Abstract
Evaluation ecosystem service value (ESV) is critical, as “lucid waters and lush mountains are invaluable assets”. To assess the incremental effects of ecological assets on soil and water conservation in subtropical mountains, we developed a remote-sensing-driven mountainous equivalent factor (RS-MEF) method to estimate the ESV of Changting County, China. This method is a hybrid of a conventional equivalent factor framework and remote sensing techniques for mountains, achieving several advancements, including spatial adjustment using vegetation activity merged with productivity, improved spatial resolution, and the removal of topographic effects. Using the RS-MEF method, we estimated that the ESV of Changting County was approximately CNY 15.80 billion in 2010 and CNY 34.83 billion in 2022. Specifically, the ESV per unit area of the major soil erosion area (MSEA) in the county was less than that of the non-major soil erosion area (n-MSEA); however, the ESV growth rate of the MSEA from 2010 to 2022 was faster than that of the n-MSEA. Therefore, the ESV gap between the two areas was reduced from 28.99% in 2010 to 15.83% in 2022. Topographic gradient analysis illustrates that areas with elevations of 385 to 658 m and steep slopes achieved a high ESV, while high-elevation areas with gentle slopes will be a focus of control in the next phase. Our study demonstrates that significant achievements have been made in ecological restoration from an ESV perspective, with a notable reduction in low-ESV areas in the MSEA; the insights gained into ESV growth and its underlying factors are valuable and instructive for future soil and water conservation efforts.
1. Introduction
Soil erosion is a naturally occurring process that affects all landforms and threatens ecosystem viability [1]. It results in soil property changes, land degradation, vegetation destruction, decreased agricultural productivity, and a decline in ecosystem service function [2,3]. Correspondingly, comprehensive ecological restoration is practiced in order to control soil erosion, leading to vegetation recovery, reforestation, land upgradation, and soil reformation, all of which underpin ecosystem services [4]. Ecosystem services are the benefits that human populations derive, either directly or indirectly, from ecosystem functions [5]. The monetary value of ecosystem services has been explored in recent decades. Following academic studies [5,6,7], international forums have addressed this issue, including the Millennium Ecosystem Assessment (MEA), the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES), and The Economics of Ecosystems and Biodiversity (TEEB) [8].
Among the various monetization methods for estimating ecosystem service value (ESV) [9,10], two kinds of approaches are widely utilized: primary-data-based and unit-value-based methods [5,11,12]. Primary-data-based approaches combine the physical quantities of ecosystem services with market price, travel cost, opportunity cost, shadow price, and ecosystem services’ replacement cost, which are complicated and require a number of parameters to calculate. Such methods are often performed on one or a few kinds of service and are usually applied to a small area or single ecosystem [13,14]. Unit-value-based approaches use the monetized value per unit area of ecosystems [5]. Following the proposal by Costanza et al., many modifications have been applied to these methods. One of them is the equivalent factor method [15], which uses equivalence coefficients to reflect the relative weights of the provisioning, regulating, supporting, and cultural service value for a certain ecosystem compared to the standard ecosystem (e.g., farmland). It is suitable for ESV evaluation under land use changes due to urbanization, ecological restoration, and so on [16,17,18]. The equivalent factor method was also improved for the accurate estimation of ESV, e.g., with an adjustment coefficient using natural resource factors and socio-economic factors, illuminating the spatial variation in ESV from any kind of land use. Natural factors include biomass, vegetation indices, net primary productivity (NPP), precipitation, and erosion prevention [19,20,21]. Socio-economic factors cover the willingness and ability to pay [22,23], the educational level and income level [24], the population [25], and so on. However, socio-economic statistics usually at least correspond to a county scale. Therefore, accurate estimation of the ESV’s heterogeneity within a county mainly depends on natural factors, in which NPP is frequently used [26,27]. NPP primarily represents the carbon deposited in the stems, branches, and roots of forests and the underlying soil, but it tends to undervalue the contributions of the vegetation canopy, e.g., green leaves, to air quality, climate regulation, and landscape esthetics. Meanwhile, the spatial resolution of the NPP products is typically 500 m or 1000 m, which makes them difficult to use in ESV evaluation for small patches of soil erosion control. Therefore, a spatial adjustment coefficient that is more physically based and a higher resolution would be preferable for the more accurate monetization of regional ESV [11,28].
In addition, topographic effects hinder land use classification and vegetation canopy evaluation in rugged mountains using remote sensing, due to the phenomena of “the same body with different spectra” and “different bodies with the same spectrum” caused by anisotropic solar illumination [29,30,31]. Surface reflectance and vegetation indices are always underestimated in topographic shadow areas, including self-shadow and cast shadow, where the pixels are obstructed from direct solar irradiance [32,33]. Therefore, removal of topographic effects is crucial for land use classification, vegetation canopy monitoring, and further ESV estimation in mountainous soil erosion areas.
The main objectives of this study are to (1) evaluate the incremental effect of ecological assets for soil erosion control in subtropical mountains and determine the spatial–temporal pattern of ESV and its underlying factors and (2) develop a remote-sensing-driven mountainous equivalent factor (RS-MEF) method for the comprehensive assessment of ESV in rugged mountains, integrating an equivalent factor framework, topographic correction techniques, and combined vegetation indicators.
2. Study Area and Data
2.1. Study Area
The study area is Changting County (116°00′45″–116°39′20″E, 25°18′40″–26°02′05″N) in Longyan City, Fujian Province, East China (Figure 1). It covers land with an elevation ranging from 156 m to 1443 m with a mean of approximately 513 m and a slope ranging from ~1° to 88° with a mean of approximately 18°. The major land cover in this area is forest, which has prominent topographic effects in remote sensing images. Due to its ecological vulnerability [34,35], Changting County has suffered intensive soil and water erosion in the last century, which has restricted local sustainable development. According to local surveys, most of the soil and water erosion is located in seven towns in central–eastern part of the county, known as the major soil erosion area (MSEA). After several decades of government-driven soil and water conservation efforts [36], particularly intensified since the 12th Five-Year Plan, there have been significant and continuous improvements in stemming soil erosion and restoring the ecology. The soil and water conservation rate improved from 68.55% in 1985 to 89.74% in 2010, and to 93.43% in 2022. At the 15th Conference of the Parties to the United Nations Convention on Biological Diversity (COP15), the soil erosion control practices in Changting were selected as a typical case of ecological restoration.
