A Comprehensive Evaluation of Dual-Polarimetric Sentinel-1 SAR Data for Monitoring Key Phenological Stages of Winter Wheat
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
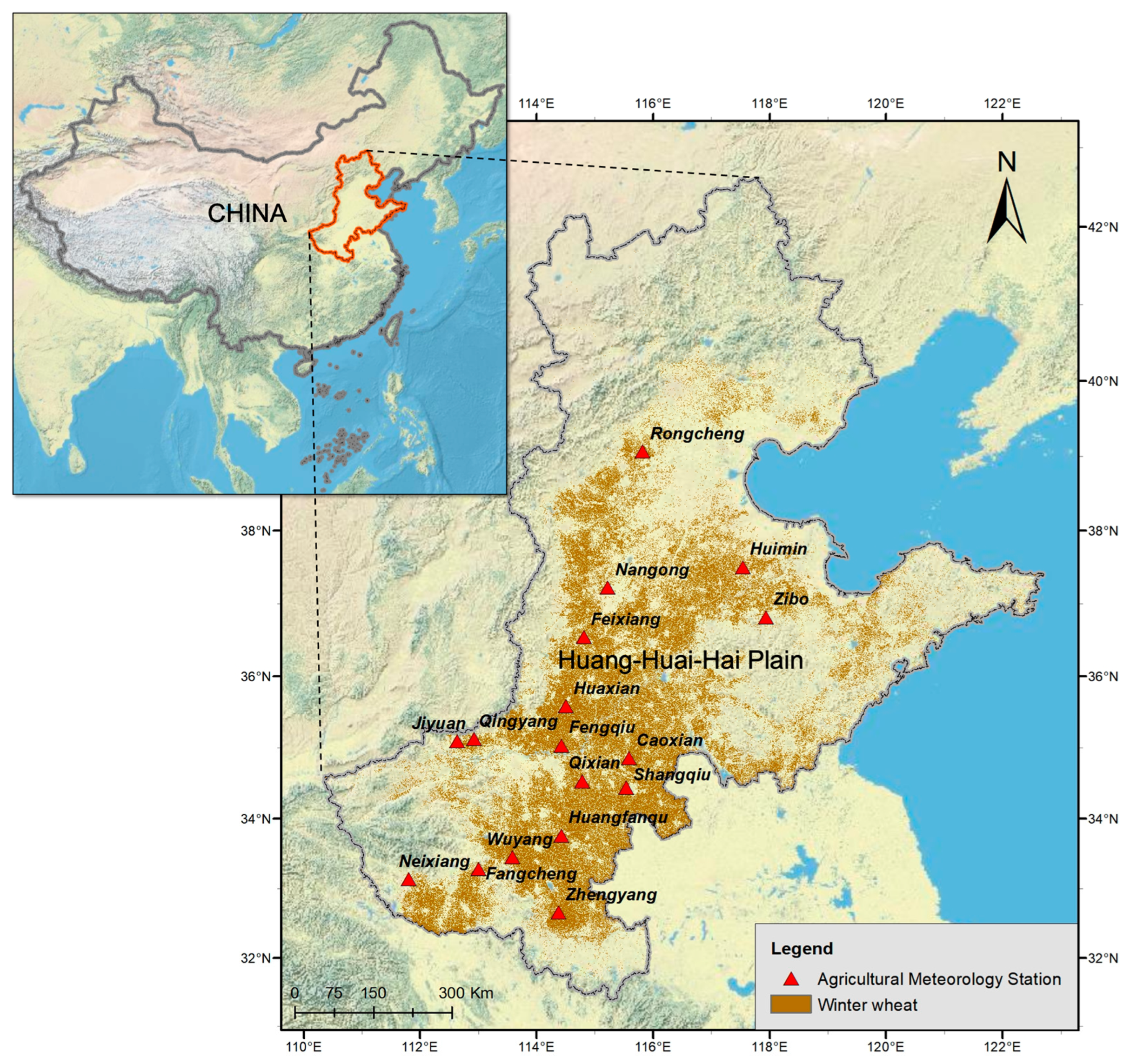
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.2.1. In Situ Wheat Phenology Observation and Wheat Map
2.2.2. Sentinel-1 SAR Imagery
2.3. Methods
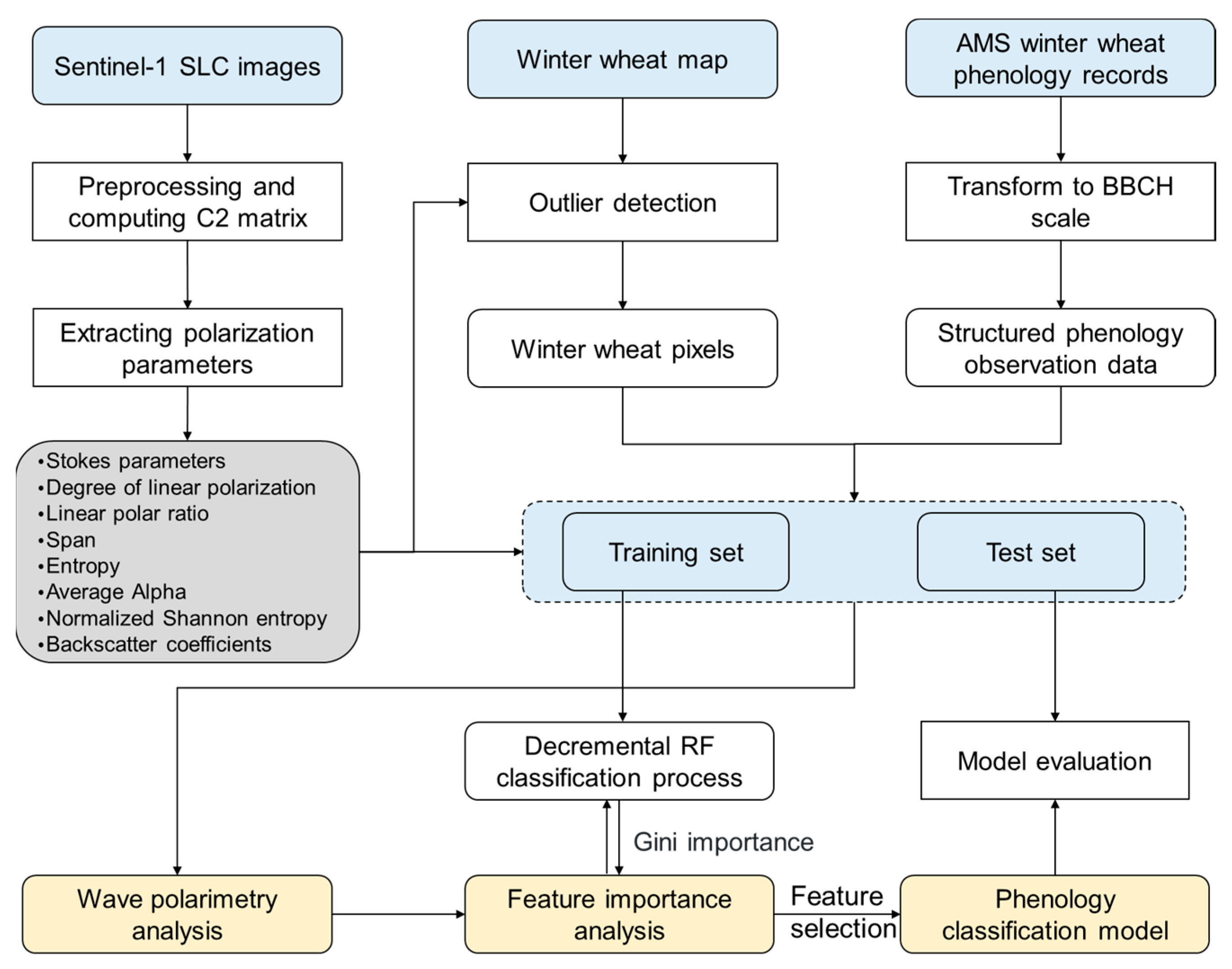
2.3.1. SAR Data Processing and Polarimetric Decomposition
- (1)
- Stokes Parameters
- (2)
- H-α decomposition for dual-polarimetric SAR data
- (3)
- Normalized Shannon Entropy
2.3.2. Outlier Detection on Wheat Cropping Pixels
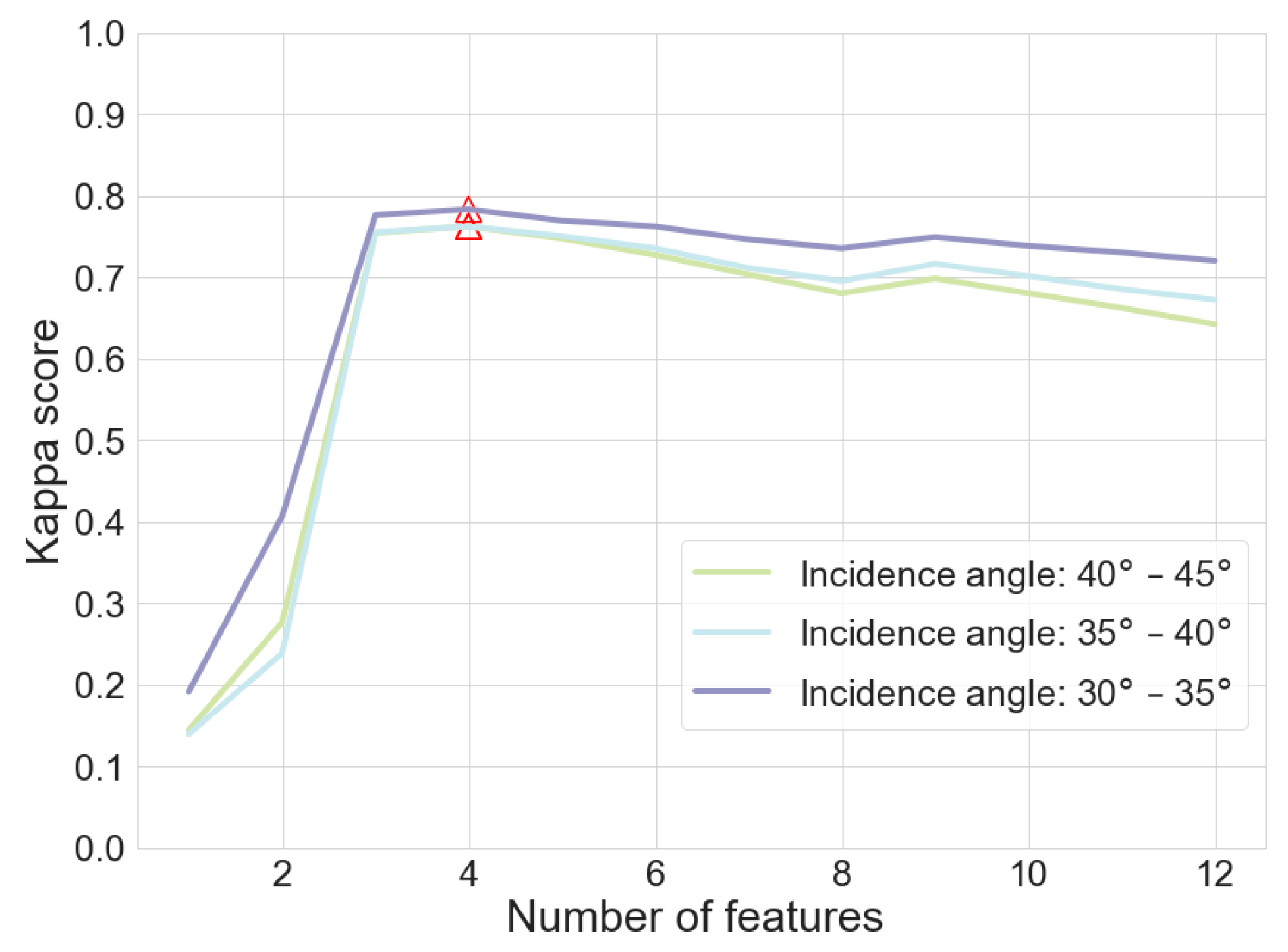
2.3.3. Feature Importance Evaluation and Decremental Classification of Phenophase
3. Results
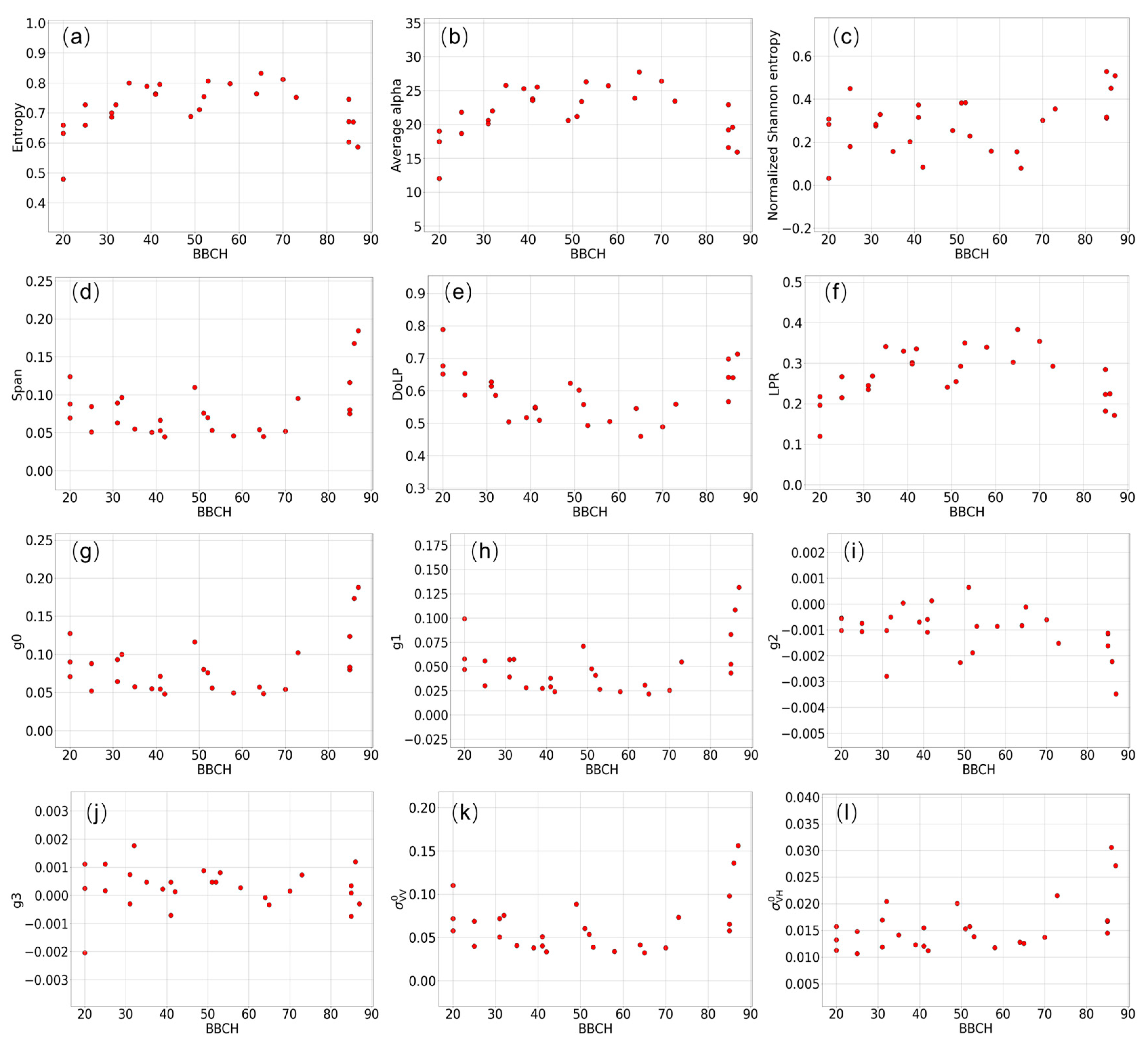
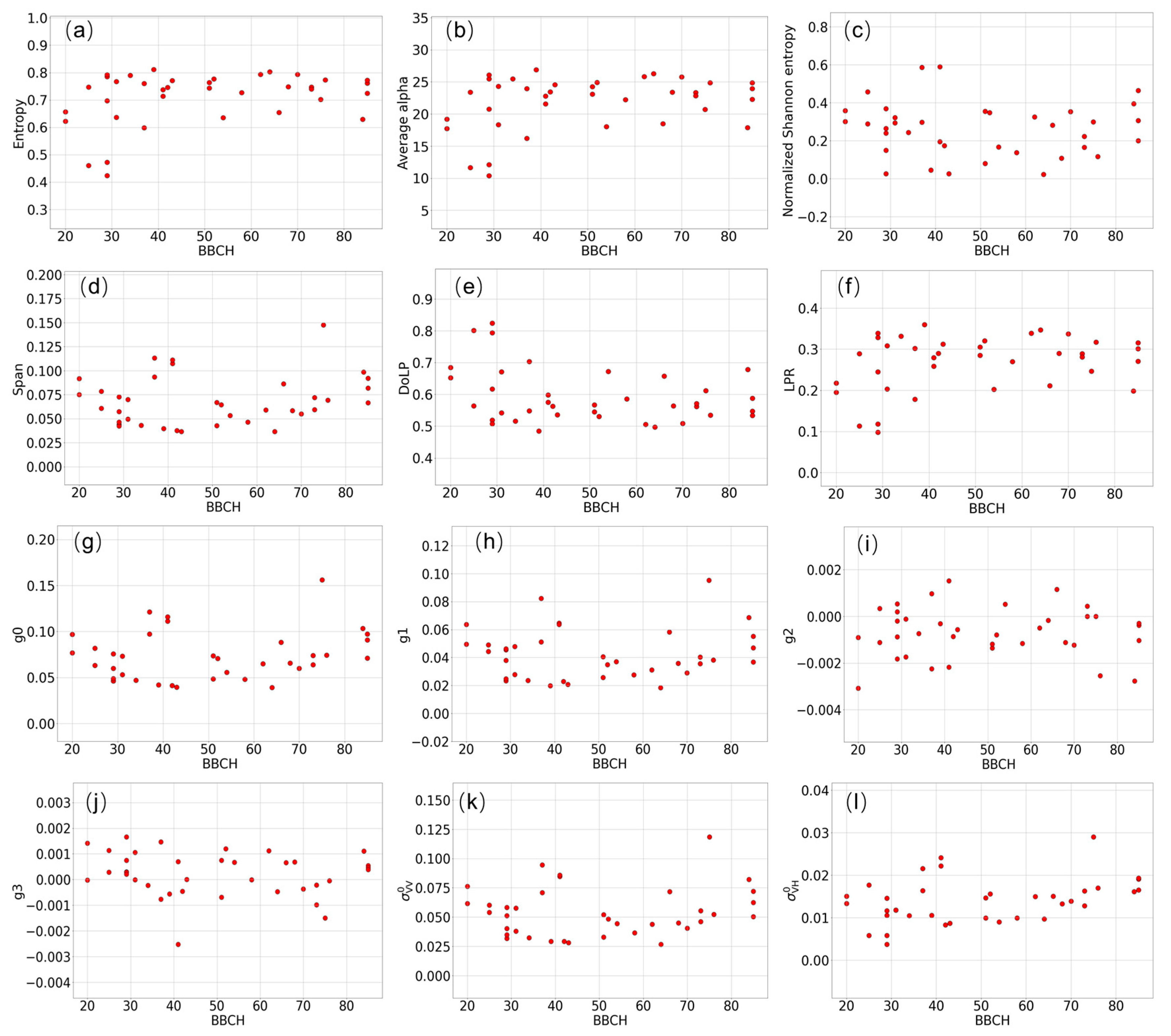
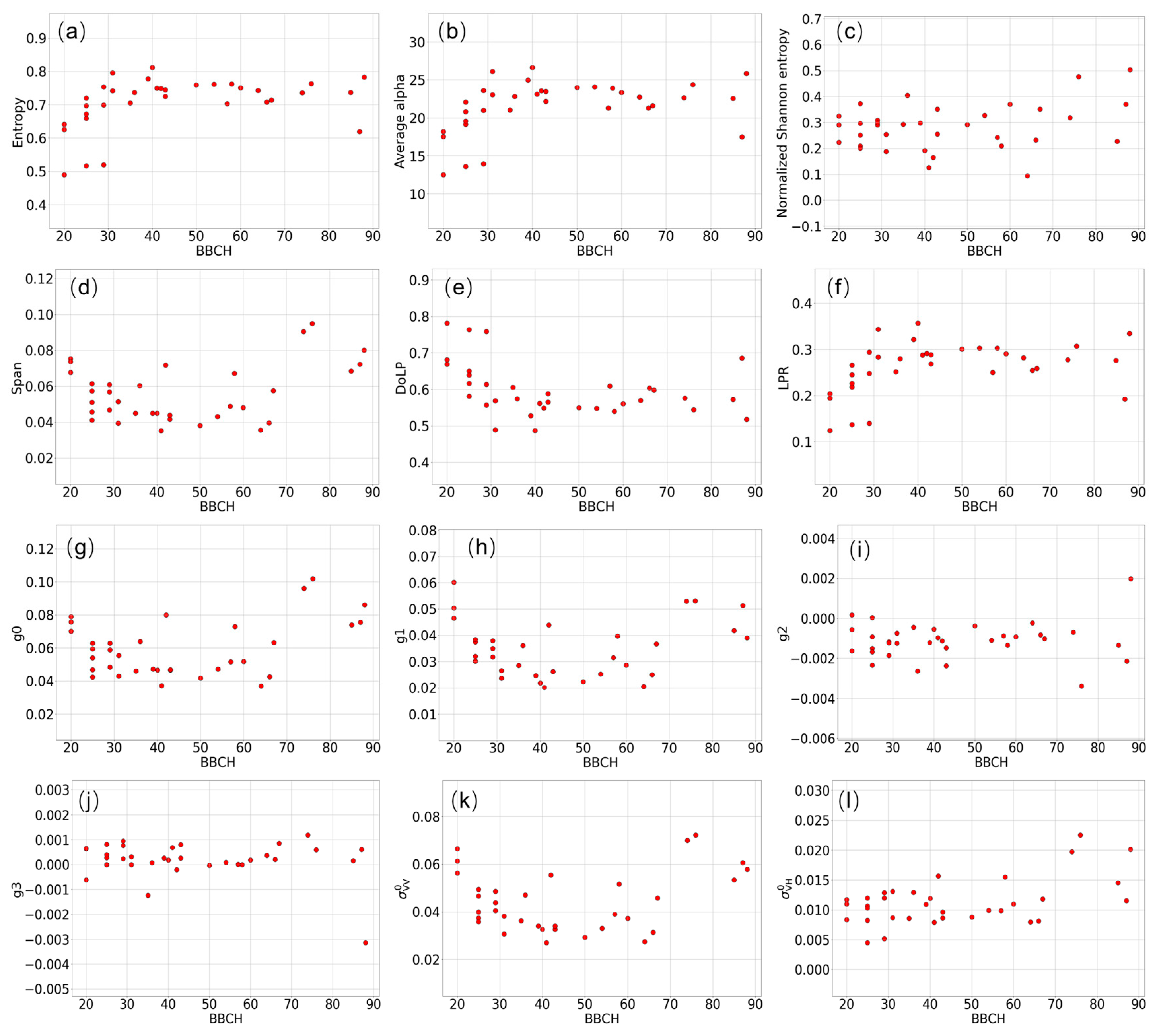
3.1. Backscattered Wave Polarimetry Analysis
3.2. SAR Parameters’ Sensitivity to Phenological Stages
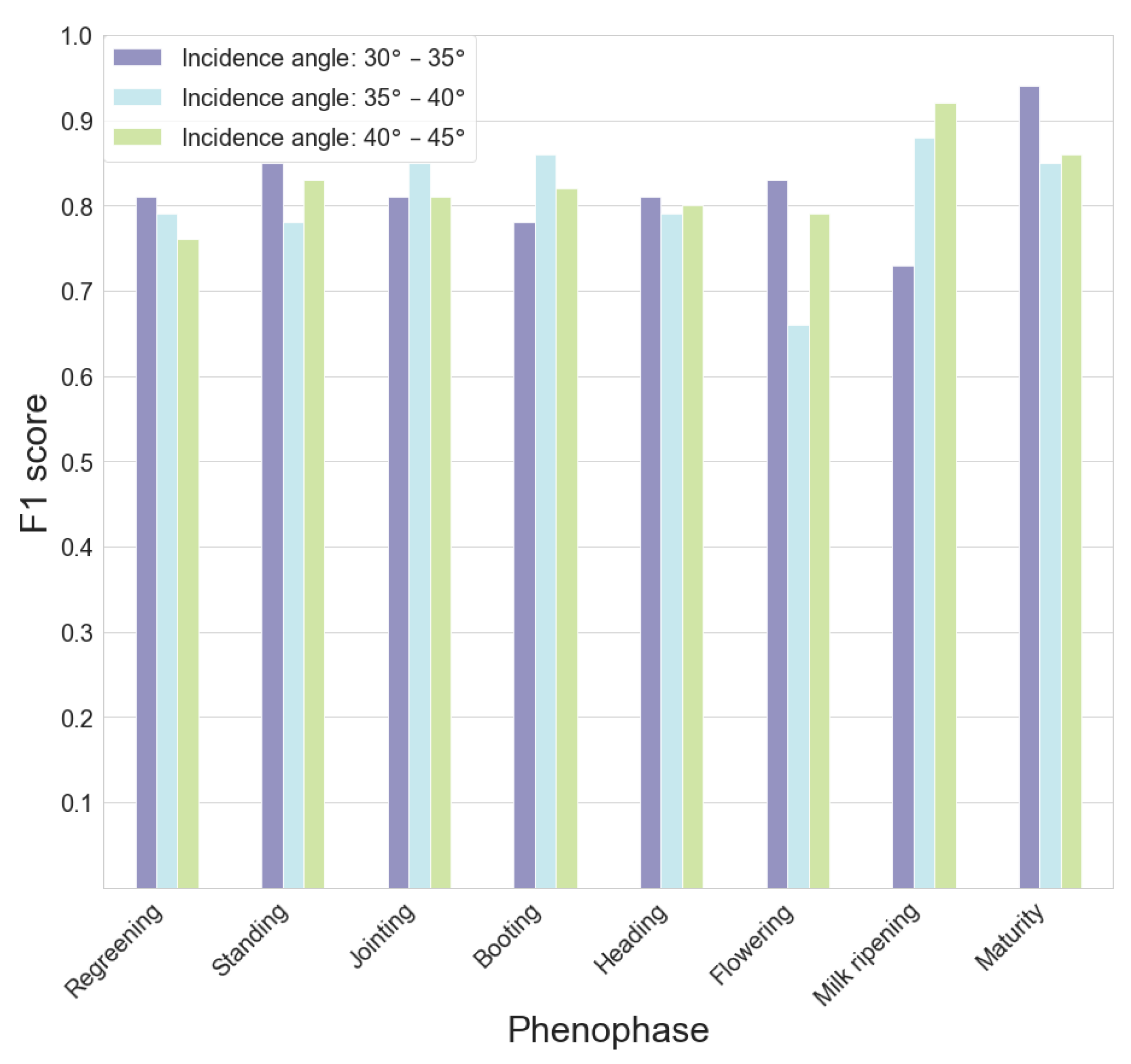
3.3. Phenophase Classification Models
4. Discussion
4.1. Wave Polarimetry
4.2. Feature Importance
4.3. Phenology Classification Results
5. Conclusions
- NSE, DoLP, and g2 are the three most important indicators for all three incidence angle groups. The three indicators of least importance for all three groups were Span, , and ;
- For the smaller-incidence-angle group (30°–35°) and larger-incidence-angle group (40°–45°), the four most important indicators were NSE, g0, , and g1 in descending order of importance. The four most important indicators for the medium-incidence-angle group were NSE, DoLP, g2, and ;
- Dual-pol SAR indicators are capable of estimating wheat phenology at a good precision. For all eight key phenophases, the average Precision and Recall were both above 0.8;
- Classification models trained on smaller-incidence-angle SAR images had better performance. The smaller-incidence-angle SAR images are better suited for estimating wheat phenology.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bouchet, A.-S.; Laperche, A.; Bissuel-Belaygue, C.; Snowdon, R.; Nesi, N.; Stahl, A. Nitrogen use efficiency in rapeseed. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2016, 36, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, T.; Yokozawa, M.; Toritani, H.; Shibayama, M.; Ishitsuka, N.; Ohno, H. A crop phenology detection method using time-series MODIS data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 96, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vreugdenhil, M.; Wagner, W.; Bauer-Marschallinger, B.; Pfeil, I.; Teubner, I.; Rüdiger, C.; Strauss, P. Sensitivity of Sentinel-1 backscatter to vegetation dynamics: An Austrian case study. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahil, M.T.; Connor, J.D.; Albiac, J. Efficient water management policies for irrigation adaptation to climate change in Southern Europe. Ecol. Econ. 2015, 120, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegulo, S.N.; Baenziger, P.S.; Nopsa, J.H.; Bockus, W.W.; Hallen-Adams, H. Management of Fusarium head blight of wheat and barley. Crop Prot. 2015, 73, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Shao, L.; Sun, H.; Chen, S. The effects of nitrogen supply and water regime on instantaneous WUE, time-integrated WUE and carbon isotope discrimination in winter wheat. Field Crops Res. 2013, 144, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Huang, J.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, L.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Blackburn, G.A.; Yan, J.; Liu, J. Mapping crop phenology using NDVI time-series derived from HJ-1 A/B data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2015, 34, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulla, D.J. Twenty five years of remote sensing in precision agriculture: Key advances and remaining knowledge gaps. Biosyst. Eng. 2013, 114, 358–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbesselt, J.; Hyndman, R.; Zeileis, A.; Culvenor, D. Phenological change detection while accounting for abrupt and gradual trends in satellite image time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2970–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betbeder, J.; Fieuzal, R.; Philippets, Y.; Ferro-Famil, L.; Baup, F. Contribution of multitemporal polarimetric synthetic aperture radar data for monitoring winter wheat and rapeseed crops. