Multimodal Prompt-Guided Bidirectional Fusion for Referring Remote Sensing Image Segmentation
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We apply multimodal prompting to RRSIS and propose a novel architecture termed multimodal prompt-guided bidirectional fusion (MPBF). This architecture leverages multimodal prompts as a medium for bidirectional fusion of visual and linguistic features. By coupling learnable prompt vectors embedded within image and text encoders, MPBF achieves deep integration of multimodal features in a shared latent space with minimal additional parameters.
- To enhance fine-grained segmentation, we introduce a scale-aware visual–language fine-grained alignment decoder. This decoder incorporates a scale refinement (SR) module that significantly improves the model’s ability to learn fine-grained scale representations. Additionally, the VLSI process establishes pixel-level semantic associations between visual and linguistic features, further enhancing the model’s robustness in recognizing multi-scale targets.
- Performance evaluations on public datasets demonstrate that our method achieved state-of-the-art (SOTA) results. Validation experiments in real-world application scenarios further confirm that our approach retains high segmentation accuracy, even in complex environments with substantial background noise interference, highlighting its practical value.
2. Related Work
2.1. Referring Image Segmentation
2.2. Prompt Learning
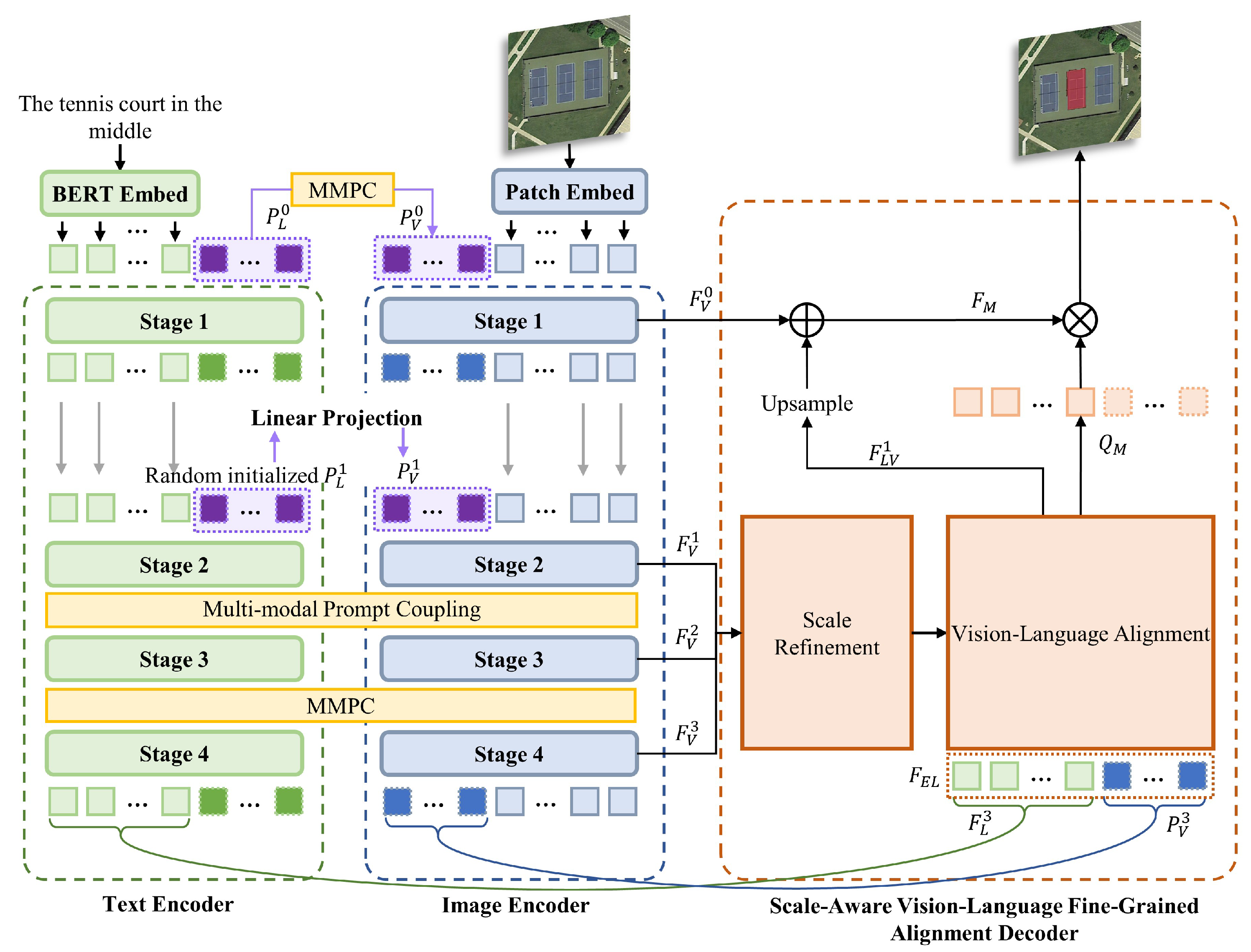
3. Methodology
3.1. Model Overview
3.2. Multi-Stage Image and Text Encoder
3.3. Multimodal Prompt-Based Cross-Modal Collaborative Encoding
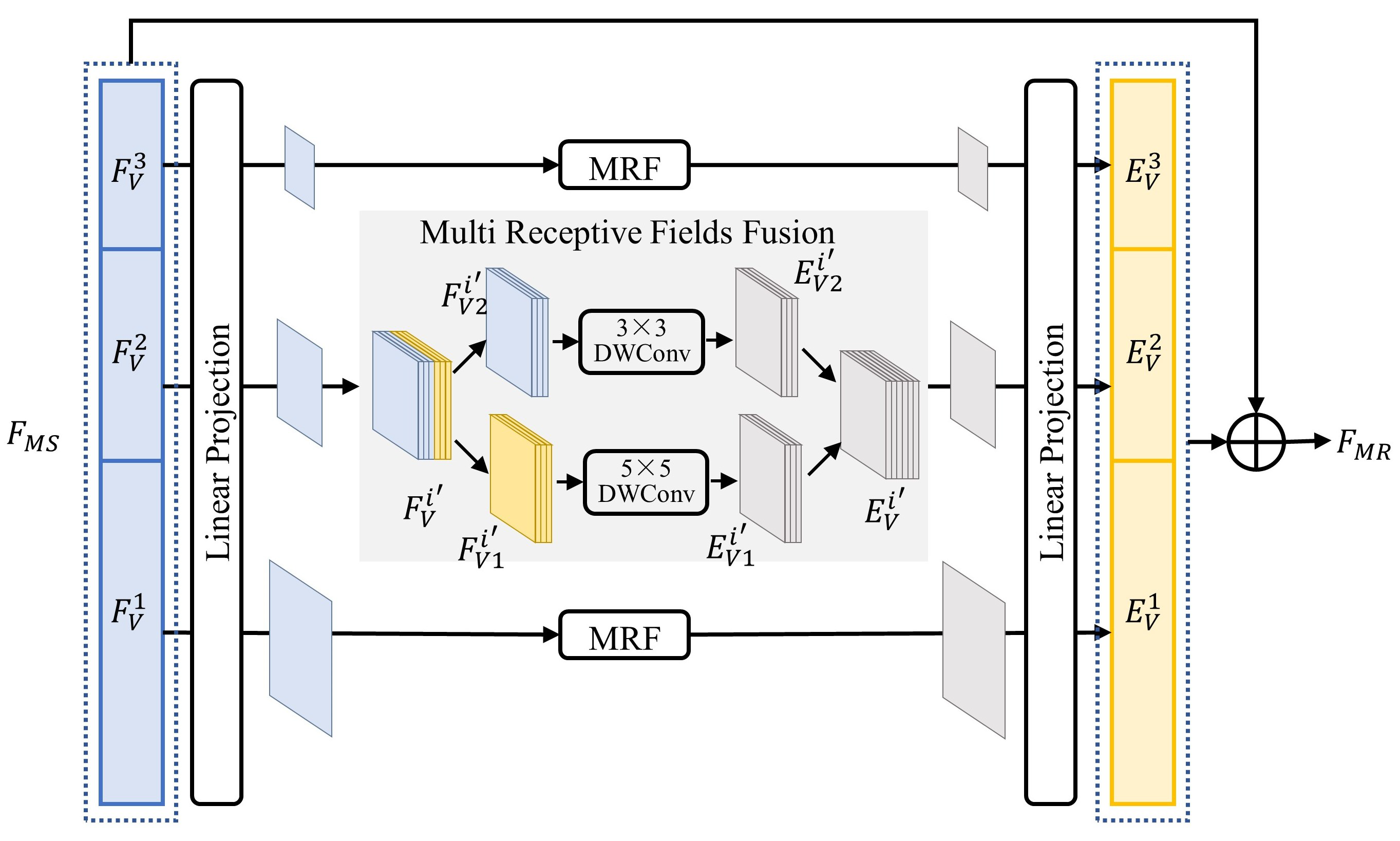
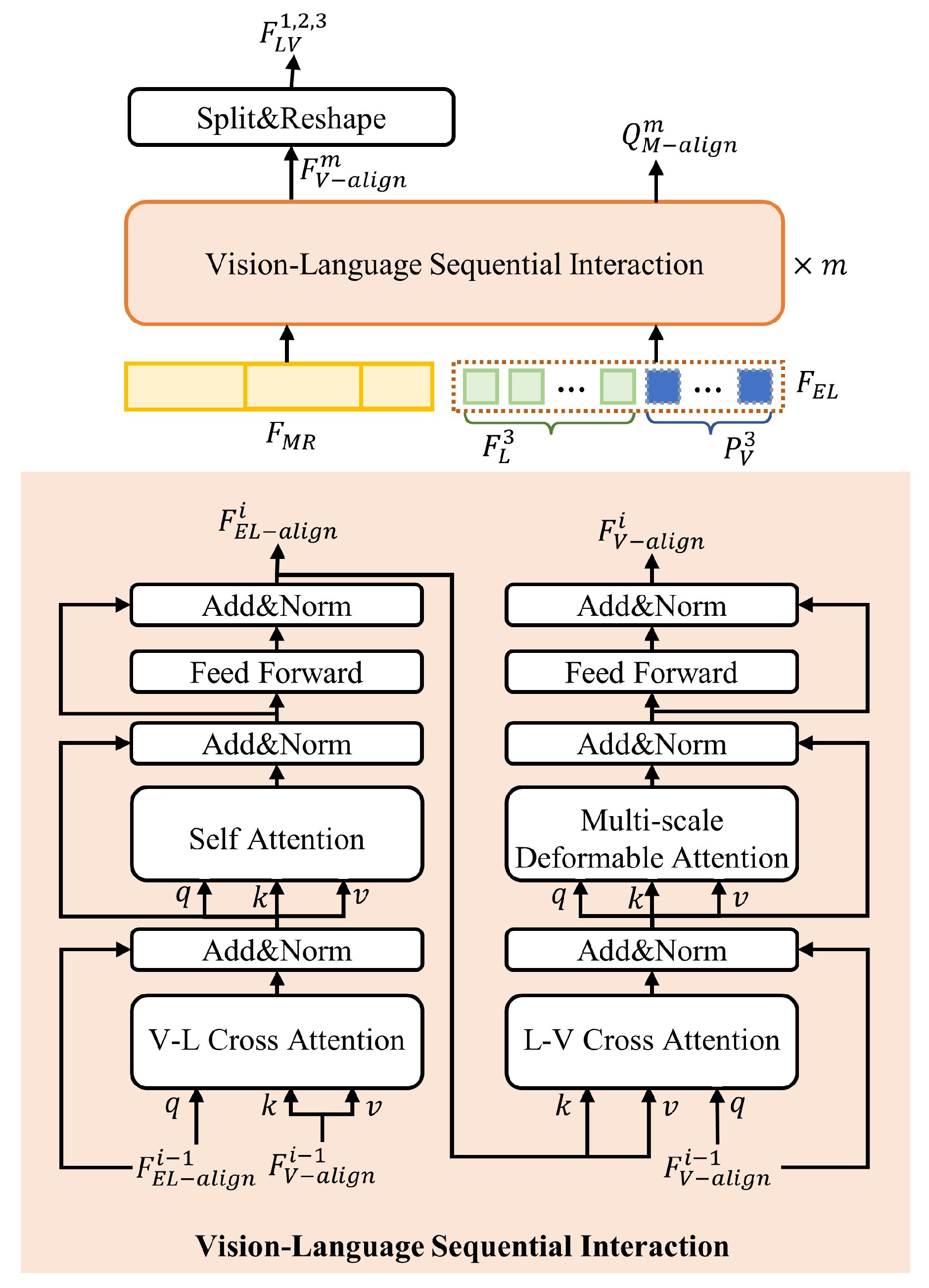
3.4. Scale-Aware Vision–Language Fine-Grained Alignment Decoder
3.4.1. Scale Refinement
3.4.2. Vision–Language Alignment
3.4.3. Mask Generation
4. Experiments and Results
4.1. Datasets
4.1.1. RRSIS-D Dataset
4.1.2. HSRMS Dataset
4.2. Comparison Algorithms
4.3. Evaluation Metrics
4.4. Experimental Settings
4.5. Comparative Experiments
4.5.1. Quantitative Comparison
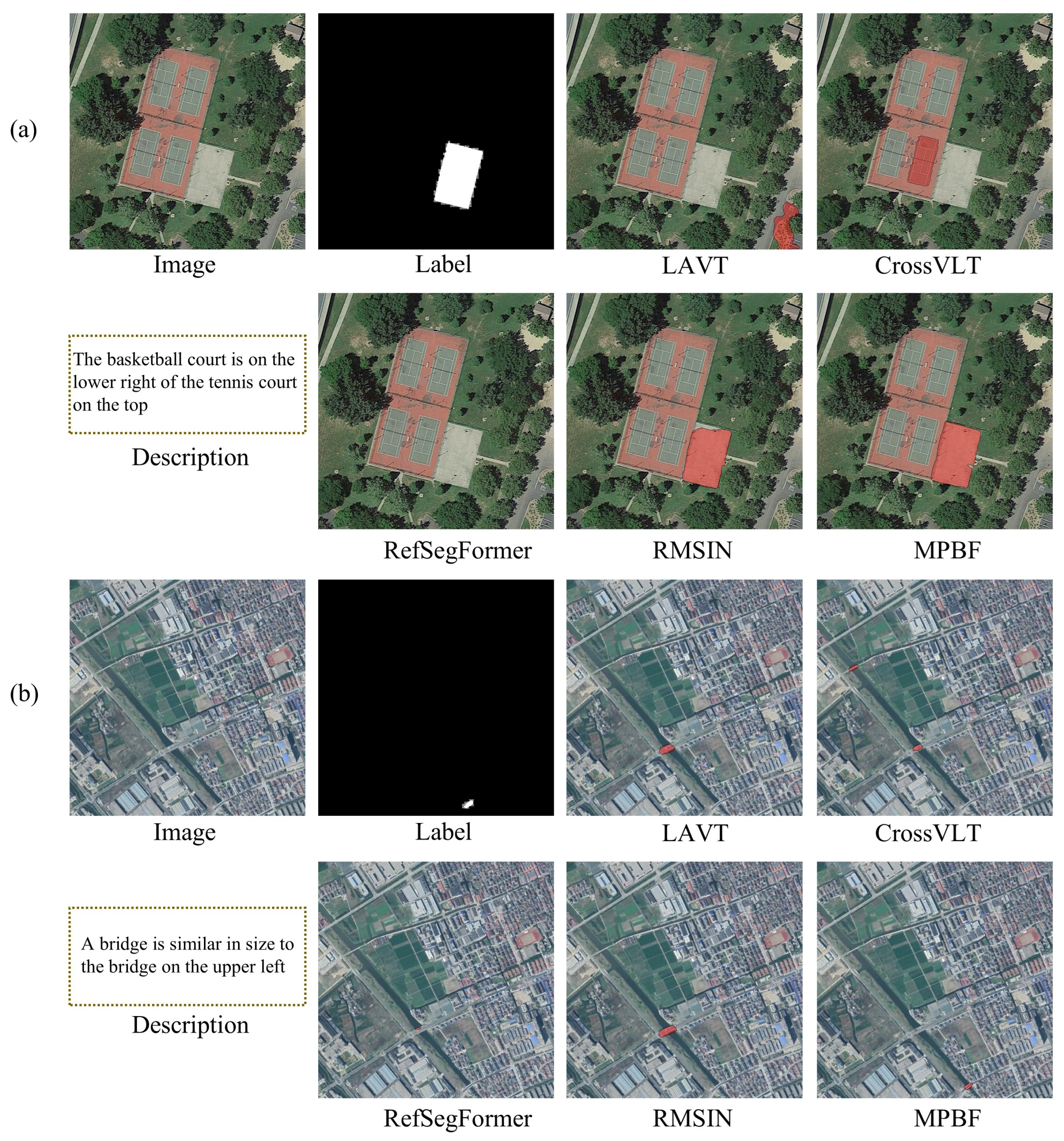
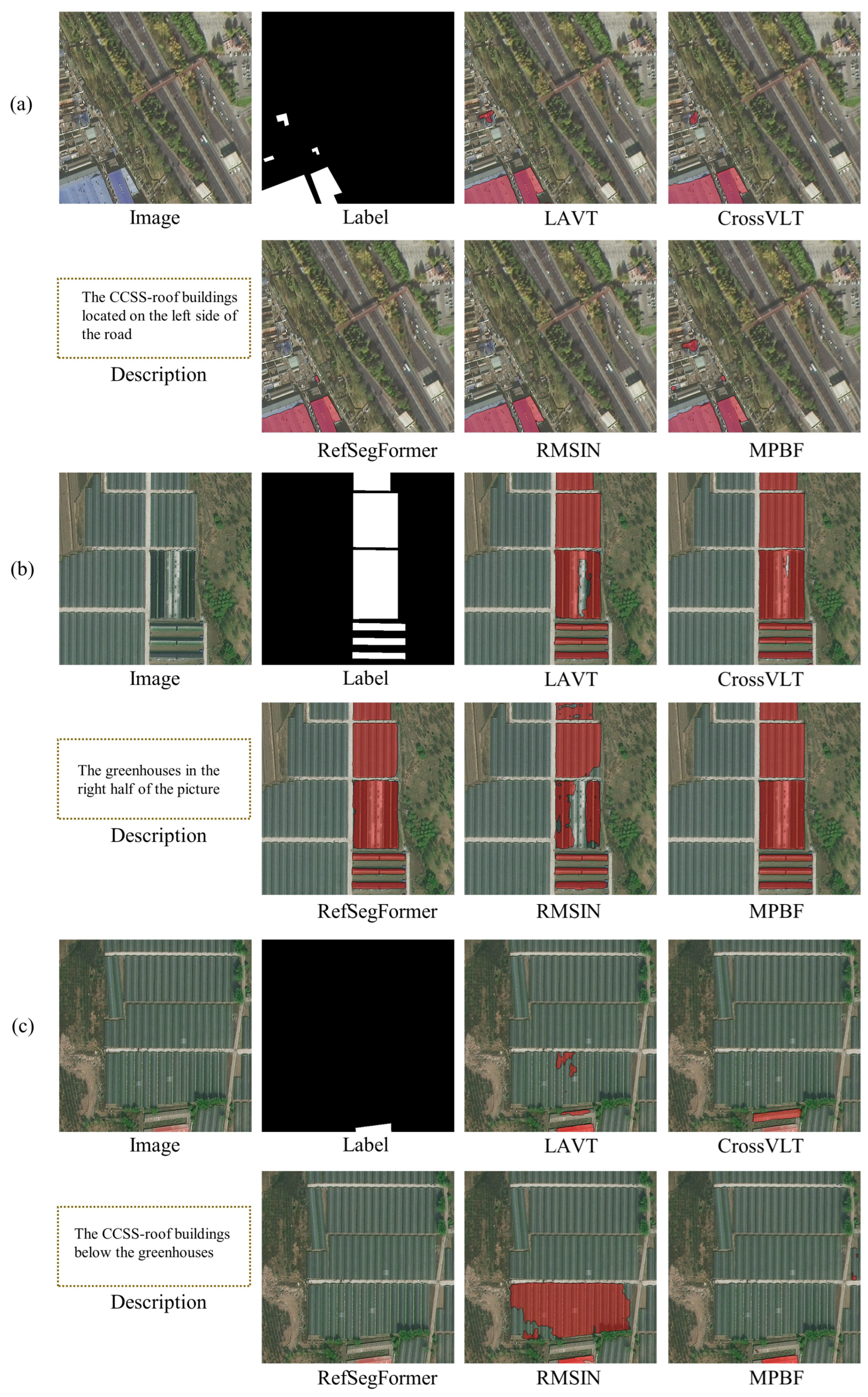
4.5.2. Qualitative Comparison
5. Discussion
5.1. Failure Case Analysis
