Abstract
Land subsidence is an environmental hazard occurring gradually over time, potentially posing significant threats to the structural stability of civilian buildings and essential infrastructures. This study presented a workflow using the SBAS-PSInSAR approach to analyze surface deformation in the Choushui River Fluvial Plain (CRFP) based on Sentinel-1 SAR images and validated against precise leveling. Integrating the InSAR results with hydrogeological data, such as groundwater levels (GWLS), multilayer compactions, and borehole loggings, a straightforward model was proposed to estimate appropriate groundwater level drops to minimize further subsidence. The results showed a huge subsidence bowl centered in Yunlin, with maximal sinking at an average 60 mm/year rate. High-resolution subsidence maps enable the quantitative analyses of safety issues for Taiwan High-Speed Rail (THSR) across the areas with considerable subsidence. In addition, the analysis of hydrogeological data revealed that half of the major compaction in the study area occurred at shallow depths that mainly included the first and second aquifers. Based on a maximal subsidence control rate of 40 mm/year specified in the CRFP, the model results indicated that the groundwater level drops from wet to dry seasons needed to be maintained from 3 to 5 m for the shallowest aquifer and 4–6 m for Aquifers 3 and 4. The workflow demonstrated the compatibility of InSAR with traditional geodetic methods and the effectiveness of integrating multiple data sources to assess the complex nature of land subsidence in the CRFP.
1. Introduction
Land subsidence, the gradual settlement of the ground surface on a large scale, is an environmental issue caused by various natural or anthropogenic factors [1,2,3]. Tectonic activities, soil consolidation, or other physicochemical processes might trigger land subsidence naturally. On the other hand, human activities, including groundwater or oil extraction, mining, or construction loading, are also the causes of ground surface settlement. Among these causes, long-term groundwater extraction stands out as the primary trigger of land subsidence, especially in populated and developed areas where the geological foundation is constituted by the recent alluvial, marine, or lacustrine deposits [2,4,5]. The consequences of land subsidence are serious since it significantly affects the buildings or transport infrastructures and might lead to inundation in low-lying areas, resulting in heavy financial burdens for local authorities. Cities or regions like the San Joaquin Valley (San Francisco) [6,7], Mexico City (Mexico) [8], Beijing (China) [9], Hanoi (Vietnam) [10], and Pingtung County (Taiwan) [11], among others, are examples of land subsidence due to excessive groundwater extraction.
The Choushui River Fluvial Plain (CRFP), one of the main agricultural areas in Taiwan, is no exception. This region is well-known for severe land subsidence due to massive groundwater exploitation [12,13,14,15], which is an urgent issue since it might potentially pose a serious threat to the Taiwan High-Speed Rail (THSR) passing through this region [16]. Groundwater exploitation leads to sediment compression [17], which might trigger an angular deflection if it occurs below the foundation of the railway pillars [18,19,20], severely affecting the THSR operation safety. Because the THSR is a continuous railway system, breakdown at any section might stagnate the entire operation; hence, THSR safety standards must be a top priority [16]. Therefore, establishing a monitoring network is necessary, especially near the THSR, to promptly obtain information on subsidence progress, based on which the local authorities can introduce appropriate policies to control the influencing factors and mitigate the sinking rates.
The subsidence monitoring network previously utilized traditional geodetic methods, such as the Continuous Global Positioning System (CGPS) and a precise leveling survey. However, the sparse density of measuring points and the time between sampling constrain the effectiveness of these techniques [21]. For example, the measurements provided by these methods are often interpolated to generate a deformation map. The interpolation process might introduce errors proportional to the distance among stations, especially when missing data exist [22]. Differential Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (DInSAR) techniques provide alternatives to overcome these intrinsic limitations. The DInSAR technique extracts surface deformation in the phase difference of at least two SAR images acquired on different days over an identical area [23] and provides wide-coverage measurements. However, DInSAR performance is significantly impaired by temporal decorrelation and atmospheric delay [24]. It is recognized that paddy fields, whose surface properties vary seasonally, primarily cover the land surface of the CRFP and may cause spatiotemporal decorrelation effects, as previously mentioned [13,25]. For this reason, time series InSAR techniques, including Permanent Scatter Interferometry (PSI) [26,27] and Small Baseline Subset (SBAS) [28], which exploit a great number of SAR images acquired in the same area over time and extract information from pixels with stable scattering properties, are developed to reduce the effects of such degradation problems [23,29]. PS-InSAR exploits pixels corresponding to stable targets, such as buildings, bridges, and other infrastructures, which contain phase information with a high signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). These points are identified based on their phase stability and amplitude coherence across all images, quantified by the amplitude dispersion index (ADI) [26]. As a result, PSI-based techniques are often preferred for monitoring subsidence in urban areas and assessing the health of infrastructures and railways [30,31,32,33]. On the other hand, SBAS-InSAR utilizes distributed scatterers (DSs), often located in non-urban areas, such as asphalt, agricultural fields, or rock surfaces, consisting of a coherent sum of multiple small scatterers without any particular one being dominant. The SBAS reliable candidates are assessed using temporal-based coherence, estimated through matrix inversion, where an unbiased weighted least-squares approach is applied for a fully connected network, or singular value decomposition (SVD) is used for a non-fully connected network [34]. For regions which require large-scale monitoring coverage, especially where gradual decorrelation occurs due to vegetation coverage, SBAS-InSAR proves to be a more suitable option [35,36].
For decades, several studies have estimated the subsidence rate in the CRFP and provided the subsidence profiles along the THSR by applying either the PSI or SBAS method. Hung, et al. [14] exploited 20 ENVISAT SAR images and then integrated the PSI results and leveling measurements to estimate the vertical displacements during 2006–2008, which showed that three townships of Tuku, whose annual subsidence rates were up to 70 mm/year at maximum, were under the THSR. Lu, et al. [37] combined PSI results extracted from 34 ENVISAT SAR images using geostatistical methods and validated them with GPS data. Then, the previously derived deformation patterns were compared with three aquifers’ annual GWL fluctuations to analyze the impact of GWL drops on land subsidence. The results showed that the highest sinking rate reached 80 mm/year in 2005–2008, and the groundwater decline in the second aquifer influenced the subsidence in the CRFP. Yang, et al. [38] utilized the GPS data to enhance the SBAS results from 2016 to 2017 in Yunlin County. The results proposed that severe subsidence occurred in Tuku, Yuanchang, and the nearby districts, and the surface deformation in the dry season accounted for 60.77% to 73.75% of the total subsidence every year. However, the result only represented one year of observation. Lu, et al. [39] applied the PSI method to analyze SAR images acquired by multiple sensors from 1996 to 2017 and provide insight into land subsidence issues of the CRFP. The subsiding velocities along the THSR were shortly described in this study, showing the decreasing subsidence rates in recent years. Chen, et al. [40] improved image processing by increasing the number of input SAR images from different satellites over time (1993–2019) and combined the results analyzed by SBAS with other monitoring sensors such as multilayer compaction and GWL monitoring wells. Their study provided historical subsidence information of the study area, showing that the largest sinking rates (over 50 mm/year) occurred in the middle-fan section of the CRFP.
While several articles have previously addressed the subsidence patterns in the CRFP, some issues remain. A number of earlier studies assumed that the effects of horizontal motions on line-of-sight (LOS) InSAR velocities were negligible; thus, the vertical components were often calculated by directly dividing the LOS velocity and the cosine of incidence angles. However, given the need to evaluate the impacts of land subsidence on the infrastructures, especially the Taiwan High-Speed Rail (THSR), this study considers horizontal components when converting LOS to vertical deformation [40]. Subsequently, a detailed analysis of angular deflections along the railway pillars, which indicate potential nonuniform surface deformation affecting the structures, is provided based on the calibrated InSAR results. In addition to solely assessing the overall subsidence patterns, this study also integrates hydrogeological observations, including borehole logging records, multilayer compaction monitoring wells, and GWL monitoring wells, to identify the specific depths at which major compaction occurs. Moreover, a straightforward model that correlates GWL drops and subsidence amplitudes is proposed, estimating the controlled GWL drops between wet and dry seasons to reduce subsidence. To accomplish these goals, we utilize an extensive dataset of 292 Sentinel-1 SAR images acquired from 2016 to 2022, offering the most recent analysis of subsidence trends in the CRFP. The SBAS-PSInSAR workflow is applied to yield a denser network of measurements and improve the accuracy and reliability of measurement points [41]. The raw InSAR line-of-sight (LOS) results are combined with CGPS data to derive the vertical displacements, which were then validated independently by leveling survey data, ensuring the reliability of the measurements. The structure of this paper is as follows: Section 2 presents a brief overview of the CRFP, the dataset information, and processing methods. Section 3 presents the results obtained from data analysis, including the InSAR-derived spatiotemporal subsidence patterns, layer-wise cumulative compactions, and the proportion of fine-grained materials. Section 4 discusses the subsidence patterns, the angular deflection estimation along the THSR, and the expected GWL drops required to mitigate land subsidence derived from the proposed simple model. Finally, conclusions are summarized in Section 5.
2. Study Area, Datasets, and Methods
2.1. Study Area
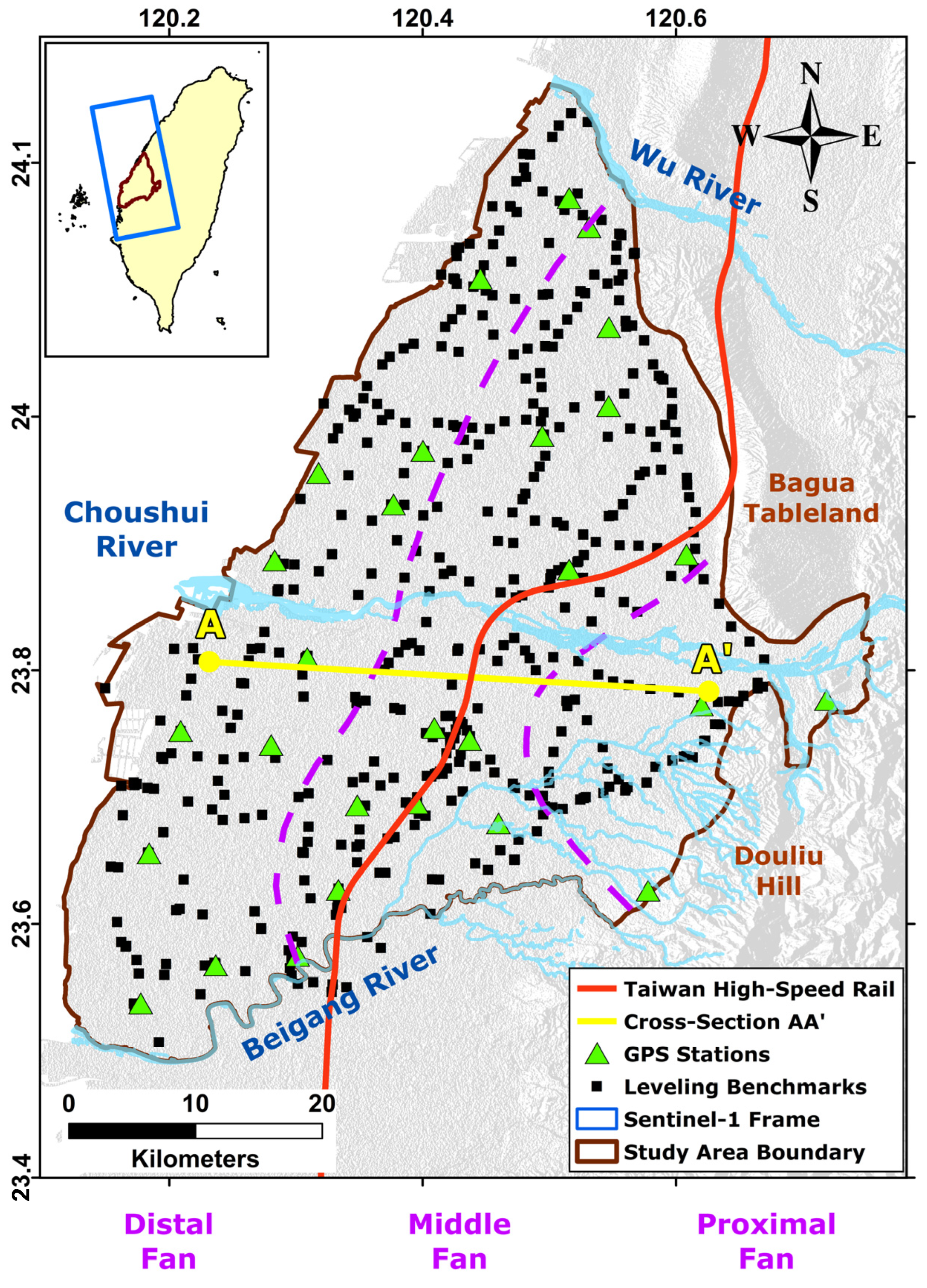
The CRFP belongs to the western coastal region of Central Taiwan. The CRFP has an area of approximately 2500 km2, which belongs to Changhua, Yunlin, and the northern part of the Chiayi Counties, with a surface elevation ranging from 0 m to 100–150 m above sea level. The CRFP boundary is shaped by Douliu Hill and the Bagua Tableland on the eastern side, the Wu River to the north, the Beigang River to the south, and the Taiwan Strait to the west (Figure 1).