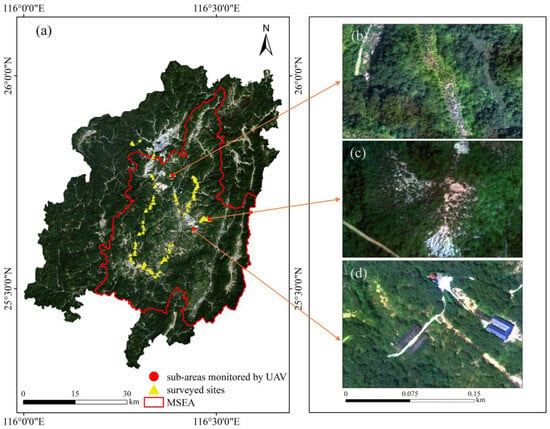
Figure 1.
Study area and field surveys: (a) major soil erosion area (MSEA, red shape), surveyed sites (yellow triangle points), and sub-areas monitored by an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) between 18 and 21 September 2022 (red round points); (b–d) sub-areas of Changting County—Huangwuqian (HWQ), Laiyoukeng (LYK), and Xianggongting (WGT), respectively. The county map is based on the standard map released by the Ministry of Natural Resources of the People’s Republic of China [No. GS(2019)1822].
2.2. Data Source
Multiple source data for the research area were collected, including satellite images, unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) images, a digital elevation model (DEM), field survey data, an NPP open product, the Changting Statistical Yearbook 2023, and Compilation of National Agricultural Cost–Benefit Data 2023 (Table 1). We acquired one Landsat 5 TM scene on 29 October 2010 and one Landsat 9 OLI scene on 22 October 2022, both of which are multi-spectral images with 30 m spatial resolution. The corresponding DEM data with a 30 m resolution from ASTER GDEM V2 were also obtained. These data were downloaded from the Computer Network Information Center, Chinese Academy of Sciences (Geospatial Data Cloud. Available online: http://www.gscloud.cn (accessed on 26 October 2023)). The NPP product was downloaded from the Earth Science Data Systems (ESDS. Available online: https://appeears.earthdatacloud.nasa.gov/ (accessed on 26 May 2024)). In addition, we carried out a field survey spanning 18–21 September 2022 to assess soil and water conservation, land use, and the vegetation canopy. We surveyed three sub-areas of Changting County—Huangwuqian (HWQ), Laiyoukeng (LYK), and Xianggongting (WGT)—using the DJI Phantom 4 pro multi-spectral UAV (Figure 1).

Table 1.
Multiple source data for research.
3. Methods
The main procedures of the RS-MEF method include topographic correction for spectral reflectance using the integrated topographic correction (ITC) [30] and the shadow-eliminated vegetation index (SEVI) calculation [32], along with ESV calculation. This involves standard equivalent factor calculation, land use classification, equivalent coefficients set for different ecosystem services from different land uses, and adjustment coefficient specification for dynamic spatial variation in ESV. Two major improvements to the RS-MEF method are the spatial adjustment coefficient using NPP coupled with SEVI and land use classification using the satellite images with removed topographic effects (Figure 2). Finally, a spatial–temporal analysis of ESV is conducted, specifically, evaluation the ESV variation since the 12th Five-Year Plan, i.e., from 2010 to 2022.
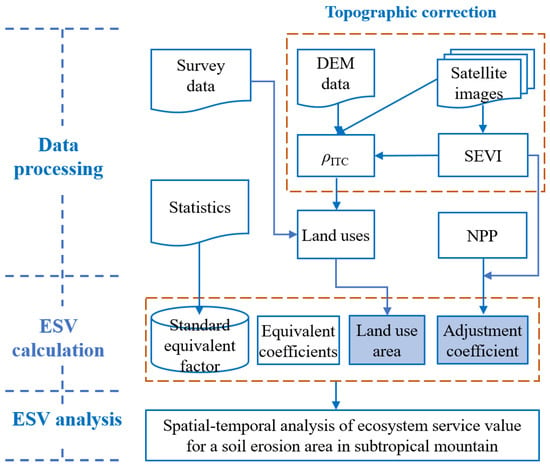
Figure 2.
Ecosystem service value (ESV) evaluation using a remote-sensing-driven mountainous equivalent factor (RS-MEF) method: DEM is the digital elevation model, ρITC is the spectral reflectance after the integrated topographic correction (ITC), SEVI is the shadow-eliminated vegetation index, and NPP is the net primary productivity.
3.1. Data Processing
Crop prices, sown area, and production data for Changting County were collected from statistics. After the pre-processing of atmospheric correction, topographic corrections of the SEVI and ITC were used for remote sensing images. The SEVI was calculated using the surface reflectance of the red band and the near-infrared (NIR) band, as shown in Equation (1), in which the adjustment factor was calculated using the block information entropy algorithm (BIE-algorithm) [37]. First, the DEM of the study area was divided into blocks of 6 km × 6 km, and the steep blocks were selected from the 5% highest slope mean of the blocks. Then, the SEVI information entropy of any steep block was calculated using Equations (2) and (3), and the target block that achieved the highest entropy was used to determine the final adjustment factor, as outlined in Equations (4) and (5). Finally, the SEVI of 2010 and 2022 was normalized using the fixed land objects and statistics.
where SEVI is the shadow-eliminated vegetation index, is the near-infrared band reflectance, is the red band reflectance, is the adjustment factor, is the information entropy of SEVI in a block, is the percentage of a SEVI pixel value in a selected block, is the number of pixels in a selected block, is a pixel value of SEVI, is an optimized adjustment factor for a block, is the final adjustment factor for an entire scene, is the maximum information entropy of SEVI in a block, and is the number of selected steep blocks in an entire scene.
