Abstract
Soil analysis using near-infrared spectroscopy has shown great potential to be an alternative to traditional laboratory analysis, and there is continuously increasing interest in building large-scale soil spectral libraries (SSLs). However, due to issues such as high non-linearity in soil spectral data and complexity in soil spatial variation, the establishment of robust prediction models for soil spectral libraries remains a challenge. This study aimed to investigate the performance of deep learning algorithms, including long short-term memory (LSTM) and LSTM–convolutional neural networks (LSTM–CNN) integrated models, to predict the soil organic matter (SOM) of a provincial-scale SSL, and compare it to the normally used local weighted regression (LWR) model. The Hebei soil spectral library (HSSL) contains 425 topsoil samples (0–20 cm), of which every 3 soil samples were collected from dry land, irrigated land, and paddy fields, respectively, in different counties of Hebei Province, China. The results show that the accuracy of the validation dataset rank as follows: LSTM–CNN (R2p = 0.96, RMSEp = 1.66 g/kg) > LSTM (R2p = 0.83, RMSEp = 3.42 g/kg) > LWR (R2p = 0.82, RMSEp = 3.79 g/kg). The LSTM–CNN model performed the best, mainly due to its comprehensive ability to effectively extract spatial and temporal features. Meanwhile, the LSTM model achieved higher accuracy than the LWR model, owing to its built-in memory unit and its advantage of faster feature band extraction. Thus, it was suggested to use deep learning algorithms for SOM predictions in SSLs. However, their performance on larger-scale SSLs such as continental/global SSLs still needs to be further investigated.
1. Introduction
Soils are vital elements of the ecosystem, and have a crucial part to play in both human survival and environmental sustainability [1,2]. With the explosive growth of the world’s population and rapid urbanization, the human demand for soil to provide food, fiber, and other resources is increasing; thus, soil resources are being intensively used, leading to various security concerns such as soil degradation and salinization [3,4,5]. These problems lead to abnormal levels of organic matter in soils, which pose a threat to agro-ecological balances, food security, and furthermore impact achievement of the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) [6]. To ensure the safety of soil organic matter and guide the rational use of soil, the demand for rapid, dynamic soil monitoring is rapidly increasing [7]. In contrast to traditional laboratory analyses, which are not only costly but also environmentally burdensome, soil spectroscopy presents a less resource-intensive alternative. This technique enables the analysis of various soil property categories from a single sample, facilitating material savings and promoting sustainable soil management [8]. When collecting soil spectral data, implementing control methods can significantly reduce errors and enhance the quality of the collected spectra. These methods include (i) standardizing the size of soil particles to ensure consistency, (ii) repeating the spectrum collection process multiple times to verify data reliability, and (iii) utilizing machine learning algorithms to select representative soil samples. Together, these strategies contribute to the precision and accuracy of soil spectral analysis [9,10]. Previous studies have shown that the use of near-infrared spectroscopy (NIR, 780–2500 nm) can accurately characterize the component information of soils [11,12,13,14,15,16]. The overtones and combinations of fundamental vibrations are the basis of using NIR spectra for predicting soil properties. As energy quanta are directly related to frequency (and inversely related to wavelength), the resulting absorption spectrum has a characteristic shape that can be used for analytical purposes.
Soil spectral libraries (SSLs), established at various geographical scales, play a crucial role in monitoring soil properties. These libraries, ranging from global to continental, as well as national and regional scales, significantly ease the process of acquiring soil information. Their availability facilitates enhanced real-time and dynamic monitoring of soil safety [17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26]. However, due to the heterogeneity of soil types, climate, topography, and vegetation within each region, it is difficult to extrapolate from predictive models developed within a given region to other study areas. This is mainly due to the redundancy of soil sample datasets, resulting in increased complexity in soil spatial variation and non-linearity of soil properties and spectral data [15]. With the development of data mining techniques in recent years, there are many studies applying various linear and non-linear machine learning algorithms to optimize the prediction of soil spectral library attributes. Ramirez-Lopez et al. (2013) used the Global Soil Visible-Near-infrared Spectrum Library to test different distance measurement algorithms [27]. Shi et al. (2014) used soil samples from the Chinese National Spectral Library for soil spectral classification. They used the linear model PLSR algorithm to predict the soil organic matter (SOM), resulting in improved accuracy (R2 = 0.89; RPD = 3.15) [23]. Rossel et al. (2016) developed and analyzed a global library of visible near-infrared (vis-NIR) spectra for soils, and the conclusions of the experiment showed that using machine learning algorithms to model the different spectra allowed finding local relationships in the data to accurately predict soil properties [28]. Zhong et al. (2021) explored the modeling potential of deep convolutional neural networks (DCNNs) for soil properties based on a large SSL [29]. Wang et al. (2022) evaluated four spectral pre-processing models and seven machine learning methods using a continental-scale SSL for model evaluation, and found that the SOM models of mineral and organic soils should be distinguished on the basis of their distinct spectral signatures [30]. Especially in larger SSLs, such as global- and national-scale SSLs, most experiments have been applied to linear models and convolutional neural network models. There are few studies on short-term memory neural networks, and there is a lack of studies comparing soil predictions using neural network deep learning algorithms and local weighted regression algorithms. And there are also fewer studies on provincial-scale SSLs, which could better balance the relationship between the number of samples and data accuracy of large-scale SSLs [31,32,33,34,35,36,37].
