SSBAS-InSAR: A Spatially Constrained Small Baseline Subset InSAR Technique for Refined Time-Series Deformation Monitoring
Abstract
1. Introduction
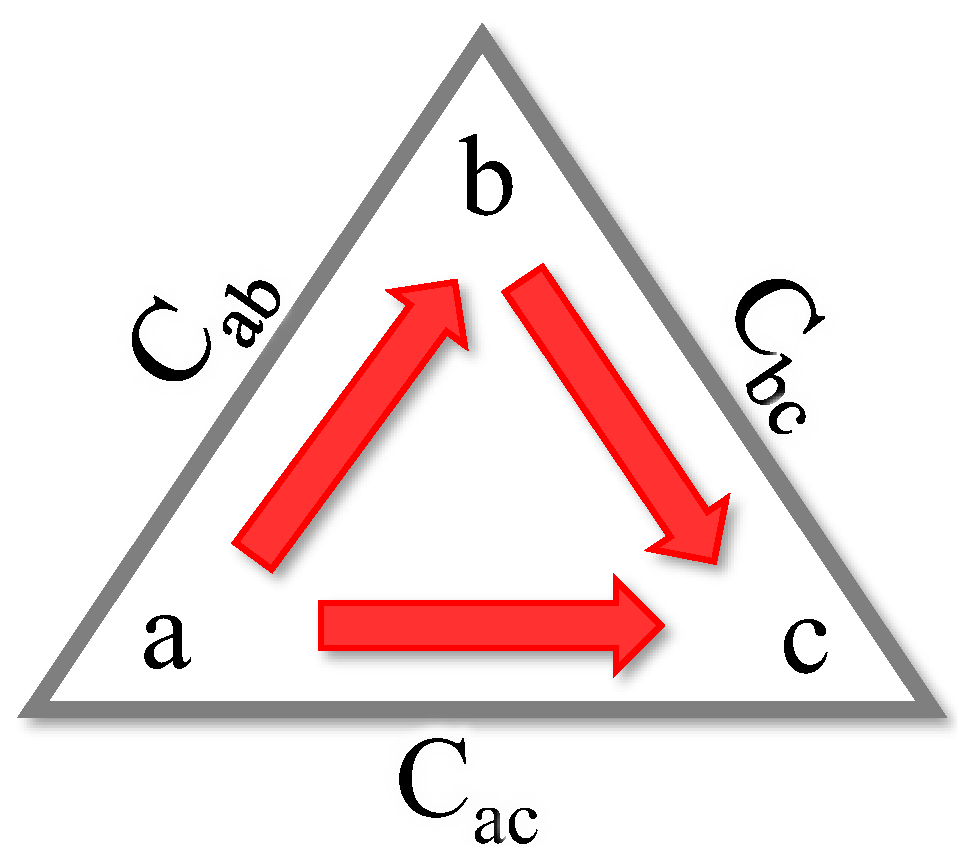
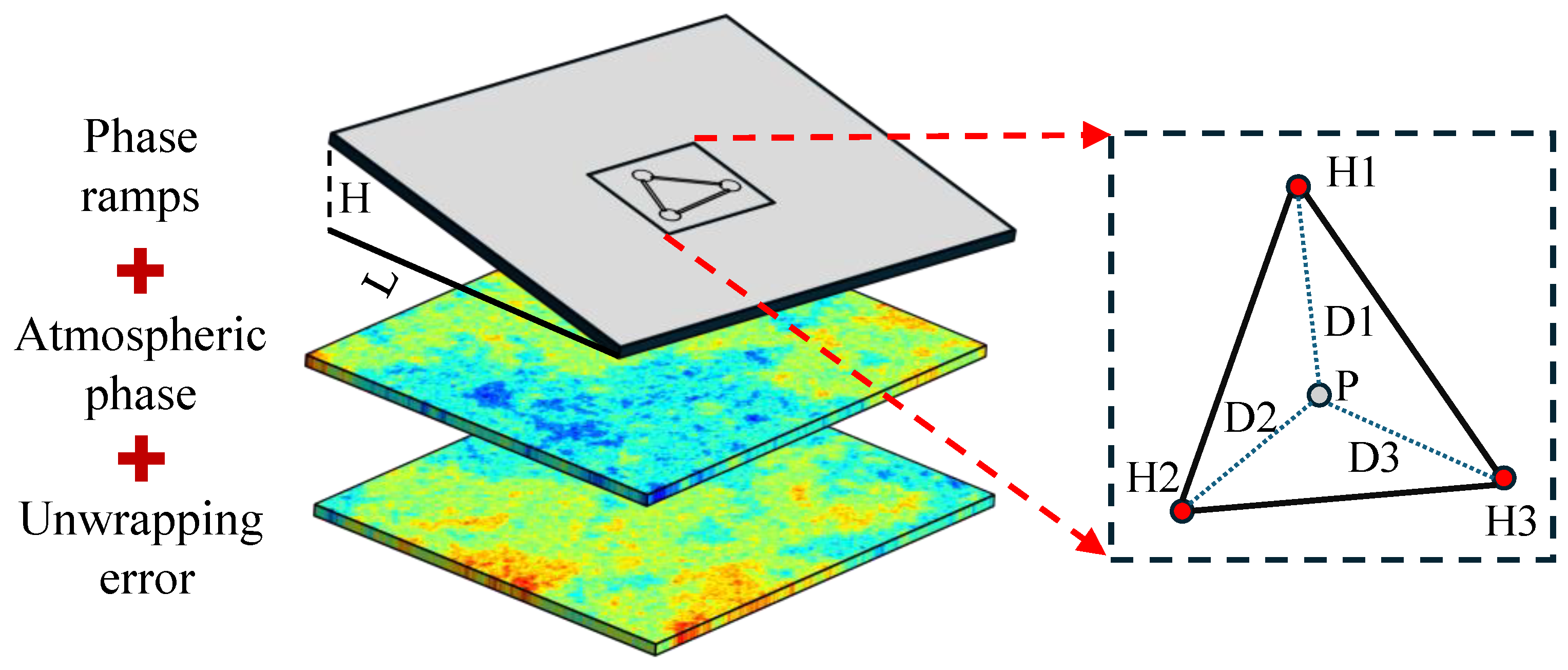
2. Phase Error Analysis
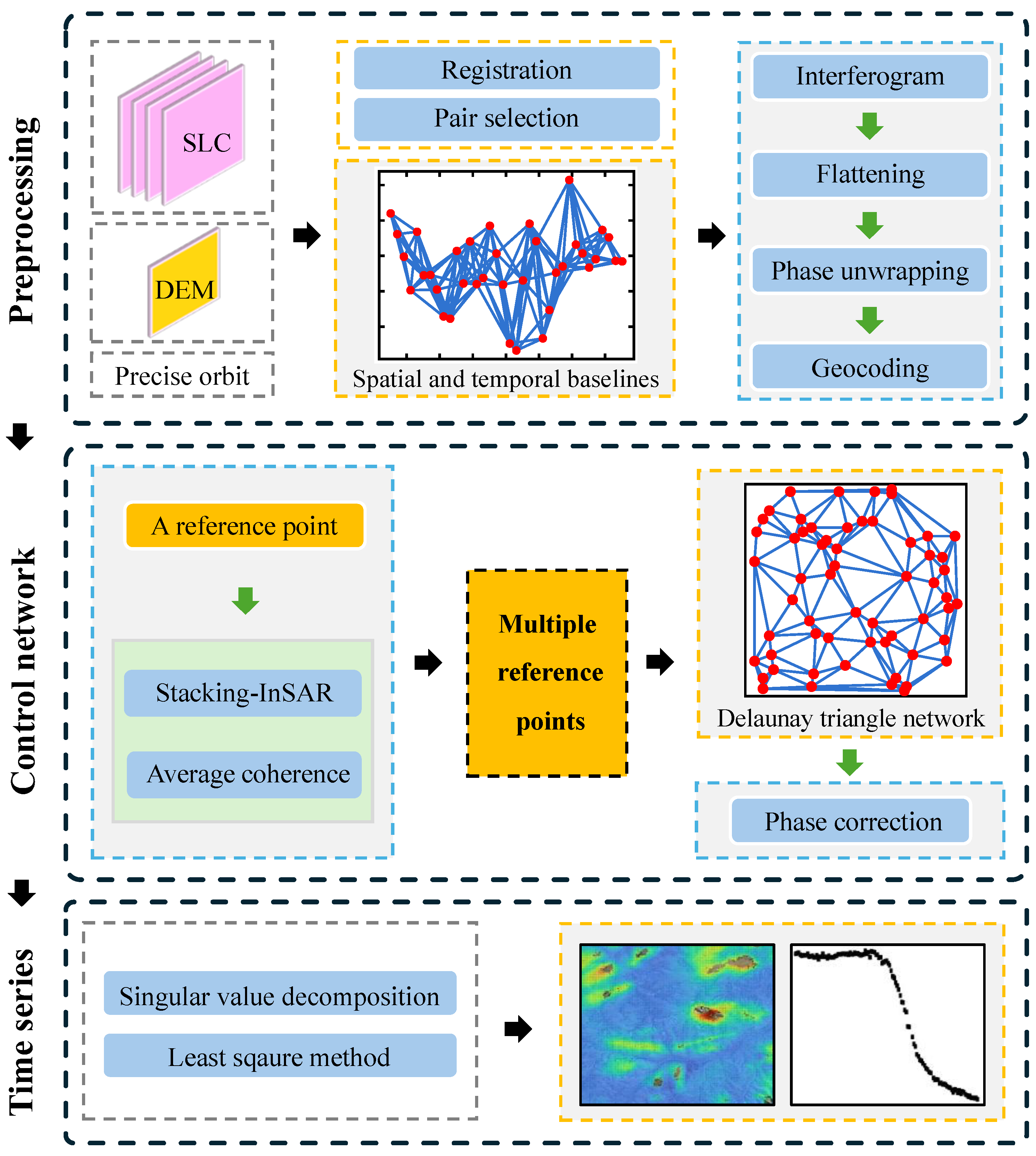
3. Methods
- (1).