The ITC is a data-driven topographic correction method (Figure 3). The main data include SEVI information and the multi-band reflectance simulated from a physically based model of sun–canopy–sensor (SCS) + C correction. Firstly, the total topographic shadow in the SCS + C corrected image was extracted. Then, randomly generated pixels in sunny areas were used as training samples, including the dependent variable from the SCS + C corrected reflectance and independent variable of the SEVI. Finally, the regressions generated from the Random Forest (RF) regressor between the SEVI and the waveband reflectance of sunny areas were used to correct the waveband reflectance of topographic shadow for the visible spectral wavebands. As for the near-infrared (NIR) waveband, the inverse calculation method was used (Equation (6)).
where ρnir_tc is the topographic corrected reflectance of the NIR waveband, RVI is the ratio vegetation index, and ρr_tc is the topographic corrected reflectance of the red waveband.
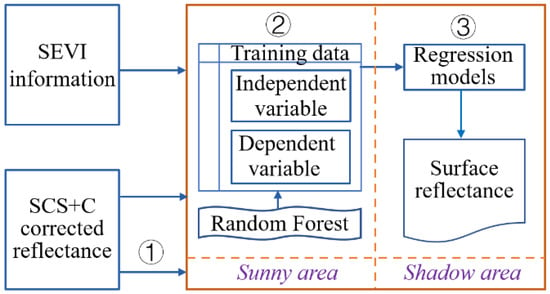
Figure 3.
Flow chart of the integrated topographic correction (ITC): ① shadow extraction, ② data training, and ③ shadow correction. SCS + C is the sun–canopy–sensor + C correction.
3.2. ESV Calculation
A general framework of the equivalent factor method is as follows (Equation (7)):
where ESV is the ecosystem services value (CNY), E is a standard equivalent factor (CNY/hm2), Ti is the conventional equivalent coefficients of the i-th land use, is the area of the i-th land use (hm2), and is the spatial adjustment coefficient of the i-th land use.
- (1)
- Standard equivalent factor
An empirical formula for the standard equivalent factor was calculated using Equation (8), using the data from the Changting Statistical Yearbook 2023 and the Compilation of National Agricultural Cost–Benefit Data 2023. In this study, the standard equivalent factor for 2010 was modified using the consumer price index (CPI) to match the benchmark of that for 2022. So, these prices are more in line with the present currency values compared to the standard equivalent factors modified to match those of earlier years, e.g., 2000 or 2010.
where ai is the area of the i-th crop in a study year (hm2), pi is the average price of the i-th crop in a study year (CNY/kg), qi is the crop yield of the i-th crop in a study year (kg/hm2), A is the total area of all crops in a study year (hm2), and C is the adjustment coefficient of consumer price index.
- (2)
- Equivalent coefficients
Equivalent coefficients provide a weight coefficient of valuation for each ecosystem service. An expert-based equivalent coefficient table was referenced (Table 2).

Table 2.
The equivalent coefficients of ESV per unit area for six ecosystems and four services [19].
- (3)
- Land use classification for mountains
Based on the land use types in Table 2 and the actual situation of study area, the Landsat images were classified as coniferous forest, broad-leaved forest, mixed forest, grassland, farmland, construction land, unused land, and water. Considering the prominent topographic effects in the research area, we used the ITC rectified images to classify land uses. The ITC is better at removing topographic shadow, especially cast shadow in rugged mountains [30]. Firstly, the training samples were selected from the images, with aid from the field survey and Google Earth (Table 3). Next, the features of spectral bands, vegetation indices, textures, and primary components calculated from the images were set and trained using machine learning based on the RF technique. Then, the classification accuracy was assessed using a confusion matrix with the overall accuracy and Kappa coefficient. Finally, eight land uses were classified to match the equivalent coefficients.

Table 3.
Land use sample images.
- (4)
- Spatial adjustment coefficient modification
Considering that vegetation indices mainly reflect the vegetation canopy of forest and grass [38], we improved the spatial adjustment coefficient using NPP coupled with vegetation indices to incorporate the stems, branches, roots, and canopy of forests in mountainous areas (Equation (9)). This was referred to as vegetation activity and productivity (VAP), since vegetation indices indicate relative the activity of green vegetation and NPP is a measure of the annual productivity of the plants in the biosphere. Specifically, we used the SEVI for rugged mountains in this study (Equation (10)), since it has additional benefits of topographic effect elimination and weak target recognition in green mountains [39]. In addition, the spatial resolution of the revised spatial adjustment coefficient was improved to 30 m from 500 m for the open NPP product.
where is the modified spatial adjustment coefficient of the i-th land use, is the vegetation activity and productivity of the i-th land use, is the NPP of the i-th land use, is the vegetation index of the i-th land use; is the modified spatial adjustment coefficient of the i-th land use with SEVI (30 m), is the vegetation activity and productivity of the i-th land use with SEVI (30 m), is the downloaded NPP product of the i-th land use with 500 m, and is the calculated SEVI of the i-th land use with 30 m.
- (5)
- ESV calculation improvement
Finally, the RS-MEF method was developed using the land use area with topographic effects removed and the modified spatial adjustment coefficient, as described in Equation (11). Considering the “general labor” from ecosystems, i.e., general ecosystem services (resources), we used the VAP mean of the non-major soil erosion area (n-MSEA) to match the standard equivalent factor outlined in Equation (12). The n-MSEA is the county area minus the MSEA.
where is the area of the i-th land use classified from the image with topographic effects removed (hm2) and is the NPP of the n-MSEA, and is the SEVI of the n-MSEA.
3.3. ESV Analysis
Using the calculated ESV result, we performed a spatial–temporal analysis to discover the spatial distribution pattern of ESV and the ESV change characteristics from 2010 to 2022. In spatial pattern analysis, we divided the county into the MSEA and n-MSEA for the comparison of ESV. In addition, the topographic gradient effect was analyzed using the topographic indicators of elevation, slope, relief amplitude, and terrain niche, with five grades set using the quantile approach (Table 4). The ESV of land use was also analyzed to recognize the major contributor. In temporal analysis, the ESV increment and growth rate from 2010 to 2022 were computed. To determine the contribution of land use change to ESV variation, Equation (11) was inverted to calculate the growth rate of this contribution from 2010 to 2022, as given by Equation (13).
where Clu is the growth rate from land use changes in ESV variation from 2010 to 2022.

Table 4.
Topographic gradient indicators and grades.
