Integration of High-Rate GNSS and Strong Motion Record Based on Sage–Husa Kalman Filter with Adaptive Estimation of Strong Motion Acceleration Noise Uncertainty
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Traditional Kalman Filter Method
2.2. A Sage–Husa Kalman Filter Method with Adaptive Estimation of Strong Motion Acceleration Noise Uncertainty
- Step 1.
- Time Update
- Step 2.
- Measurement Update
- Step 3.
- Adaptive Estimation of Noise Uncertainty
3. Experiments, Results and Discussion
3.1. Data Processing Strategy
3.2. Result and Discussion
3.2.1. Shake Table Simulation Experiment
3.2.2. Application to Mw 7.8 and Mw 7.6 Earthquake Doublet
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saunders, J.K.; Goldberg, D.E.; Haase, J.S.; Bock, Y.; Offield, D.G.; Melgar, D.; Restrepo, J.; Fleischman, R.B.; Nema, A.; Geng, J.; et al. Seismogeodesy Using GPS and Low-Cost MEMS Accelerometers: Perspectives for Earthquake Early Warning and Rapid Response. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2016, 106, 2469–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emore, G.L.; Haase, J.S.; Choi, K.; Larson, K.M.; Yamagiwa, A. Recovering Seismic Displacements through Combined Use of 1-Hz GPS and Strong-Motion Accelerometers. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2007, 97, 357–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahmen, N.; Hohensinn, R.; Clinton, J. Comparison and Combination of GNSS and Strong-Motion Observations: A Case Study of the 2016 Mw 7.0 Kumamoto Earthquake. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2020, 110, 2647–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwan, W.D.; Moser, M.A.; Peng, C.Y. Some Observations on Strong-Motion Earthquake Measurement Using a Digital Accelerograph. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 1985, 75, 1225–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boore, D.M. Comments on Baseline Correction of Digital Strong-Motion Data: Examples from the 1999 Hector Mine, California, Earthquake. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2002, 92, 1543–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boore, D.M.; Bommer, J.J. Processing of strong-motion accelerograms: Needs, options and consequences. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2005, 25, 93–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.M.; Wu, C.F. Approximate Recovery of Coseismic Deformation from Taiwan Strong-Motion Records. J. Seismol. 2007, 11, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, W.A.; Wu, Y.M.; Zhao, L. An Automatic Scheme for Baseline Correction of Strong-Motion Records in Coseismic Deformation Determination. J. Seismol. 2010, 14, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Schurr, B.; Milkereit, C.; Shao, Z.; Jin, M.P. An Improved Automatic Scheme for Empirical Baseline Correction of Digital Strong-Motion Records. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2011, 101, 2029–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, K.M.; Bodin, P.; Gomberg, J. Using 1-Hz GPS Data to Measure Deformations Caused by the Denali Fault Earthquake. Science 2003, 300, 1421–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ge, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, B.; Wang, R.; Klotz, J.; Wickert, J. Real-time high-rate co-seismic displacement from ambiguity-fixed precise point positioning: Application to earthquake early warning. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, R.; Shi, C.; Song, W.; Wang, G.; Liu, J. Determination of earthquake magnitude using GPS displacement waveforms from real-time precise point positioning. Geophys. J. Int. 2014, 196, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, Y.; Nikolaidis, R.M.; de Jonge, P.J.; Bevis, M. Instantaneous geodetic positioning at medium distances with the Global Positioning System. J. Geophys. Res. 2000, 105, 28223–28253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, Y.; Prawirodirdjo, L.; Melbourne, T.I. Detection of arbitrarily large dynamic ground motions with a dense high-rate GPS network. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L06604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Tsushima, H.; Miura, S.; Hino, R.; Takasu, T.; Fujimoto, H.; Iinuma, T.; Tachibana, K.; Demachi, T.; et al. Quasi real-time fault model estimation for near-field tsunami forecasting based on RTK-GPS analysis: Application to the 2011 Tohoku-Oki earthquake (Mw 9.0). J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2012, 117, B02311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouba, J. Measuring