Driving Factors and Trade-Offs/Synergies Analysis of the Spatiotemporal Changes of Multiple Ecosystem Services in the Han River Basin, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
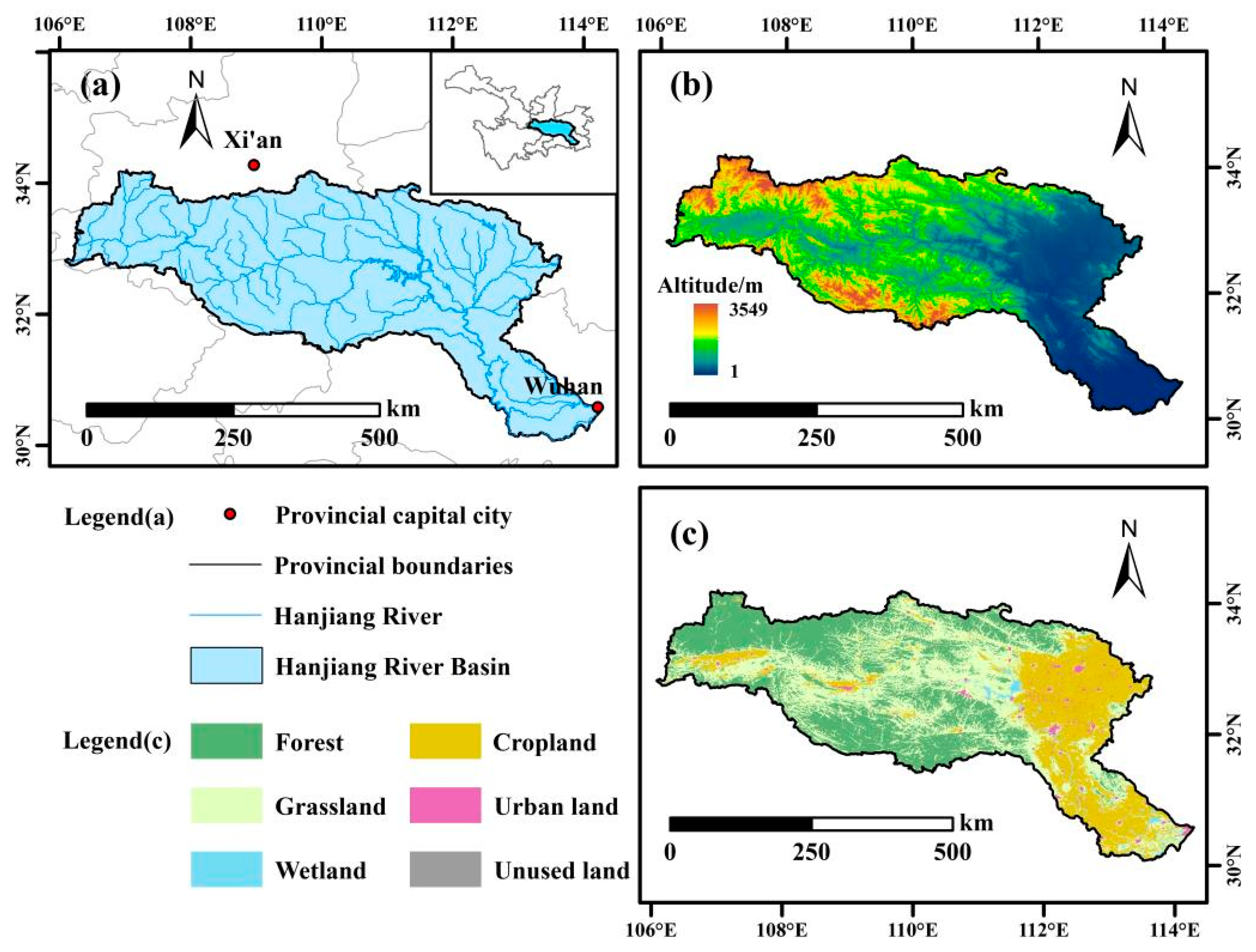
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources and Processing
2.3. Quantification of ESs
2.3.1. Quantification of Water Yield (WY)
2.3.2. Quantification of Carbon Storage (CS)
2.3.3. Quantification of Habitat Quality (HQ)
2.3.4. Quantification of Soil Conservation (SC)
2.4. Spatial Autocorrelation and Hot Spot Analysis of ESs
2.5. Analyses of Trade-Offs/Synergies among ESs
2.6. Identification of ES Bundles (ESBs)
2.7. Model of Geographical Detector
3. Results
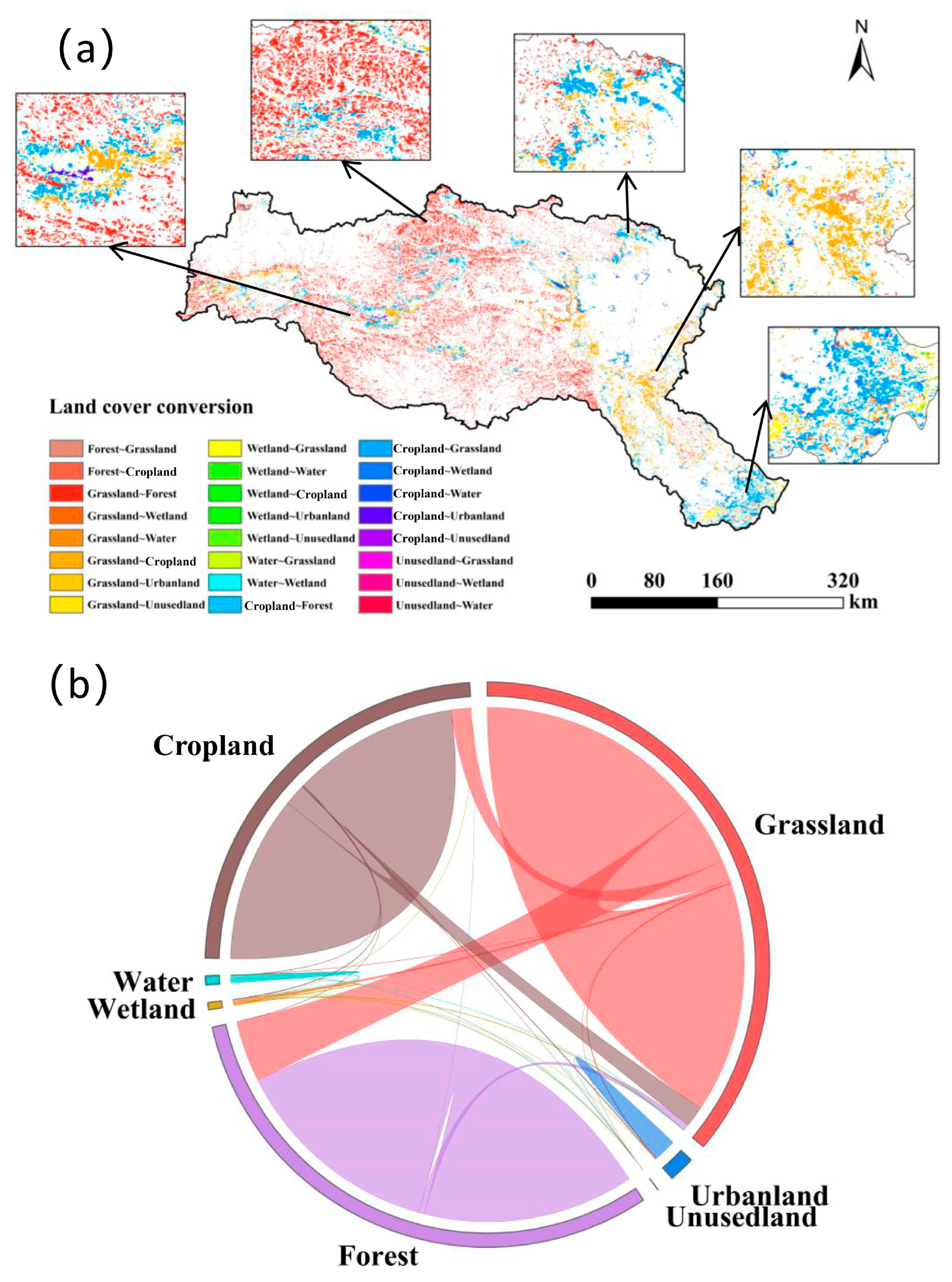
3.1. Land Use Change in the HRB
3.2. ES Patterns in the HRB
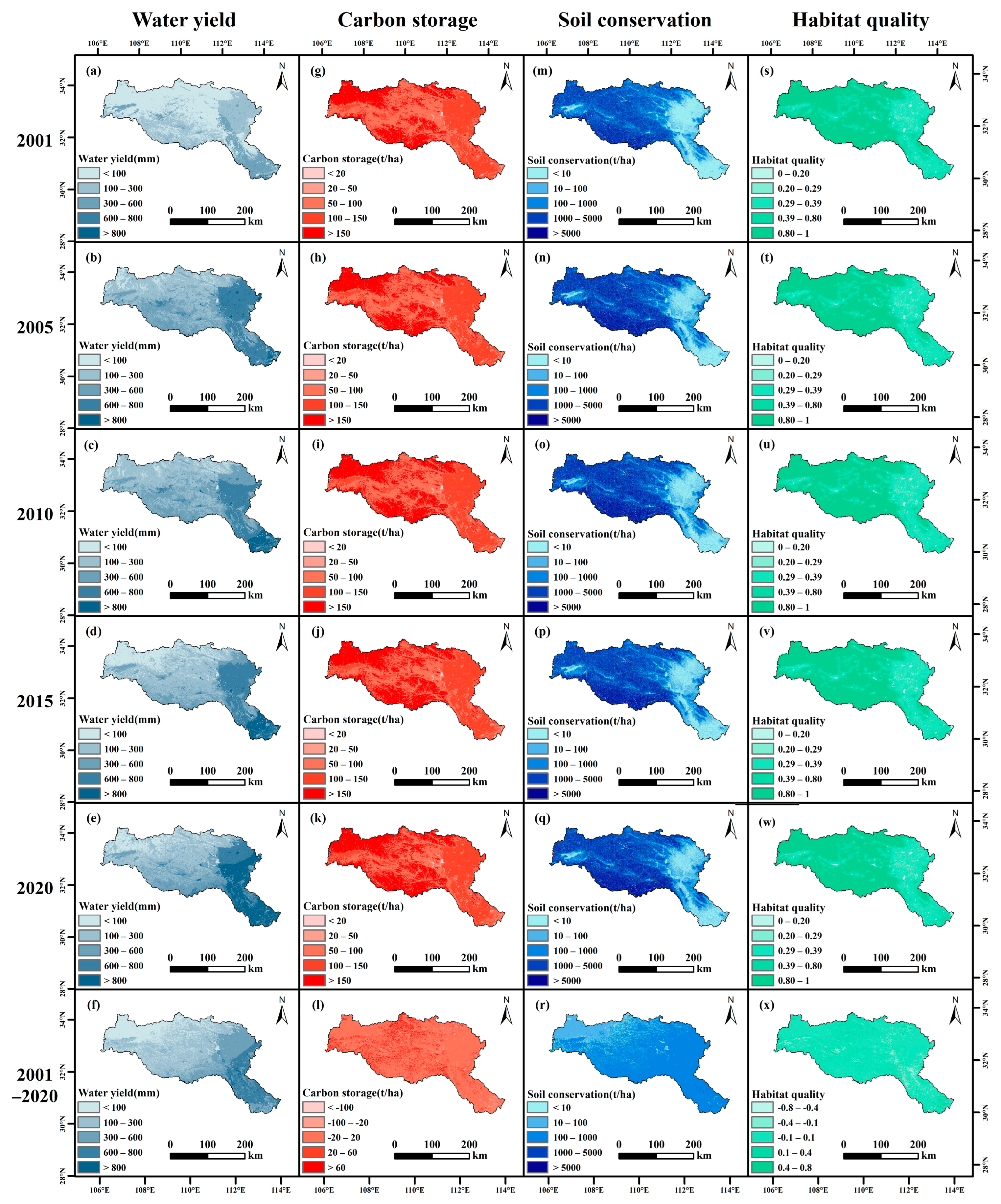
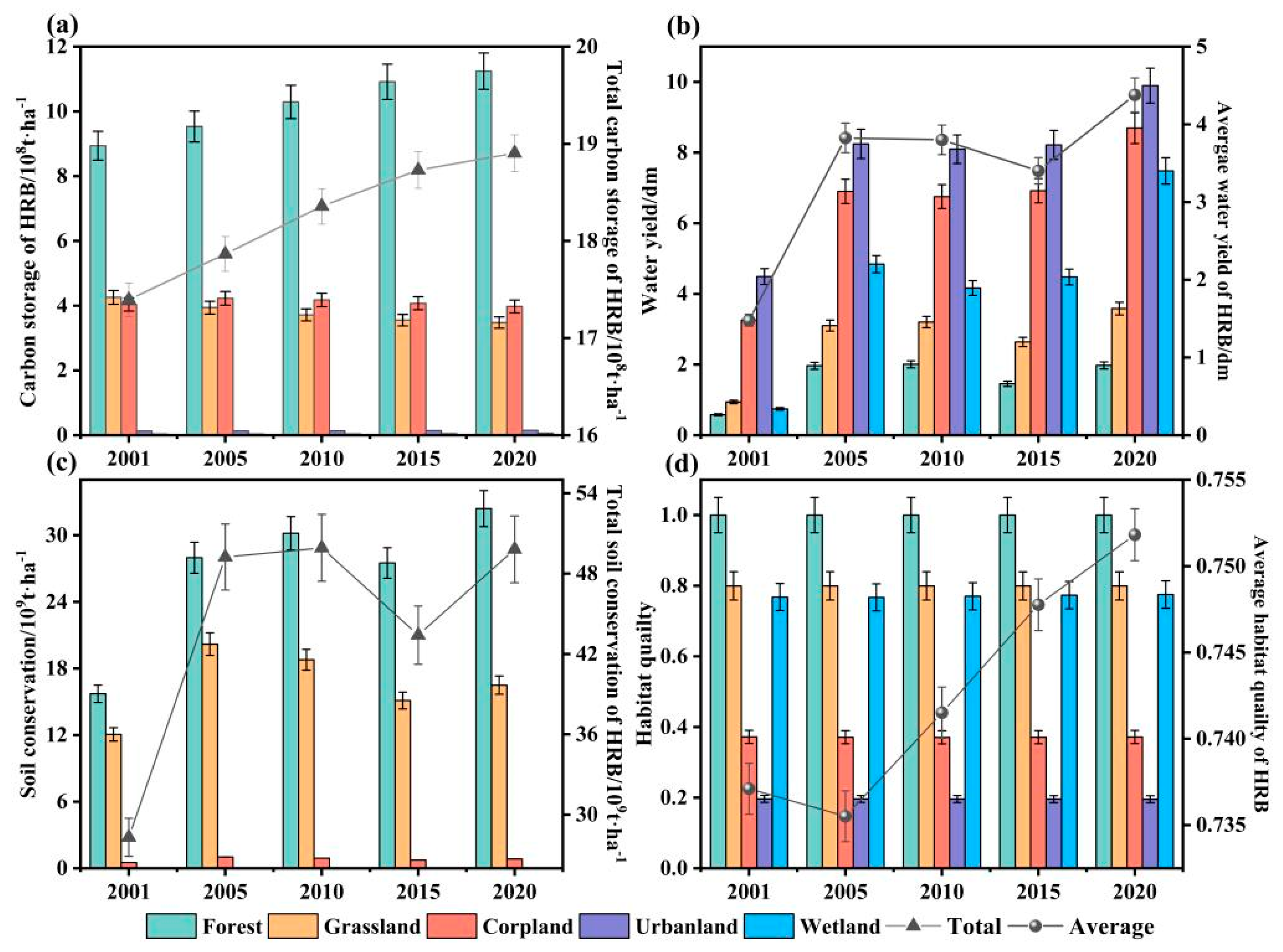
3.2.1. Spatial and Temporal Changes in ESs
3.2.2. Global Spatial Autocorrelation of ESs
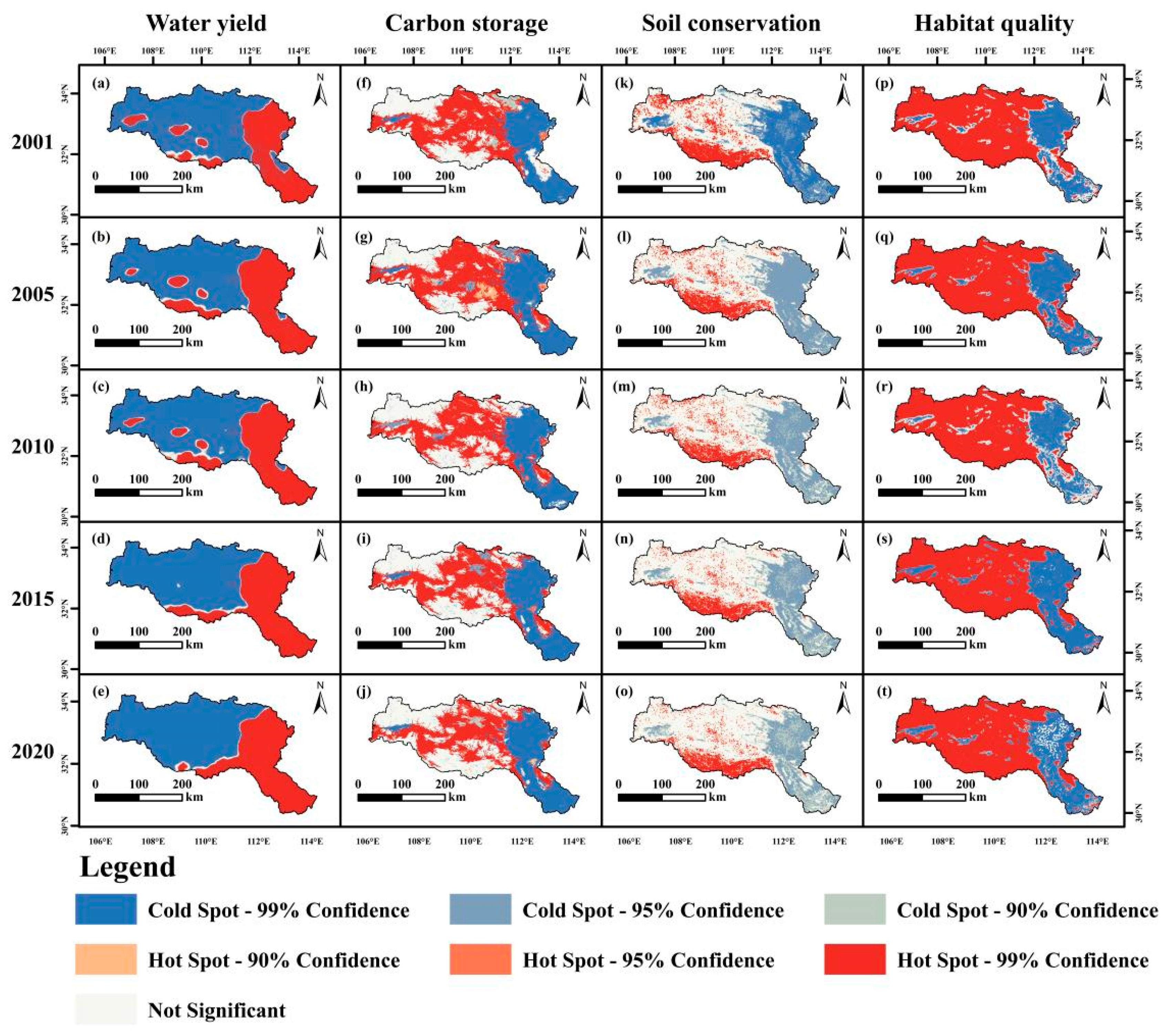
3.2.3. The Cold Hot Spots of ESs
3.3. Trade-Off and Synergy between ESs
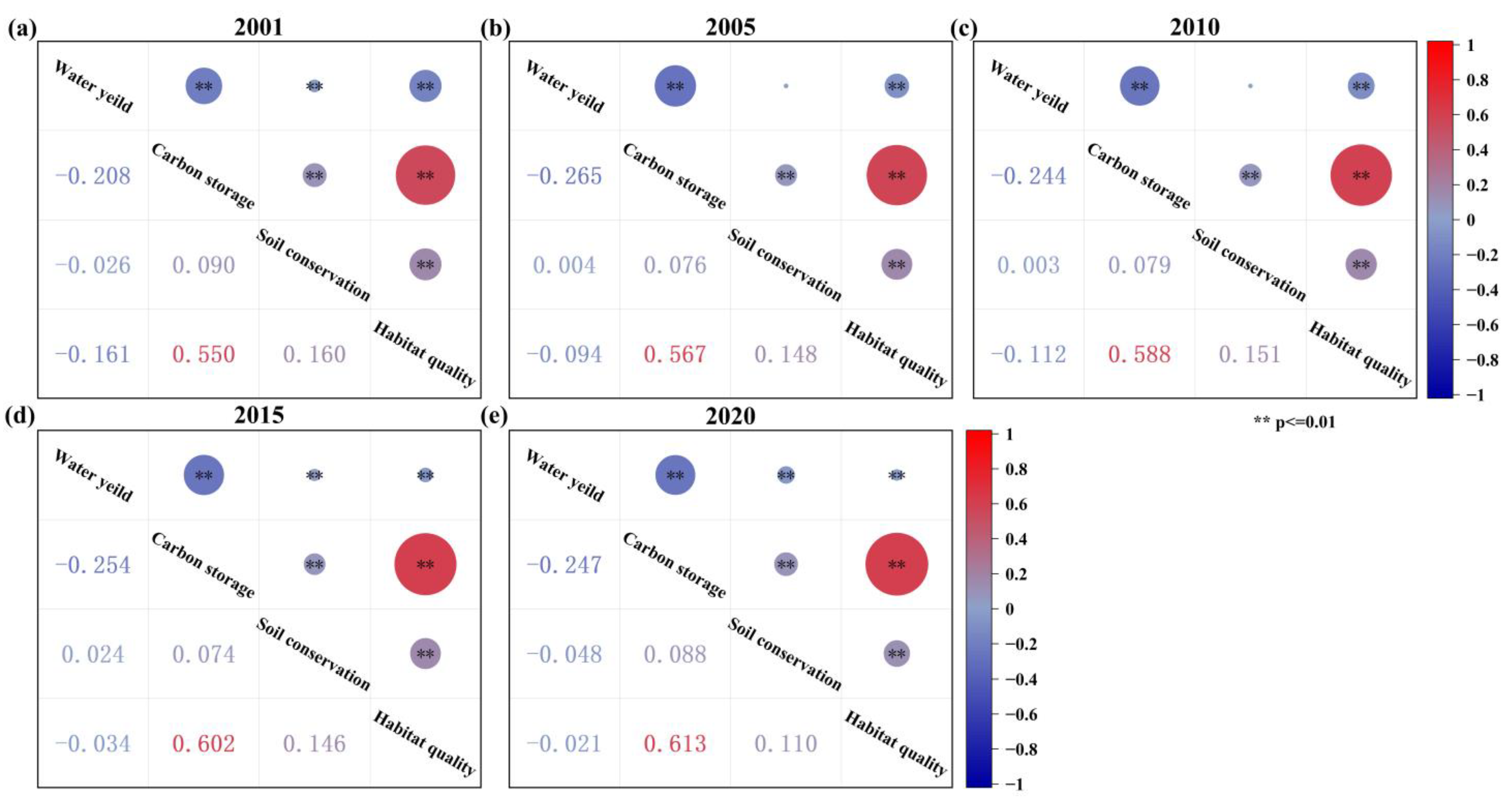
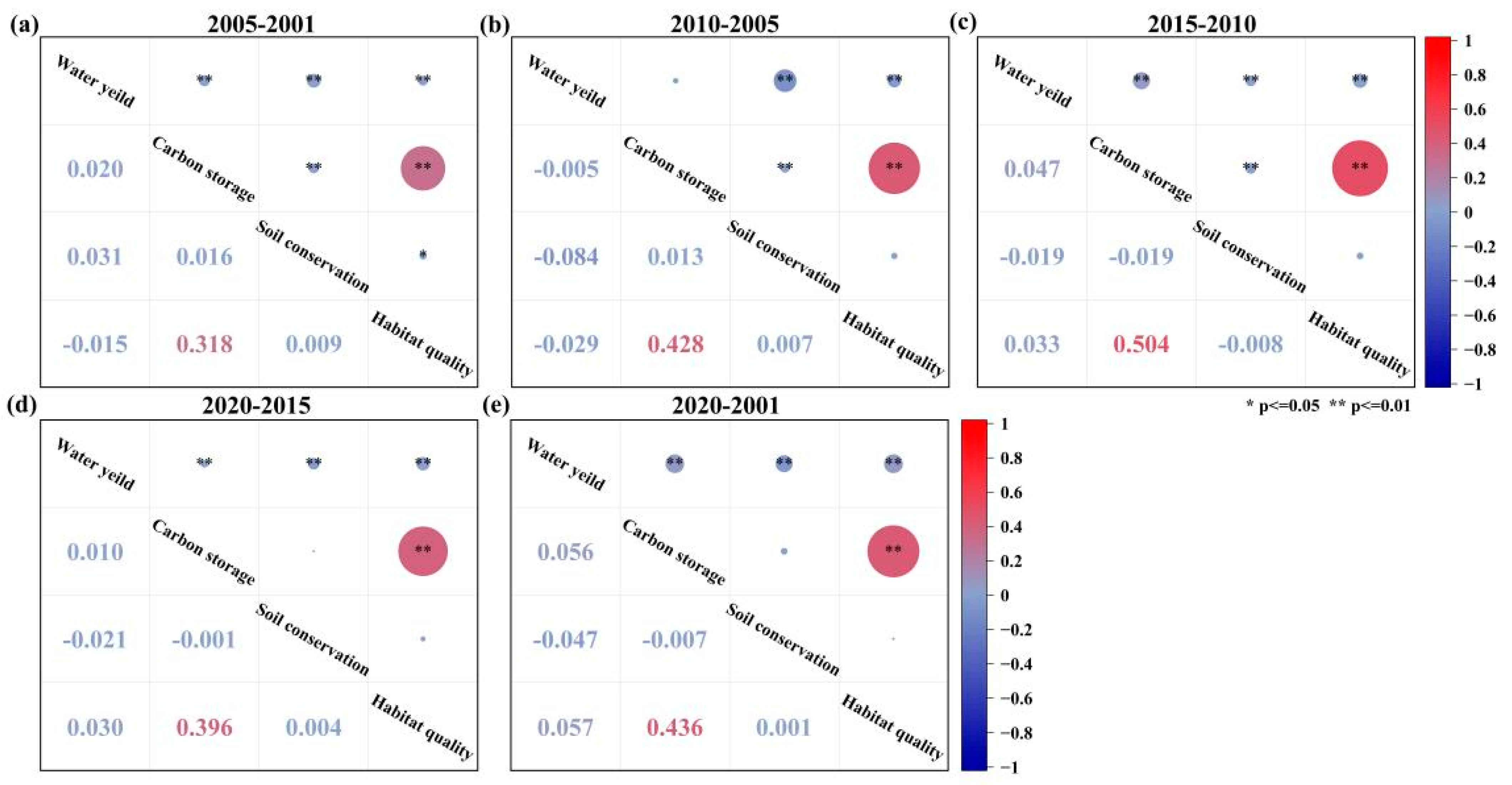
3.3.1. Correlation Analysis
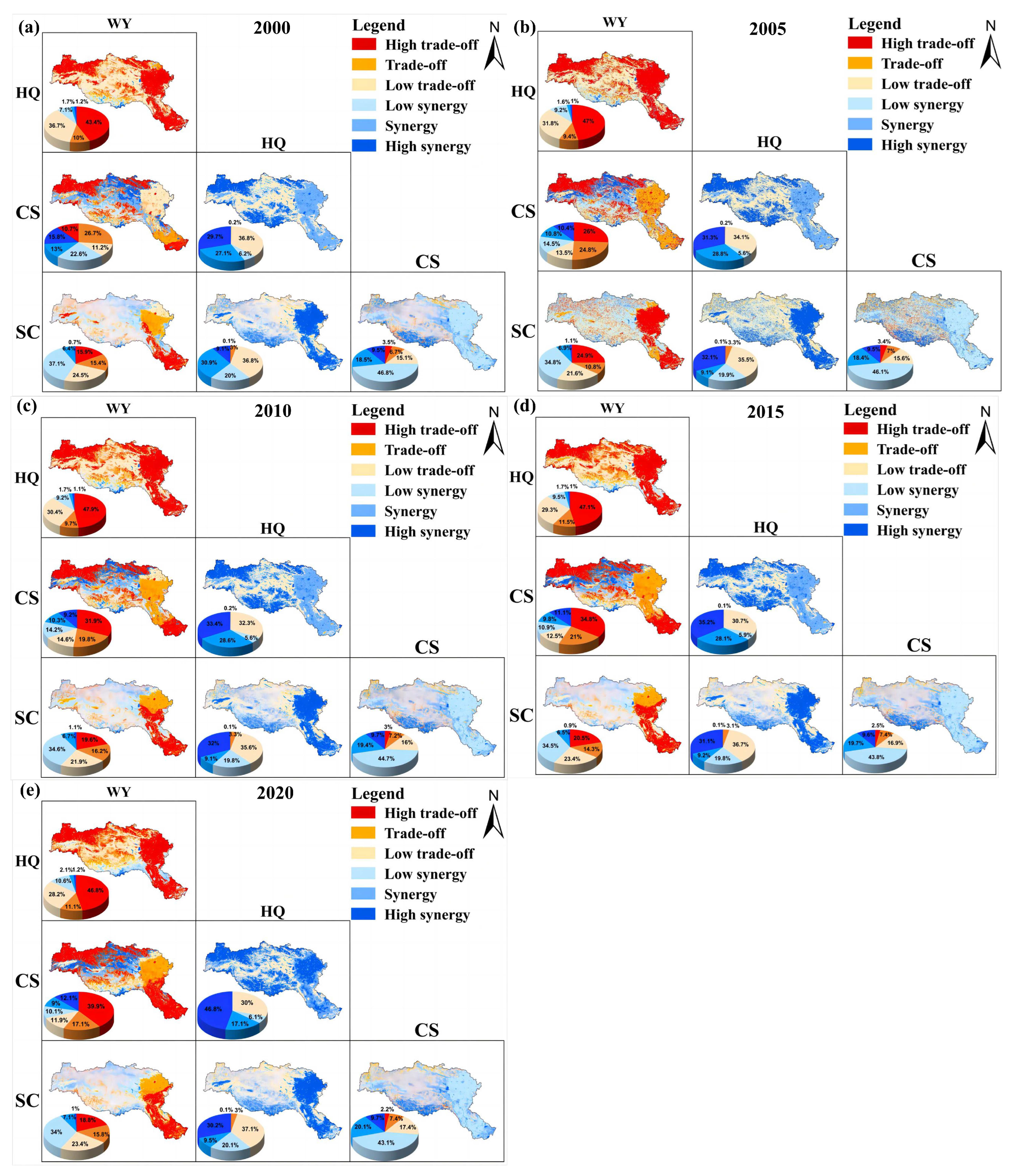
3.3.2. Trade-Off and Synergy between Ecosystem Services
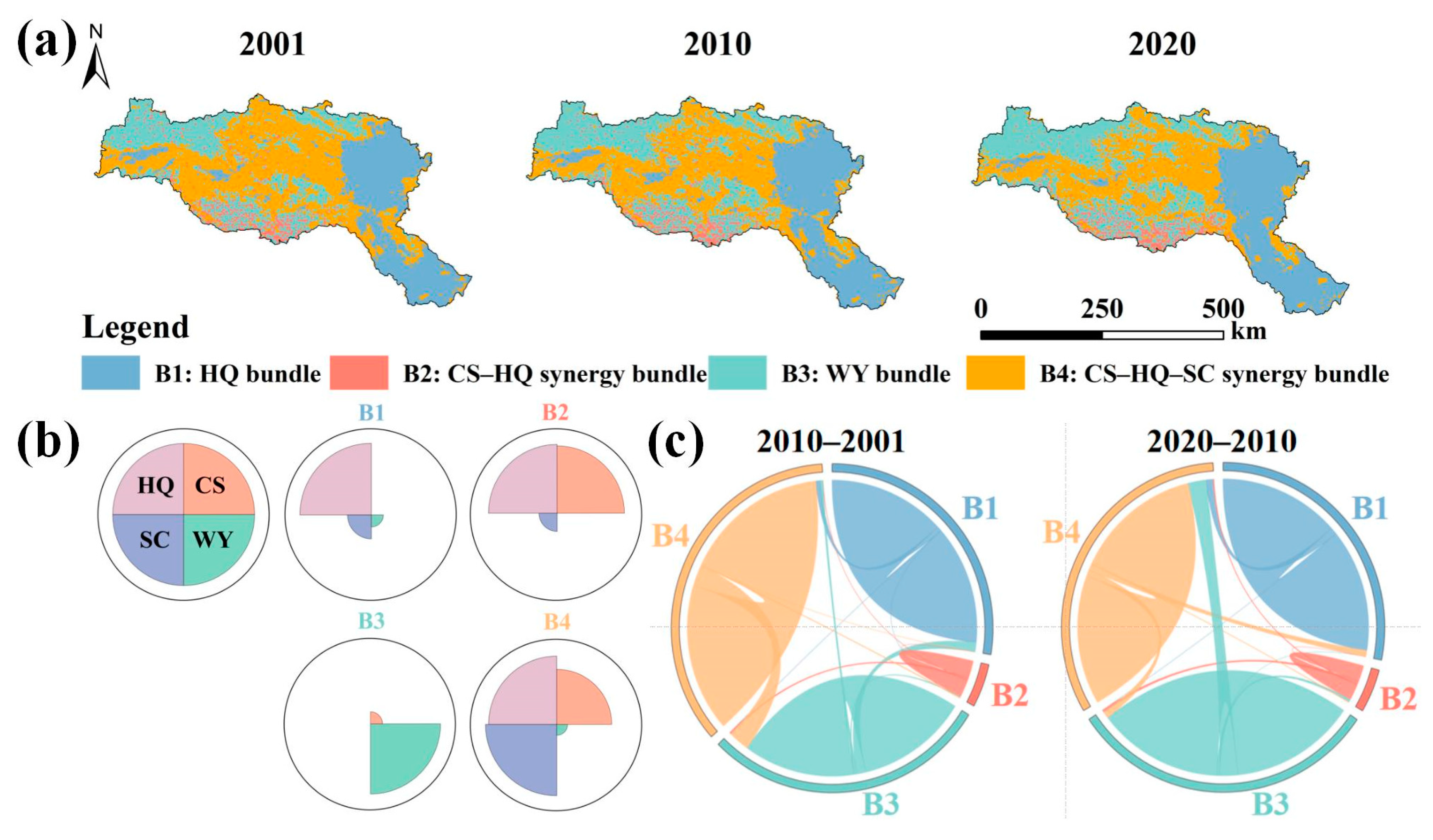
3.4. Spatial-Temporal Patterns of ESBs
3.5. Analysis of Driving Factors of ESs
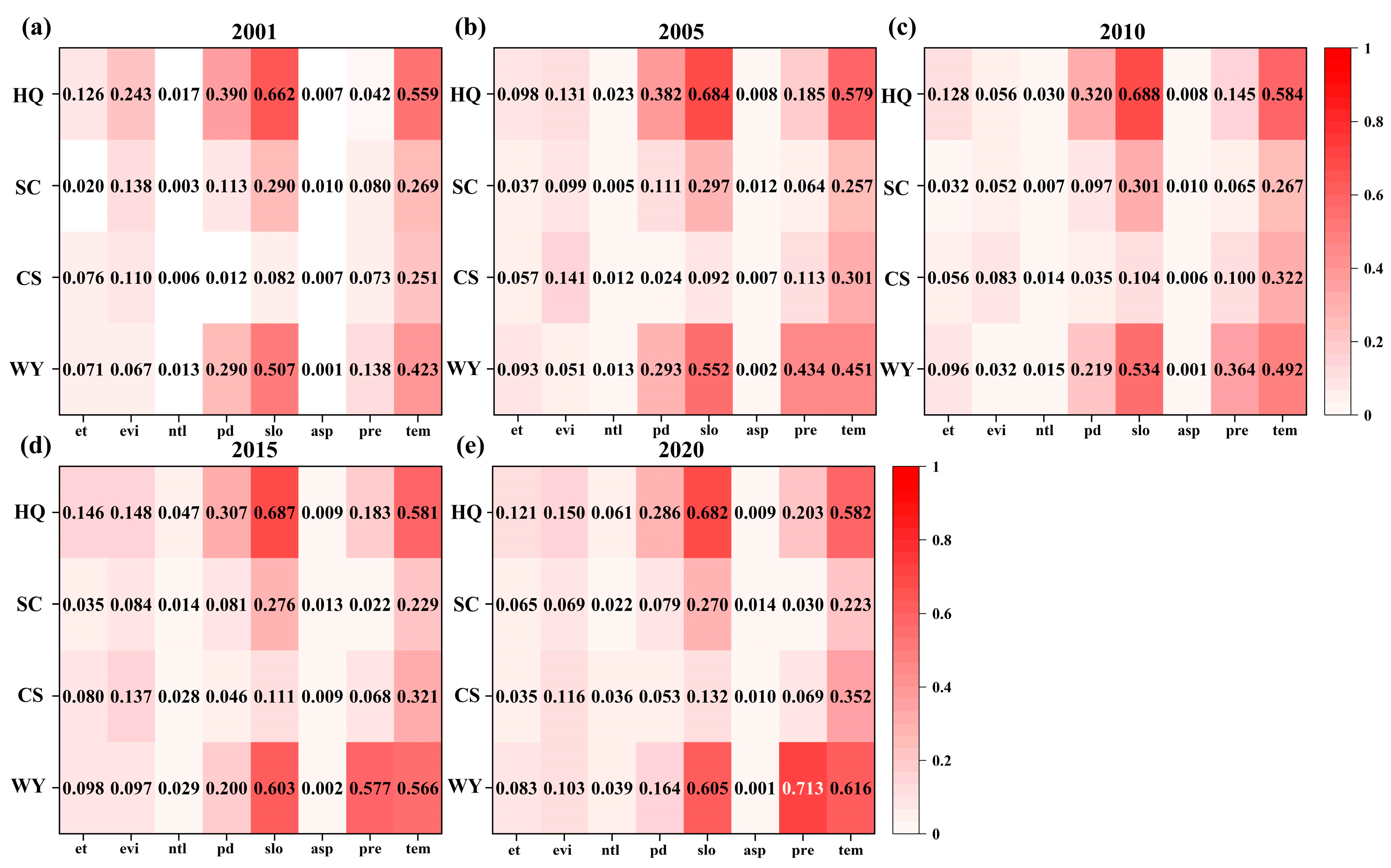
3.5.1. Factor Impact Detection Analysis
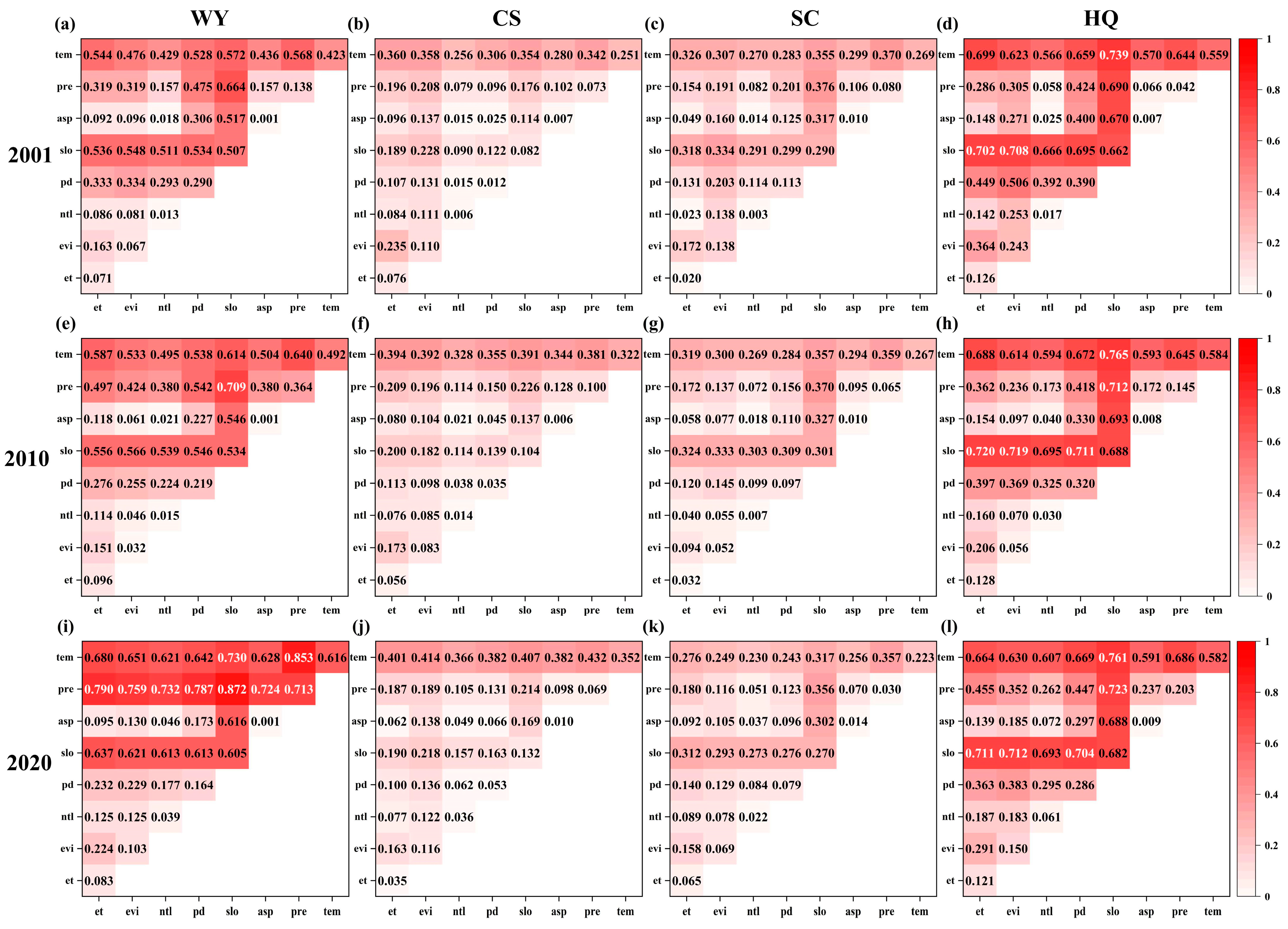
3.5.2. Factor Interaction Detection Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatiotemporal Dynamics and Driving Factors of ESs
4.2. The Trade-Offs/Synergies among Multiple ESs
4.3. Implications for Landscape Management
4.4. Limitations and Next Steps
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- MEA. Ecosystems and Human Well-Being: Synthesis; Millennium Ecosystem Assessment; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Luo, H. Trade-off/synergistic changes in ecosystem services and geographical detection of its driving factors in typical karst areas in southern China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ding, J.; Zhao, W. Divergent responses of ecosystem services to afforestation and grassland restoration in the Tibetan Plateau. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 344, 118471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, W.; Li, Y.; Zhang, P.; Yang, D.; Jing, W.; Rong, T. Analyzing spatio-temporal changes and trade-offs/synergies among ecosystem services in the Yellow River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 138, 108825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Dai, E. Spatial-temporal changes in ecosystem services and the trade-off relationship in mountain regions: A case study of Hengduan Mountain region in Southwest China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 264, 121573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.; Liu, M. An ecosystem service trade-off management framework based on key ecosystem services. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Jiang, C.; Gao, Y.; Du, J. Natural driving mechanism and trade-off and synergy analysis of the spatiotemporal dynamics of multiple typical ecosystem services in Northeast Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 374, 134075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Li, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, K. Forest restoration efforts drive changes in land-use/land-cover and water-related ecosystem services in China’s Han River Basin. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 126, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, J. Quantifying the spatial impact of landscape fragmentation on habitat quality: A multi-temporal dimensional comparison between the Yangtze River Economic Belt and Yellow River Basin of China. Land Use Policy 2023, 125, 106463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vačkářová, D.; Medková, H.; Krpec, P.; Weinzettel, J. Ecosystem services footprint of international trade: Economic value of ecosystem services lost due to crop production. Ecosyst. Serv. 2023, 64, 101560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Dong, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z. Terrestrial transect study on pattern and driving mechanism of ecosystem services in the China–Mongolia–Russia Economic Corridor. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 884, 163880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Li, C.; Yuan, Z.; Luo, Y.; Yin, Q.; Wang, Q.; Hao, Z. How do mountain ecosystem services respond to changes in vegetation and climate? An evidence from the Qinling Mountains, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Guo, W.; Cheng, C.; Tang, Z.; Qi, L. Trade-offs and driving factors of multiple ecosystem services and bundles under spatiotemporal changes in the Danjiangkou Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 144, 109550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, P.; Hu, S.; Frazier, A.E.; Yang, S.; Song, X.; Qu, S. The dynamic relationships between landscape structure and ecosystem services: An empirical analysis from the Wuhan metropolitan area, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 325, 116575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Wang, D.; Lu, H.; Liu, G. Temporal and spatial heterogeneity of land use, urbanization, and ecosystem service value in China: A national-scale analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 418, 137911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Chen, X.; Xue, L.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J.; Li, D. Modeling the spatially heterogeneous relationships between tradeoffs and synergies among ecosystem services and potential drivers considering geographic scale in Bairin Left Banner, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 855, 158834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, M.; He, S.; Gan, M.; Yang, L.; Wang, K. Impacts of urbanization and landscape pattern on habitat quality using OLS and GWR models in Hangzhou, China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 106654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Huang, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, X. Spatial identification of restored priority areas based on ecosystem service bundles and urbanization effects in a megalopolis area. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 308, 114627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Sun, C.; Fan, F. Multi-criteria framework for identifying the trade-offs and synergies relationship of ecosystem services based on ecosystem services bundles. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 144, 109453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Yuan, S.; Prishchepov, A.V. Spatial-temporal heterogeneity of ecosystem service interactions and their social-ecological drivers: Implications for spatial planning and management. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 189, 106767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, D.; Cai, Y.; Liu, M. Coupling coordination analysis and spatiotemporal heterogeneity between ecosystem services and new-type urbanization: A case study of the Yangtze River Economic Belt in China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wen, Z.; Zhang, S.; Huang, P.; Ma, M.; Zhou, X.; Liao, T.; Wu, S. Effects of long-term and large-scale ecology projects on forest dynamics in Yangtze River Basin, China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 496, 119463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Chen, W.; Pan, S.; Gu, T.; Zeng, J. Identifying the driving forces of global ecosystem services balance, 2000–2020. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 426, 139019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Zhang, G.; Hou, J.; Xie, J.; Lv, M.; Liu, F. Hybrid forecasting model for non-stationary daily runoff series: A case study in the Han River Basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2019, 577, 123915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jing, Y.; Han, S. Multi-scenario simulation of land use/land cover change and water yield evaluation coupled with the GMOP-PLUS-InVEST model: A case study of the Nansi Lake Basin in China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 155, 110926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Cao, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, J.; Liu, F.; Li, W. The responses of riparian plant communities to environmental and spatial factors in the upper Han River Basin, China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2022, 36, e02118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Zhao, W. Impacts of climate change and anthropogenic stressors on runoff variations in major river basins in China since 1950. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 898, 165349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.; Hu, T.; Yang, L.; Liu, X.; Zheng, X.; Pan, H.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, S.; Deng, S. Matching ecosystem services supply and demand in China’s urban agglomerations for multiple-scale management. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 420, 138351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamel, P.; Bryant, B.P. Uncertainty assessment in ecosystem services analyses: Seven challenges and practical responses. Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 24, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Soil Carbon Sequestration Impacts on Global Climate Change and Food Security. Science 2004, 304, 1623–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, E.; Polasky, S.; Lewis, D.J.; Plantinga, A.J.; Lonsdorf, E.; White, D.; Bael, D.; Lawler, J.J. Efficiency of incentives to jointly increase carbon sequestration and species conservation on a landscape. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 9471–9476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renard, K.G.; Freimund, J.R. Using monthly precipitation data to estimate the R-factor in the revised USLE. J. Hydrol. 1994, 157, 287–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Predicting Rainfall Erosion Losses: A guide to Conservation Planning; Agriculture Handbook No. 537; U.S. Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, B.; Jiang, S.; Yang, Y.; Wen, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Assessing the Spatio-Temporal Dynamics of Land Use Carbon Emissions and Multiple Driving Factors in the Guanzhong Area of Shaanxi Province. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselin, L. Local indicator of Spatial Association-LISA. Geogr. Anal. 1998, 27, 93–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raudsepp-Hearne, C.; Peterson, G.D.; Bennett, E.M. Ecosystem service bundles for analyzing tradeoffs in diverse landscapes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 5242–5247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, E.M.; Peterson, G.D.; Gordon, L.J. Understanding relationships among multiple ecosystem services. Ecol. Lett. 2009, 12, 1394–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farley, K.A.; Jobbágy, E.G.; Jackson, R.B. Effects of afforestation on water yield: A global synthesis with implications for policy. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2005, 11, 1565–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Chu, K. Determination of corporate water consumption: Evidence from precipitation risks in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 894, 164979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Zhou, S. A study on the dynamic evaluation of ecosystem health in the Yangtze river Basin of China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 153, 110445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Wang, L.; Chen, W.; Sun, J.; Cao, Q.; Wang, S.; Wang, L. Identifying the impacts of natural and human factors on ecosystem service in the Yangtze and Yellow River Basins. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 314, 127995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Wen, Z.; Liu, Y.; Lin, Z.; Han, P.; Shi, H.; Wang, Z.; Su, T. Vegetation response to changes in climate across different climate zones in China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 155, 110932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osawa, T.; Kohyama, K.; Mitsuhashi, H. Trade-off relationship between modern agriculture and biodiversity: Heavy consolidation work has a long-term negative impact on plant species diversity. Land Use Policy 2016, 54, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.-A.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, X.-B.; Wang, X.-Y.; Wang, J.-J.; Zhou, M.-H.; Zhang, J.-H.; He, Z.-Y.; Zhang, R.-C. A Preliminary Study of the Impacts of Shelter Forest on Soil Erosion in Cultivated Land: Evidence from integrated 137Cs and 210Pbex Measurements. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 206, 104843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lin, Z.; Wang, Z.; Chen, X.; Han, P.; Wang, B.; Wang, Z.; Wen, Z.; Shi, H.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Discriminating the impacts of vegetation greening and climate change on the changes in evapotranspiration and transpiration fraction over the Yellow River Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 904, 166926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, H.; Li, X.; Li, S.; Dang, D.; Li, X.; Lyu, X.; Li, M.; Liu, S. Mapping ecosystem services bundles for analyzing spatial trade-offs in inner Mongolia, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 256, 120444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Gong, Z. Evaluation and analysis of water conservation function of ecosystem in Shaanxi Province in China based on “Grain for Green” Projects. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 83878–83896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šafanda, J. Ground surface temperature as a function of slope angle and slope orientation and its effect on the subsurface temperature field. Tectonophysics 1999, 306, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Pei, X.; Zhu, W.; Jiao, J. Understanding the intricate tradeoffs among ecosystem services in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration across spatiotemporal features. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 898, 165453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Bi, H.; Peng, R.; Zhao, D.; Liu, Z. Disparities in soil and water conservation functions among different forest types and implications for afforestation on the Loess Plateau. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 155, 110935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Noguchi, T.; Nozaki, T. Increasing efficiency of carbon dioxide sequestration through high temperature carbonation of cement-based materials. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 238, 117980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Gong, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, B.; Zhu, C.; Shi, J.; Liu, M.; Liu, Y.; Li, X. Stabilization of carbon sequestration in a Chinese desert steppe benefits from increased temperatures and from precipitation outside the growing season. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 691, 263–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, W.; Xu, Z.; Ding, J.; Yan, Y.; Sofia Santos Ferreira, C. Plant functional traits explain long-term differences in ecosystem services between artificial forests and natural grasslands. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 345, 118853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Li, Z.; Duan, L.; Gu, Z.; Liu, X. Vegetation types and rainfall regimes impact on surface runoff and soil erosion over 10 years in karst hillslopes. CATENA 2023, 232, 107443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zi, R.; Zhao, L.; Fang, Q.; Qian, X.; Fang, F.; Fan, C. Path analysis of the effects of hydraulic conditions, soil properties and plant roots on the soil detachment capacity of karst hillslopes. CATENA 2023, 228, 107177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Fang, M.; Yu, Q.; Niu, T.; Liu, H.; Wang, F.; Xu, C.; Ai, M.; Zhang, J. Study of spatialtemporal changes in Chinese forest eco-space and optimization strategies for enhancing carbon sequestration capacity through ecological spatial network theory. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 859, 160035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.-J.; Zhang, G.-H.; Yang, H.-Y.; Zhu, P.-Z. Temporal variation in soil erosion resistance of steep slopes restored with different vegetation communities on the Chinese Loess Plateau. CATENA 2019, 182, 104170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, W.; Wang, G.; Yang, S.; Pereira, P. Effects of long-term afforestation and natural grassland recovery on soil properties and quality in Loess Plateau (China). Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 770, 144833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, J.A.; Durán, M.; Luquin, J.; San Emeterio, L.; Yeste, A.; Canals, R.M. Soil C/N ratios cause opposing effects in forests compared to grasslands on decomposition rates and stabilization factors in southern European ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 888, 164118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Gao, G.; Luo, Y.; Xu, M.; Liu, G.; Fu, B. Carbon stock and sequestration of planted and natural forests along climate gradient in water-limited area: A synthesis in the China’s Loess plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2023, 333, 109419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Q.; Chen, X. Efficiency analysis of metacoupling of water transfer based on the parallel data envelopment analysis model: A case of the South–North Water Transfer Project-Middle Route in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 313, 127952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, K.; Wang, T. Spatial effects of urban expansion on air pollution and eco-efficiency: Evidence from multisource remote sensing and statistical data in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 367, 132973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Sun, X.