Forecasting Chlorophyll-a in the Murray–Darling Basin Using Remote Sensing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Data
2.2. Estimate Chl-a Level from Sentinel MSI Data
2.3. Seasonal Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average Model for Forecasting Chl-a Level from Sentinel MSI Data
- , and are polynomials of the order , and , respectively;
- is the backward shift operator and ;
- is the backward shift operator for the seasonal term and ;
- are the order of integrated and seasonal integrated components;
- is the seasonal period;
- is the white noise error term at time .
2.4. Model Validation
3. Results
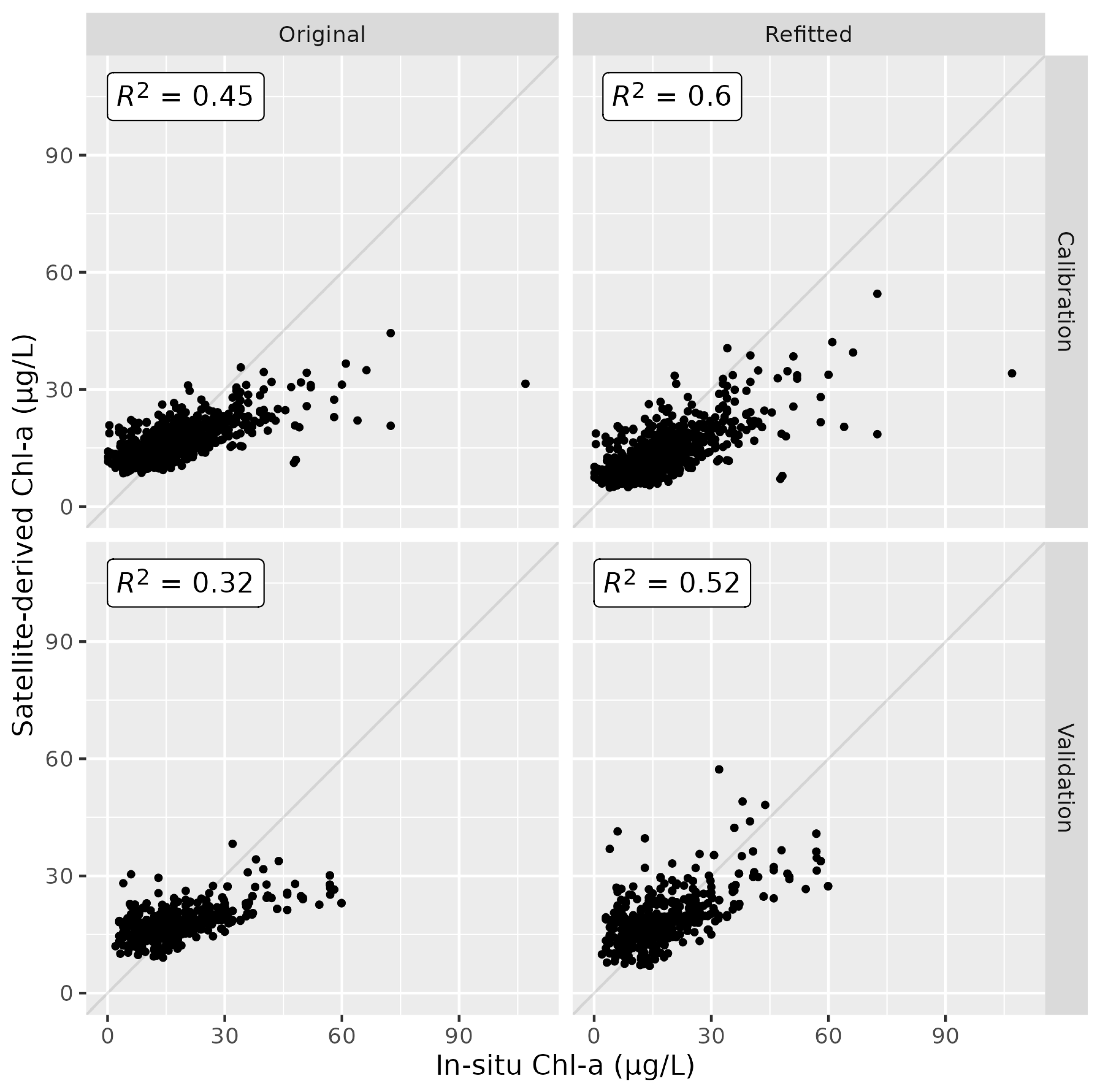
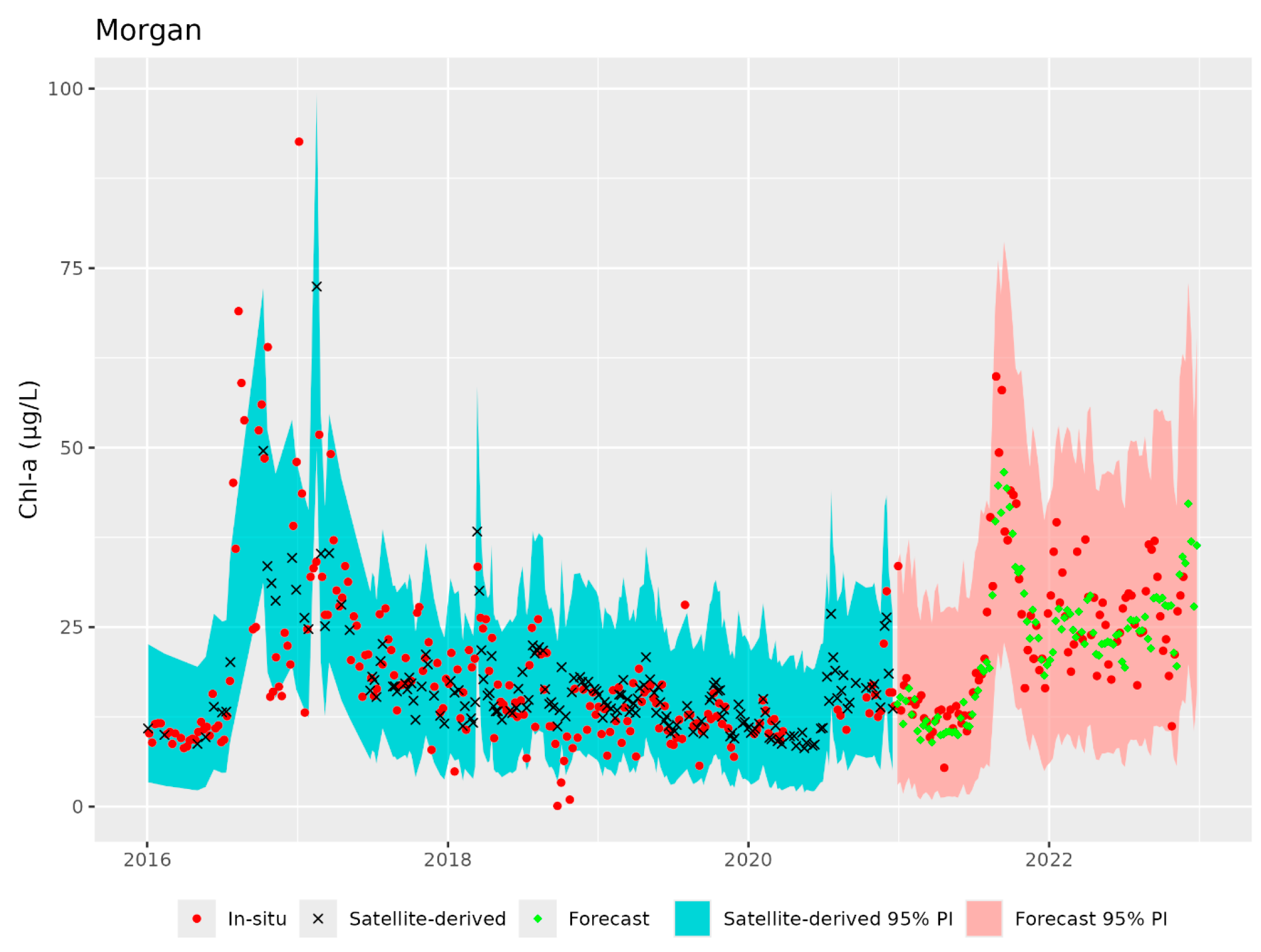
