Long-Term Spatial Pattern Predictors (Historically Low Rainfall, Benthic Topography, and Hurricanes) of Seagrass Cover Change (1984 to 2021) in a Jamaican Marine Protected Area
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Satellite Imagery
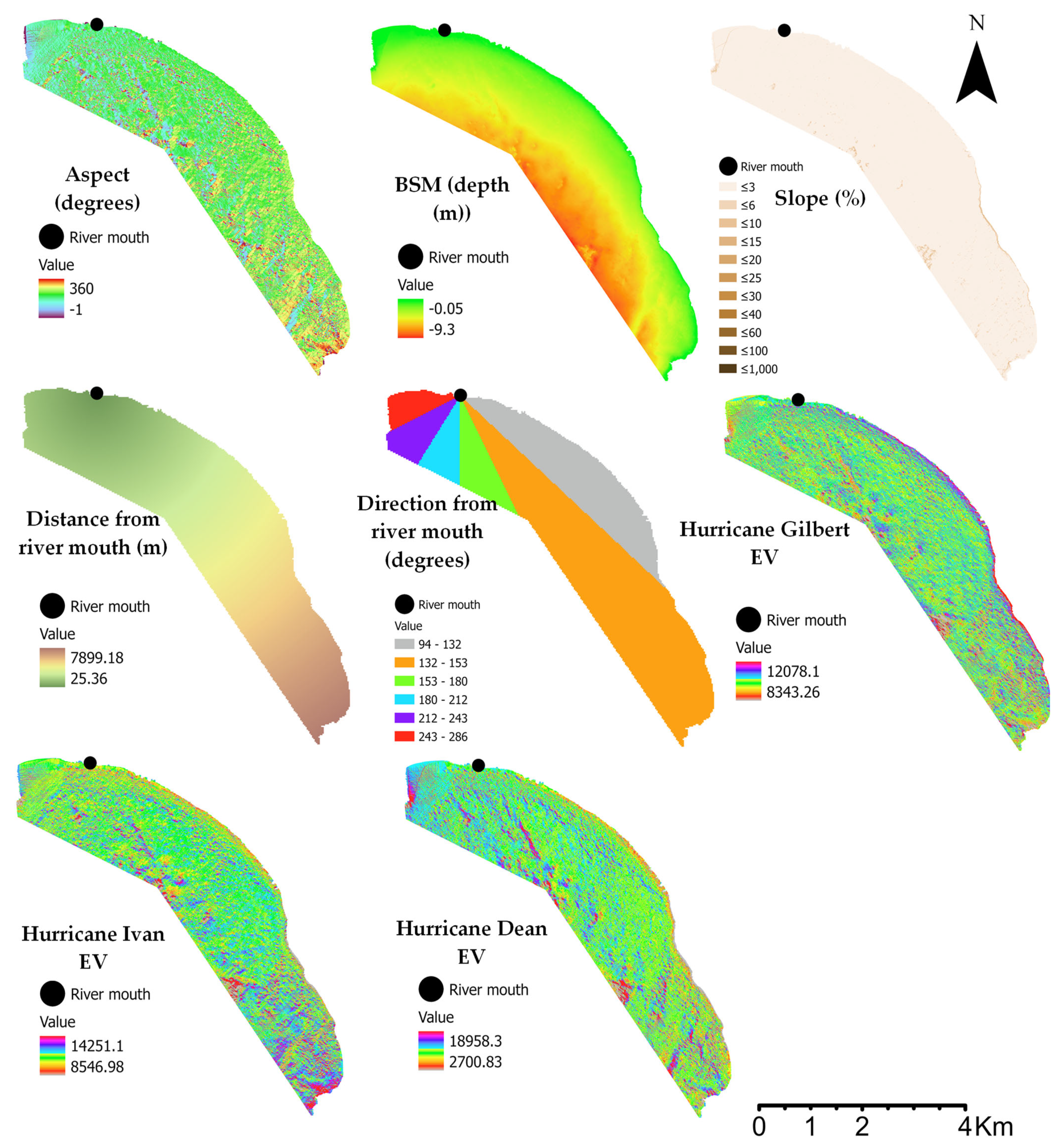
2.3. Hydroacoustic Auxiliary Data
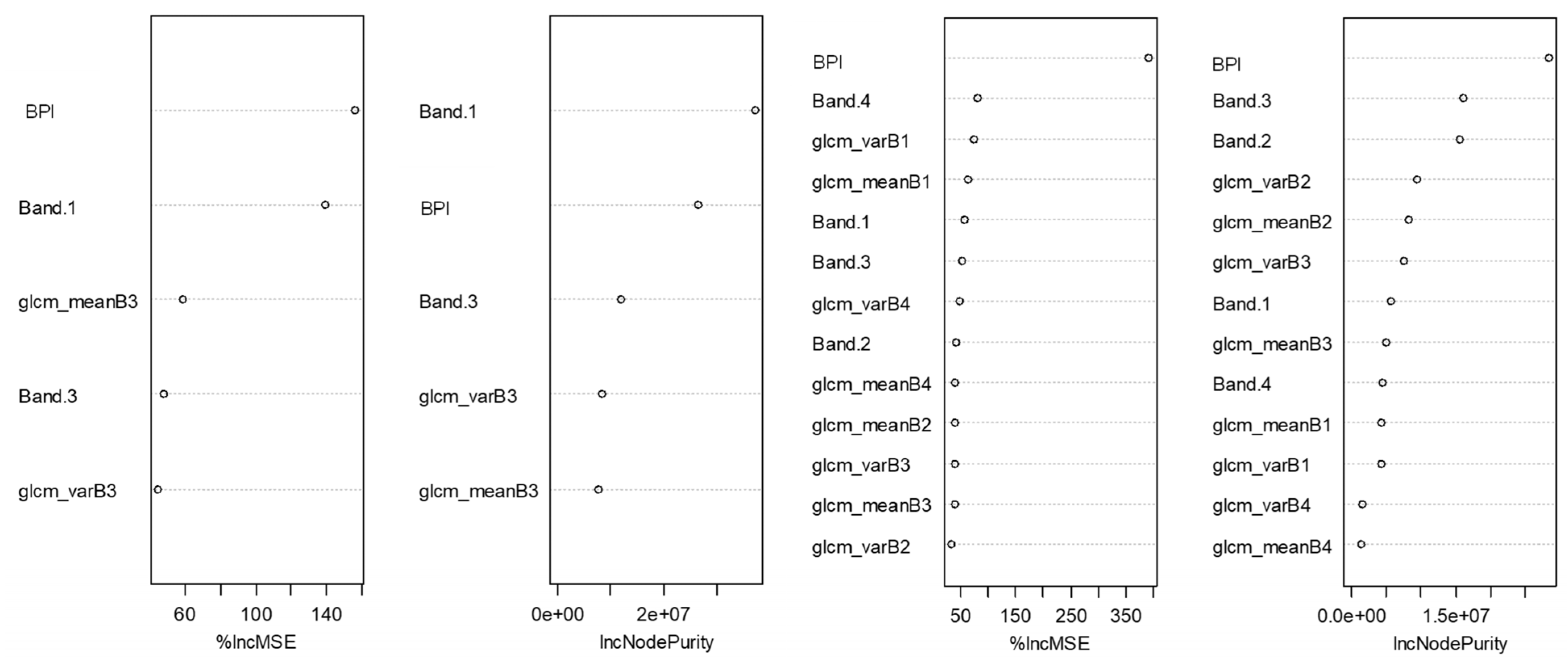
2.4. Random Forest Models and Model Validation
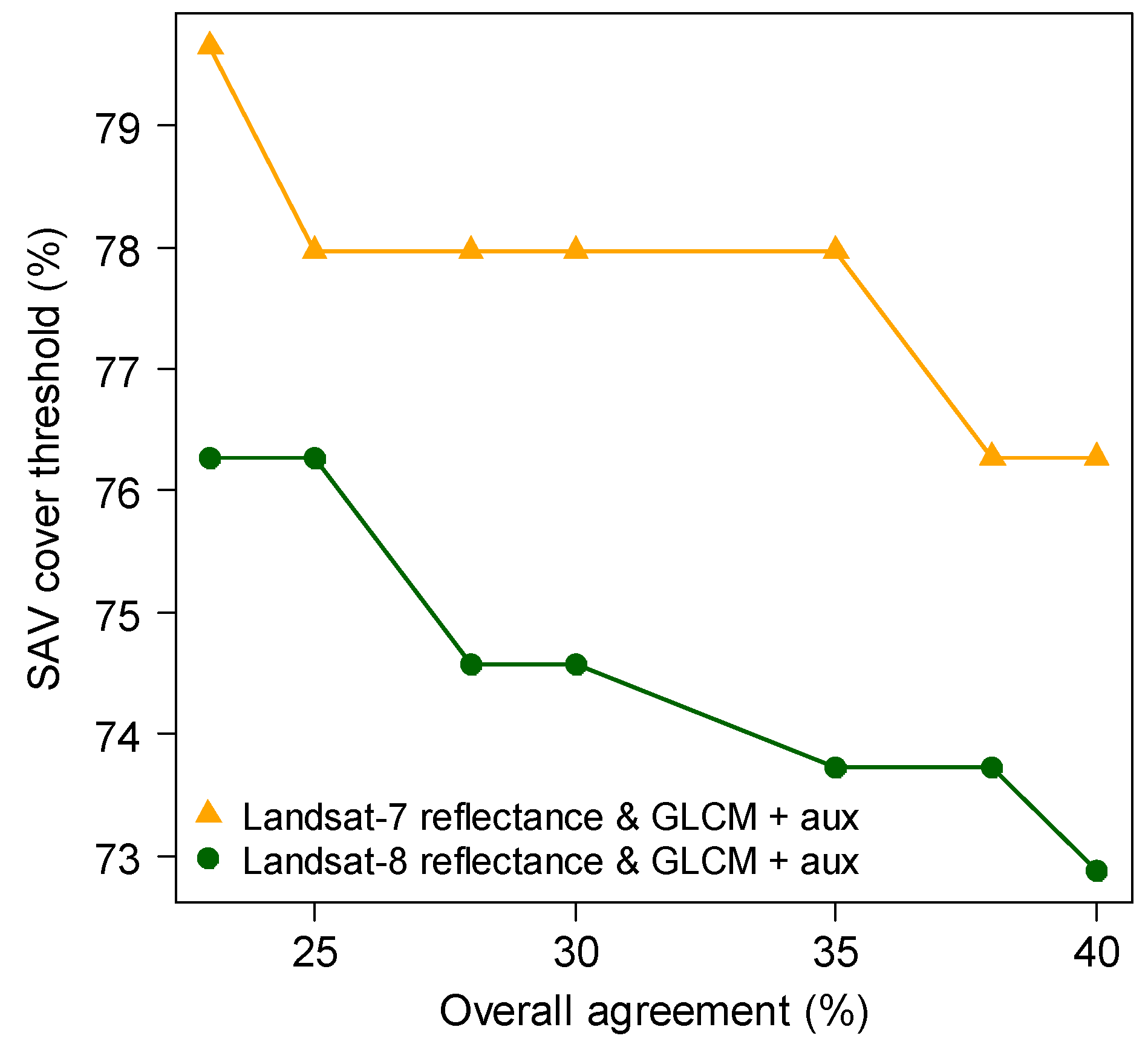
2.5. Benthic Habitat Maps and Accuracy Assessments
2.6. Assessment of Landscape Scale Change and Predictors of Change in SAV Cover and Area over Time
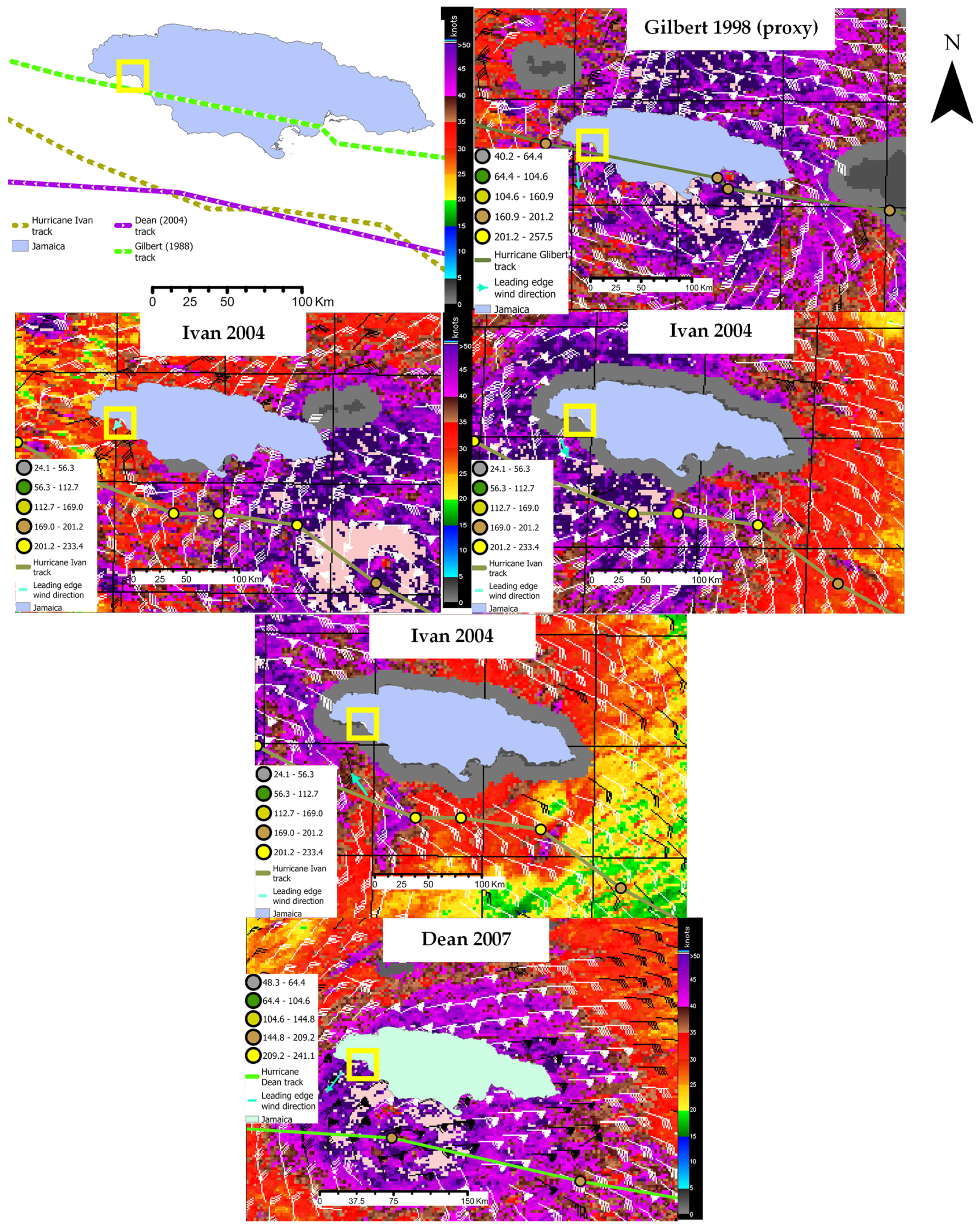
2.7. The Spatial Pattern Predictors of SAV Change
2.8. Hierarchical Bayesian Modelling Framework Used to Identify Spatial Pattern Predictors of SAV Change
3. Results
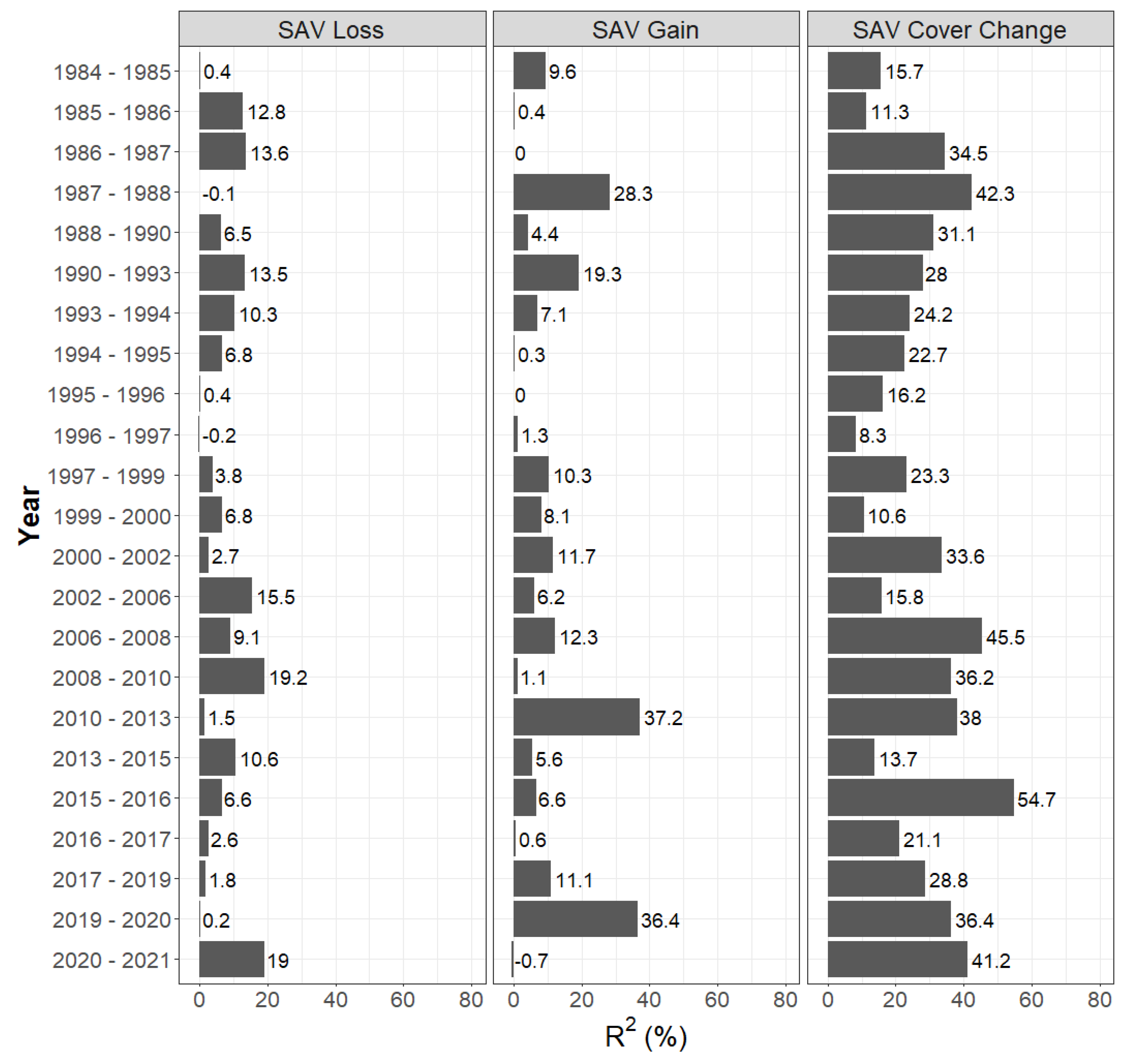
3.1. Landscape Scale Changes and Predictors
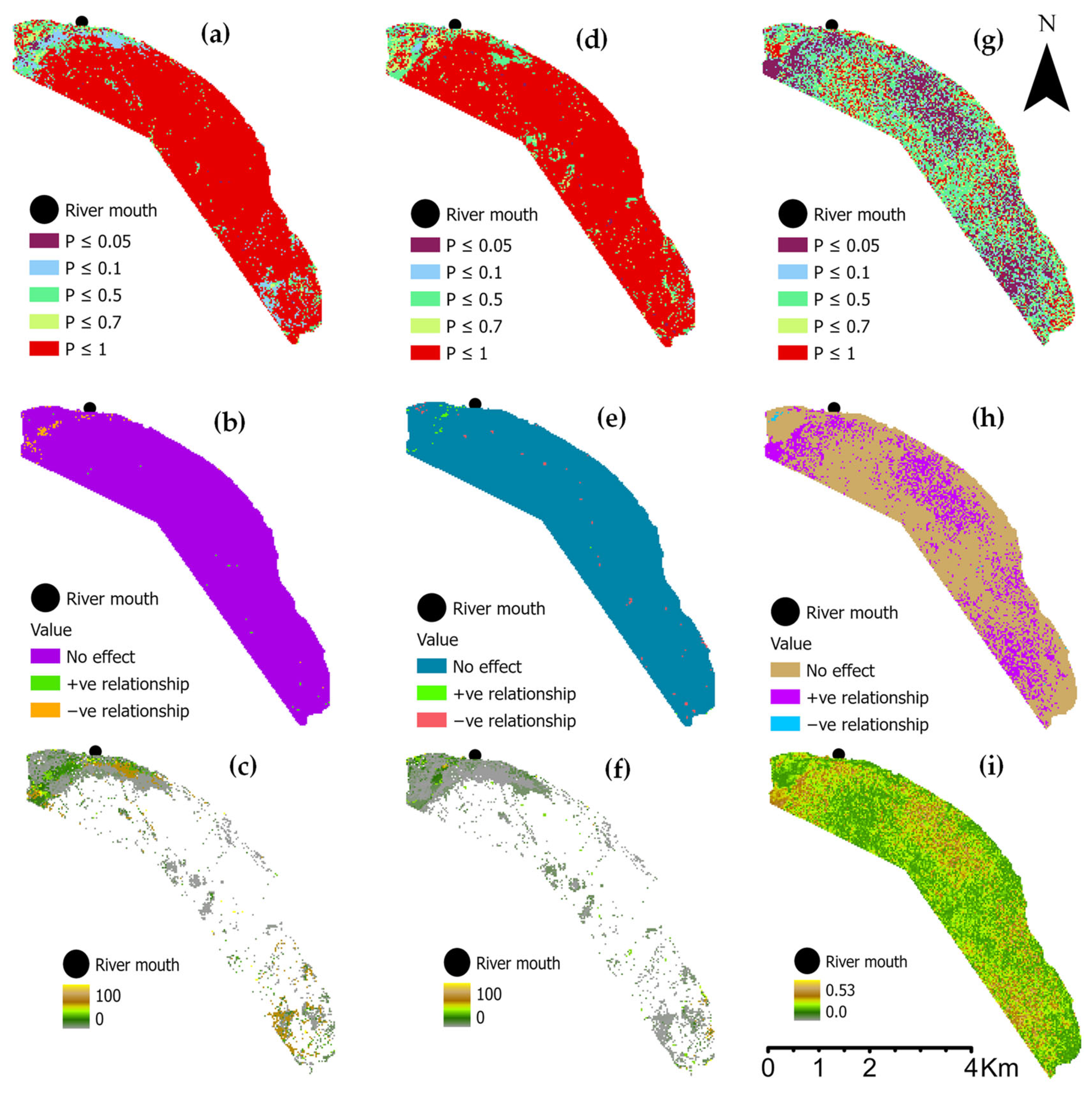
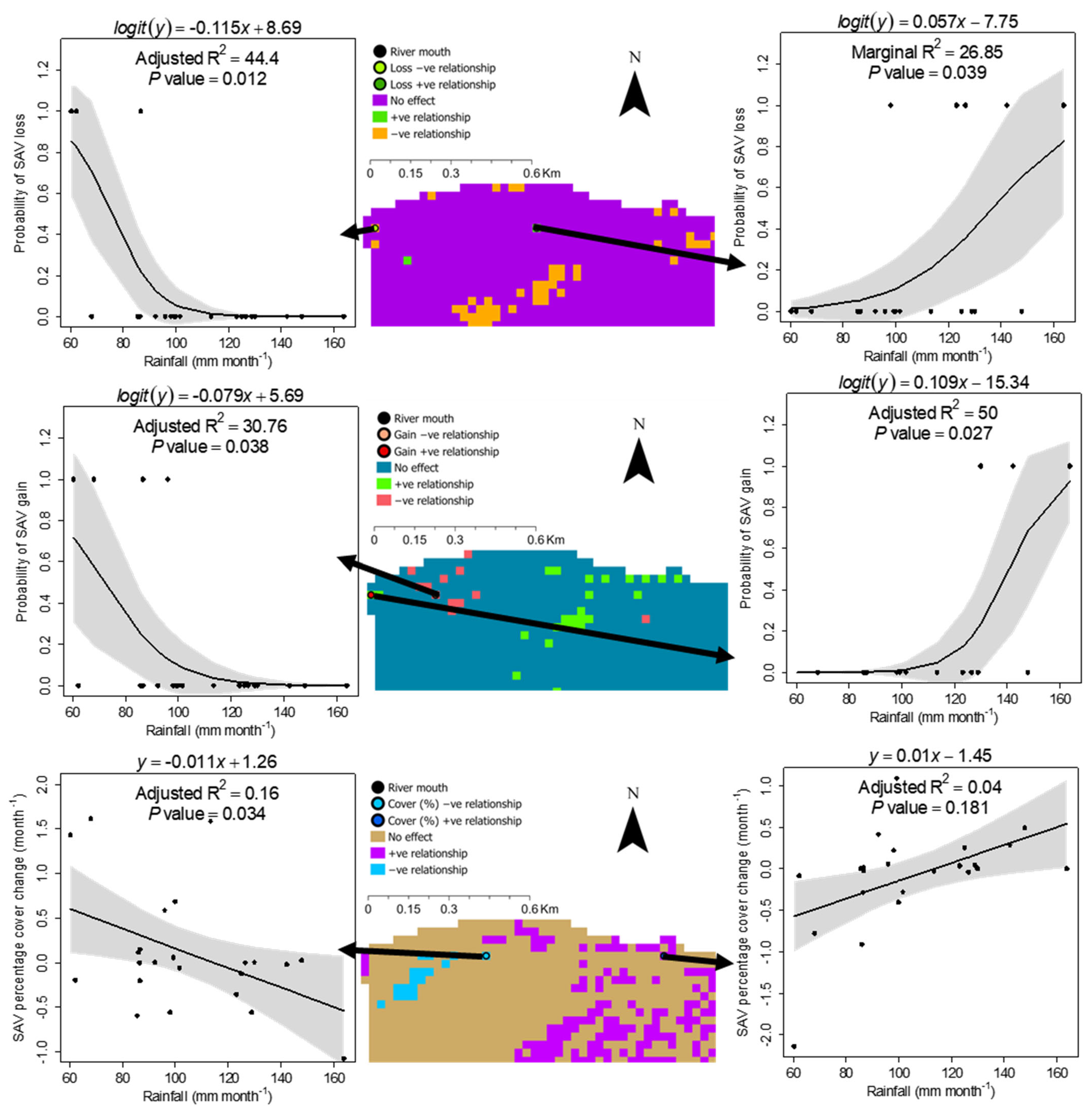
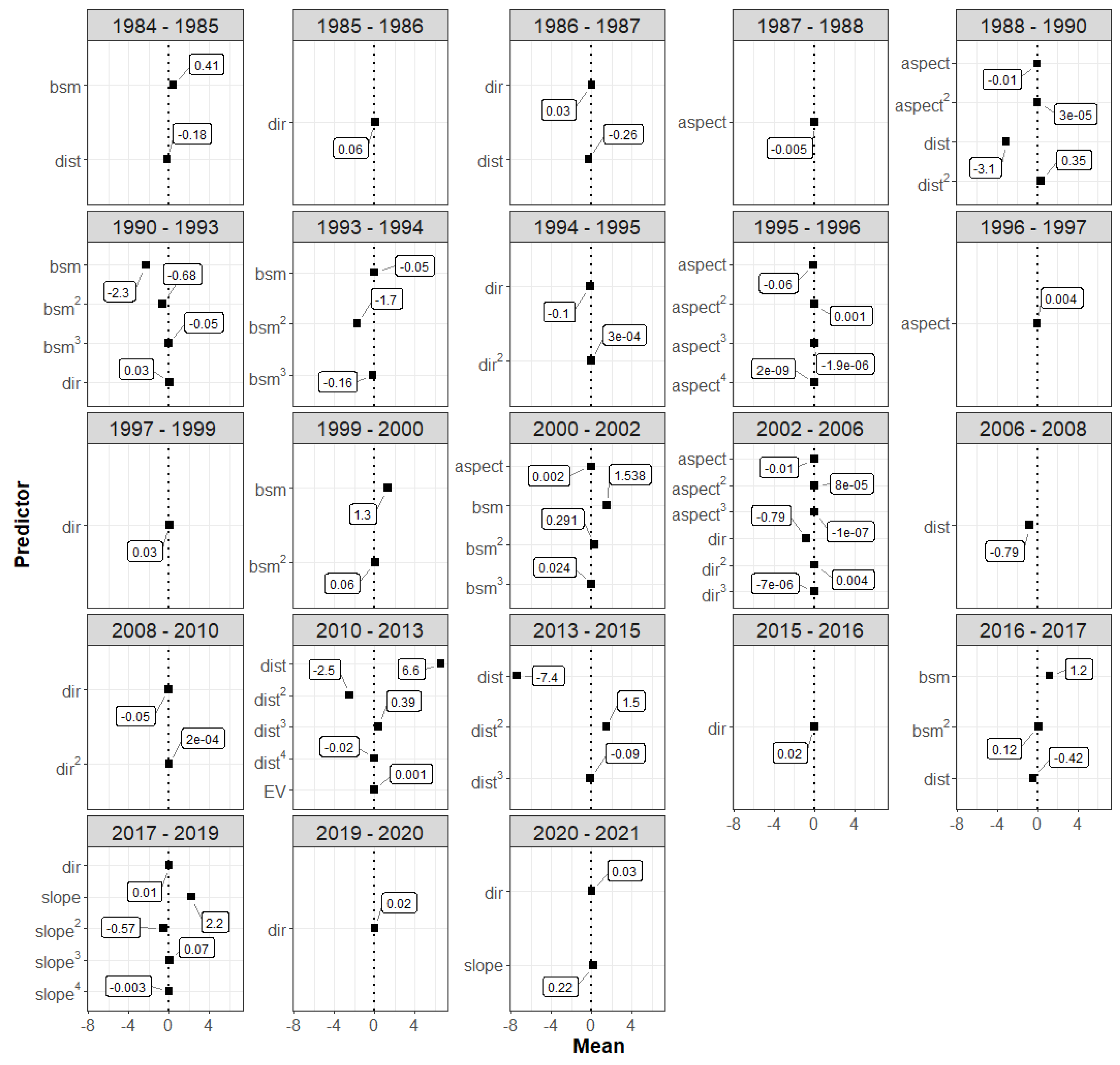
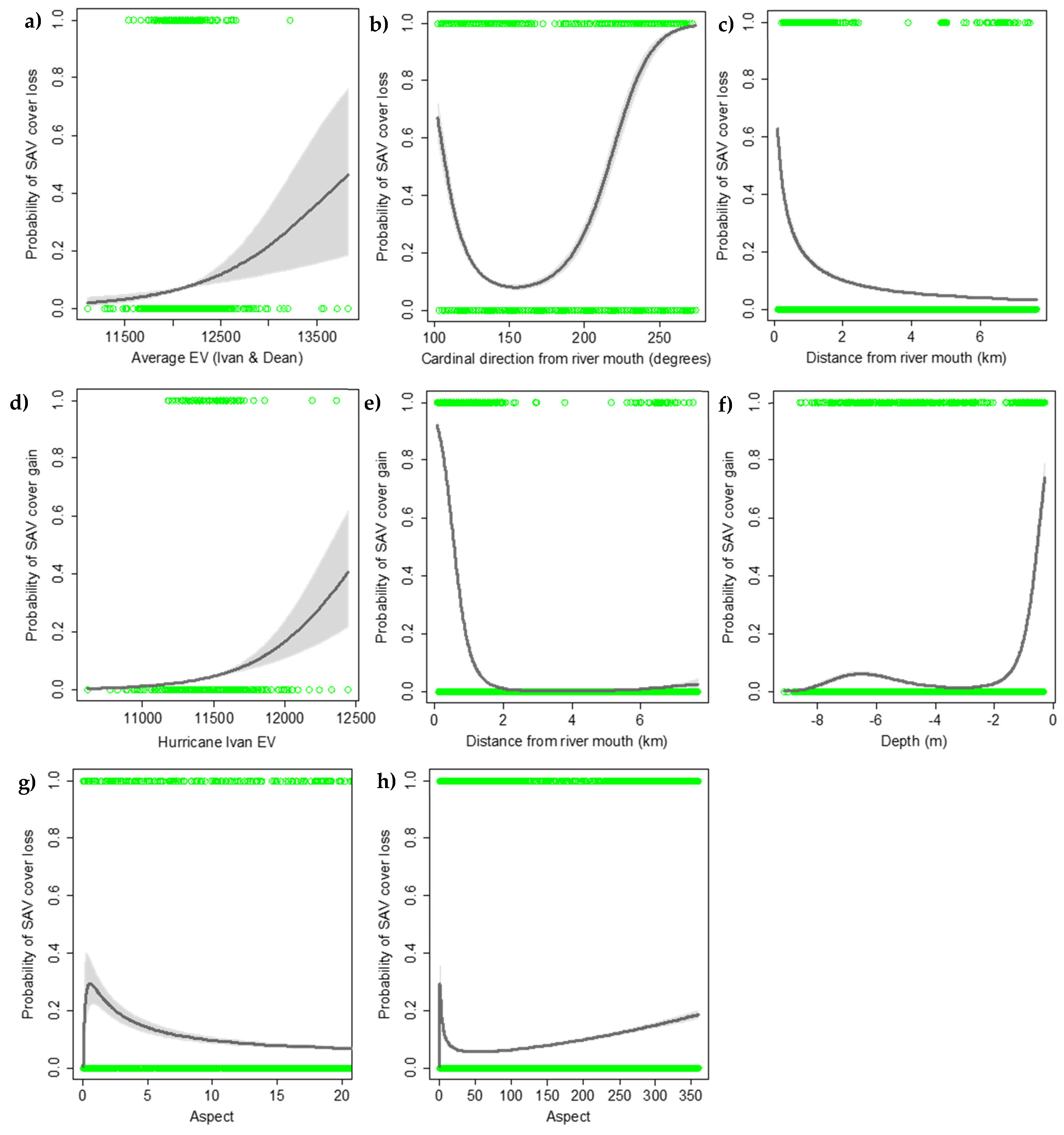
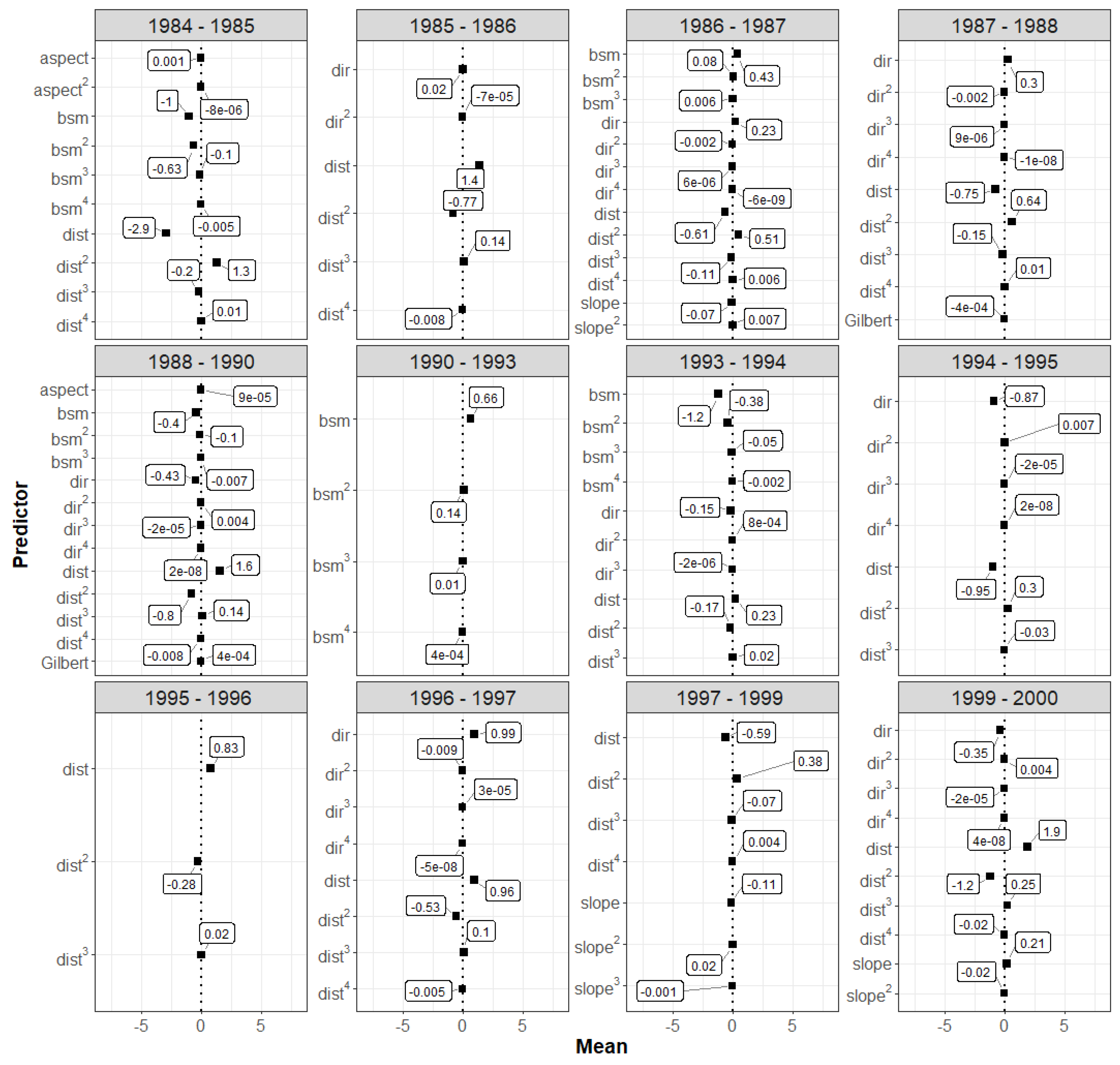
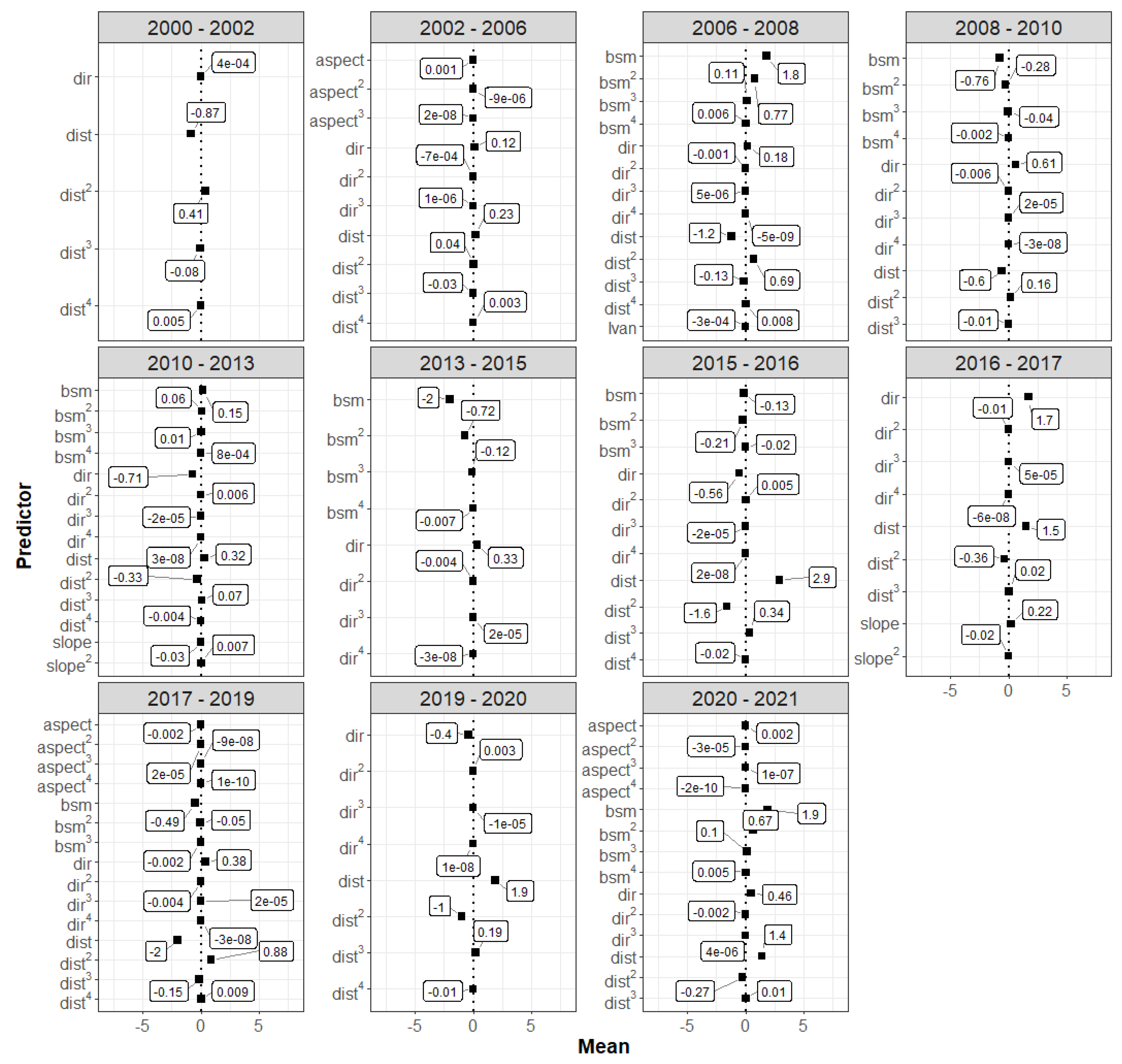
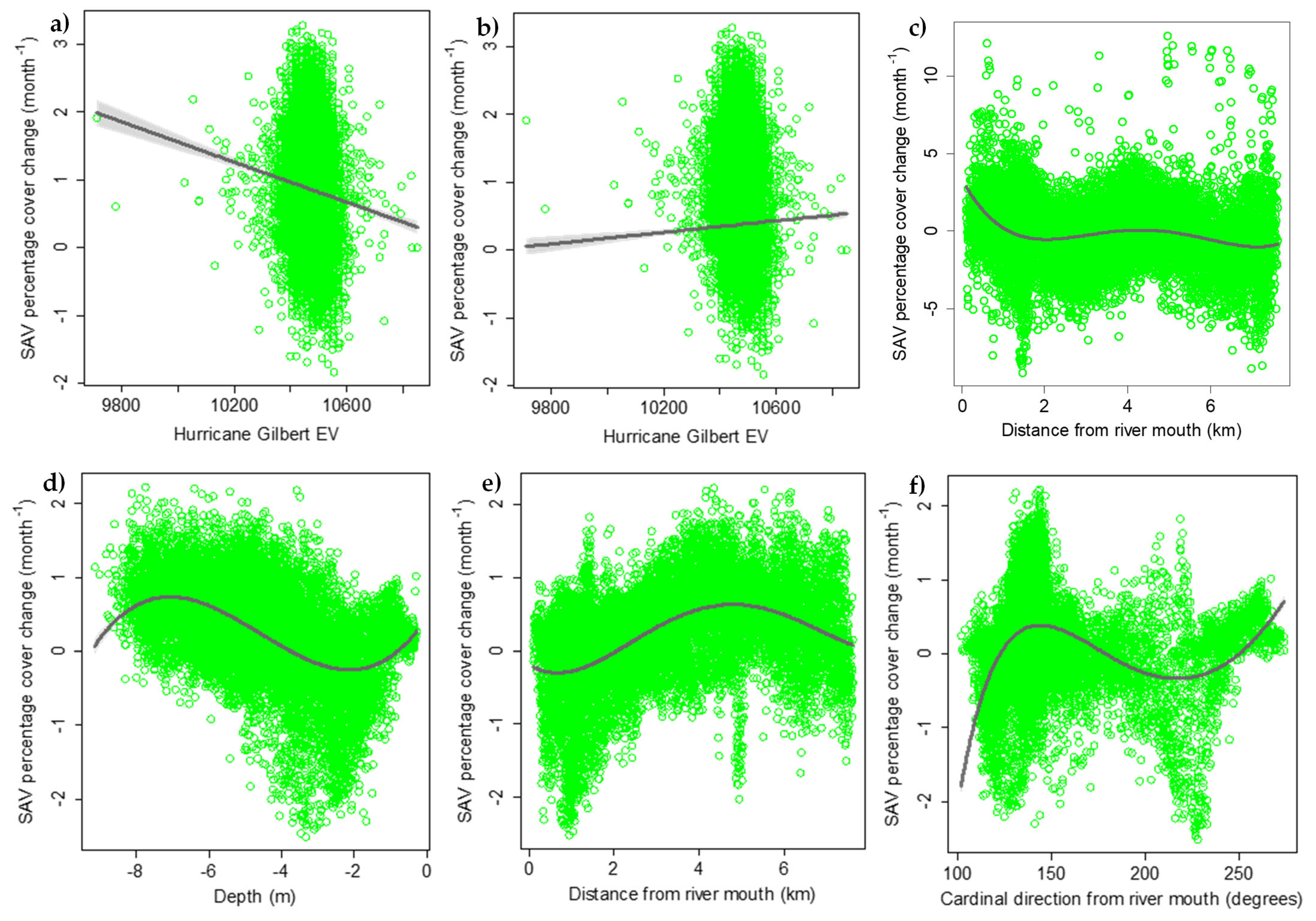
3.2. Spatial Pattern Predictors
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatial Pattern Predictors of SAV Change
4.2. Implications for Management
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Name of File | Landsat Series | Path | Row | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LT05_L2SP_012047_19841009_20200918_02_T1 | Landsat 4–5 | 12 | 47 | 9 October 1984 |
| LT05_L2SP_012047_19850302_20200918_02_T1 | Landsat 4–5 | 12 | 47 | 2 March 1985 |
| LT05_L2SP_012047_19860217_20200918_02_T1 | Landsat 4–5 | 12 | 47 | 17 February 1986 |
| LT05_L2SP_012047_19870628_20201014_02_T1 | Landsat 4–5 | 12 | 47 | 28 June 1987 |
| LT04_L2SP_012047_19880926_20200917_02_T1 | Landsat 4–5 | 12 | 47 | 26 September 1988 |
| LT05_L2SP_012047_19900503_20200915_02_T1 | Landsat 4–5 | 12 | 47 | 3 May 1990 |
| LT04_L2SP_012047_19930111_20200914_02_T1 | Landsat 4–5 | 12 | 47 | 11 January 1993 |
| LT05_L2SP_012047_19940223_20200913_02_T1 | Landsat 4–5 | 12 | 47 | 23 February 1994 |
| LT05_L2SP_012047_19950330_20200912_02_T1 | Landsat 4–5 | 12 | 47 | 30 March 1995 |
| LT05_L2SP_012047_19960316_20200911_02_T1 | Landsat 4–5 | 12 | 47 | 16 March 1996 |
| LT05_L2SP_012047_19970404_20200910_02_T1 | Landsat 4–5 | 12 | 47 | 4 April 1997 |
| LT05_L2SP_012047_19991019_20200907_02_T1 | Landsat 4–5 | 12 | 47 | 19 October 1999 |
| LE07_L2SP_012047_20000131_20200918_02_T1 | Landsat 4–5 | 12 | 47 | 31 January 2000 |
| LE07_L2SP_012047_20021120_20200916_02_T1 | Landsat 7 | 12 | 47 | 20 November 2002 |
| LE07_L2SP_012047_20060304_20200914_02_T1 | Landsat 7 | 12 | 47 | 4 March 2006 |
| LE07_L2SP_012047_20060421_20200914_02_T1 | Landsat 7 | 12 | 47 | 21 April 2006 |
| LT05_L2SP_012047_20080520_20200829_02_T1 | Landsat 4–5 | 12 | 47 | 20 May 2008 |
| LT05_L2SP_012047_20100118_20200825_02_T1 | Landsat 4–5 | 12 | 47 | 18 January 2010 |
| LE07_L2SP_012048_20130510_20200907_02_T1 | Landsat 7 | 12 | 48 | 10 May 2013 |
| LE07_L2SP_012047_20131017_20200907_02_T1 | Landsat 7 | 12 | 47 | 17 October 2013 |
| LC08_L2SP_012047_20131126_20200912_02_T1 | Landsat 8 | 12 | 47 | 26 November 2013 |
| LC08_L2SP_012047_20150116_20200910_02_T1 | Landsat 8 | 12 | 47 | 16 January 2015 |
| LC08_L2SP_012047_20160220_20200907_02_T1 | Landsat 8 | 12 | 47 | 20 February 2016 |