5.2. Complexity Analysis
5.3. Ablation Study
5.3.1. Ablation Evaluation of Early Fusion
5.3.2. Ablation Evaluation of Late Fusion
5.4. Application Experiments
5.4.1. Quantitative Comparison
5.4.2. Qualitative Comparison
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yuan, Z.; Mou, L.; Hua, Y.; Zhu, X.X. Rrsis: Referring remote sensing image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5613312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Ji, J.; Sun, X.; Ji, R. Rotated multi-scale interaction network for referring remote sensing image segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 17–18 June 2024; pp. 26658–26668. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, R.; Rohrbach, M.; Darrell, T. Segmentation from Natural Language Expressions. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2016; Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., Welling, M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 108–124. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Qu, H. DDFAV: Remote Sensing Large Vision Language Models Dataset and Evaluation Benchmark. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; He, J.; Li, P.; Zhong, S.; Li, H.; He, G. Unified Transformer with Cross-Modal Mixture Experts for Remote-Sensing Visual Question Answering. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Lin, Z.; Shen, X.; Yang, J.; Lu, X.; Bansal, M.; Berg, T.L. Mattnet: Modular attention network for referring expression comprehension. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 1307–1315. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Chen, T.; Wang, L.; Luo, J. Improving one-stage visual grounding by recursive sub-query construction. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Proceedings, Part XIV 16. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 387–404. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Yuan, Y. Rsvg: Exploring data and models for visual grounding on remote sensing data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5604513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, W.; Bi, H.; Li, J.; Li, S.; Yu, H.; Sun, X.; Wang, H. Injecting Linguistic Into Visual Backbone: Query-Aware Multimodal Fusion Network for Remote Sensing Visual Grounding. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5637814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Lu, H. Encoder fusion network with co-attention embedding for referring image segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 15506–15515. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, S.; Wang, H.; Xie, S.; Niu, Z.; Tong, R.; Chen, Y.W.; Lin, L. SLViT: Scale-Wise Language-Guided Vision Transformer for Referring Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IJCAI, Macao, China, 19–25 August 2023; pp. 1294–1302. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Ding, H.; Tong, Y.; Tao, D. Toward Robust Referring Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2024, 33, 1782–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ding, H.; Cai, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Satzoda, R.K.; Mahadevan, V.; Manmatha, R. Polyformer: Referring image segmentation as sequential polygon generation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 18653–18663. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.; Hui, T.; Liu, S.; Li, G.; Wei, Y.; Han, J.; Liu, L.; Li, B. Referring image segmentation via cross-modal progressive comprehension. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 10488–10497. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Jiang, X.; Ding, H. Instance-specific feature propagation for referring segmentation. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2022, 25, 3657–3667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Wang, D.; Xu, H.; Zhong, H.; Wang, C. Language-Guided Progressive Attention for Visual Grounding in Remote Sensing Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5631413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, P.; Xiao, G.; Liu, J. Multimodal Features Alignment for Vision–Language Object Tracking. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. Adv. Neural inform. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 6000–6010. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, P.; Zhu, X.; Clifton, D.A. Multimodal learning with transformers: A survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 45, 12113–12132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, J.; Liang, X.; Ke, W. Coupalign: Coupling word-pixel with sentence-mask alignments for referring image segmentation. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 14729–14742. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, Y.; Yu, H.; Kang, S.J. Cross-aware early fusion with stage-divided vision and language transformer encoders for referring image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2023, 26, 5823–5833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Lin, Z.; Shen, X.; Yang, J.; Lu, X.; Yuille, A. Recurrent multimodal interaction for referring image segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 1271–1280. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Li, K.; Kuo, Y.C.; Shu, M.; Qi, X.; Shen, X.; Jia, J. Referring image segmentation via recurrent refinement networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 5745–5753. [Google Scholar]
- Margffoy-Tuay, E.; Pérez, J.C.; Botero, E.; Arbeláez, P. Dynamic multimodal instance segmentation guided by natural language queries. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 630–645. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.W.; Tsai, Y.H.; Wang, T.; Lin, Y.Y.; Yang, M.H. Referring expression object segmentation with caption-aware consistency. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1910.04748. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, J.; Tang, Y.; Chen, K.; Zhao, H.; Torr, P.H. Lavt: Language-aware vision transformer for referring image segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 18155–18165. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 10012–10022. [Google Scholar]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies; Association for Computational Linguistics: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2019; Volume 1 (long and short papers), pp. 4171–4186. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, J.; Tang, Y.; Chen, K.; Zhao, H.; Torr, P.H. Semantics-aware dynamic localization and refinement for referring image segmentation. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Washington, DC, USA, 7–14 February 2023; Volume 37, pp. 3222–3230. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Yuan, W.; Fu, J.; Jiang, Z.; Hayashi, H.; Neubig, G. Pre-train, prompt, and predict: A systematic survey of prompting methods in natural language processing. ACM Comput. Surv. 2023, 55, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Guan, H.; Qiu, J.; Spratling, M. One prompt word is enough to boost adversarial robustness for pre-trained vision-language models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 24408–24419. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhan, M.; Hu, P.; Zhu, X. Adaptive Multi-Modality Prompt Learning. In Proceedings of the 32nd ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Melbourne, Australia, 28 October—1 November 2024; pp. 8672–8680. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Yan, K.; Ding, S. Bilateral Adaptive Cross-Modal Fusion Prompt Learning for CLIP. In Proceedings of the 32nd ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Melbourne, Australia, 28 October—1 November 2024; pp. 9001–9009. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, K.; Yang, J.; Loy, C.C.; Liu, Z. Learning to prompt for vision-language models. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2022, 130, 2337–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Yang, J.; Loy, C.C.; Liu, Z. Conditional prompt learning for vision-language models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 16816–16825. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, M.; Tang, L.; Chen, B.C.; Cardie, C.; Belongie, S.; Hariharan, B.; Lim, S.N. Visual prompt tuning. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 709–727. [Google Scholar]
- Khattak, M.U.; Rasheed, H.; Maaz, M.; Khan, S.; Khan, F.S. Maple: Multi-modal prompt learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 19113–19122. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.A.; Zhang, Y.; Qiu, Z.; Xie, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, T. CARIS: Context-aware referring image segmentation. In Proceedings of the 31st ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 29 October–3 November 2023; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Kampffmeyer, M.; Zhao, X. Prompt-guided bidirectional deep fusion network for referring image segmentation. Neurocomputing 2025, 616, 128899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.; Schwing, A.; Kirillov, A. Per-pixel classification is not all you need for semantic segmentation. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 17864–17875. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, B.; Misra, I.; Schwing, A.G.; Kirillov, A.; Girdhar, R. Masked-attention mask transformer for universal image segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 1290–1299. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Su, W.; Lu, L.; Li, B.; Wang, X.; Dai, J. Deformable detr: Deformable transformers for end-to-end object detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.04159. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zuo, D.; Jin, W.; Qiu, S. Intelligent Detection of Hidden Hazards Along High-Speed Rail Based on Optical Remote Sensing Images. Acta Optica Sinica 2025, 45, 0728004. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, C.; Song, Z.; Qiu, H.; Wang, L.; Meng, F.; Li, H. Prompt-driven referring image segmentation with instance contrasting. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 4124–4134. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.; Yin, X.; Yue, H.; Yang, J. MARIS: Referring Image Segmentation via Mutual-Aware Attention Features. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2311.15727. [Google Scholar]





| Satellite Model | SuperView-1 | GaoFen-2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Type | CCSS Roof Building | Plastic Greenhouse | CCSS Roof Building | Plastic Greenhouse |
| Hazard Number | 25,711 | 7889 | 21,613 | 7257 |
| Minimum Area (m2) | 1.14 | 0.12 | 1.14 | 0.12 |
| Maximum Area (m2) | 29,692.80 | 10,920.70 | 29,692.80 | 3609.65 |
| Total Area (m2) | 9,781,844.09 | 3,786,570.52 | 8,176,613.10 | 3,121,702.59 |
| Mean Area (m2) | 380.45 | 479.98 | 378.32 | 430.16 |
| Area Standard Deviation (m2) | 932.36 | 448.29 | 994.83 | 241.81 |
| Method | Dataset Type | Pr@0.5 (%) | Pr@0.6 (%) | Pr@0.7 (%) | Pr@0.8 (%) | Pr@0.9 (%) | oIoU (%) | mIoU (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LAVT | Test | 69.26 | 62.28 | 52.08 | 40.33 | 23.64 | 76.04 | 60.58 |
| Validation | 70.06 | 62.59 | 52.36 | 42.30 | 24.89 | 76.68 | 61.40 | |
