Neural Network-Based Fusion of InSAR and Optical Digital Elevation Models with Consideration of Local Terrain Features
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
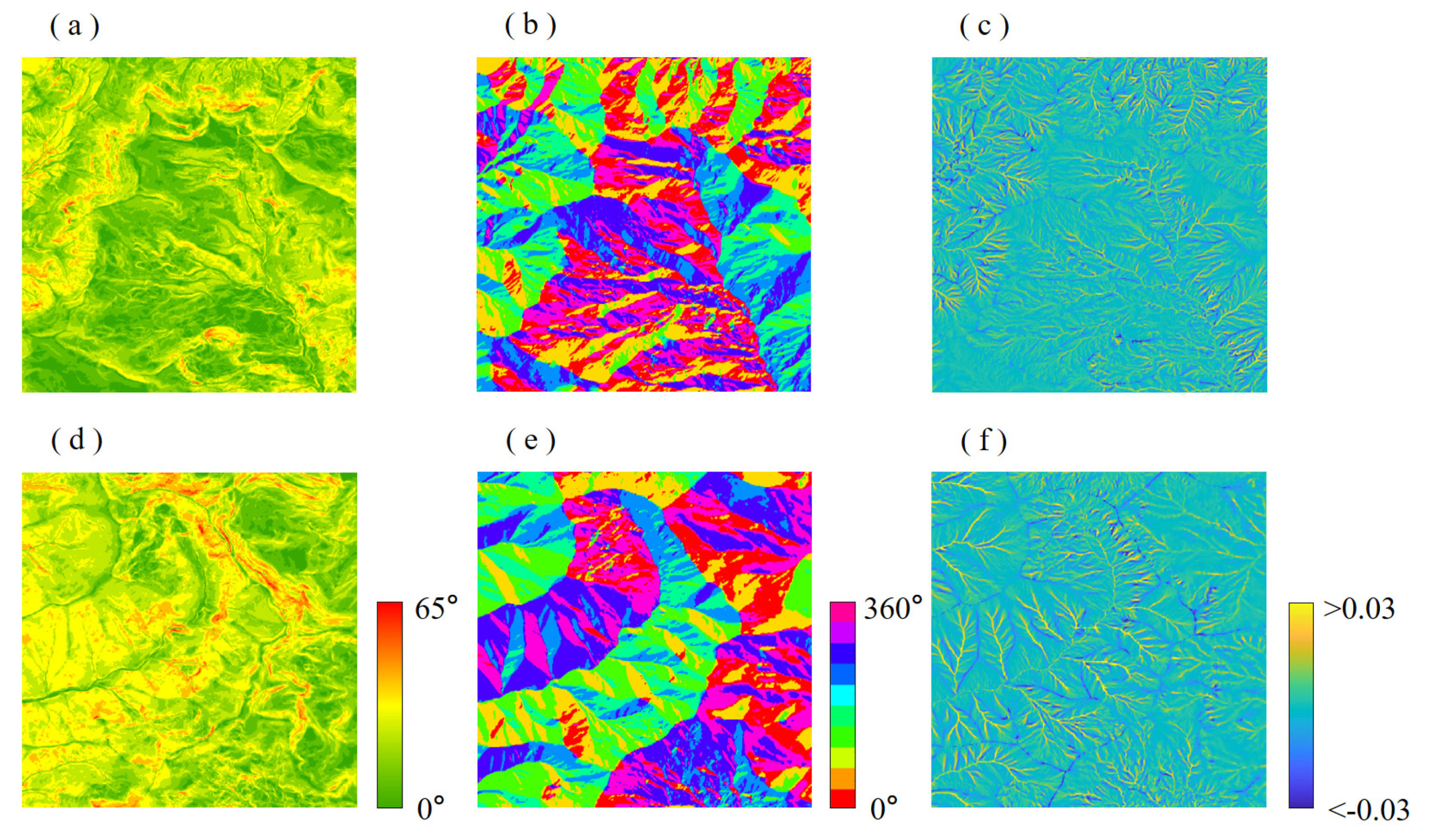
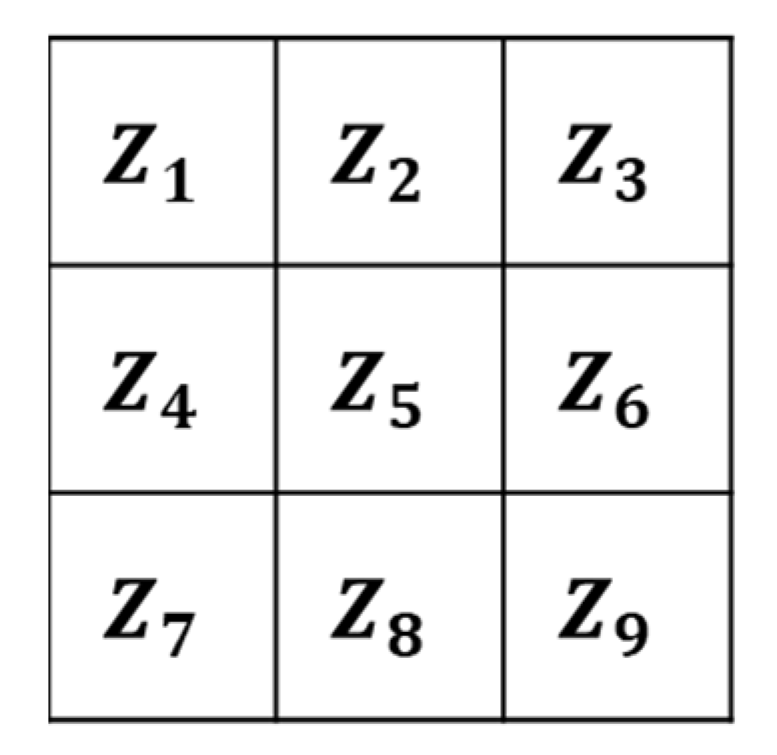
2.1. Local Terrain Feature Extraction and Training Sample Preparation
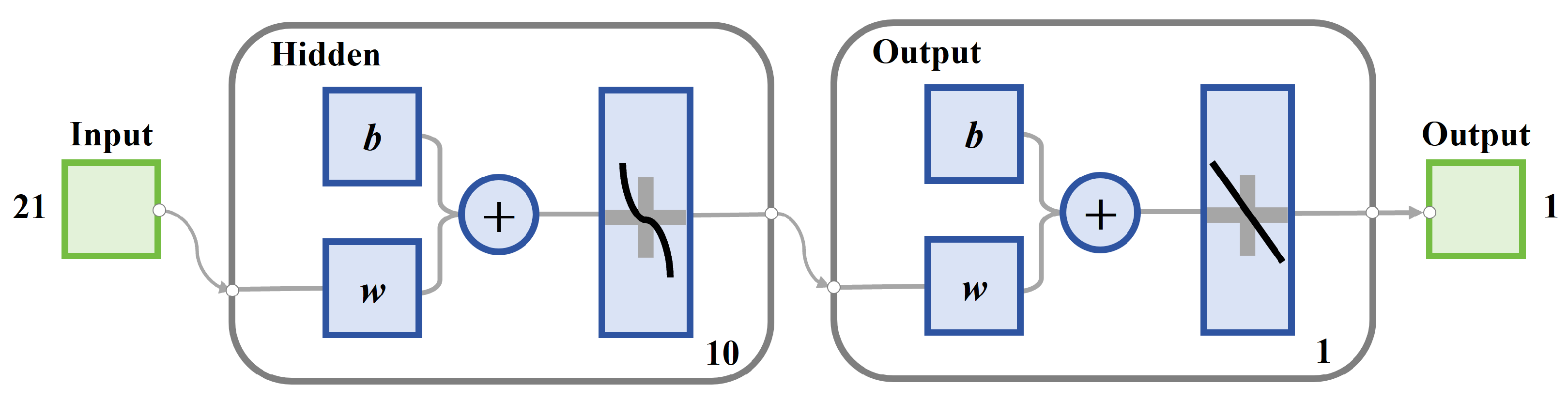
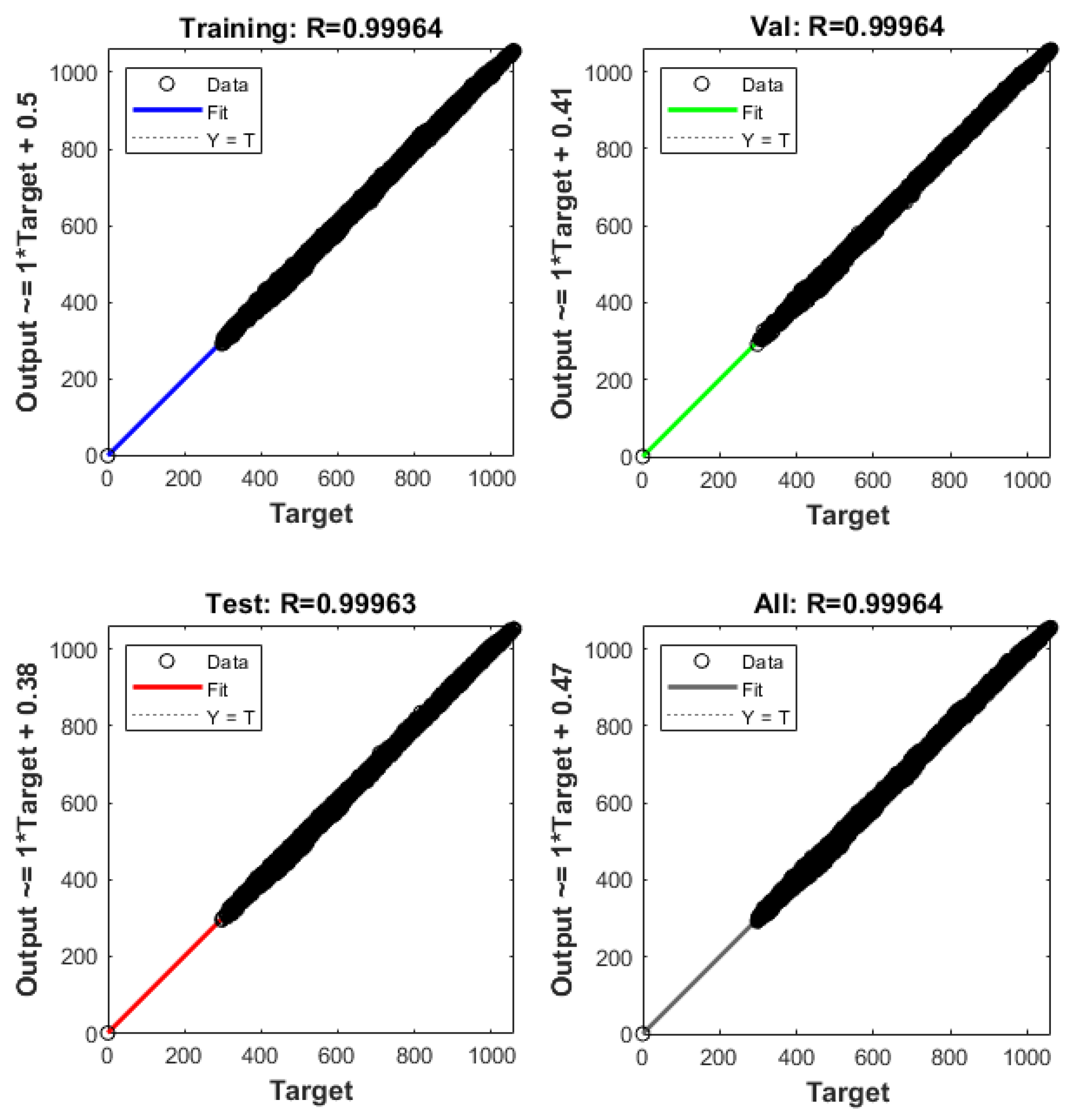
2.2. Neural Network Design and Hyperparameter Setting
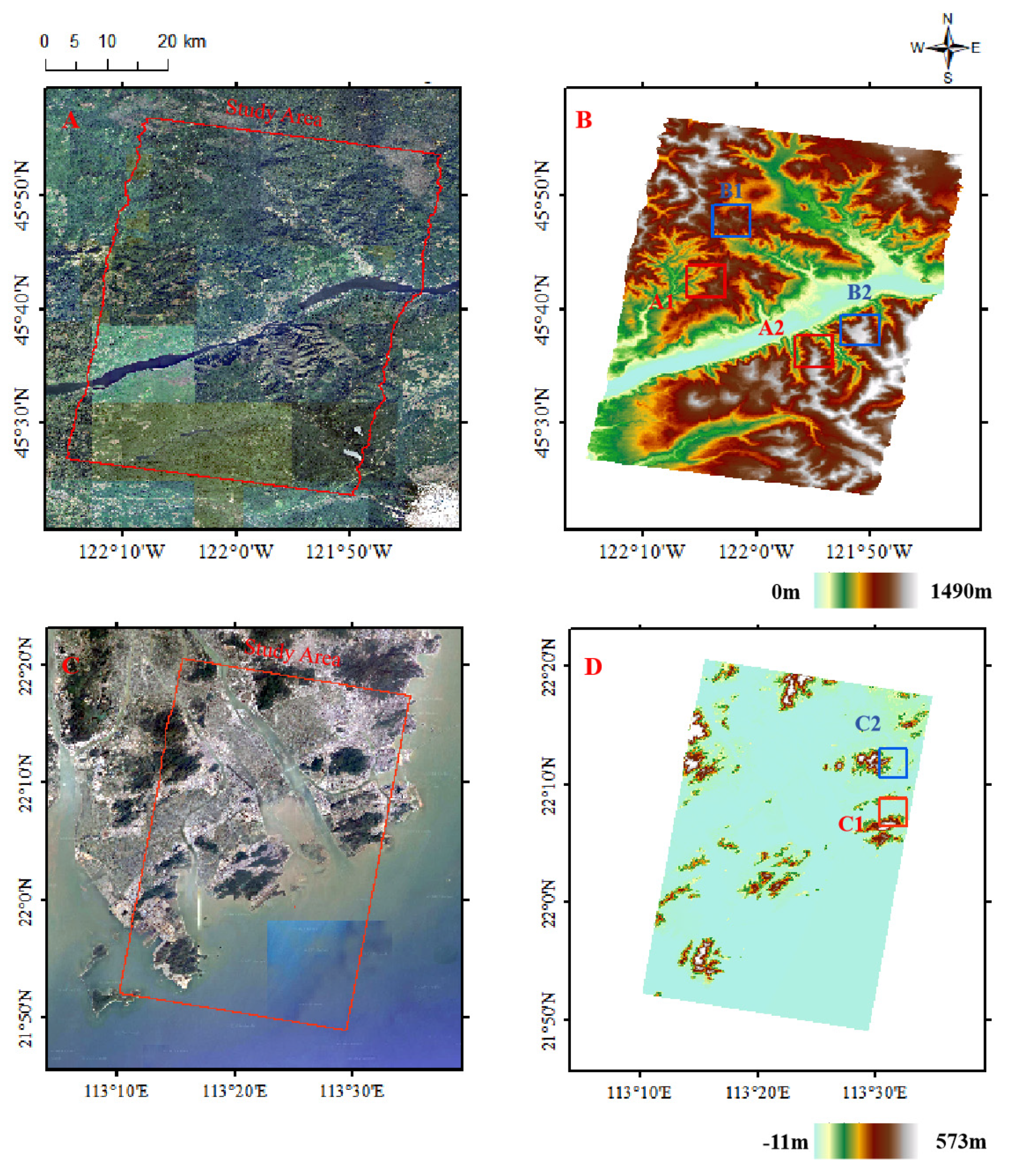
2.3. Study Area and Experimental Data
3. Results
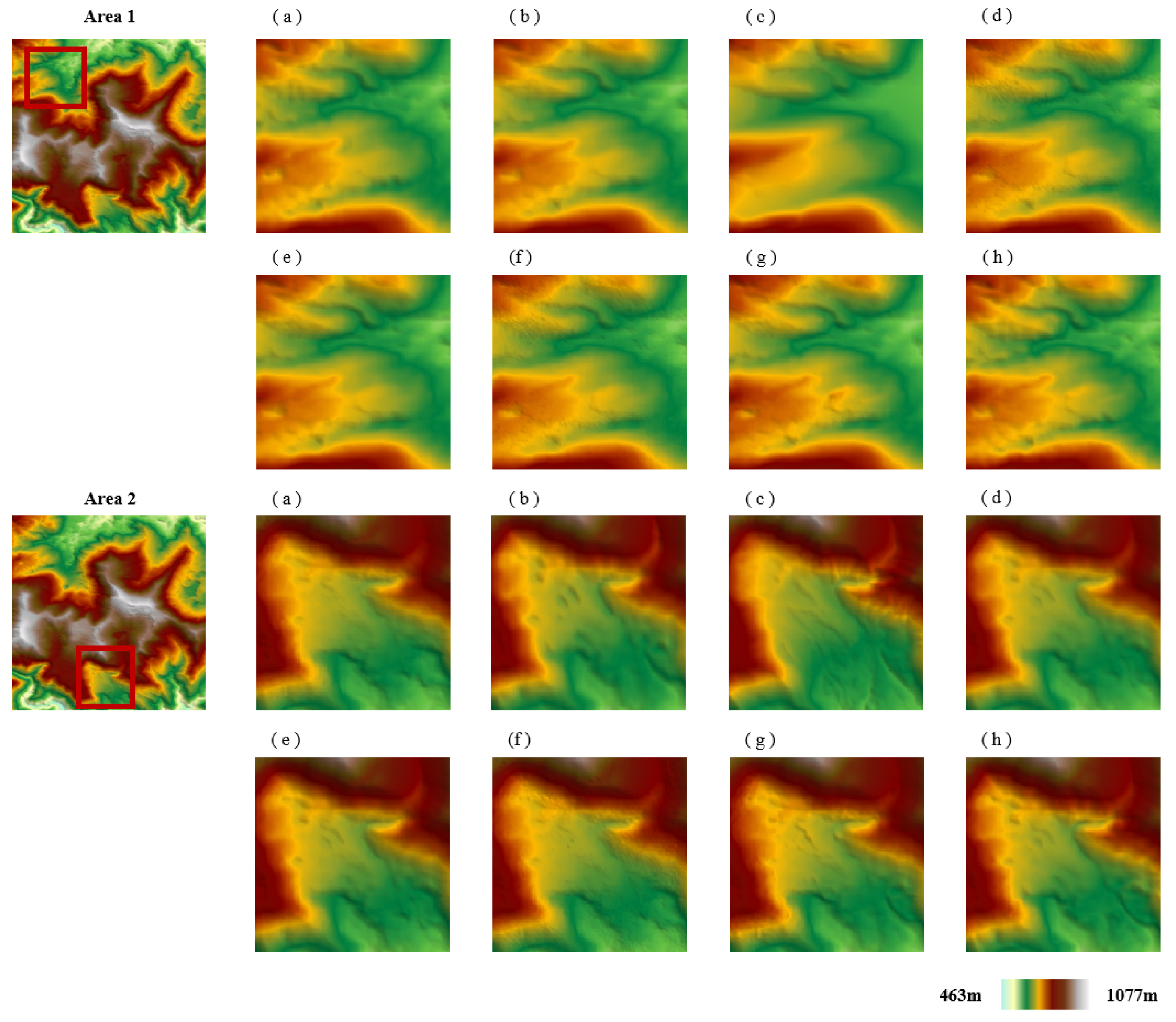
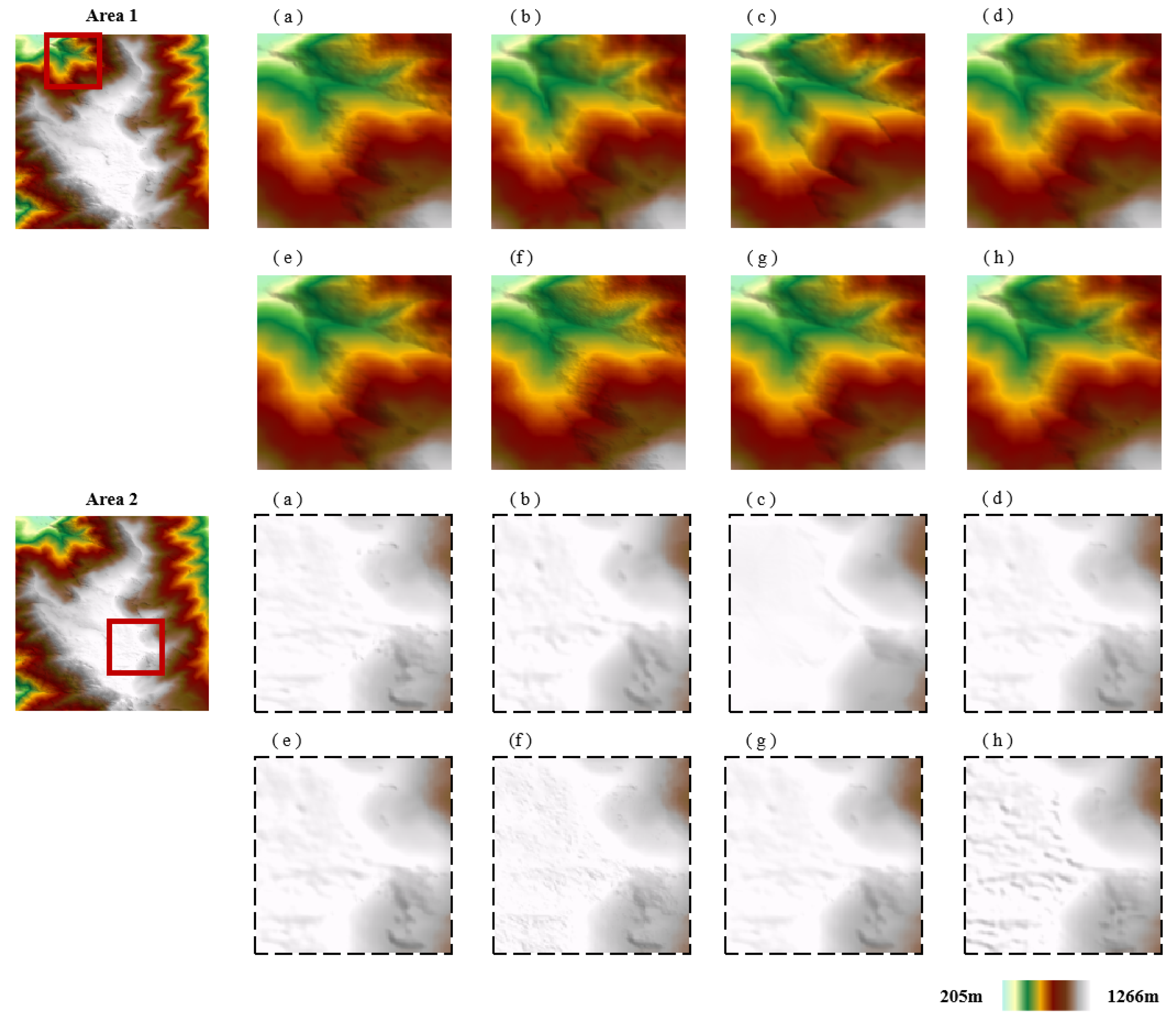
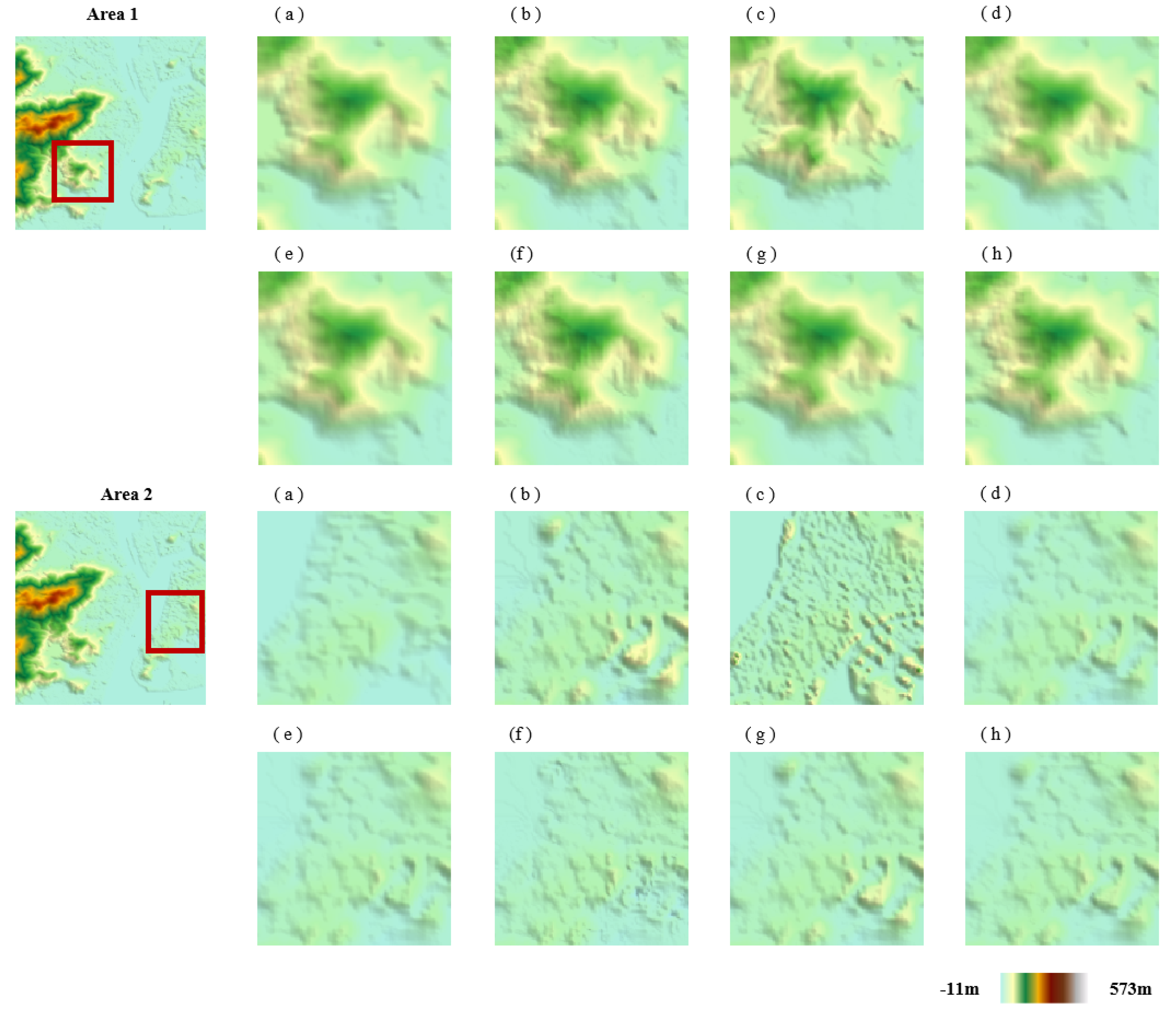
3.1. DEM Fusion Results via Different Methods
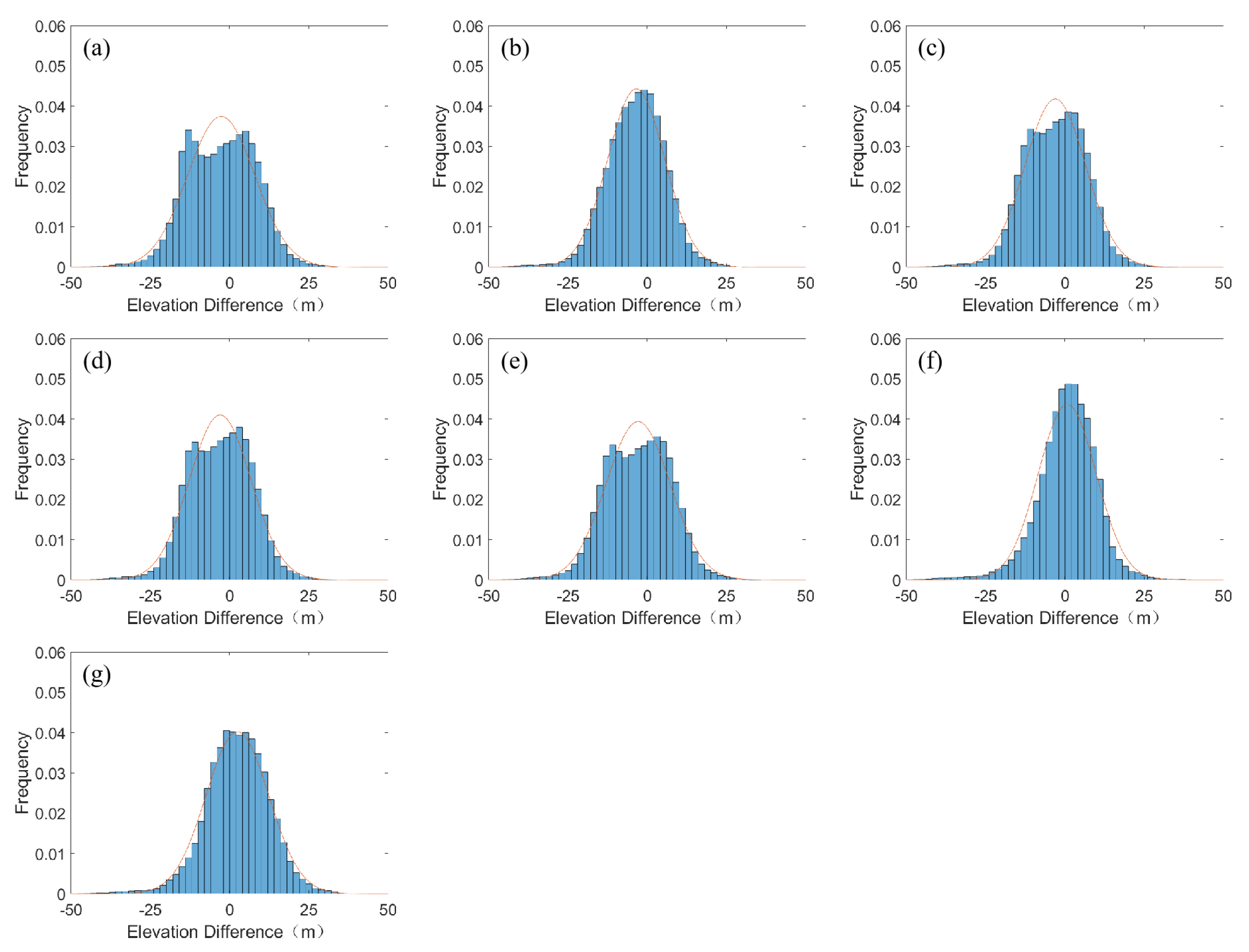
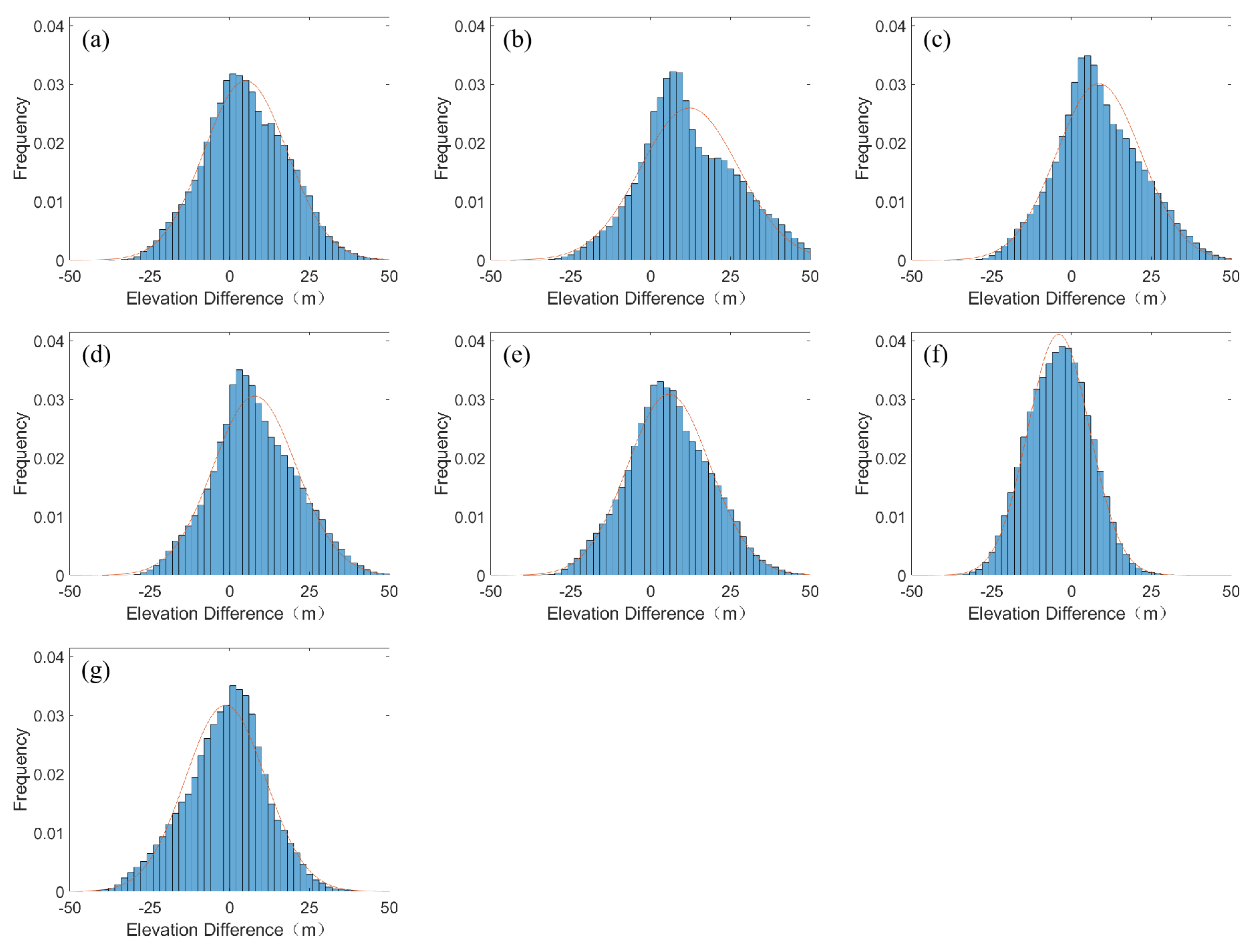
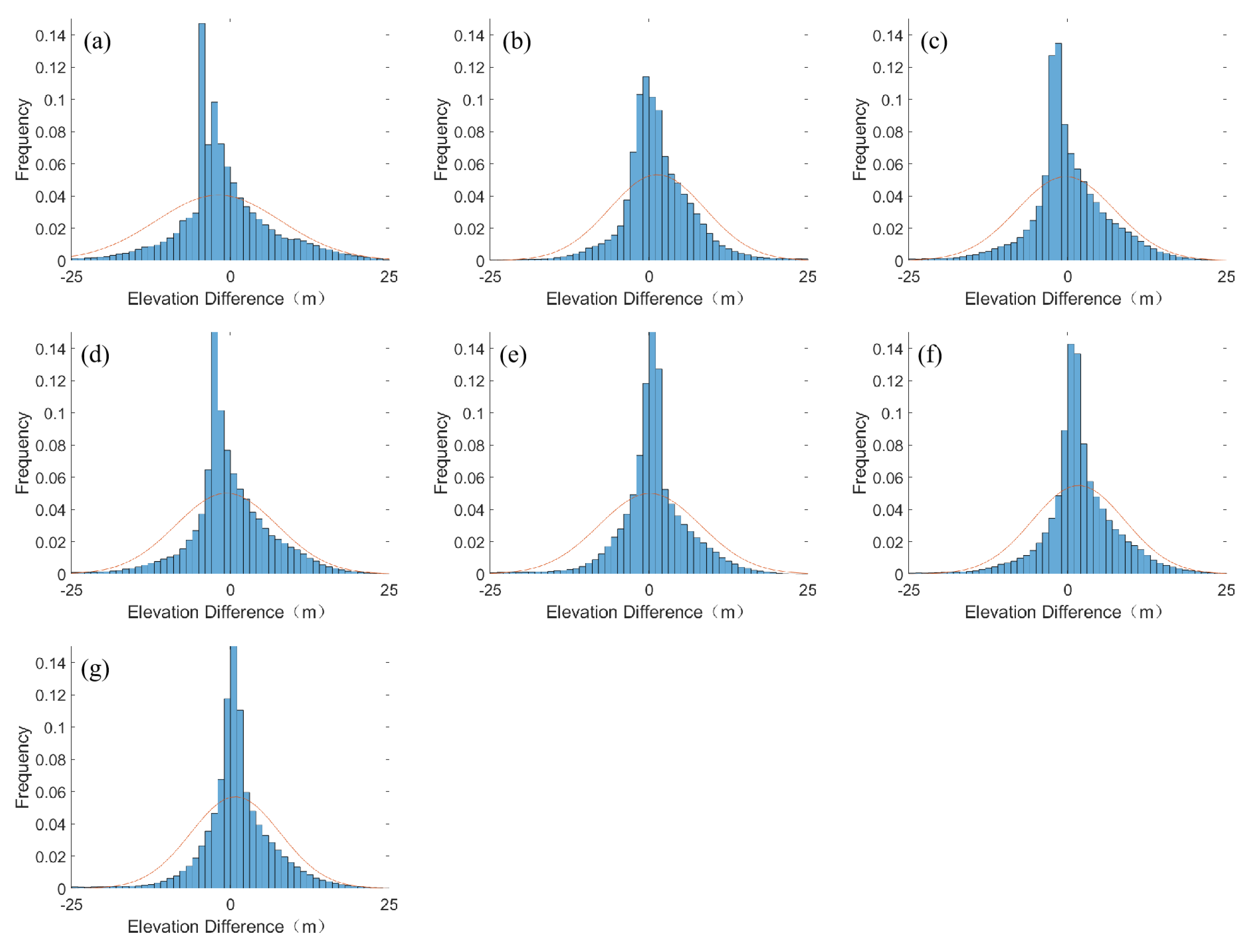
3.2. Elevation Difference Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Neural Network Hyperparameters and Window Size
4.2. Verification of Curvature Characteristics and Surrounding Elevations
4.3. Suitable Situations and Future Improvement Directions of the Proposed Method
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Song, H.; Jung, J. An object-based ground filtering of airborne lidar data for large-area dtm generation. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoja, D.; Reinartz, P.; Schroeder, M. Comparison of DEM generation and combination methods using high resolution optical stereo imagery and interferometric SAR data. Rev. Française Photogrammétrie Télédétection 2007, 2006, 89–94. [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt, M.; Zhu, X.X. Data fusion and remote sensing: An ever-growing relationship. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2016, 4, 6–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banu, R.S. Medical Image Fusion by the analysis of Pixel LevelMulti-sensor Using Discrete Wavelet Transform. In Proceedings of the National Conference on Emerging Trends in Computing Science, Shillong, India, 4–5 March 2011; pp. 291–297. [Google Scholar]
- Leitão, J.; De Sousa, L. Towards the optimal fusion of high-resolution Digital Elevation Models for detailed urban flood assessment. J. Hydrol. 2018, 561, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, A.; Wessel, B.; Martone, M.; Roth, A. The TanDEM-X DEM mosaicking: Fusion of multiple acquisitions using InSAR quality parameters. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 9, 1047–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deo, R.; Rossi, C.; Eineder, M.; Fritz, T.; Rao, Y. Framework for fusion of ascending and descending pass TanDEM-X raw DEMs. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 3347–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.; Raghavan, V.; Masumoto, S.; Vinayaraj, P.; Yonezawa, G. A geomorphology-based approach for digital elevation model fusion–case study in Danang city, Vietnam. Earth Surf. Dyn. 2014, 2, 403–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Schindler, K.; Papasaika-Hanusch, H.; Schütz, S.; Baltsavias, E. Improving wide-area DEMs through data fusion-chances and limits. In Proceedings of the Photogrammetric Week, Stuttgart, Germany, 1–4 April 2011; pp. 159–170. [Google Scholar]