| LC08_L2SP_012047_20170222_20200905_02_T1 | Landsat 8 | 12 | 47 | 22 February 2017 |
| LC08_L2SP_012047_20190111_20200830_02_T1 | Landsat 8 | 12 | 47 | 11 January 2019 |
| LC08_L2SP_012048_20200318_20200822_02_T1 | Landsat 8 | 12 | 48 | 18 March 2020 |
| LC08_L2SP_012047_20210422_20210430_02_T1 | Landsat 8 | 12 | 47 | 22 April 2021 |
| RFr Models | Var (%) | MSE | RMSE | MAE | MAPE | BIAS | rBIAS | rMSEP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAV × BPI + Landsat 7 reflectance and GLCM data | 62.7 | 656.5 | 25.6 | 19.2 | 39.1 | 1.3 | 0.0202 | 0.4 |
| SAV × BPI + Landsat 8 reflectance and GLCM data | 69.8 | 595.2 | 24.4 | 17.7 | 37.7 | 0.1 | 0.0008 | 0.4 |
References
- Orth, R.J.; Carruthers, T.J.; Dennison, W.C.; Duarte, C.M.; Fourqurean, J.W.; Heck, K.L.; Hughes, A.R.; Kendrick, G.A.; Kenworthy, W.J.; Olyarnik, S. A global crisis for seagrass ecosystems. Bioscience 2006, 56, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unsworth, R.K.; McKenzie, L.J.; Collier, C.J.; Cullen-Unsworth, L.C.; Duarte, C.M.; Eklöf, J.S.; Jarvis, J.C.; Jones, B.L.; Nordlund, L.M. Global challenges for seagrass conservation. Ambio 2019, 48, 801–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ralph, P.; Durako, M.J.; Enriquez, S.; Collier, C.; Doblin, M. Impact of light limitation on seagrasses. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2007, 350, 176–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horinouchi, M. Distribution patterns of benthic juvenile gobies in and around seagrass habitats: Effectiveness of seagrass shelter against predators. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2007, 72, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unsworth, R.K.; Nordlund, L.M.; Cullen-Unsworth, L.C. Seagrass meadows support global fisheries production. Conserv. Lett. 2019, 12, e12566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, G.J.; Shaw, C. The production and trophic ecology of shallow-water fish assemblages in southern Australia I. Species richness, size-structure and production of fishes in Western Port, Victoria. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1995, 194, 53–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grech, A.; Chartrand-Miller, K.; Erftemeijer, P.; Fonseca, M.; McKenzie, L.; Rasheed, M.; Taylor, H.; Coles, R. A comparison of threats, vulnerabilities and management approaches in global seagrass bioregions. Environ. Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 024006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waycott, M.; Duarte, C.M.; Carruthers, T.J.; Orth, R.J.; Dennison, W.C.; Olyarnik, S.; Calladine, A.; Fourqurean, J.W.; Heck Jr, K.L.; Hughes, A.R. Accelerating loss of seagrasses across the globe threatens coastal ecosystems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 12377–12381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefcheck, J.S.; Orth, R.J.; Dennison, W.C.; Wilcox, D.J.; Murphy, R.R.; Keisman, J.; Gurbisz, C.; Hannam, M.; Landry, J.B.; Moore, K.A. Long-term nutrient reductions lead to the unprecedented recovery of a temperate coastal region. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 3658–3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordlund, L.M.; de la Torre-Castro, M.; Erlandsson, J.; Conand, C.; Muthiga, N.; Jiddawi, N.; Gullström, M. Intertidal zone management in the Western Indian Ocean: Assessing current status and future possibilities using expert opinions. Ambio 2014, 43, 1006–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlson, R.R.; Foo, S.A.; Asner, G.P. Land use impacts on coral reef health: A ridge-to-reef perspective. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fache, E.; Pauwels, S. The ridge-to-reef approach on Cicia Island, Fiji. Ambio 2022, 51, 2376–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brierley, A.S.; Kingsford, M.J. Impacts of climate change on marine organisms and ecosystems. Curr. Biol. 2009, 19, R602–R614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knutson, T.R.; McBride, J.L.; Chan, J.; Emanuel, K.; Holland, G.; Landsea, C.; Held, I.; Kossin, J.P.; Srivastava, A.; Sugi, M. Tropical cyclones and climate change. Nat. Geosci. 2010, 3, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, F.; Mazdiyasni, O.; AghaKouchak, A. Evidence of anthropogenic impacts on global drought frequency, duration, and intensity. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thornton, P.K.; Ericksen, P.J.; Herrero, M.; Challinor, A.J. Climate variability and vulnerability to climate change: A review. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2014, 20, 3313–3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Choi, J.-K.; Ryu, J.-H.; Jeong, H.J.; Lee, K.; Park, M.G.; Kim, K.Y. Observation of typhoon-induced seagrass die-off using remote sensing. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 154, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Côté-Laurin, M.-C.; Benbow, S.; Erzini, K. The short-term impacts of a cyclone on seagrass communities in Southwest Madagascar. Cont. Shelf Res. 2017, 138, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, M.O.; Furman, B.T.; Merello, M.; Durako, M.J. Recurrence of Thalassia testudinum seagrass die-off in Florida Bay, USA: Initial observations. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2016, 560, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León-Pérez, M.C.; Armstrong, R.A.; Hernández, W.J.; Aguilar-Perera, A.; Thompson-Grim, J. Seagrass cover expansion off Caja de Muertos Island, Puerto Rico, as determined by long-term analysis of historical aerial and satellite images (1950–2014). Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 106561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congdon, V.M.; Hall, M.O.; Furman, B.T.; Campbell, J.E.; Durako, M.J.; Goodin, K.L.; Dunton, K.H. Common ecological indicators identify changes in seagrass condition following disturbances in the Gulf of Mexico. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 156, 111090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chollett, I.; Bone, D.; Pérez, D. Effects of heavy rainfall on Thalassia testudinum beds. Aquat. Bot. 2007, 87, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, S.M.; Griffin, K.J.; Blick, R.A.; Poore, A.G.; Vergés, A. Seagrass on the brink: Decline of threatened seagrass Posidonia australis continues following protection. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancini, G.; Mastrantonio, G.; Pollice, A.; Lasinio, G.J.; Belluscio, A.; Casoli, E.; Pace, D.S.; Ardizzone, G.; Ventura, D. Detecting trends in seagrass cover through aerial imagery interpretation: Historical dynamics of a Posidonia oceanica meadow subjected to anthropogenic disturbance. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 150, 110209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecours, V. On the use of maps and models in conservation and resource management (warning: Results may vary). Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrell, J.; Grant, J. Detecting hot and cold spots in a seagrass landscape using local indicators of spatial association. Landsc. Ecol. 2013, 28, 2005–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phinn, S.; Roelfsema, C.; Dekker, A.; Brando, V.; Anstee, J. Mapping seagrass species, cover and biomass in shallow waters: An assessment of satellite multi-spectral and airborne hyper-spectral imaging systems in Moreton Bay (Australia). Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3413–3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumstark, R.; Dixon, B.; Carlson, P.; Palandro, D.; Kolasa, K. Alternative spatially enhanced integrative techniques for mapping seagrass in Florida’s marine ecosystem. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 1248–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahtmäe, E.; Paavel, B.; Kutser, T. How much benthic information can be retrieved with hyperspectral sensor from the optically complex coastal waters? J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2020, 14, 016504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntyre, K.; McLaren, K.; Prospere, K. Mapping shallow nearshore benthic features in a Caribbean marine-protected area: Assessing the efficacy of using different data types (hydroacoustic versus satellite images) and classification techniques. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 1117–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaren, K.; McIntyre, K.; Prospere, K. Using the random forest algorithm to integrate hydroacoustic data with satellite images to improve the mapping of shallow nearshore benthic features in a marine protected area in Jamaica. GISci. Remote Sens. 2019, 56, 1065–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, M.E.; McLaren, K.P.; Wilson, B.S. Long-term socio-economic and spatial pattern drivers of land cover change in a Caribbean tropical moist forest, the Cockpit Country, Jamaica. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 186, 185–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, E.F.; Geist, H.J.; Lepers, E. Dynamics of land-use and land-cover change in tropical regions. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2003, 28, 205–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamwi, J.M.; Cho, M.A.; Kaetsch, C.; Manda, S.O.; Graz, F.P.; Chirwa, P.W. Assessing the spatial drivers of land use and land cover change in the protected and communal areas of the Zambezi Region, Namibia. Land 2018, 7, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntyre, K. Benthic Mapping of the Bluefields Bay Fish Sanctuary, Jamaica. Master’s Thesis, Lund University, Lund, Sweden, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- McLaren, K.; Luke, D.; Tanner, E.; Bellingham, P.J.; Healey, J.R. Reconstructing the effects of hurricanes over 155 years on the structure and diversity of trees in two tropical montane rainforests in Jamaica. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 276, 107621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majka, D.; Jenness, J.; Beier, P. CorridorDesigner: ArcGIS Tools for Designing and Evaluating Corridors. Available online: http://corridordesign.org (accessed on 15 February 2024).
- R Core Team, R. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing-4.3.1. Available online: http://www.R-project.org (accessed on 25 October 2023).