4. Results
4.1. Land Use Change
The overall accuracy and Kappa coefficient of land use classification were 0.812 and 0.780 in 2010 and 0.819 and 0.782 in 2022, respectively. The classified result shows that the major land uses are mixed forest, coniferous forest, grassland, and farmland (Figure 4 and Figure 5). From 2010 to 2022, the areas of mixed forest and coniferous forest in the MSEA grew from 393.97 km2 to 433.74 km2 and 283.27 km2 to 380.56 km2, with area increments of 39.77 km2 (growth rate: 10.09%) and 97.29 km2 (growth rate: 34.35%), respectively. Meanwhile, those in the n-MSEA grew from 744.44 km2 to 805.81 km2 and 436.73 km2 to 523.31 km2, with area increments of 61.37 km2 (growth rate: 8.24%) and 86.58 km2 (growth rate: 19.82%), respectively. Coniferous forest, which experienced the largest increase in area (and growth rate) in the county, expanded by 183.87 km2 (from 720.00 km2 to 903.87 km2), with a growth rate of 25.54%. The second largest increase was in mixed forest, which saw an increment of 101.14 km2 (growth rate: 8.88%), growing from 1138.41 km2 to 1239.55 km2. On the contrary, the areas of grassland and farmland shrank in the same period from 475.81 km2 to 268.07 km2 and 346.09 km2 to 304.92 km2, with area decrements of 207.75 km2 (growth rate: −43.66%) and 41.17 km2 (growth rate: −11.90%), respectively. The matrix of land use change shows that mixed forest primarily developed from coniferous forest. Meanwhile, the enlargement of the coniferous forest area was due to the transition of various land types, e.g., unused land, grassland, and mixed forest. According to the expert-based equivalent coefficients (Table 2), the land use change from coniferous forest to mixed forest results in a significant increase in ESV.
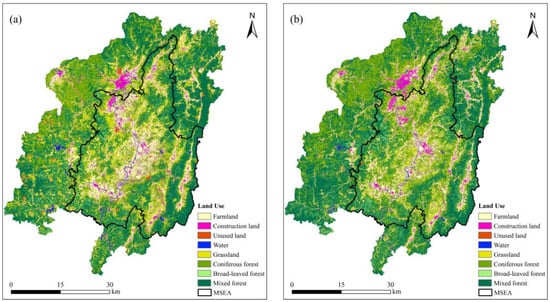
Figure 4.
Land use classification of Changting County: (a) 2010 and (b) 2022.
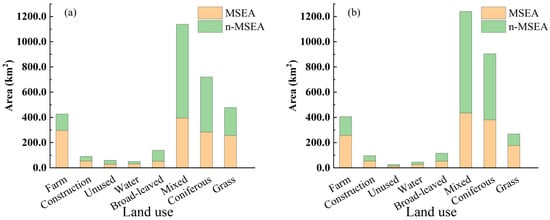
Figure 5.
Stacked histogram of land uses in Changting County: (a) 2010 and (b) 2022.
4.2. Spatial Adjustment Coefficients
The spatial adjustment coefficients of NPP, SEVI, and VAP are displayed in Figure 6. The adjustment coefficient of NPP illuminates rough pixels (500 m) with clear fragmentation. It achieved a mean of 789.09 gC/m2a in 2010 and 827.13 gC/m2a in 2022 (growth rate: 4.82%), with a generally low–medium value in the MSEA. Meanwhile, the adjustment coefficient of SEVI shows smooth pixels (30 m) with a mean of 0.56 in 2010 and 0.64 in 2022 (growth rate: 12.95%), with a low–medium value in the MSEA. Evidently, the value distribution of SEVI is more continuous than that of NPP. Finally, the adjustment coefficient of VAP illustrates the merged features in spatial resolution and value distribution, with a mean of 20.16 in 2010 and 21.82 in 2022 (growth rate: 8.23%).
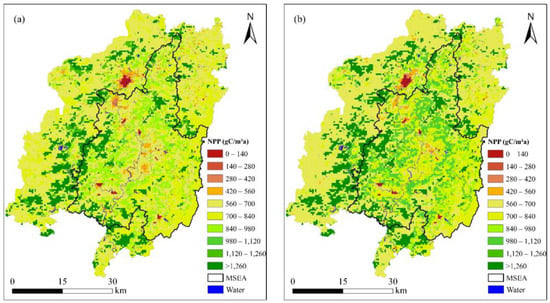
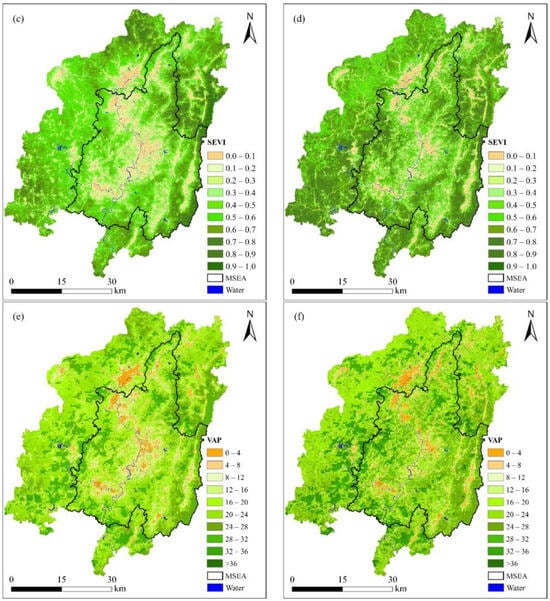
Figure 6.
Spatial adjustment coefficients: (a,b) NPP in 2010 and 2022, (c,d) SEVI of 2010 and 2022, and (e,f) VAP in 2010 and 2022, respectively. VAP is vegetation activity and productivity.
4.3. ESV Comparison
Using the calculated standard equivalent factor of Changting County, China, i.e., CNY 2858.42/hm2 in 2010 and CNY 5535.70/hm2 in 2022, the ESV of the county was estimated (Figure 7). The total ESV and ESV per unit area using the adjustment coefficient of VAP were CNY 15.80 billion and CNY 50,913/hm2 in 2010 and CNY 34.83 billion and CNY 112,244/hm2 in 2022 (Figure 7a,b), respectively. Those that used the adjustment coefficient of NPP were CNY 15.67 billion and CNY 50,530/hm2 in 2010 and CNY 31.86 billion and CNY 102,714/hm2 in 2022 (Figure 7c,d), respectively. The estimated ESV using VAP was higher than that using NPP, and the spatial distribution of the ESV using VAP showed higher integrity and smoothness than that using NPP. Therefore, we adopted the ESV result using the adjustment coefficient of VAP, i.e., the ESV calculated from the RS-MEF method.