To address the above scientific research questions, this study aimed to (i) investigate the performance of deep learning algorithms, including long short-term memory (LSTM) and long short-term memory–convolutional neural networks (LSTM–CNN) integrated models to predict the soil organic matter (SOM) of a provincial-scale SSL, and (ii) compared it to the normally used local weighted regression (LWR) model.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Hebei Soil Spectral Library
Hebei Province is located in northern China and covers a total area of 188,000 km2, with a gradual rise in terrain from the southeast to the northwest, and an average altitude of 1200 to 1500 m above sea level. The region has a temperate continental monsoon climate with an average annual temperature of 10–20 °C, and an average annual rainfall of 484.5 mm. According to the World Soil Classification System (WRB), the main soil types in Hebei province are anthrosol, cambisol, calcaric, and fluvisol soils [38].
Figure 1 shows the locations of the sampling points. The Hebei Soil Spectral Library (HSSL) contains 440 samples. The samples were collected from highlands and plains, and contain three different secondary land use classifications including paddy fields, dry land, and irrigated land. Using the method of uniform sampling, the soil types, landforms, and land use types at various sampling points were selected across each county, ensuring a representative mix. In this process, three soil samples were collected from each county. The soil samples were collected to a depth of 20 cm. Prior to laboratory analysis and spectroscopic measurements, all of the soil samples were air dried and ground, passed through a 2 mm diameter sieve, and split into two using the quadrat method, one part for soil property determination and the other part for soil spectral data collection. The SOM was determined with the H2SO4–K2Cr2O7 oxidation method at 180 °C Celsius for 5 min, and SOM data were recorded for 431 soil samples [39].
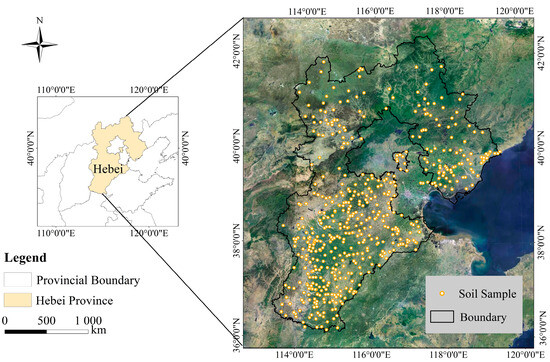
Figure 1.
The location of the study area and soil sampling sites.
2.2. Spectra Measurement
Soil NIR spectra were measured using a Bruker NIR spectrometer in a dark room. The spectral range was 12,800–4000 cm−1 (780 nm–2500 nm) with a resolution of 2 cm−1. To improve the signal-to-noise ratio and minimize interference, each soil sample underwent three random measurements. These measurements were averaged to yield a representative spectrum, thereby enhancing the accuracy and reliability of the soil analysis.
2.3. Spectral Pre-Processing
The spectral edge noise was first removed, leaving the 800–2500 nm region. Given that spectral outliers can impede subsequent data analysis, their influence on the model was minimized by calculating the Mahalanobis distance (MD) to identify and remove these outliers [40]. Figure 2 shows the use of the Mahalanobis distance to remove outliers; a total of 6 abnormal samples were removed.
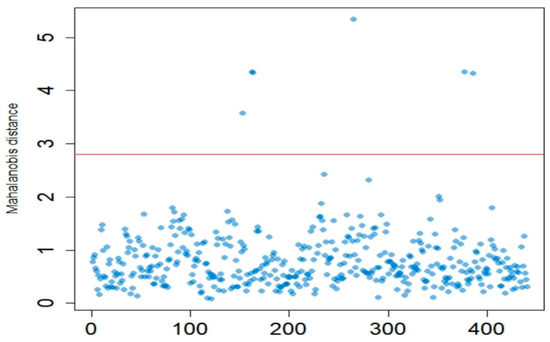
Figure 2.
Outliers removal based on Mahalanobis distance.
In addition, to amplify information and further reduce noise, the following methods were applied to spectral pretreatment: (i) Savitzky–Golay smoothing: A window of size 5 and a polynomial of order 2 were chosen for smoothing to achieve maximum noise removal [41]. (ii) First derivatives: First derivatives were used to achieve the effect of enhancing the detailed features of a spectrum and eliminating baseline drift and background noise interference [42].
After spectral pre-processing, the data were modeled to verify the performance of all models.
2.4. Predictive Algorithms
2.4.1. Locally Weighted Regression
The LWR model is a non-parametric regression method based on locally weighted regression, proposed by Cleveland and later developed by Næs et al. (1988, 1992) [43,44]. The model estimates the local nature of the data using a weighted least squares regression, which allows the data to be modeled on otherwise different subsets of the data. The sample points that are closer to the prediction point have a higher weight attached to them, thus better reflecting the similarity between the sample points. The idea in soil attribute prediction is to find the closest sample to the predicted sample in the spectral library, and to fit a local linear regression equation with that sample.