- Image pair combination
- (2).
- Interferometry and phase unwrapping
- (3).
- Stacking-InSAR
- (4).
- Establish control network
- (5).
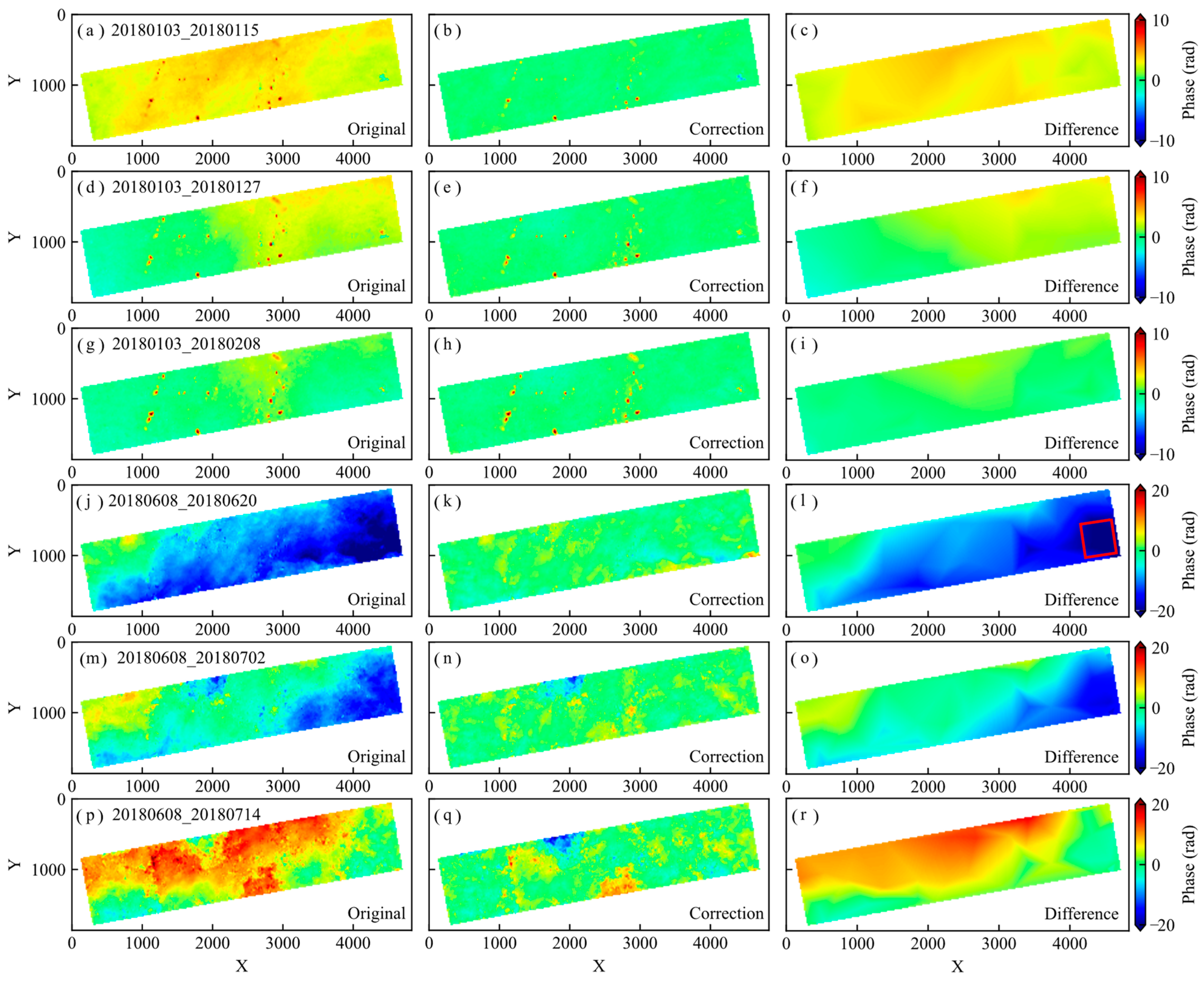
- Unwrapped phase correction
- (6).
- Time-series solution
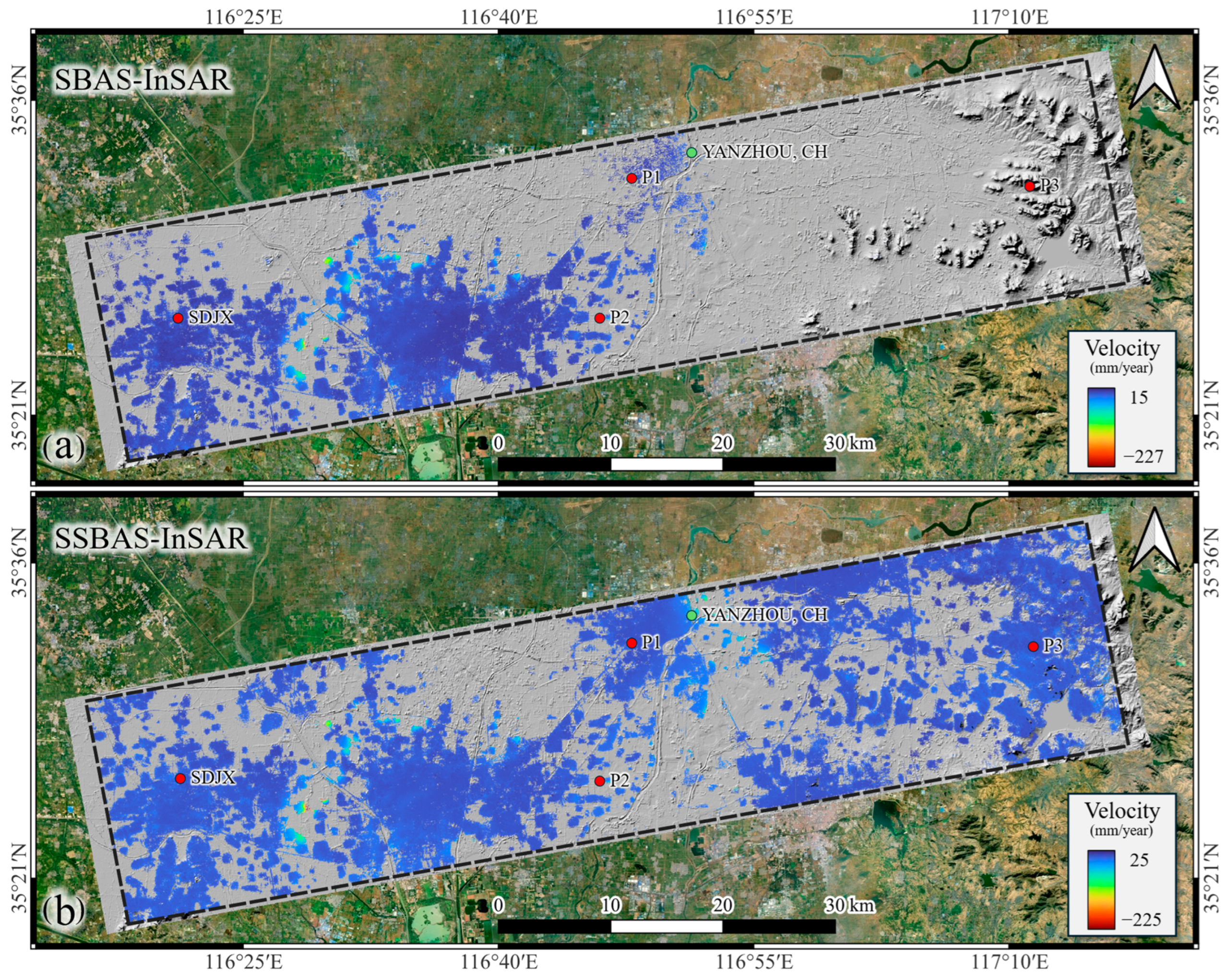
4. Application and Comparison
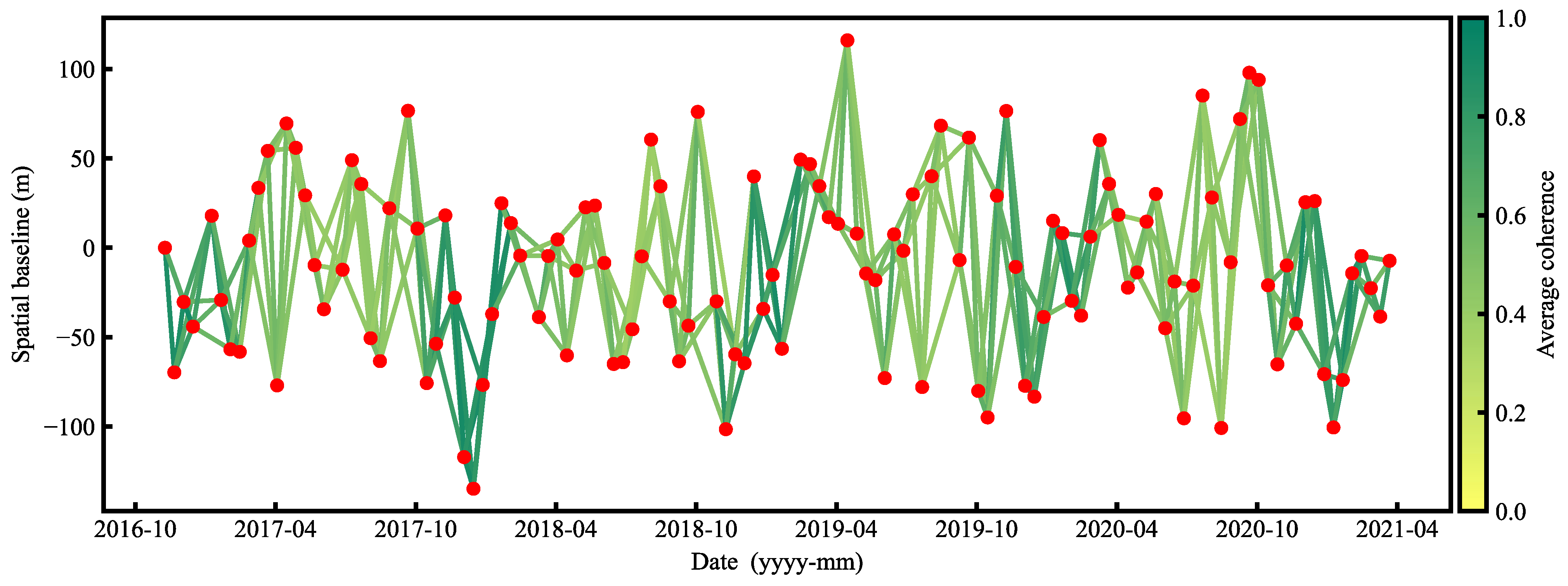
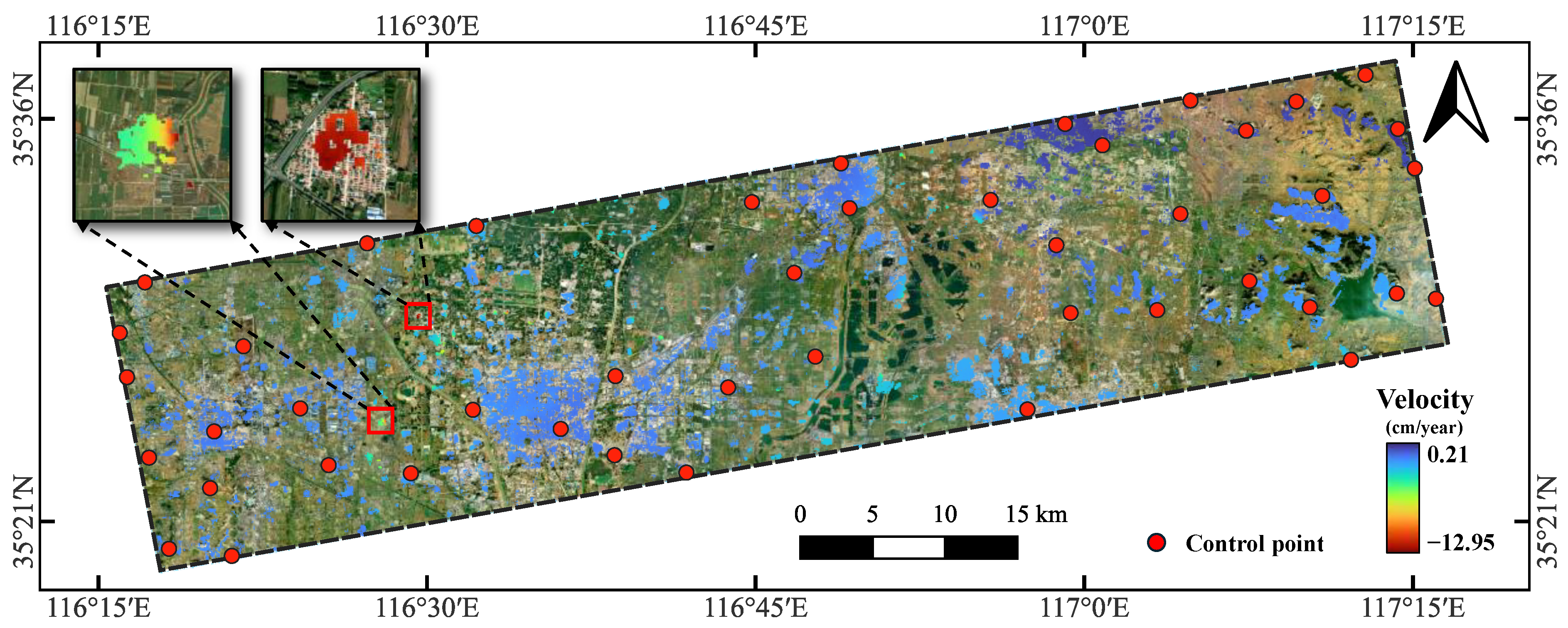
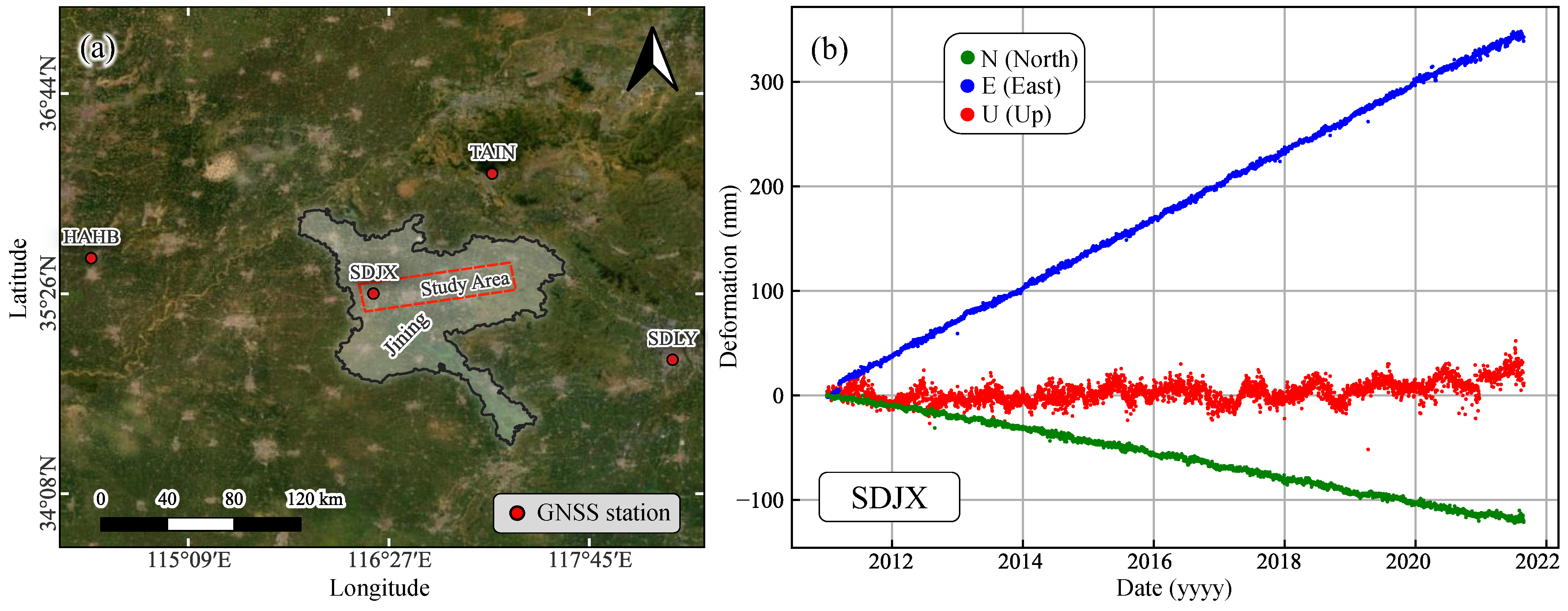
4.1. Data and Processing
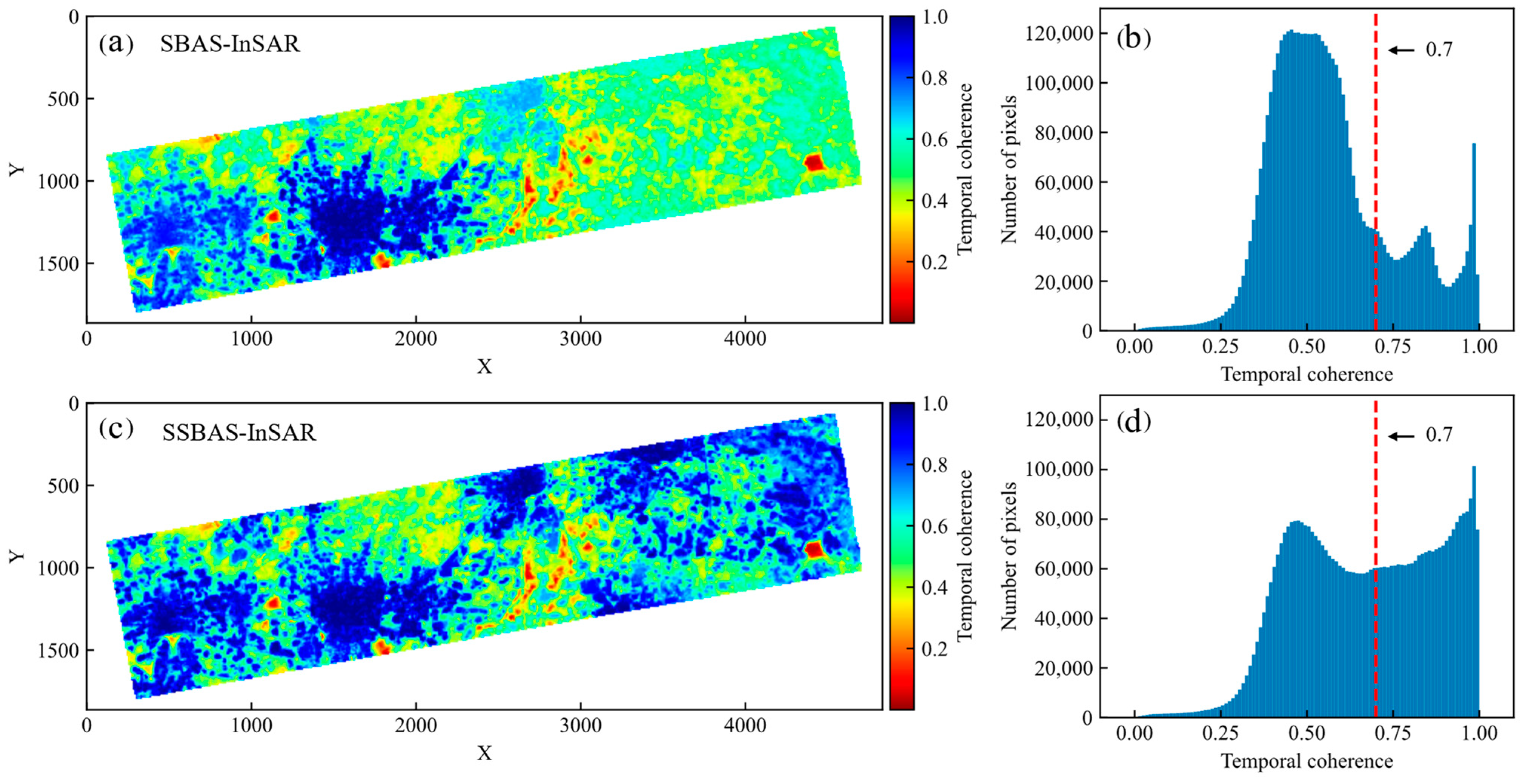
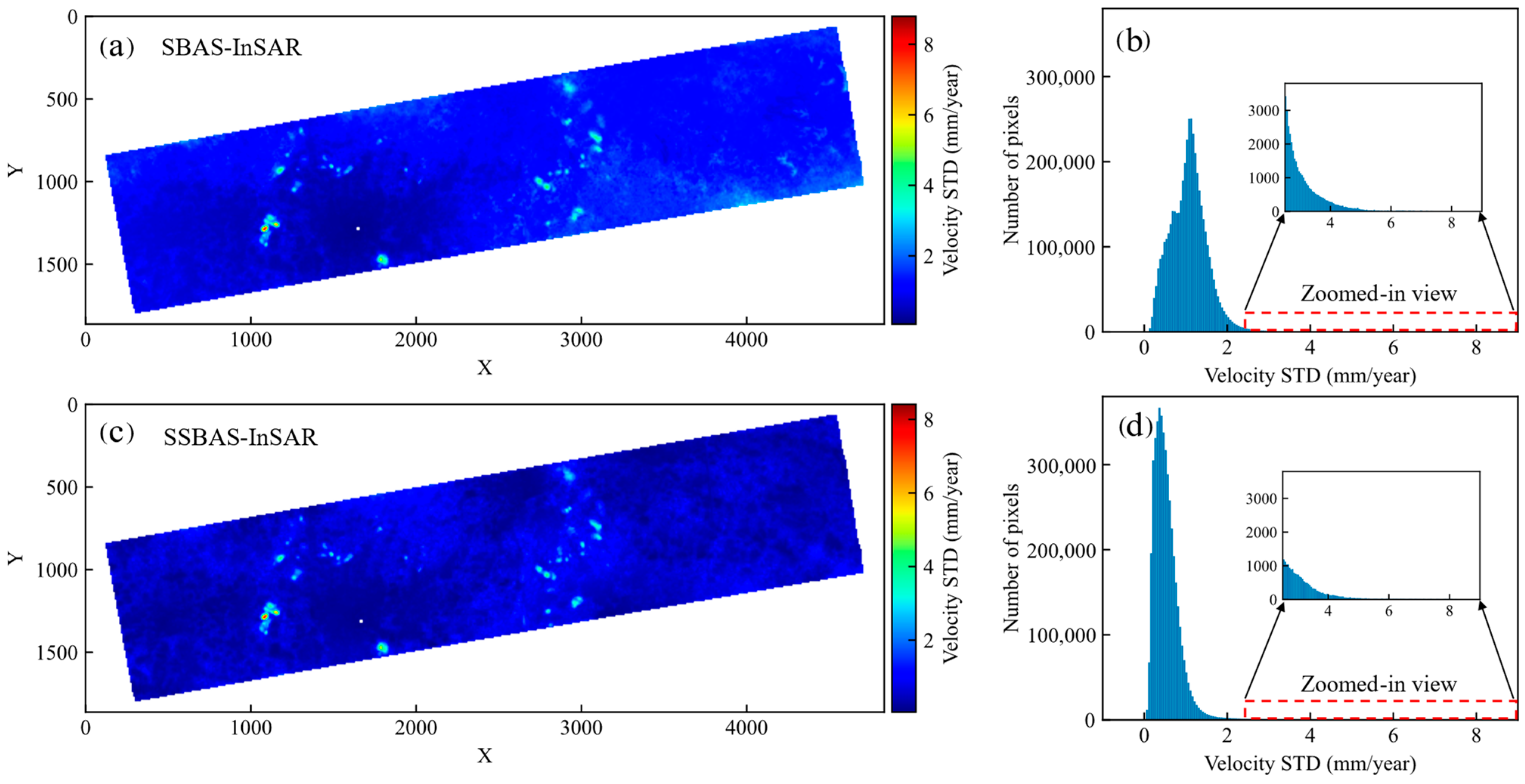
4.2. Precision Analysis
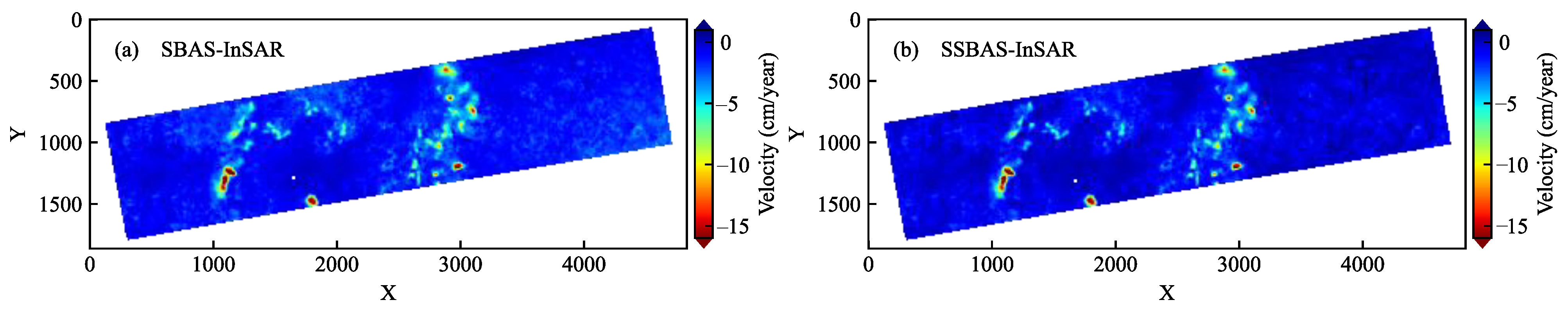
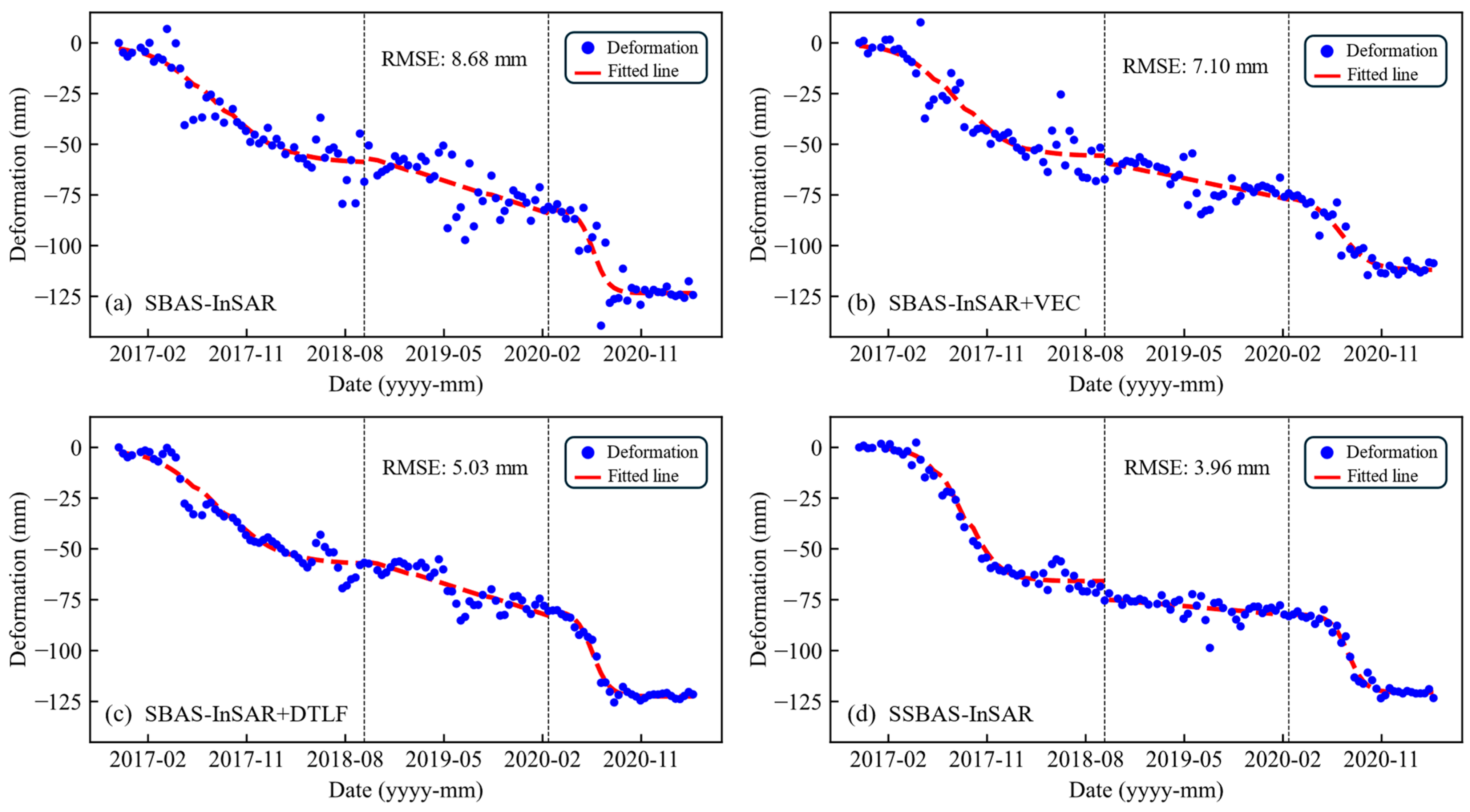
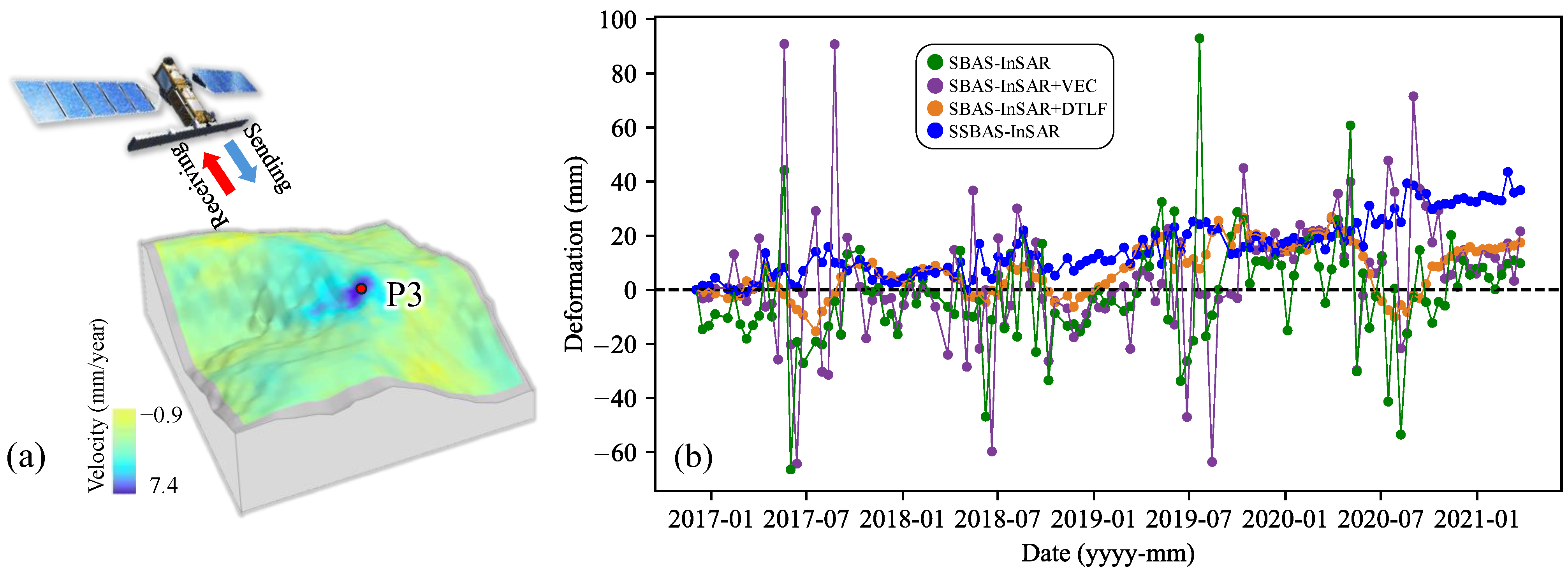
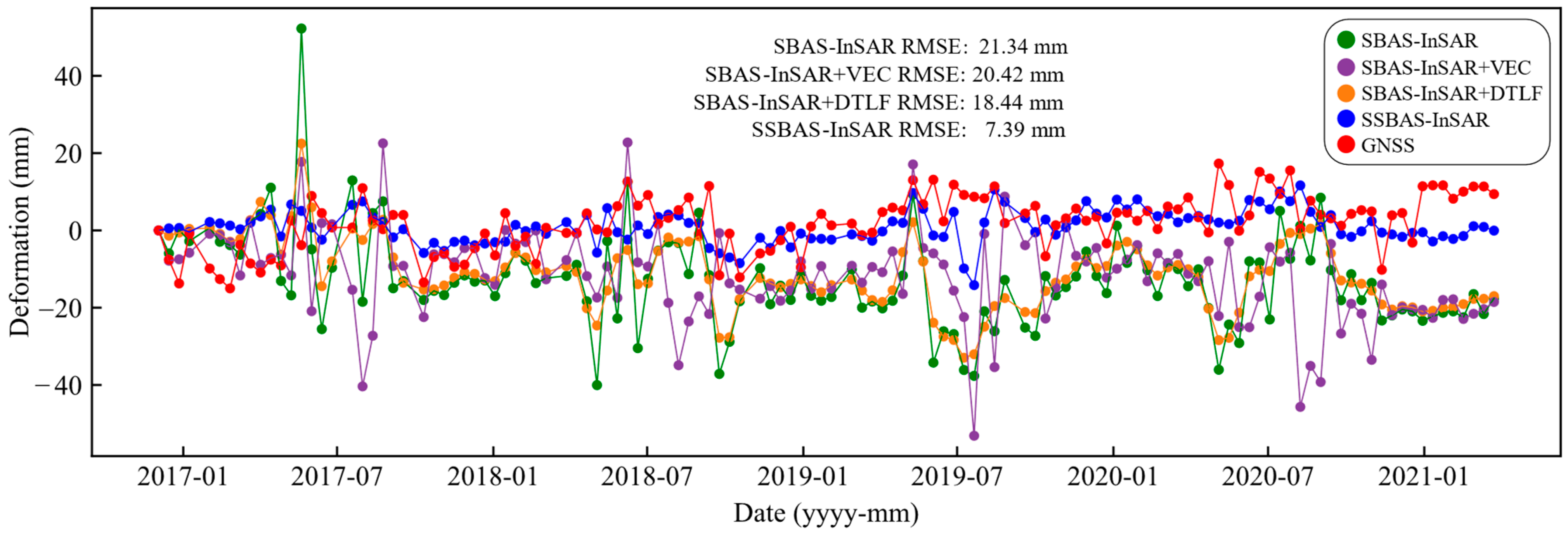
4.3. Comparative Analysis of Time-Series Deformation
5. Discussion
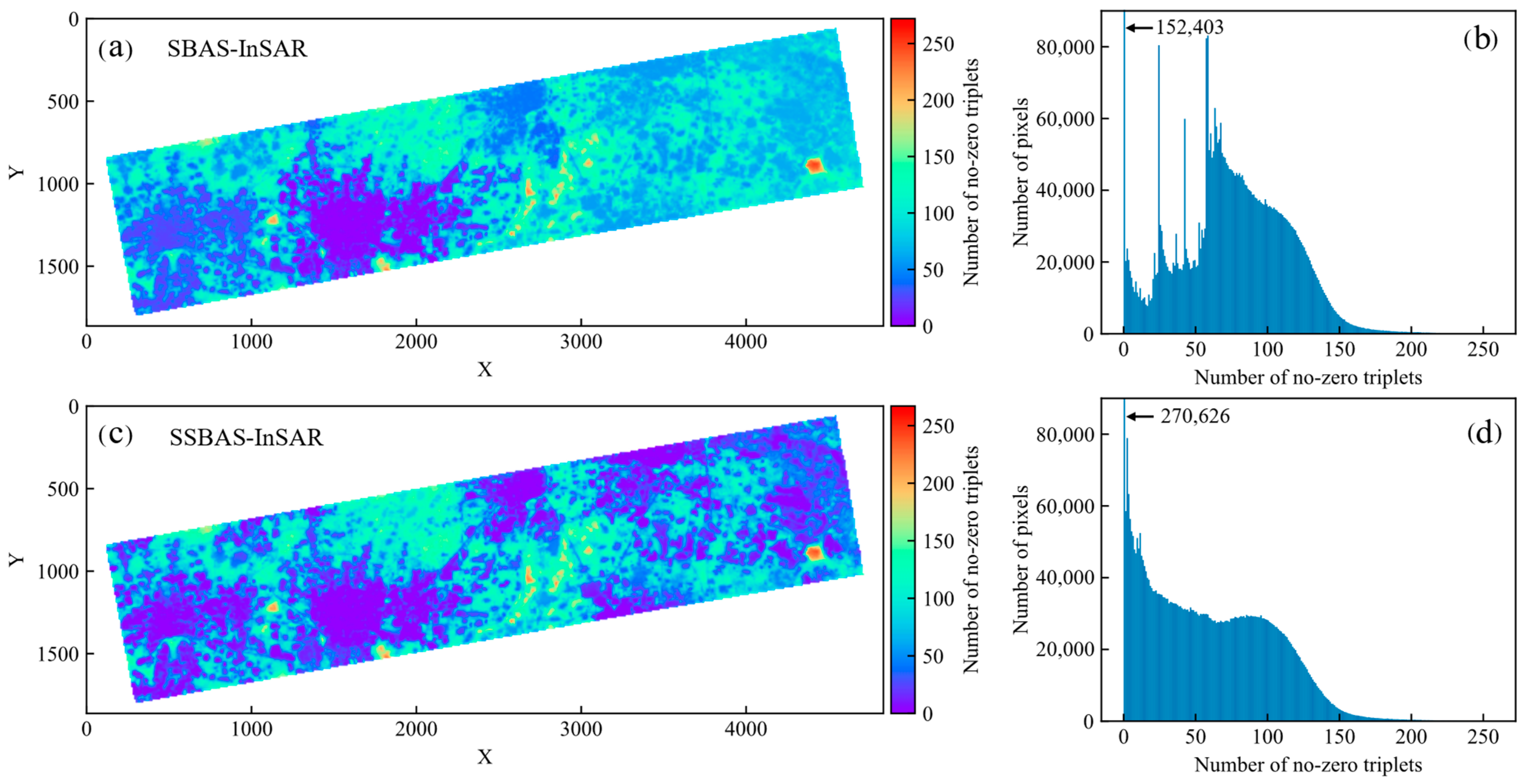
5.1. Reliability of the SSBAS-InSAR Method
5.2. Characteristics of the SSBAS-InSAR Method
6. Conclusions
- (1).
- The concept of spatial scale is introduced to constrain the transmission of errors in the spatial dimension, thereby improving the accuracy of deformation monitoring;
- (2).
- The control points are selected by combining the Stacking-InSAR results with the average coherence, which improves the reliability of the control point selection;
- (3).
- The phase is corrected by inverse distance weighting only based on the Delaunay triangulation, without applying any other spatiotemporal filtering methods, which retains the time-series deformation details.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| No. | Date | No. | Date | No. | Date | No. | Date | No. | Date | No. | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 20161203 | 22 | 20170905 | 43 | 20180608 | 64 | 20190311 | 85 | 20191130 | 106 | 20200808 |
| 2 | 20161215 | 23 | 20170917 | 44 | 20180620 | 65 | 20190323 | 86 | 20191212 | 107 | 20200820 |
| 3 | 20161227 | 24 | 20171011 | 45 | 20180702 | 66 | 20190404 | 87 | 20191224 | 108 | 20200901 |
| 4 | 20170108 | 25 | 20171023 | 46 | 20180714 | 67 | 20190416 | 88 | 20200105 | 109 | 20200913 |
| 5 | 20170201 | 26 | 20171104 | 47 | 20180726 | 68 | 20190428 | 89 | 20200117 | 110 | 20200925 |
| 6 | 20170213 | 27 | 20171116 | 48 | 20180807 | 69 | 20190510 | 90 | 20200129 | 111 | 20201007 |
| 7 | 20170225 | 28 | 20171128 | 49 | 20180819 | 70 | 20190522 | 91 | 20200210 | 112 | 20201019 |
| 8 | 20170309 | 29 | 20171210 | 50 | 20180831 | 71 | 20190603 | 92 | 20200222 | 113 | 20201031 |
| 9 | 20170321 | 30 | 20171222 | 51 | 20180912 | 72 | 20190615 | 93 | 20200305 | 114 | 20201112 |
