Abstract
Urban floods caused by extreme rainstorm events have increased in recent decades, particularly in concave-down bridge zones. To simulate urban flooding processes accurately, an integrated urban flood model (IUFM) was constructed by coupling a distributed urban surface runoff model based on the cellular automata framework (CA-DUSRM), a widely used pipe convergence module in the storm water management model (SWMM), with an inundation module that describes the overflow expansion process associated with terrain and land-cover. The IUFM was used in a case study of the Anhua Bridge (a typical concave-down overpass) study area in Beijing, China. The spatial-temporal variations in flood depth modeled by the IUFM were verified to be reliable by comparison with actual measurements and other simulations. The validated IUFM was used to obtain temporal variations in flood range, depth, and volume under four rainstorm scenarios (return periods of 3-year, 10-year, 50-year, and 100-year). The results showed that the surface runoff process, overflow from drainage networks, and overflow expansion process could affect the flooding status by changing the composition and spatial configuration of pervious or impervious patches, drainage capacity, and underlying surface characteristics (such as terrain and land-cover). Overall, although the simulation results from the IUFM contain uncertainties from the model structures and inputs, the IUFM is an effective tool that can provide accurate and timely information to prevent and control urban flood disasters and provide decision-making support for long-term storm water management and sponge city construction.
1. Introduction
Extreme rainfall events have occurred frequently in recent decades, increasing the frequency of flood disasters. This influence is greatly intensified in urban areas experiencing accelerated urbanization processes [1,2]. In downtown Beijing, China, the current urbanization rate exceeds 86%, and many concave-down overpasses were built with underpasses 2–3 m lower than their surrounding areas [3]. These underpasses of concave-down overpasses are artificial “converging water basins” where large inundated areas can be generated quickly during extreme rainfall events [4,5]. For example, a heavy rainstorm in Beijing on 23 June 2011 inundated 20 bridge areas and caused traffic interruptions [6]. The heavy rainstorm in Beijing on 21 July 2012 caused waterlogging in 95 bridge areas, and the flood depths in some bridge areas exceeded 2 m [7]. Therefore, concave-down overpasses and their surrounding areas have received special attention in urban storm water management. Rapid and accurate simulation and forecasting of flood depth and range are indispensable for mitigating flooding losses and safeguarding the lives and property of residents.
Physics-based models can simplify intricate urban water cycle, integrate diverse hydrological and hydrodynamic processes, and clarify causal relationships among variables. Consequently, these models have emerged as vital instruments for exploring and comprehending complex flooding process and characteristics, particularly in urban areas with concave-down overpasses [8,9].
From the 1960s to the 1970s, some countries in Europe and the United States began to develop urban stormwater models that could meet the requirements of urban drainage, flood control, and environmental governance. For example, the storm water management model (SWMM) is one of the most widely used models [10,11,12]. The SWMM comprises hydrological, hydraulic, and water quality modules [8]. The surface runoff module of the SWMM is a 1D model based on subcatchments, which has high computational efficiency and requires less input data. However, the simulation accuracy may not be high because it fails to present runoff variations resulting from the spatial heterogeneity of underlying surface characteristics (such as elevation, slope, soil, surface, and vegetation-related parameters) at the scales finer than a subcatchment. The urban land-cover types are diverse and complex in spatial distribution. It is necessary to establish a 2D distributed model after improving the accuracy of underlying surface parameters and variables. The 2D distributed model can reveal the spatial-temporal relationships and hydrological–hydrodynamic connections between adjacent spatial units and describe the redistribution and transmission of overland flows within a subcatchment after runoff outflows are generated and before they converge into the drainage network [13,14].
The 2D distributed hydrological or hydrodynamic models based on physical processes use strict mathematical physical equations to describe the various physical processes, and the effects of topography on surface runoff and infiltration have been well studied (e.g., TOPMODEL (topography based hydrological model), MIKE21, IFMS Urban (integrated urban flood modeling system), and InfoWorks ICM (integrated catchment management)). Most models often use simplified St. Venant equations, shallow water equations, or Boltzmann equations [15], which are suitable for continuous processes on 1D or 2D free surfaces. However, they cannot accurately simulate hydrological and hydrodynamic processes on the surface with great undulation; that is, they are not suitable for simulating discontinuous runoff processes on a depressed surface with large undulations [16,17,18], for instance, the underpass and their surrounding areas. In addition, they require a significant amount of computation time and thus possible high computation costs.
Some studies have tried to quantify the real microtopography-controlled overland flow dynamics by explicitly incorporating the hydrologic elements of depressions. For example, Chu et al. (2013) proposed a modeling framework for characterizing puddle-to-puddle (P2P) overland flow processes through cell-to-cell (C2C) [18]. However, developing the algorithms for filling, spilling, merging, and splitting processes is extremely challenging, and their complexity also impedes their wide application in real areas. Feng et al. (2023) developed a distributed urban surface runoff model based on a simple cellular automata framework (CA-DUSRM) to simulate the generation of surface runoff outflow at grid cell scale and flow interactions among cells [19]. Compared with SWMM, CA-DUSRM performs better overall and is more sensitive to variation in terrain undulation.
The CA approach has strong potential advantages in simulating water diffusion processes controlled by microtopography and has already been applied in simulating surface runoff, flooding, soil and water erosion, and mudslide [20,21,22]. Different from subcatchment-based models, CA-based models use grid cells as spatial units to present fine spatial heterogeneities (including terrain variability) within a subcatchment [23]. This allows for the convenient realization of a more detailed simulation of hydrological and hydrodynamic processes at the grid cell scale and the flow interactions among adjacent cells [24]. The CA approach provides a simple simulation framework in which vertical and horizontal processes can be involved within a cell at a certain time and change with the states of the cell and its neighboring cells at the immediately preceding time. The bottom-up simulation approach of CA greatly reduces model complexity by first establishing simple local rules and then applying them to each cell to realize the upscaling of simulation results from cells to a subcatchment [19]. Therefore, CA-based models can inherently couple spatial and temporal elements to realize the simultaneous evolution of processes in space and time. Moreover, CA-based models can be highly efficient because of their simple structures and parallel computing rules [25,26].