| CrossVLT | Test | 70.30 | 63.80 | 53.81 | 42.20 | 25.92 | 75.92 | 61.45 |
| Validation | 70.11 | 63.05 | 53.51 | 42.93 | 25.63 | 77.44 | 61.89 | |
| RefSegFormer | Test | 65.59 | 59.45 | 50.89 | 39.35 | 23.15 | 76.39 | 58.17 |
| Validation | 68.51 | 60.92 | 52.76 | 42.18 | 25.40 | 76.50 | 59.11 | |
| RMSIN | Test | 75.44 | 68.31 | 56.33 | 43.03 | 24.19 | 77.78 | 64.65 |
| Validation | 75.29 | 68.22 | 56.78 | 44.02 | 24.60 | 77.57 | 65.25 | |
| MPBF | Test | 75.90 | 69.18 | 57.84 | 44.04 | 26.57 | 78.20 | 65.32 |
| Validation | 75.63 | 69.08 | 58.79 | 46.55 | 27.07 | 78.37 | 65.68 |
| Method | Params(M) | FLOPs(G) | oIoU(%) | FPS(fps) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LAVT | 203.70 | 193.97 | 76.04 | 14.10 |
| CrossVLT | 212.68 | 200.39 | 75.92 | 14.04 |
| RefSegFormer | 195.00 | 103.64 | 76.39 | 11.95 |
| RMSIN | 196.65 | 149.51 | 77.78 | 13.71 |
| MPBF | 159.12 | 146.94 | 78.20 | 11.82 |
| Method | Fusion Setting | Pr@0.5 (%) | Pr@0.6 (%) | Pr@0.7 (%) | Pr@0.8 (%) | Pr@0.9 (%) | oIoU (%) | mIoU (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prompt Insertion Position | Shallow Prompting | 73.28 | 66.70 | 56.45 | 43.00 | 25.28 | 77.37 | 63.77 |
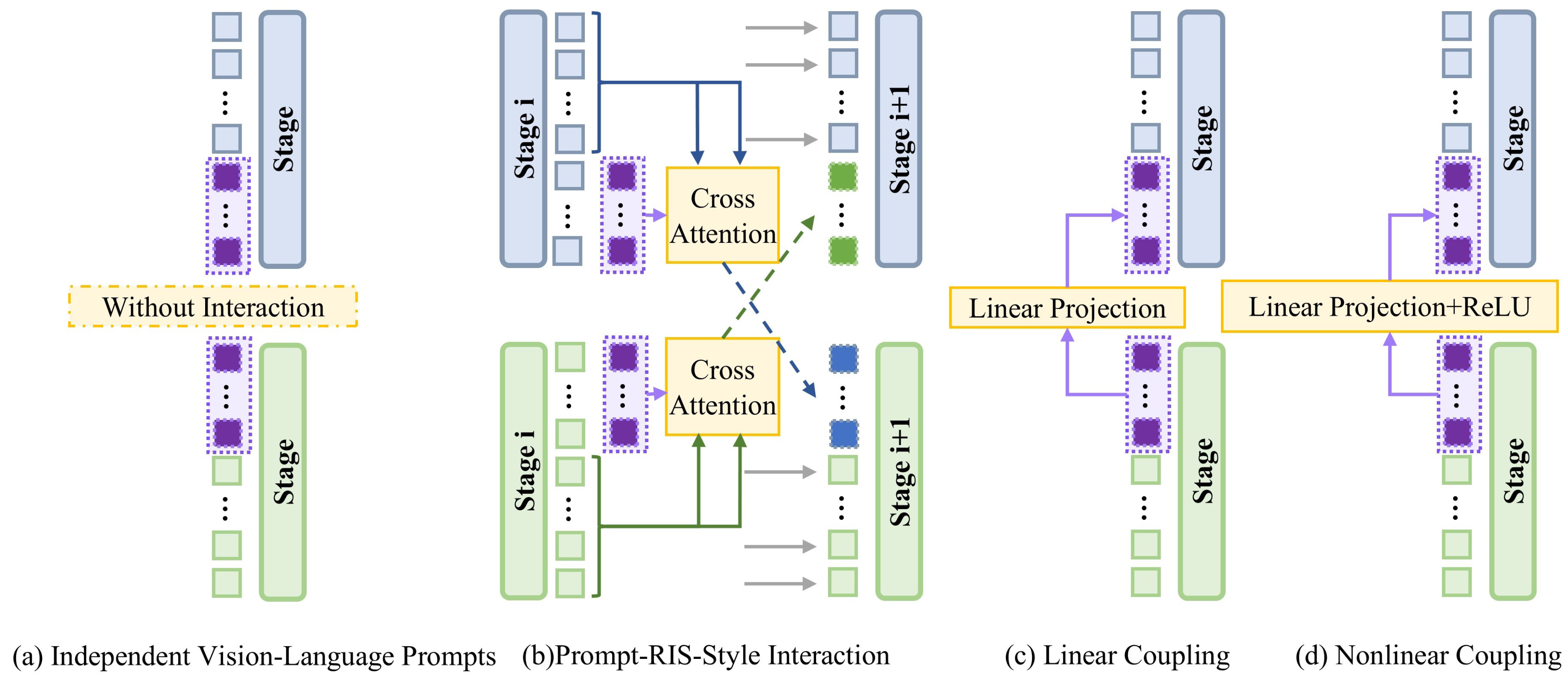
| Prompt Interaction Mode | Independent Vision–Language Prompts | 75.50 | 68.54 | 57.60 | 44.01 | 25.83 | 78.09 | 65.01 |
| Prompt-RIS-Style Interaction | 74.23 | 67.62 | 56.94 | 44.10 | 26.72 | 77.63 | 64.53 | |
| Nonlinear Coupling | 75.06 | 68.60 | 58.26 | 44.15 | 26.80 | 78.22 | 65.19 | |
| Number of Prompts | 0 | 74.78 | 68.11 | 57.28 | 44.07 | 26.66 | 77.28 | 64.53 |
| 3 | 74.23 | 68.00 | 56.85 | 44.15 | 26.66 | 77.66 | 64.73 | |
| 4 | 75.09 | 68.77 | 58.49 | 44.87 | 26.34 | 77.85 | 65.29 | |
| 6 | 75.75 | 68.80 | 57.68 | 44.84 | 26.77 | 78.14 | 65.33 | |
| 10 | 75.84 | 69.29 | 58.80 | 44.79 | 27.09 | 78.19 | 65.30 | |
| MPBF | Deep Prompting/Linear Coupling/5 | 75.90 | 69.18 | 57.80 | 44.04 | 26.57 | 78.20 | 65.32 |
| Method | Fusion Setting | Pr@0.5 (%) | Pr@0.6 (%) | Pr@0.7 (%) | Pr@0.8 (%) | Pr@0.9 (%) | oIoU (%) | mIoU (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| w/o SR Module | - | 74.00 | 67.42 | 56.36 | 43.84 | 26.66 | 77.79 | 64.50 |
| Prompt Source in VLA | 75.41 | 68.46 | 58.35 | 44.30 | 26.77 | 78.09 | 65.18 | |
