Historical Marine Cold Spells in the South China Sea: Characteristics and Trends
Abstract
1. Introduction
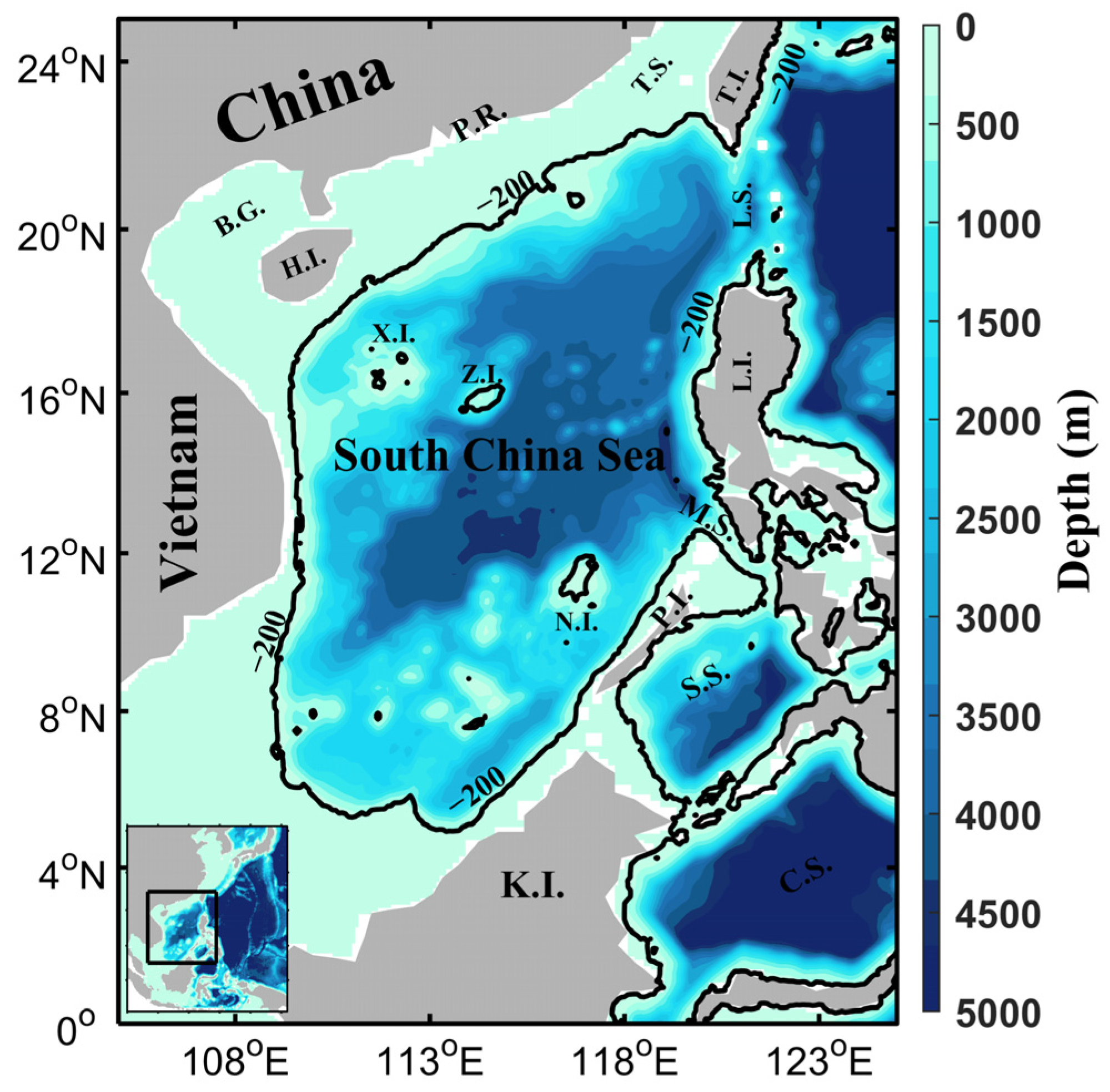
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. OISST V2.1