However, most urban hydrological models (both subcatchment-based and cell-based models) fail to incorporate the water cycle within the soil-vegetation-atmosphere continuum, such as canopy interception, vegetation transpiration, soil evaporation, and infiltration, or coarsely simulate ecological processes by simplifying relationships (for instance, in the SWMM) or directly inputting values or ratios into models (for instance, in the P2P model). Although evapotranspiration affects little of the runoff dynamics during a single rainfall event, its effect on soil water and thus runoff and flood cannot be ignored when deriving long-term runoff (for instance, during the whole flood season) [27]. There are complex relationships between vegetation (e.g., leaf area and leaf stomatal conductance) and soil conditions and the water cycle, which cannot be revealed sufficiently with simplified processes or values. Therefore, coupling ecological processes into hydrological models is necessary to simulate continuous hydrological processes that have a cumulative effect on rainfall runoff and flood.
Additionally, although the SWMM has satisfactory performance in simulating runoff transport through a pipe network system, it cannot simulate the 2D expansion process of overflow spilled from the pipe nodes [28,29]. Most urban flood simulations based on the SWMM require secondary development to incorporate a 2D inundation process. Shi et al. (2015) addressed this problem by generalizing the inundated area as a simple reservoir in the SWMM to simulate the waterlogging situations on the roads [28]. Wang et al. (2016) used the SWMM to obtain the overflow in a concave-down overpass area and then established statistical equations for flood range and depth corresponding to different flood volumes based on high-precision digital elevation model (DEM) data for subsequent predictions [29]. These simplified or statistical methods are mostly simple and feasible, but their accuracy is not high. On the contrary, the physics-based methods with high accuracy are usually time-consuming, for example, those based on shallow water equations. Importantly, these methods can only simulate water flow on a continuous surface [15]. By contrast, the cell-based inundation algorithm can be efficient in simulating discontinuous inundation processes under terrain changes because it can simulate a series of expansion processes from cells to cells and from depressions to depressions [16,30,31].
We tried to take full advantage of the SWMM in simulating hydraulic process through drainage networks. For the surface runoff process before pipe convergence, we tried to utilize the developed CA-DUSRM to simulate overland flows at each cell resulting from both internal ecohydrological processes and exchanges with neighboring cells, from which lumped overland flows within the subcatchment outlets can also be obtained. For the overflow expansion process after pipe convergence, we tried to develop a cell-based module to describe the gradually elevating and expanding process of overflow along the surface microtopography. This study intends to construct an integrated urban flood model (IUFM) by coupling the three processes mentioned above.
The Anhua Bridge, a concave-down overpass in the Chaoyang district of Beijing, and its surroundings were selected as the study area. The study area experienced multiple waterlogging events. There are relatively large amounts of flood-related data in this area, making it feasible for model calibration and validation. The flooding processes modeled by the IUFM were validated using four actual rainstorm events from 2007 to 2016. After demonstrating the temporal dynamics and spatial patterns of the modeled flooding status under different rainfall scenarios, we analyzed the generation and expansion of floods in the study area. Finally, we evaluated the model and provided suggestions for preventing and controlling urban waterlogging.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The Anhua Bridge is located at the intersection of Beichen Road and the North Third Ring Road in Beijing (Figure 1). The Anhua Bridge study area includes the Anhua Bridge and its surrounding regions, from where surface runoff outflows and belowground pipe flows converge under the bridge, according to DEM data (Figure 2a) and drainage network data (Figure 1). As a typical concave-down overpass, the Anhua Bridge area is vulnerable to flood disasters during rainstorms, and floods always spread to the surrounding regions.
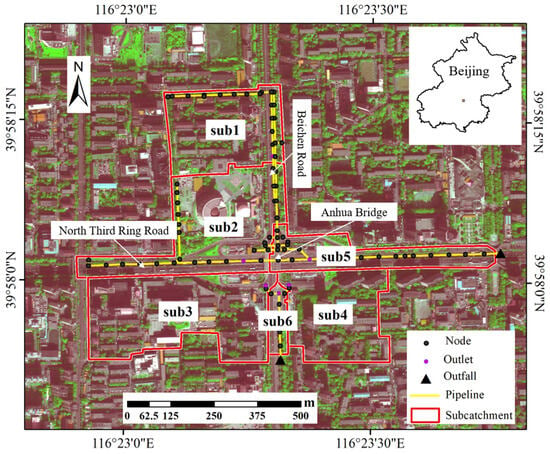
Figure 1.
Anhua Bridge study area in Beijing and six subcatchments (sub1, sub2, sub3, sub4, sub5, and sub6).
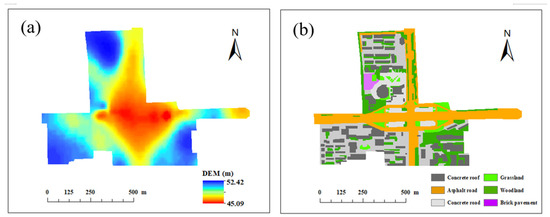
Figure 2.
Digital elevation model (DEM) data (a) and land-cover types (b) in the Anhua Bridge study area, Beijing.
The study area covers approximately 0.43 km2, with a mean elevation of 50.0 m and a mean slope of 16.1°. The area experiences a typical semi-humid continental warm temperate monsoon climate, characterized by cold and dry winters and hot and rainy summers. The average annual air temperature is 12 °C. The average annual precipitation is approximately 585 mm, and 76% of total rainfall tends to fall during the summer. Rainstorms (including rainstorms (50–100 mm), heavy rainstorms (100–200 mm), and extraordinary rainstorms (>200 mm)) frequently occur in July and August [32].
2.2. Discretization of Subcatchments
The study area was discretized into six subcatchments based on the surface topographic and hydrographic features, the spatial variability in land-cover (especially roads), and the locations of drainage elements. There was only one outlet for each subcatchment.
The subcatchment areas ranged between 1.10 ha (sub6) and 11.60 ha (sub3) (Table 1). Most of these subcatchments had relatively uniform natural characteristics (e.g., soil types and precipitation) but different pervious areas, elevations, slopes, land-cover, and drainage capacities, forming the basis for the overland hydrologic and belowground hydraulic characterizations. The six subcatchments were relatively enclosed and possessed distinct watershed boundaries.

Table 1.
Descriptions for the six subcatchments in the Anhua Bridge study area, Beijing.