| 10 | 20170402 | 31 | 20180103 | 52 | 20180924 | 73 | 20190627 | 94 | 20200317 | 115 | 20201124 |
| 11 | 20170414 | 32 | 20180115 | 53 | 20181006 | 74 | 20190709 | 95 | 20200329 | 116 | 20201206 |
| 12 | 20170426 | 33 | 20180127 | 54 | 20181018 | 75 | 20190721 | 96 | 20200410 | 117 | 20201218 |
| 13 | 20170508 | 34 | 20180208 | 55 | 20181111 | 76 | 20190802 | 97 | 20200422 | 118 | 20201230 |
| 14 | 20170520 | 35 | 20180220 | 56 | 20181123 | 77 | 20190814 | 98 | 20200504 | 119 | 20210111 |
| 15 | 20170601 | 36 | 20180304 | 57 | 20181205 | 78 | 20190826 | 99 | 20200516 | 120 | 20210123 |
| 16 | 20170613 | 37 | 20180328 | 58 | 20181217 | 79 | 20190919 | 100 | 20200528 | 121 | 20210204 |
| 17 | 20170625 | 38 | 20180409 | 59 | 20181229 | 80 | 20191001 | 101 | 20200609 | 122 | 20210216 |
| 18 | 20170719 | 39 | 20180421 | 60 | 20190110 | 81 | 20191013 | 102 | 20200621 | 123 | 20210228 |
| 19 | 20170731 | 40 | 20180503 | 61 | 20190122 | 82 | 20191025 | 103 | 20200703 | 124 | 20210312 |
| 20 | 20170812 | 41 | 20180515 | 62 | 20190203 | 83 | 20191106 | 104 | 20200715 | 125 | 20210324 |
| 21 | 20170824 | 42 | 20180527 | 63 | 20190227 | 84 | 20191118 | 105 | 20200727 |
Appendix B
References
- Yang, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, L. Use of SAR/InSAR in Mining Deformation Monitoring, Parameter Inversion, and Forward Predictions: A Review. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2020, 8, 71–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Lombardo, L.; Chang, L.; Sadhasivam, N.; Hu, X.; Fang, Z.; Dahal, A.; Fadel, I.; Luo, G.; Tanyas, H. Investigating Earthquake Legacy Effect on Hillslope Deformation Using InSAR-Derived Time Series. Earth Surf. Proc. Landf. 2024, 49, 980–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Sandwell, D.T.; Smith-Konter, B. Coseismic Displacements and Surface Fractures from Sentinel-1 InSAR: 2019 Ridgecrest Earthquakes. Seismol. Res. Lett. 2020, 91, 1979–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amico, F.; Gagliardi, V.; Bianchini Ciampoli, L.; Tosti, F. Integration of InSAR and GPR Techniques for Monitoring Transition Areas in Railway Bridges. NDT E Int. 2020, 115, 102291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmanoğlu, B.; Sunar, F.; Wdowinski, S.; Cabral-Cano, E. Time Series Analysis of InSAR Data: Methods and Trends. Isprs J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 115, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aswathi, J.; Binoj Kumar, R.B.; Oommen, T.; Bouali, E.H.; Sajinkumar, K.S. InSAR as a Tool for Monitoring Hydropower Projects: A Review. Energy Geosci. 