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, S.; Zheng, W.; Zhai, B. Changes in nutrient balance, environmental effects, and green development after returning farmland to forests: A case study in Ningxia, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 735, 139370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nassani, A.A.; Aldakhil, A.M.; Zaman, K. Ecological footprints jeopardy for mineral resource extraction: Efficient use of energy, financial development and insurance services to conserve natural resources. Resour. Policy 2021, 74, 102271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.; Li, M.; Christie, P.; Du, X.; Tian, L.; Gao, X. Evaluating carbon dynamics in soil aggregates using δ13C following long-term vegetation restoration near a surface mine in a semi-arid region. CATENA 2023, 231, 107281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Z.; Shi, J.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Esteban Lucas-Borja, M.; López-Vicente, M.; Wu, G.-L. Restoration of a hillslope grassland with an ecological grass species (Elymus tangutorum) favors rainfall interception and water infiltration and reduces soil loss on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. CATENA 2022, 219, 106632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Liu, Y.; Wen, Z.; Shi, H.; Zhou, R.; Wang, Z.; Kareem, H.A.; Zhang, W. Untangling the effects of climate variation and human interference on grassland dynamics in North China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2023, 35, 467–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Data Type | Spatial Resolution | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Precipitation | 500 m | Loess Plateau Science Data Center, National Earth System Science Data Sharing Infrastructure, National Science & Technology Infrastructure of China. (http://loess.geodata.cn, accessed on 21 March 2024) |
| Land use/land cover | 500 m | Earth Data Search (https://search.earthdata.nasa.gov/search, accessed on 21 March 2024) |
| Temperature | 500 m | Loess Plateau Science Data Center, National Earth System Science Data Sharing Infrastructure, National Science & Technology Infrastructure of China. (http://loess.geodata.cn, accessed on 21 March 2024) |
| Evapotranspiration | 500 m | Loess Plateau Science Data Center, National Earth System Science Data Sharing Infrastructure, National Science & Technology Infrastructure of China. (http://loess.geodata.cn, accessed on 21 March 2024) |
| Digital elevation model (DEM) | 90 m | Geospatial Data Cloud |
| (https://www.gscloud.cn/, accessed on 21 March 2024) | ||
| Carbon Pools | Harmonized World Soil Database version | |
| Watershed boundary | Geographic remote sensing ecological network platform (www.gisrs.cn, accessed on 21 March 2024) | |
| EVI | 500 m | https://earthengine.google.com/, accessed on 21 March 2024 |
| Chinese population density | 1 km | https://www.worldometers.info/world-population/, accessed on 21 March 2024 |
| Nighttime lighting index | 500 m | https://www.earthdata.nasa.gov/, accessed on 21 March 2024 |