To obtain the best model performance, cross-validation was used for parameter selection. The root mean square error (RMSE) of the model was calculated using 5-fold cross-validation, with different numbers of K and PLS components as an evaluation metric. Finally, the corresponding K and PLS component numbers that minimized the RMSE were selected as the optimal parameters. In this way, the optimal parameters for modeling were obtained to achieve the best prediction results.
2.4.2. Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) Model
LSTM is a deep learning model for sequential data analysis, and is considered to be an extension of recurrent neural networks (RNN), proposed by Sepp Hochreiter and Jürgen Schmidhuber in 1997 [45]. LSTM can effectively solve the problem of gradient disappearance and gradient explosion during reverse transfer in ordinary convolutional neural networks [46].
This study used an LSTM model for SOM prediction. The model consists of an input layer, a hidden layer, and an output layer whose model memory is dependent on one or more memory units of the hidden layer. A memory cell (Figure 3) can be regarded as a neuron with the ability to remember; each cell contains an internal state and an external state , representing the long-term and short-term memory of the cell, respectively; the memory cell state indicates that the model retains information accumulated from previous time steps; the hidden state indicates the output at the current time step.
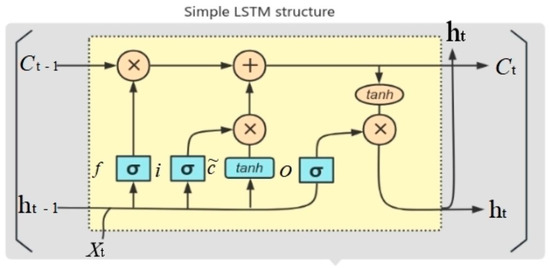
Figure 3.
Architecture of a typical LSTM model. , , and denote forgetting gates, input gates, and output gates, respectively; denotes input at time step ; , denotes output; and denote cell states.
The memory cell can decide which information to retain at the previous time step () and what information to output at the current time step (), which is controlled mainly by three gates: the forgetting gate (), the input gate (), and the output gate (). The forgetting gate () (Equation (1)) determines which information should be discarded from the memory cell before entering the current cell state (); the input gate () (Equation (2)) controls which information from the memory cell state is updated during the current time step, which is calculated by a weighted average of the input data and the previous cell state (Equations (3) and (4)); finally, the output gate () (Equation (5)) determines how much information in the memory cell should be output from the hidden state at the current moment (); the final hidden state () (Equation (6)) is the result of the information in the memory cell being weighted by the output gate.
In the SOM prediction process, the time step can be interpreted as the step length of the spectral band, rather than the time interval in the traditional time series. Specifically, each spectral band is treated as a distinct time step within the series.
To enable the model to predict the target value more accurately, the Adam was selected as the optimizer to update the model parameters within the model [47]. This is an adaptive learning rate optimization algorithm that adaptively adjusts the learning rate according to the gradient of each parameter, and has a faster convergence rate compared to the traditional stochastic gradient descent (SGD); moreover, it enables better model generalization. In addition to the optimizer, the mean square error (MSE) was chosen as the loss function to measure the error of the model, allowing calculation of the mean quadratic deviation between the predicted and true values of the model. By minimizing the MSE loss function, the model can be made to become a more accurate predictor of target values. Finally, the rectified linear unit (RELU) was used in the models as an activation function to improve the non-linear properties of the model [48]. The non-linear transformation helps the model learn the spectral multicollinearity, thus solving the spectral multicollinearity existing between the soil samples and the spectral data, and adding a dropout layer to prevent the model from overfitting [49]. For model hyperparameter selection, according to the theory of Dominic Masters and Carlo Luschi et al. (2018) [50], a batch size of 2–32 can provide more up-to-date gradient calculations, which can lead to more stable and reliable training and enable the model to obtain the best performance.
2.4.3. LSTM–CNN Integration Model
Figure 4 displays the LSTM–CNN integration model that was created. The basic concept is to use the CNN model to extract the background features of the embedded space, and the LSTM model to extract the temporal features of the variables. After analyzing a soil spectrum, the relevant bands are immediately extracted, the extracted spatial and temporal features are linked, and the output is then computed using the fully connected layer (e.g., the expected SOM).
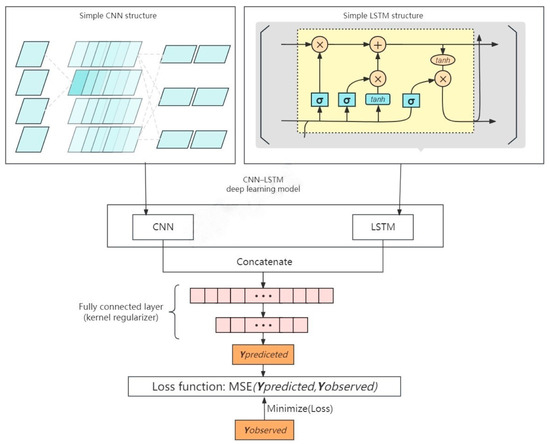
Figure 4.
Flowchart of LSTM–CNN model iteration.