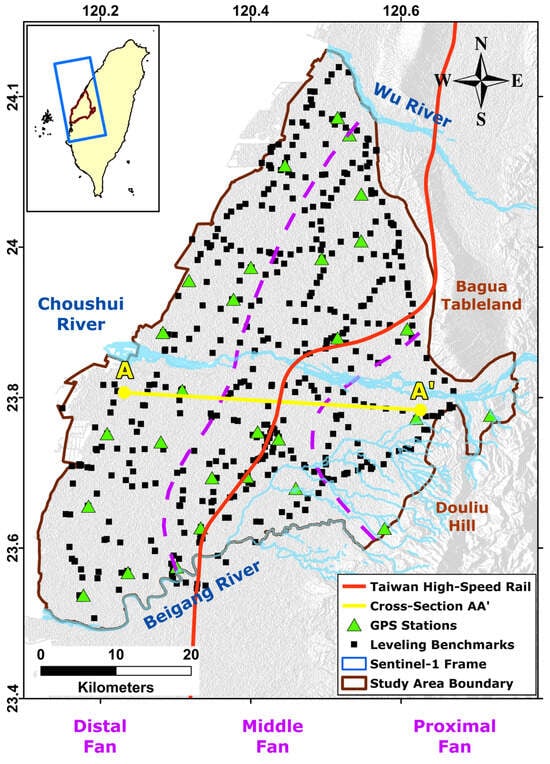
Figure 1.
The location of the study area (bounded by a gray line) and the coverage of Sentinel-1’s SAR images (blue rectangle). The green triangles and black squares stand for GPS stations and leveling benchmarks, respectively. The hydrogeological structures are roughly separated by purple dash lines.
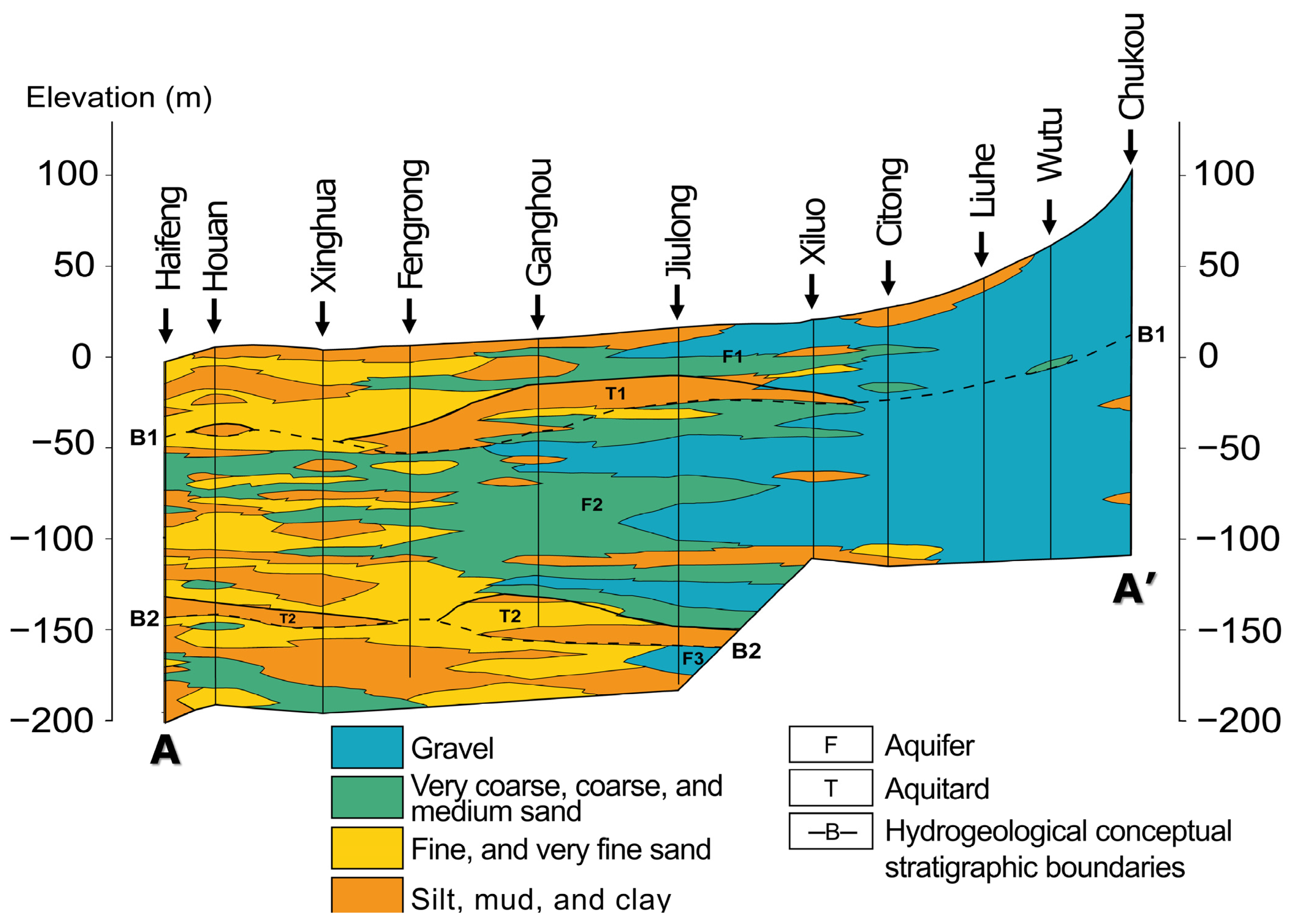
The hydrogeological structures of the study area are divided into three sections from the east to the west, including the proximal fan, middle fan, and distal fan [42]. Each section comprises various sedimentary materials, with average grain sizes decreasing from hilly regions to coastal areas. The sedimentary materials in the CRFP are divided into four primary groups, grading from very coarse grains to very fine grains, which are gravel, coarse sand, fine sand, and clay or silt [42]. These materials are weathered products of rock formations located in the upstream watershed of the study area, such as slate, quartzite, shale, sandstone, and mudstone [12,43]. The borehole profiles suggest that gravel and coarse sand are primarily present at the proximal fan and part of the middle fan, whereas the distal fan mainly witnesses fine-grained materials, including fine sand, clay, and silt Figure 2.
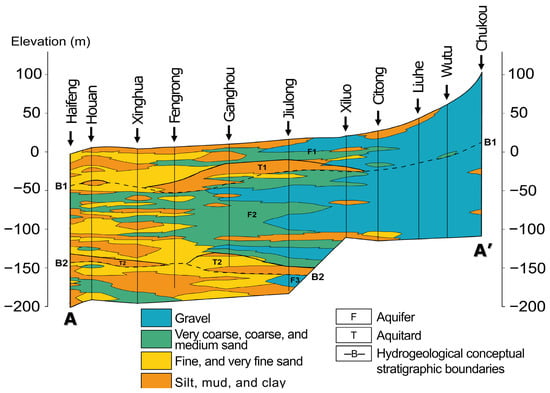
Figure 2.
The selected cross-section shows the sedimentary materials’ distribution along the AA′ profile shown in Figure 1.
As it plays an important role in agricultural production areas in Taiwan, the CRFP also demands massive amounts of water for irrigation and civilian usage, mainly supplied from groundwater exploitation due to surface water insufficiency in the dry season of a year [13,15,39,44,45]. Based on electricity consumption, Chu, et al. [46] estimated that 13.2 to 26.7 million m3 of groundwater was extracted monthly for irrigation within three townships of Yunlin County (Huwei, Tuku, and Yuanchang) from 2007 to 2017. However, the annual groundwater recharge rates in the alluvial regions are only around 0 to 200 mm/year, much lower than those observed in the eastern hilly areas (800–2000 mm/year) [47,48]. The significant difference between the discharge and recharge of groundwater over a long time was one of the causes resulting in severe land subsidence.
2.2. Geodetic Datasets
2.2.1. Continuous Global Positioning System and Precise Leveling Survey
The CGPS measurements employed in this study were managed by the Institute of Earth Sciences, Academia Sinica (IESAS) [49], with over 400 stations operated by multiple organizations, including the IESAS, the Central Weather Bureau (CWB), the Geological Survey and Mining Management Agency, the Ministry of Economic Affairs (GSMMA), and the Ministry of the Interior (MOI). The Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) data collected in 2006–2023 were processed with GAMIT 10.7/GLOBK 5.35 software packages [50] to obtain GPS position time series. First, double-differenced carrier-phase measurements were used to obtain daily solutions with loose constraints. We then used FES2004 (Finite Element Solution tidal mode) [51] to correct ocean loading and pole-tide. The GMF (Global Mapping Function) [52] was used for the removal of tropospheric delay. The products obtained from the GAMIT software, including the variance and covariance matrices of the Taiwan and International GNSS Service (IGS) station positions, together with other parameters, were subsequently processed with GLOBK to achieve a combined global daily solution in the ITRF2008 reference frame [53].
The precise leveling data were utilized to validate the calibrated InSAR-derived vertical displacements. There are 500 leveling benchmarks in the area of CRFP provided by the Water Resources Agency (WRA). The data measurements were conducted once a year, with the earliest records in the study area dating back to 1992. Leveling surveys were carried out along lines forming loops of hundreds of kilometers. The leveling procedure required that any loop misclosure should be below the criterion of (where K is the distance between two adjacent benchmarks in kilometers (km)) [13]. The leveling surveys followed the mean sea level on 1 January 2001 of the Keelung Harbor tide gauge in northern Taiwan [39,54].
2.2.2. SAR Dataset Overview
This study employed 292 SAR images in the ascending track and Interferometric Wide (IW) swath mode [55], acquired by both Sentinel-1A and 1B satellites. The image acquisition time window ranged from April 2016 to October 2022. Sentinel-1 is the European Space Agency’s sun-synchronous imaging radar mission (ESA), providing continuous all-weather, day-and-night imagery at a C-band radar wavelength. The orbit altitude is around 693 km, with an inclination of 98.18°. The satellite couples have the same orbital plane but opposite flight paths and monitor the targeted area together within six days of revisiting. Detailed parameters of the Sentinel-1 data are given in Table 1. The external 30 m Digital Elevation Model (DEM) for topographic phase removal was provided freely by NASA’s Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) [56].

Table 1.
Information on the SAR images employed in this study.