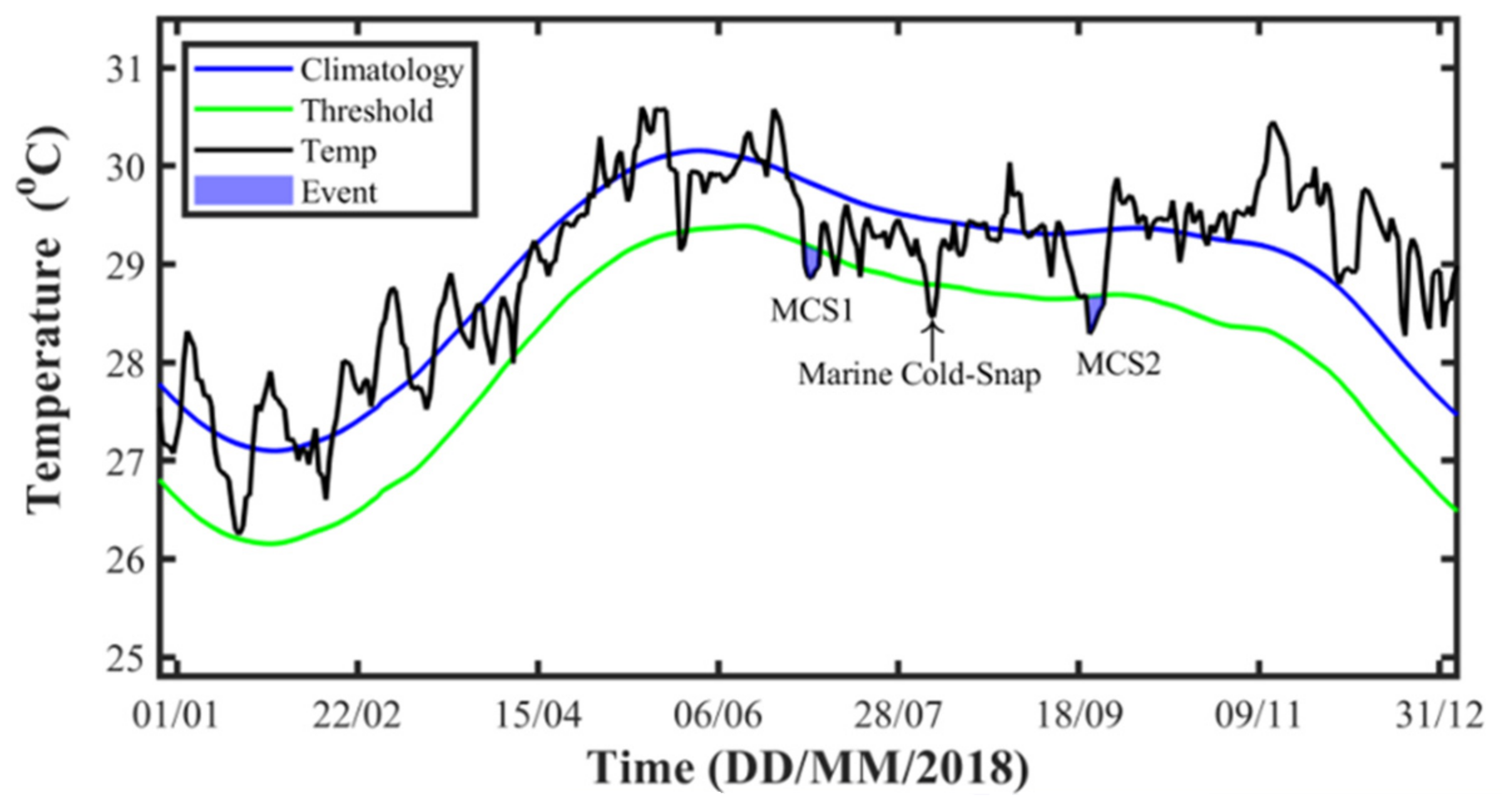
2.2. Definition of Marine Cold Spells
3. Results
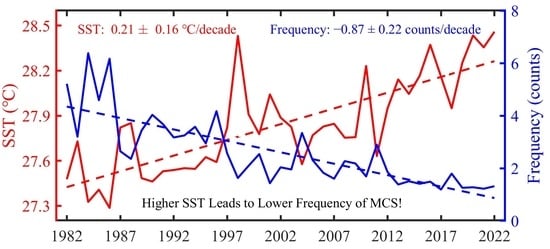
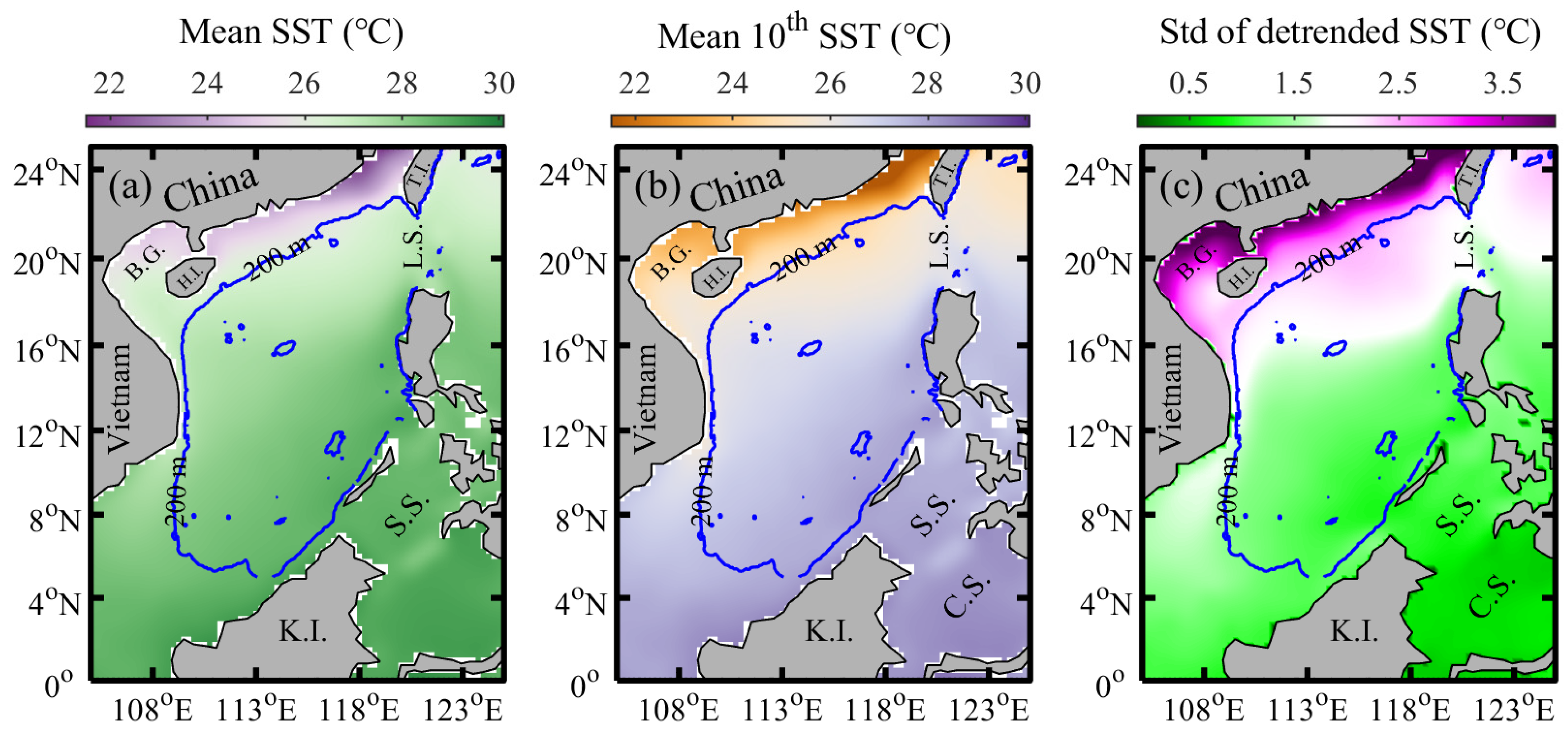
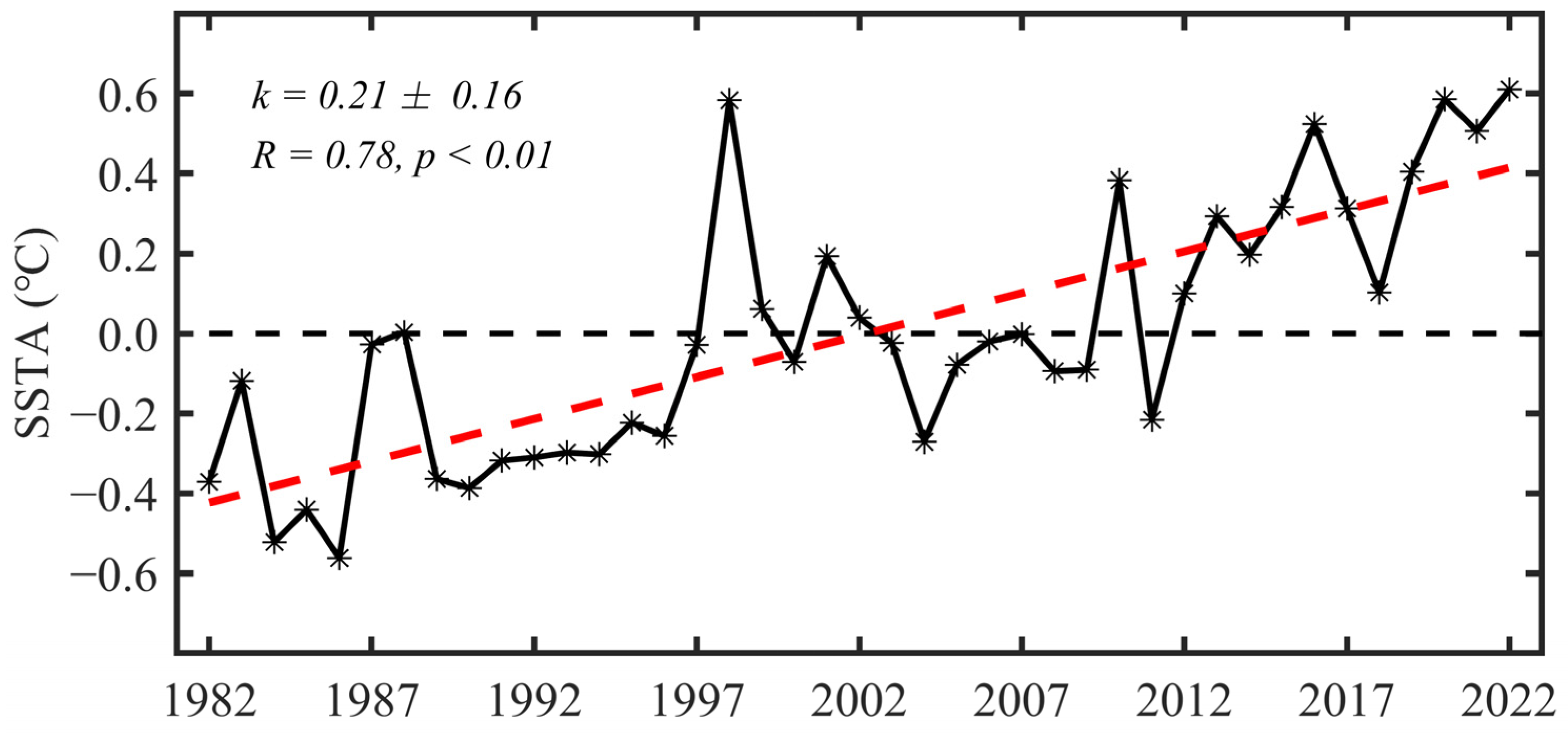
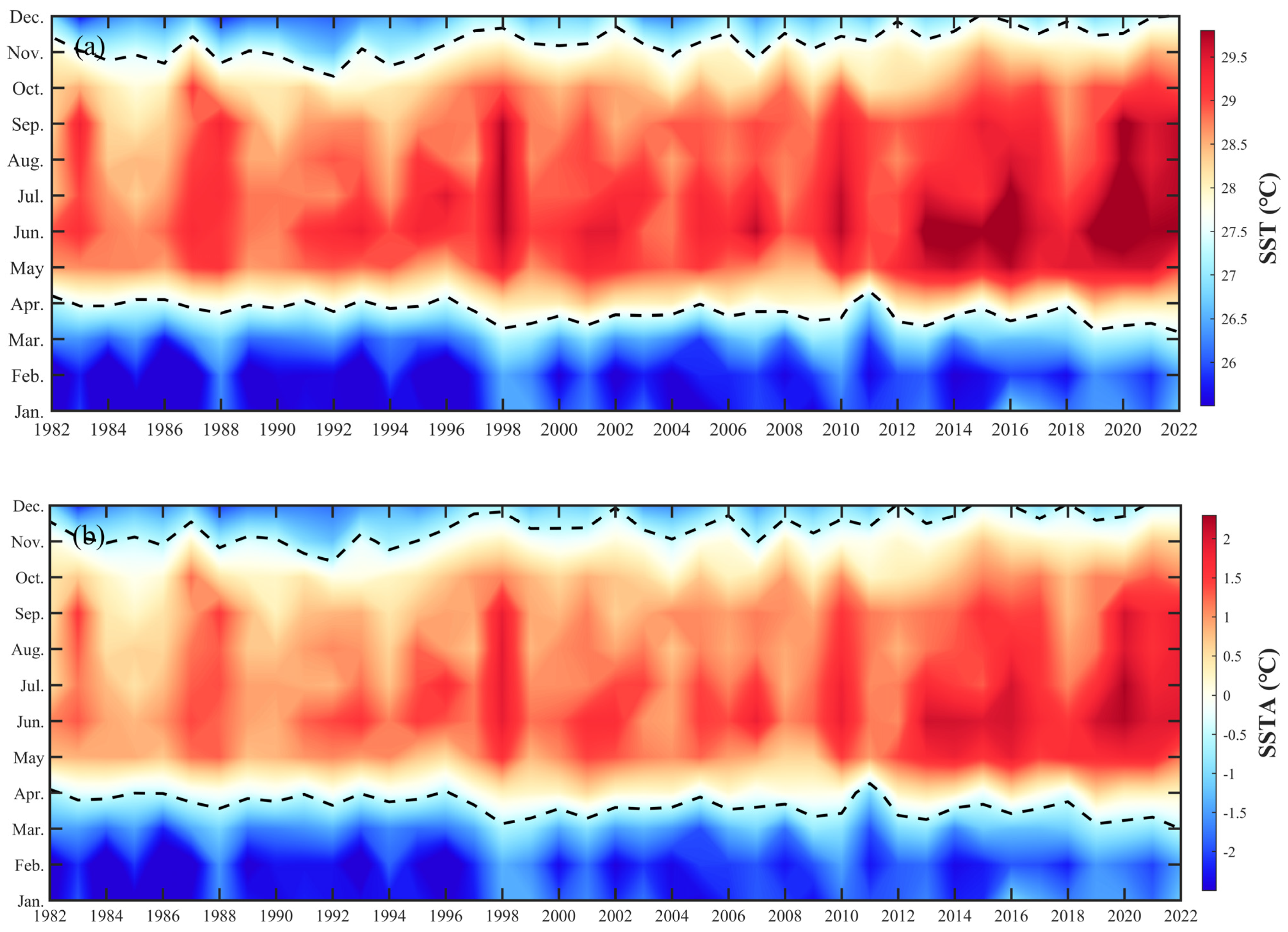