2022, 3, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xu, W.; Li, Z. Review of the SBAS InSAR Time-Series Algorithms, Applications, and Challenges. Geod. Geodyn. 2022, 13, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-Y.; Madson, A. Error Sources of Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar Satellites. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirui, P.K.; Reinosch, E.; Isya, N.; Riedel, B.; Gerke, M. Mitigation of Atmospheric Artefacts in Multi Temporal InSAR: A Review. PFG–J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Geoinf. Sci. 2021, 89, 251–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Duan, M.; Cao, Y.; Mu, M.; He, X.; Wei, J. Mitigation of Time-Series InSAR Turbulent Atmospheric Phase Noise: A Review. Geod. Geodyn. 2022, 13, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Zhang, L.; Lu, Z.; Li, X. Correction of Spatially Varying Stratified Atmospheric Delays in Multitemporal InSAR. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 285, 113382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Huang, G.; Zhao, Z.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, G. A Multi-Scale Spatial Difference Approach to Estimating Topography Correlated Atmospheric Delay in Radar Interferograms. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Li, Z.; Penna, N.T.; Crippa, P. Generic Atmospheric Correction Model for Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar Observations. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2018, 123, 9202–9222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Penna, N.T.; Li, Z. Generation of Real-time Mode High-resolution Water Vapor Fields from GPS Observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 2008–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Li, Z.; Penna, N.T. Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar Atmospheric Correction Using a GPS-Based Iterative Tropospheric Decomposition Model. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 204, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanssen, R.F. Radar Interferometry: Data Interpretation and Error Analysis; Remote Sensing and Digital Image Processing; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; ISBN 978-0-306-47633-4. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.; Hanssen, R.F.; Guo, H.; Yue, H.; Perski, Z. Nonlinear Model for InSAR Baseline Error. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sensing 2016, 54, 5341–5351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Fu, H.; Liu, L.; Feng, G.; Peng, X.; Wen, D. Orbit Error Removal in InSAR/MTInSAR with a Patch-Based Polynomial Model. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 102, 102438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, G.; Chen, Z.; Cui, H.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, Z.; Li, Q. Surface Deformation Extraction from Small Baseline Subset Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry (SBAS-InSAR) Using Coherence-Optimized Baseline Combinations. GIScience Remote Sens. 2022, 59, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Duan, P.; Chang, J. Creep Identification by the Baseline Optimized TS-InSAR Technique Considering the Monthly Variation in Coherence. Geocarto Int. 2022, 38, 2159071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunjun, Z.; Fattahi, H.; Amelung, F. Small Baseline InSAR Time Series Analysis: Unwrapping Error Correction and Noise Reduction. Comput. Geosci. 2019, 133, 104331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morishita, Y.; Lazecky, M.; Wright, T.; Weiss, J.; Elliott, J.; Hooper, A. LiCSBAS: An Open-Source InSAR Time Series Analysis Package Integrated with the LiCSAR Automated Sentinel-1 InSAR Processor. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver-Cabrera, T.; Jones, C.E.; Yunjun, Z.; Simard, M. InSAR Phase Unwrapping Error Correction for Rapid Repeat Measurements of Water Level Change in Wetlands. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5215115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Kang, Y.; Wei, J.; Lu, Z.; Yan, W.; Wang, H.; Liu, Z.; Lv, X.; Zhou, M.; et al. SAR Interferometry on Full Scatterers: Mapping Ground Deformation with Ultra-High Density from Space. Remote Sens. Environ. 2024, 302, 113965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekaert, D.P.S.; Handwerger, A.L.; Agram, P.; Kirschbaum, D.B. InSAR-Based Detection Method for Mapping and Monitoring Slow-Moving Landslides in Remote Regions with Steep and Mountainous Terrain: An Application to Nepal. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 249, 111983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Lu, Z.; Zhao, C.; Xu, Y.; Kim, J.; Gallegos, A.J. InSAR Monitoring of Creeping Landslides in Mountainous Regions: A Case Study in Eldorado National Forest, California. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 258, 112400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Li, Z.; Amelung, F. Mapping Ground Displacement by a Multiple Phase Difference-Based InSAR Approach: With Stochastic Model Estimation and Turbulent Troposphere Mitigation. J. Geod. 2019, 93, 1313–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zebker, H. Accuracy of a Model-Free Algorithm for Temporal InSAR Tropospheric Correction. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Hestir, E.; Yunjun, Z.; Reiter, M.E.; Viers, J.H.; Schaffer-Smith, D.; Sesser, K.; Oliver-Cabrera, T. Automated Reference Points Selection for InSAR Time Series Analysis on Segmented Wetlands. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2024, 21, 4008705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Feng, G.; Li, Z.; Luo, S.; Wang, H.; Xiong, Z.; Zhu, J.; Hu, J. A Strategy for Variable-Scale InSAR Deformation Monitoring in a Wide Area: A Case Study in the Turpan–Hami Basin, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.W.; Ding, X.L.; Huang, C.; Zou, Z.R.; Chen, Y.L. Atmospheric Effects on Repeat-Pass InSAR Measurements over Shanghai Region. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2007, 69, 1344–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattahi, H.; Simons, M.; Agram, P. InSAR Time-Series Estimation of the Ionospheric Phase Delay: An Extension of the Split Range-Spectrum Technique. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 5984–5996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Agram, P.; Simons, M.; Fielding, E.J. Ionospheric Correction of InSAR Time Series Analysis of C-Band Sentinel-1 TOPS Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 6755–6773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uuemaa, E.; Ahi, S.; Montibeller, B.; Muru, M.; Kmoch, A. Vertical Accuracy of Freely Available Global Digital Elevation Models (ASTER, AW3D30, MERIT, TanDEM-X, SRTM, and NASADEM). Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.W.; Zebker, H.A. Two-Dimensional Phase Unwrapping with Use of Statistical Models for Cost Functions in Nonlinear Optimization. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2001, 18, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karra, K.; Kontgis, C.; Statman-Weil, Z.; Mazzariello, J.C.; Mathis, M.; Brumby, S.P. Global Land Use / Land Cover with Sentinel 2 and Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium IGARSS, Brussels, Belgium, 11 July 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 4704–4707. [Google Scholar]