2.2.3. SBAS-PSInSAR Processing and Deformation Extraction
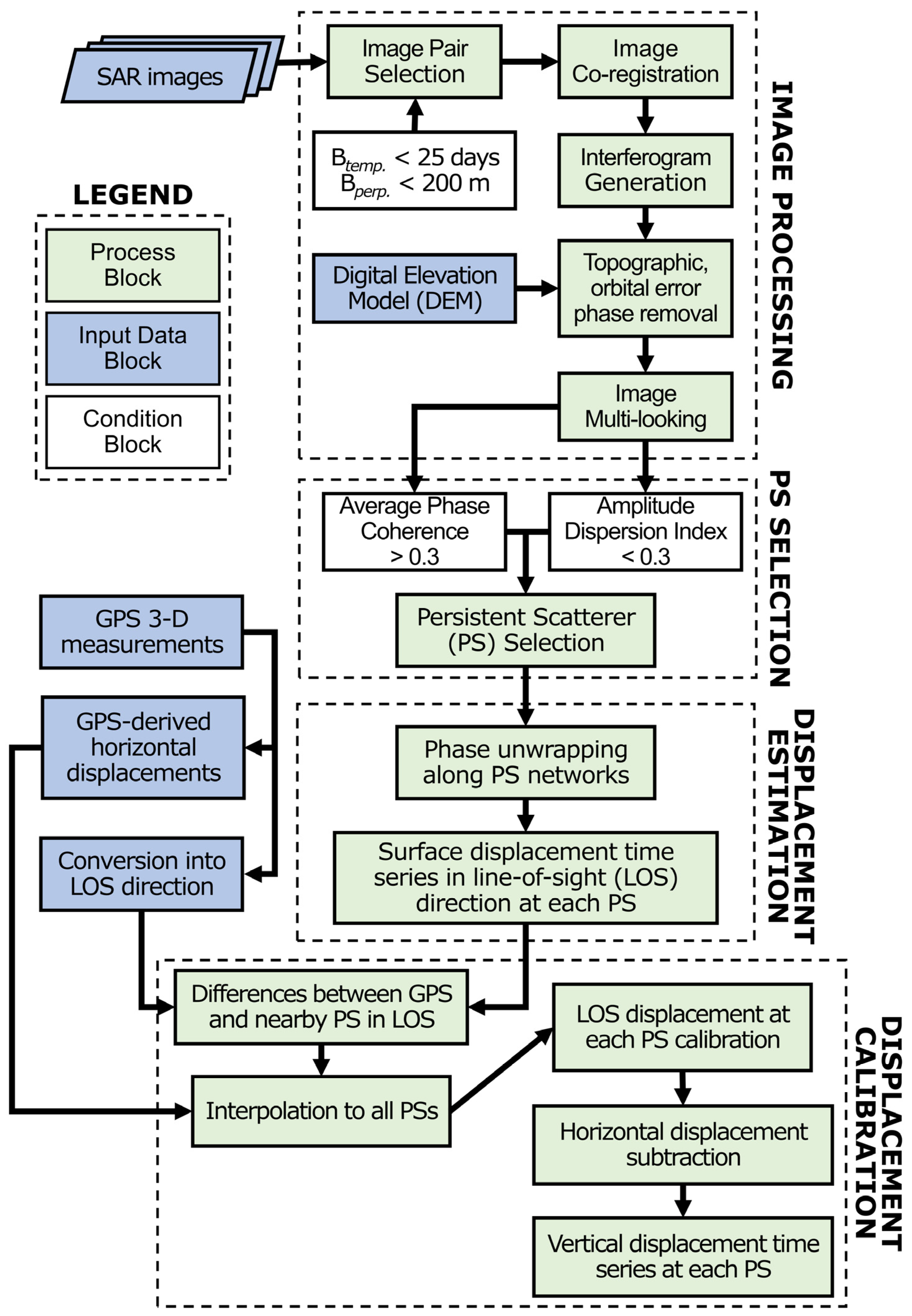
Figure 3 shows the SAR image processing workflow for this study. First, pairs of SAR images with perpendicular and temporal baselines less than 200 m and 25 days were co-registered to produce raw interferograms with maximized total correlation. Then, the interferograms were subjected to the Goldstein filter [57] and multi-looking by a factor of 3 × 1 (3 in the range and 1 in the azimuth direction) to lower the noise caused by decorrelation [28]. In addition, the flat-Earth and topographic phases were removed utilizing the 30 m SRTM DEM. Next, persistent scatterers (PSs), or consistently high-coherence pixels, were identified based on the amplitude dispersion index (ADI) and the phase coherence stability [26,27]. Following this, the Delaunay triangulation method was applied to generate a connected network of all PSs, from which the linear deformation rate and topographic error were extracted through an integration process using the classical growing algorithm for phase unwrapping [58]. The remaining nonlinear deformation rate was separated from the atmospheric perturbation component by applying a low-pass filter in space and a high-pass filter in time [59]. Finally, the atmospheric-free deformation components, including linear and nonlinear deformation rates, from all interferograms were obtained.
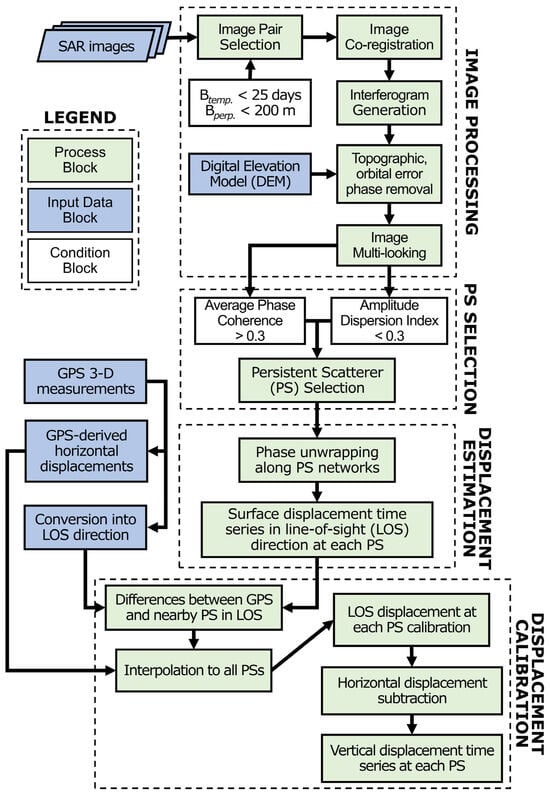
Figure 3.
The SAR image processing workflow for this study. Notations βtemp and βperp stand for the temporal and perpendicular baselines, respectively.
The InSAR-derived results were adjusted utilizing the entire network of GPS stations as multiple reference points [14,39,60]. The process started with projecting the GPS three-dimensional measurements into the Sentinel-1A/B satellites’ line-of-sight (LOS) vector. Next, PSs within a 200 m radius of each GPS station were selected to identify the discrepancies between their average LOS displacements and GPS-derived ones. We assumed that these discrepancies between the GPS stations and the surrounding PSs existed in systematical similarity and could be described by a geostatistical structure. Based on the geostatistical structure, this study employed the Kriging interpolation method to obtain the discrepancy map. All the PS data in the CRFP were then corrected by subtracting the original PS results from the discrepancies. For a specific time of the InSAR result, the repeated process must be conducted by collecting the GPS data for the date of the available SAR image.
2.3. Hydrogeological Datasets
2.3.1. Groundwater Level Dataset Overview
Since 1990, the Water Resources Agency (WRA) has established a dense GWL monitoring network throughout Taiwan to manage groundwater resources. The network comprises over 350 stations, predominantly located in the western corridor of Taiwan, each station equipped with 1 to 5 wells [61]. These wells provide hourly recordings of GWL from various aquifers at different depths (24 to 307 m). The study area includes 95 GWL monitoring stations, summarized in Table 2. Because the second aquifer in the CRFP is significantly thick, the GWL monitoring wells for this layer are separated into shallow and deep sublayers.

Table 2.
The GWL monitoring wells distributed in the CRFP.
2.3.2. Linear Relation between Groundwater Level Drops and Subsidence
The groundwater level has been recognized as the main factor controlling land subsidence. Previous studies have focused on the determination of the pre-consolidation head to manage land subsidence. The pre-consolidation head for a specific aquifer layer could be useful to quantify the allowed pumped groundwater so that the elastic behavior of the subsidence remains (e.g., [61]). However, the limited long-term observations and complex aquifer systems might make it challenging to determine a pre-consolidation head for managing the land subsidence. Such a condition is evident when the historical data are short in time, and the aquifer layers have high interactions. This study proposes a straightforward model to establish thresholds for groundwater extraction to mitigate further land subsidence. These thresholds are determined through linear regression analysis between annual GWL drops and the corresponding subsidence amplitudes over the same periods. The processing workflow is described as follows. A 500 m buffer region was generated surrounding each GWL monitoring station, within which all PSs detected from InSAR processing were selected. The cumulative displacements of all selected PSs located within the buffer were then averaged to obtain a representative cumulative displacement time series for each monitoring station. This displacement time series was subsequently analyzed alongside the GWL monitoring data in each well.
Since the GWL monitoring data showed a sinusoidal pattern, they could be treated as waveforms, based on which the annual GWL drops were defined as the absolute differences between the peaks (crests) and troughs within each cycle. The same calculation was repeated on the time series of cumulative displacements, as their temporal patterns were also sinusoidal. Subsequently, the calculations conducted at each GWL monitoring well produced a scatter plot comparing annual GWL drops to subsidence amplitudes. Finally, linear regression was applied to each scatter plot to model the relationship, which allowed for the estimation of an expected GWL drop required to maintain the subsidence amplitudes below 40 mm per year, as proposed by the Water Resources Agency (WRA) of the Ministry of Economic Affairs of Taiwan (e.g., [62]). Finally, the expected GWL drops were interpolated using the Kriging method to obtain each aquifer’s contour map of thresholds.
2.3.3. Multilayer Compaction Monitoring Wells
Apart from leveling surveys and GPS monitoring for total surface deformation measurements, multilayer compaction monitoring wells (MLCWs) offer detailed insight into deformation at specific strata, allowing for a comprehensive analysis within the aquifer system. This study employed 32 WRA MLCWs, primarily in Yunlin and partially in Changhua Counties. Each well reaches a depth of 300 m and is anchored with 21 to 26 magnetic rings. The positions of these rings were strategically designed based on a combination of hydrogeological models, borehole logging data, and geophysical logging data. Typically, the magnetic rings are installed at critical points, including the boundaries between significant aquifers identified by the Central Geology Survey (CGS), and transitions between fine and coarse sedimentary materials. The depth variations in each magnetic ring are carefully tracked monthly using a probe attached to an indium-alloy measuring tape, ensuring an accuracy of 1 mm. Detailed methodologies for the installation and measurement procedures of the MLCWs can be found in [63].
2.3.4. Estimation of Fine-Grained Sedimentary Material Percentage
Fine-grained sedimentary materials are those in which more than 50% of particles may pass through a No. 200 sieve, whose openings are around 74 µm [64]. These materials are further classified as either silt or clay. The percentage of fine-grained sedimentary materials is estimated as the ratio of the aggregate thickness of silt and clay sequences in a borehole to the total drilling length, as follows:
where stands for the percentage of fine-grained sedimentary materials, is the thickness of fine-grained materials (m), and is the total drilling length (m).
The borehole logging data used for percentage calculation were from WRA MLCWs and CGS boreholes [65]. The percentages obtained from all boreholes were subsequently interpolated using the Kriging method to produce a continuous map.
3. Results
3.1. SBAS-PSInSAR Average Deformation Map
The spatial distribution of InSAR-derived average deformation rates in the CRFP is illustrated in Figure 4. Over 1.6 million PSs, corresponding to 760 points/km2, were identified across the area. Because of their stable backscattering properties, the PSs were mainly detected in structures like houses, buildings, highways, railways, and bridges. Conversely, PSs were scarce in paddy fields, where vegetation or water coverage during rice cropping seasons reduced signal coherence.