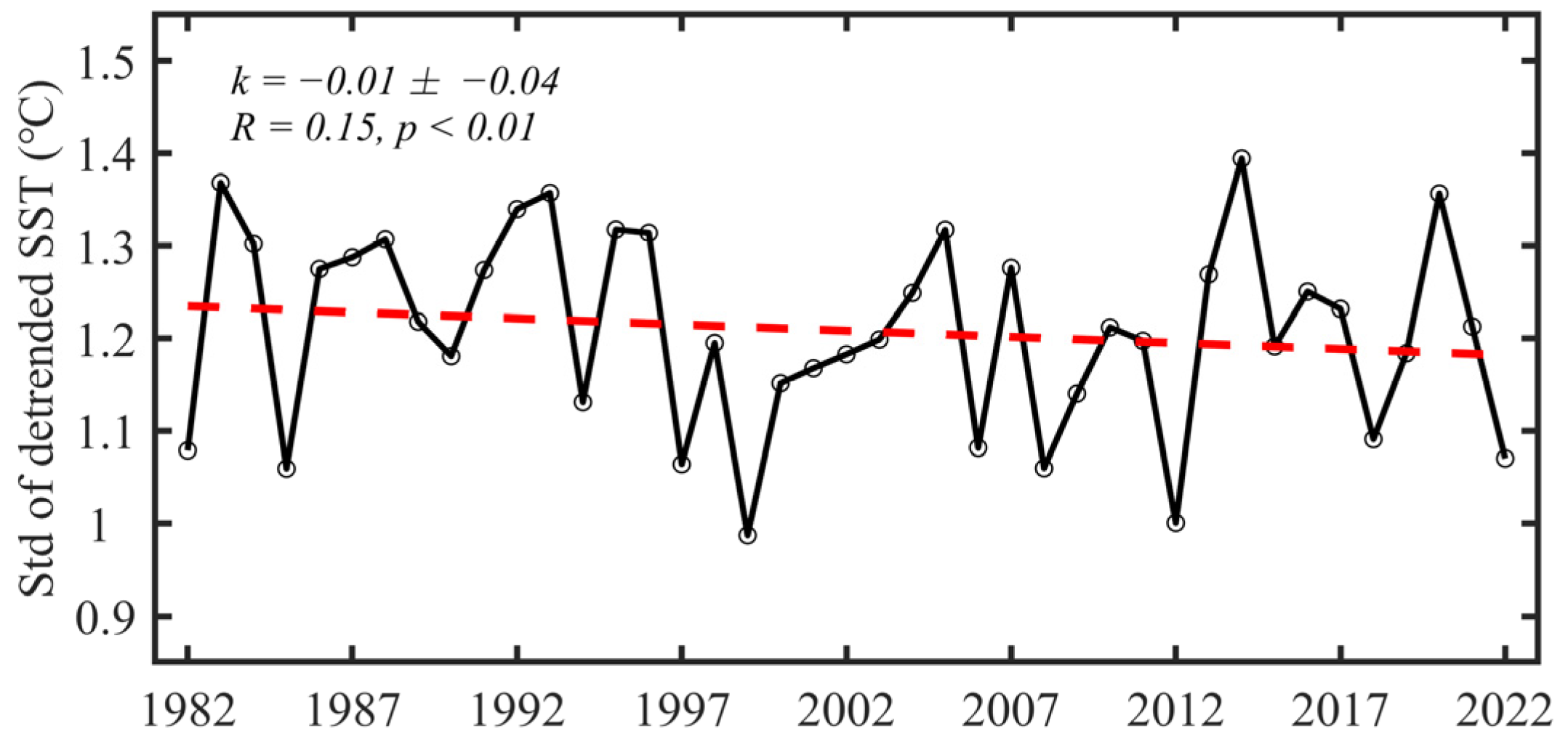
3.1. Spatial Distribution and Temporal Trends in SST and Its Variability
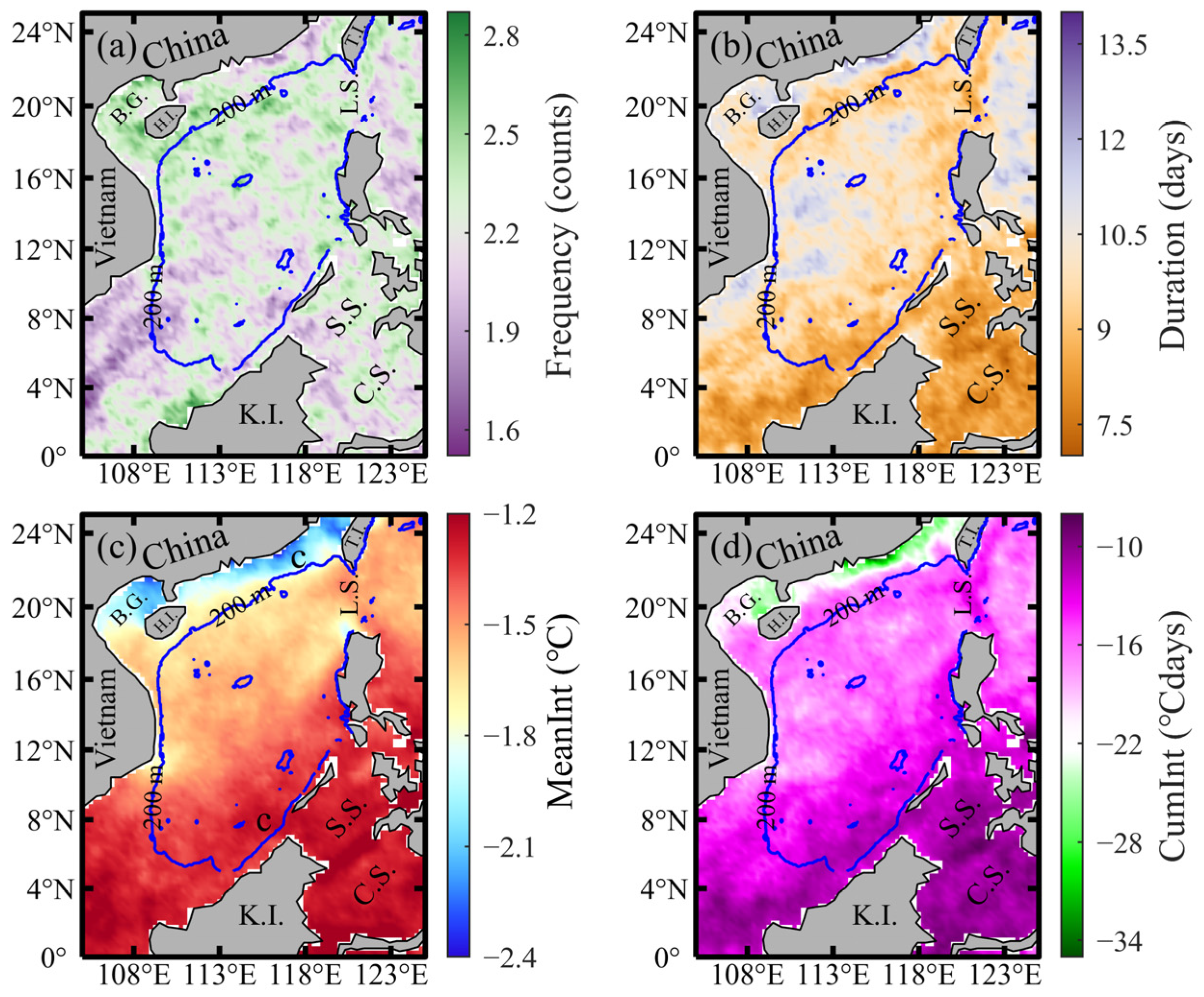
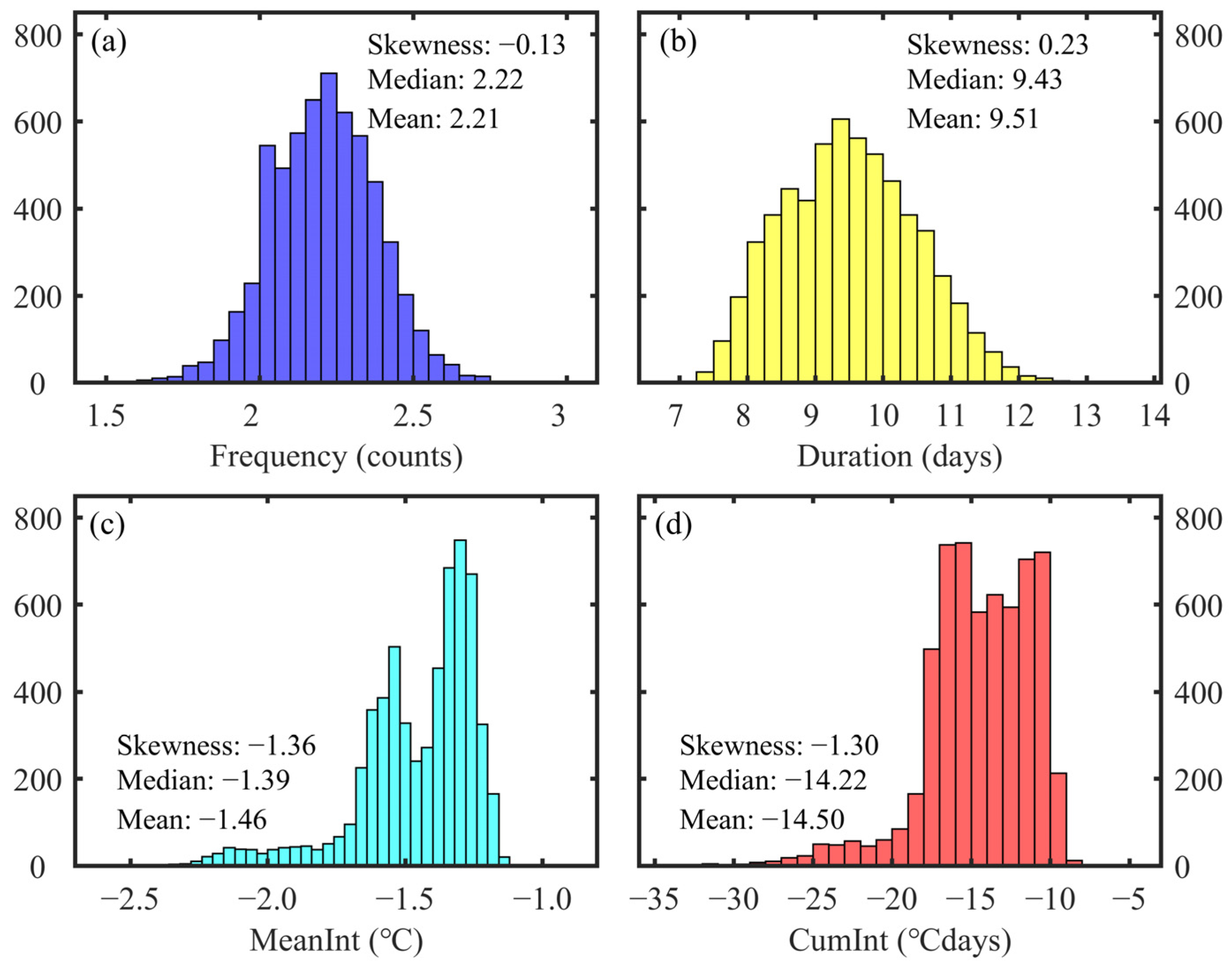