| Random Prompting | 74.83 | 68.20 | 57.02 | 44.01 | 25.94 | 77.69 | 64.86 | |
| Vision–Language Alignment Mode | Parallel Mode | 75.27 | 68.74 | 57.54 | 44.33 | 26.69 | 77.88 | 64.95 |
| MPBF | /Serial Mode | 75.90 | 69.18 | 57.80 | 44.04 | 26.57 | 78.20 | 65.32 |
| Method | Dataset Type | Pr@0.5 (%) | Pr@0.6 (%) | Pr@0.7 (%) | Pr@0.8 (%) | Pr@0.9 (%) | oIoU (%) | mIoU (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LAVT | Test | 89.69 | 84.87 | 78.88 | 67.37 | 38.74 | 80.21 | 79.05 |
| Validation | 88.05 | 82.81 | 75.51 | 63.43 | 35.58 | 78.99 | 77.16 | |
| CrossVLT | Test | 90.15 | 85.95 | 79.78 | 69.88 | 43.79 | 82.30 | 80.29 |
| Validation | 88.94 | 84.28 | 78.77 | 67.60 | 41.44 | 80.42 | 79.33 | |
| RefSegFormer | Test | 90.22 | 86.54 | 80.36 | 70.33 | 45.71 | 82.34 | 80.48 |
| Validation | 89.39 | 84.98 | 79.14 | 68.86 | 42.78 | 81.27 | 79.39 | |
| RMSIN | Test | 90.61 | 86.49 | 79.78 | 68.17 | 40.57 | 81.58 | 80.14 |
| Validation | 89.85 | 85.14 | 78.45 | 67.11 | 39.65 | 80.32 | 79.35 | |
| MPBF | Test | 90.83 | 86.79 | 80.87 | 70.80 | 46.25 | 83.03 | 81.43 |
| Validation | 91.00 | 87.01 | 80.10 | 69.98 | 44.08 | 82.18 | 81.11 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Jin, W.; Qiu, S.; Sun, Q. Multimodal Prompt-Guided Bidirectional Fusion for Referring Remote Sensing Image Segmentation. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1683. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17101683
Li Y, Jin W, Qiu S, Sun Q. Multimodal Prompt-Guided Bidirectional Fusion for Referring Remote Sensing Image Segmentation. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(10):1683. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17101683
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yingjie, Weiqi Jin, Su Qiu, and Qiyang Sun. 2025. "Multimodal Prompt-Guided Bidirectional Fusion for Referring Remote Sensing Image Segmentation" Remote Sensing 17, no. 10: 1683. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17101683
APA StyleLi, Y., Jin, W., Qiu, S., & Sun, Q. (2025). Multimodal Prompt-Guided Bidirectional Fusion for Referring Remote Sensing Image Segmentation. Remote Sensing, 17(10), 1683. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17101683