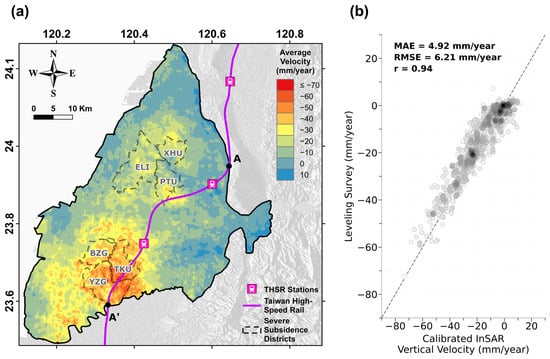
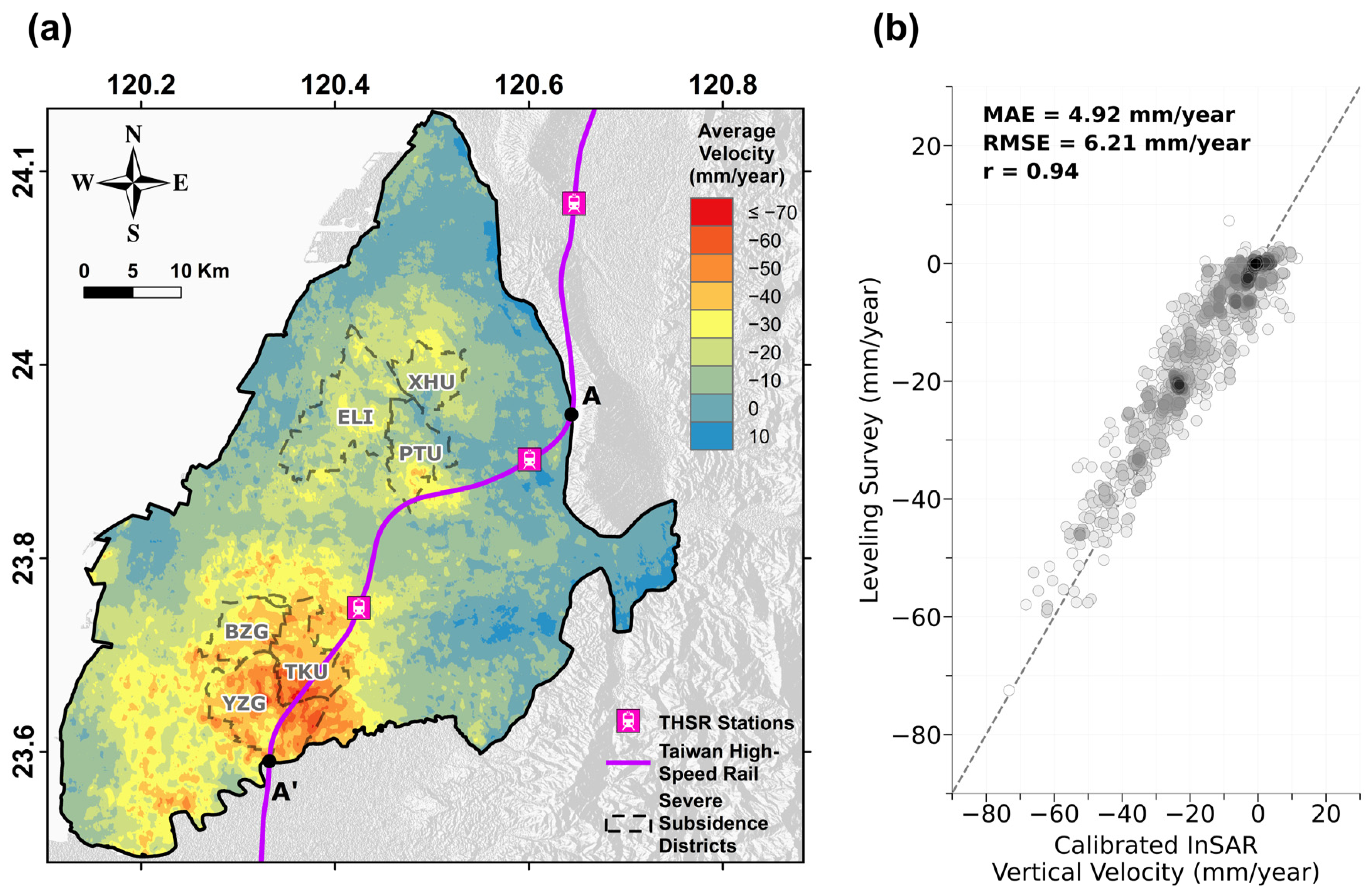
Figure 4.
The results obtained based on the InSAR data: (a) InSAR-derived average velocities (April 2016–October 2022) in the CRFP. Gray dash-lined polygons indicate severely subsidence-prone districts. Profile AA shows the THSR railway. All features are overlapped onto a raster of the DEM. (b) Comparison between the deformation rates derived by InSAR processing and the leveling survey.
The analysis revealed a significant subsidence bowl in Yunlin County, centered in the Tuku (TKU) and Yuanzhang (YGZ) Districts, with average subsiding velocities between 40 and 60 mm/year and some areas exceeding 70 mm/year. The subsidence rates decreased to around 30 mm/year in the outer regions of this subsidence bowl. Approximately 26% of the study area in Yunlin experienced subsidence rates over 20 mm/year. It can be noticed that a 13 km section of the THSR was situated within this severe subsidence zone. In Changhua County, three moderate subsidence bowls in Erlin (ELI), Pitou (PTU), and Xihu (XHU) showed subsidence rates between 20 and 40 mm/year, covering about one-third of the size of those in Yunlin.
The InSAR-derived vertical displacements were validated using leveling survey data, the locations of which are shown in Figure 4a. The PSs within a 200 m radius of each benchmark were selected, and their average deformation time series was calculated for validation. Due to the different temporal sampling intervals, validation was performed by comparing the average deformation rates derived from their respective time series. The evaluation metrics, displayed in Figure 4b, included a mean absolute error (MAE) of 4.92 mm/year, a root mean square error (RMSE) of 6.21 mm/year, and a correlation coefficient (r) of 0.91, indicating strong agreement between the measurements from both geodetic techniques.
3.2. The Analysis of Cumulative Compactions
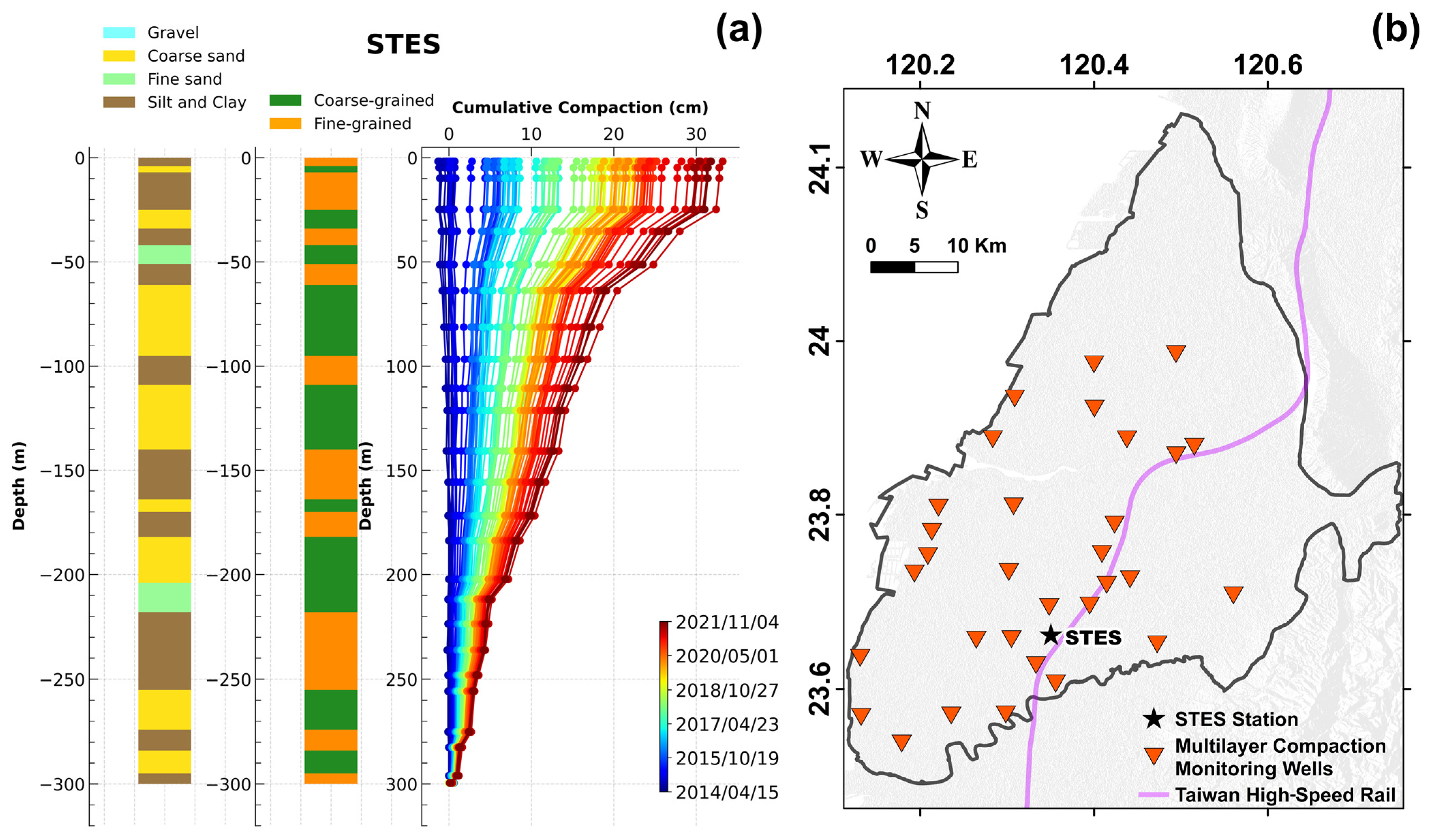
In addition to the InSAR-derived total displacement, which identified areas at risk of severe subsidence, the layer-wise compaction recorded by MLCWs could offer more insights into the underlying mechanism of subsidence. The MLCW measurements were sampled monthly, providing the depths of magnetic rings with respect to the deep foundation of the well (around 300 m depth). The difference in depth recordings at the same ring in different periods is the soil deformation (compaction or expansion) that occurred at the stratigraphic sequence of the ring. The total deformation equals the sum of all deformation values recorded by all rings. Specifically, the sources of groundwater usage might reasonably be inferred based on the depths where major compaction occurred. For example, the presence of major compaction in shallow layers (i.e., Aquifers 1 and 2) may suggest that the groundwater resource was used for agricultural purposes [63]. On the other hand, if the phenomenon occurs in deep layers, groundwater might reasonably be extracted for domestic and industrial purposes. Figure 5 shows the cumulative compactions recorded by the STES station, which is located near the center of Yunlin’s subsidence bowl. At the first 60 m depth, the primary major compaction can be observed, followed by a secondary major compaction extending to 200 m, corresponding to the highly compressible sand sequences interbedded with fine-grained material layers.
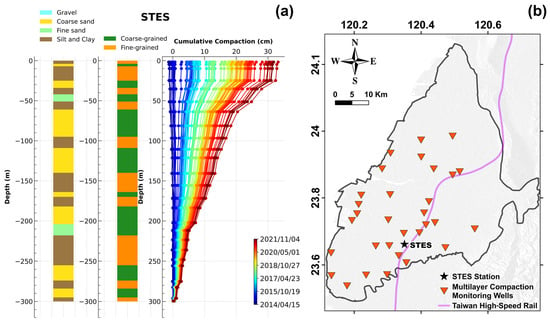
Figure 5.
(a) The stratigraphic profiles originally classified by CGS and reclassified based on the Unified Soil Classification System [64] are shown in the first and second columns, respectively. The third column indicates the cumulative compactions at the STES station. (b) The location of the STES station along with other MLCWs.