3.2. Spatial Distribution of MCS Characteristics
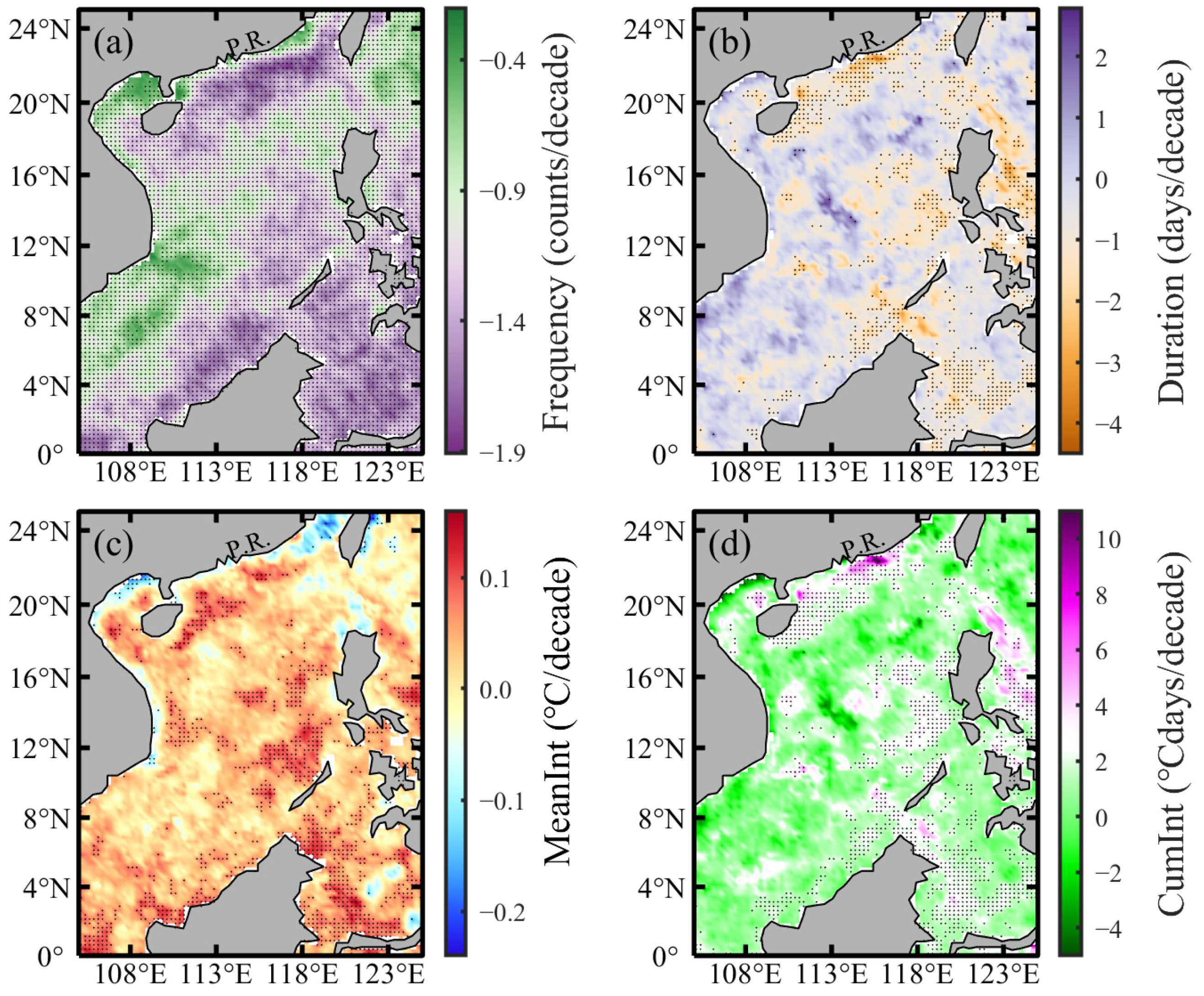
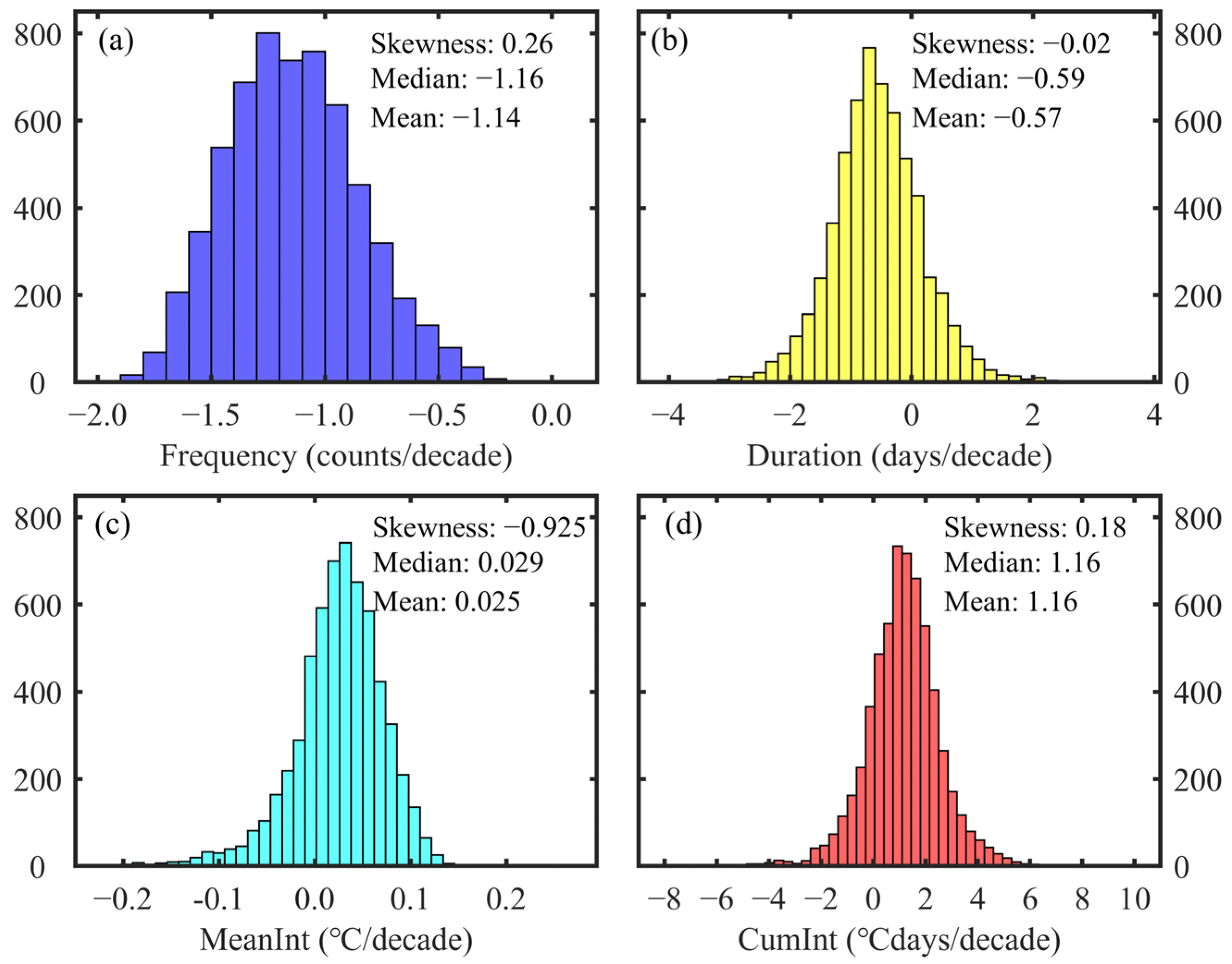
3.3. Spatial Distribution Trends of MCS Characteristics
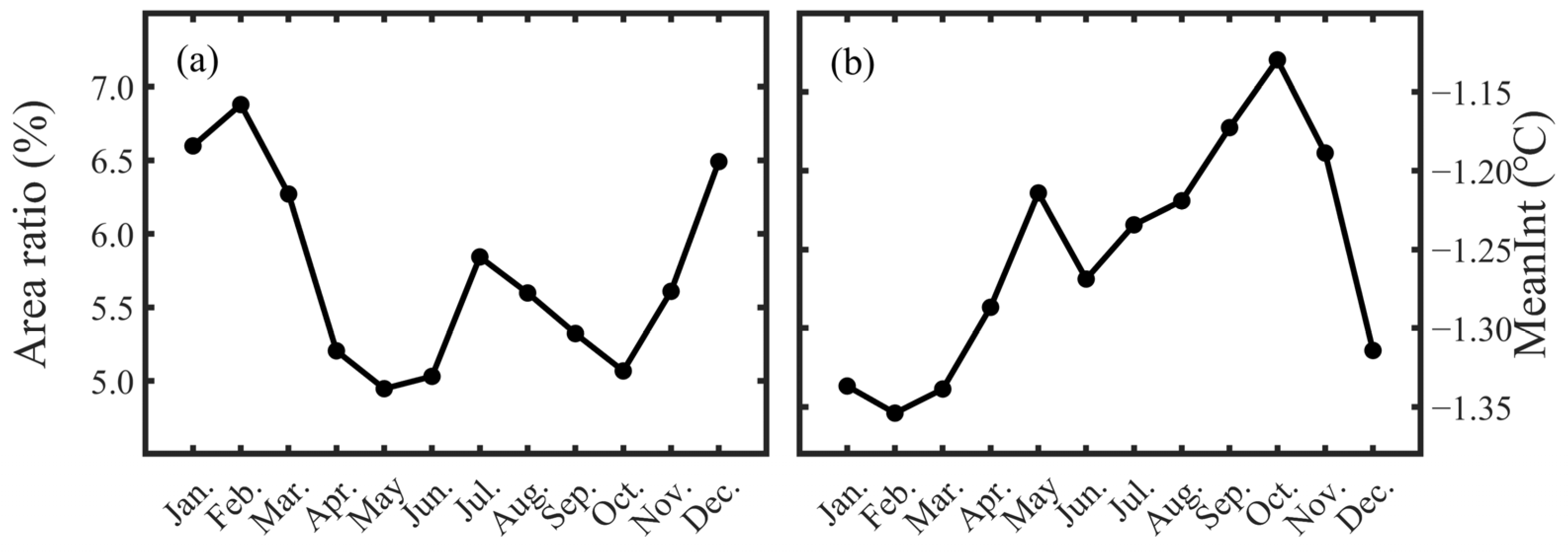
3.4. Seasonal Variations in Marine Cold Spells
4. Discussion
4.1. Selection of Climate Baseline Periods
4.2. Mechanisms of MCS Formation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IPCC. Summary for policymakers. In Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis; Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2021; Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar6/wg1/chapter/summary-for-policymakers/ (accessed on 25 March 2024).