- Fattahi, H.; Agram, P.; Simons, M. A Network-Based Enhanced Spectral Diversity Approach for TOPS Time-Series Analysis. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 777–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geudtner, D.; Miranda, N.; Navas-Traver, I.; Ceba, F.V.; Prats, P.; Yague-Martinez, N.; Breit, H.; de Zan, F.; Larsen, Y.; Recchia, A.; et al. Sentinel-1A/B SAR and InSAR Performance. In Proceedings of the EUSAR 2018; 12th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Aachen, Germany, 4–7 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Pepe, A.; Lanari, R. On the Extension of the Minimum Cost Flow Algorithm for Phase Unwrapping of Multitemporal Differential SAR Interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 2374–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattahi, H.; Amelung, F. InSAR Bias and Uncertainty Due to the Systematic and Stochastic Tropospheric Delay. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2015, 120, 8758–8773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Ma, Q.; Xu, J.; Liu, M. Structural Health Monitoring Research under Varying Temperature Condition: A Review. J. Civ. Struct. Health Monit. 2021, 11, 149–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Yu, C.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Chen, J. Mining-Related Subsidence Measurements Using a Robust Multi-Temporal InSAR Method and Logistic Model. IEEE J. Miniaturiz. Air Space Syst. 2024, 5, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Z.; Liu, X.; Chen, Q. Prediction of Mining-Induced 3-D Deformation by Integrating Single-Orbit SBAS-InSAR, GNSS, and Log-Logistic Model (LL-SIG). IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5222213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Shen, Z. Present-day Crustal Deformation of Continental China Derived from GPS and Its Tectonic Implications. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2020, 125, e2019JB018774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephenson, O.L.; Liu, Y.-K.; Yunjun, Z.; Simons, M.; Rosen, P.; Xu, X. The Impact of Plate Motions on Long-Wavelength InSAR-Derived Velocity Fields. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2022GL099835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Xu, Z.; Chen, Z.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Gong, X. Analyzing Surface Deformation throughout China’s Territory Using Multi-Temporal InSAR Processing of Sentinel-1 Radar Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2024, 305, 114105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sentinel-1 Bursts. Available online: https://asf.alaska.edu/datasets/daac/sentinel-1-bursts/ (accessed on 19 June 2024).