3.3. The Percentage of Fine-Grained Materials for the CRFP
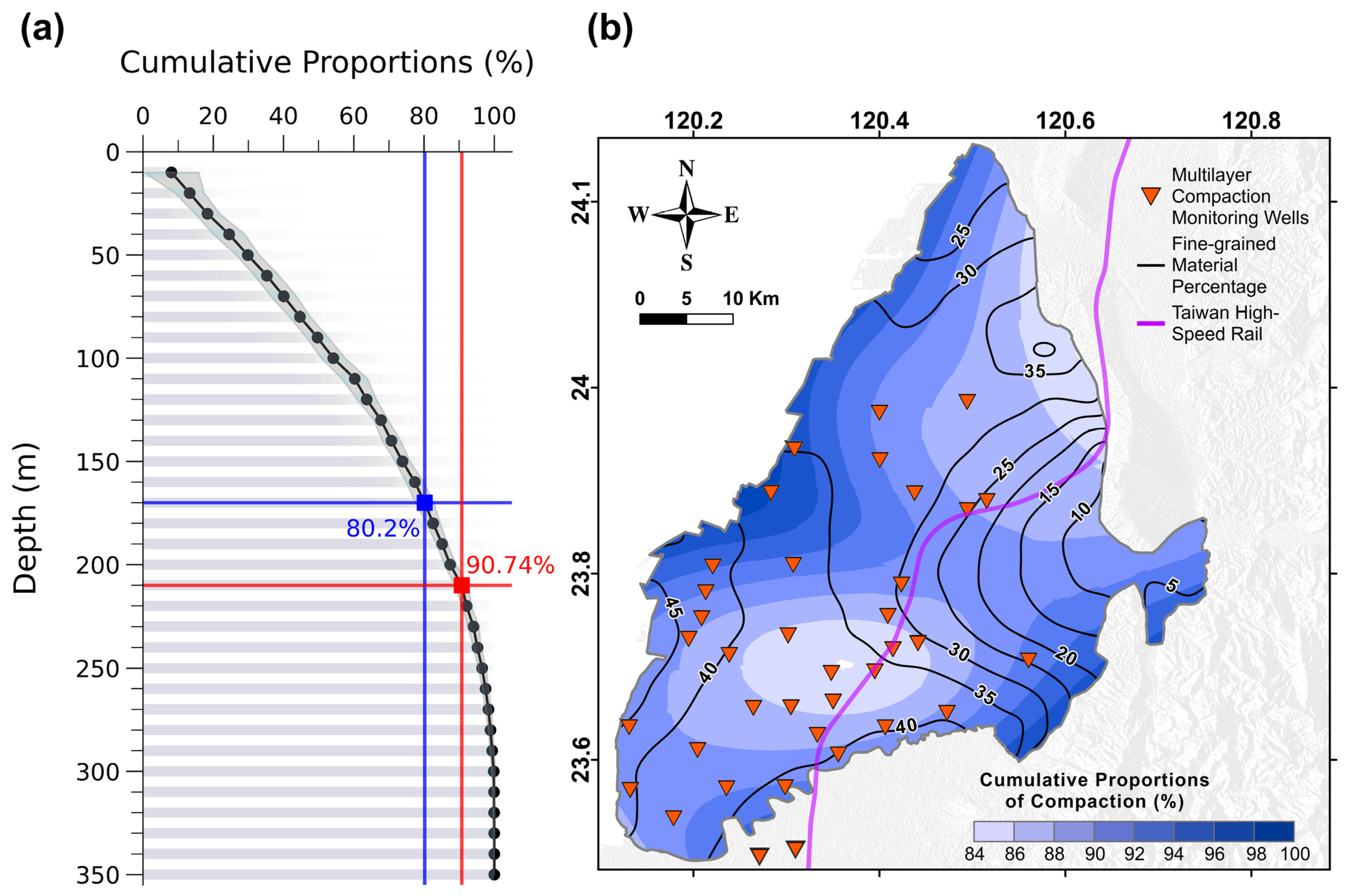
An analysis of the cumulative proportion of compaction recorded by MLCWs for every 10 m depth interval revealed that, on average, 50% of cumulative compaction occurred at the first 90 m depth for the entire study area. The proportions increased to 80% and 90% when reaching 170 m and 210 m depths, respectively (see Figure 6a). Based on the analysis, half of the compaction (i.e., 50%) in the study area occurred mainly in the shallow layers at depths less than 100 m. In the CRFP, the available depths of MLCW and geological logging data were inconsistent depending on the practical conditions of the wells. We then used data within the depth of 210 m for the assessment because the data covered more than 90% of the subsidence.
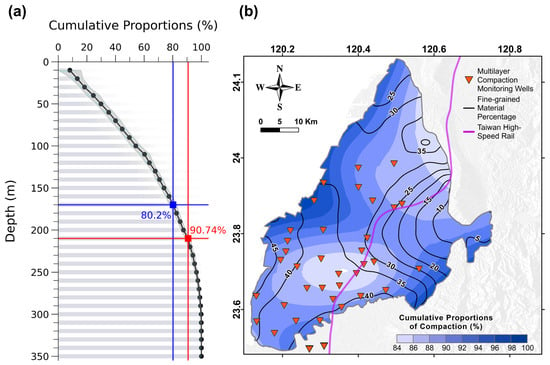
Figure 6.
The relationship between the depth and cumulative subsidence in the entire CRFP. (a) The cumulative proportions of compaction of all MLCWs were calculated based on every 10 m depth interval. The black dots indicate the average values of these proportions. (b) The contours of cumulative proportions of compaction overlapped by the fine-grained material percentage. The borehole logging and MLCW data were collected for the depths of 210 m in the CRFP.
Figure 6b shows the contour lines depicting the percentage of fine-grained materials overlapped on the cumulative compactions within 210 m. The percentage of fine-grained sedimentary materials is calculated only at the first 210 m depth of each borehole to demonstrate the distribution of major compaction in the study area. The results show a positive correlation between the high proportion of fine-grained materials and the resulting cumulative compactions. These two main areas are located on the eastern side of Changhua County and in the center of Yunlin County (Figure 6b). As recognized by many other cases in other studies, there is a high consistency between the cumulative subsidence and fine-grained material proportions in the aquifer systems. The expected high-subsidence bowls could commonly be found in areas composed of fine-grained materials. Notably, grain sizes less than the silt material type were selected as the fine-grained materials included in the calculations. The clay depositions showed a relatively small percentage compared to the silt material based on the borehole loggings obtained from the CRFP.
4. Discussion
4.1. Subsidence Profile along the THSR
The long-term subsidence progress in the CRFP has had a harmful impact on the THSR section, potentially disrupting operations through technical issues. In addition, land subsidence can weaken railway pillars’ bearing capacity due to negative frictional forces [18,19]. Therefore, for a comprehensive assessment of subsidence impacts on the negative frictional forces which impair THSR operational safety, it is essential to evaluate both vertical and horizontal displacements, as recommended by [40].
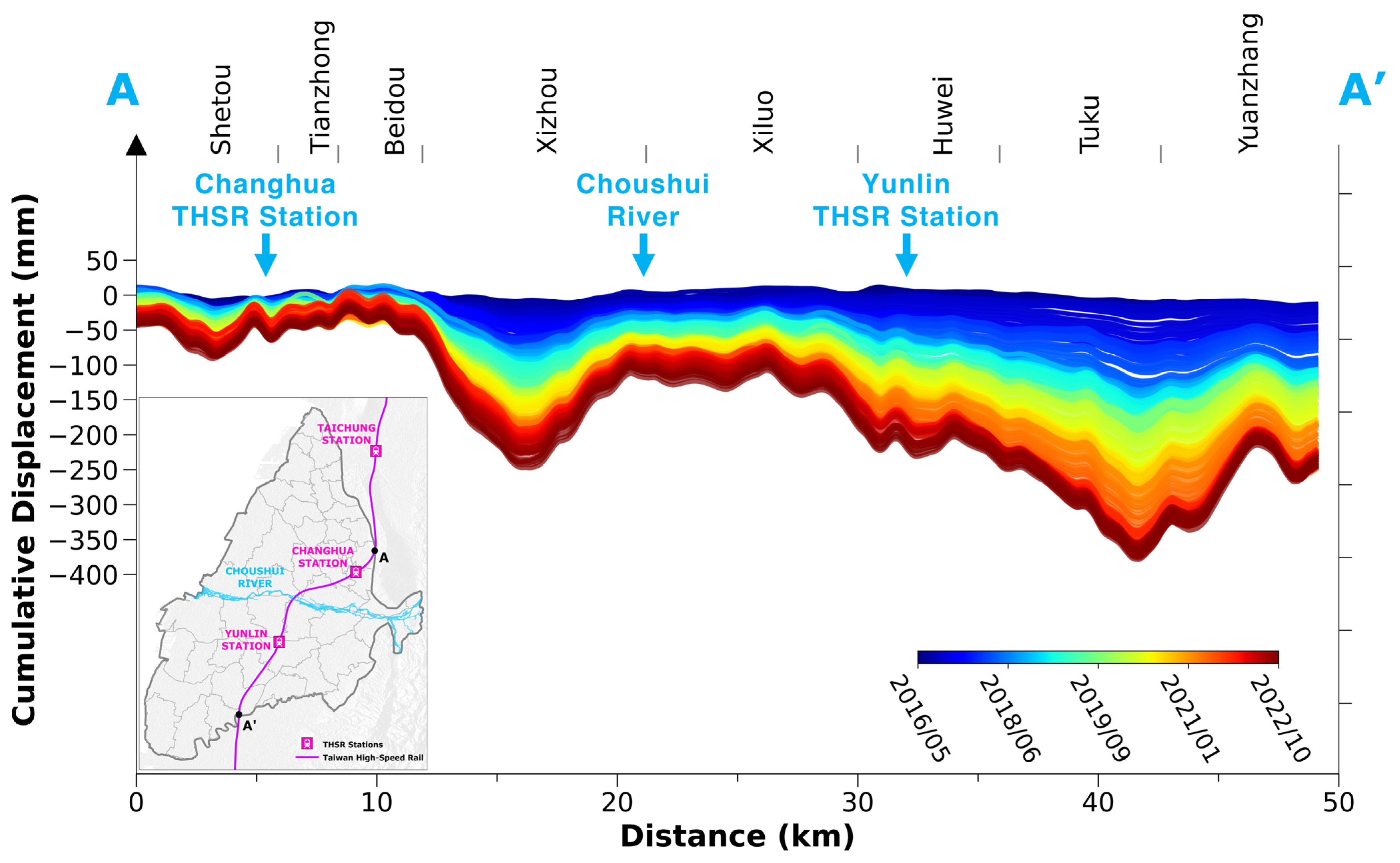
Figure 7 shows the cumulative displacements along the THSR section passing through the CRFP study area, as observed at profile AA′, shown in Figure 4. This 49 km railway section is part of a 350 km long high-speed railway system that runs along the western corridor of Taiwan, from Taipei Station (Taipei City) to Zuoying Station (Kaohsiung City). In Figure 7, the color bar from blue to red visually represents the timeline, with wider gaps between the lines indicating higher deformation rates. The subsidence values along the railway were extracted based on the InSAR PS points in the windows of 100 m bandwidth and 50 m distance along the railway. The subsidence profile indicates three remarkably subsiding spots in Xizhou (XZU), Huwei (HWI), and Tuku–Yuangzhang (TKU-YZG) areas, respectively. The sinking spot in Xizhou observed a subsidence rate of up to 45 mm/year at the center and around 30 mm/year in the surrounding areas. Towards the south, the subsidence rates significantly increased from HWI to YGZ, with the THSR segments through these areas lying on a massive subsidence bowl, exhibiting sinking rates from 40 to over 60 mm/year. These findings underscore the need to prioritize THSR pillar safety in subsidence assessments and serve as crucial reminders for local officials and researchers. These areas with severe subsidence are shown in Figure 6b. The relatively less subsidence in the XZU than in the HWI could be due to the relatively small percentage of fine-grained materials.
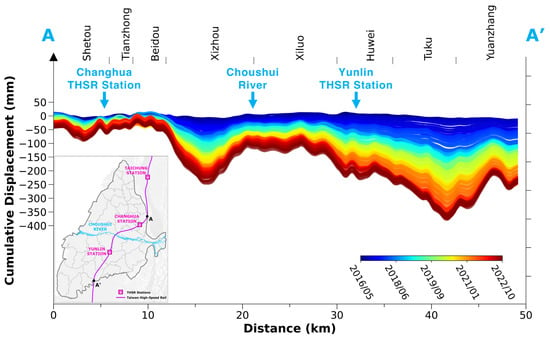
Figure 7.
The cumulative displacement profile along the THSR (i.e., the AA′ profile along the railway shown in Figure 4). Each line represents the cumulated values temporally relative to the first image acquired on 14 April 2016. The districts that the railway passes through are shown at the top of the figure.
4.2. The Effects of Angular Deflection on the THSR
Land subsidence can lead to the gradual deterioration of buildings and infrastructure over time. The vulnerability of structures to damage caused by subsidence is determined by the degrees of subsidence-related intensity (SRI) parameters commonly utilized in practical geotechnical engineering [66]. An important indicator for assessing potential damage to railways is angular deflection or angular rotation (θ), which can result from differential settlements. Angular deflection at railway pillars is influenced by the compression or rebound of sediment beneath the foundations. The heterogeneity of the material could also influence the vertical variations between pillars. Excessive angular deflection poses a significant risk to the safety of THSR operations. Therefore, the safety code requires that the angular deflection at railway pillars remains under 1/1000 [18,19,67]. The angular deflection at the kth railway pillar is estimated as follows:
where , , and are the displacements at three consecutive pillars: (k − 1)th, kth, and (k + 1)th. and are the distances from the railway pillar kth to the (k − 1)th and (k + 1)th pillars, respectively.