This integrated model encompasses complex iterative calibration steps, wherein the parameters and methodologies deployed by LSTM are akin to those described in Section 2.4.2 of this study. The CNN captures spatial features of the data using convolution and pooling layers. Convolution layers can detect local patterns in the data, while pooling layers can reduce the dimensionality of the data and preserve important features. Within this integration model, the outputs from the LSTM and CNN are merged via concatenation operations, ensuring the preservation of both the temporal dependencies identified by the LSTM and the spatial features ascertained by the CNN.
The LSTM–CNN model was built in Python 3.7 using Keras with Tensorflow as the backend. The other two models were also built using Python.
2.5. Model Evaluation
In this study, the data set was divided into two parts: the training set and the validation set. The soil samples were ranked from lowest to highest in terms of SOM content, with the training and validation sets representing 80% and 20% of the total data set, respectively. In the model evaluation, the coefficient of determination (R2) and the root mean square error (RMSE) were used as the main indicators for evaluation, where the better the performance of the model, the higher the R2 and the lower the RMSE.
where is the total number of samples, and are the average predicted and measured values, respectively; and are the predicted and measured values, respectively.
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Statistical Results
Table 1 shows the SOM statistics recorded in the HSSL. The soil samples in the HSSL have a wide range of SOM, distributed between 2.76 and 58.30 g/kg, with an average of 16.69 g/kg, showing strong heterogeneity with a coefficient of variation (CV) of 51.34%. The skewness is 2.03.

Table 1.
Soil property statistics for the HSSL.
Figure 5 displays the absorbance spectra of soil samples with different levels of organic matter content in the HSSL. From the representative samples selected on the graph, it can be clearly observed that the value of the absorbance curve is higher for samples with a high SOM; when the SOM is low, the absorbance is lower. The results indicate a positive correlation between absorbance and SOM, with absorbance increasing as the SOM increases. Clear water absorption bands were observed at around 1400 and 1900 nm; these bands are formed due to the hydroxyl groups in clay minerals present in the soil.
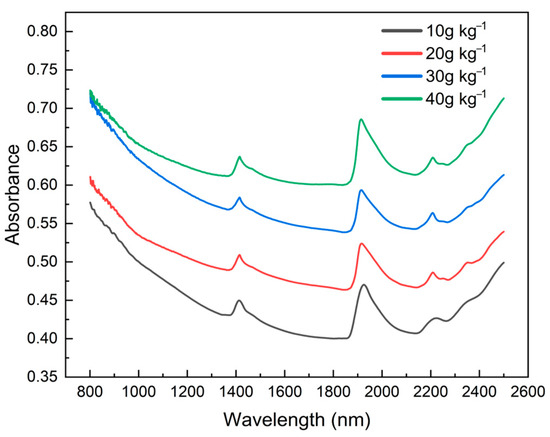
Figure 5.
Soil spectra with different SOM content levels in the Hebei soil spectral library.
3.2. Models for SOM Content Prediction of HSSL
The LWR model determined the optimal parameters through cross validation. Figure 6 shows the scatter plot of the model prediction results for the HSSL (validation R2p = 0.82, RMSEp = 3.79 g/kg).
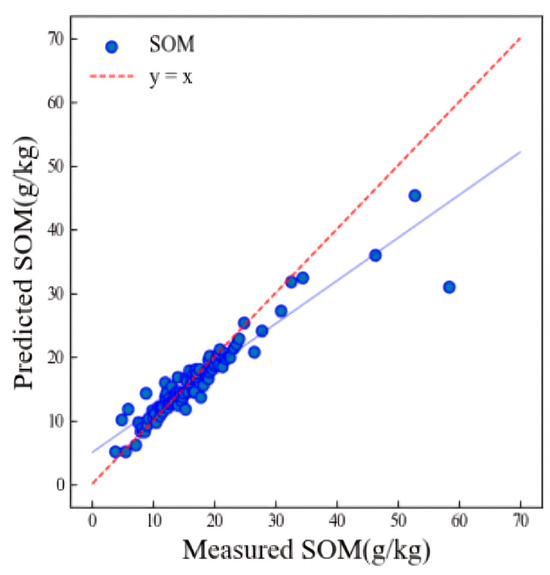
Figure 6.
Scatter plot of SOM prediction results of the validation set using the LWR algorithm.
Figure 7 shows the scatter plot of the LSTM model used to predict SOM in the HSSL. The model used a batch size of 8, two LSTM layers, and a dropout rate of 0.1. This configuration facilitated better training and convergence of the model, allowing the inversion of soil physical and chemical properties. The results indicate that the R2 values for both the training and validation sets are greater than 0.8. The training set has an R2 value of 0.86, while the validation set has an R2 value of 0.83 (as shown in Figure 7). Furthermore, the validation set has an RMSE of 3.42 g/kg.
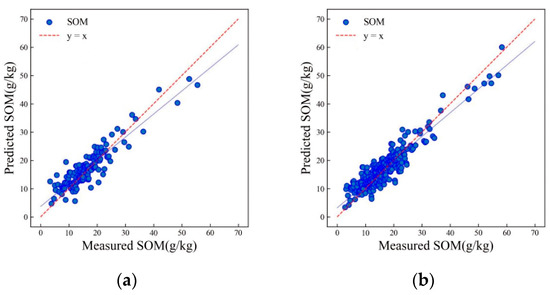
Figure 7.