2.3. Model Development
The IUFM combined a surface runoff module, a pipe convergence module, and an inundation module to simulate the generation, accumulation, expansion, and recession of floods and obtain flood information such as flood range, depth, volume, and duration (Figure 3). Water exchange among surface runoff, pipe flow, and floods occurs at drain wells or utility holes (referred to as nodes) in the pipe network. In the surface runoff module, grid cells are the fundamental simulation units. Subcatchments discretized based on the grid cells offer a hydrological unit for linking with pipe networks. The coupling between the surface runoff and pipe convergence modules was realized by determining the corresponding outlet of the overland flow for each subcatchment according to the ground elevation at the nodes and the flow direction among the nodes of the pipe network. Surface runoff of each subcatchment was modeled using a distributed urban surface runoff model based on the cellular automata framework (CA-DUSRM) [33], which was developed by our research team. The lumped surface runoff outflow at the outlet of each subcatchment was input into the pipe convergence module to simulate the flow routing process within the pipes. When the water volume in a pipe network exceeds the drainage capacity of the pipe network, rainwater spills over the ground through the nodes of the pipe network, as simulated by the pipe convergence module. The overflow expands in the horizontal and vertical directions and causes inundation. When the drainage capacity of the pipe network is restored, the overflow returns to the pipes through the nodes and gradually converges with higher-level pipes or rivers. The dynamic processes of the expansion and recession of overflows were simulated using the developed inundation module.
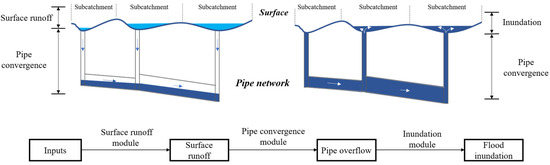
Figure 3.
Developed integrated urban flood model (IUFM).
2.3.1. Surface Runoff Module
In the CA-DUSRM, we adopted an improved nonlinear reservoir algorithm combined with a weighting system to develop a 2D urban surface runoff outflow rule [19]. The surface runoff outflow for a grid cell at a time was the product of the balance between water inputs (including precipitation, upstream flow, and irrigation) from external systems or neighboring cells and the outputs (including canopy evaporation from interception, soil evaporation, vegetation transpiration, and infiltration) from internal cells at the immediately preceding time (Figure 4). Soil water conditions directly affect soil evaporation and infiltration and thus surface runoff, making it crucial to estimate soil water content (SWC). In addition to the surface runoff process during rainfall, daily ecohydrological processes are simulated based on the forest landscape productivity model [34] and the grassland landscape productivity model [35], which can provide information on soil water conditions preceding and during rainfall runoff. Daily SWC is a bridge that links the second or minute simulation of surface runoff with the daily simulation of ecohydrological processes.
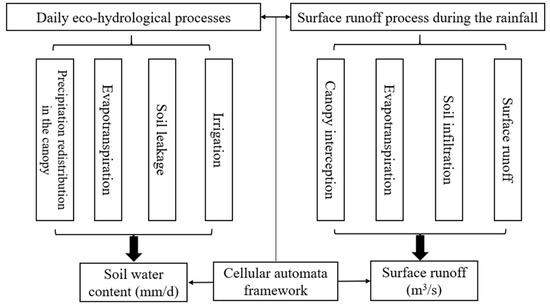
Figure 4.
Conceptual model of a distributed urban surface runoff model based on the cellular automata framework (CA-DUSRM) [33].
The simulation results of daily ecohydrological processes have been validated by Zhang and Yu (2006) [34] and Zhang and Liu (2014) [35]. The simulation results of surface runoff processes during different rainfall events have been validated in Feng et al. (2023) [19].
The surface runoff outflow from each grid cell converged into the outlet of a subcatchment, not entering the inlets (nodes) along the flow routes. Therefore, the surface runoff within a subcatchment was the total overland flow going through the entire land surface rather than the remaining outflow after being drained into the distinct inlets along the flow routes.
2.3.2. Pipe Convergence Module
Pipe flow at a node of the pipe network comes from the overland flows converging into the outlets of one or multiple subcatchments. For a gradually varying and unsteady free-surface flow through a conveyance network of pipes, water movement is governed by the conservation of mass and momentum in the St. Venant equations [36]. In the IUFM, the dynamic wave analysis method in the hydraulic module of the SWMM is used to solve the complete form of these equations for each conduit [37]. The equation for each node is based on the conservation of water volume. These solutions can produce theoretically accurate results for channel storage, backwater effects, entrance/exit losses, flow reversal, and pressurized flow, providing information on the spatial and temporal variations in water levels and discharge rates throughout the network.
The equations for conduits can be expressed as follows [36]:
where Q is the flow rate (m3/s); A is the flow cross-sectional area (m2); x is the distance (m); t is the time (s); g is the acceleration of gravity (m/s2); H is the hydraulic head of water in the conduit (m); and Sf is the friction slope (head loss per unit length) (N).
The equation for a node can be expressed as follows [36]:
where Qt is the instantaneous flow rate (m3/s) at the moment when the water enters the node; and As is the node assembly surface area (m2).
2.3.3. Inundation Module
The essence of the inundation module is a multi-source dynamic diffusion inundation algorithm [30,31]. Based on the water balance principle, the simulation uses the cut-and-trial method to continuously judge the rationality of the estimated flood range, volume, and depth during the multi-source dynamic expansion of overflow. The simulation was conducted at a grid-cell scale (Figure 5).
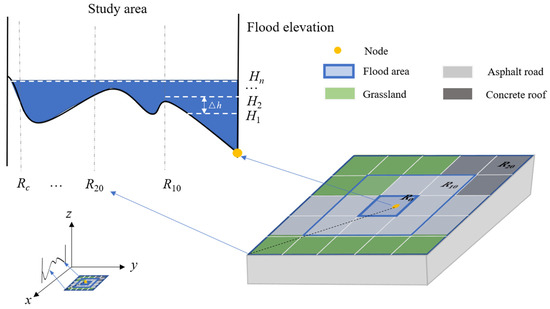
Figure 5.
Conceptual model of overflow inundation simulation in the integrated urban flood model (IUFM). Rc is the expanding range in the horizontal direction from the central cell (node) outward; c is the number of cells on a side; n is the total number of calculations in the vertical direction, one calculation for one given water level during the cut-and-trial process; Hn is the nth flood elevation at the node (m); and Δh is the given increment in water level for one calculation in vertical direction (m).
If overflow occurs at a single node in the study area, it accumulates and expands outward, centered at the node. During the cut-and-trial process, the potential flood elevation (H) is raised once by a unit water level (Δh) until the estimated total flood volume over the inundated sites equals the total volume of overflow from the node (simulated by pipe convergence module) after conducting n calculations and comparisons, when the ultimately determined H is Hn (Equation (4)). If Hn at the node is greater than the elevation at the adjacent grid cells, the water flow expands to a larger neighborhood of the node. The expansion is stopped when Hn is less than the minimum elevation at the potentially inundated grid cells, the nearest neighbors to the outermost inundated sites centered on the node.
where m is the total number of inundated grid cells; Ei is the elevation at inundated grid cell i adjacent to the central node; A is the area of a cell (m2), assumed to be the same for all cells; and Vp is the node overflow at a certain time simulated by the pipe convergence module (m3).