Traditionally, angular deflections along the THSR are estimated based on yearly leveling survey measurements with a low measurement density and limited temporal resolution. In this study, utilizing the PSs obtained from the SBAS-PSInSAR process could capture surface deformations in high temporal resolution, which enabled the calculation of pseudo-real-time values for angular deflections, providing a more accurate and detailed assessment of the risk and potential damage through relatively short periods [68]. This study considered that the inter-pillar distances were approximately 50 m for the analysis.
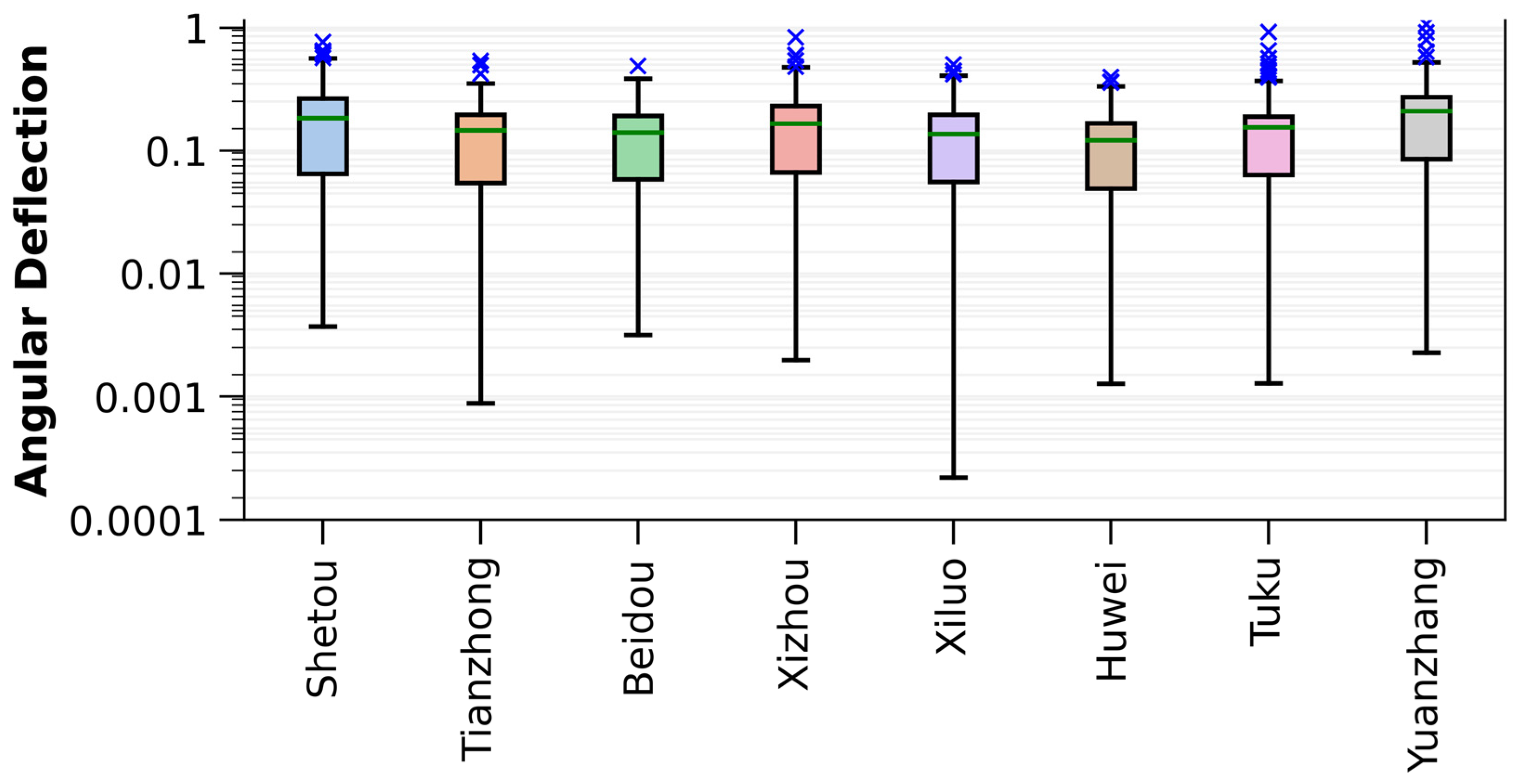
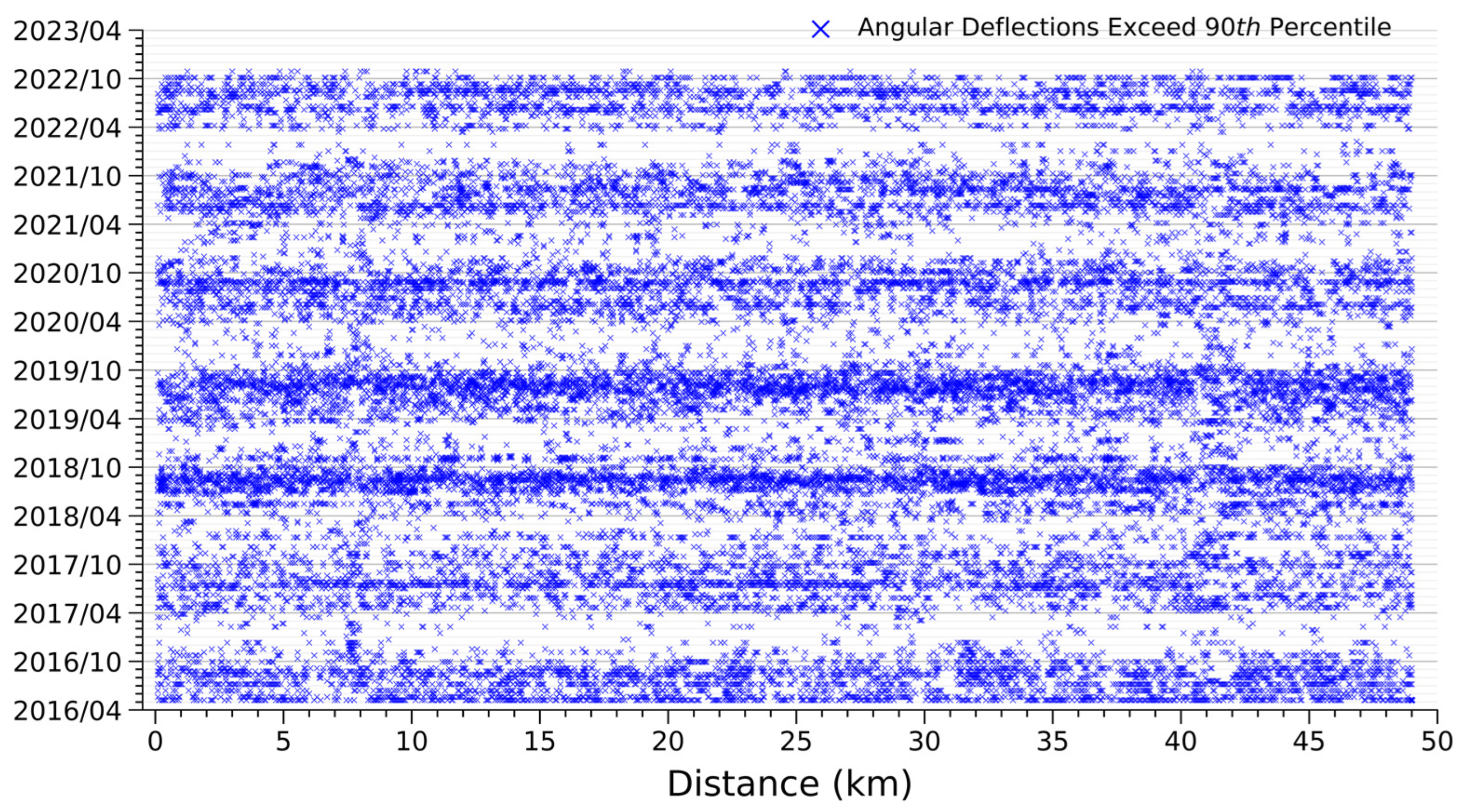
Variations in angular deflections over time are derived from high-temporal measurements of differential settlement, and the results could provide an assessment of potential damage to railway pillars. This approach differs from typical leveling survey calculations, which analyze angular deflections at a specific time. Figure 8 represents the box plot analysis of angular deflections calculated from the cumulative displacements at the end of the research period and categorized based on the districts crossed by the railway system. This analysis shows that the angular deflections in the Shetou, Xizhou, Tuku, and Yuanzhang Districts were higher than those in the other areas, with plenty of pillars approaching the safety code. This observation suggests that the THSR segments in these places are more likely to suffer damage induced by nonuniform vertical variations (i.e., the subsidence or rebound). In addition to the spatial viewpoint, a temporal perspective of angular deflections can be achieved by analyzing the angular deflections calculated from differential displacements between successive SAR image acquisition dates. Figure 9 shows that the values exceeding the 90th percentile of angular deflections along the railway occurred primarily between April and October. This result indicates that high angular deflections are commonly observed in wet seasons, which are not the period with significant subsidence, i.e., dry seasons. It is noted that the formula of angular deflection in Equation (2) implies that this parameter demonstrates the extent of nonuniformity in surface deformation rather than subsidence magnitude. The possible factors that control this nonuniform deformation might be the heterogeneity of the material under the foundations of the railway. This heterogeneity could be the natural deposition of the aquifer materials and the soil reinforcement for railway construction. In summary, the spatiotemporal analysis of angular deflections derived from PSs sheds light on the THSR segments susceptible to nonuniform surface deformation and when the nonuniformity occurred at its peak. For safety issues, more angular deflection measurements in the wet seasons might be required.
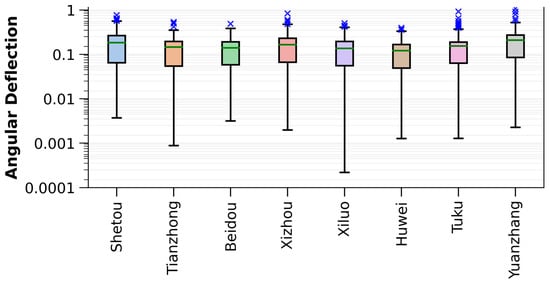
Figure 8.
The box plot illustrating the angular deflection values for railway pillars, calculated by cumulative displacements at the end of the research period and categorized by districts along the THSR. The horizontal green lines within the boxes indicate the means, while the boxes represent the interquartile ranges. The blue crossed marks denote outliers for the specific districts in the Changhua and Yunlin Counties.
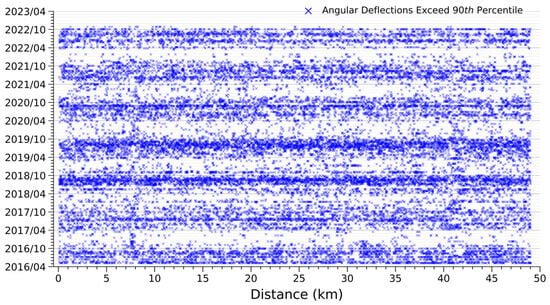
Figure 9.
The occurrence times of angular deflections that are derived from the differential displacements between successive SAR image acquisition dates exceed the 90th percentile.