- Bagheri, H.; Schmitt, M.; Zhu, X.X. Fusion of TanDEM-X and Cartosat-1 elevation data supported by neural network-predicted weight maps. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 144, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, C.; Ng, M.K. Variational model for simultaneously image denoising and contrast enhancement. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 18751–18777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuschk, G.; d’Angelo, P.; Gaudrie, D.; Reinartz, P.; Cremers, D. Spatially regularized fusion of multiresolution digital surface models. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 55, 1477–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, H.; Schmitt, M.; Zhu, X.X. Fusion of TanDEM-X and Cartosat-1 DEMs using TV-norm regularization and ANN-predicted weights. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Fort Worth, TX, USA, 23–28 July 2017; pp. 3369–3372. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, L.; Hu, J.; Pan, H.; Wu, W.; Sun, Q.; Chen, S.; Fan, H. Fusion of public DEMs based on sparse representation and adaptive regularization variation model. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 169, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slatton, K.C.; Crawford, M.; Teng, L. Multiscale fusion of INSAR data for improved topographic mapping. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Toronto, ON, Canada, 24–28 June 2002; pp. 69–71. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Foerster, S.; Medeiros, P.; de Araújo, J.C.; Motagh, M.; Waske, B. Bathymetric survey of water reservoirs in north-eastern Brazil based on TanDEM-X satellite data. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 571, 575–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Atkinson, P.M.; Zhang, J. Downscaling remotely sensed imagery using area-to-point cokriging and multiple-point geostatistical simulation. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 101, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeq, H.; Drummond, J.; Li, Z. Merging digital surface models implementing Bayesian approaches. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2016, 41, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Liao, M. Fusion of high-resolution DEMs derived from COSMO-SkyMed and TerraSAR-X InSAR datasets. J. Geod. 2014, 88, 587–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuss, C.E.; Berg, A.A.; Lindsay, J.B. DEM Fusion using a modified k-means clustering algorithm. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2016, 9, 1242–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girohi, P.; Bhardwaj, A. ANN-Based DEM Fusion and DEM Improvement Frameworks in Regions of Assam and Meghalaya using Remote Sensing Datasets. Eur. J. Environ. Earth Sci. 2022, 3, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girohi, P.; Bhardwaj, A. A Neural Network-Based Fusion Approach for Improvement of SAR Interferometry-Based Digital Elevation Models in Plain and Hilly Regions of India. AI 2022, 3, 