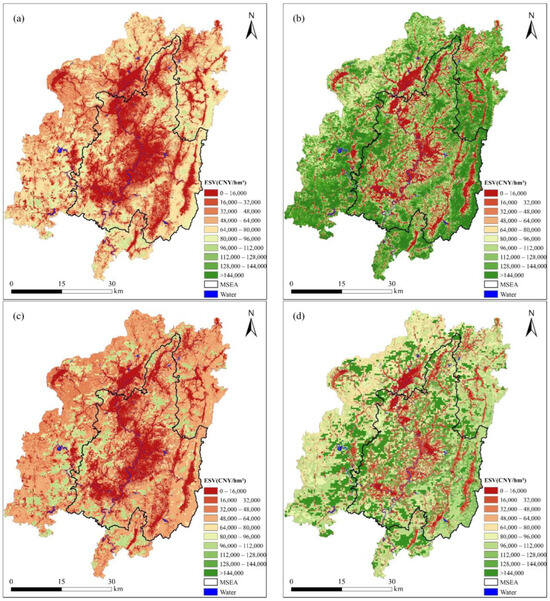
Figure 7.
ESV of Changting County, China: (a,b) the estimated ESV using VAP in 2010 and in 2022, and (c,d) the estimated ESV using NPP in 2010 and in 2022.
4.4. ESV Distribution Characteristics
Figure 7a,b show that a low ESV is primarily seen in downtown areas and the MSEA. The ESV per unit area of the MSEA was approximately CNY 43,885/hm2 in 2010 and CNY 103,186/hm2 in 2022, less than that of the n-MSEA, with approximately CNY 56,606/hm2 in 2010 and CNY 119,523/hm2 in 2022. From 2010 to 2022, the total ESV of the county increased by 120.47%. The total ESV of the MSEA in 2010 and 2022 was CNY 6.14 billion and CNY 14.44 billion, with a growth rate of 135.13%; the total ESV of the n-MSEA in 2010 and 2022 was CNY 9.66 billion and CNY 20.39 billion, with a growth rate of 111.10%. Evidently, the ESV growth rate of the MSEA was faster than that of the n-MSEA. The difference rate between the ESV per unit area of the MSEA and that of the n-MSEA in 2010 was 28.99%, while that in 2022 declined to 15.83%. The gap between them was reduced, with the low-ESV area significantly shrinking in the MSEA (dark red in Figure 7a,b).
Topographic gradient effect analysis shows that the ESV of the county displays an inverted U curve with the elevation and relief amplitude, while the incremental curves with the slope and terrain niche show a strong positive correlation between ESV and slope (Figure 8a,b). Specifically, the ESV of the MSEA displays an inverted V curve with the elevation with the summit in gradient II, with incremental curves with the slope, relief amplitude, and terrain niche. Specifically, areas with a high terrain niche gradient (V) achieved a high ESV (Figure 8c,d). The ESV of the n-MSEA displays an inverted V curve with the elevation with the summit in gradient III, inverted U curves with the relief amplitude and terrain niche, and an incremental curve with the slope (Figure 8e,f). From 2010 to 2022, the ESV of the county with the elevation shows a change, with the summit being altered from gradient III to II, which indicates that soil erosion control and ecological restoration were improved in the relatively low-elevation area in gradient II. These analyses indicate that the area in elevation II and III with a high slope achieved a high ESV; however, the area with high elevation and gradient V coupled with a low slope had a low ESV. This region should be a focus of control in the next phase.
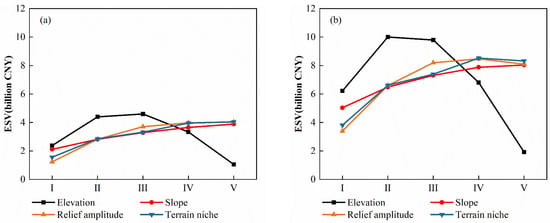
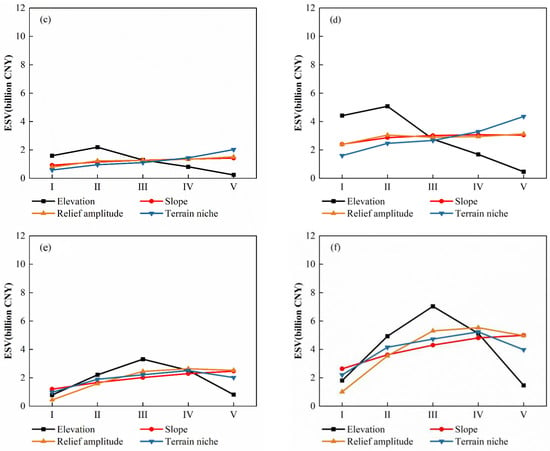
Figure 8.
Topographic gradient effect of ESV: (a,c,e) ESV of the county, MSEA, and n-MSEA in 2010; and (b,d,f) ESV of the county, MSEA, and n-MSEA in 2022.
Further analysis shows that the majority of ESV was attributed to mixed forest and coniferous forest, with approximately CNY 8.57 billion (54.28%) and CNY 3.50 billion (22.21%) in 2010 and CNY 19.85 billion (57.13%) and CNY 9.38 billion (26.99%) in 2022 (Figure 9). This is in accordance with the dominant land uses and their changes (Figure 4 and Figure 5). Specifically, the ESV of mixed forest in the MSEA was CNY 3.04 billion in 2010 and CNY 7.14 billion in 2022, with a growth rate of 134.72%; meanwhile, that in the n-MSEA was CNY 5.40 billion in 2010 and CNY 12.30 billion in 2022, with a growth rate of 127.75%. The ESV of coniferous forest in the MSEA was CNY 1.38 billion in 2010 and CNY 4.05 billion in 2022, with a growth rate of 194.67%; meanwhile, that in the n-MSEA was CNY 2.13 billion in 2010 and CNY 5.16 billion in 2022, with a growth rate of 142.32%. The coniferous forest in the MSEA attained the fastest ESV growth rate over the examined period.