Seismic Waves Induced by Large Earthquakes with GPS. Stud. Geophys. Geod. 2003, 47, 741–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Lou, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Q.; Geng, J.; Wang, R.; Fang, R.; Liu, J. Seismic deformation of the Mw 8.0 Wenchuan earthquake from high-rate GPS observations. Adv. Space Res. 2010, 46, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ge, M.; Lu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, R.; Wickert, J.; Schuh, H. High-Rate GPS Seismology Using Real-Time Precise Point Positioning with Ambiguity Resolution. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 6165–6180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zhao, Q. Near-field surface displacement and permanent deformation induced by the Alaska Mw 7.5 earthquake determined by high-rate real-time ambiguity-fixed PPP solutions. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2014, 59, 4781–4789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, X.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, X.; Wickert, J. Multi-GNSS phase delay estimation and PPP ambiguity resolution: GPS, BDS, GLONASS, Galileo. J. Geod. 2018, 92, 579–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, P.; Henton, J.; Mireault, Y.; Heroux, P.; Schmidt, M.; Dragert, H.; Bisnath, S. Precise point positioning for real-time determination of co-seismic crustal motion. In Proceedings of the ION GNSS 2009, Savannah, GA, USA, 22–25 September 2009; pp. 2479–2488. [Google Scholar]
- Colosimo, G.; Crespi, M.; Mazzoni, A. Real-time GPS seismology with a stand-alone receiver: A preliminary feasibility demonstration. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2011, 116, B11302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, T.; Xie, X.; Fang, R.; Su, X.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, G.; Li, H.; Shi, C.; Liu, J. Real-time capture of seismic waves using high-rate multi-GNSS observations: Application to the 2015 Mw 7.8 Nepal earthquake. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.; Fang, R.; Li, M.; Shi, C.; Li, M.; Liu, J. Very high-rate GPS for measuring dynamic seismic displacements without aliasing: Performance evaluation of the variometric approach. GPS Solut. 