3.1. Satellite-Derived Chl-a Estimates
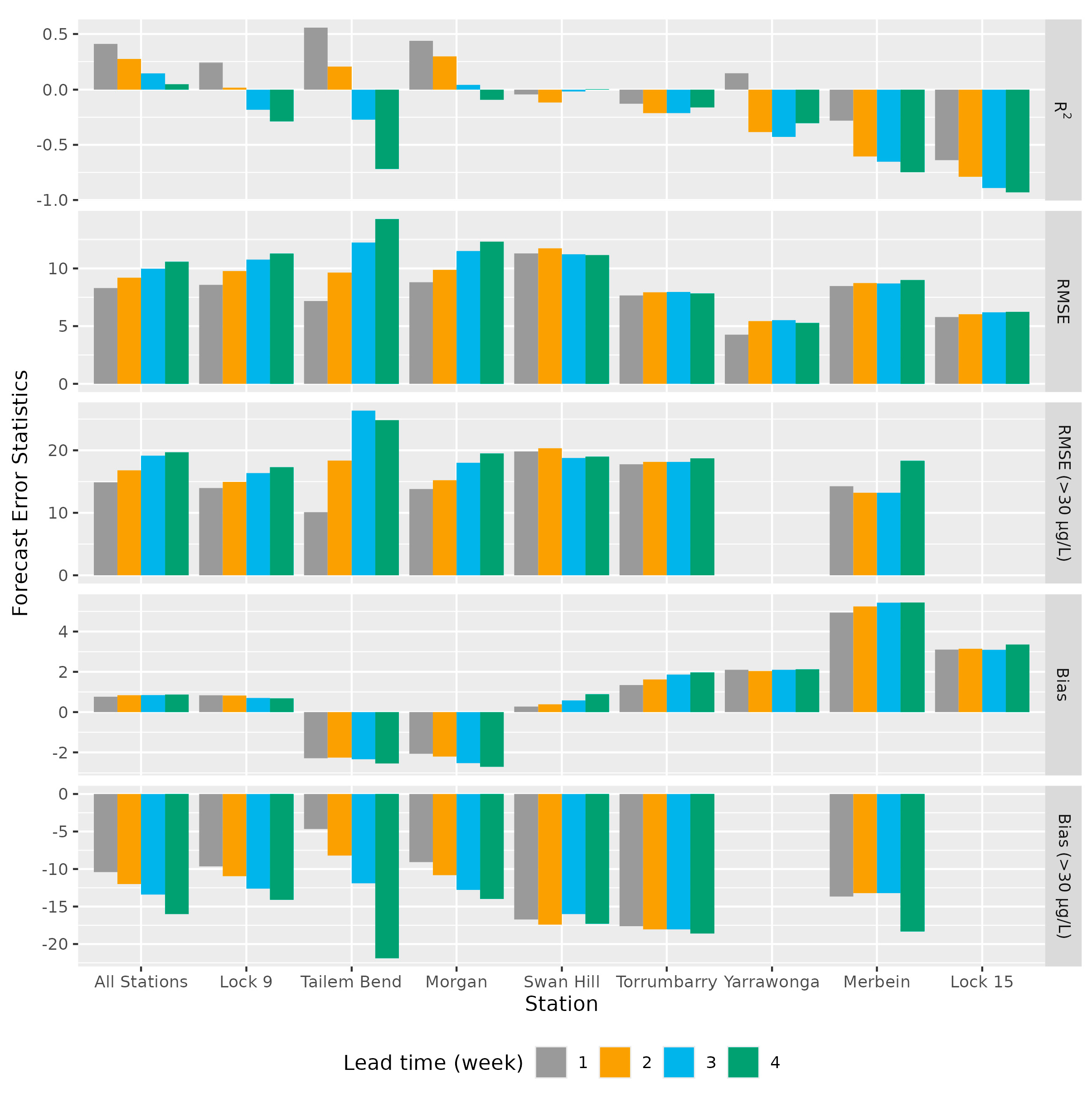
3.2. Chl-a Forecasts
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, S.; Crossman, N.D.; Nolan, M.; Ghirmay, H. Bringing ecosystem services into integrated water resources management. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 129, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, D.H.; Bark, R.H.; Coggan, A. Is ecosystem service research used by decision-makers? A case study of the Murray-Darling Basin, Australia. Landsc. Ecol. 2014, 29, 1447–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MDBA. Why the Murray–Darling Basin Matters. Available online: https://www.mdba.gov.au/basin/why-murray-darling-basin-matters (accessed on 22 July 2024).