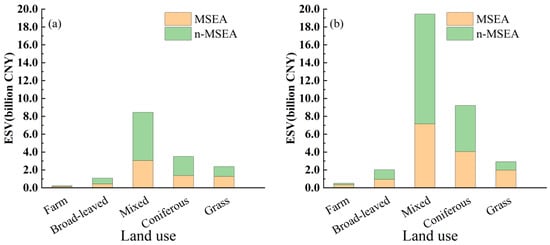
Figure 9.
Stacked histogram of ESV by land use in Changting County: (a) 2010 and (b) 2022.
In addition, the VAP mean of the MSEA was 18.51 in 2010 and 21.08 in 2022, with a growth rate of 13.88%; meanwhile, that of the n-MSEA was 21.51 in 2010 and 22.43 in 2022, with a growth rate of 4.25%. From 2010 to 2022, the growth rate of VAP of the MSEA was three times higher than that of the n-MSEA. The result calculated using Equation (13) indicates that the growth rate of contribution from land use change to the ESV variation from 2010 to 2022 was 5.18% for the county, 6.62% for the MSEA, and 4.59% for the n-MSEA, respectively. Combined with the contribution from the spatial adjustment coefficient of VAP, the growth rate of the contribution from ecosystem resources (land use changes coupled with VAP changes) was 13.84% for the county, 21.41% for the MSEA, and 9.03% for the n-MSEA, respectively.
5. Discussion
5.1. ESV Changes in Changting County and Their Underlying Factors
Considering that “lucid waters and lush mountains are invaluable assets”, it is important to assess the incremental effect of ESV for ecological restoration in subtropical mountainous soil erosion areas. In this study, the ESV of Changting County, China, was estimated and analyzed. Compared to the total ESV of the county in 2010, that in 2022 increased by approximately 120.47%, in which the growth rates of the standard equivalent factor, land use, and VAP were approximately 93.66%, 5.18%, and 8.23%, respectively. The contribution from the standard equivalent factor was dominant in the ESV increment from 2010 to 2022, mainly due to the increase in crop prices, e.g., the prices of rice, vegetables, and tobacco increased by approximately 18.13%, 67.08%, and 123.54%, respectively. The area percentage of these farm products ranges from approximately 87.37 to 90.10%. In addition, the VAP growth rate comprised a 12.95% increase from SEVI and a 4.82% increased from NPP.
In terms of spatial–temporal heterogeneity, the ESV per unit area of the MSEA was less than that of the n-MSEA; however, the ESV growth rate of the MSEA was higher than that of the n-MSEA from 2010 to 2022. Therefore, the difference rate between ESV per unit area of the MSEA and that of the n-MSEA was decreased by almost half (from 28.99% to 15.83%). The main reasons are that the growth rate of VAP, as a spatial adjustment coefficient, in the MSEA was three times higher than that in the n-MSEA (13.88% vs. 4.25%). Additionally, the growth rate of the contribution from land use changes to ESV variation in the MSEA was also higher than that in the n-MSEA (6.62% vs. 4.59%). These changes illustrate that the vegetation coverage, land use structure, carbon sink, and canopy density in the MSEA were inferior to those in the n-MSEA; however, the quality improvements of vegetation coverage, land use structure, carbon deposit, and canopy density in the MSEA were higher than those in the n-MSEA. In the n-MSEA, the growth rate of VAP (4.25%) and that of land use change (4.59%) were similar; in the MSEA, that of VAP (13.88%) was more than double that of land use change (6.62%). This indicates that the improvement of vegetation activity and productivity remains crucial for soil erosion and water conservation at present and in the future. In addition, topographic gradient effect analysis also illustrates that high-elevation areas with gentle slopes will be a focus of control in the next phase.
As a secondary succession of ecological restoration in subtropical soil erosion areas, the process is still poorly understood since the intermingled biophysical and societal factors and drivers are often complex [34,40,41]. Theoretically, the successional pathway is from naked soil to grassland, coniferous forest, mixed forest, and evergreen broad-leaved forest in subtropical mountainous areas. In this study, we observed that the dominant ESV in Changting County comes from mixed forest, while the most significantly increasing ESV is attributed to coniferous forest, particularly the vast, expanding coniferous forest in the MSEA. This is in accordance with the finding that vegetation plays an important role in ESV supply, with forest providing the highest contribution [17]. These characteristics of spatial variation and ESV changes indicate that the current vegetation successional phase in Changting County is in a critical transition stage, and both positive and negative succession processes [42] are still present. ESV will be improved if positive succession of land use continues; however, it will fluctuate if positive succession of land use is disturbed. Therefore, in the next phase, restoration measures that balance ecological benefits with economic costs should be prioritized, e.g., closing hillsides for afforestation [36].
Finally, this study indicates that the achieved knowledge of the regional ESV growth characteristics and inherent factors is valuable and instructive for soil erosion control and ecological restoration, despite the difficulty in validating ESV under the current socio-economic conditions.
5.2. Advantages and Disadvantages of Employing the RS-MEF Method for the Valuation of Ecosystem Services
Aiming to achieve the accurate evaluation of ESV in mountainous soil erosion areas, we developed the RS-MEF method, which couples a general equivalent factor framework with remote sensing techniques for mountains. This method achieved several advancements, including spatial adjustment using carbon sinks and the vegetation canopy, improved spatial resolution, and the removal of topographic effects.
Firstly, an improved spatial adjustment coefficient of VAP using NPP coupled with a vegetation index is developed, which is suitable for quantifying the spatial heterogeneity of the ESV in mountainous areas. NPP primarily represents the dry matter increment of the stems, branches, and roots of forests, while the SEVI reflects forest green leaves and grass and implies some ecological esthetics and cultural service value. As lucid waters and lush mountains are ideal, the greenness reflected by the vegetation index complements NPP. Using the improved adjustment coefficient, the spatial variation in the ESV in mountains is more reasonable and accurate. As for the adjustment coefficient of socio-economic factors, its efficacy diminishes within a county due to the reliance on a single statistic, such as the Engel coefficient, the urban population ratio, or the per-capita GDP in a county. Therefore, we did not consider the adjustment coefficient of socio-economic factors in the ESV assessment for this study.