- R Core Team, R. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing-glcm” Package. Available online: http://www.R-project.org (accessed on 25 October 2023).
- Zvoleff, A. Package ‘glcm’. Calculate Textures from Grey-Level Co-Occurence Matrices (GLCMs). Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/glcm/index.html (accessed on 25 October 2022).
- Liaw, A.; Wiener, M. Classification and regression by randomForest. R News 2002, 2, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Bakar, K.S.; Sahu, S.K. spTimer: Spatio-temporal Bayesian modeling using R. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 63, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aho, K. Asbio: A Collection of Statistical Tools for Biologists_. R package Version 1.9-6. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=asbio (accessed on 15 February 2022).
- Wood, S.N. Fast stable restricted maximum likelihood and marginal likelihood estimation of semiparametric generalized linear models. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 2011, 73, 3–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S.N. Generalized Additive Models: An Introduction with R; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, S.N. Stable and efficient multiple smoothing parameter estimation for generalized additive models. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2004, 99, 673–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S.N.; Pya, N.; Säfken, B. Smoothing parameter and model selection for general smooth models. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2016, 111, 1548–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuur, A.F.; Ieno, E.N.; Walker, N.J.; Saveliev, A.A.; Smith, G.M. Mixed Effects Models and Extensions in Ecology with R; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; Volume 574. [Google Scholar]
- Hyndman, R.; Athanasopoulos, G.; Bergmeir, C.; Caceres, G.; Chhay, L.; O’Hara-Wild, M.; Petropoulos, F.; Razbash, S.; Wang, E.; Yasmeen, F. Forecast: Forecasting Functions for Time Series and Linear Models. R package Version 8.21.1. Available online: https://pkg.robjhyndman.com/forecast/ (accessed on 15 February 2023).
- Hyndman, R.J.; Khandakar, Y. Automatic time series forecasting: The forecast package for R. J. Stat. Softw. 2008, 27, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1406.5823. [Google Scholar]
- Luke, D.; McLaren, K.; Wilson, B. Modeling hurricane exposure in a Caribbean lower montane tropical wet forest: The effects of frequent, intermediate disturbances and topography on forest structural dynamics and composition. Ecosystems 2016, 19, 1178–1195. [Google Scholar]
- Lindgren, F.; Rue, H. Bayesian spatial modelling with R-INLA. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 63, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindgren, F.; Rue, H.; Lindström, J. An explicit link between Gaussian fields and Gaussian Markov random fields: The stochastic partial differential equation approach. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 2011, 73, 423–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rue, H.; Martino, S.; Chopin, N. Approximate Bayesian inference for latent Gaussian models by using integrated nested Laplace approximations. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 2009, 71, 319–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rue, H.; Riebler, A.; Sørbye, S.H.; Illian, J.B.; Simpson, D.P.; Lindgren, F.K. Bayesian computing with INLA: A review. Annu. Rev. Stat. Its Appl. 2017, 4, 395–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, T.G.; Simpson, D.; Lindgren, F.; Rue, H. Bayesian computing with INLA: New features. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2013, 67, 68–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rue, H.; Martino, S. Approximate Bayesian inference for hierarchical Gaussian Markov random field models. J. Stat. Plan. Inference 2007, 137, 3177–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosandey-Godin, A.; Krainski, E.T.; Worm, B.; Flemming, J.M. Applying Bayesian spatiotemporal models to fisheries bycatch in the Canadian Arctic. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2015, 72, 186–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuglstad, G.-A.; Simpson, D.; Lindgren, F.; Rue, H. Constructing priors that penalize the complexity of Gaussian random fields. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2019, 114, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illian, J.B.; Sørbye, S.H.; Rue, H.; Hendrichsen, D.K. Using INLA to fit a complex point process model with temporally varying effects-a case study. J. Environ. Stat. 2012, 3, 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelhalter, D.J.; Best, N.G.; Carlin, B.P.; Van Der Linde, A. Bayesian measures of model complexity and fit. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 2002, 64, 583–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B. Summarizing the goodness of fit of generalized linear models for longitudinal data. Stat. Med. 2000, 19, 1265–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robin, X.; Turck, N.; Hainard, A.; Tiberti, N.; Lisacek, F.; Sanchez, J.-C.; Müller, M. pROC: An open-source package for R and S+ to analyze and compare ROC curves. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sørbye, S.H. Tutorial: Scaling IGMRF-Models in R-INLA; University of Tromsø, Department of Mathematics and Statistics: Tromsø, Norway, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Rodemann, J.R.; James, W.R.; Santos, R.O.; Furman, B.T.; Fratto, Z.W.; Bautista, V.; Lara Hernandez, J.; Viadero, N.M.; Linenfelser, J.O.; Lacy, L.A. Impact of extreme disturbances on suspended sediment in western Florida Bay: Implications for seagrass resilience. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 633240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, S.; Jarvis, J.; Sankey, T.; Reason, C.; Coles, R.; Rasheed, M. Declines of seagrasses in a tropical harbour, North Queensland, Australia, are not the result of a single event. J. Biosci. 2015, 40, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shelton, A.O.; Francis, T.B.; Feist, B.E.; Williams, G.D.; Lindquist, A.; Levin, P.S. Forty years of seagrass population stability and resilience in an urbanizing estuary. J. Ecol. 2017, 105, 458–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad-Kamil, E.; Ramli, R.; Jaaman, S.; Bali, J.; Al-Obaidi, J. The effects of water parameters on monthly seagrass percentage cover in Lawas, East Malaysia. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 892746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marbà, N.; Duarte, C.M. Interannual changes in seagrass (Posidonia oceanica) growth and environmental change in the Spanish Mediterranean littoral zone. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1997, 42, 800–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, S.J.; McKenzie, L.J. Flood related loss and recovery of intertidal seagrass meadows in southern Queensland, Australia. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2004, 60, 477–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Fouw, J.; Govers, L.L.; van de Koppel, J.; van Belzen, J.; Dorigo, W.; Cheikh, M.A.S.; Christianen, M.J.; van der Reijden, K.J.; van der Geest, M.; Piersma, T. Drought, mutualism breakdown, and landscape-scale degradation of seagrass beds. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, 1051–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khogkhao, C.; Hayashizaki, K.-I.; Tuntiprapas, P.; Prathep, A. Changes in seagrass communities along the runoff gradient of the Trang river, Thailand. Sci. Asia 2017, 43, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivers, S.D.; Golladay, S.W.; Waters, M.N.; Wilde, S.B.; Ashford, P.D.; Covich, A.P. Changes in submerged aquatic vegetation (SAV) coverage caused by extended drought and flood pulses. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2018, 34, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agawin, N.S.; Duarte, C.M.; Fortes, M.D. Nutrient limitation of Philippine seagrasses (Cape Bolinao, NW Philippines): In situ experimental evidence. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1996, 138, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrados, J.; Agawin, N.S.; Duarte, C.M.; Fortes, M.D.; Kamp-Nielsen, L.; Borum, J. Nutrient limitation of the tropical seagrass Enhalus acoroides (L.) Royle in Cape Bolinao, NW Philippines. Aquat. Bot. 1999, 65, 123–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, V.M.; Lobo-Arteaga, J.; Santos, R.; Leitão-Silva, D.; Veronez, A.; Neves, J.M.; Nogueira, M.; Creed, J.C.; Bertelli, C.M.; Samper-Villarreal, J. Seagrasses benefit from mild anthropogenic nutrient additions. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 960249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, R.; Houk, P. Decoupling seasonal and temporal dynamics of macroalgal canopy cover in seagrass beds. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2020, 525, 151310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Delgado, E.A.; Toledo-Hernández, C.; Ruíz-Díaz, C.; Gómez-Andújar, N.; Medina-Muñiz, J.; Canals-Silander, M.; Suleimán-Ramos, S. Hurricane impacts and the resilience of the invasive sea vine, Halophila stipulacea: A case study from Puerto Rico. Estuaries Coasts 2020, 43, 1263–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oprandi, A.; Mucerino, L.; De Leo, F.; Bianchi, C.; Morri, C.; Azzola, A.; Benelli, F.; Besio, G.; Ferrari, M.; Montefalcone, M. Effects of a severe storm on seagrass meadows. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 748, 141373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marco-Méndez, C.; Marbà, N.; Amores, Á.; Romero, J.; Minguito-Frutos, M.; García, M.; Pagès, J.F.; Prado, P.; Boada, J.; Sánchez-Lizaso, J.L. Evaluating the extent and impact of the extreme Storm Gloria on Posidonia oceanica seagrass meadows. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 908, 168404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correia, K.M.; Smee, D.L. A meta-analysis of tropical cyclone effects on seagrass meadows. Wetlands 2022, 42, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enríquez, S.; Olivé, I.; Cayabyab, N.; Hedley, J.D. Structural complexity governs seagrass acclimatization to depth with relevant consequences for meadow production, macrophyte diversity and habitat carbon storage capacity. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause-Jensen, D.; Quaresma, A.L.; Cunha, A.H.; Greve, T. How are seagrass distribution and abundance monitored. Eur. Seagrasses Introd. Monit. Manag. 2004, 45–53. [Google Scholar]