Scatter plots of SOM prediction results of the validation (a) and training (b) sets using the LSTM algorithm.
The importance index of each band in the range of 800–2500 nm was extracted using the updated LSTM model selected by memory cells (Figure 8). After ranking, it was found that the most obvious responses to SOM were in the 800–900 nm, 1800–1900 nm, and 2200–2400 nm bands [14,51,52].
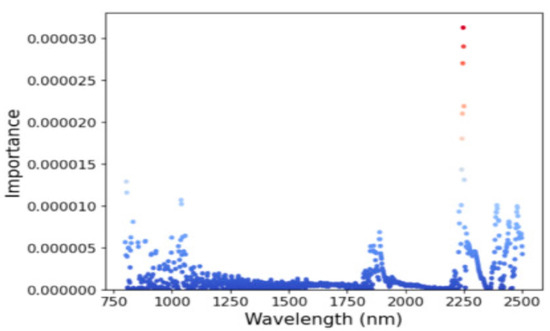
Figure 8.
Important features of the soil spectrum extracted by the LSTM model.
Figure 9 shows the prediction results of the LSTM–CNN integrated model for SOM in the HSSL. The training results were significantly improved compared to the previous two models, with both the training and validation sets achieving accuracies of over 0.95. The R2 of the training set is 0.99, and the R2 of the validation set is 0.96. In addition, the RMSE of the training set is 0.47 g/kg, and the RMSE of the validation set is 1.66 g/kg. The integrated model produced more accurate results than other deep learning and machine learning models used by Wang et al. (2022) [27]. Additionally, the LSTM–CNN model outperformed other models in similar soil spectral libraries studies [17,36].
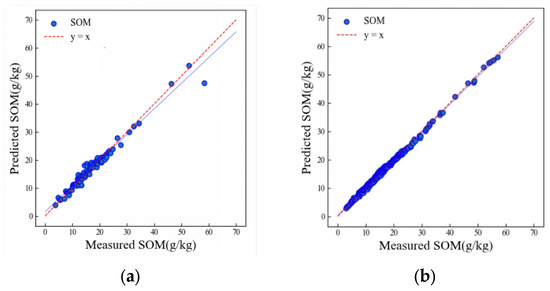
Figure 9.
Scatter plots of SOM prediction results of the validation (a) and training (b) sets using the LSTM–CNN algorithm.
Table 2 shows the accuracy of the three models. The R2p order among the three models is LSTM–CNN > LSTM > LWR, and the RMSEp order is LWR > LSTM > LSTM–CNN. From these two indexes, it can be seen that the convolutional neural network model is superior to the locally weighted regression model overall, and the LSTM–CNN integrated model has the best effect among the three models. In comparison, the LSTM–CNN integrated model demonstrates enhanced generalizability, evidenced by its superior predictive performance on soil samples with high coefficients of variation in the spectral data from Hebei province. This model can be better applied in provincial-scale spectral libraries.

Table 2.
Table of SOM accuracy for the three prediction models.
4. Discussion
4.1. The Application Ability of Provincial-Scale Soil Spectral Library
This study used 425 representative soil samples in the HSSL, covering 13 counties in Hebei Province. The performances of the three models—LSTM–CNN, LSTM, and LWR—were evaluated, demonstrating their efficacy in predicting soil organic matter (SOM). All of the models achieved validation R2 values above 0.8. Specifically, the LSTM–CNN model yielded the highest accuracy (R2p = 0.96, RMSE = 1.66 g/kg), followed by the LSTM (R2p = 0.83, RMSE = 3.42 g/kg), and LWR (R2p = 0.82, RMSE = 3.79 g/kg) models. These results underscore the potential of spectral databases for rapid, non-destructive soil analysis within the study area, paving the way for real-time dynamic soil property monitoring across Hebei Province. This study also highlights the balance between sample quantity and data accuracy afforded by a spectral database of this scale, contributing valuable insights into soil characteristics within the region.
Based on the results of this study, it was found that the SOM from the HSSL can be successfully predicted using a deep learning model or machine learning model, which is in line with previous research [53,54]. The prediction of SOM in the NIR region is a frequently evaluated metric, mainly because the overtone and combination bands of organic molecules occur in this band. The bands around 1100 nm, 1600 nm, 1700 nm~1800 nm, 2000 nm, and 2200 nm~2400 nm are recognized as the most important bands for SOM prediction, which correspond to the feature bands extracted by the LSTM model in this study, which can confirm the good predictive ability of the LSTM model for soil spectra.
The accuracy of all three algorithms surpassing 0.8 demonstrates the successful application of a provincial-scale spectral library, enabling the comprehensive and dynamic monitoring of soil information throughout the province. This approach effectively addresses the limitations of field-scale spectral libraries and laboratory-based soil property analysis, offering enhanced detail and representativeness of soil information at a larger scale.
4.2. The Potential of Deep Learning Models for Soil Spectral Property Prediction
Among the evaluated models, the LSTM–CNN model demonstrated superior fitting capabilities, particularly in managing the connections between complex variables. This model leverages a unique memory unit to understand long-term dependencies within sequences, enabling effective screening and modification of sequence issues by integrating both long-term and short-term memory. Compared to traditional linear models, the LSTM–CNN model exhibits enhanced stability in extracting features from complex soil spectral data, thereby simplifying the extraction of feature bands [55,56].