| 2020 | Percent | 2001 | Percent | Change | Change Percent | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grassland | 54,307.11 | 34.95 | 66,448.43 | 42.77 | −12,141.30 | −18.27 |
| Urbanland | 2734.08 | 1.76 | 2326.88 | 1.50 | 407.20 | 17.50 |
| Unused land | 11.35 | 0.01 | 33.45 | 0.02 | −22.10 | −66.07 |
| Forest | 57,279.16 | 36.88 | 45,547.06 | 29.32 | 11,732.10 | 25.76 |
| Wetland | 940.89 | 0.61 | 455.04 | 0.29 | 485.85 | 106.77 |
| Water | 944.14 | 0.61 | 781.78 | 0.50 | 162.36 | 20.77 |
| Cropland | 39,149.97 | 25.20 | 39,774.06 | 25.60 | −624.09 | −1.57 |
| Year | Carbon Storage | Soil Conservation | Water Yield | Habitat Quality | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moran’s I | Z Value | General G | Moran’s I | Z Value | General G | Moran’s I | Z Value | General G | Moran’s I | Z Value | General G | |
| 2001 | 0.569 | 163.391 | −0.000075 | 0.138 | 581.803 | −0.000001 | 0.584 | 1885.455 | −0.000003 | 0.452 | 111.978 | −0.000223 |
| 2005 | 0.563 | 185.712 | −0.000075 | 0.140 | 495.329 | −0.000001 | 0.661 | 1174.107 | −0.000003 | 0.284 | 165.436 | −0.000212 |
| 2010 | 0.552 | 170.525 | −0.000075 | 0.142 | 459.956 | −0.000001 | 0.661 | 1324.447 | −0.000003 | 0.474 | 98.815 | −0.000209 |
| 2015 | 0.482 | 170.991 | −0.00007 | 0.148 | 479.615 | −0.000001 | 0.678 | 2735.286 | −0.000003 | 0.382 | 112.375 | −0.000198 |
| 2020 | 0.447 | 159.576 | −0.000065 | 0.148 | 481.331 | −0.000001 | 0.763 | 1457.987 | −0.000003 | 0.458 | 93.964 | −0.000198 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, P.; Yang, G.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Wen, Z.; Shi, H.; Lin, Z.; et al. Driving Factors and Trade-Offs/Synergies Analysis of the Spatiotemporal Changes of Multiple Ecosystem Services in the Han River Basin, China. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2115. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16122115
Han P, Yang G, Wang Z, Liu Y, Chen X, Zhang W, Zhang Z, Wen Z, Shi H, Lin Z, et al. Driving Factors and Trade-Offs/Synergies Analysis of the Spatiotemporal Changes of Multiple Ecosystem Services in the Han River Basin, China. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(12):2115. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16122115
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Peidong, Guang Yang, Zijun Wang, Yangyang Liu, Xu Chen, Wei Zhang, Zhixin Zhang, Zhongming Wen, Haijing Shi, Ziqi Lin, and et al. 2024. "Driving Factors and Trade-Offs/Synergies Analysis of the Spatiotemporal Changes of Multiple Ecosystem Services in the Han River Basin, China" Remote Sensing 16, no. 12: 2115. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16122115
APA StyleHan, P., Yang, G., Wang, Z., Liu, Y., Chen, X., Zhang, W., Zhang, Z., Wen, Z., Shi, H., Lin, Z., & Ren, H. (2024). Driving Factors and Trade-Offs/Synergies Analysis of the Spatiotemporal Changes of Multiple Ecosystem Services in the Han River Basin, China. Remote Sensing, 16(12), 2115. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16122115