820–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiante, M.; Di Benedetto, A.; Aloia, A. A Comparison of Landforms and Processes Detection Using Multisource Remote Sensing Data: The Case Study of the Palinuro Pine Grove (Cilento, Vallo di Diano and Alburni National Park, Southern Italy). Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlisle, B.H. Modelling the spatial distribution of DEM error. Trans. GIS 2005, 9, 521–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, F.J.; Agüera, F.; Aguilar, M.A.; Carvajal, F. Effects of terrain morphology, sampling density, and interpolation methods on grid DEM accuracy. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2005, 71, 805–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arun, P.V. A comparative analysis of different DEM interpolation methods. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2013, 16, 133–139. [Google Scholar]
- Heritage, G.L.; Milan, D.J.; Large, A.R.; Fuller, I.C. Influence of survey strategy and interpolation model on DEM quality. Geomorphology 2009, 112, 334–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guth, P.; Kane, M. Slope, aspect, and hillshade algorithms for non-square digital elevation models. Trans. GIS 2021, 25, 2309–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.P. Digital terrain modeling. Geomorphology 2012, 137, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höhle, J.; Höhle, M. Accuracy assessment of digital elevation models by means of robust statistical methods. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2009, 64, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, S.; Zhou, Y. A review of convolutional neural network architectures and their optimizations. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2023, 56, 1905–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kermani, B.G.; Schiffman, S.S.; Nagle, H.T. Performance of the Levenberg–Marquardt neural network training method in electronic nose applications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2005, 110, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Gui, R.; Hu, J.; Fu, H.; Yuan, Y.; Jiang, K.; Liu, L. InSAR Digital Elevation Model Void-Filling Method Based on Incorporating Elevation Outlier Detection. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altunel, A.O. Questioning the effects of raster-resampling and slope on the precision of TanDEM-X 90 m digital elevation model. Geocarto Int. 2021, 36, 2366–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

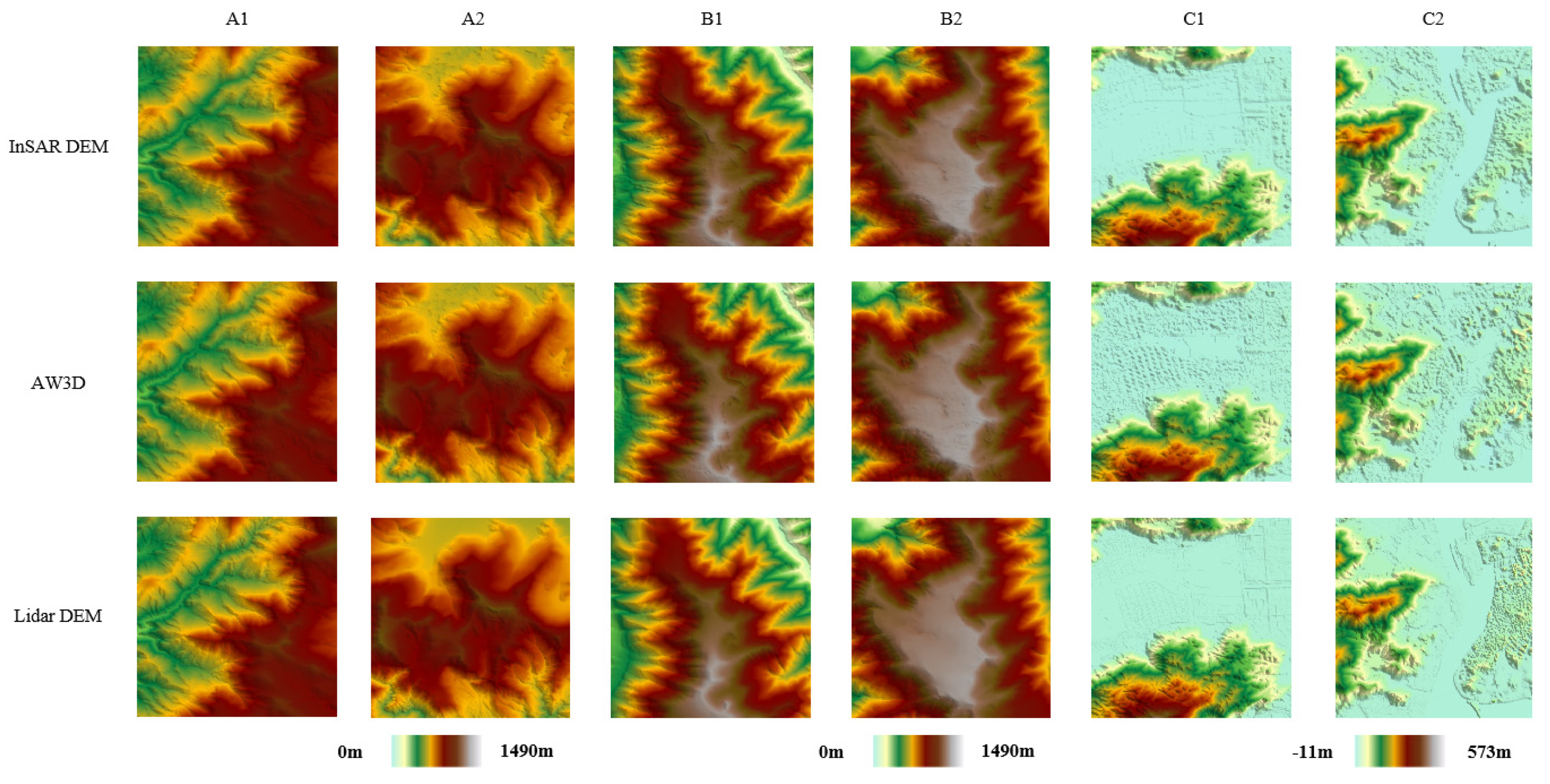



| Horizontal Datum | Vertical Datum | Resolution (m) | Image Size (Pixels) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| InSAR−DEM | WGS-84 | EGM08 | 10 | 6043 × 4986 |
| AW3D30 DEM | WGS-84 | EGM96 | 30 | 2019 × 2001 |
| LiDAR DEM | NAD83 | NAVD88 | 10 | 6043 × 4986 |
| A1, A2, B1, B2, C1, C2 | WGS-84 | EGM08 | 10 | 500 × 500 |
| Fused DEM | WGS-84 | EGM08 | 10 | 500 × 500 |
| High-Mountain Areas (A2) | Low-Mountain Areas (B2) | Urban Areas (C2) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | NMAD | RMSE | NMAD | RMSE | NMAD | |
| InSAR−DEM | 13.81 | 12.94 | 10.90 | 12.36 | 9.60 | 3.94 |