Secondly, the spatial resolution of the critical parameters calculated from remote sensing images is improved. These parameters include land use classification and the spatial adjustment coefficient of the SEVI, derived from the used Landsat images with a 30 m resolution. Therefore, we did not depend on the external products of land use classification or vegetation indices, which typically have resolutions of 500 m or lower [19,43,44,45]. The RS-MEF method reduces the major uncertainties resulting from heterogeneous data and provides better results for regional ESV evaluation. It is especially advantageous for ESV evaluation using land use changes. For example, we observed that mixed forest primarily transitioned from coniferous forest, resulting in an increase in ESV and aligning with the ecological succession rule. Evidently, remote sensing can play a significant role in ESV evaluation, which can provide increasingly accurate spatial and temporal resolution.
Thirdly, effective topographic correction improves ESV evaluation accuracy in rugged mountains. Spectral characteristic variation in land use between sunny areas and topographic shadows decreases after integrated topographic correction, which improves the spectral homogeneity of the same land use in rugged mountains [30]. For example, the spectral reflectance in topographic shadows and that in sunny areas are corrected to that in the adjacent flat area. Therefore, the land use classification accuracy was improved, allowing for the more precise quantification of ESV in mountainous areas. In addition, the spatial adjustment coefficient of SEVI () improves vegetation canopy quantification in mountainous areas by eliminating topographic effects [32] and addressing weak target recognition in rugged green mountains [39]. They are beneficial for ESV evaluation in rugged mountains.
These improvements are effective for the quantitative estimation of ecosystem resources and ESV in mountainous areas. However, the disadvantages of the RS-MEF method still exist. Firstly, the standard equivalent factor calculation and expert-based equivalent coefficients are empirical. These factors can be improved or modified locally, e.g., the equivalent coefficient of regulation of water flows for water area (102.24) can be adjusted for subtropical mountains. Secondly, spatial adjustment coefficients and land use classification can be improved using higher-resolution images, e.g., developing the NPP with a 30 m resolution. Finally, ESV validation remains a significant challenge, making value transformation an urgent area for study and exploration.
6. Conclusions
(1) Ecosystem service value is an essential indicator for evaluating ecological restoration in mountainous soil erosion areas. The estimated ESV of Changting County, China, drastically increased from 2010 to 2022 and displays distinguished spatial–temporal characteristics. The ESV per unit area of the MSEA in the county was less than that of the n-MSEA; however, the ESV growth rate of the MSEA was higher than that of the n-MSEA. Notably, the growth rate of VAP in the MSEA was three times higher than that in the n-MSEA. The gap in ESV per unit area between the two areas was reduced by approximately 45%. The insights gained into ESV growth and inherent factors are valuable and instructive for the next phase of restoration. This should include improving the vegetation canopy and carbon sinks as well as focusing on areas with high elevation and gentle slope.
(2) We proposed an RS-MEF method that achieved several advancements in ESV estimation in mountainous soil erosion areas, including spatial adjustment using carbon sinks and the vegetation canopy, improved spatial resolution, and the removal of topographic effects. In the next step, this method can be improved for higher accuracy and more extensive applications.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.J., H.Y. and J.L. (Jinglan Lin); methodology, H.J., J.L. (Jing Lin) and B.L.; software, J.L. (Jing Lin), B.L. and H.J.; validation, H.J. and B.L.; formal analysis, H.J. and W.S.; investigation, H.J., J.L. (Jing Lin), B.L., H.Y. and J.L. (Jinglan Lin); resources, H.Y., J.L. (Jinglan Lin) and H.J.; data curation, H.J.; writing—original draft preparation, H.J.; writing—review and editing, H.J., W.S., M.G. and Y.C.; visualization, B.L. and H.J.; project administration, H.J.; funding acquisition, J.L. (Jinglan Lin) and H.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Science and Technology Plan Leading Project of Fujian Province, China, grant numbers 2021Y0005, 2023N0031; the Water Conservancy Science and Technology Project of Fujian Province, China, grant numbers MSK202301, MSK202431; and the project from Changting County, China.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully thank the editors and three anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and advice in improving this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Wuepper, D.; Borrelli, P.; Finger, R. Countries and the global rate of soil erosion. Nat. Sustain. 2020, 3, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagos, P.; Standardi, G.; Borrelli, P.; Lugato, E.; Montanarella, L.; Bosello, F. Cost of agricultural productivity loss due to soil erosion in the European Union: From direct cost evaluation approaches to the use of macroeconomic models. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 471–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, D.A.; Fraser, I.; Dominati, E.J.; Davísdóttir, B.; Jónsson, J.O.G.; Jones, L.; Jones, S.B.; Tuller, M.; Lebron, I.; Bristow, K.L.; et al. On the value of soil resources in the context of natural capital and ecosystem service delivery. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2014, 78, 685–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millennium Ecosystem Assessment (MEA). Ecosystems and Human Wellbeing: Synthesis; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Costanza, R.; d’Arge, R.; deGroot, R.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; Oneill, R.V.; Paruelo, J.; et al. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daily, G.C. Nature’s Services: Societal Dependence on Natural Ecosystems; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, Z.; Zheng, H.; Xiao, Y.; Polasky, S.; Liu, J.; Xu, W.; Rao, E. Improvements in ecosystem services from investments in natural capital. Science 2016, 352, 1455–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braat, L.C.; De Groot, R. The ecosystem services agenda: Bridging the worlds of natural science and economics, conservation and development, and public and private policy. Ecosyst. Serv. 2012, 1, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, A.V.; Tiwari, C.; Atkinson, S.F. Progress in ecosystem services research: A guide for scholars and practitioners. Ecosyst. Serv. 2021, 49, 101267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W. Ecosystem services research in China: A critical review. Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 26, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanza, R.; deGroot, R.; Sutton, P.; Van der Ploeg, S.; Anderson, S.J.; Kubiszewski, I.; Turner, R.K. Changes in the global value of ecosystem services. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2014, 26, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, K.G.; Anderson, S.; Gonzales-Chang, M.; Costanza, R.; Courville, S.; Dalgaard, T.; Porfirio, L. A review of methods, data, and models to assess changes in the value of ecosystem services from land degradation and restoration. Ecol. Model. 2016, 319, 190–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Min, Q.; Liu, M.; Cheng, S. Ecosystem service tradeoff between traditional and modern agriculture: A case study in Congjiang County, Guizhou Province, China. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2012, 6, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Dong, S.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Shi, J.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Y. Effect of degradation intensity on grassland ecosystem services in the alpine region of Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, G.; Lu, C.; Leng, Y.; Zheng, D.; Cheng, L. Ecological assets valuation of the Tibetan Plateau. J. Nat. Res. 2003, 18, 189–196. [Google Scholar]