If there are multiple overflow nodes in a study area and water may move among the inundated areas from the adjacent nodes (according to the simulated expansion process of the overflow for each node), the overflows for all associated nodes are updated. We assumed that the overflow for the node with the lowest elevation was the sum of the overflows from all associated nodes. After updating the overflow, the simulation of the expansion process for each node was repeated.
In the inundation module, the elevation data were obtained from the DEM, in which the altitudes of the surface buildings and vegetation cover were not considered. Given that some water flow can be blocked by buildings and short vegetation (such as grasses and shrubs) above the terrain’s surface, we raised the elevations at the sites where buildings and short vegetation were located by 30 m and 0.2 m, respectively, based on the actual situations in the study area.
Moreover, water is partially lost when it expands outward from an overflow node because of the physical interception and chemical absorption of the underlying surface or soil infiltration at the sites where water passes. Therefore, we introduced loss coefficients that mainly depend on the land-cover type. We defined the loss coefficient as the ratio of the water loss volume to the total overflow volume. Thus, the actual volume of water that expanded to a site was obtained after deducting the loss based on the underlying surface characteristics of the site.
2.4. Precipitation Data
Considering the small area of the study area (0.43 km2) and the ignorable spatial het-erogeneity in rainfall, we adopted unified rainfall data throughout the area.
2.4.1. Actual Rainstorm Events
We selected four actual rainstorm events on 1 August 2007, 6 August 2007, 21 July 2012, and 20 July 2016, for which literature on the study area could be obtained to validate the modeled flood depth or volume. Except for the rainstorm on 6 August 2007, the others were heavy rainstorm events, according to the standards issued by the China Meteorological Administration.
Daily meteorological data, such as precipitation and temperature, were obtained from the China Meteorological Data Sharing Service System (CMDSSS) (http://data.cma.cn/ (accessed on 9 December 2012)). Daily meteorological data can satisfy the daily continuous simulation of ecohydrological processes to obtain soil water conditions immediately before a rainfall event. However, finer (e.g., minute) precipitation data are required to derive transient hydrological and hydraulic processes during rainfall events.
The Chicago rain-pattern generator has been widely used in the scientific literature for generating synthetic rainfall events or designing rainstorm events [37,38,39]. We used this method to obtain minute precipitation data for 1 and 6 August 2007 according to actual rainfall information such as total rainfall volume, rainfall duration, and approximate peak rainfall and time. For example, the heavy rainstorm on 1 August 2007 suddenly occurred and concentrated between 20:00 and 21:00; thus, we defined the peak time within this rainfall period; the rainstorm on 6 August 2007 concentrated at 3:00–4:00 p.m.; thus, the peak time was set within this period (Table 2).

Table 2.
Descriptions of selected actual rainstorm events in the Anhua Bridge study area of Beijing.
We downloaded the spatially interpolated hourly precipitation data for 21 July 2012 from CMDSSS. The data fused the precipitation data measured at automatic weather stations in China with the U.S. Climate Prediction Center MORPHing technique. From these hourly data, we obtained minute-level data using the cubic polynomial interpolation method (Table 2).
The precipitation data for 20 July 2016, were measured in May 2016 using a rain gauge (HOBO RG3-M) installed on a building rooftop within the study area. The gauge recorded rainfall in 0.2 mm increments, from which we calculated the minute data (Table 2).
2.4.2. Designed Rainfall Events
To systematically analyze the dependence of floods on rainstorm intensity, we designed four rainfall events with return periods of 3-year, 10-year, 50-year, and 100-year and a duration of 1 h according to the formula for rainfall intensity in the local standard for Beijing (DB11/T 1440-2017) [39], which is the standard of load calculation for municipal infrastructure planning. The formula is as follows:
where q is the rainfall intensity (L/(s·ha)); P is the rainfall return period (year), ranging from 2 to 100 years; and t is the rainfall duration (min), ranging from 5 min to 1440 min. In this standard, the parameters were derived from a directly fitted equation using 1406 rainstorm data points for 19 rainfall durations from 1941 to 2014 in Beijing.
Rainfall intensities generated using Equation (5) were 47.38, 64.57, 87.54, and 97.44 mm/h, corresponding to the return periods of 3-year, 10-year, 50-year, and 100-year, respectively. We designed a unimodal rain pattern with peaks occurring two-fifths of the way through the rainfall event, which followed the general characteristics of rainfall processes in the study area [40,41]. A Chicago rain-pattern generator yielded four minute-level rainstorm scenarios with the same rainfall characteristics but different return periods (3-year, 10-year, 50-year, and 100-year).
2.5. Model Parameterization and Calibration
To balance the efficiency and accuracy of the simulation, the spatial grain was set to 5 m and the temporal grain to 5 s when modeling the surface runoff process in the study area, according to an analysis of the spatial-temporal grain effects on the modeled surface runoff process [19].
The parameters in the surface runoff module of the IUFM were related to vegetation, soil, underlying material, and topographic characteristics. The values or ranges of some parameters were obtained from literature and field measurements (Table S1) [10,33,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54].
The topographic characteristics were derived from DEM data. We downloaded the DEM data at the resolution of 7.8 × 10−5 in latitude and longitude from the Google Earth platform and then projected it using China Geodetic Coordinate System 2000 to obtain the DEM data at the approximate resolution of 7.0 m. After that, we first resampled the 7.0 m DEM data to 1.0 m. Meanwhile, the DEM data at the resolution of 1 m was created from control point data (cartographic scale of 1:2000) by using ArcGIS. Then, we fused the two types of DEM data [55]. The resolution of the final DEM data is about 1 m (Figure 2a).
The variable parameters included the leaf area index (LAI) and initial SWC, which were obtained from the remote sensing data. Based on the availability and quality of remote sensing data, we selected Landsat thematic mapper (TM) 7 images with few clouds for 5 June 2007, 17 May 2012, and 5 June 2016. From each image, normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) values were inverted using red light and near-infrared band reflectance data at a 30 m pixel resolution, and land surface temperature values were derived using thermal infrared band reflectance data at a 60 m pixel resolution. Using these NDVI and land surface temperature values, we calculated the temperature vegetation dryness indices (TVDIs) at a 30 m pixel resolution as follows:
where TS is the land surface temperature for a pixel; and are the maximum and minimum land surface temperatures corresponding to certain NDVI values, respectively; and a, b, c, and d are the fitted coefficients in the linear equations for the wet and dry edges, respectively, obtained using the TVDI extension tool in ENVI 5.2.