- MDBA. Plants and Wildlife. Available online: https://www.mdba.gov.au/basin/plants-and-wildlife (accessed on 20 March 2024).
- Swirepik, J.L.; Burns, I.C.; Dyer, F.J.; Neave, I.A.; O’Brien, M.G.; Pryde, G.M.; Thompson, R.M. Establishing Environmental Water Requirements for the Murray-Darling Basin, Australia’s Largest Developed River System. River Res. Appl. 2016, 32, 1153–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beare, S.; Heaney, A. Irrigation, Water Quality and Water Rights in the Murray Darling Basin, Australia. Nat. Res. Manag. Policy 2006, 29, 177–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grafton, R.Q.; Wheeler, S.A. Economics of Water Recovery in the Murray-Darling Basin, Australia. Annu. Rev. Resour. Econ. 2018, 10, 487–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, T.; Lawrence, B. Revision of the River Murray Water Quality Monitoring Program; Internal MDBA Report 18/15; 2013; p. 29. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/323571660_Revision_of_the_River_Murray_Water_Quality_Monitoring_Program?channel=doi&linkId=5a9e0ad6aca272cd09c229f7&showFulltext=true (accessed on 8 May 2025).
- Holland, A.; Gionfriddo, C.; McPhan, L.; Lewis, S.; Shackleton, M.; Silvester, E. Synthesis of Blue Green Algae (Cyanobacteria) Bloom Knowledge and Analysis of Recent Trends in the Murray Darling Basin; 1; La Trobe Biogeochemistry and Ecotoxicology Group: 2023. Available online: https://www.mdba.gov.au/sites/default/files/publications/synthesis-blue-green-algae-bloom-knowledge-analysis-recent-trends-mdb.pdf (accessed on 8 May 2025).
- Biswas, T.; Mosley, L.M. From Mountain Ranges to Sweeping Plains, in Droughts and Flooding Rains; River Murray Water Quality over the Last Four Decades. Water Resour. Manag. 2019, 33, 1087–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowling, L.; Baldwin, D.; Merrick, C.; Brayan, J.; Panther, J. Possible drivers of a Chrysosporum ovalisporum bloom in the Murray River, Australia, in 2016. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2018, 69, 1649–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, G.H.; Weis, E. Chlorophyll Fluorescence and Photosynthesis—The Basics. Annu. Rev. Plant Phys. 1991, 42, 313–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowan, K.S. Photosynthetic Pigments of Algae; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 1989; p. 334. [Google Scholar]
- Wetzel, R.G. Limnology: Lake and River Ecosystems, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Arnold, J.G.; Moriasi, D.N.; Gassman, P.W.; Abbaspour, K.C.; White, M.J.; Srinivasan, R.; Santhi, C.; Harmel, R.D.; van Griensven, A.; Van Liew, M.W.; et al. Swat: Model Use, Calibration, and Validation. Trans. ASABE 2012, 55, 1491–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, D.P.; Schladow, S.G. Prediction of water quality in lakes and reservoirs.1. Model description. Ecol. Model. 1997, 96, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benndorf, J.; Recknagel, F. Problems of Application of the Ecological Model Salmo to Lakes and Reservoirs Having Various Trophic States. Ecol. Model. 1982, 17, 129–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.W.; Guan, T.S.; Yun, L.; Li, R.N.; Recknagel, F. Online forecasting chlorophyll a concentrations by an auto-regressive integrated moving average model: Feasibilities and potentials. Harmful Algae 2015, 43, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; He, J.Y.; Huang, H.M.; Miller, T.R.; Christakos, G.; Reichwaldt, E.S.; Ghadouani, A.; Lin, S.P.; Xu, X.H.; Shi, J.Y. A novel single-parameter approach for forecasting algal blooms. Water Res. 2017, 108, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Shin, H.S.; Plummer, J.D. A wavelet-based autoregressive fuzzy model for forecasting algal blooms. Environ. Model. Softw. 2014, 62, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.H.; Qin, M.J.; Zhang, F.; Liu, R.Y. Multistep-ahead forecasting of chlorophyll a using a wavelet nonlinear autoregressive network. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2018, 160, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.W.; Huang, Y.; Dickman, M.; Jayawardena, A.W. Neural network modelling of coastal algal blooms. Ecol. Model. 2003, 159, 179–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.E.; Shon, T.S.; Shin, H.S. Forecasting algal bloom (chl-a) on the basis of coupled wavelet transform and artificial neural networks at a large lake. Desalin. Water Treat. 2013, 51, 4118–4128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yajima, H.; Derot, J. Application of the Random Forest model for chlorophyll-a forecasts in fresh and brackish water bodies in Japan, using multivariate long-term databases. J. Hydroinform 2018, 20, 206–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaee, T.; Boroumand, A. Forecasting of chlorophyll-a concentrations in South San Francisco Bay using five different models. Appl. Ocean. Res. 2015, 53, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.; Park, M.; Baek, S.S.; Cho, K.H. Deep learning-based algorithms for long-term prediction of chlorophyll-a in catchment streams. J. Hydrol. 2023, 626, 130240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.L.; Wang, X.P.; Zhang, J.H.; Yu, X.; Zhang, S.C.; Li, Q. Prediction of Sea Surface Chlorophyll-a Concentrations Based on Deep Learning and Time-Series Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen, H.B.; Jiang, J.H.; Han, G.Q.; Lin, X.Y.; Liu, Y.; Jia, X.Y.; Ji, Q.Y.; Li, B. Applying Deep Learning in the Prediction of Chlorophyll-a in the East China Sea. