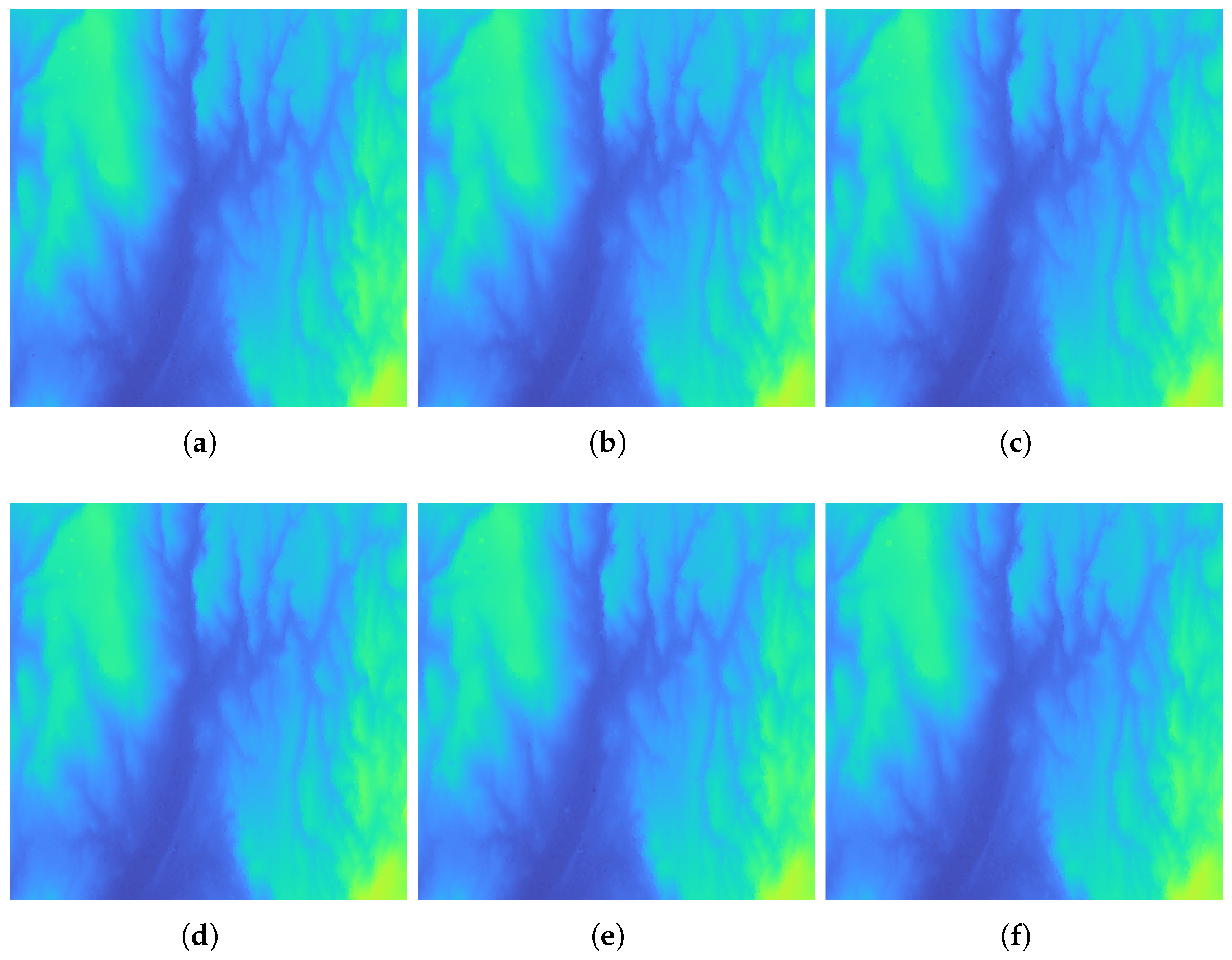
5.2. Inversion and Validation
5.3. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PolInSAR | Polarimetric Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar |
| JPO | Joint Pixel Optimization |
| ADMM | Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers |
| LiDAR | Light Detection and Ranging |
| MAP | Maximum a Posteriori |
| SLIC | Simple Linear Iterative Clustering |
| RVoG | Random Volume over Ground |
| RMSE | Root Mean Square Error |
Appendix A. Parallelizable ADMM and Convergence Analysis
Appendix A.1. The Parallelizable ADMM
Appendix A.2. The Proximal Operator Demonstration
Appendix A.3. The Convergence Rate Analysis
- To show that is contractive and the optimal solution satisfies
- To show that is monotonically non-increasing
- To derive the convergence rate
References
- Sheil, D. Forests, atmospheric water and an uncertain future: The new biology of the global water cycle. For. Ecosyst. 2018, 5, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchard, E.T.A. The tropical forest carbon cycle and climate change. Nature 2018, 559, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, T.; Montesano, P.M.; Cook, B.D.; Chavanon, E.; Neigh, C.S.; Shean, D.; Peng, D.; Lauret, N.; Mkaouar, A.; Morton, D.C.; et al. Modeling forest canopy surface retrievals using very high-resolution spaceborne stereogrammetry: (I) methods and comparisons with actual data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 298, 113825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; He, B.; Quan, X.; van Dijk, A.I.J.M.; Qiu, S.; Yin, C. Biomass estimation in dense tropical forest using multiple information from single-baseline P-band PolInSAR data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 221, 489–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treuhaft, R.; Goncalves, F.; dos Santos, J.R.; Keller, M.; Palace, M.; Madsen, S.N.; Sullivan, F.; Graca, P.M.L.A. Tropical-Forest Biomass Estimation at X-Band From the Spaceborne TanDEM-X Interferometer. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Toan, T.; Quegan, S.; Davidson, M.W.J.; Balzter, H.; Paillou, P.; Papathanassiou, K.; Plummer, S.; Rocca, F.; Saatchi, S.; Shugart, H. The BIOMASS mission: Mapping global forest biomass to better understand the terrestrial carbon cycle. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2850–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, P.W. Tree Height. In Tree and Forest Measurement; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Nie, S.; Wang, C.; Xi, X.; Lao, J.; Li, D. Consistency analysis of forest height retrievals between GEDI and ICESat-2. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 281, 113244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajnsek, I.; Kugler, F.; Lee, S.; Papathanassiou, K.P. Tropical-Forest-Parameter Estimation by Means of Pol-InSAR: The INDREX-II Campaign. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 481–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois-Fernandez, P.C.; Le Toan, T.; Daniel, S.; Oriot, H.; Chave, J.; Blanc, L.; Villard, L.; Davidson, M.W.; Petit, M. The TropiSAR airborne campaign in French Guiana: Objectives, description, and observed temporal behavior of the backscatter signal. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 3228–3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potapov, P.; Li, X.; Hernandez-Serna, A.; Tyukavina, A.; Hansen, M.C.; Kommareddy, A.; Pickens, A.; Turubanova, S.; Tang, H.; Silva, C.E.; et al. Mapping global forest canopy height through integration of GEDI and Landsat data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 253, 112165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Niu, Z.; Shang, R.; Qin, Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, H. High-resolution mapping of forest canopy height using machine learning by coupling ICESat-2 LiDAR with Sentinel-1, Sentinel-2 and Landsat-8 data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2020, 92, 102163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, M.; Saatchi, S.; Ustin, S.; Balzter, H. Modelling forest canopy height by integrating airborne LiDAR samples with satellite Radar and multispectral imagery. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 66, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourshamsi, M.; Xia, J.; Yokoya, N.; Garcia, M.; Lavalle, M.; Pottier, E.; Balzter, H. Tropical forest canopy height estimation from combined polarimetric SAR and LiDAR using machine-learning. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 172, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kugler, F.; Lee, S.; Hajnsek, I.; Papathanassiou, K.P. Forest Height Estimation by Means of Pol-InSAR Data Inversion: The Role of the Vertical Wavenumber. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 5294–5311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garestier, F.; Dubois-Fernandez, P.C.; Champion, I. Forest height inversion using high-resolution P-band Pol-InSAR data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 3544–3559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Chen, E.; Li, Z.; Zhang, W.; Fan, Y. A New Approach for Forest Height Inversion Using X-Band Single-Pass InSAR Coherence Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 5206018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloude, S.R.; Papathanassiou, K.P. Polarimetric SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 1551–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloude, S.R. Pol-InSAR training course. In Radio Science; Blackwell Publishing: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Treuhaft, R.N.; Chapman, B.D.; dos Santos, J.R.; Dutra, L.V.; Goncalves, F.G.; Freitas, C.d.C.; Mura, J.C.; de Alencastro Graca, P.M.; Drake, J.B.; IEEE. Tropical-Forest Density Profiles from Multibaseline Interferometric SAR. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Symposium on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, Denver, CO, USA, 31 July–4 August 2006; pp. 2205–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treuhaft, R.N.; Siqueira, P.R. Vertical structure of vegetated land surfaces from interferometric and polarimetric radar. Radio Sci. 2000, 35, 141–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papathanassiou, K.P.; Cloude, S.R. Single-baseline polarimetric SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 2352–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloude, S.; Papathanassiou, K. Three-stage inversion process for polarimetric SAR interferometry. IEE Proc.-Radar Sonar Navig. 2003, 150, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, T.; Tabb, M.; Carande, R. Coherence region shape extraction for vegetation parameter estimation in polarimetric SAR interferometry. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Toronto, ON, Canada, 24–28 June 2002; Volume 5, pp. 2596–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mark, T.; Jeffrey, O.; Thomas, F.; Richard, C. Phase diversity: A decomposition for vegetation parameter estimation using polarimetric SAR interferometry. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar EUSAR, Cologne, Germany, 4–6 June 2002; pp. 721–724. [Google Scholar]
- Papathanassiou, K.P.; Cloude, S.R. The effect of temporal decorrelation on the inversion of forest parameters from Pol-InSAR data. In Proceedings of the International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Toulouse, France, 21–25 July 2003; Volume 3, pp. 1429–1431. [Google Scholar]
- Mette, T.; Kugler, F.; Papathanassiou, K.; Hajnsek, I. Forest and the random volume over ground-nature and effect of 3 possible error types. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar (EUSAR), Dresden, Germany, 16–18 May 2006; VDE Verlag GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2006; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Lavalle, M.; Hensley, S. Extraction of Structural and Dynamic Properties of Forests from Polarimetric-Interferometric SAR Data Affected by Temporal Decorrelation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 4752–4767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabb, M.; Flynn, T.; Carande, R. Full maximum likelihood inversion of PolInSAR scattering models. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2004, 2004 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Anchorage, AK, USA, 20–24 September 2004; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2004; Volume 2, pp. 1232–1235. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Lv, X.; Li, X.; Chai, H. Maximum a Posteriori Inversion for Forest Height Estimation Using Spaceborne Polarimetric SAR Interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 4406514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Siqueira, P.; Torbick, N.; Ducey, M.; Chowdhury, D.; Salas, W. Generation of large-scale moderate-resolution forest height mosaic with spaceborne repeat-pass SAR interferometry and lidar. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 57, 770–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Wang, B.; Xiang, M.; Zhou, L.; Wang, S.; Jiang, S. Machine-Learning Inversion of Forest Vertical Structure Based on 2-D-SGVBVoG Model for P-Band Pol-InSAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5225115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nico, G.; Palubinskas, G.; Datcu, M. Bayesian approaches to phase unwrapping: Theoretical study. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2000, 48, 2545–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, F.; Guo, J.; Lang, F. Superpixel segmentation for polarimetric SAR imagery using local iterative clustering. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 12, 13–17. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Jiao, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, S.; Liu, F.; Hua, W. Fuzzy superpixels for polarimetric SAR images classification. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2018, 26, 2846–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felzenszwalb, P.F.; Huttenlocher, D.P. Efficient graph-based image segmentation. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2004, 59, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Malik, J. Normalized cuts and image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2000, 22, 888–905. [Google Scholar]
- Veksler, O.; Boykov, Y.; Mehrani, P. Superpixels and supervoxels in an energy optimization framework. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2010: 11th European Conference on Computer Vision, Heraklion, Crete, Greece, 5–11 September 2010; Proceedings, Part V 11. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 211–224. [Google Scholar]
- Achanta, R.; Shaji, A.; Smith, K.; Lucchi, A.; Fua, P.; Süsstrunk, S. SLIC superpixels compared to state-of-the-art superpixel methods. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2012, 34, 2274–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, S.; Parikh, N.; Chu, E.; Peleato, B.; Eckstein, J. Distributed Optimization and Statistical Learning via the Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers; Foundation Trends® in Machine Learning: Hanover, MA, USA, 2011; Volume 3, pp. 1–122. [Google Scholar]
- Cloude, S.R. Polarization coherence tomography. Radio Sci. 2006, 41, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conradsen, K.; Nielsen, A.A.; Schou, J.; Skriver, H. A test statistic in the complex Wishart distribution and its application to change detection in polarimetric SAR data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 4–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Yazıcı, B.; Zeghal, M.; Bennett, V.; Abdoun, T. Joint-scatterer processing for time-series InSAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 7205–7221. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, W.; Ling, Q.; Yuan, K.; Wu, G.; Yin, W. On the linear convergence of the ADMM in decentralized consensus optimization. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2014, 62, 1750–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yin, W.; Zeng, J. Global convergence of ADMM in nonconvex nonsmooth optimization. J. Sci. Comput. 2019, 78, 29–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, N.; Boyd, S. Proximal Algorithms; Foundations and Trends® in Optimization: Hanover, MA, USA, 2014; Volume 1, pp. 127–239. [Google Scholar]
- Kiefer, J. Sequential minimax search for a maximum. Proc. Am. Math. Soc. 1953, 4, 502–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinderlehrer, D.; Stampacchia, G. An Introduction to Variational Inequalities and Their Applications; SIAM: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- He, B.; Yuan, X. On non-ergodic convergence rate of Douglas–Rachford alternating direction method of multipliers. Numer. Math. 2015, 130, 567–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Z.; Gao, J.; Lv, X.; Li, X. Joint-Pixel Inversion for Ground Phase and Forest Height Estimation Using Spaceborne Polarimetric SAR Interferometry. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1726. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17101726
Huang Z, Gao J, Lv X, Li X. Joint-Pixel Inversion for Ground Phase and Forest Height Estimation Using Spaceborne Polarimetric SAR Interferometry. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(10):1726. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17101726
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Zenghui, Jingyu Gao, Xiaolei Lv, and Xiaoshuai Li. 2025. "Joint-Pixel Inversion for Ground Phase and Forest Height Estimation Using Spaceborne Polarimetric SAR Interferometry" Remote Sensing 17, no. 10: 1726. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17101726
APA StyleHuang, Z., Gao, J., Lv, X., & Li, X. (2025). Joint-Pixel Inversion for Ground Phase and Forest Height Estimation Using Spaceborne Polarimetric SAR Interferometry. Remote Sensing, 17(10), 1726. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17101726






