Emission-Based Machine Learning Approach for Large-Scale Estimates of Black Carbon in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
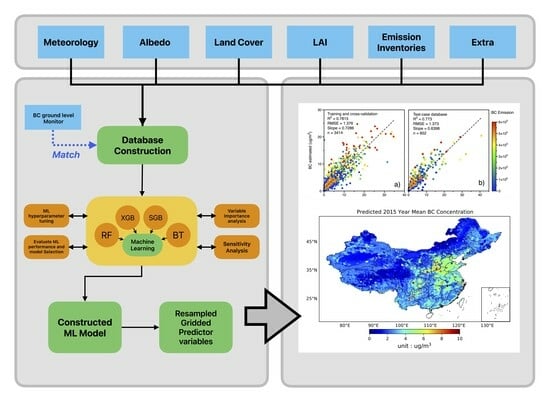
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Utilization
2.1.1. BC Ground-Based Measurements
2.1.2. Satellite Products
2.1.3. Meteorological and Other Parameters
2.1.4. Gridded Emission Inventory
2.2. Data Integration and Database Creation
2.3. Machine Learning Algorithms
2.3.1. Boosting Algorithms
2.3.2. Random Forest (RF)
2.4. Model Training, Cross-Validation, and Testing
2.5. Variable Importance Measures
3. Results and Discussions
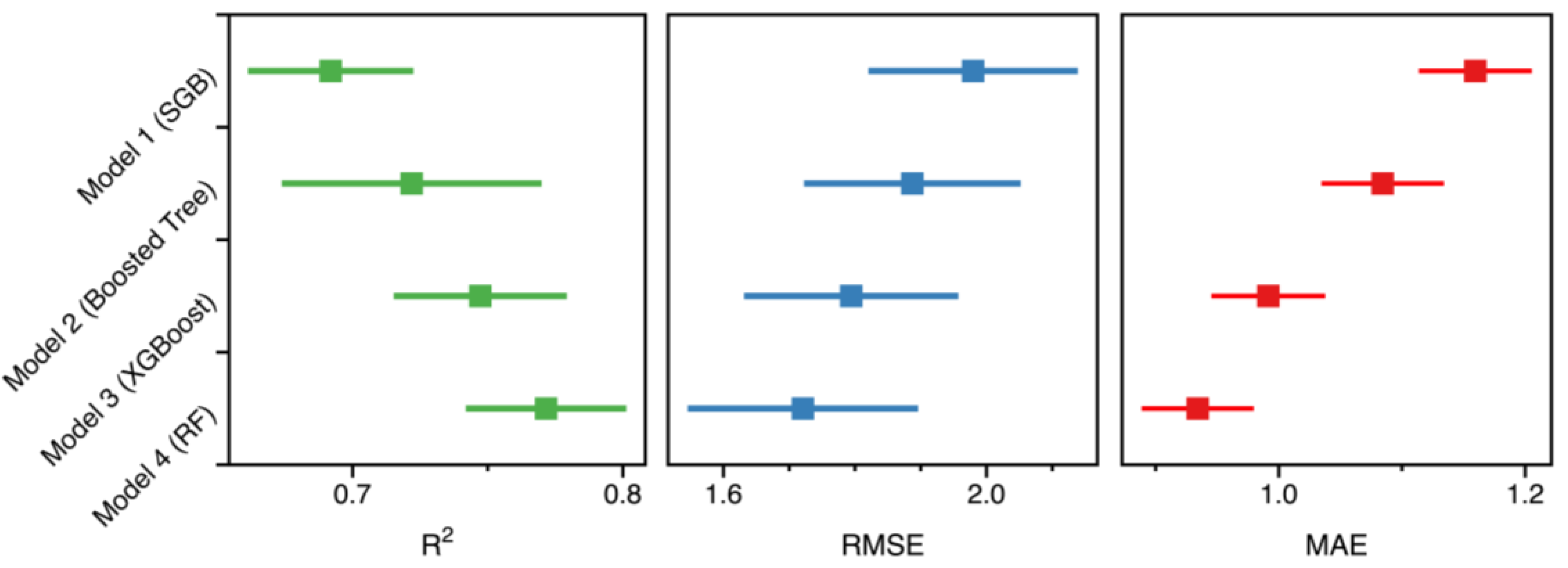
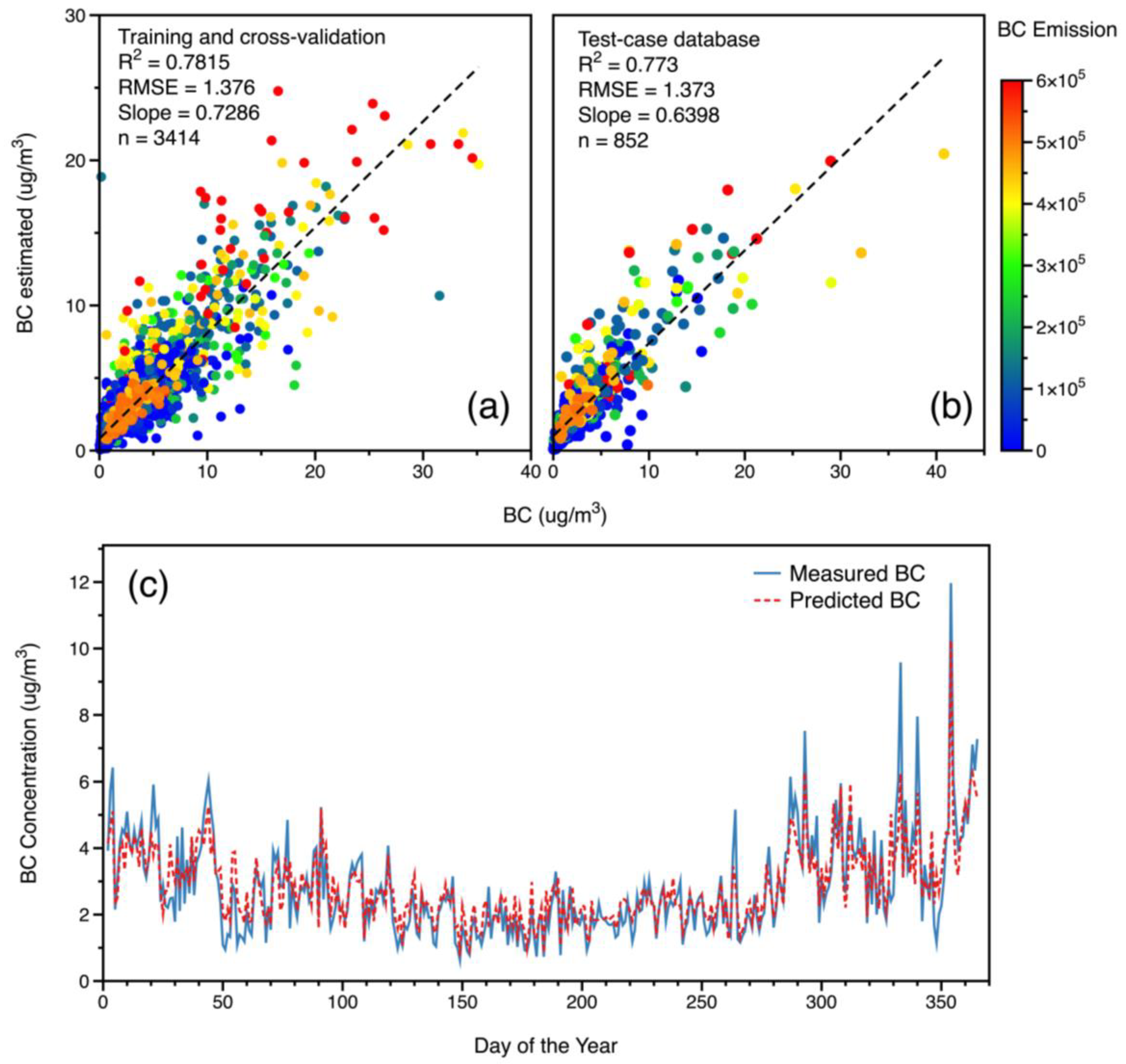
3.1. Model Performance
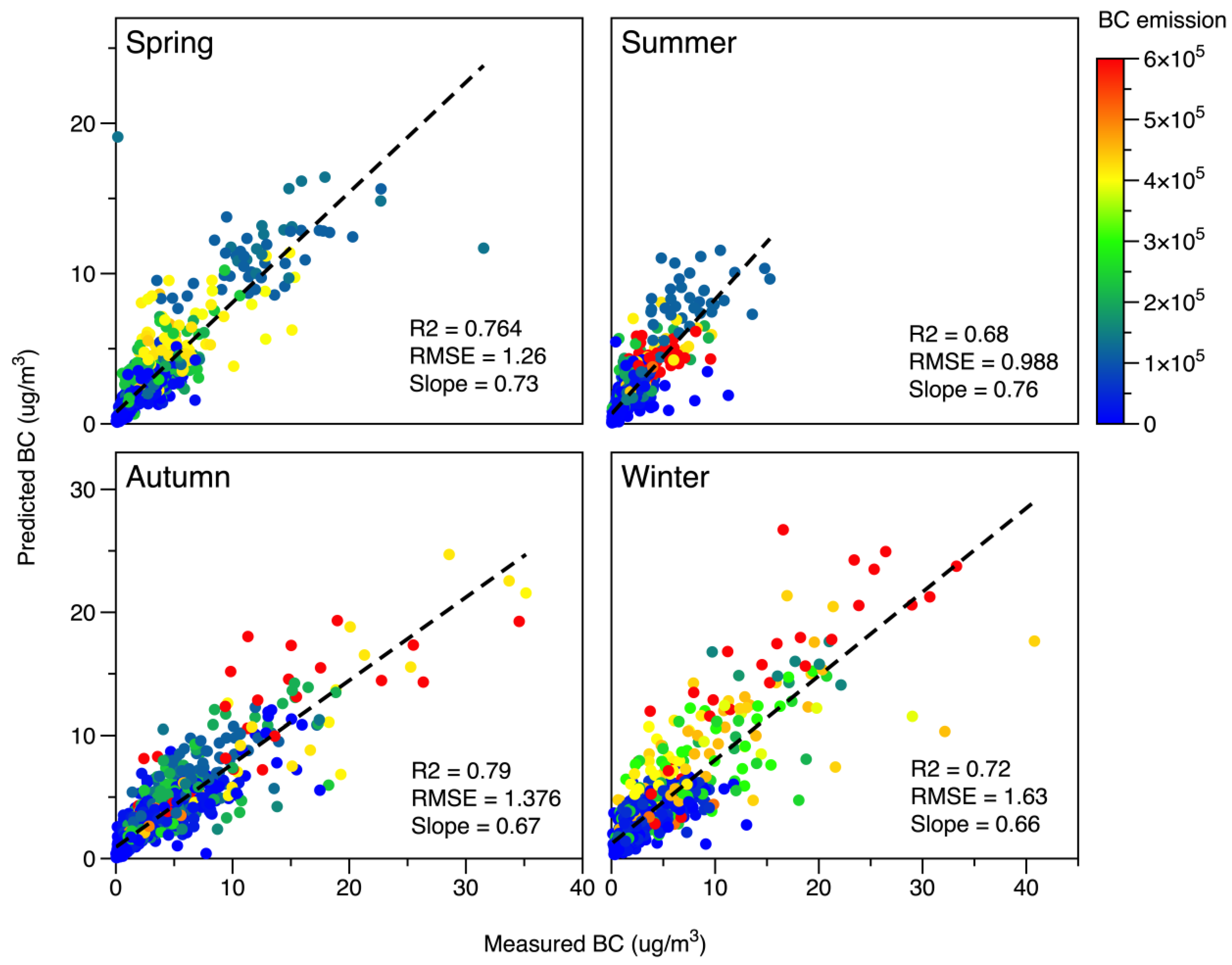
3.2. Seasonal Model Validation
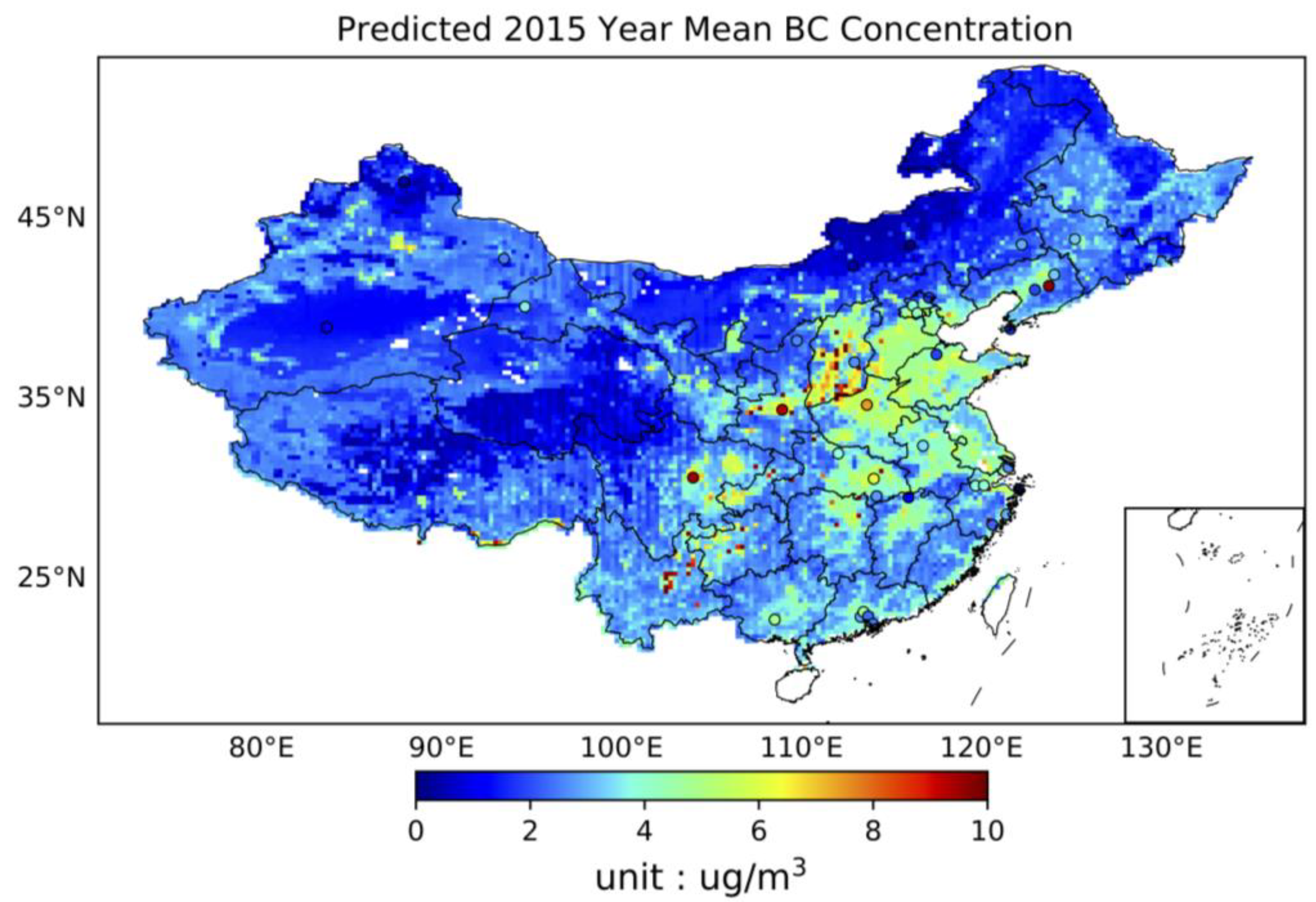
3.3. BC Spatial Distribution
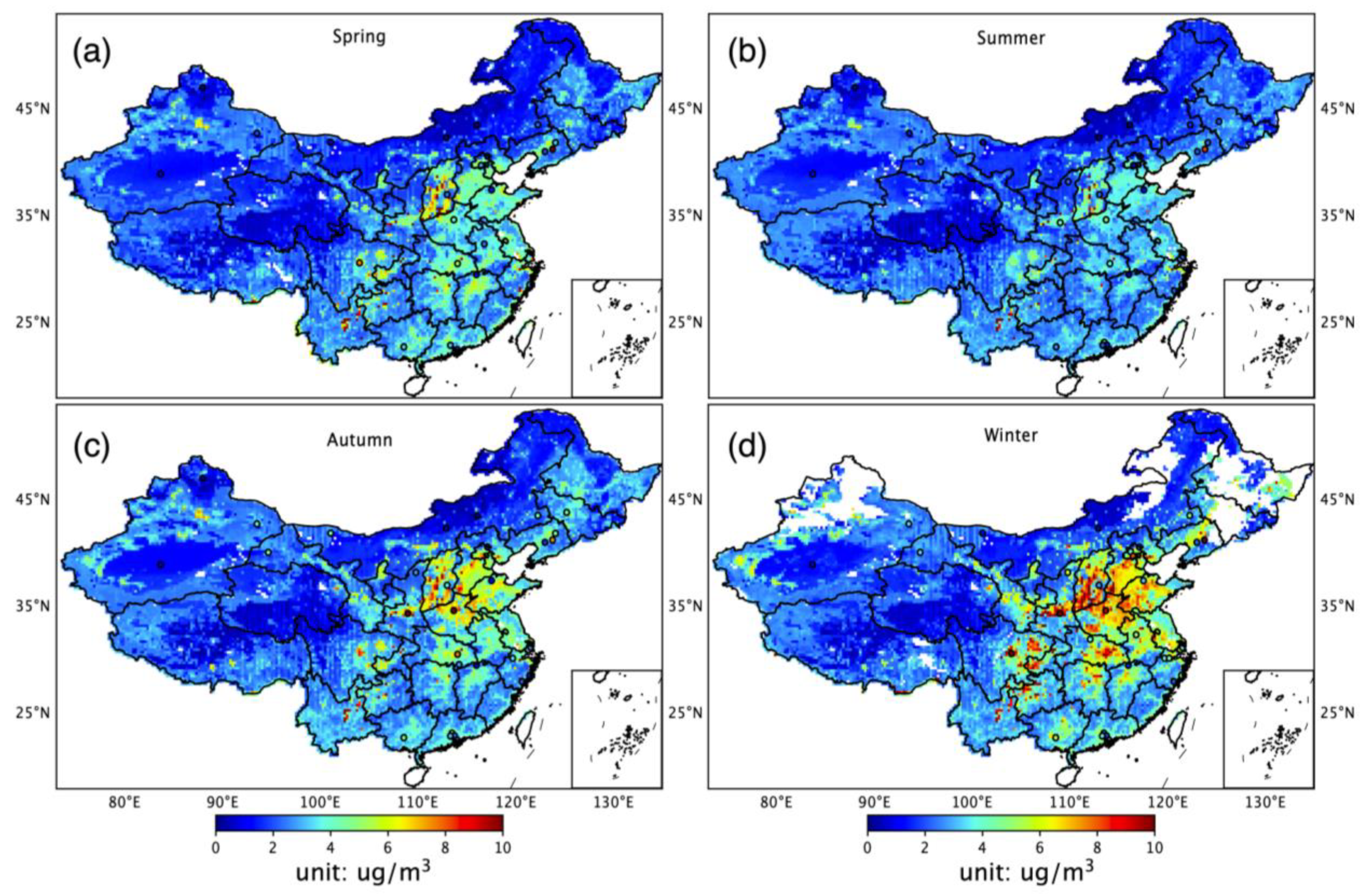
3.4. Spatial Distribution of Seasonal BC Concentration
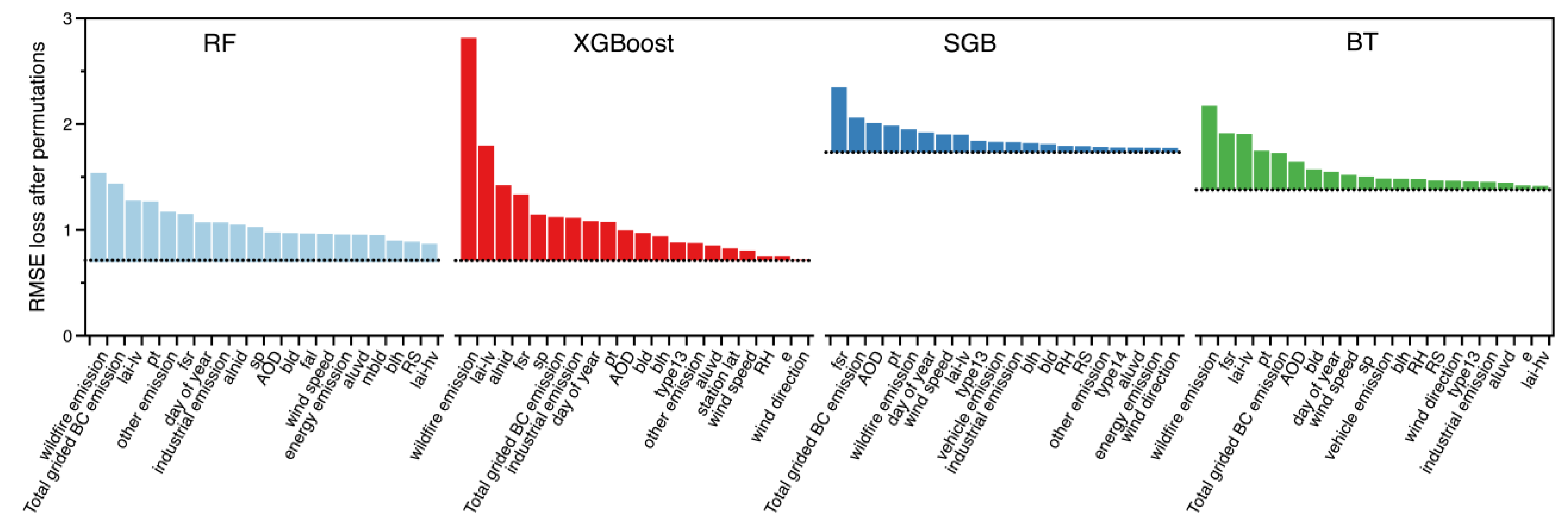
3.5. Variable Importance
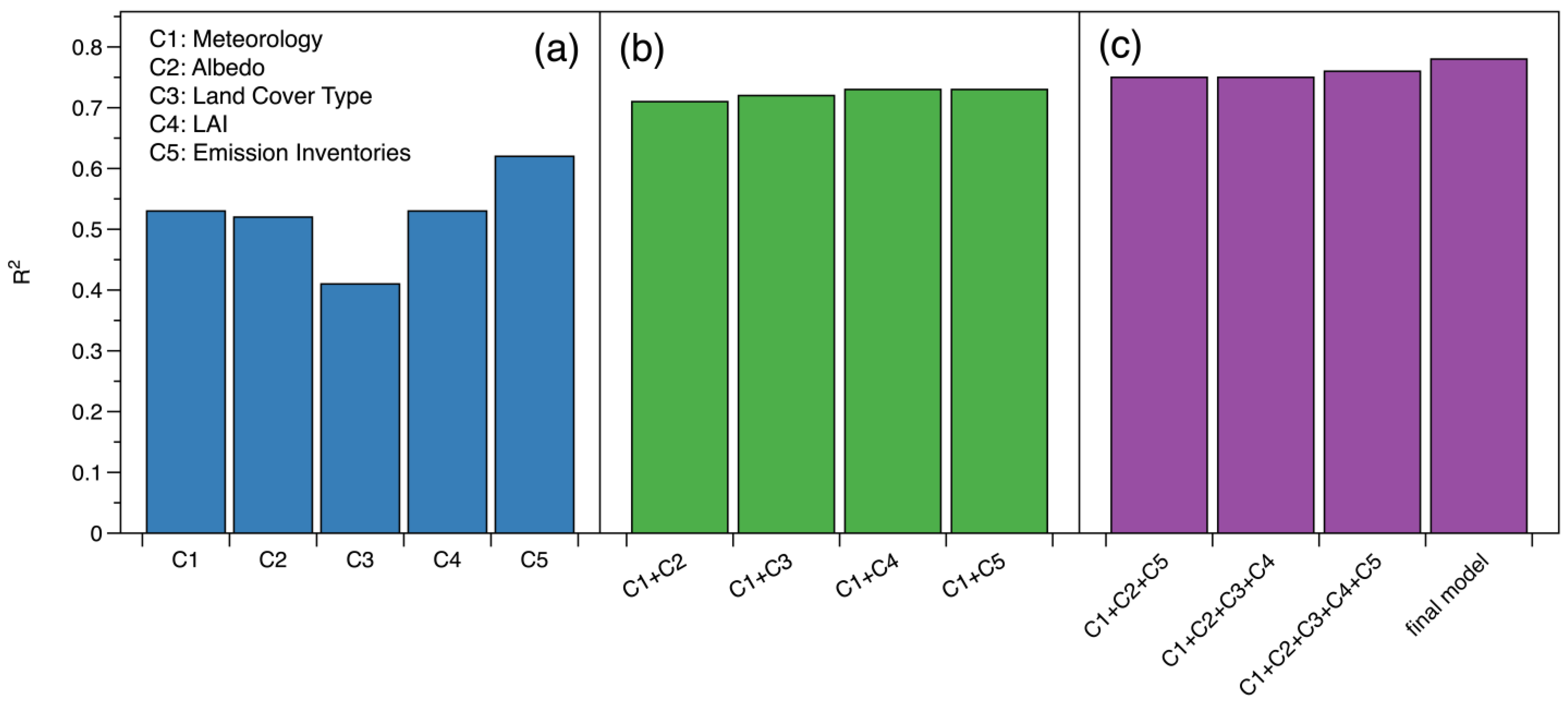
3.6. Sensitivities Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Takemura, T.; Suzuki, K. Weak global warming mitigation by reducing black carbon emissions. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeganeh, B.; Khuzestani, R.B.; Taheri, A.; Schauer, J.J. Temporal trends in the spatial-scale contributions to black carbon in a Middle Eastern megacity. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 792, 148364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Wang, Z.; Yu, F.; Pan, X.; Li, J.; Ge, B.; Wang, Z.; Hu, M.; Yang, W.; Chen, H. Estimation of atmospheric aging time of black carbon particles in the polluted atmosphere over central-eastern China using microphysical process analysis in regional chemical transport model. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 163, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.Y.; Wu, C.; Wu, D.; Cheng, C.; Li, M.; Li, L.; Deng, T.; Yu, J.Z.; Li, Y.J.; Zhou, Q. Amplification of black carbon light absorption induced by atmospheric aging: Temporal variation at seasonal and diel scales in urban Guangzhou. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 2445–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, T.; Hu, M.; Du, Z.; Zhao, G.; Shang, D.; Zheng, J.; Qin, Y.; Li, M.; Wu, Y.; Zeng, L. Strong Light Absorption Induced by Aged Biomass Burning Black Carbon over the Southeastern Tibetan Plateau in Pre-monsoon Season. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2020, 2020, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Baumgartner, J.; Zhang, Y.; Schauer, J.J.; Huang, W.; Wang, Y.; Ezzati, M. Highway proximity and black carbon from cookstoves as a risk factor for higher blood pressure in rural China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 13229–13234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, M.; Hansen, J.; Koch, D.; Lacis, A.; Ruedy, R.; Dubovik, O.; Holben, B.; Chin, M.; Novakov, T. Global atmospheric black carbon inferred from AERONET. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 6319–6324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, G.L.; Dubovik, O.; Holben, B.N.; Clothiaux, E.E. Inferring black carbon content and specific absorption from Aerosol Robotic Network (AERONET) aerosol retrievals. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2005, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chen, J.; Wang, L.; Melluki, W.; Zhou, H. Aerosol single scattering albedo affected by chemical composition: An investigation using CRDS combined with MARGA. Atmos. Res. 2013, 124, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Tian, Q.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Li, K.; Li, L. Estimate of aerosol absorbing components of black carbon, brown carbon, and dust from ground-based remote sensing data of sun-sky radiometers. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 6534–6543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovik, O.; Herman, M.; Holdak, A.; Lapyonok, T.; Tanré, D.; Deuzé, J.; Ducos, F.; Sinyuk, A.; Lopatin, A. Statistically optimized inversion algorithm for enhanced retrieval of aerosol properties from spectral multi-angle polarimetric satellite observations. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2011, 4, 975–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, F.; Cheng, T.; Li, Y.; Gu, X.; Guo, H.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gao, J. Retrieval of black carbon aerosol surface concentration using satellite remote sensing observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 226, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Che, H.; Derimian, Y.; Dubovik, O.; Schuster, G.L.; Chen, C.