The calculated TVDIs were converted into soil volumetric water content (VWC) using Equation (9), which was developed based on 44 VWC values measured from 2019 to 2022 using soil temperature and moisture sensors (HSTL-102STRWS) and derived TVDIs from Landsat TM images for the same time and field plots [33].
This VWC was then converted into SWC, with a soil bulk density of 1.35–1.40 g cm−3, measured in the study area. The SWC values determined on the days (5 June 2007, 17 May 2012, and 5 June 2016) were set as the initial values for the daily simulation of ecohydrological processes. Daily ecohydrological simulations were conducted until the selected rainstorm days (1 August 2007, 6 August 2007, 21 July 2012, and 20 July 2016) to obtain the SWC values immediately before these rainstorms.
In addition, to derive SWC values at a targeted resolution of 5 m, we needed to realize the downscaling of SWC values at a resolution of 30 m. In a previous study, Moran’s I correlogram of NDVI values computed from a WorldView-2 image showed that vegetation growth conditions presented a significantly positive autocorrelation within a range of approximately 60 m surrounding a site; this implies that single or invariant factors and processes drive vegetation growth variation within a scale domain of 60 m [20]. Given that vegetation growth is closely associated with soil moisture, we assumed that vegetation growth and soil moisture would vary within an approximate scale domain. Thus, there were similar spatial pattern characteristics of SWC across scales from 1 m to 60 m. Accordingly, the SWC values at a resolution of 30 m could be scaled down to 5 m by resampling [56], and these 5 m SWC values were input into the IUFM.
To simulate daily ecohydrological processes from the initial days (5 June 2007, 17 May 2012, and 5 June 2016), we also needed to derive the daily LAI, which is closely associated with vegetation evapotranspiration and precipitation redistribution in the canopy and thus greatly impacts soil water conditions. We obtained the LAI values for grasses, shrubs, and trees (averaging broad-leaved and coniferous trees) over the study area from the NDVI-LAI look-up table. The look-up table was derived from the statistical relationship between NDVI values from Landsat TM images and LAI values inverted based on radiative transfer and geometrical optics principles in vegetation and the atmosphere [57]. In the present study, the NDVI values used for estimating the LAI values were inverted using red light and near-infrared band reflectance data at a resolution of 2 m from a WorldView-2 image taken on 13 October 2017. The LAI values obtained on 13 October represented the maximum LAI values during the entire flood season, given that the leaves did not start falling in mid-October in Beijing. We assumed that the interannual variation in LAI during the flood season (with maximum vegetation growth) could be ignored; thus, the obtained LAI values for 2017 could be used for 2007–2016.
The parameters in the pipe convergence module are primarily associated with the nodes and conduits. These data were obtained from actual drainage network data in the present study (Table S2).
The parameters in the inundation module primarily included the node position from the drainage network data, elevation from the DEM data, and land-cover from the interpreted WorldView-2 image. Furthermore, when the effect of land-cover on the overflow expansion could not be ignored, the loss coefficient for the land-cover type was considered (Table S3) [51]. The loss coefficients were obtained from Manning’s roughness coefficients for different land-cover types.
Some parameters in the three modules were calibrated, such as depression storage and Manning’s roughness coefficients (Mnrc) for different land-cover types in the surface runoff module, Mnrc for pipes in the pipe convergence module, and loss coefficients for different land-cover types in the inundation module (Tables S1, S2, and S3) [10,33,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54]. We first assigned initial ranges to the parameters based on the literature in the urban areas of Beijing and Rossman and Huber (2016) [10]. Given that the loss coefficient is highly positively correlated with Mnrc, we determined the range of Mnrc for a land-cover type as the initial loss coefficient for the land-cover type (Table S3) [51]. These initial ranges were then calibrated using actual flood data from the rainstorm on 6 August 2007.
2.6. Landscape Pattern
A land-cover map was visually interpreted from a WorldView-2 image involving RGB and near-infrared bands at a 2.0 m pixel resolution for 13 October 2017 (Figure 2b). Image preprocessing (including radiometric and atmospheric calibration and geometric rectification) was conducted using ENVI 5.2 software. Manual digitization was performed to classify the land-cover types. Pervious cover types included vegetation-covered green spaces (i.e., grassland and woodland) and brick pavements. Impervious cover types included asphalt roads, concrete roads, and concrete roofs. The interpreted land-cover types were tested and verified by comparison with those at the 30 sample sites. The final accuracy is 96.7%.
The land-cover data were input into the landscape pattern analysis package FRAGSTATS 4.2 [58] to calculate the spatial pattern metrics for impervious cover types within each subcatchment (Figure 6). Adjacent cells (using the eight-cell neighbor rule) with the same land-cover type composed a patch. The selected metrics included the percentage of landscape (PLAND), the largest patch index (LPI), the percentage of like adjacencies (PLADJ), and the patch cohesion index (COHESION) (Table S4) [58]. The rationale for metric selection is the same as that used by Zhang et al. (2018) [52].
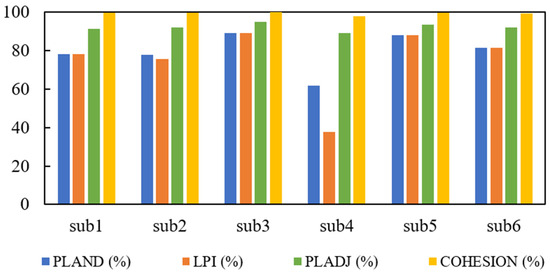
Figure 6.
Landscape pattern metrics for impervious patches in the six subcatchments (sub1, sub2, sub3, sub4, sub5, and sub6) of the Anhua Bridge study area in Beijing. PLAND, percentage of landscape; LPI, largest patch index; PLADJ, percentage of like adjacencies; COHESION, patch cohesion index.
The total PLAND for impervious cover types was 79.45% in the study area. The PLAND of the six subcatchments ranged from 61.79% (sub4) to 89.13% (sub3) (Figure 6). This indicates that the predominant land-cover was overwhelmingly impervious, even though sub4 had the largest percent pervious cover (PPC) (Table 1).