4.3. Proposing Groundwater Level Drop Threshold for Subsidence Mitigation
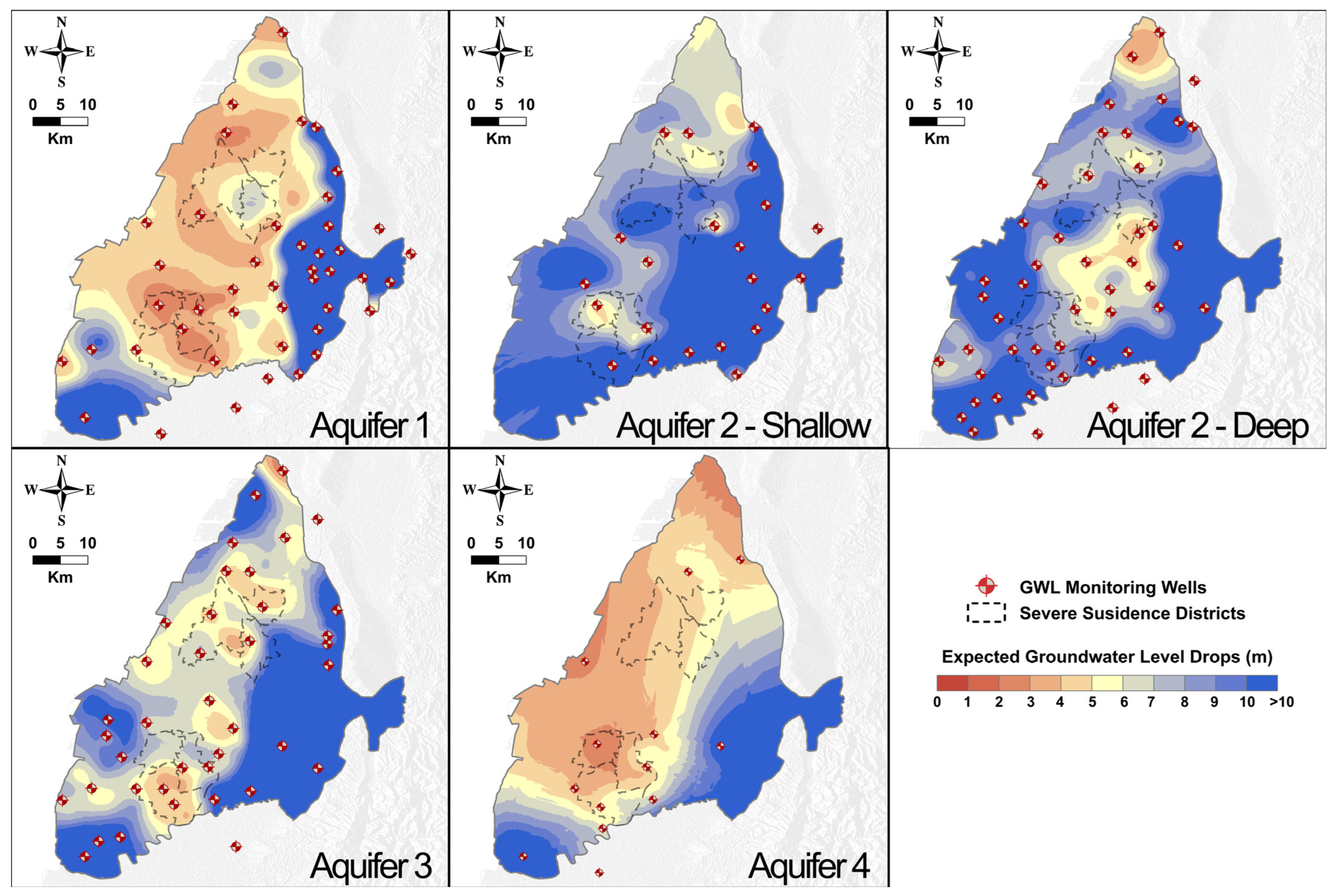
A large number of GWL monitoring stations and leveling benchmarks have been installed in the CRFP. This study integrated the groundwater monitoring data with the PSs identified during InSAR processing. Data integration was implemented by constructing linear regression models between the annual GWL drops and the subsidence magnitudes, as mentioned in Section 3.2. Due to seasonal effects on the variations in GWL and subsidence [69], the time series of GWL monitoring and surface deformations exhibited periodic patterns. Therefore, the annual GWL drops and the subsidence amplitudes were equal to the peak-to-peak values of the sinusoidal waveform. In this study, the InSAR provided maximal subsidence between the wet and dry seasons, marked as total subsidence near the groundwater monitoring wells. The GWL drops corresponding to the total subsidence were identified based on the multilevel groundwater monitoring network in different aquifers in the CRFP. For an observation well at a specific aquifer depth, the relationship between total subsidence and GWL drops was derived based on the data from 2016 to 2023. With a specified subsidence mitigation target, for example, 30 or 40 mm/year at the monitoring well location, the allowable GWL drops could be obtained based on the relationship. Figure 10 shows the estimated GWL drops for each aquifer to mitigate subsidence amplitudes under 40 mm/year, overlapped by the borders of areas suffering from severe subsidence. The warmer colors indicate lower thresholds of GWL drops and imply that the annual GWL drops in a specific layer are significantly sensitive to the total subsidence. With this perspective, Aquifers 1, 3, and 4, from shallow to deep, may need more attention for subsidence mitigation, and the controls of the GWL drops in these layers might be critical. Notably, Aquifer 2 in the study was further divided into two sub-aquifers named Aquifer 2-shallow and Aquifer 2-deep.
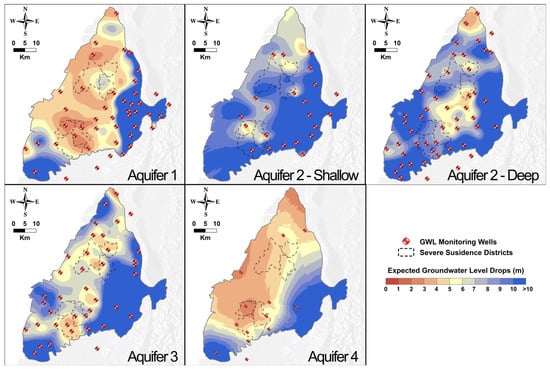
Figure 10.
The estimated GWL drops at each aquifer layer to keep the subsidence amplitudes under 40 mm/year, overlapped by the borders of areas suffering from severe subsidence.
In the first aquifer layer, the GWL drop thresholds, ranging from 3 to 5 m, corresponded to the areas prone to severe subsidence and their vicinity, implying that substantial GWL drops in this aquifer remarkably impacted the total subsidence. The first aquifer was the shallowest layer and was known as the cost-effective source of irrigation for agricultural activities. Notably, we had specified the subsidence rate of 40 mm/year for the study area. Other desired subsidence rates could follow the same strategies to quantify the controlled GWL drops for different aquifers. A similar range of GWL drop thresholds could be observed in the deepest aquifer, the source of industrial and domestic water usage. However, the estimated GWL drops in Aquifer 4 may be uncertain due to the limited GWL monitoring wells. Aquifer 3 was also worthy of consideration due to the moderate GWL drop thresholds, which ranged from 4 to 6 m and primarily coincided with the subsidence-prone areas. The GWL drop thresholds observed in Aquifers 3 and 4 reminded the local authorities to pay attention to the amount of groundwater usage for domestic and industrial purposes. On the other hand, urgent actions are required to manage the groundwater usage of the shallowest aquifer, since the estimated GWL drops for this layer were remarkably low, and half of the major compaction in the study area occurred at the shallow sequences, as shown in Figure 6.
4.4. Research Limitations
Despite the comprehensive analysis conducted in this study, it is important to acknowledge the limitations, as addressing them in future research would lead to more thorough findings. First, the InSAR processing in this study relies solely on ascending Sentinel-1 SAR images due to the lack of a stabilized descending path in the same time frame. Although the descending path eventually stabilized in 2018, the images failed to cover Changhua and Yunlin within a single frame. Consequently, achieving consistent data integration between ascending and descending images would be challenging. The lack of descending data limits the ability to capture the three-dimensional deformation independently of the InSAR-based techniques. This study employed horizontal movements from GPS data to compensate for the unavailability of SAR data. For simplicity, this study assumes a linear relationship between GWL drops and subsidence amplitudes. However, this assumption may not fully cover the practical interactions in such heterogeneous geological conditions in fluvial plains. Finally, the coarse resolution of Sentinel-1 SAR images may not capture small-scale subsidence. This constraint is particularly relevant in agricultural areas with numerous unregistered groundwater pumping wells, where localized subsidence can indicate pumping anomalies.
5. Conclusions
This study employed geodetical and hydrogeological datasets to assess land subsidence evolution in the CRFP and suggest a straightforward model for subsidence mitigation. The data analysis of WRA MLCWs and CGS boreholes suggested that 50% of major compaction occurred within the first 90 m depth, corresponding to the first and second aquifer layers of the study area. Additionally, the major compaction positively correlated with the proportion of fine-grained materials. The InSAR results showed a prominent subsidence bowl centered in Yunlin County, with average subsidence velocities around 40 to 60 mm/year. Three medium-sized subsidence bowls were also detected in Changhua County, with subsiding rates varying from 20 to 40 mm/year. The InSAR results agreed well with precise leveling data, as proven by three evaluation metrics (MAE = 4.92 mm/year; RMSE = 6.21 mm/year; and r = 0.91). The subsidence profile along the THSR revealed multiple sinking spots in the XZU, HWI, TKU, and YZG Districts. In addition, the analysis of angular deflections identified railway segments highly prone to nonuniform subsiding rates. These findings could bring the attention of the local officials to the subsidence escalation in these areas and urge them to introduce appropriate subsidence-control policies. The model developed based on the linear relationship between the annual records of GWL drops and subsidence amplitudes suggested that Aquifers 1, 3, and 4 require more attention in terms of subsidence mitigation. Specifically, to maintain the subsidence rate under 40 mm/year, the GWL drop should be limited to 3–5 m for the shallowest aquifer and below 4–6 m for Aquifers 3 and 4. This study demonstrated the reliability of fusing InSAR results with traditional CGPS and leveling survey data and the potential of integrating geodetic and hydrogeological monitoring data for further subsidence mitigation research.
Author Contributions
T.-V.-T.N., C.-F.N. and Y.-J.H. conceived and designed this research, providing valuable insights during its conception. I.-H.L., C.-P.L., N.H.H., P.-E.R.C., I.-H.L. and C.-P.L. collected and analyzed the hydrogeological data for the study area. Y.-J.H. contributed to the preparation and processing of GPS data. P.-E.R.C. and G.G. contributed to the preprocessing of SAR images. T.-V.-T.N. conducted this study, carried out the analyses, and drafted the initial manuscript. C.-F.N. and Y.-J.H. further refined and finalized the manuscript for communication with the journal. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was partially supported by the National Science and Technology Council, Taiwan, under grants NSTC 111-2621-M-008-003, NSTC 112-MOEA-M-008-001, NSTC 112-2123-M-008-001, NSTC 112-2122-M-007-002 and NSTC 113-MOEA-M-008-001.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Taiwan Water Resource Agency (WRA) and Central Geological Survey (CGS) for the groundwater data, precipitation data, hydrogeological loggings, and lithology data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Poland, J.F. Guidebook to Studies of Land Subsidence Due to Groundwater Withdrawal; UNESCO: Paris, France, 1984; Volume 40. [Google Scholar]
- Galloway, D.L.; Jones, D.R.; Ingebritsen, S.E. Land Subsidence in the United States; US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Bagheri-Gavkosh, M.; Hosseini, S.M.; Ataie-Ashtiani, B.; Sohani, Y.; Ebrahimian, H.; Morovat, F.; Ashrafi, S. Land subsidence: A global challenge. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 778, 146193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gambolati, G.; Teatini, P.; Ferronato, M. Anthropogenic Land Subsidence. In Encyclopedia of Hydrological Sciences; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2006; pp. 231–245. [Google Scholar]
- Galloway, D.L.; Burbey, T.J. Review: Regional land subsidence accompanying groundwater extraction. Hydrogeol. J. 2011, 19, 1459–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faunt, C.C.; Sneed, M.; Traum, J.; Brandt, J.T. Water availability and land subsidence in the Central Valley, California, USA. Hydrogeol. J. 2016, 24, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ireland, R.L.; Poland, J.F.; Riley, F.S. Land Subsidence in the San Joaquin Valley, California, as of 1980; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1984.