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Guo, B.; Zhang, X. Retrievals of fine mode light-absorbing carbonaceous aerosols from POLDER/PARASOL observations over East and South Asia. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 247, 111913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brajard, J.; Jamet, C.; Moulin, C.; Thiria, S. Use of a neuro-variational inversion for retrieving oceanic and atmospheric constituents from satellite ocean colour sensor: Application to absorbing aerosols. Neural Netw. 2006, 19, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, F.; Li, Y.; Cheng, T.; Gao, J.; Yuan, S. Estimating the columnar concentrations of black carbon aerosols in China using MODIS products. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 11025–11036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, S.; Bao, F.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.J.R.S. Severe Biomass-Burning Aerosol Pollution during the 2019 Amazon Wildfire and Its Direct Radiative-Forcing Impact: A Space Perspective from MODIS Retrievals. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogoi, M.M.; Babu, S.S.; Imasu, R.; Hashimoto, M. Satellite (GOSAT-2 CAI-2) retrieval and surface (ARFINET) observations of aerosol black carbon over India. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2023, 23, 8059–8079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Rasch, P.J.; Easter, R.C.; Singh, B.; Zhang, R.; Ma, P.L.; Qian, Y.; Ghan, S.J.; Beagley, N. Using an explicit emission tagging method in global modeling of source-receptor relationships for black carbon in the Arctic: Variations, sources, and transport pathways. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 12,888–12,909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Gong, S.; Jia, C.; Lavoué, D. Relative contributions of anthropogenic emissions to black carbon aerosol in the Arctic. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Jacob, D.J.; Fisher, J.A.; Mao, J.; Leibensperger, E.; Carouge, C.; Le Sager, P.; Kondo, Y.; Jimenez, J.; Cubison, M. Sources of carbonaceous aerosols and deposited black carbon in the Arctic in winter-spring: Implications for radiative forcing. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 12453–12473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Chin, M.; West, J.J.; Atherton, C.S.; Bellouin, N.; Bergmann, D.; Bey, I.; Bian, H.; Diehl, T.; Forberth, G. A multimodel assessment of the influence of regional anthropogenic emission reductions on aerosol direct radiative forcing and the role of intercontinental transport. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 700–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, M.; Diehl, T.; Tan, Q.; Prospero, J.; Kahn, R.; Remer, L.; Yu, H.; Sayer, A.; Bian, H.; Geogdzhayev, I. Multi-decadal aerosol variations from 1980 to 2009: A perspective from observations and a global model. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 3657–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, B.; Jiang, F.; Wang, T.; Li, S.; Zhu, B. Investigation on the direct radiative effect of fossil fuel black-carbon aerosol over China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2011, 104, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhao, C.; Liu, X.; Zhang, M.; Leung, L.R. WRF-Chem simulations of aerosols and anthropogenic aerosol radiative forcing in East Asia. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 92, 250–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Hu, Z.; Qian, Y.; Ruby Leung, L.; Huang, J.; Huang, M.; Jin, J.; Flanner, M.; Zhang, R.; Wang, H. Simulating black carbon and dust and their radiative forcing in seasonal snow: A case study over North China with field campaign measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 11475–11491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Kang, S.; Chen, D.; Ji, Z.; Tripathee, L.; Chen, X.; Du, W.; Qiu, G. Quantifying the contributions of various emission sources to black carbon and assessment of control strategies in western China. Atmos. Res. 2019, 215, 178–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, H.; Smith, S.J.; Ma, P.-L.; Rasch, P.J. Source attribution of black carbon and its direct radiative forcing in China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 4319–4336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Paciorek, C.J.; Koutrakis, P. Estimating regional spatial and temporal variability of PM2. 5 concentrations using satellite data, meteorology, and land use information. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 886–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, G.; Meng, X.; He, K.; Liu, Y. Random forest models for PM2. 5 speciation concentrations using MISR fractional AODs. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 034056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, G.; Murray, N.L.; Tong, D.; Fu, J.S.; Hu, X.; Lee, P.; Meng, X.; Chang, H.H.; Liu, Y. Satellite-based daily PM2. 5 estimates during fire seasons in Colorado. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 8159–8171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, Q.; Koutrakis, P.; Schwartz, J. A hybrid prediction model for PM2. 5 mass and components using a chemical transport model and land use regression. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 131, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Hand, J.L.; Schichtel, B.A.; Liu, Y. Space-time trends of PM2. 5 constituents in the conterminous United States estimated by a machine learning approach, 2005–2015. Environ. Int. 2018, 121, 1137–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Lau, A.H.; Fung, J.H.; Zheng, J.; Zhong, L.; Louie, P.K.K. Ozone source apportionment (OSAT) to differentiate local regional and super-regional source contributions in the Pearl River Delta region, China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lau, A.K.; Fung, J.C.; Zheng, J.; Liu, S. Importance of NOx control for peak ozone reduction in the Pearl River Delta region. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 9428–9443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, X.; Deng, X.; Gao, J. The impact of peripheral circulation characteristics of typhoon on sustained ozone episodes over the Pearl River Delta region, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 3861–3873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Shen, H.; Li, T.; Li, Z.; Li, S.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, H.; Tan, W.; Yang, Q.; Wang, J.; et al. Deep learning in environmental remote sensing: Achievements and challenges. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 241, 111716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Y.; Lu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Hu, X.; Wang, F.; Li, L.; Gu, S. A review of advances in the retrieval of aerosol properties by remote sensing multi-angle technology. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 244, 117928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Huang, W.; Li, Z.; Xue, W.; Peng, Y.; Sun, L.; Cribb, M. Estimating 1-km-resolution PM2. 