2.7. Drainage Capacity
If an urban drainage system fails to discharge the surface runoff promptly, overflow can occur from drain wells or utility holes and eventually form inundated areas. Therefore, the drainage capacity of a subcatchment directly affects the occurrence (presence or absence) and intensity of floods. The ponding of the study area originated from multiple subcatchments through the outlets of overland flow and belowground pipelines. For each subcatchment, there were multiple pipelines to the outfall of the study area (Figure 1). The drainage capacity (D) of a subcatchment is influenced by the physical characteristics of drainage networks (such as pipeline length (L) and pipe diameter (P)) and the altitude difference between the outlet of the overland flow within the subcatchment and the outfall of the study area (E) [59]. We defined D for subcatchment i as the average of the normalized P, L, and E:
where Li is the total length of all pipelines from the outlet of the overland flow within subcatchment i to the outfall of the study area (m); Lmax and Lmin are the maximum and minimum L among all subcatchments, respectively (m); Pi is the pipeline length-weighted mean pipe diameter for subcatchment i (m); Pmax and Pmin are the maximum and minimum P among all subcatchments, respectively (m); Ei is E for subcatchment i; and Emax and Emin are the maximum and minimum E among all the subcatchments, respectively (m).
In descending order of drainage capacity, the Anhua Bridge study area involved sub1, sub2, sub6, sub5, sub4, and sub3 (Table 3).

Table 3.
Drainage capacity of pipe networks for the six subcatchments in the Anhua Bridge study area of Beijing.
3. Results
3.1. Validation of Flood Simulation
We simulated the dynamics of the flooding processes during four rainstorms on 1 August 2007, 6 August 2007, 21 July 2012, and 20 July 2016 (Table 2) in the Anhua Bridge study area using the IUFM.
The modeled minute flood ranges, depths, and volumes changed with the rainfall processes. Their peaks appeared at the approximate times, lagging behind rain peaks by 0.7–3.2 h, with the longer lagging for the rainstorm with the longer rainfall duration (Figure 7). The maximum flood depth during each rainstorm was extracted for each grid cell, from which the spatial distributions of the maximum flood depth and potential flood range were derived (Figure 8). The simulation results show that waterlogging in the study area occurred mainly on the North Third Ring Road (main road) under the Anhua Bridge, covering up to 300 m from east to west along the main road. The surrounding surface flows easily converged toward the bridge at lower altitudes, and water could not be discharged promptly because of the limited drainage capacity.
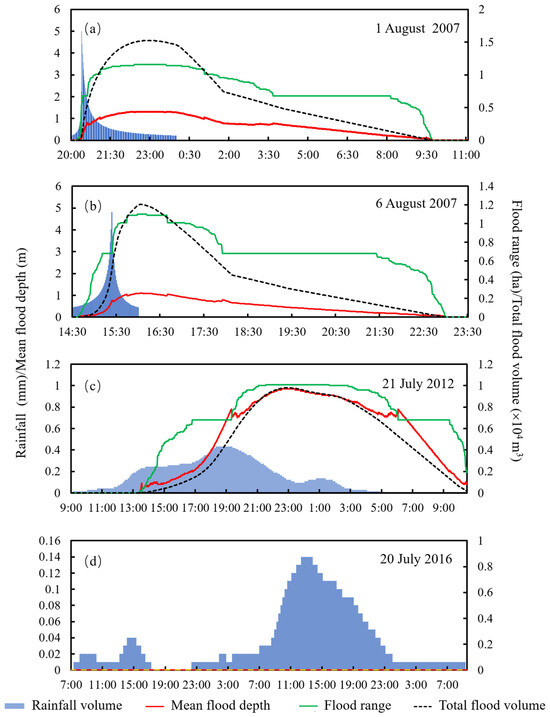
Figure 7.
Rainfall and modeled flooding processes during the four actual rainfall events on 1 August 2007 (a), 6 August 2007 (b), 21 July 2012 (c), and 20 July 2016 (d) (see Table 2) over the entire Anhua Bridge study area in Beijing.
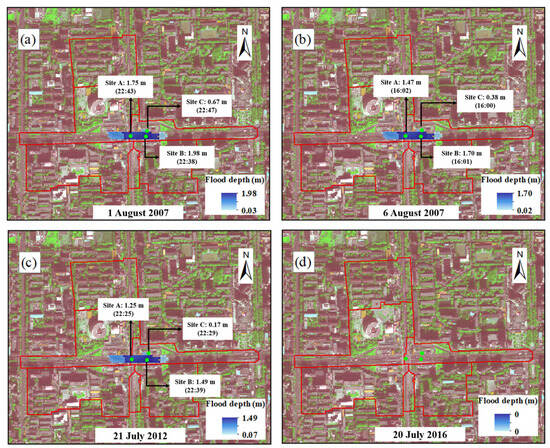
Figure 8.
Spatial distribution of the modeled maximum flood depth during the four actual rainfall events on 1 August 2007 (a), 6 August 2007 (b), 21 July 2012 (c), and 20 July 2016 (d) in the Anhua Bridge study area of Beijing.
We selected three sites in the study area for which some literature could be obtained to validate the modeled flood depths. These were located on the main road under the Anhua Bridge (Site A), east of the main road at the lowest altitude (Site B), and on an auxiliary road north of the main road (Site C) (Figure 8). The temporal trends of the modeled flood depths at the three sites were approximate. Flood depths reached their peaks simultaneously during the same rainstorm events (Figure 9) because of the close locations of these three sites and the same rainfall processes. However, there were considerable differences in the modeled flood depth peaks, and the sites, in decreasing order of peaks, were Sites B, A, and C. Moreover, compared with the floods at Sites A and B, the floods at Site C appeared later and disappeared earlier. These differences could be due to differences in spatial locations. During the flooding processes, floods first converged toward the main road with the lowest altitude (e.g., Site B) and the areas under the bridge (e.g., Site A) and gradually expanded toward the surrounding areas (e.g., Site C), whereas floods recessed in the opposite order.
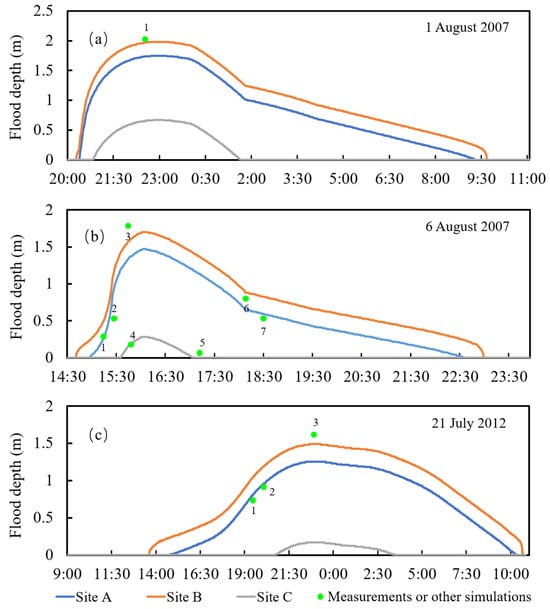
Figure 9.