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.; Kim, T.; Hong, S.; Lee, S.; Lee, E.; Hong, S.; Lee, C.; Kim, T.; Park, M.S.; Park, J.; et al. Prediction of Chlorophyll-a Concentrations in the Nakdong River Using Machine Learning Methods. Water 2020, 12, 1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Chen, S.Y.; Cheng, Z.Y.; Wang, X.; Xiao, Y.; Xiao, L.; Gong, Y.W.; Wang, T.T.; Zhang, X.F.; Liu, S.Q. Long-term prediction of sea surface chlorophyll-a concentration based on the combination of spatio-temporal features. Water Res. 2022, 211, 118040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, Q.W.; Yao, S.Y.; He, M.N.; Zhang, J.Y.; Li, G.; Lin, Y.Q. Combining physical-based model and machine learning to forecast chlorophyll-a concentration in freshwater lakes. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 907, 168097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, Y.J.; Kampbell, D.H. Monitoring chlorophyll-a as a measure of algae in Lake Texoma marinas. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2003, 70, 606–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, C.H.; Ajani, P.; Armbrecht, L.; Atkins, N.; Baird, M.E.; Beard, J.; Bonham, P.; Burford, M.; Clementson, L.; Coad, P.; et al. A database of chlorophyll a in Australian waters. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filazzola, A.; Mahdiyan, O.; Shuvo, A.; Ewins, C.; Moslenko, L.; Sadid, T.; Blagrave, K.; Imrit, M.A.; Gray, D.K.; Quinlan, R.; et al. A database of chlorophyll and water chemistry in freshwater lakes. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, R.I.; Wahid, K.A.; Nugent, K.; Baulch, H. Design and Development of Low-Cost, Portable, and Smart Chlorophyll-A Sensor. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 7362–7371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.H.; Li, D.L. Development of Sensors for Chlorophyll Concentration Measurement. J. Sens. 2015, 2015, 903509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, J.E.; Werdell, P.J. Chlorophyll algorithms for ocean color sensors-OC4, OC5 & OC6. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 229, 32–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitelson, A. The Peak near 700 Nm on Radiance Spectra of Algae and Water—Relationships of Its Magnitude and Position with Chlorophyll Concentration. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1992, 13, 3367–3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholizadeh, M.H.; Melesse, A.M.; Reddi, L. A Comprehensive Review on Water Quality Parameters Estimation Using Remote Sensing Techniques. Sensors 2016, 16, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.M.; Lee, Z.; Franz, B. Chlorophyll a algorithms for oligotrophic oceans: A novel approach based on three-band reflectance difference. J. Geophys. Res.-Ocean. 2012, 117, C01011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moses, W.J.; Gitelson, A.A.; Berdnikov, S.; Saprygin, V.; Povazhnyi, V. Operational MERIS-based NIR-red algorithms for estimating chlorophyll-a concentrations in coastal waters—The Azov Sea case study. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 121, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.E.; Lain, L.R.; Bernard, S. An optimized Chlorophyll-a switching algorithm for MERIS and OLCI in phytoplankton-dominated waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 215, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Mishra, D.R. Normalized difference chlorophyll index: A novel model for remote estimation of chlorophyll-a concentration in turbid productive waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 117, 394–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moses, W.J.; Gitelson, A.A.; Berdnikov, S.; Povazhnyy, V. Satellite estimation of chlorophyll-a concentration using the red and NIR bands of MERIS—The Azov sea case study. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2009, 6, 845–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogliotti, A.I.; Gossn, J.I.; Gonzalez, C.; Yema, L.; Sanchez, M.; Farrell, I.L.O. Evaluation of Multi- and Hyper- Spectral Chl-A Algorithms in the RÍo De La Plata Turbid Waters During a Cyanobacteria Bloom. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium IGARSS, Brussels, Belgium, 11–16 July 2021; pp. 7442–7445. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.X.; Sun, D.Q.; Liu, W.H.; You, Y.F.; Wang, S.Y.; Sun, Z.C.; Wang, S.H. Using a Remote-Sensing-Based Piecewise Retrieval Algorithm to Map Chlorophyll-a Concentration in a Highland River System. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geoscience Australia. Longest Rivers. Available online: https://www.ga.gov.au/scientific-topics/national-location-information/landforms/longest-rivers (accessed on 25 September 2024).
- MDBA. Climate—The Murray–Darling Basin. Available online: https://www.mdba.gov.au/climate-and-river-health/climate (accessed on 7 May 2024).
- Mallen-Cooper, M.; Zampatti, B.; Hillman, T.; King, A.; Koehn, J.; Saddlier, S.; Sharpe, C.; Stuart, I. Managing the Chowilla Creek Environmental Regulator for Fish Species at Risk. South Australian Murray-Darling Basin Natural Resources Management Technical Report. 2011. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/287841440_Managing_the_Chowilla_creek_environmental_regulator_for_fish_species_at_risk?channel=doi&linkId=567a146808ae40c0e27dfa97&showFulltext=true (accessed on 8 May 2025).