5 concentrations across China using the space-time random forest approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 231, 111221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drinovec, L.; Močnik, G.; Zotter, P.; PrÈvÙt, A.S.H.; Ruckstuhl, C.; Coz, E.; Rupakheti, M.; Sciare, J.; Müller, T.J.; Wiedensohler, A.; et al. The “dual-spot” Aethalometer: An improved measurement of aerosol black carbon with real-time loading compensation. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 8, 1965–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Knyazikhin, Y.; Park, T.; Yan, K.; Lyapustin, A.I.; Wang, Y.; Yang, B.; Myneni, R.B. Prototyping of LAI and FPAR Retrievals from MODIS Multi-Angle Implementation of Atmospheric Correction (MAIAC) Data. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Li, S.; Knibbs, L.D.; Hamm, N.A.; Cao, W.; Li, T.; Guo, J.; Ren, H.; Abramson, M.J.; Guo, Y. A machine learning method to estimate PM2. 5 concentrations across China with remote sensing, meteorological and land use information. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stafoggia, M.; Bellander, T.; Bucci, S.; Davoli, M.; De Hoogh, K.; De’Donato, F.; Gariazzo, C.; Lyapustin, A.; Michelozzi, P.; Renzi, M. Estimation of daily PM10 and PM2. 5 concentrations in Italy, 2013–2015, using a spatiotemporal land-use random-forest model. Environ. Int. 2019, 124, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mhawish, A.; Banerjee, T.; Sorek-Hamer, M.; Bilal, M.; Lyapustin, A.I.; Chatfield, R.; Broday, D.M. Estimation of high-resolution PM2. 5 over the indo-gangetic plain by fusion of satellite data, meteorology, and land use variables. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 7891–7900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedl, M.A.; Sulla-Menashe, D.; Tan, B.; Schneider, A.; Ramankutty, N.; Sibley, A.M.; Huang, X. MODIS Collection 5 global land cover: Algorithm refinements and characterization of new datasets. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 168–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidhu, N.; Pebesma, E.; Wang, Y.-C. Usability study to assess the IGBP land cover classification for Singapore. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dee, D.P.; Uppala, S.M.; Simmons, A.J.; Berrisford, P.; Poli, P.; Kobayashi, S.; Andrae, U.; Balmaseda, M.; Balsamo, G.; Bauer, D.P. The ERA-Interim reanalysis: Configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 553–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Li, Z.; Cribb, M.; Huang, W.; Xue, W.; Sun, L.; Guo, J.; Peng, Y.; Li, J.; Lyapustin, A. Improved 1 km resolution PM 2.5 estimates across China using enhanced space–time extremely randomized trees. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 3273–3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cape, J.; Coyle, M.; Dumitrean, P. The atmospheric lifetime of black carbon. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 59, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Tao, S.; Wang, W.; Liu, J.; Shen, H.; Shen, G.; Wang, B.; Liu, X.; Li, W.; Huang, Y. Black carbon emissions in China from 1949 to 2050. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 7595–7603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Shao, M.; Chen, W.; Yuan, B.; Lu, S.; Zhang, Q.; Zeng, L.; Wang, Q. A temporally and spatially resolved validation of emission inventories by measurements of ambient volatile organic compounds in Beijing, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 5871–5891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Huang, Y.; Shen, H.; Chen, Y.; Ru, M.; Chen, Y.; Lin, N.; Su, S.; Zhuo, S.; Zhong, Q. Modeling temporal variations in global residential energy consumption and pollutant emissions. Appl. Energy 2016, 184, 820–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schapire, R.E. The strength of weak learnability. Mach. Learn. 1990, 5, 197–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natekin, A.; Knoll, A. Gradient boosting machines, a tutorial. Front. Neurorobotics 2013, 7, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2004, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, M. Building predictive models in R using the caret package. J. Stat. Softw. 2008, 28, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, A.; Rudin, C.; Dominici, F. All Models are Wrong, but Many are Useful: Learning a Variable’s Importance by Studying an Entire Class of Prediction Models Simultaneously. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2019, 20, 1–81. [Google Scholar]