- Drijfhout, S.; Bathiany, S.; Beaulieu, C.; Brovkin, V.; Claussen, M.; Huntingford, C.; Scheffer, M.; Sgubin, G.; Swingedouw, D. Catalogue of abrupt shifts in Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change climate models. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E5777–E5786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlegel, R.W.; Darmaraki, S.; Benthuysen, J.A.; Filbee-Dexter, K.; Oliver, E.C. Marine cold-spells. Prog. Oceanogr. 2021, 198, 102684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kajtar, J.B.; Alexander, L.V.; Pilo, G.S.; Holbrook, N.J. Understanding the changing nature of marine cold-spells. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2021GL097002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, T.P. Causes and consequences of winter mortality in fishes. J. Fish Biol. 2007, 71, 315–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Espinosa, P.; Donner, S. Predicting cold-water bleaching in corals: Role of temperature, and potential integration of light exposure. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2020, 642, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlas, M.E.; Deutsch, C.J.; de Wit, M.; Ward-Geiger, L.I. Florida Manatee Cold-Related Unusual Mortality Event, January–April 2010; Final Report to USFWS (grant 40181AG037); Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission: St. Petersburg, FL, USA, 2011; p. 138. Available online: https://downloads.regulations.gov/FWS-R4-ES-2015-0178-3824/content.pdf (accessed on 25 March 2024).
- Cavanaugh, K.C.; Kellner, J.R.; Forde, A.J.; Gruner, D.S.; Parker, J.D.; Rodriguez, W.; Feller, I.C. Poleward expansion of mangroves is a threshold response to decreased frequency of extreme cold events. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 111, 723–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecl, G.T.; Araújo, M.B.; Bell, J.D.; Blanchard, J.; Bonebrake, T.C.; Chen, I.-C.; Clark, T.D.; Colwell, R.K.; Danielsen, F.; Evengård, B.; et al. Biodiversity redistribution under climate change: Impacts on ecosystems and human well-being. Science 2017, 355, eaai9214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiswell, S.M. Global trends in marine heatwaves and cold spells: The impacts of fixed versus changing baselines. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2022, 127, e2022JC018757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Wang, C.; Fu, Y. Global marine heatwaves and cold-spells in present climate to future projections. Earth’s Futur. 2022, 10, e2022EF002787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalsin, M.; Walter, R.K.; Mazzini, P.L.F. Effects of basin-scale climate modes and upwelling on nearshore marine heatwaves and cold spells in the California Current. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 12389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciappa, A.C. Effects of Marine Heatwaves (MHW) and Cold Spells (MCS) on the surface warming of the Mediterranean Sea from 1989 to 2018. Prog. Oceanogr. 2022, 205, 102828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schopmeyer, S.A.; Lirman, D.; Bartels, E.; Byrne, J.; Gilliam, D.S.; Hunt, J.; Johnson, M.E.; Larson, E.A.; Maxwell, K.; Nedimyer, K.; et al. In situ coral nurseries serve as genetic repositories for coral reef restoration after an extreme cold-water event. Restor. Ecol. 2011, 20, 696–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, J.J.V.; Kenkel, C.D.; Bourne, D.G.; Despringhere, L.; Mocellin, V.J.L.; Bay, L.K. Physiological effects of heat and cold exposure in the common reef coral Acropora millepora. Coral Reefs 2020, 39, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D. Dynamics of the cold-water event off the southeast coast of the United States in the summer of 2003. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2006, 36, 1912–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Lee, M.-A.; Lee, K.-T.; Shao, K.-T. Adaptation of fisheries and mariculture management to extreme oceanic environmental changes and climate variability in Taiwan. Mar. Policy 2013, 38, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-A.; Yang, Y.-C.; Shen, Y.-L.; Chang, Y.; Tsai, W.-S.; Lan, K.-W.; Kuo, Y.-C. Effects of an unusual cold-water intrusion in 2008 on the catch of coastal fishing methods around Penghu Islands, Taiwan. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. 2014, 25, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colella, M.A.; Ruzicka, R.R.; Kidney, J.A.; Morrison, J.M.; Brinkhuis, V.B. Cold-water event of January 2010 results in catastrophic benthic mortality on patch reefs in the Florida Keys. Coral Reefs 2012, 31, 621–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, K.; Collins, J.; Paxton, C.H.; Hardy, R.; Downs, J. Weather patterns associated with green turtle hypothermic stunning events in St. Joseph Bay and Mosquito Lagoon, Florida. Phys. Geogr. 2014, 35, 134–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirhalla, D.E.; Sheridan, S.C.; Ransibrahmanakul, V.; Lee, C.C. Assessing cold-snap and mortality events in south Florida coastal ecosystems: Development of a biological cold stress index using satellite SST and weather pattern forcing. Estuaries Coasts 2014, 38, 2310–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lirman, D.; Schopmeyer, S.; Manzello, D.; Gramer, L.J.; Precht, W.F.; Muller-Karger, F.; Banks, K.; Barnes, B.; Bartels, E.; Bourque, A.; et al. Severe 2010 cold-water event caused unprecedented mortality to corals of the Florida reef tract and reversed previous survivorship patterns. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, H.J.; Hsien, Y.L.; Jeng, M.S.; Tsai, W.S.; Su, W.C.; Chen, C.A. Tropical fishes killed by the cold. Coral Reefs 2008, 27, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotterhos, K.E.; Markel, R.W. Oceanographic drivers of offspring abundance may increase or decrease reproductive variance in a temperate marine fish. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 5009–5026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, S.; Duarte, C.M.; Marbà, N.; Wernberg, T. Integrating within-species variation in thermal physiology into climate change ecology. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2019, 374, 20180550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donders, T.H.; de Boer, H.J.; Finsinger, W.; Grimm, E.C.; Dekker, S.C.; Reichart, G.J.; Wagner-Cremer, F. Impact of the Atlantic Warm Pool on precipitation and temperature in Florida during North Atlantic cold spells. Clim. Dyn. 2009, 36, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell-Staton, S.C.; Cheviron, Z.A.; Rochette, N.; Catchen, J.; Losos, J.B.; Edwards, S.V. Winter storms drive rapid phenotypic, regulatory, and genomic shifts in the green anole lizard. Science 2017, 357, 495–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlegel, R.W.; Oliver, E.C.; Wernberg, T.; Smit, A.J. Nearshore and offshore co-occurrence of marine heatwaves and cold-spells. Prog. Oceanogr. 2017, 151, 189–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuckett, C.A.; Wernberg, T. High latitude corals tolerate severe cold spell. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Wang, C. Marine heatwaves and cold-spells in global coral reef zones. Prog. Oceanogr. 2022, 209, 102920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, X.; Su, F.; Wu, W.; Chen, Z.; Shi, W. Spatial and temporal variability of thermal stress to China’s coral reefs in South China Sea. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2015, 25, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Dong, C.; Tan, W.; Liu, Y.; He, Y.; Wang, J. Vertical structure anomalies of oceanic eddies and eddy-induced transports in the South China Sea. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Wang, C. Variations in summer marine heatwaves in the South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2021, 126, e2021JC017792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Zhou, S.; Yang, J.; Gao, X.; Ji, J.; Dong, C. Artificial intelligence forecasting of marine heatwaves in the South China Sea using a combined U-Net and ConvLSTM system. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, W.; Xie, S.; Wang, D.; Taguchi, B.; Aiki, H.; Sasaki, H. Intraseasonal variability in sea surface height over the South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2010, 115, C04010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zu, T. Progress on shelf and slope circulation in the northern South China Sea. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2018, 61, 560–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Sun, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Xu, T.; Wei, Z.; Qu, T. Overview of the multi-layer circulation in the South China Sea. Prog. Oceanogr. 