Furthermore, the spectral library’s larger area range often presents nonlinear relationships due to spectral multicollinearity and data redundancy. This study incorporated the ReLu algorithm into both the LSTM and LSTM–CNN models, facilitating a non-linear transformation that addresses the challenge of high non-linearity in spectral data analysis.
As a result of its great ability to fully extract spatial and temporal characteristics, the LSTM–CNN model is better able to complete relevant soil prediction over a wide variety of soil spectral libraries. The LSTM–CNN model created in this research is a promising technology for soil prediction, as few similar studies in the past have used it to perform SOM prediction in provincial-scale soil spectral libraries.
This model’s hyperparameters were tuned in this study. However, additional research is required to explore the optimal hyperparameter selection algorithm for both the LSTM and LSTM–CNN models. This will improve the models’ performance and broaden their application in predicting soil spectral properties. Further research could enhance our understanding of the performance of these models and better support their application in predicting soil spectral properties.
5. Conclusions
In previous studies related to large-scale SSLs, the majority of methods used in predicting SOM were based on traditional machine learning algorithms such as support vector regression and random forest, as well as local methods such as LWR. However, the modeling capability of these models for regional spectral libraries still requires improvement [23,57,58]. The use of deep learning algorithms has shown great potential, and thus needs to be further investigated.
A provincial-scale spectral library was utilized in this study, and the results show that both the LSTM (R2p = 0.83, RMSEp = 3.42 g/kg) and LSTM–CNN (R2p = 0.96, RMSEp = 1.66 g/kg) algorithms obtained higher accuracy when predicting SOM content than the LWR model (R2p = 0.82, RMSEp = 3.79 g/kg). Upon sorting the importance of bands, it was discovered that the response bands for soil organic matter are primarily located at the 800–900 nm, 1800–1900 nm, and 2200–2400 nm bands. Compared with traditional statistical models, LSTM–CNN has stronger time-series modeling capabilities, and can better capture correlations between SOM content and spectra, thus improving the prediction accuracy.
By applying deep learning algorithms such as LSTM and LSTM–CNN on a provincial-scale spectral library, it is possible to perform rapid, non-invasive, real-time monitoring of soil properties within the study area. However, their performance on larger-scale SSLs such as continental/global SSLs still needs to be further investigated. This study holds significance in refining the method for SOM prediction, while also presenting a novel approach to the use of deep learning in soil science. This advances the precision of basic soil property prediction, and facilitates efficient agricultural land utilization.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.J.; methodology, T.M. and W.J.; software, T.M., J.Y. (Jianxin Yin) and Y.C.; validation, T.M. and J.Y. (Jianxin Yin); formal analysis, T.M. and W.J.; investigation, D.Y. and T.M.; resources, W.J.; data curation, T.M. and J.Y. (Jiajie Yang); writing—original draft preparation, T.M.; writing—review and editing, W.J., B.L., X.Z., Y.H. and X.K.; visualization, T.M. and J.Y. (Jianxin Yin); supervision, W.J. and B.L.; project administration, W.J.; funding acquisition, W.J. and X.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research is an output of Cropland Degradation Monitoring; Supported by Open Fund of State Key Laboratory of Remote Sensing Science (Grant No. OFSLRSS202121); the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42001048); Key Project of “Rejuvenating Mongolia with Science and Technology” (NMKJXM202303); and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42171289).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon reasonable request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Winfried, E.H.B. Functions of soil for society and the environment. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2005, 4, 75–79. [Google Scholar]
- Amundson, R.; Berhe, A.A.; Hopmans, J.W.; Olson, C.; Sztein, A.E.; Sparks, D.L. Soil and human security in the 21st century. Science 2015, 348, 1261071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jie, C.; Jing-Zhang, C.; Man-Zhi, T.; Zi-Tong, G. Soil degradation: A global problem endangering sustainable development. J. Geogr. Sci. 2002, 12, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, P. Soil Erosion: A Food and Environmental Threat. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2006, 8, 119–137. [Google Scholar]
- Evangelista, S.J.; Field, D.J.; McBratney, A.B.; Minasny, B.; Ng, W.; Padarian, J.; Dobarco, M.R.; Wadoux, A.M. A proposal for the assessment of soil security: Soil functions, soil services and threats to soil. Soil Secur. 2023, 10, 100086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. The Sustainable Development Goals Report. 2022. Available online: https://unstats.un.org/sdgs/report/2022/ (accessed on 10 September 2022).