- Kuenzer, C.; Zhang, J.; Tetzlaff, A.; Van Dijk, P.; Voigt, S.; Mehl, H.; Wagner, W. Uncontrolled coal fires and their environmental impacts: Investigating two arid mining regions in north-central China. Appl. Geogr. 2007, 27, 42–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Xie, S.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, J.; Zhang, L.; Lei, X.; Zhong, L.; Hao, Y.; Shi, F. Characteristics and sources of carbonaceous aerosol across urban and rural sites in a rapidly urbanized but low-level industrialized city in the Sichuan Basin, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 26646–26663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Kong, S.; Wu, F.; Cheng, Y.; Zheng, S.; Qin, S.; Liu, X.; Yan, Q.; Zheng, H.; Zheng, M. The moving of high emission for biomass burning in China: View from multi-year emission estimation and human-driven forces. Environ. Int. 2020, 142, 105812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Ma, Y.; Ma, L. Utilization of straw in biomass energy in China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2007, 11, 976–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Li, J.; Yang, X.; Jin, J. Wheat straw burning and its associated impacts on Beijing air quality. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2008, 51, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Li, Y.; Gao, J.; Bao, F. A New Coupling Method for PM2. 5 Concentration Estimation by the Satellite-Based Semiempirical Model and Numerical Model. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Liu, S.; Bashiri Khuzestani, R.; Huang, K.; Bao, F. Emission-Based Machine Learning Approach for Large-Scale Estimates of Black Carbon in China. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 837. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16050837
Li Y, Liu S, Bashiri Khuzestani R, Huang K, Bao F. Emission-Based Machine Learning Approach for Large-Scale Estimates of Black Carbon in China. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(5):837. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16050837
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Ying, Sijin Liu, Reza Bashiri Khuzestani, Kai Huang, and Fangwen Bao. 2024. "Emission-Based Machine Learning Approach for Large-Scale Estimates of Black Carbon in China" Remote Sensing 16, no. 5: 837. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16050837
APA StyleLi, Y., Liu, S., Bashiri Khuzestani, R., Huang, K., & Bao, F. (2024). Emission-Based Machine Learning Approach for Large-Scale Estimates of Black Carbon in China. Remote Sensing, 16(5), 837. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16050837