Modeled temporal variations in flood depths at three sites (A, B, and C) during the three actual rainfall events on 1 August 2007 (a), 6 August 2007 (b), and 21 July 2012 (c) in the Anhua Bridge study area of Beijing. The spatial locations of the three sites are shown in Figure 8. The numbers of 1, 2, 3, …, 7 correspond to the numbers of flood depth data from measurements or other simulations in Table 4.
The modeled flood depth values at the three sites were compared with the measured and other modeled values. For the rainstorm on 1 August 2007, the modeled maximum flood depth at Site B within the inundated area could reach 1.98 m (Figure 7a and Figure 8a), which was close to the measured maximum flood depth reported in Beijing News (about 2 m) (Table 4).

Table 4.
Comparisons between modeled flood depths and measurements or other simulations at the three sites in the Anhua Bridge study area of Beijing.
For the rainstorm on 6 August 2007, we obtained multiple measured data at different times throughout the flooding process at Sites A and C from the Beijing Flood Control Office. The absolute errors between the modeled and measured flood depths ranged from −0.02 m to 0.09 m, and the absolute values of relative errors were not higher than 18% for Sites A and C (Table 4). Site B yielded a higher absolute error (−0.19 m) and a −11.2% relative error. The modeled maximum flood depth at Site B was 1.70 m, which occurred at 16:01 (Figure 7b and Figure 8b), whereas the actual maximum flood depth (1.7 m) occurred at 15:40, according to records from the Beijing Flood Control Office (Table 4). The mismatch between the two flood peak times may be attributed to the coarse time resolution (5 s) used in the IUFM surface runoff module [19]. In particular, the times at which the measurements could be obtained spanned throughout the flooding processes, including nearly peak times and times before and after peaks (Figure 9b). Therefore, the flood depths at these times could represent temporal dynamics of flooding processes.
For the rainstorm on 21 July 2012, the modeled flood depth at 19:30 at Site A was 0.84 m (Figure 9c), which was higher than that reported in Beijing News (0.70–0.80 m) (Table 4). During the rainstorm, the local government used large drainage facilities to accelerate the drainage of floods under the bridge, which reduced the actual flood depth. However, this was not considered in our simulation. Moreover, Li et al. (2017) [60] used the overflow-flood depth curve method to derive flood depth at each time and showed that the modeled flood depth at 20:53 at Site A was 0.81 m, close to our modeled one (Table 4). For Site B, our modeled flood depth at flood peak time (22:39) was 1.49 m (Figure 8c and Figure 9c), close to the measured value (1.50 m) determined by Zhao (2016) [61] (Table 4).
3.2. Flood Simulation under Different Rainstorm Scenarios
We used the four designed rainstorm scenarios described in 2.4.2 to model the entire flooding processes from the initial rainfall time to the final flood recession time in the study area. We calculated the flood range, mean flood depth, and total flood volume over the modeled inundated area for each rainstorm.
The results showed that the modeled flood range, mean flood depth, and total flood volume exhibited similar temporal trends under different rainfall return periods (Figure 10). They increased slowly within the initial 20 min of the start of the rainfall. Subsequently, they rapidly increased to peaks approximately 1 h after the rainfall started, regardless of the rainstorm intensity. All peaks lagged behind the rain peaks by approximately 35 min. After their peaks, the flood depth and volume decreased rapidly and then slowly with temporal variations in rainfall (Figure 10b, c). However, the flood range remained unchanged for a period after the peaks, lasting from 1.0 h for a 3-year return period to 2.5 h for a 100-year return period (Figure 10d). The invariant flood range usually occurs in a large and nearly cuboid depression, such as the underpass of the Anhua Bridge, where overflow can rapidly converge but cannot be drained in a short time because of the limited pipe drainage capacity. In addition, a resolution of 5 m × 5 m masked small changes in the flood ranges.
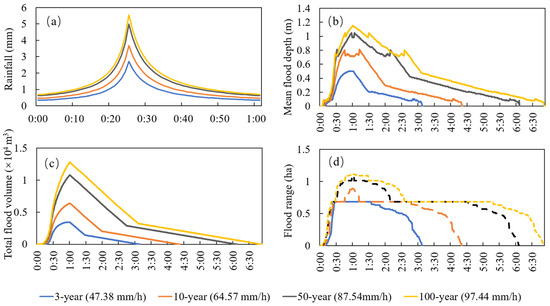
Figure 10.
Modeled rainfall (a), mean flood depth (b), total flood volume (c) and flood range (d) during the four rainstorms with different return periods over the entire Anhua Bridge study area in Beijing.
The modeled maximum flood range, mean flood depth, and total flood volume over the entire study area for the 50-year- and 100-year-return-period rainstorms were similar: 1.09–1.11 ha, 1.05–1.15 m, and 1.10–1.28×104 m3, respectively. These were much greater than those for the 3-year- and 10-year-return-period rainstorms (Figure 10b–d), reaching 2–4 times the maximum flood volume (Figure 10c). Consequently, there were considerable differences in the flooding duration, although the start and peak times of the flooding were similar (Figure 10). The floods caused by the 50-year- and 100-year-return-period rainstorms could last for 6.0 h and 6.8 h, which are 1.8–3.1 h and 2.6–3.8 h more than the floods caused by the 3-year- and 10-year-return-period rainstorms, respectively.
3.3. Hydrological and Hydraulic Processes That Affect Flood Conditions
In the IUFM, urban flooding results from three sequential processes: surface runoff, overflow from drainage networks, and overflow expansion. From these three processes, we analyzed the causes of flooding within different subcatchments and at different spatial locations in the Anhua Bridge study area.
3.3.1. Surface Runoff Process
Rainfall runoff is the initial source of flooding. We modeled surface runoff under four rainstorm scenarios (return periods of 3-year, 10-year, 50-year, and 100-year) using CA-DUSRM for the six subcatchments in the study area. The results showed that the total surface runoff values in the study area were 15.26–31.83 mm, 27.05–44.23 mm, 41.74–62.30 mm, and 48.01–70.05 mm under the four rainstorm scenarios. Sub4 had the lowest mean runoff coefficient (0.43), whereas sub3 and sub5 had the highest values (0.69) and, secondly, sub6 (0.65), sub1 (0.56), and sub2 (0.54) (Figure 11a).