- Knapp, K.R.; Kruk, M.C.; Levinson, D.H.; Diamond, H.J.; Neumann, C.J. The international best track archive for climate stewardship (IBTrACS) unifying tropical cyclone data. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2010, 91, 363–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, K.R.; Diamond, H.J.; Kossin, J.P.; Kruk, M.C.; Schreck, C.J. International Best Track Archive for Climate Stewardship (IBTrACS) Project, Version 4. North Atlantic. NOAA Natl. Cent. Environ. Inf. 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikita, T.; Klimánek, M. Topographic exposure and its practical applications. J. Landsc. Ecol. 2010, 3, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batke, S.P.; Jocque, M.; Kelly, D.L. Modelling hurricane exposure and wind speed on a mesoclimate scale: A case study from Cusuco NP, Honduras. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
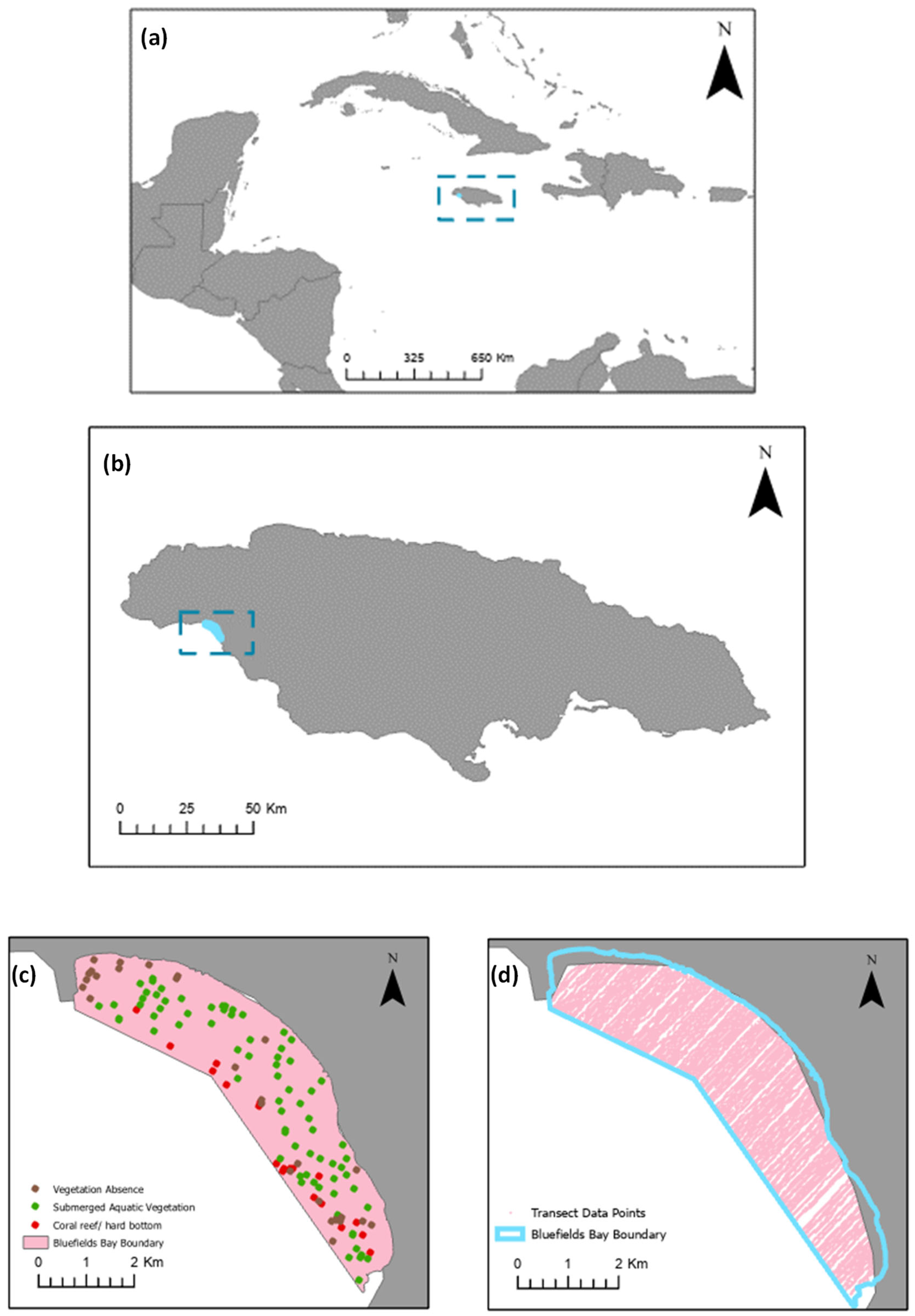
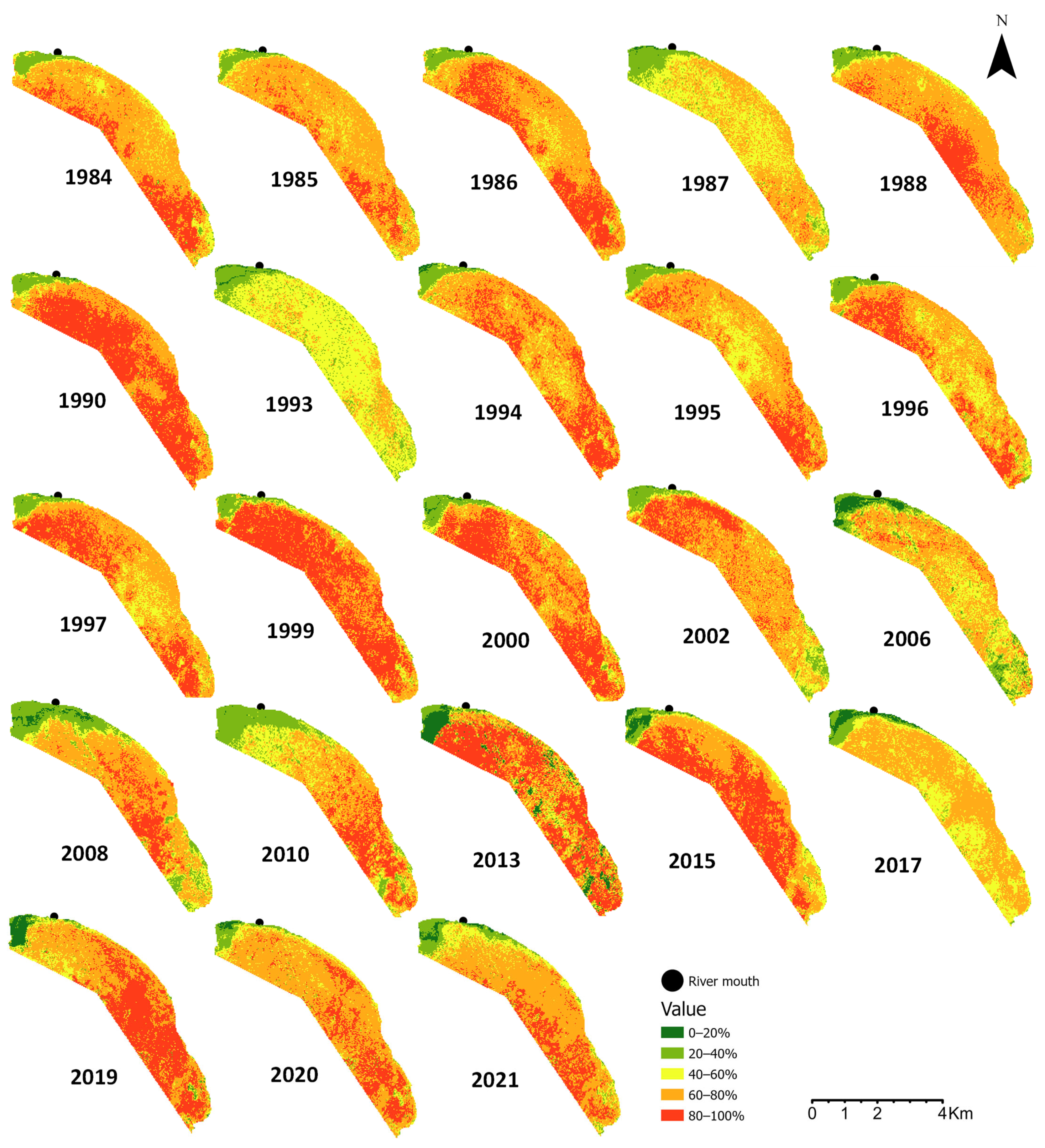
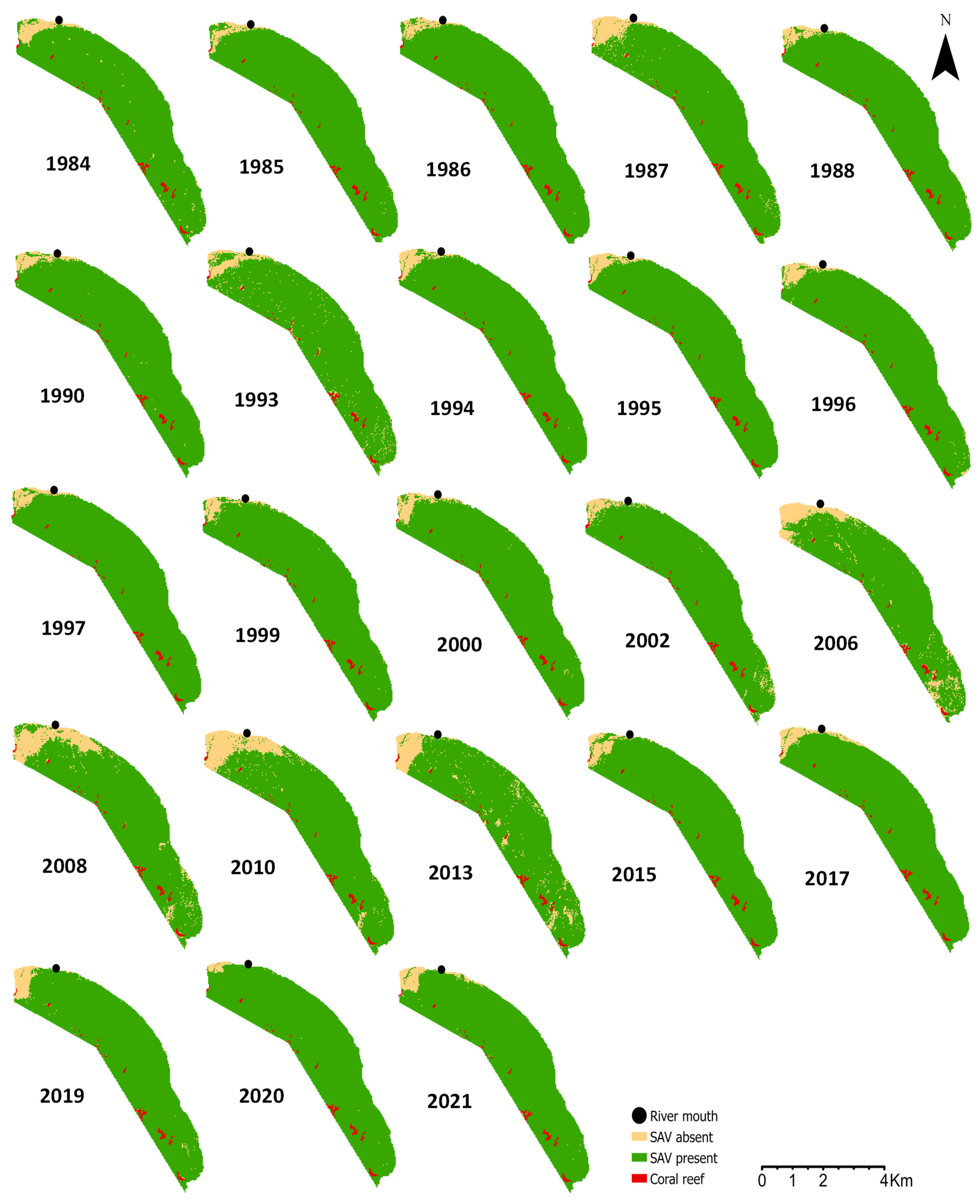
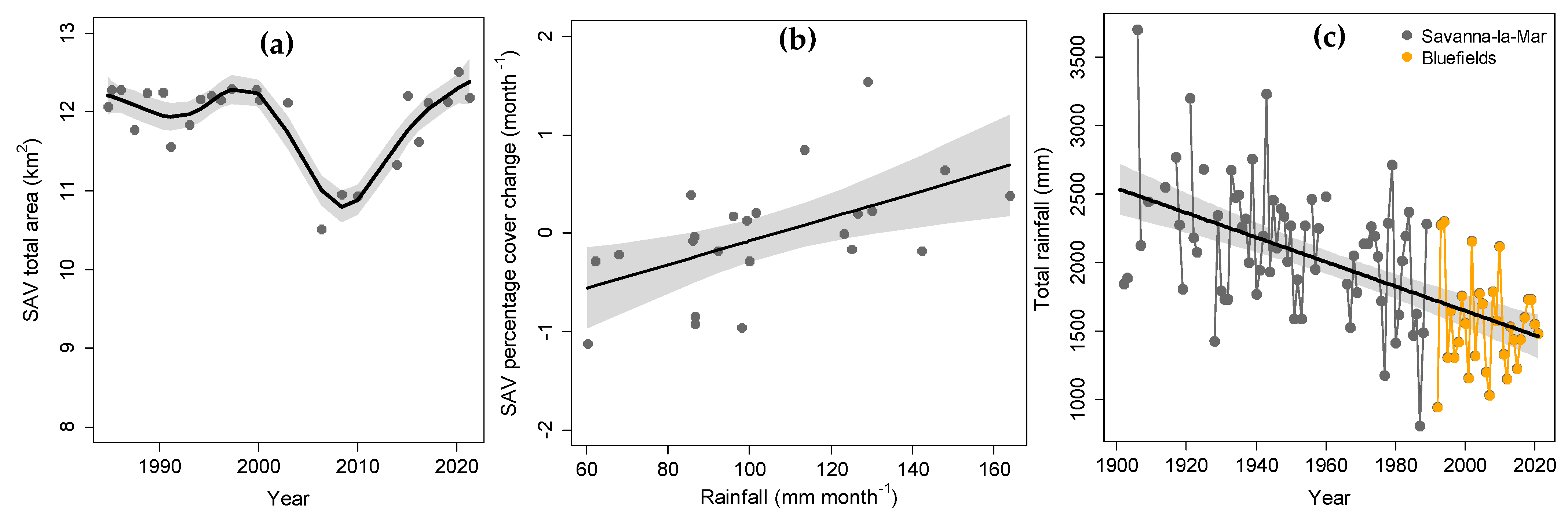

| Models and Correlation Structure | Parameter | Value | L 95% CI | U 95% CI | S.E. | t/F | p | Adj. R2/R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rainfall (mm) × Year (GAM) | Intercept | 1943.6 | 42.4 | 45.9 | <0.001 | 34.7% | ||
| s(Year) | 50.5 † | <0.001 | ||||||
| SAV total area (km2) × Year (GAMM) | Intercept | 11.9 | 0.02 | 686.5 | <0.001 | 69.5% | ||
| ARMA (2, 0) | s(Year) | 71.7 † | <0.001 | |||||
| Phi 1 | −0.76 | −1.25 | −0.26 | |||||
| Phi 2 | −0.43 | −0.77 | 0.02 | |||||
| SAV perc. cover change (month−1) | Intercept | −1.28 | 0.43 | −2.95 | 0.0077 | 28.9% | ||
| × Rainfall (mm month−1) (GLM) | Rainfall | 0.012 | 0.004 | 2.99 | 0.007 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
McLaren, K.; Sedman, J.; McIntyre, K.; Prospere, K. Long-Term Spatial Pattern Predictors (Historically Low Rainfall, Benthic Topography, and Hurricanes) of Seagrass Cover Change (1984 to 2021) in a Jamaican Marine Protected Area. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1247. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16071247
McLaren K, Sedman J, McIntyre K, Prospere K. Long-Term Spatial Pattern Predictors (Historically Low Rainfall, Benthic Topography, and Hurricanes) of Seagrass Cover Change (1984 to 2021) in a Jamaican Marine Protected Area. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(7):1247. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16071247
Chicago/Turabian StyleMcLaren, Kurt, Jasmine Sedman, Karen McIntyre, and Kurt Prospere. 2024. "Long-Term Spatial Pattern Predictors (Historically Low Rainfall, Benthic Topography, and Hurricanes) of Seagrass Cover Change (1984 to 2021) in a Jamaican Marine Protected Area" Remote Sensing 16, no. 7: 1247. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16071247
APA StyleMcLaren, K., Sedman, J., McIntyre, K., & Prospere, K. (2024). Long-Term Spatial Pattern Predictors (Historically Low Rainfall, Benthic Topography, and Hurricanes) of Seagrass Cover Change (1984 to 2021) in a Jamaican Marine Protected Area. Remote Sensing, 16(7), 1247. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16071247