- Francesca, C.; Deodato, T. Present-day land subsidence rates, surface faulting hazard and risk in Mexico City with 2014–2020 Sentinel-1 IW InSAR. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 253, 112161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Gong, H.; Zhang, Y.; Warner, T.A.; Wang, C. Spatiotemporal Evolution of Land Subsidence in the Beijing Plain 2003–2015 Using Persistent Scatterer Interferometry (PSI) with Multi-Source SAR Data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.; Lin, Y.N.; Tran, Q.C.; Ni, C.-F.; Chan, Y.-C.; Tseng, K.-H.; Chang, C.-P. Assessment of long-term ground subsidence and groundwater depletion in Hanoi, Vietnam. Eng. Geol. 2022, 299, 106555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, D.H.; Wang, S.J. Land subsidence due to groundwater extraction and tectonic activity in Pingtung Plain, Taiwan. Proc. Int. Assoc. Hydrol. Sci. 2020, 382, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-H.; Pan, Y.-W.; Liao, J.-J.; Huang, C.-T.; Ouyang, S. Characterization of land subsidence in the Choshui River alluvial fan, Taiwan. Environ. Geol. 2004, 45, 1154–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, W.-C.; Hwang, C.; Chang, C.-P.; Yen, J.-Y.; Liu, C.-H.; Yang, W.-H. Monitoring severe aquifer-system compaction and land subsidence in Taiwan using multiple sensors: Yunlin, the southern Choushui River Alluvial Fan. Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 59, 1535–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, W.-C.; Hwang, C.-w.; Chen, Y.-A.; Chang, C.-P.; Yen, J.-Y.; Hooper, A.; Yang, C.-Y. Surface deformation from persistent scatterers SAR interferometry and fusion with leveling data: A case study over the Choushui River Alluvial Fan, Taiwan. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 957–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, W.-C.; Hwang, C.; Liou, J.-C.; Lin, Y.-S.; Yang, H.-L. Modeling aquifer-system compaction and predicting land subsidence in central Taiwan. Eng. Geol. 2012, 147–148, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-C.; Wang, T.-N. GPS monitoring ground subsidence associated with seasonal underground water level decline: Case analysis for a section of Taiwan High Speed Rail. Surv. Land Inf. Sci. 2006, 66, 45–54. [Google Scholar]
- Terzaghi, K.; Peck, R.B.; Mesri, G. Soil Mechanics in Engineering Practice; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1996; p. 592. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, C.; Hung, W.-C.; Liu, C.-H. Results of geodetic and geotechnical monitoring of subsidence for Taiwan High Speed Rail operation. Nat. Hazards 2008, 47, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, C.; Yang, Y.; Kao, R.; Han, J.; Shum, C.K.; Galloway, D.L.; Sneed, M.; Hung, W.-C.; Cheng, Y.-S.; Li, F. Time-varying land subsidence detected by radar altimetry: California, Taiwan and north China. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tung, H.; Hu, J.-C. Assessments of serious anthropogenic land subsidence in Yunlin County of central Taiwan from 1996 to 1999 by Persistent Scatterers InSAR. Tectonophysics 2012, 578, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teatini, P.; Tosi, L.; Strozzi, T.; Carbognin, L.; Wegmüller, U.; Rizzetto, F. Mapping regional land displacements in the Venice coastland by an integrated monitoring system. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 98, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polcari, M.; Palano, M.; Fernández, J.; Samsonov, S.V.; Stramondo, S.; Zerbini, S. 3D displacement field retrieved by integrating Sentinel-1 InSAR and GPS data: The 2014 South Napa earthquake. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 49, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosetto, M.; Monserrat, O.; Cuevas-González, M.; Devanthéry, N.; Crippa, B. Persistent scatterer interferometry: A review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 115, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanssen, R.F. Radar Interferometry: Data Interpretation and Error Analysis, 1st ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2001; Volume 2, p. 308. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, C.-H.; Ni, C.-F.; Chang, C.-P.; Yen, J.-Y.; Chuang, R.Y. Coherence Difference Analysis of Sentinel-1 SAR Interferogram to Identify Earthquake-Induced Disasters in Urban Areas. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Nonlinear subsidence rate estimation using permanent scatterers in differential SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 2202–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, F.; Lv, X.; Dou, F.; Yun, Y. A Review of Time-Series Interferometric SAR Techniques: A Tutorial for Surface Deformation Analysis. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2020, 8, 22–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, X.; Zhang, R.; Shama, A.; Li, S.; Xie, L.; Lv, J.; Fu, Y.; Wu, R.; Liu, G. Ground Deformation Pattern Analysis and Evolution Prediction of Shanghai Pudong International Airport Based on PSI Long Time Series Observations. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, L.K.; Le, P.V.V.; Dao, P.D.; Long, N.Q.; Pham, H.V.; Tran, H.H.; Xie, L. Recent land deformation detected by Sentinel-1A InSAR data (2016–2020) over Hanoi, Vietnam, and the relationship with groundwater level change. GISci. Remote Sens. 2021, 58, 161–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Wit, K.; Lexmond, B.R.; Stouthamer, E.; Neussner, O.; Dörr, N.; Schenk, A.; Minderhoud, P.S.J. Identifying Causes of Urban Differential Subsidence in the Vietnamese Mekong Delta by Combining InSAR and Field Observations. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y. Monitoring Subsidence over the Planned Jakarta–Bandung (Indonesia) High-Speed Railway Using Sentinel-1 Multi-Temporal InSAR Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; San, L.H.; Zhu, Y. Flood Inundation Analysis in Penang Island (Malaysia) Based on InSAR Maps of Land Subsidence and Local Sea Level Scenarios. Water 2021, 13, 1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzadeh, S.M.J.; Jin, S.; Parizi, E.; Chaussard, E.; Bürgmann, R.; Delgado Blasco, J.M.; Amani, M.; Bao, H.; Mirzadeh, S.H. Characterization of Irreversible Land Subsidence in the Yazd-Ardakan Plain, Iran From 2003 to 2020 InSAR Time Series. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2021, 126, e2021JB022258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.H.; Ni, C.F.; Chang, C.P.; Yen, J.Y.; Hung, W.C. Combination with precise leveling and PSInSAR observations to quantify pumping-induced land subsidence in central Taiwan. Proc. IAHS 2015, 372, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yang, Y.-J.; Hwang, C.; Hung, W.-C.; Fuhrmann, F.; Chen, Y.-A.; Wei, S.-H. Surface Deformation from Sentinel-1A InSAR: Relation to Seasonal Groundwater Extraction and Rainfall in Central Taiwan. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.-Y.; Hu, J.-C.; Chan, Y.-C.; Su, Y.-F.; Chang, C.-H. The Relationship between Surface Displacement and Groundwater Level Change and Its Hydrogeological Implications in an Alluvial Fan: Case Study of the Choshui River, Taiwan. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-A.; Chang, C.-P.; Hung, W.-C.; Yen, J.-Y.; Lu, C.-H.; Hwang, C. Space-Time Evolutions of Land Subsidence in the Choushui River Alluvial Fan (Taiwan) from Multiple-Sensor Observations. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, A. A multi-temporal InSAR method incorporating both persistent scatterer and small baseline approaches. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Central Geological Survey. The Investigation of Hydrogeology in the Choshui River Alluvial Fan, Taiwan; Central Geological Survey of Taiwan: Taipei, Taiwan, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Hung, W.C.; Wang, C.; Hwang, C.; Chen, Y.A.; Chiu, H.C.; Lin, S.H. Multiple sensors applied to monitor land subsidence in Central Taiwan. Proc. IAHS 2015, 372, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.; Ng, A.H.-M.; Du, Z.; Chen, H.-Y.; Li, X. Integrated space geodesy for mapping land deformation over Choushui River Fluvial Plain, Taiwan. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 6319–6345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nainggolan, L.; Ni, C.-F.; Darmawan, Y.; Lo, W.-C.; Lee, I.-H.; Lin, C.-P.; Hiep, N.H. Cost-Effective Groundwater Potential Mapping by Integrating Multiple Remote Sensing Data and the Index–Overlay Method. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.-J.; Lin, C.-W.; Burbey, T.J.; Ali, M.Z. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Extracted Groundwater Volumes Estimated from Electricity Consumption. Groundwater 2020, 58, 962–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-H.; Chen, W.-P.; Lee, R.-H. Estimation of groundwater recharge using water balance coupled with base-flow-record estimation and stable-base-flow analysis. Environ. Geol. 2006, 51, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nainggolan, L.; Ni, C.-F.; Darmawan, Y.; Lee, I.-H.; Lin, C.-P.; Li, W.-C. Data-Driven Approach to Assess Spatial-Temporal Interactions of Groundwater and Precipitation in Choushui River Groundwater Basin, Taiwan. Water 2020, 12, 3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- G.P.S. Lab of Academia Sinica. GPS Processed Data. 2022. Available online: https://gps.imb.sinica.edu.tw/ (accessed on 16 August 2024).
- Herring, T.A.; King, R.W.; McClusky, S.C. Documentation for the GAMIT GPS Analysis Software; Release 10.0; Department of Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences, MIT: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Lyard, F.; Lefevre, F.; Letellier, T.; Francis, O. Modelling the global ocean tides: Modern insights from FES2004. Ocean. Dyn. 2006, 56, 394–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm, J.; Niell, A.; Tregoning, P.; Schuh, H. Global Mapping Function (GMF): A new empirical mapping function based on numerical weather model data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L07304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altamimi, Z.; Collilieux, X.; Métivier, L. ITRF2008: An improved solution of the international terrestrial reference frame. J. Geod. 2011, 85, 457–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.-H.; Yang, M.; Huang, Y.-T.; Ching, K.-E.; Rau, R.-J. Vertical displacement rate field of taiwan from geodetic levelling data 2000–2008. Surv. Rev. 2011, 43, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Zan, F.; Guarnieri, A.M. TOPSAR: Terrain Observation by Progressive Scans. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 2352–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farr, T.G.; Kobrick, M. Shuttle Radar Topography Mission produces a wealth of data. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2000, 81, 583–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, R.M.; Werner, C.L. Radar interferogram filtering for geophysical applications. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1998, 25, 4035–4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Cumming, I. A region-growing algorithm for InSAR phase unwrapping. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1999, 37, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, O.; Mallorqui, J.J.; Broquetas, A. Linear and nonlinear terrain deformation maps from a reduced set of interferometric SAR images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 2243–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.-H.; Ni, C.-F.; Chang, C.-P.; Chen, Y.-A.; Yen, J.-Y. Geostatistical Data Fusion of Multiple Type Observations to Improve Land Subsidence Monitoring Resolution in the Choushui River Fluvial Plain, Taiwan. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. 2016, 27, 505–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, S.-K. Plan for a groundwater monitoring network in Taiwan. Hydrogeol. J. 1998, 6, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G. New Preconsolidation Heads Following the Long-Term Hydraulic-Head Decline and Recovery in Houston, Texas. Ground Water 2023, 61, 674–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ku, C.-Y.; Liu, C.-Y. Modeling of land subsidence using GIS-based artificial neural network in Yunlin County, Taiwan. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 4090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, W.-C.; Hwang, C.; Sneed, M.; Chen, Y.-A.; Chu, C.-H.; Lin, S.-H. Measuring and Interpreting Multilayer Aquifer-System Compactions for a Sustainable Groundwater-System Development. Water Resour. Res. 2021, 57, e2020WR028194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D2487-17e1; Standard Practice for Classification of Soils for Engineering Purposes (Unified Soil Classification System). ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017.
- Geological Survey and Mining Management Agency, MOEA. Hydrogeological Information System of Taiwan. 2023. Available online: https://hydro.geologycloud.tw/swagger/api-docs/api#/ (accessed on 16 August 2024).
- Burland, J.B.; Wroth, C.P. Settlement of Buildings and Associated Damage; Building Research Establishment: Hertfordshire, UK, 1975; Volumes 33–75. [Google Scholar]
- Montenegro, P.A.; Carvalho, H.; Ribeiro, D.; Calçada, R.; Tokunaga, M.; Tanabe, M.; Zhai, W.M. Assessment of train running safety on bridges: A literature review. Eng. Struct. 2021, 241, 112425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Yu, C. Building risk monitoring and prediction using integrated multi-temporal InSAR and numerical modeling techniques. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 114, 103076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.-H.; Bürgmann, R.; Hu, J.-C. Fifteen years of surface deformation in Western Taiwan: Insight from SAR interferometry. Tectonophysics 2016, 692, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).