- Drusch, M.; Del Bello, U.; Carlier, S.; Colin, O.; Fernandez, V.; Gascon, F.; Hoersch, B.; Isola, C.; Laberinti, P.; Martimort, P.; et al. Sentinel-2: ESA’s Optical High-Resolution Mission for GMES Operational Services. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohin, F.; Van der Zande, D.; Tilstone, G.; Eleveld, M.A.; Lefebvre, M.; Andrieux-Loyer, F.; Blauw, A.N.; Bryère, P.; Devreker, D.; Gamesson, P.; et al. Twenty years of satellite and observations of surface chlorophyll-a from the northern Bay of Biscay to the eastern English Channel. Is the water quality improving? Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 233, 111343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neil, C.; Spyrakos, E.; Hunter, P.D.; Tyler, A.N. A global approach for chlorophyll-a retrieval across optically complex inland waters based on optical water types. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 229, 159–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogashawara, I.; Kiel, C.; Jechow, A.; Kohnert, K.; Ruhtz, T.; Grossart, H.P.; Hölker, F.; Nejstgaard, J.C.; Berger, S.A.; Wollrab, S. The Use of Sentinel-2 for Chlorophyll-a Spatial Dynamics Assessment: A Comparative Study on Different Lakes in Northern Germany. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geoscience Australia. Geoscience Australia Sentinel-2A MSI Analysis Ready Data Collection 3—DEA Surface Reflectance (Sentinel-2A MSI). Available online: https://ecat.ga.gov.au/geonetwork/srv/eng/catalog.search#/metadata/146552 (accessed on 8 May 2024).
- Geoscience Australia. Geoscience Australia Sentinel-2B MSI Analysis Ready Data Collection 3—DEA Surface Reflectance (Sentinel-2B MSI). Available online: https://ecat.ga.gov.au/geonetwork/srv/eng/catalog.search#/metadata/146551 (accessed on 8 May 2024).
- Li, F.Q.; Jupp, D.L.B.; Reddy, S.; Lymburner, L.; Mueller, N.; Tan, P.; Islam, A. An Evaluation of the Use of Atmospheric and BRDF Correction to Standardize Landsat Data. IEEE J.-Stars. 2010, 3, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skakun, S.; Wevers, J.; Brockmann, C.; Doxani, G.; Aleksandrov, M.; Batic, M.; Frantz, D.; Gascon, F.; Gómez-Chova, L.; Hagolle, O.; et al. Cloud Mask Intercomparison eXercise (CMIX): An evaluation of cloud masking algorithms for Landsat 8 and Sentinel-2. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 274, 112990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahlevan, N.; Smith, B.; Schalles, J.; Binding, C.; Cao, Z.G.; Ma, R.H.; Alikas, K.; Kangro, K.; Gurlin, D.; Hà, N.; et al. Seamless retrievals of chlorophyll-a from Sentinel-2 (MSI) and Sentinel-3 (OLCI) in inland and coastal waters: A machine-learning approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 240, 111604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victorian Fisheries Authority. The Murray River. Available online: https://vfa.vic.gov.au/recreational-fishing/fishing-locations/inland-angling-guide/special-articles/the-murray-river#:~:text=The%20river%20is%2040%2D50,pools%204%2D5%20m%20deep. (accessed on 31 January 2025).
- Yang, X.; Pavelsky, T.M.; Allen, G.H.; Donchyts, G. RivWidthCloud: An Automated Google Earth Engine Algorithm for River Width Extraction From Remotely Sensed Imagery. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 17, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.W. Improved Automated Detection of Subpixel-Scale Inundation—Revised Dynamic Surface Water Extent (DSWE) Partial Surface Water Tests. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.Q. Modification of normalised difference water index (NDWI) to enhance open water features in remotely sensed imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 3025–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.G.; Ma, R.H.; Duan, H.T.; Pahlevan, N.; Melack, J.; Shen, M.; Xue, K. A machine learning approach to estimate chlorophyll-a from Landsat-8 measurements in inland lakes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 248, 111974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werther, M.; Odermatt, D.; Simis, S.G.H.; Gurlin, D.; Lehmann, M.K.; Kutser, T.; Gupana, R.; Varley, A.; Hunter, P.D.; Tyler, A.N.; et al. A Bayesian approach for remote sensing of chlorophyll-a and associated retrieval uncertainty in oligotrophic and mesotrophic lakes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 283, 113295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.J.; Song, K.S.; Wang, S.; Liu, G.; Wen, Z.D.; Shang, Y.X.; Lyu, L.L.; Chen, F.F.; Xu, S.Q.; Tao, H.; et al. Quantification of chlorophyll-a in typical lakes across China using Sentinel-2 MSI imagery with machine learning algorithm. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 778, 146271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.F.; Li, J.S.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, B.; Wu, C.Q.; Wu, Y.F.; Wang, G.L.; Wang, S.L.; Lu, Z.Y. Algorithms and Schemes for Chlorophyll a Estimation by Remote Sensing and Optical Classification for Turbid Lake Taihu, China. IEEE J.-Stars. 2015, 8, 350–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buma, W.G.; Lee, S.I. Evaluation of Sentinel-2 and Landsat 8 Images for Estimating Chlorophyll-a Concentrations in Lake Chad, Africa. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geoscience Australia. Monitoring Chlorophyll-a in Australian Waterbodies. Available online: https://knowledge.dea.ga.gov.au/notebooks/Real_world_examples/Chlorophyll_monitoring/ (accessed on 9 August 2024).
