Influence of Abnormal Eddies on Seasonal Variations in Sonic Layer Depth in the South China Sea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Construction of Three-Dimensional Sound Speed Field
2.2. SLD Anomaly (SLDA)
2.3. Identification of Eddies
2.4. SLD Heat Budget Equation
3. Spatiotemporal Characteristics of SLD Induced by Abnormal Eddy
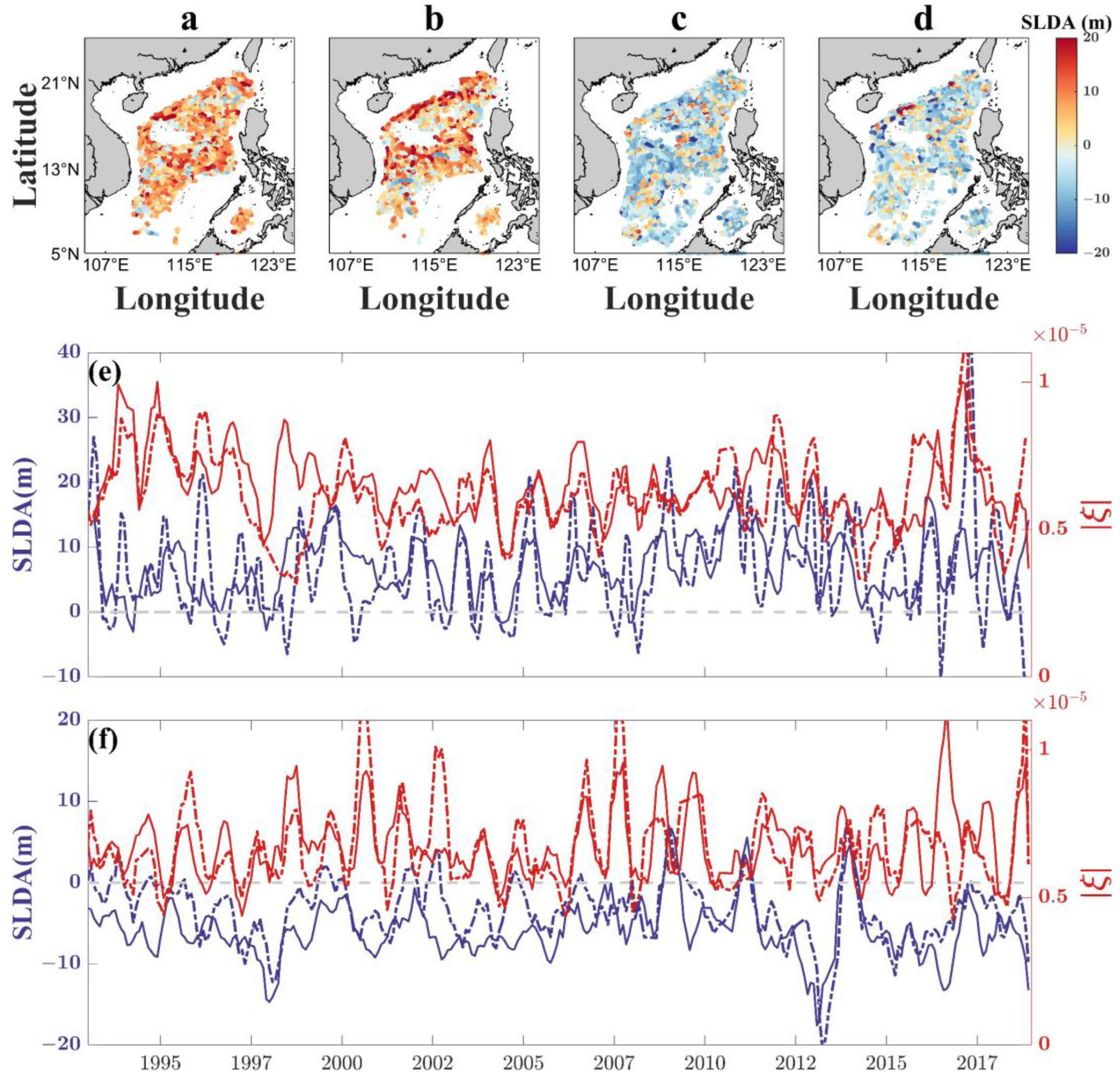
3.1. Spatial Distribution of SLD Induced by Abnormal Eddy
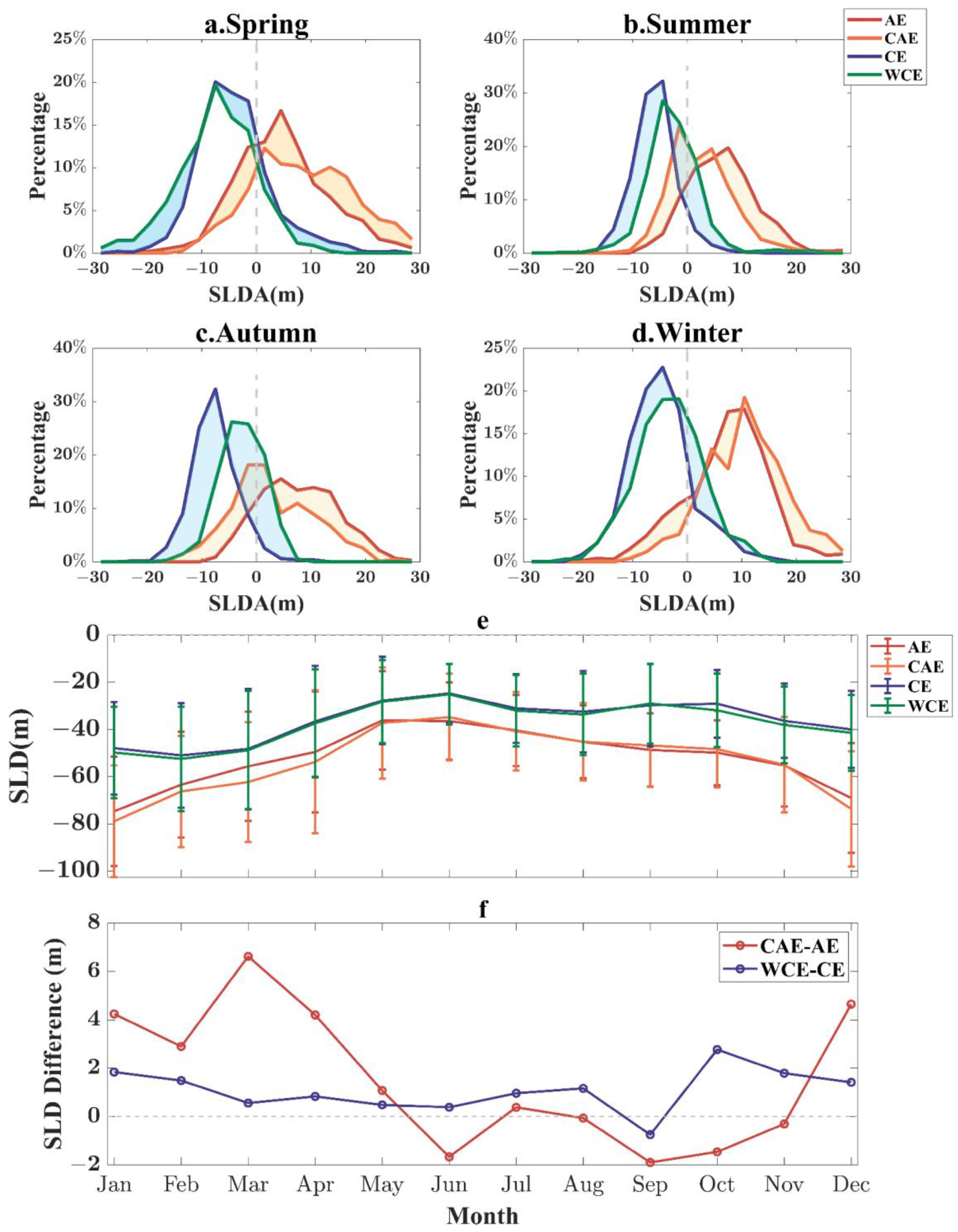
3.2. Seasonal Variation in SLDA Induced by Abnormal Eddies
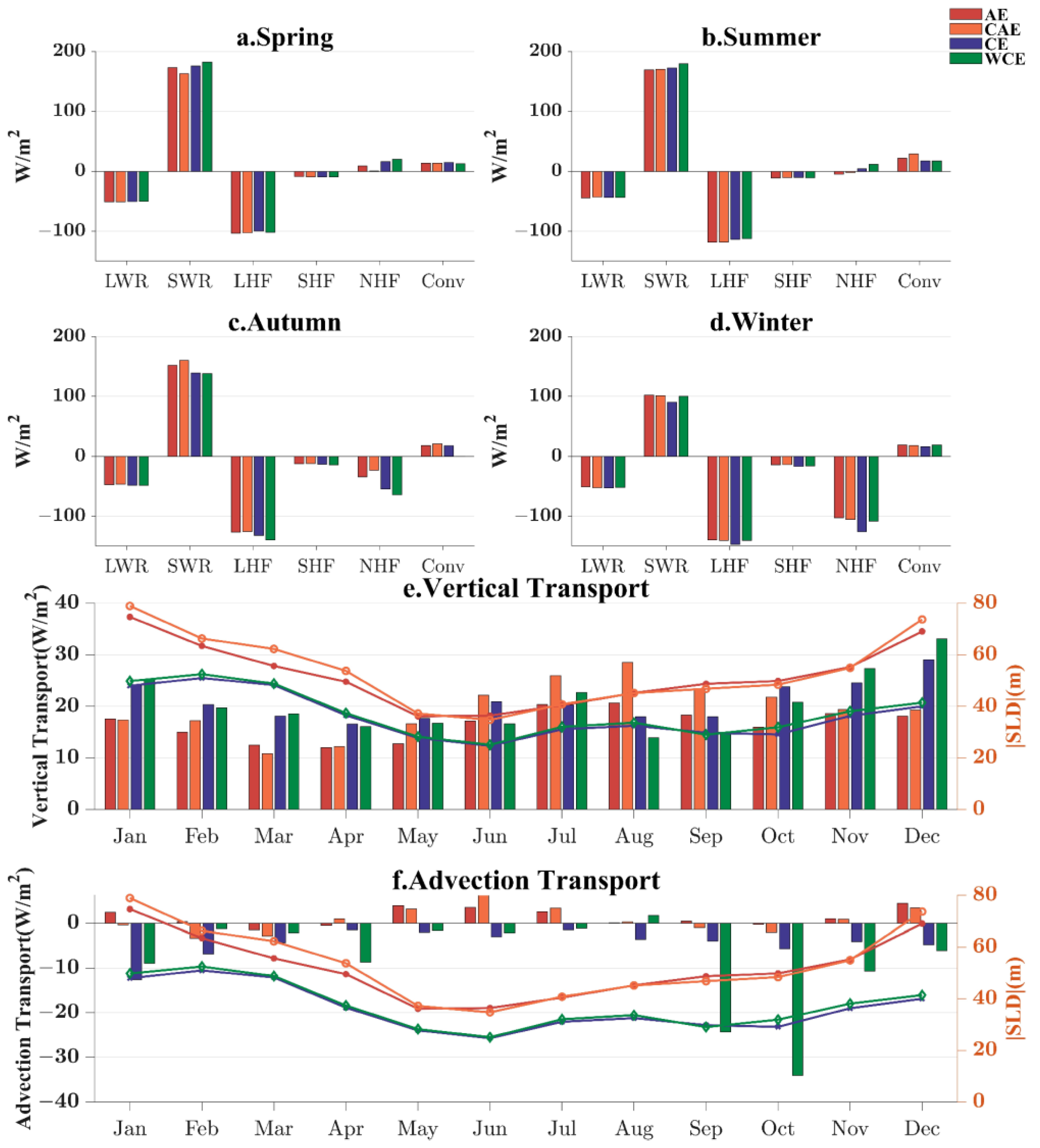
3.3. Mechanism of Seasonal Variations in SLD
4. Conclusions and Discussions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jensen, F.B.; Kuperman, W.A.; Porter, M.B.; Schmidt, H. Fundamentals of Ocean Acoustics. In Computational Ocean Acoustics, Modern Acoustics and Signal Processing; Jensen, F.B., Kuperman, W.A., Porter, M.B., Schmidt, H., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 1–64. ISBN 978-1-4419-8678-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S. A study on the sonic layer depth and the cutoff frequency in the East Sea/Japan Sea. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2014—TAIPEI, Taipei, Taiwan, China, 7–10 April 2014; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colosi, J.A.; Rudnick, D.L. Observations of upper ocean sound-speed structures in the North Pacific and their effects on long-range acoustic propagation at low and mid-frequencies. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2020, 148, 2040–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyc, C.D.; Geoffroy, M.; Knudsen, F.R. An evaluation of active acoustic methods for detection of marine mammals in the Canadian Beaufort Sea. Mar. Mamm. Sci. 2016, 32, 202–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyack, P.L. Implications for marine mammals of large-scale changes in the marine acoustic environment. J. Mammal. 2008, 89, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Spain, G.L.; D’Amico, A.; Fromm, D.M. Properties of the underwater sound fields during some well documented beaked whale mass stranding events. J. Cetacean Res. Manage. 2005, 7, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskar, T.U.; Swain, D. Relation between Sonic Layer and Mixed layer depth in the Arabian Sea. Indian J. Geo-Mar. Sci. 2016, 45, 1264–1271. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, S. Analysis of Differences between the Sonic Layer Depth and the Mixed Layer Depth in the East Sea. J. Korea Inst. Inf. Commun. Eng. 2015, 19, 1259–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Helber, R.W.; Barron, C.N.; Carnes, M.R.; Zingarelli, R.A. Evaluating the sonic layer depth relative to the mixed layer depth. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2008, 113, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercer, J.A.; Booker, J.R. Long-range propagation of sound through oceanic mesoscale structures. J. Geophys. Res. 1983, 88, 689–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Piao, S.; Gong, L.; Zhang, M.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, S. The Effect of Mesoscale Eddy on the Characteristic of Sound Propagation. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ma, L.; Wang, H.; Ren, K.; Chen, S. Parametric Model for Eddies-Induced Sound Speed Anomaly in Five Active Mesoscale Eddy Regions. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2022, 127, e2022JC018408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munk, W.H. Horizontal Deflection of Acoustic Paths by Mesoscale Eddies. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1980, 10, 596–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellberg, L.E.; Johannessen, O.M.; Connors, D.N.; Botseas, G.; Browning, D. Modeled acoustic propagation through an ice edge eddy in the East Greenland Sea Marginal Ice Zone. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1987, 92, 6857–6868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, R.; Chen, Y.; Jin, B. Ocean mesoscale eddy modeling and its application in studying the effect on underwater acoustic propagation. J. Ocean. Technol. 2011, 30, 37–46. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, F.; Zhang, H.; Qu, K. Influence of mesoscale warm eddies on sound propagation in the northeastern South China Sea. J. Harbin Eng. Univ. 2021, 42, 1496–1502. Available online: http://www.cnki.net/kcms/detail/23.1390.u.20210702.1704.008.html (accessed on 16 July 2021).
- Wu, Y.; Qin, J.; Li, Z.; Wu, S.; Wang, M.; Li, W.; Guo, Y. Warm-core eddy effects on sound propagation in the South China sea. Appl. Acoust. 2023, 211, 109551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udaya Bhaskar, T.; Swain, D.; Ravichandran, M. Seasonal variability of sonic layer depth in the Central Arabian Sea. Ocean Sci. J. 2008, 43, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hausmann, U.; Czaja, A. The observed signature of mesoscale eddies in sea surface temperature and the associated heat transport. Deep. Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2012, 70, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villas Bôas, A.B.; Sato, O.T.; Chaigneau, A.; Castelão, G.P. The signature of mesoscale eddies on the air-sea turbulent heat fluxes in the South Atlantic Ocean. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 1856–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaube, P.; McGillicuddy, D.J., Jr.; Moulin, A.J. Mesoscale Eddies Modulate Mixed Layer Depth Globally. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 1505–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, L.; Chen, G. Characterization of Sea Surface Temperature and Air-Sea Heat Flux Anomalies Associated With Mesoscale Eddies in the South China Sea. JGR Ocean. 2020, 125, e2019JC015470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Q.; Zhai, X.; Wang, G.; Hughes, C.W. Widespread Mesoscale Dipoles in the Global Ocean. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2020, 125, e2020JC016479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Li, X. Characteristics of Global Ocean Abnormal Mesoscale Eddies Derived From the Fusion of Sea Surface Height and Temperature Data by Deep Learning. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2021GL094772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Q.; Zhai, X.; Jiang, X.; Chen, D. Abundant Cold Anticyclonic Eddies and Warm Cyclonic Eddies in the Global Ocean. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2021, 51, 2793–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashmachnikov, I.; Boutov, D.; Dias, J. Manifestation of two meddies in altimetry and sea-surface temperature. Ocean. Sci. 2013, 9, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assassi, C.; Morel, Y.; Vandermeirsch, F.; Chaigneau, A.; Pegliasco, C.; Morrow, R.; Colas, F.; Fleury, S.; Carton, X.; Klein, P.; et al. An Index to Distinguish Surface- and Subsurface-Intensified Vortices from Surface Observations. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2016, 46, 2529–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilmahamod, A.F.; Aguiar-González, B.; Penven, P.; Reason, C.J.C.; De Ruijter, W.P.M.; Malan, N.; Hermes, J.C. SIDDIES Corridor: A Major East-West Pathway of Long-Lived Surface and Subsurface Eddies Crossing the Subtropical South Indian Ocean. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2018, 123, 5406–5425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.G. Modification of ocean eddies by air-sea interaction. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1988, 93, 15523–15533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelton, D.; Xie, S.-P. Coupled Ocean-Atmosphere Interaction at Oceanic Mesoscales. Oceanography 2010, 23, 52–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenger, I.; Gruber, N.; Knutti, R.; Münnich, M. Imprint of Southern Ocean eddies on winds, clouds and rainfall. Nat. Geosci. 2013, 6, 608–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufois, F.; Hardman-Mountford, N.J.; Greenwood, J.; Richardson, A.J.; Feng, M.; Matear, R.J. Anticyclonic eddies are more productive than cyclonic eddies in subtropical gyres because of winter mixing. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1600282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hausmann, U.; McGillicuddy, D.J., Jr.; Marshall, J. Observed mesoscale eddy signatures in Southern Ocean surface mixed-layer depth. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2017, 122, 617–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Yang, J.; Chen, G. The effect of normal and abnormal eddies on the mixed layer depth in the global ocean. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 9, 981505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Jin, T.; Zhou, Z. Effect of eddy on acoustic propagation from the surface duct perspective. Appl. Acoust. 2019, 150, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barboni, A.; Coadou-Chaventon, S.; Stegner, A.; Le Vu, B.; Dumas, F. How subsurface and double-core anticyclones intensify the winter mixed-layer deepening in the Mediterranean Sea. Ocean. Sci. 2023, 19, 229–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-T.; Millero, F.J. Speed of sound in seawater at high pressures. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1977, 62, 1129–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Chen, C.; Lin, L. Analysis of applicable scope of empirical equation for sound velocity. Tech. Acoust. 2014, 33, 504–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaigneau, A.; Gizolme, A.; Grados, C. Mesoscale eddies off Peru in altimeter records: Identification algorithms and eddy spatio-temporal patterns. Prog. Oceanogr. 2008, 79, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, C.; Yang, Z.; Wang, D.; Feng, M.; Su, J. The Enhancement of Submesoscale Ageostrophic Motion on the Mesoscale Eddies in the South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2022, 127, e2022JC018736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, E.L.; Colosi, J.A. Observations of ocean spice and isopycnal tilt sound-speed structures in the mixed layer and upper ocean and their impacts on acoustic propagation. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2023, 154, 2154–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, B. Interannual Variability of the Kuroshio Extension System and Its Impact on the Wintertime SST Field. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2000, 30, 1486–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Fang, Y.; Liu, B.; Tana, C. Coupling between SST and wind speed over mesoscale eddies in the South China Sea. Ocean. Dyn. 2016, 66, 1467–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, W.; Chen, S.; Fang, R.; Li, Z. Atmospheric Response to Mesoscale Ocean Eddies over the South China Sea. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2018, 35, 1189–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Q.; Zhai, X.; Yang, Z.; Chen, D. Generation of Cold Anticyclonic Eddies and Warm Cyclonic Eddies in the Tropical Oceans. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2023, 53, 1485–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Marez, C.; Le Corre, M.; Gula, J. The influence of merger and convection on an anticyclonic eddy trapped in a bowl. Ocean. Model. 2021, 167, 101874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Qiu, C.; Wang, T.; Mao, H.; Xiao, P. Influence of Abnormal Eddies on Seasonal Variations in Sonic Layer Depth in the South China Sea. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2845. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16152845
Liu X, Qiu C, Wang T, Mao H, Xiao P. Influence of Abnormal Eddies on Seasonal Variations in Sonic Layer Depth in the South China Sea. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(15):2845. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16152845
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xintong, Chunhua Qiu, Tianlin Wang, Huabin Mao, and Peng Xiao. 2024. "Influence of Abnormal Eddies on Seasonal Variations in Sonic Layer Depth in the South China Sea" Remote Sensing 16, no. 15: 2845. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16152845
APA StyleLiu, X., Qiu, C., Wang, T., Mao, H., & Xiao, P. (2024). Influence of Abnormal Eddies on Seasonal Variations in Sonic Layer Depth in the South China Sea. Remote Sensing, 16(15), 2845. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16152845