2018, 22, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ge, M.; Guo, B.; Wickert, J.; Schuh, H. Temporal point positioning approach for real-time GNSS seismology using a single receiver. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 5677–5682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Guo, B.; Lu, C.; Ge, M.; Wickert, J.; Schuh, H. Real-time GNSS seismology using a single receiver. Geophys. J. Int. 2014, 198, 72–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Zhang, X.; Ren, X.; Li, X. High-precision coseismic displacement estimation with a single-frequency GPS receiver. Geophys. J. Int. 2015, 202, 612–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Ge, M.; Babeyko, A.; Li, X.; Diao, F.; Tu, R. Retrieving real-time co-seismic displacements using GPS/GLONASS: A preliminary report from the September 2015 Mw 8.3 Illapel earthquake in Chile. Geophys. J. Int. 2016, 206, 941–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Nie, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wu, H.; Xu, X. Real-Time Coseismic Displacement Retrieval Based on Temporal Point Positioning with IGS RTS Correction Products. Sensors 2021, 21, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genrich, J.F.; Bock, Y. Instantaneous geodetic positioning with 10–50 Hz GPS measurements: Noise characteristics and implications for monitoring networks. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2006, 1111, B03403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, K.M.; Bilich, A.; Axelrad, P. Improving the precision of high-rate GPS. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, B05422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Li, Y.; Shan, X.; Zhu, C. Earthquake Magnitude Estimation from High-Rate GNSS Data: A Case Study of the 2021 Mw 7.3 Maduo Earthquake. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zang, J.; Fan, S.; Wen, Y.; Xu, C.; Yang, F.; Peng, X.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, X. Real-Time Source Modeling of the 2022 Mw 6.6 Menyuan, China Earthquake with High-Rate GNSS Observations. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boore, D.M. Effect of Baseline Corrections on Displacements and Response Spectra for Several Recording of the 1999 Chi-Chi, Taiwan, Earthquake. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2001, 91, 1199–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Parolai, S.; Ge, M.; Jin, M.P.; Walter, T.R.; Zschau, J. The 2011 Mw 9.0 Tohoku earthquake: Comparison of GPS and strong-motion data. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2013, 103, 1336–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, R.; Wang, R.; Ge, M.; Walter, T.R.; Ramatschi, M.; Milkereit, C.; Bindi, D.; Dahm, T. Cost-effective monitoring of ground motion related to earthquakes, landslides, or volcanic activity by joint use of a single-frequency GPS and a MEMS accelerometer. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 3825–3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melgar, D.; Bock, Y.; Sanchez, D.; Crowell, B.W. On robust and reliable automated baseline corrections for strong motion seismology. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2013, 118, 1177–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, A.; Wu, M. Multi-rate Kalman filtering for the data fusion of displacement and acceleration response measurements in dynamic system monitoring. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2007, 21, 706–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, Y.; Melgar, D.; Crowell, B.W. Real-Time Strong-Motion Broadband Displacements from Collocated GPS and Accelerometers. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2011, 101, 2904–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Xu, C. Loose integration of high-rate GPS and strong motion data considering coloured noise. Geophys. J. Int. 2018, 215, 1530–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.; Fang, R.; Geng, J.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, J. Broadband Velocities and Displacements From Integrated GPS and Accelerometer Data for High-Rate Seismogeodesy. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 8939–8948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Bock, Y.; Melgar, D.; Crowell, B.W.; Haase, J.S. A new seismogeodetic approach applied to GPS and accelerometer observations of the 2012 Brawley seismic swarm: Implications for earthquake early warning. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2013, 14, 2124–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ge, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, R.; Klotz, J.; Wicket, J. High-rate coseismic displacements from tightly-integrated processing of raw GPS and accelerometer data. Geophys. J. Int. 2013, 195, 612–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, R.; Ge, M.; Wang, R.; Walter, T.R. A new algorithm for tight integration of real-time GPS and strong-motion records, demonstrated on simulated, experimental, and real seismic data. J. Seismol. 2014, 18, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Di, M.; Song, F.; Li, J.; Shi, S.; Limsupavanich, N. Integrated coseismic displacement derived from high-rate GPS and strong-motion seismograph: Application to the 2017 Ms 7.0 Jiuzhaigou Earthquake. Measurement 2021, 182, 109735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, R.; Zheng, J.; Shu, Y.; Lv, H.; Shi, C.; Liu, J. A new tightly coupled method for high-rate seismogeodesy: A shake table experiment and application to the 2016 Mw 6.6 central Italy earthquake. Geophys. J. Int. 2021, 227, 1846–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, S.; Geng, J.; Zeng, R.; Zhang, Q.; Ortega-Culaciati, F.; Wang, T. In-situ real-time seismogeodesy by integrating multi-GNSS and accelerometers. Measurement 2021, 179, 109453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Lin, X.; Li, W.; Cheng, L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Z. Adaptive coloured noise multirate Kalman filter and its application in coseismic deformations. Geophys. J. Int. 2023, 234, 1236–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, C.; Huang, G.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X.; Bai, Z.; Du, Y. GNSS/Accelerometer Adaptive Coupled Landslide Deformation Monitoring Technology. Remote Sens. 2023, 14, 3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paziewski, J.; Stepniak, K.; Sieradzki, R.; Yigit, C.O. Dynamic displacement monitoring by integrating high-rate GNSS and accelerometer: On the possibility of downsampling GNSS data at reference stations. GPS Solut. 2023, 27, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, C.; Huang, G.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, H.; Zhang, K.; Liu, G. GNSS/accelerometer integrated deformation monitoring algorithm based on sensors adaptive noise modeling. Measurement 2023, 179, 113179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Wen, Q.; Zhang, T.; Li, C. Strong-motion seismogeodesy by deeply coupling GNSS receivers with inertial measurement units. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL087161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Ding, X.; Xu, Y.; Yu, W. Real-time outlier detection in integrated GNSS and accelerometer structural health monitoring systems based on a robust multi-rate Kalman filter. J. Geod. 2023, 97, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Lay, T.; Wang, R.; Taymaz, T.; Xie, Z.; Xiong, X.; Irmak, T.S.; Kahraman, M.; Erman, C. Complex multi-fault rupture and triggering during the 2023 earthquake doublet in southeastern Türkiye. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 5564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, J.; Chen, X.; Pan, Y.; Mao, S.; Li, C.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, K. PRIDE PPP-AR: An open-source software for GPS PPP ambiguity resolution. GPS Solut. 2019, 23, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


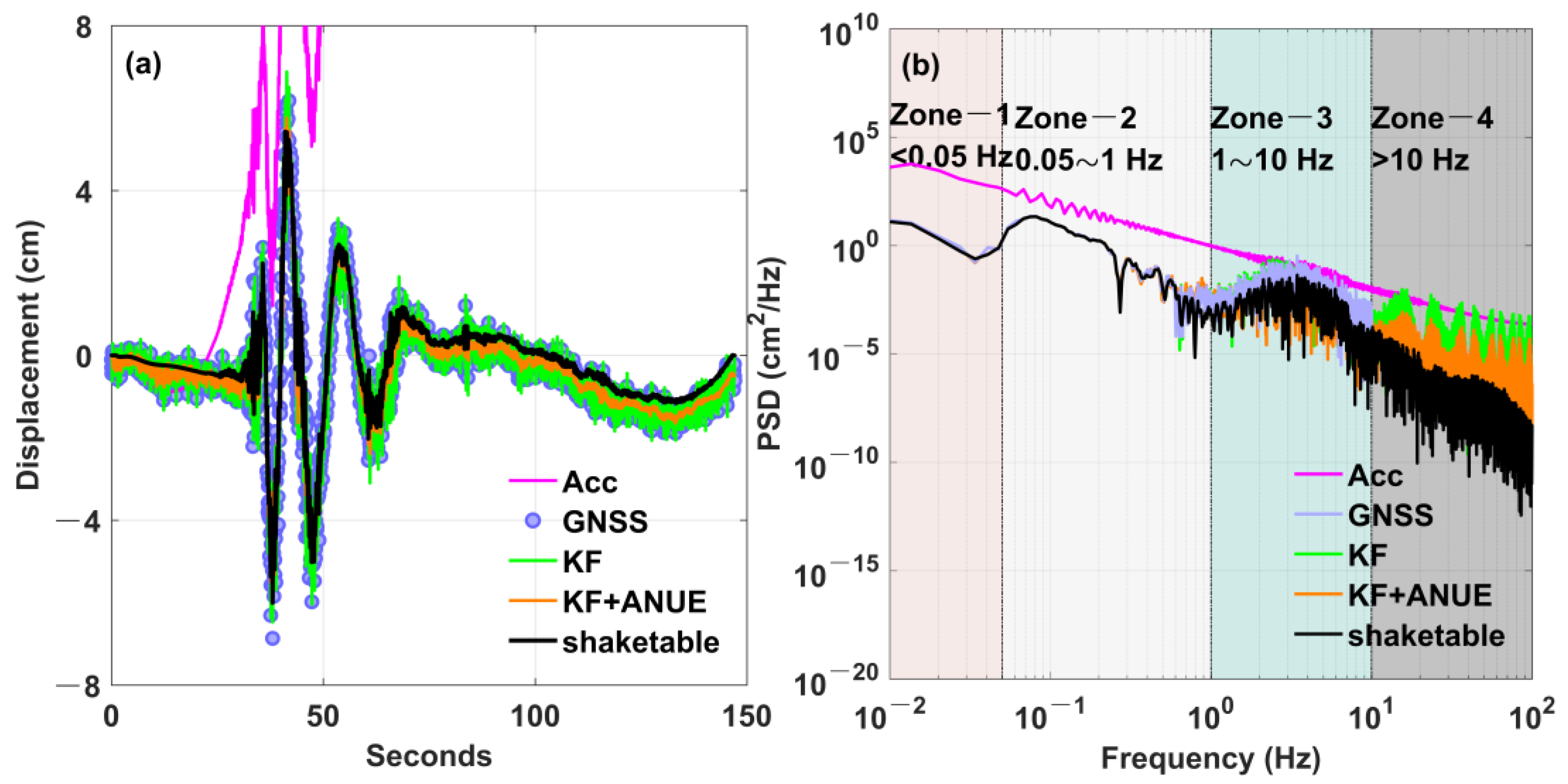
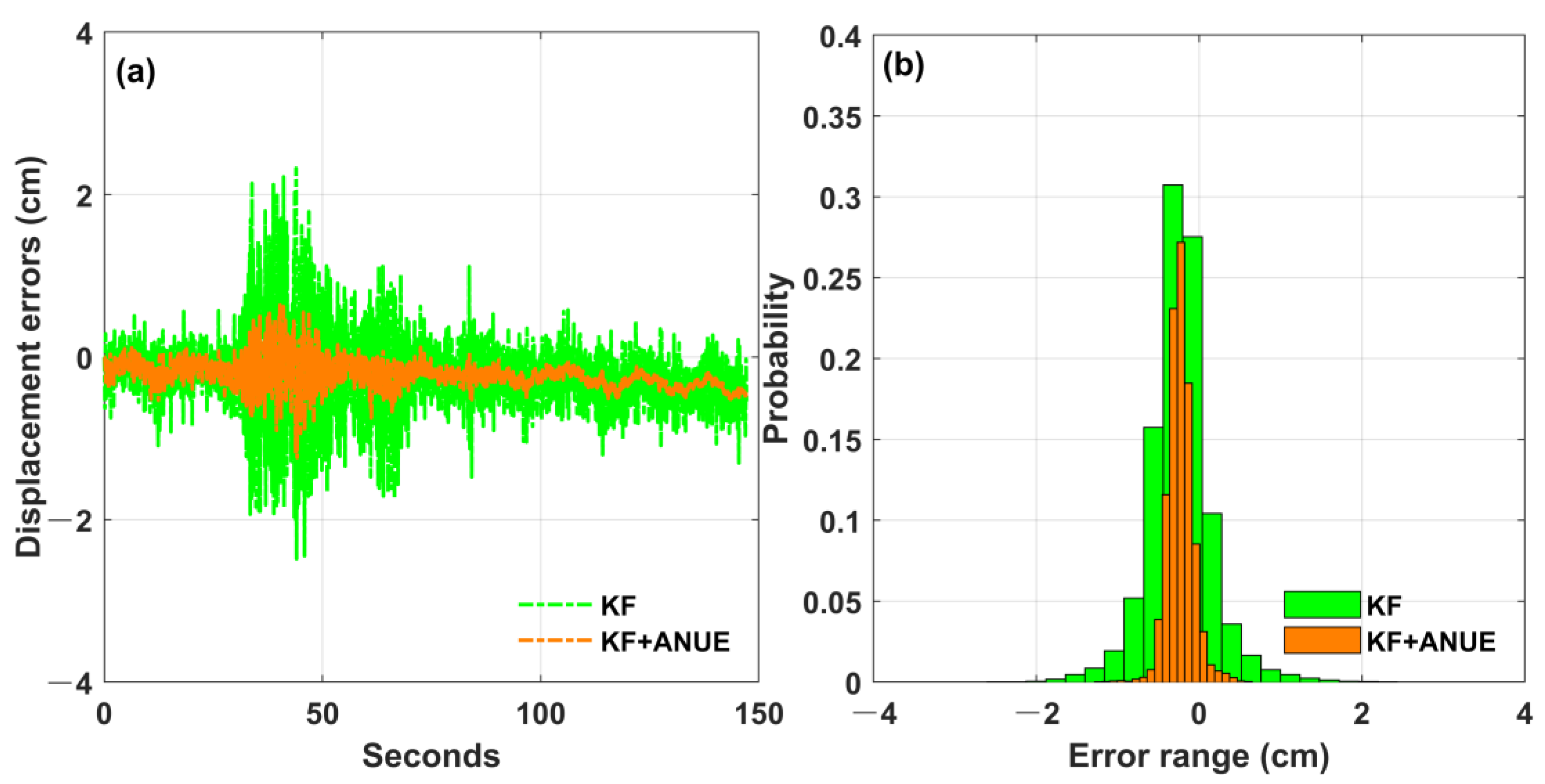

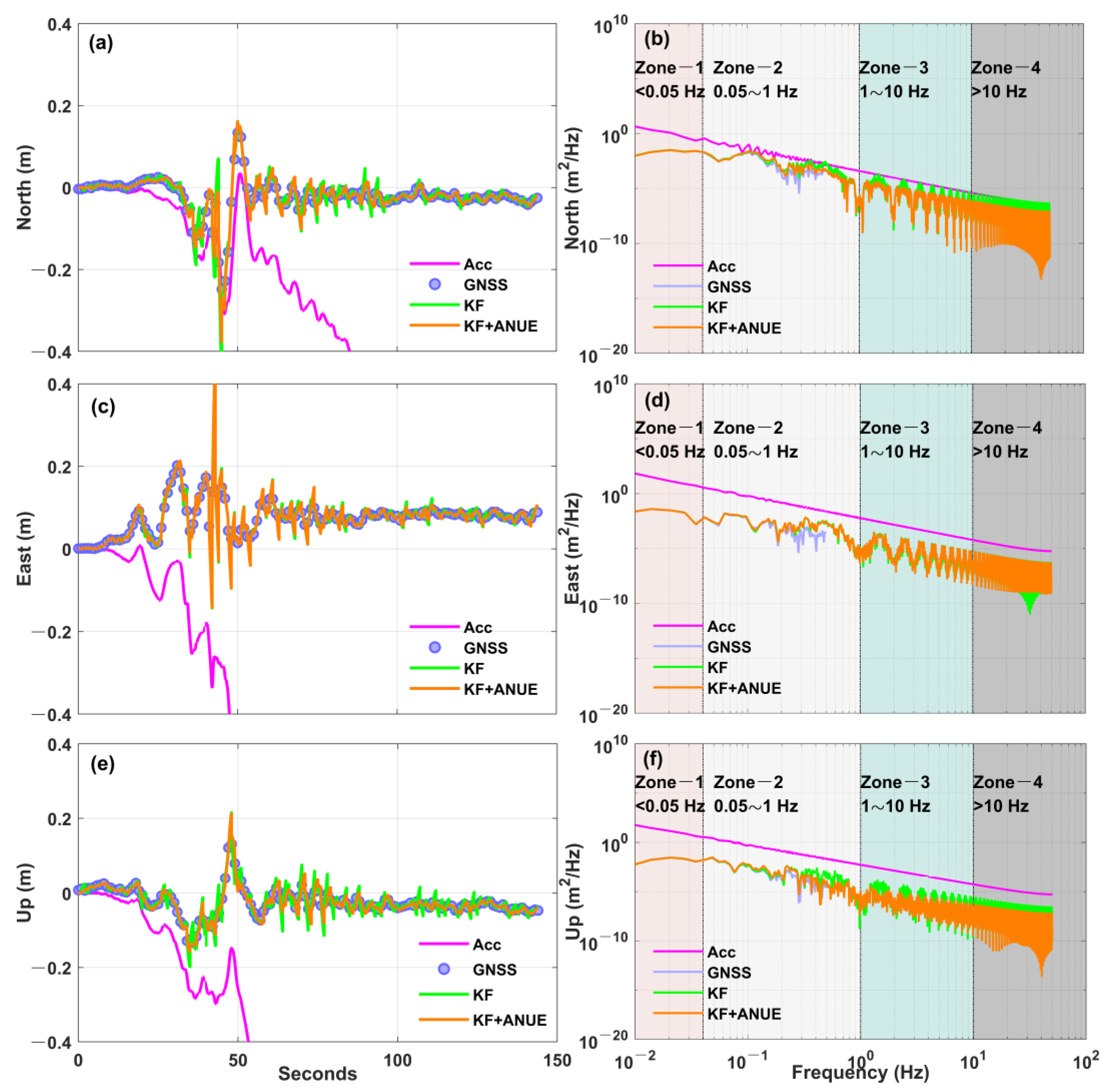

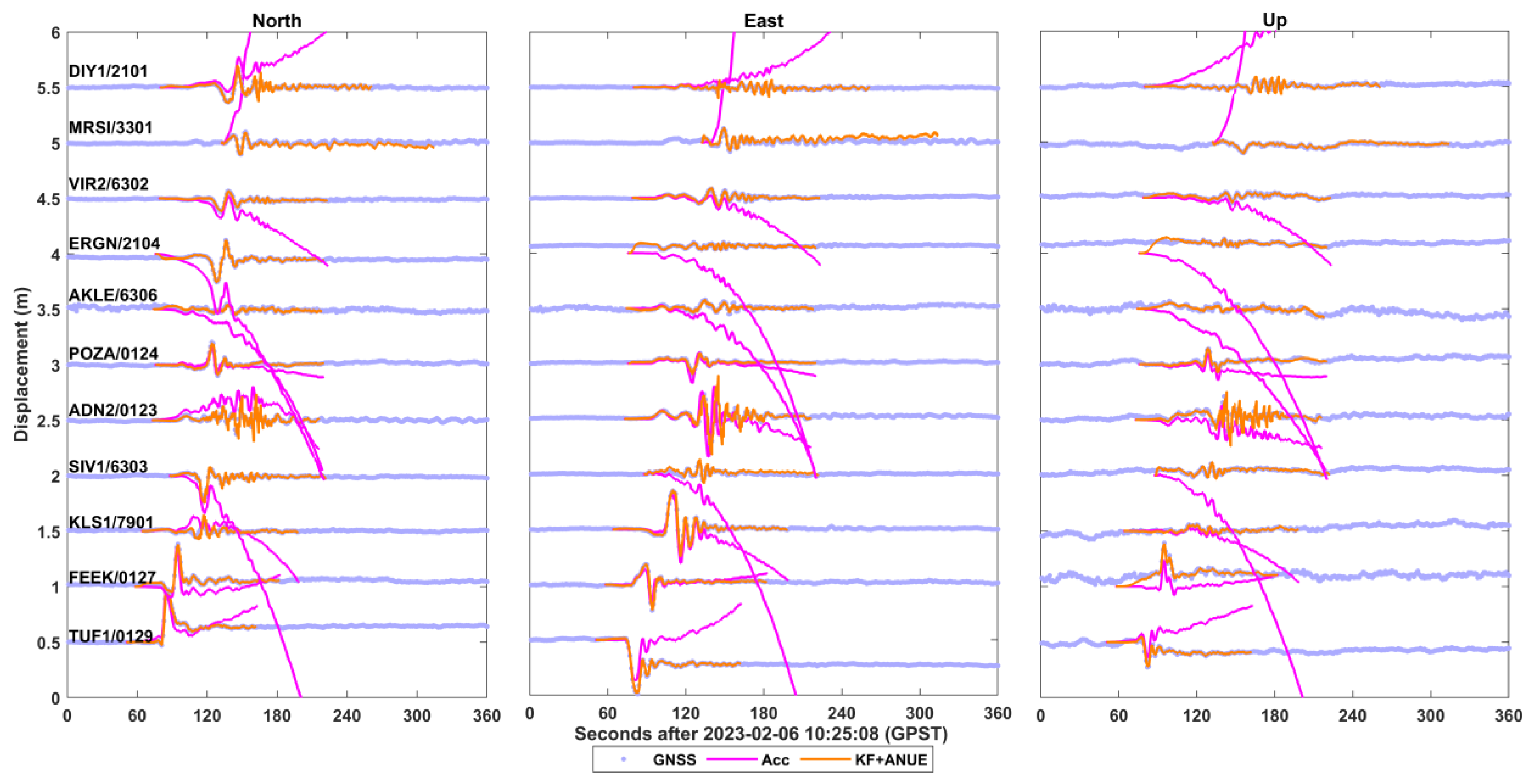
| Items | Processing Information |
|---|---|
| Strong motion acceleration | De-mean the first 5 s from acceleration records |
| Covariance matrix of process noise | Determined by pre-event acceleration noises |
| GNSS displacement | Retrieved from TPP method |
| Covariance matrix of displacement noise | Determined by pre-event displacement noises |
| Scheme | Method | Acceleration Noise Uncertainty |
|---|---|---|
| KF | Traditional Kalman filter method | Determined based on the pre-event noise with a multiplier |
| KF + ANUE | The proposed method | Adaptively estimated based on the Sage–Husa sliding-window estimation |
| Scheme | CC | RMSE (cm) |
|---|---|---|
| KF | 0.95 | 0.45 |
| KF + ANUE | 0.99 | 0.32 |
| Station | Latitude (°N) | Longitude (°E) | Dist to Epic 1 (km) | Separation Distance (km) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANTE/2703 | 37.06 | 37.37 | 38.74 | 2.23 |
| MAR1/4617 | 37.59 | 36.86 | 49.92 | 2.89 |
| MAR1/4620 | 37.59 | 36.86 | 49.92 | 3.37 |
| ONIY/8003 | 37.10 | 36.25 | 61.95 | 2.43 |
| TUF1/0129 | 38.26 | 36.21 | 87.30 | 0.26 |
| FEEK/0127 | 37.81 | 35.91 | 110.51 | 0.72 |