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2016, 10, 026020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phung, H.-P.; Lam-Dao, N.; Nguyen-Huy, T.; Le-Toan, T.; Apan, A.A. Monitoring rice growth status in the Mekong Delta, Vietnam using multitemporal Sentinel-1 data. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2020, 14, 014518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercier, A.; Betbeder, J.; Baudry, J.; Le Roux, V.; Spicher, F.; Lacoux, J.; Roger, D.; Hubert-Moy, L. Evaluation of Sentinel-1 & 2 time series for predicting wheat and rapeseed phenological stages. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 163, 231–256. [Google Scholar]
- Steele-Dunne, S.C.; McNairn, H.; Monsivais-Huertero, A.; Judge, J.; Liu, P.-W.; Papathanassiou, K. Radar remote sensing of agricultural canopies: A review. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 2249–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlund, M.; Erasmi, S. Sentinel-1 time series data for monitoring the phenology of winter wheat. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 246, 111814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harfenmeister, K.; Spengler, D.; Weltzien, C. Analyzing temporal and spatial characteristics of crop parameters using Sentinel-1 backscatter data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrallah, A.; Baghdadi, N.; El Hajj, M.; Darwish, T.; Belhouchette, H.; Faour, G.; Darwich, S.; Mhawej, M. Sentinel-1 data for winter wheat phenology monitoring and mapping. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNairn, H.; Jiao, X.; Pacheco, A.; Sinha, A.; Tan, W.; Li, Y. Estimating canola phenology using synthetic aperture radar. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 219, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, A.; Prats-Iraola, P.; Younis, M.; Krieger, G.; Hajnsek, I.; Papathanassiou, K.P. A tutorial on synthetic aperture radar. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2013, 1, 6–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloude, S.R.; Pottier, E. An entropy based classification scheme for land applications of polarimetric SAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1997, 35, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canisius, F.; Shang, J.; Liu, J.; Huang, X.; Ma, B.; Jiao, X.; Geng, X.; Kovacs, J.M.; Walters, D. Tracking crop phenological development using multi-temporal polarimetric Radarsat-2 data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 210, 508–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Dai, L.; Lin, S. Monitoring Rice Phenology Based on Backscattering Characteristics of Multi-Temporal RADARSAT-2 Datasets. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascolo, L.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.M.; Vicente-Guijalba, F.; Nunziata, F.; Migliaccio, M.; Mazzarella, G. A Complete Procedure for Crop Phenology Estimation with PolSAR Data Based on the Complex Wishart Classifier. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 6505–6515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Magagi, R.; Goïta, K.; Trudel, M.; McNairn, H.; Powers, J. Crop phenology retrieval via polarimetric SAR decomposition and Random Forest algorithm. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 231, 111234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Magagi, R.; Goita, K. Polarimetric Decomposition for Monitoring Crop Growth Status. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 13, 870–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, S.; Atkinson, P.M. Full year crop monitoring and separability assessment with fully-polarimetric L-band UAVSAR: A case study in the Sacramento Valley, California. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2019, 74, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Sanchez, J.M.; Vicente-Guijalba, F.; Ballester-Berman, J.D.; Cloude, S.R. Polarimetric response of rice fields at C-band: Analysis and phenology retrieval. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 52, 2977–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Guijalba, F.; Martinez-Marin, T.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.M. Crop phenology estimation using a multitemporal model and a Kalman filtering strategy. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 11, 1081–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küçük, Ç.; Taşkın, G.; Erten, E. Paddy-rice phenology classification based on machine-learning methods using multitemporal co-polar X-band SAR images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 2509–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Shao, Y.; Li, K.; Liu, Q.; Liu, L.; Brisco, B. An improved scheme for rice phenology estimation based on time-series multispectral HJ-1A/B and polarimetric RADARSAT-2 data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 195, 184–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloude, S. The dual polarization entropy/alpha decomposition: A PALSAR case study. Sci. Appl. SAR Polarim. Polarim. Interferom. 2007, 644, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, K.; Wu, Y. Scattering mechanism extraction by a modified Cloude-Pottier decomposition for dual polarization SAR. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 7447–7470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J. H-alpha decomposition and alternative parameters for dual Polarization SAR data. PIERS Suzhou China 2011, 4, 1386–1390. [Google Scholar]
- Harfenmeister, K.; Itzerott, S.; Weltzien, C.; Spengler, D. Agricultural monitoring using polarimetric decomposition parameters of sentinel-1 data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, S.; Bhogapurapu, N.; Homayouni, S.; Bhattacharya, A.; McNairn, H. Unsupervised classification of crop growth stages with scattering parameters from dual-pol sentinel-1 SAR data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harfenmeister, K.; Itzerott, S.; Weltzien, C.; Spengler, D. Detecting phenological development of winter wheat and winter barley using time series of sentinel-1 and sentinel-2. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 5036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haldar, D.; Verma, A.; Kumar, S.; Chauhan, P. Estimation of mustard and wheat phenology using multi-date Shannon entropy and Radar Vegetation Index from polarimetric Sentinel-1. Geocarto Int. 2022, 37, 5935–5962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Sanchez, J.M.; Cloude, S.R.; Ballester-Berman, J.D. Rice phenology monitoring by means of SAR polarimetry at X-band. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 50, 2695–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, A.; McNairn, H.; Li, Y.; Lampropoulos, G.; Powers, J. Using RADARSAT-2 and TerraSAR-X satellite data for the identification of canola crop phenology. In Remote Sensing for Agriculture, Ecosystems, and Hydrology XVIII; SPIE: Edinburgh, UK, 2016; p. 999802. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, J.; Fu, Y.; Wang, J.; Tian, H.; Fu, S.; Niu, Z.; Han, W.; Zheng, Y.; Huang, J.; Yuan, W. Early-season mapping of winter wheat in China based on Landsat and Sentinel images. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2020, 12, 3081–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloude, S.R.; Goodenough, D.G.; Chen, H. Compact polarimetry for C-band land-use classification: A pre-study for the Canadian Radar Constellation Mission (RCM). In Sar Image Analysis, Modeling, and Techniques XII; SPIE: Edinburgh, UK, 2011; pp. 36–49. [Google Scholar]
- Mascolo, L.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.M.; Cloude, S.R. Thermal noise removal from polarimetric Sentinel-1 data. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, S.; Darvishzadeh, R.; Boschetti, M.; Nelson, A. Discriminant analysis for lodging severity classification in wheat using RADARSAT-2 and Sentinel-1 data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 164, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-S.; Pottier, E. Polarimetric Radar Imaging: From Basics to Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hajj, M.E.; Baghdadi, N.; Belaud, G.; Zribi, M.; Cheviron, B.; Courault, D.; Hagolle, O.; Charron, F. Irrigated grassland monitoring using a time series of terraSAR-X and COSMO-skyMed X-Band SAR Data. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 10002–10032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cookmartin, G.; Saich, P.; Quegan, S.; Cordey, R.; Burgess-Allen, P.; Sowter, A. Modeling microwave interactions with crops and comparison with ERS-2 SAR observations. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 658–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Magagi, R.; Goïta, K. Potential of a two-component polarimetric decomposition at C-band for soil moisture retrieval over agricultural fields. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 217, 38–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fieuzal, R.; Baup, F.; Marais-Sicre, C. Monitoring wheat and rapeseed by using synchronous optical and radar satellite data—From temporal signatures to crop parameters estimation. Adv. Remote Sens. 2013, 2, 33222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattia, F.; Le Toan, T.; Picard, G.; Posa, F.I.; D’Alessio, A.; Notarnicola, C.; Gatti, A.M.; Rinaldi, M.; Satalino, G.; Pasquariello, G. Multitemporal C-band radar measurements on wheat fields. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 1551–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balenzano, A.; Mattia, F.; Satalino, G.; Davidson, M.W. Dense temporal series of C-and L-band SAR data for soil moisture retrieval over agricultural crops. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2010, 4, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Phenophase | Description | BBCH Scale |
|---|---|---|
| Regreening | The wintering period ends and leaf turns green | 25 |
| Standing | Wheat plants transit from growing horizontally close to the ground to growing vertically upright | 29 |
| Jointing | Beginning of stem elongation | 32 |
| Booting | Flag leaf sheath extending | 41 |
| Heading | Tip of inflorescence emerged from the sheath, the first spikelet just visible | 51 |
| Flowering | Beginning of flowering: first anthers visible | 61 |
| Milk ripening | Watery ripe: first grains have reached half their final size | 71 |
| Maturity | Early dough | 83 |
| Indicators | Details | Equations |
|---|---|---|
| Stokes parameters | The partial polarization state of an electromagnetic (EM) wave (, , , ) | See Equation (2) |
| Degree Of Linear Polarization (DoLP) | DoLP measures the proportion of linearly polarized components in the total signal received by the radar. | |
| Linear Polar Ratio (LPR) | The ratio of VV and VH intensities | |
| Wave Entropy () | A measure of the uncertainty in the polarization of the received wave | See Equations (3)–(5) |
| Average Alpha () | Represents the angular separation, on the Poincaré sphere, between the polarization state of the transmitted wave and received wave | See Equations (3)–(5) |