- Arowolo, A.O.; Deng, X.; Olatunji, O.A.; Obayelu, A.E. Assessing changes in the value of ecosystem services in response to land-use/land-cover dynamics in Nigeria. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 597–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sannigrahi, S.; Bhatt, S.; Rahmat, S.; Paul, S.K.; Sen, S. Estimating global ecosystem service values and its response to land surface dynamics during 1995–2015. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 223, 115–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Das, M.; Houqe, R.; Pereira, P. Mapping ecosystem services for ecological planning and management: A case from a tropical planning region, Eastern India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 7543–7560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Zhang, C.; Zhen, L.; Zhang, L. Dynamic changes in the value of China’s ecosystem services. Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 26, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Cui, J.; Zhang, S.; Xin, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y. Spatio-temporal distribution and driving factors of ecosystem service value in a fragile hilly area of north China. Land 2022, 11, 2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, X. Spatiotemporal change in ecosystem service value in response to land use change in Guizhou Province, southwest China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 144, 109514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, K.; Wei, D.Z.; Lin, W.X. Evaluation of ecosystem services value and its implications for policy making in China–A case study of Fujian province. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 108, 105752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhan, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, M. Response of ecosystem services to land use and cover change: A case study in Chengdu City. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 132, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Xue, M.; Wang, X. Spatial correction of ecosystem service value and the evaluation of eco-efficiency: A case for China’s provincial level. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 95, 841–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, L.; Zhang, S.; Yang, J.; Bu, K.; Wang, Q.; Tang, J.; Chang, L. The effects of population density changes on ecosystem services value: A case study in Western Jilin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 61, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Huang, M.; Xie, G.; Zhen, L. Evaluating the impacts of land use change on ecosystem service values under multiple scenarios in the Hunshandake region of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 850, 158067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Huang, H.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Y.; Li, L. Identification of ecological sources using ecosystem service value and vegetation productivity indicators: A case study of the Three-River Headwaters Region, Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau, China. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Xiong, K.; Zhang, Z. Ecosystem services and ecological compensation of world heritage: A literature review. J. Nat. Conserv. 2021, 60, 125968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xu, L.; Shen, H.; Zhang, L. A general variational framework considering cast shadows for the topographic correction of remote sensing imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. 2016, 117, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Chen, A.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Chi, Z.; Li, M.; Wang, X. Vegetation monitoring for mountainous regions using a new integrated topographic correction (ITC) of the SCS + C Correction and the shadow-eliminated vegetation index. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Liu, Q.; Xiao, Q.; Liu, Q.; You, D.; Hao, D.; Wu, S.; Lin, X. Characterizing land surface anisotropic reflectance over rugged terrain: A review of concepts and recent developments. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Wang, S.; Cao, X.; Yang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X. A shadow-eliminated vegetation index (SEVI) for removal of self and cast shadow effects on vegetation in rugged terrains. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2019, 12, 1013–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zuo, X.; Xie, W.; Li, Y.; Guo, S.; Zhang, H. A correction method of NDVI topographic shadow effect for rugged terrain. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 8456–8472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zha, X.; Bai, Y.; Wang, L. Evaluation of soil erosion vulnerability on the basis of exposure, sensitivity, and adaptive capacity: A case study in the Zhuxi watershed, Changting, Fujian Province, Southern China. Catena 2019, 177, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhu, C.; Yu, J.; Zhai, L.; Zhang, H.; Yang, K.; Hou, X. Ecological vulnerability in the red soil erosion area of Changting under continuous ecological restoration: Spatiotemporal dynamic evolution and prediction. Forests 2022, 13, 2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Cost-effective targeting soil and water conservation: A case study of Changting county in southeast China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2016, 27, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Yao, M.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, W.; Mao, Z. Vegetation monitoring of protected areas in rugged mountains using an improved shadow-eliminated vegetation index (SEVI). Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, J.R. Remote Sensing of the Environment: An Earth Resource Perspective, 2nd ed.; Person Education: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, J.; Zheng, X.; Yue, H.; Chen, Y. Developing a new red band–SEVI–blue band (RSB) enhancement method for recognition the extra-high-voltage transmission line corridor in green mountains. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2023, 16, 806–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo-Rodríguez, V.; Melo, F.P.; Martínez-Ramos, M.; Bongers, F.; Chazdon, R.L.; Meave, J.A.; Tabarelli, M. Multiple successional pathways in human-modified tropical landscapes: New insights from forest succession, forest fragmentation and landscape ecology research. Biol. Rev. 2017, 92, 326–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, S.; Xia, C.; Yue, H.; Ma, H.; Lin, G. Targeted control measures for ecological restoration in Western Fujian, China. Land Use Policy 2018, 76, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Zhou, S.L.; Wu, S.H.; Liao, F.Q. Relationships between intensity gradation and evolution of soil erosion: A case study of Changting in Fujian Province, China. Pedosphere 2012, 22, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Li, Y.; Yin, B.; Wu, N.; Ye, R.; Liu, G. Spatiotemporal variation of net primary productivity and its response to drought in Inner Mongolian desert steppe. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2022, 33, e01991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Jia, Y.; Zhao, J.; Shen, Y.; Pei, H.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y. Revegetation projects significantly improved ecosystem service values in the agro-pastoral ecotone of northern China in recent 20 years. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 788, 147756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Liu, S.; Wang, F.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q. Cost-benefit analysis of ecological restoration based on land use scenario simulation and ecosystem service on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2022, 34, e02006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).