| KLS1/7901 | 36.71 | 37.12 | 143.17 | 1.10 |
| SIV1/6303 | 37.75 | 39.32 | 192.57 | 0.66 |
| ADN2/0123 | 36.98 | 35.32 | 196.85 | 2.87 |
| POZA/0124 | 37.40 | 34.87 | 210.46 | 1.63 |
| AKLE/6306 | 36.71 | 38.95 | 214.09 | 1.97 |
| ERGN/2104 | 38.27 | 39.76 | 230.07 | 0.58 |
| VIR2/6302 | 37.22 | 39.75 | 244.56 | 0.98 |
| MRSI/3301 | 36.78 | 34.60 | 262.70 | 0.02 |
| DIY1/2101 | 37.95 | 40.19 | 266.92 | 2.32 |
| Scheme | The First Mw 7.8 Event | The Second Mw 7.6 Event | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CC | RMSE (cm) | CC | RMSE (cm) | |||||||||
| North | East | Up | North | East | Up | North | East | Up | North | East | Up | |
| KF | 0.85 | 0.87 | 0.86 | 2.24 | 1.92 | 2.11 | 0.93 | 0.90 | 0.93 | 1.44 | 1.72 | 1.47 |
| KF + ANUE | 0.95 | 0.98 | 0.91 | 1.31 | 1.02 | 1.64 | 0.95 | 0.93 | 0.94 | 1.33 | 1.43 | 1.35 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Nie, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, G.; Shan, X. Integration of High-Rate GNSS and Strong Motion Record Based on Sage–Husa Kalman Filter with Adaptive Estimation of Strong Motion Acceleration Noise Uncertainty. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2000. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16112000
Zhang Y, Nie Z, Wang Z, Zhang G, Shan X. Integration of High-Rate GNSS and Strong Motion Record Based on Sage–Husa Kalman Filter with Adaptive Estimation of Strong Motion Acceleration Noise Uncertainty. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(11):2000. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16112000
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yuanfan, Zhixi Nie, Zhenjie Wang, Guohong Zhang, and Xinjian Shan. 2024. "Integration of High-Rate GNSS and Strong Motion Record Based on Sage–Husa Kalman Filter with Adaptive Estimation of Strong Motion Acceleration Noise Uncertainty" Remote Sensing 16, no. 11: 2000. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16112000
APA StyleZhang, Y., Nie, Z., Wang, Z., Zhang, G., & Shan, X. (2024). Integration of High-Rate GNSS and Strong Motion Record Based on Sage–Husa Kalman Filter with Adaptive Estimation of Strong Motion Acceleration Noise Uncertainty. Remote Sensing, 16(11), 2000. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16112000