2019, 175, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, B.; Xiu, P.; Liu, N.; He, X.; Chai, F. Biological response to the interaction of a mesoscale eddy and the river plume in the northern South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2021, 126, e2021JC017244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Liu, Y.; Chen, G.; Tan, W.; Lin, X.; Guan, Y.; Dong, C. Three-dimensional properties of mesoscale cyclonic warm-core and anticyclonic cold-core eddies in the South China Sea. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2021, 40, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.; Qi, Y.; Qiu, C.; Luan, Z.; Wang, X.; Cen, X.; Yu, L.; Lian, S.; Shang, X. High-resolution observations of upwelling and front in Daya Bay, South China Sea. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X. Assessing the spatio-temporal features and mechanisms of symmetric instability activity probability in the central part of the South China Sea based on a regional ocean model. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Xue, H.; Chai, F. Asymmetric chlorophyll responses enhanced by internal waves near the Dongsha Atoll in the South China Sea. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2023, 41, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, T.; Mitsudera, H.; Yamagata, T. Intrusion of the North Pacific waters into the South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2000, 105, 6415–6424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, T.; Kim, Y.Y.; Yaremchuk, M.; Tozuka, T.; Ishida, A.; Yamagata, T. Can Luzon Strait transport play a role in conveying the impact of ENSO to the South China Sea? J. Clim. 2004, 17, 3644–3657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, T.; Du, Y.; Meyers, G.; Ishida, A.; Wang, D. Connecting the tropical Pacific with Indian Ocean through South China Sea. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L24609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, T.; Du, Y.; Sasaki, H. South China Sea throughflow: A heat and freshwater conveyor. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L23617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yihui, D.; Chongyin, L.; Yanju, L. Overview of the South China sea monsoon experiment. Adv. Atmospheric Sci. 2004, 21, 343–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Ling, Z.; Wang, C. Influence of tropical cyclones on seasonal ocean circulation in the South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114, C10022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajikawa, Y.; Wang, B. Interdecadal change of the South China Sea summer monsoon onset. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 3207–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, R.; Tan, H.; Qi, Q. Impacts of and adaptation to inter-decadal marine climate change in coastal China seas. Int. J. Clim. 2015, 36, 3770–3780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ren, G.; Wang, Q.; Mu, L.; Niu, Q. Marine heatwaves in the South China Sea: Tempo-Spatial pattern and its association with Large-Scale circulation. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Xu, K.; Zhu, C.; Liu, B. Diversity of marine heatwaves in the South China Sea regulated by ENSO phase. J. Clim. 2022, 35, 877–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, S.; Chen, T.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, W.; Li, S. Marine heatwaves impair the thermal refugia potential of marginal reefs in the northern South China Sea. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 825, 154100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, B.; Zeng, L.; He, Y.; Wu, Z.; Chen, J. Properties and drivers of marine heat waves in the northern South China Sea. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2022, 52, 917–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.; Xu, K.; Wang, L.; Liu, B.; Tam, C.-Y.; Liu, K.; Wang, W. Extremely long-lived marine heatwave in South China Sea during summer 2020: Combined effects of the seasonal and intraseasonal variations. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2023, 230, 104261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Yao, Y.; Wang, C. Response of future summer marine heatwaves in the South China Sea to enhanced western pacific subtropical high. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2023, 50, e2023GL103667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Tian, S.; Chen, Q.; Li, S.; Zeng, J.; Wei, Z.; Xie, S. Seasonal cycle of marine heatwaves in the northern South China Sea. Clim. Dyn. 2023, 61, 3367–3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Lao, Q.; Zhou, X.; Jin, G.; Chen, C.; Chen, F. Impacts of marine heatwave events on three distinct upwelling systems and their implications for marine ecosystems in the Northwestern South China Sea. Remote Sens. 2023, 16, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, R.W.; Smith, T.M.; Liu, C.; Chelton, D.B.; Casey, K.S.; Schlax, M.G. Daily high-resolution-blended analyses for sea surface temperature. J. Clim. 2007, 20, 5473–5496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banzon, V.; Smith, T.M.; Chin, T.M.; Liu, C.; Hankins, W. A long-term record of blended satellite and in situ sea-surface temperature for climate monitoring, modeling and environmental studies. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2016, 8, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Liu, C.; Banzon, V.; Freeman, E.; Graham, G.; Hankins, B.; Smith, T.; Zhang, H.-M. Improvements of the Daily Optimum Interpolation Sea Surface Temperature (DOISST) Version 2.1. J. Clim. 2021, 34, 2923–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Benthuysen, J.; A Smith, G.; Spillman, C.M.; Steinberg, C.R. Subseasonal prediction of the 2020 Great Barrier Reef and Coral Sea marine heatwave. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 124050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holbrook, N.J.; Hernaman, V.; Koshiba, S.; Lako, J.; Kajtar, J.B.; Amosa, P.; Singh, A. Impacts of marine heatwaves on tropical western and central Pacific Island nations and their communities. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2021, 208, 103680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobday, A.J.; Alexander, L.V.; Perkins, S.E.; Smale, D.A.; Straub, S.C.; Oliver, E.C.J.; Benthuysen, J.A.; Burrows, M.T.; Donat, M.G.; Feng, M.; et al. A hierarchical approach to defining marine heatwaves. Prog. Oceanogr. 2016, 141, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holbrook, N.J.; Gupta, A.S.; Oliver, E.C.J.; Hobday, A.J.; Benthuysen, J.A.; Scannell, H.A.; Smale, D.A.; Wernberg, T. Keeping pace with marine heatwaves. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 482–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, E.C.; Benthuysen, J.A.; Darmaraki, S.; Donat, M.G.; Hobday, A.J.; Holbrook, N.J.; Schlegel, R.W.; Gupta, A.S. Marine Heatwaves. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2021, 13, 313–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacox, M.G. Marine heatwaves in a changing climate. Nature 2019, 571, 485–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiswell, S.M. Atmospheric wavenumber-4 driven South Pacific marine heat waves and marine cool spells. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Marin, M. A MATLAB toolbox to detect and analyze marine heatwaves. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yang, H.; Liu, Q. Regional dynamics of seasonal variability in the South China Sea. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2001, 31, 272–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Xie, Q.; Wang, D.; Liu, W.T. Summer upwelling in the South China Sea and its role in regional climate variations. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2003, 108, 3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, C.; Sun, W.; Ji, J.; Zhu, Y. Historical Marine Cold Spells in the South China Sea: Characteristics and Trends. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16071171
Li C, Sun W, Ji J, Zhu Y. Historical Marine Cold Spells in the South China Sea: Characteristics and Trends. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(7):1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16071171
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Chunhui, Wenjin Sun, Jinlin Ji, and Yuxin Zhu. 2024. "Historical Marine Cold Spells in the South China Sea: Characteristics and Trends" Remote Sensing 16, no. 7: 1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16071171
APA StyleLi, C., Sun, W., Ji, J., & Zhu, Y. (2024). Historical Marine Cold Spells in the South China Sea: Characteristics and Trends. Remote Sensing, 16(7), 1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16071171