- Beck, R.; Zhan, S.G.; Liu, H.X.; Tong, S.; Yang, B.; Xu, M.; Ye, Z.X.; Huang, Y.; Shu, S.; Wu, Q.S.; et al. Comparison of satellite reflectance algorithms for estimating chlorophyll-a in a temperate reservoir using coincident hyperspectral aircraft imagery and dense coincident surface observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 178, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, D.R.; Schaeffer, B.A.; Keith, D. Performance evaluation of normalized difference chlorophyll index in northern Gulf of Mexico estuaries using the Hyperspectral Imager for the Coastal Ocean. Gisci Remote Sens. 2014, 51, 175–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravitz, J.; Matthews, M. Chlorophyll-a for Cyanobacteria Blooms from Sentinel-2. Available online: https://custom-scripts.sentinel-hub.com/custom-scripts/sentinel-2/cyanobacteria_chla_ndci_l1c/ (accessed on 9 August 2024).
- Manuel, A.; Blanco, A.C. Transformation of the normalized difference chlorophyll index to retrieve chlorophyll-a concentrations in Manila Bay. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2023, XLVIII-4/W6-2022, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makridakis, S.; Hibon, M. ARMA models and the Box-Jenkins methodology. J. Forecast. 1997, 16, 147–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyndman, R. Forecasting Weekly Data. Available online: https://robjhyndman.com/hyndsight/forecasting-weekly-data/ (accessed on 19 August 2024).
- Hyndman, R.; Athanasopoulos, G.; Bergmeir, C.; Caceres, G.; Chhay, L.; O’Hara-Wild, M.; Petropoulos, F.; Razbash, S.; Wang, E.; Yasmeen, F. Forecast: Forecasting Functions for Time Series and Linear Models, R package version 8.23.0; 2024. Available online: https://github.com/robjhyndman/forecast (accessed on 8 May 2025).