| Normalized Shannon Entropy (NSE) | NSE characterizes the diversity or randomness of polarimetric backscattering. The sum of total backscatter power and the Barakat degree of polarization, normalized to between 0 and 1 | See Equations (6) and (7) |
| Backscattering coefficient () | Sigma naught VV and VH intensity. The measure of the radar return from a distributed target, defined as per unit area on the ground | |
| Span | The total intensity (VH + VV) received |
| Random Forest Classifier Models | Performance Metrics | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Weighted Average Precision | Weighted Average Recall | Kappa | |
| Smaller incidence angle (30–35°) | 0.835 | 0.834 | 0.799 |
| Medium incidence angle (35–40°) | 0.811 | 0.812 | 0.783 |
| Larger incidence angle (40–45°) | 0.815 | 0.815 | 0.785 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, M.; Wang, L.; Guo, Y.; Cui, Y.; Liu, J.; Chen, L.; Wang, T.; Li, H. A Comprehensive Evaluation of Dual-Polarimetric Sentinel-1 SAR Data for Monitoring Key Phenological Stages of Winter Wheat. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1659. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16101659
Wang M, Wang L, Guo Y, Cui Y, Liu J, Chen L, Wang T, Li H. A Comprehensive Evaluation of Dual-Polarimetric Sentinel-1 SAR Data for Monitoring Key Phenological Stages of Winter Wheat. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(10):1659. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16101659
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Mo, Laigang Wang, Yan Guo, Yunpeng Cui, Juan Liu, Li Chen, Ting Wang, and Huan Li. 2024. "A Comprehensive Evaluation of Dual-Polarimetric Sentinel-1 SAR Data for Monitoring Key Phenological Stages of Winter Wheat" Remote Sensing 16, no. 10: 1659. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16101659
APA StyleWang, M., Wang, L., Guo, Y., Cui, Y., Liu, J., Chen, L., Wang, T., & Li, H. (2024). A Comprehensive Evaluation of Dual-Polarimetric Sentinel-1 SAR Data for Monitoring Key Phenological Stages of Winter Wheat. Remote Sensing, 16(10), 1659. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16101659