- Sanchez, P.A.; Ahamed, S.; Carré, F.; Hartemink, A.E.; Hempel, J.; Huising, J.; Lagacherie, P.; McBratney, A.B.; McKenzie, N.G.; Mendonça-Santos, M.D.; et al. Digital Soil Map of the World. Science 2009, 325, 680–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenberg, B.; Rossel, R.A.; Mouazen, A.M.; Wetterlind, J. Visible and Near Infrared Spectroscopy in Soil Science. Adv. Agron. 2010, 107, 163–215. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Chen, S.; Lu, P.; Wang, Z.; Li, A.; Zeng, Q.; Chen, L. Optimizing a Standard Spectral Measurement Protocol to Enhance the Quality of Soil Spectra: Exploration of Key Variables in Lab-Based VNIR-SWIR Spectral Measurement. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poppiel, R.R.; da Silveira Paiva, A.F.; Demattê, J.A.M. Bridging the gap between soil spectroscopy and traditional laboratory: Insights for routine implementation. Geoderma 2022, 425, 116029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Ji, W.; Viscarra Rossel, R.A.; Chen, S.; Zhou, Y. Prediction of soil organic matter using a spatially constrained local partial least squares regression and the Chinese vis–NIR spectral library. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2015, 66, 679–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.; Viscarra Rossel, R.A.; Shi, Z. Improved estimates of organic carbon using proximally sensed vis-NIR spectra corrected by piecewise direct standardization. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2015, 66, 670–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocita, M.; Stevens, A.; Noon, C.; Wesemael, B.V. Prediction of soil organic carbon for different levels of soil moisture using Vis-NIR spectroscopy. Geoderma 2013, 199, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, A.; Nocita, M.; Tóth, G.; Montanarella, L.; van Wesemael, B. Prediction of Soil Organic Carbon at the European Scale by Visible and Near InfraRed Reflectance Spectroscopy. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nocita, M.; Stevens, A.; Tóth, G.; Panagos, P.; Wesemael, B.V.; Montanarella, L. Prediction of soil organic carbon content by diffuse reflectance spectroscopy using a local partial least square regression approach. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 68, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawar, S.; Mouazen, A.M. On-line vis-NIR spectroscopy prediction of soil organic carbon using machine learning. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 190, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, W.D.; Demattê, J.A.; Rosin, N.A.; Terra, F.D.; Poppiel, R.R.; Urbina-Salazar, D.; Boechat, C.L.; Silva, E.B.; Curi, N.; Silva, S.H.; et al. The Brazilian soil Mid-infrared Spectral Library: The Power of the Fundamental Range. Geoderma 2022, 415, 115776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura-Bueno, J.M.; Dalmolin, R.S.; ten Caten, A.; Dotto, A.C.; Demattê, J.A. Stratification of a local VIS-NIR-SWIR spectral library by homogeneity criteria yields more accurate soil organic carbon predictions. Geoderma 2019, 337, 565–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijewardane, N.K.; Ge, Y.; Wills, S.; Libohova, Z. Predicting Physical and Chemical Properties of US Soils with a Mid-Infrared Reflectance Spectral Library. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2018, 82, 722–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clairotte, M.; Grinand, C.; Kouakoua, E.; Thébault, A.; Saby, N.P.; Bernoux, M.; Barthès, B.G. National calibration of soil organic carbon concentration using diffuse infrared reflectance spectroscopy. Geoderma 2016, 276, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xue, J.; Xiao, Y.; Shi, Z.; Chen, S. Towards Optimal Variable Selection Methods for Soil Property Prediction Using a Regional Soil Vis-NIR Spectral Library. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, S.R.; Wetterlind, J.; Demattê, J.A.; Stenberg, B. Improving the prediction performance of a large tropical vis-NIR spectroscopic soil library from Brazil by clustering into smaller subsets or use of data mining calibration techniques. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2014, 65, 718–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Wang, Q.; Peng, J.; Ji, W.; Liu, H.; Li, X.; Viscarra Rossel, R.A. Development of a national VNIR soil-spectral library for soil classification and prediction of organic matter concentrations. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2014, 57, 1671–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodský, L.; Klement, A.; Penížek, V.; Kodešová, R.; Borůvka, L. Building soil spectral library of the Czech soils for quantitative digital soil mapping. Soil Water Res. 2011, 6, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.J.; Bricklemyer, R.S.; Miller, P.R. Validation requirements for diffuse reflectance soil characterization models with a case study of VNIR soil C prediction in Montana. Geoderma 2005, 129, 251–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francos, N.; Chabrillat, S.; Tziolas, N.V.; Milewski, R.; Brell, M.; Samarinas, N.; Angelopoulou, T.; Tsakiridis, N.L.; Liakopoulos, V.; Ruhtz, T.; et al. Estimation of water-infiltration rate in Mediterranean sandy soils using airborne hyperspectral sensors. Catena 2023, 233, 107476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Lopez, L.; Behrens, T.; Schmidt, K.; Rossel, R.A.; Demattê, J.A.; Scholten, T. Distance and similarity-search metrics for use with soil vis—NIR spectra. Geoderma 2013, 199, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossel, R.A.; Behrens, T.; Ben-Dor, E.; Brown, D.J.; Demattê, J.A.; Shepherd, K.D.; Shi, Z.; Stenberg, B.; Stevens, A.; Adamchuk, V.I.; et al. A global spectral library to characterize the world’s soil. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2016, 155, 198–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Guo, X.; Xu, Z.; Ding, M. Soil properties: Their prediction and feature extraction from the LUCAS spectral library using deep convolutional neural networks. Geoderma Int. J. Soil Sci. 2021, 402, 115366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Guan, K.; Zhang, C.; Lee, D.; Margenot, A.J.; Ge, Y.; Peng, J.; Zhou, W.; Zhou, Q.; Huang, Y. Using soil library hyperspectral reflectance and machine learning to predict soil organic carbon: Assessing potential of airborne and spaceborne optical soil sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 271, 112914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Yang, A.; Wang, J.; Sagan, V.; Yu, D. Machine-learning-based quantitative estimation of soil organic carbon content by VIS/NIR spectroscopy. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morellos, A.; Pantazi, X.E.; Moshou, D.; Alexandridis, T.K.; Whetton, R.L.; Tziotzios, G.; Wiebensohn, J.; Bill, R.; Mouazen, A.M. Machine learning based prediction of soil total nitrogen, organic carbon and moisture content by using VIS-NIR spectroscopy. Biosyst. Eng. 2016, 152, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.; Li, S.; Chen, S.; Shi, Z.; Rossel, R.A.; Mouazen, A.M. Prediction of soil attributes using the Chinese soil spectral library and standardized spectra recorded at field conditions. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 155, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, W.; Minasny, B.; Montazerolghaem, M.; Padarian, J.; Ferguson, R.; Bailey, S.; McBratney, A.B. Convolutional neural network for simultaneous prediction of several soil properties using visible/near-infrared, mid-infrared, and their combined spectra. Geoderma 2019, 352, 251–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, B.; Greenberg, I.; Vohland, M.; Michel, K. Optimised use of data fusion and memory-based learning with an Austrian soil library for predictions with infrared data. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2023, 74, e13394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Xie, M.; Hu, B.; Zhou, Y.; Li, H.; Zhao, W.; Deng, W.; Shi, Z. Prediction of Soil Organic Carbon Contents in Tibet Using a Visible Near-Infrared Spectral Library. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2023, 56, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Chen, S.; Xu, D.; Hong, Y.; Li, S.; Peng, J.; Ji, W.; Guo, X.; Zhao, X.; Shi, Z. Strategies for predicting soil organic matter in the field using the Chinese Vis-NIR soil spectral library. Geoderma 2023, 433, 116461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattan, L. Encyclopedia of Soil Science; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, S. Soil Agrochemical Analysis; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Haaland, D.M.; Thomas, E.V. Partial least-squares methods for spectral analyses. 1. Relation to other quantitative calibration methods and the extraction of qualitative information. Anal. Chem. 2002, 60, 1193–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinier, J.; Termonia, Y.; Deltour, J. Smoothing and differentiation of data by simplified least square procedure. Anal. Chem. 1972, 44, 1906–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, P.; Alexander, J.D.; Butler, B.J.; Hummel, J.W. Reflectance Technique for Predicting Soil Organic Matter 1. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1980, 44, 1282–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, W.S.; Devlin, S.J. Locally Weighted Regression: An Approach to Regression Analysis by Local Fitting. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1988, 83, 596–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Næs, T.; Isaksson, T. Locally Weighted Regression in Diffuse Near-Infrared Transmittance Spectroscopy. Appl. Spectrosc. 1992, 46, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural. Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Houdt, G.; Mosquera, C.; Nápoles, G. A review on the long short-term memory model. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2020, 53, 5929–5955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diederik, P.K.; Jimmy, B. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. In Proceedings of the ICLR 2015, San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015. CoRR, abs/1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Agarap, A.F. Deep Learning using Rectified Linear Units (ReLU). arXiv 2018, arXiv:1803.08375. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, L.; Guo, M.; Li, A.; Zhou, C. A deep learning method to predict soil organic carbon content at a regional scale using satellite-based phenology variables. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 102, 102428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masters, D.; Luschi, C. Revisiting Small Batch Training for Deep Neural Networks. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.07612. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, W.; Liu, S.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y. Estimation of soil organic matter content using selected spectral subset of hyperspectral data. Geoderma 2022, 409, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.B.; Li, D.C.; Shi, X.R. A Preliminary Study on Identification of Clay Minerals in Soils with Reference to Reflectance Spectra. Pedosphere 1995, 5, 135–142. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Zhao, X.; Guo, X.; Guo, J. Deep Learning Application for Predicting Soil Organic Matter Content by VIS-NIR Spectroscopy. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2019, 2019, 3563761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Xu, D.; Chen, S.; Li, H.; Shi, Z. Evaluation of Machine Learning Approaches to Predict Soil Organic Matter and pH Using vis-NIR Spectra. Sensors 2019, 19, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Cai, Y.; Huang, H.; Li, A.; Yang, L.; Zhou, C. A CNN-LSTM Model for Soil Organic Carbon Content Prediction with Long Time Series of MODIS-Based Phenological Variables. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Wu, S.; Liu, J.; Wang, C.; Guo, Z.; Xu, A.; Pan, K.; Pan, X. Predicting soil moisture content over partially vegetation covered surfaces from hyperspectral data with deep learning. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2021, 85, 989–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Lopez, L.; Behrens, T.; Schmidt, K.; Stevens, A.; Demattê, J.A.; Scholten, T. The spectrum-based learner: A new local approach for modeling soil vis–NIR spectra of complex datasets. Geoderma 2013, 195–196, 268–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, K.D.; Walsh, M.G. Development of Reflectance Spectral Libraries for Characterization of Soil Properties. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2002, 66, 988–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).