- Nash, J.E.; Sutcliffe, J.V. River flow forecasting through conceptual models part I—A discussion of principles. J. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Yu, Y.X.; Yi, Y.J. Spatial distribution of nutrient loads and thresholds in large shallow lakes: The case of Chaohu Lake, China. J. Hydrol. 2022, 613, 128466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruns, N.E.; Heffernan, J.B.; Ross, M.R.V.; Doyle, M. A simple metric for predicting the timing of river phytoplankton blooms. Ecosphere 2022, 13, e4348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, J.L.; Dubrovsky, N.M.; Foster, G.M.; King, L.R.; Loftin, K.A.; Rosen, B.H.; Stelzer, E.A. Cyanotoxin occurrence in large rivers of the United States. Inland. Waters 2020, 10, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stauffer, B.A.; Bowers, H.A.; Buckley, E.; Davis, T.W.; Johengen, T.H.; Kudela, R.; McManus, M.A.; Purcell, H.; Smith, G.J.; Vander Woude, A.; et al. Considerations in Harmful Algal Bloom Research and Monitoring: Perspectives From a Consensus-Building Workshop and Technology Testing. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wozniak, M.; Bradtke, K.M.; Darecki, M.; Krezel, A. Empirical Model for Phycocyanin Concentration Estimation as an Indicator of Cyanobacterial Bloom in the Optically Complex Coastal Waters of the Baltic Sea. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Stumpf, R.P.; Schaeffer, B.A.; Werdell, P.J.; Loftin, K.A.; Meredith, A. Measurement of Cyanobacterial Bloom Magnitude using Satellite Remote Sensing. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumpf, R.P.; Davis, T.W.; Wynne, T.T.; Graham, J.L.; Loftin, K.A.; Johengen, T.H.; Gossiaux, D.; Palladino, D.; Burtner, A. Challenges for mapping cyanotoxin patterns from remote sensing of cyanobacteria. Harmful Algae 2016, 54, 160–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
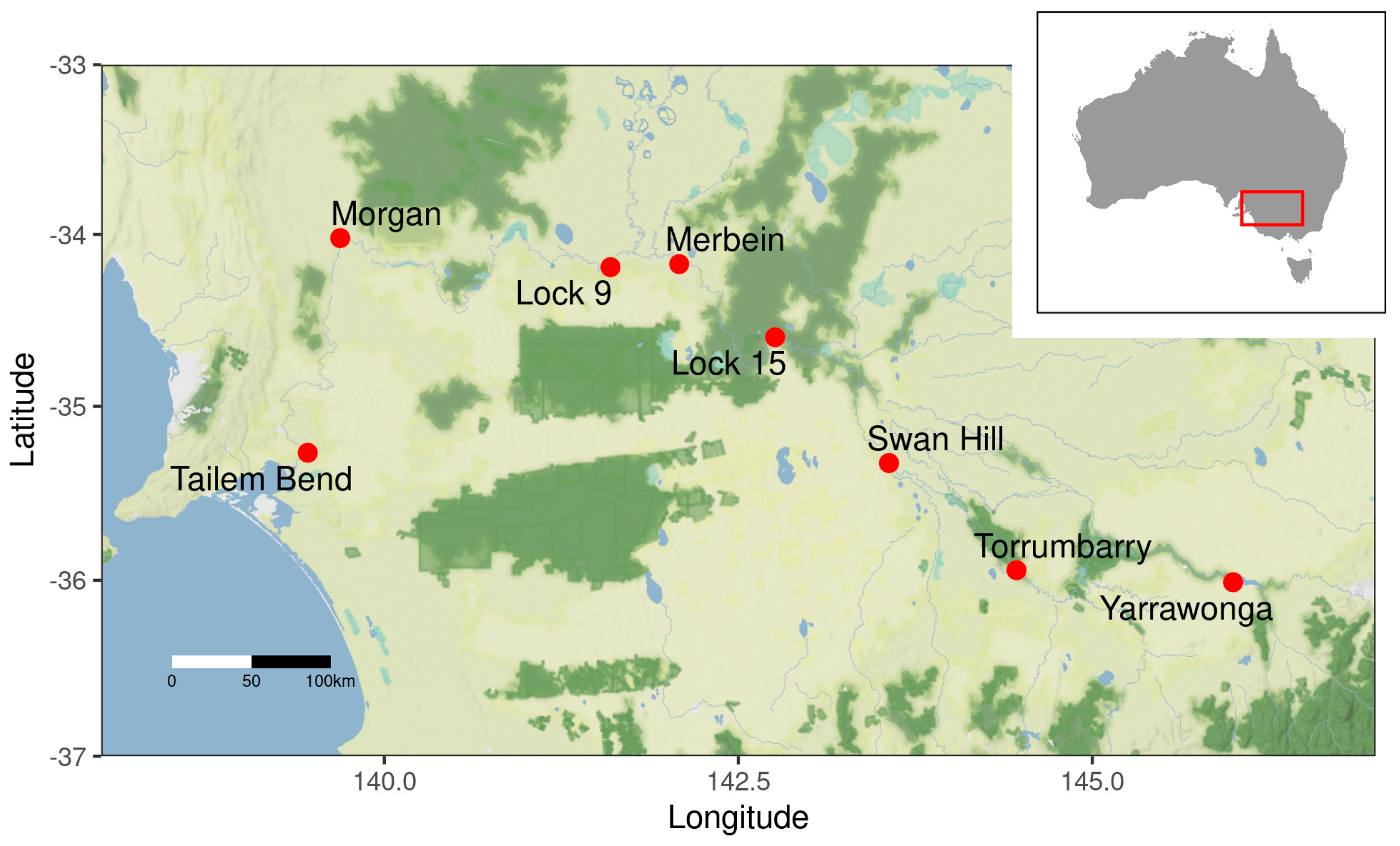
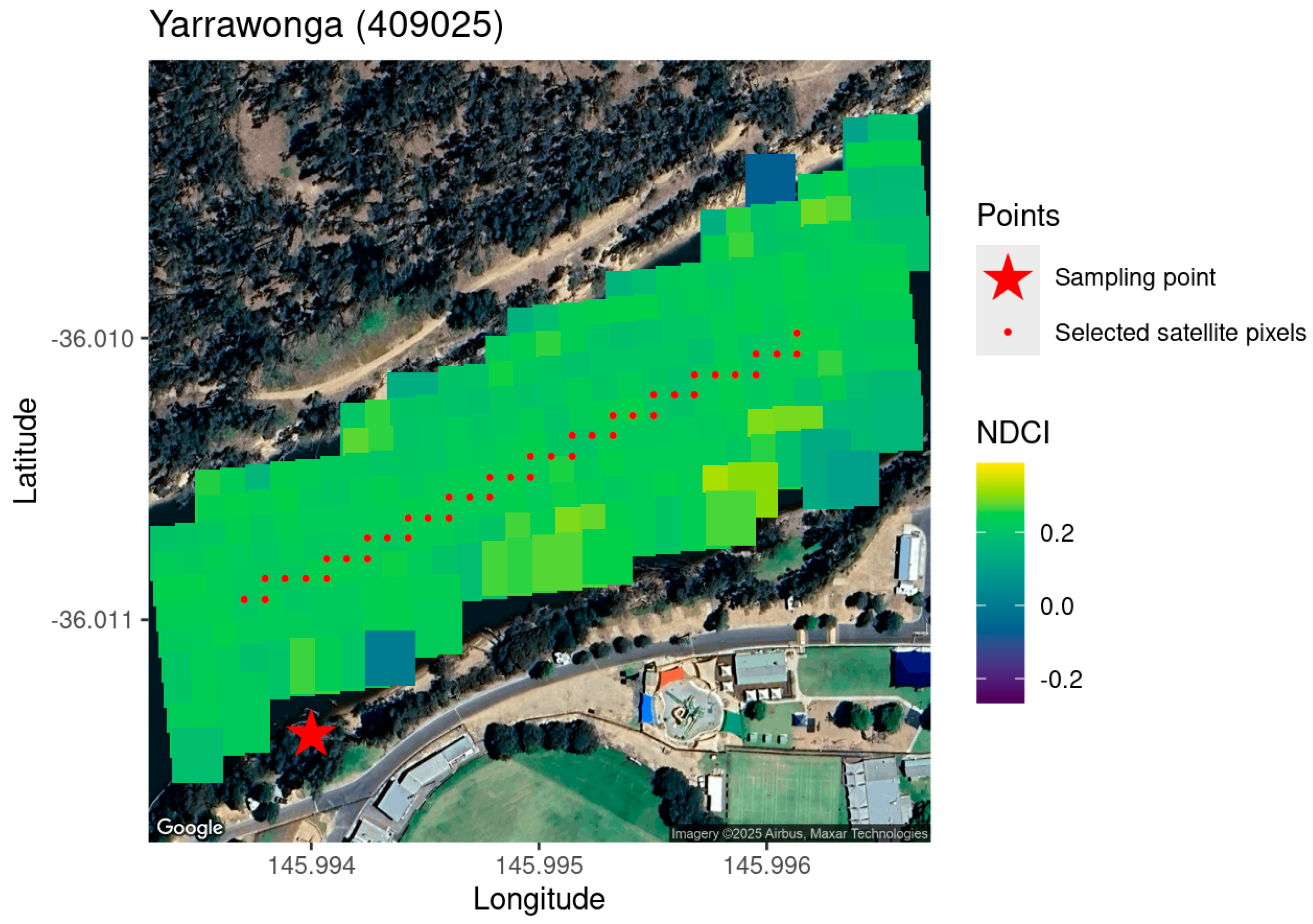
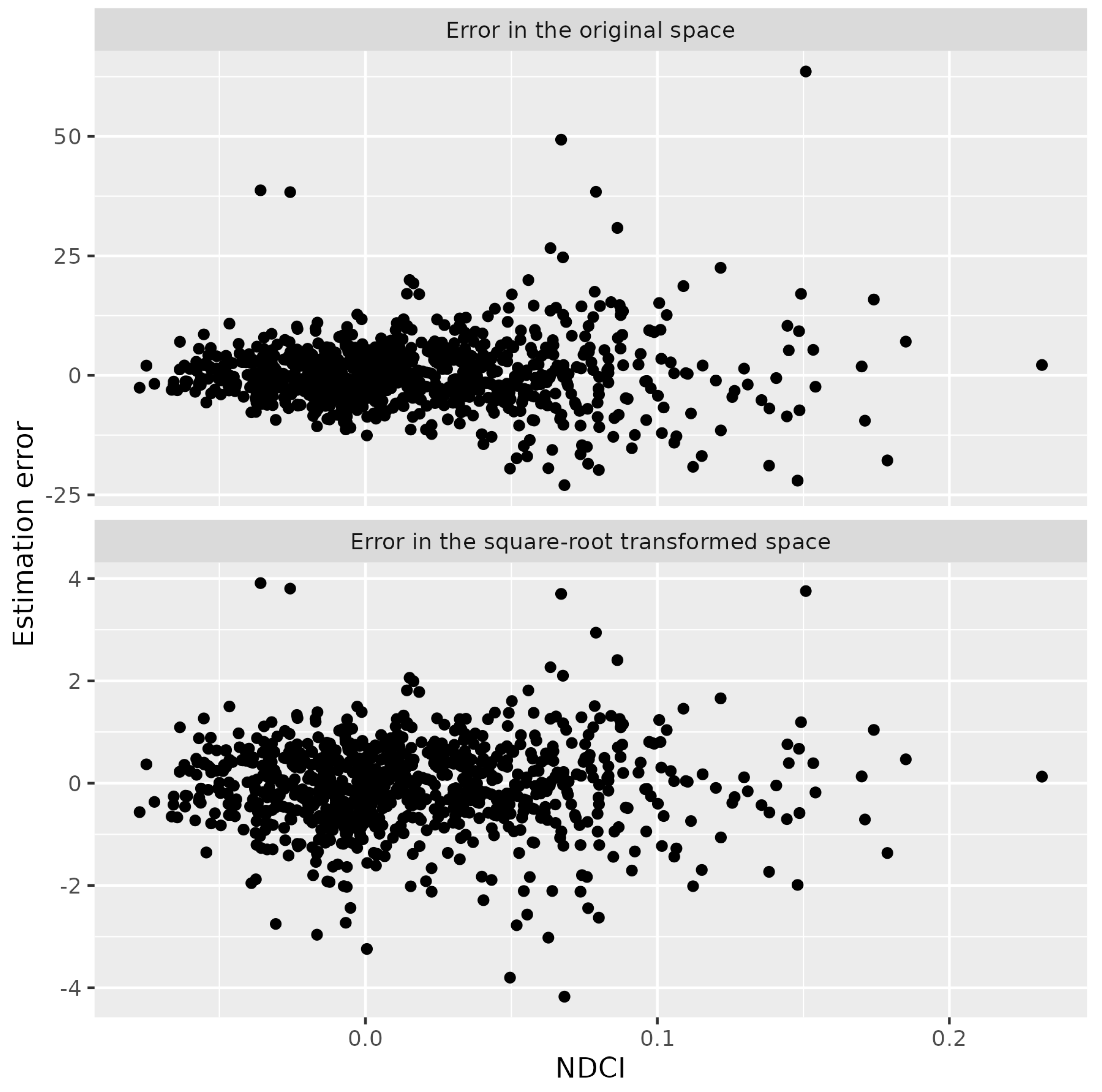


| ID | Name | Number of In Situ Measurements | Number of Sentinel 2A/B MSI Data | Number of Match-Up Pairs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 409025 | Yarrawonga | 224 | 460 | 140 |
| 409207B | Torrumbarry | 276 | 255 | 137 |