| AW3D30 DEM | 19.02 | 14.74 | 9.51 | 9.12 | 7.55 | 4.11 |
| Simple Average Fusion | 15.38 | 12.66 | 9.85 | 10.45 | 7.44 | 3.62 |
| Maximum Likelihood Estimation | 14.87 | 12.48 | 10.01 | 10.82 | 7.74 | 3.69 |
| Adaptive Regularization Variation Model | 13.93 | 12.53 | 10.45 | 11.43 | 7.64 | 2.95 |
| Terrain-based Neural Network | 13.24 | 12.49 | 10.19 | 9.60 | 7.20 | 3.15 |
| Proposed | 11.29 | 10.28 | 9.16 | 8.18 | 6.84 | 2.89 |
| High-Mountain Areas/A1 | Low-Mountain Areas/B1 | Urban Areas/C1 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | NMAD | RMSE | NMAD | RMSE | NMAD | |
| 3 × 3 | 11.06 | 9.79 | 9.17 | 8.50 | 6.84 | 2.89 |
| 5 × 5 | 11.14 | 9.65 | 9.45 | 8.76 | 6.93 | 2.99 |
| 7 × 7 | 11.23 | 9.68 | 9.65 | 8.51 | 11.27 | 2.95 |
| 9 × 9 | 11.14 | 9.65 | 9.31 | 8.63 | 7.11 | 3.15 |
| High-Mountain Areas/A1 | Low-Mountain Areas/B1 | Urban Areas/C1 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | NMAD | RMSE | NMAD | RMSE | NMAD | Time(s) | |
| 5 | 11.63 | 10.73 | 10.09 | 8.90 | 7.02 | 3.14 | 86 |
| 10 | 11.18 | 10.25 | 9.36 | 8.41 | 6.84 | 3.20 | 158 |
| 15 | 11.23 | 10.27 | 9.88 | 8.88 | 7.04 | 2.9 | 252 |
| 20 | 11.19 | 10.27 | 9.98 | 8.94 | 6.96 | 2.93 | 351 |
| 10-5 | 11.00 | 10.34 | 10.02 | 8.80 | 6.84 | 3.01 | 212 |
| 15-8 | 11.10 | 10.28 | 10.30 | 9.10 | 6.93 | 3.19 | 366 |
| 10-8-5 | 11.23 | 9.96 | 10.14 | 8.89 | 6.89 | 3.23 | 287 |
| 20-15-5 | 12.32 | 10.15 | 10.14 | 9.45 | 7.03 | 3.16 | 744 |
| Input Feature | Accuracy | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DEM | Slope, Aspect | Curvature | Surrounding Elevation | High-Mountain Areas | Low-Mountain Areas |