- Biggs, J.; Wright, T.; Lu, Z.; Parsons, B. Multi-Interferogram Method for Measuring Interseismic Deformation: Denali Fault, Alaska. Geophys. J. Int. 2007, 170, 1165–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



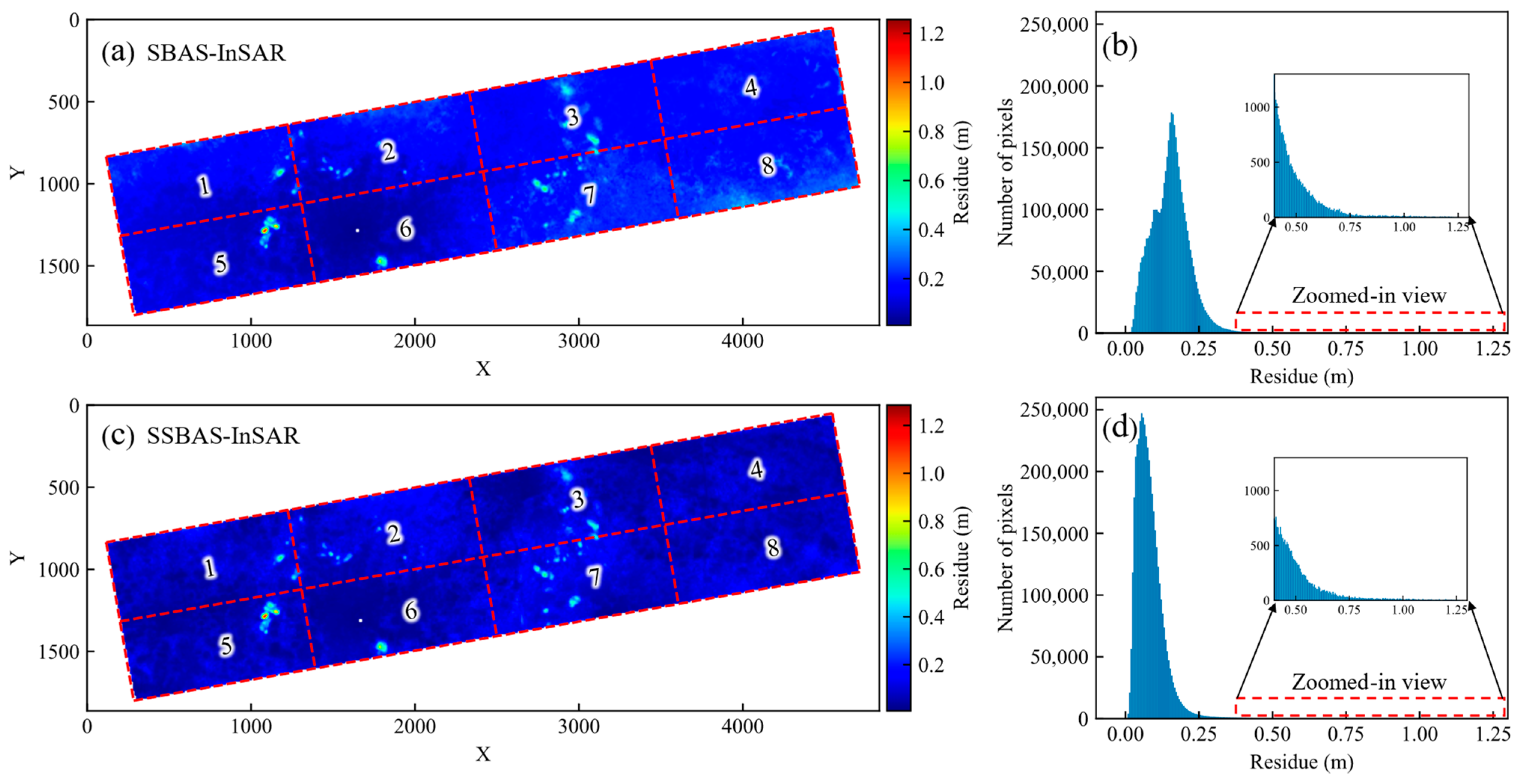
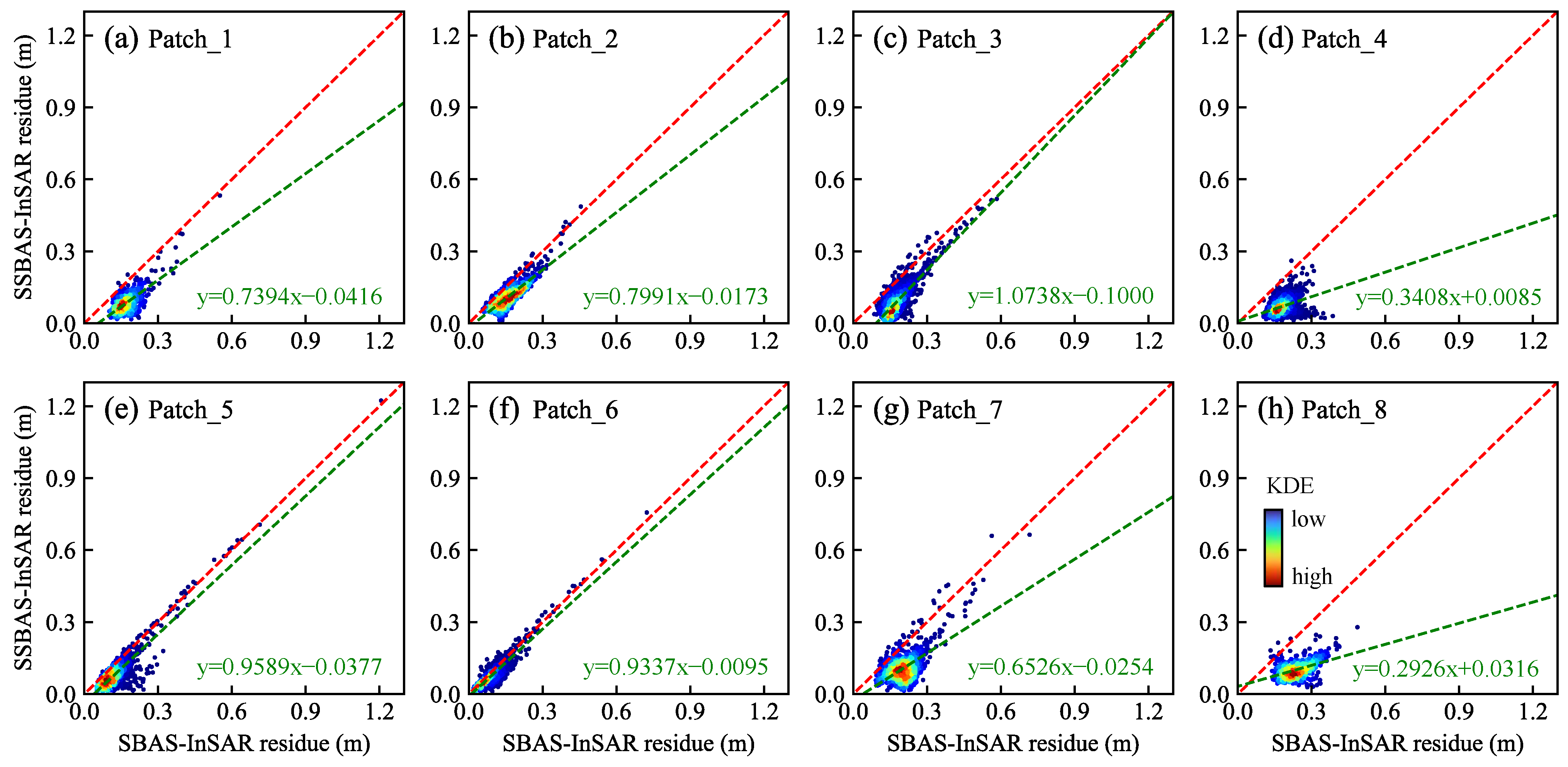


| Method | Patch_1 | Patch_2 | Patch_3 | Patch_4 | Patch_5 | Patch_6 | Patch_7 | Patch_8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBAS-InSAR | 0.1767 | 0.1620 | 0.1731 | 0.1788 | 0.1156 | 0.0820 | 0.2034 | 0.2467 |
| SSBAS-InSAR | 0.0891 | 0.1115 | 0.0854 | 0.0696 | 0.0742 | 0.0668 | 0.1066 | 0.1037 |
| Method | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| SBAS-InSAR | Single control point. |
| SBAS-InSAR+VEC | Single control point; linear phase ramp correction; atmospheric phase correction based on GACOS; DEM error phase correction. |
| SBAS-InSAR+DTLF | Single control point; dual-scale temporal low-pass filtering (small-scale time window size: 36 days, large-scale time window size: 72 days). |
| SSBAS-InSAR | Multiple control points. |
| Direction | SDJX | HAHB | TAIN | SDLY | Maximum Difference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| North | −11.66 | −11.65 | −11.56 | −12.18 | 0.62 |
| East | 31.92 | 32.02 | 31.13 | 31.57 | 0.89 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, Z.; Zhang, G.; Huang, G.; Cheng, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, C. SSBAS-InSAR: A Spatially Constrained Small Baseline Subset InSAR Technique for Refined Time-Series Deformation Monitoring. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3515. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16183515
Yu Z, Zhang G, Huang G, Cheng C, Zhang Z, Zhang C. SSBAS-InSAR: A Spatially Constrained Small Baseline Subset InSAR Technique for Refined Time-Series Deformation Monitoring. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(18):3515. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16183515
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Zhigang, Guanghui Zhang, Guoman Huang, Chunquan Cheng, Zhuopu Zhang, and Chenxi Zhang. 2024. "SSBAS-InSAR: A Spatially Constrained Small Baseline Subset InSAR Technique for Refined Time-Series Deformation Monitoring" Remote Sensing 16, no. 18: 3515. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16183515
APA StyleYu, Z., Zhang, G., Huang, G., Cheng, C., Zhang, Z., & Zhang, C. (2024). SSBAS-InSAR: A Spatially Constrained Small Baseline Subset InSAR Technique for Refined Time-Series Deformation Monitoring. Remote Sensing, 16(18), 3515. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16183515