| 409204C | Swan Hill | 286 | 505 | 277 |
| 414209 | Lock 15 | 282 | 245 | 114 |
| 414206 | Merbein | 304 | 272 | 136 |
| A4260501 | Lock 9 | 343 | 546 | 287 |
| A4260554 | Morgan | 339 | 274 | 134 |
| A4260551 | Tailem Bend | 347 | 210 | 106 |
| Original | 14.039 | 86.11 | 194.325 | Not applicable |
| Refitted | 15.7 | 217.18 | 51.76 | 0.74 |
| R2 | RMSE | Bias | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calibration | Original | 0.45 | 7.95 | 20.38 | −0.26 | −16.92 |
| Refitted | 0.60 | 6.75 | 16.15 | −0.29 | −10.16 | |
| Validation | Original | 0.32 | 9.53 | 19.33 | −0.75 | −17.28 |
| Refitted | 0.52 | 8.01 | 14.12 | 0.50 | −10.50 |
| 90% | 95% | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Estimate | 89% | 93.1% | |
| Forecast | Lead time (weeks) | ||
| 1 | 86.2% | 90.6% | |
| 2 | 85% | 89.7% | |
| 3 | 87.2% | 92.2% | |
| 4 | 87.1% | 92.8% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, M.; Joehnk, K.; Toscas, P.; Garcia, L.R.; Jin, H.; Biswas, T.K. Forecasting Chlorophyll-a in the Murray–Darling Basin Using Remote Sensing. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1684. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17101684
Li M, Joehnk K, Toscas P, Garcia LR, Jin H, Biswas TK. Forecasting Chlorophyll-a in the Murray–Darling Basin Using Remote Sensing. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(10):1684. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17101684
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Ming, Klaus Joehnk, Peter Toscas, Luis Riera Garcia, Huidong Jin, and Tapas K. Biswas. 2025. "Forecasting Chlorophyll-a in the Murray–Darling Basin Using Remote Sensing" Remote Sensing 17, no. 10: 1684. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17101684
APA StyleLi, M., Joehnk, K., Toscas, P., Garcia, L. R., Jin, H., & Biswas, T. K. (2025). Forecasting Chlorophyll-a in the Murray–Darling Basin Using Remote Sensing. Remote Sensing, 17(10), 1684. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17101684