| ✓ | 13.05 | 9.34 | |||
| ✓ | ✓ | 11.13 | 9.55 | ||
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 12.26 | 9.29 | |
| ✓ | ✓ | 11.63 | 9.32 | ||
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 11.06 | 9.17 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gui, R.; Qin, Y.; Hu, Z.; Dong, J.; Sun, Q.; Hu, J.; Yuan, Y.; Mo, Z. Neural Network-Based Fusion of InSAR and Optical Digital Elevation Models with Consideration of Local Terrain Features. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3567. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16193567
Gui R, Qin Y, Hu Z, Dong J, Sun Q, Hu J, Yuan Y, Mo Z. Neural Network-Based Fusion of InSAR and Optical Digital Elevation Models with Consideration of Local Terrain Features. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(19):3567. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16193567
Chicago/Turabian StyleGui, Rong, Yuanjun Qin, Zhi Hu, Jiazhen Dong, Qian Sun, Jun Hu, Yibo Yuan, and Zhiwei Mo. 2024. "Neural Network-Based Fusion of InSAR and Optical Digital Elevation Models with Consideration of Local Terrain Features" Remote Sensing 16, no. 19: 3567. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16193567
APA StyleGui, R., Qin, Y., Hu, Z., Dong, J., Sun, Q., Hu, J., Yuan, Y., & Mo, Z. (2024). Neural Network-Based Fusion of InSAR and Optical Digital Elevation Models with Consideration of Local Terrain Features. Remote Sensing, 16(19), 3567. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16193567