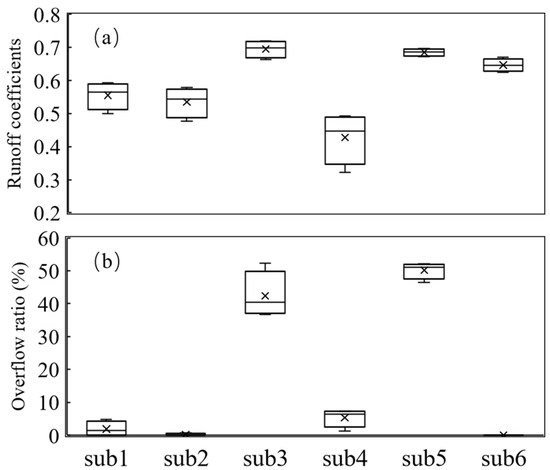
Figure 11.
Surface runoff coefficients (a) and overflow ratios (b) for the six subcatchments (sub1, sub2, sub3, sub4, sub5, and sub6) in the Anhua Bridge study area of Beijing. The five horizontal lines from top to bottom in the box plot represent the maximum, upper quartile, median, lower quartile, and minimum values, respectively, and “×” denotes the mean value. For each subcatchment, the samples came from the four surface runoff coefficients and four overflow ratios under the four rainstorm scenarios (return periods of 3-year, 10-year, 50-year, and 100-year).
The changes in underlying surface conditions directly affect the water cycle, such as the regulation and storage of surface water and the soil infiltration process, ultimately leading to changes in surface runoff, convergence processes, and rainfall runoff effects. In particular, the composition and spatial configuration of impervious patches significantly affected the occurrence and process of surface runoff within a subcatchment. Correlation analysis showed significant positive correlations between the surface runoff coefficient and PLAND, LPI, PLADJ, and COHESION for impervious patches (p < 0.05). Compared with other subcatchments, sub4 had the lowest PLAND, LPI, PLADJ, and COHESION for impervious patches (Figure 6) and thus had the lowest runoff coefficient (Figure 11a). In contrast, sub3 and sub5 had the maximum PLAND, LPI, PLADJ, and COHESION for impervious patches (Figure 6) and thus the highest runoff coefficients (Figure 11a).
3.3.2. Overflow from Drainage Networks
We modeled the overflow under the four rainstorm scenarios using the pipe convergence module and calculated the overflow ratios for the six subcatchments in the study area (Figure 11b). The overflow ratio is the ratio of the overflow within each subcatchment to the total overflow in the study area. The overflow ratio can be used to denote the potential waterlogging contribution of each subcatchment to the entire study area, given that the overflows from the six subcatchments eventually converged under the Anhua Bridge and generated waterlogging.
The results showed that the total overflows in the study area were 3.4 × 103 m3, 6.4 × 103 m3, 1.1 × 104 m3, and 1.3 × 104 m3 under the four rainstorm scenarios. The overflows in sub4 were lower, and the potential waterlogging contribution was smaller (Figure 11b) because of the lowest surface runoff (Figure 11a), although the drainage capacity was the second lowest (0.27) (Table 3). In contrast, there were the highest overflows in sub3 and sub5 and the greatest potential waterlogging contribution (average 36–52%) (Figure 11b) because of the highest surface runoff (Figure 11a) and the lowest and lower drainage capacity (0.26 and 0.35, respectively) (Table 3). Sub1, sub2, and sub6 had the highest drainage capacity (0.38–0.59) (Table 3) and could drain more surface runoff outflow in a shorter time, so they generated much less overflow (Figure 11b).
3.3.3. Overflow Expansion Process
In the IUFM, overflow expands from a node and forms an inundated area around the node. The spatial distribution of the inundated area depends on the terrain and land-cover of the underlying surface. To determine the effects of different factors, we used the inundation module to model the overflow expansion processes impacted by different factors under the assumption of an input total overflow of 5 × 104 m3.
We first modeled the overflow expansion process, as land-cover was not considered when the overflow expansion varied with the terrain. The results show that the buildings near the roads in the study area were completely submerged (Figure 12a), which is different from the actual situation. When the effect of land-cover was considered, as in the IUFM, the terrain data were corrected—for instance, rising by 30 m for buildings to prevent them from being completely submerged. The corrected results showed that the buildings near roads were not submerged when the roads were completely flooded, whereas flood depths differed surrounding the buildings at different locations (from 0.12–0.37 m in the north to 0.01–0.35 m in the south) (Figure 12b), which followed the actual occurrences.
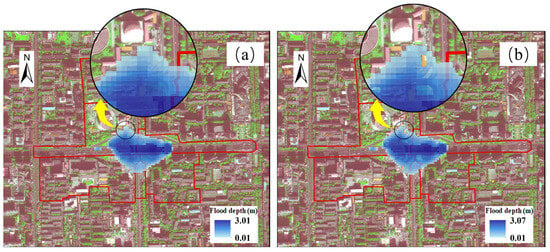
Figure 12.
Comparisons in flood range and depth from the modeled overflow expansion process when not considering (a) and considering (b) the differences in land-cover types under the assumption of an input total overflow of 5 × 104 m3. The red polygons represent the subcatchments; the yellow arrows point to the enlarged image in the black circle area.
Furthermore, overflow loss coefficients were introduced to the IUFM and differed among different land-cover types (Table S3) [51] to model the lost overflow when it passed through land-cover. During the overflow expansion process, an overflow loss of 0.73% occurred, making the total flood volume 364 m3 lower than the initial overflow of 5 × 104 m3.
4. Discussion
4.1. Model Evaluation
In the IUFM, surface ecohydrological, pipe convergence, and inundation processes are combined, and simulations of urban surface runoff, pipe overflow, and flood expansion can be realized progressively. The simulated urban flooding processes and flood depth were validated to be reliable.
Compared with traditional physics-based models (e.g., the SWMM, MIKE FLOOD, and InfoWorks ICM), CA-DUSRM for simulating surface runoff is more suitable for urban areas that have complex surface environments [19]. The cell-based model structure and simulation mechanism enable it to describe the effect of spatially heterogeneous underlying surface information (especially terrain undulation) on the runoff processes and to reflect the lateral water exchanges between adjacent areas. Different from most physics-based models, this model fully expresses the daily ecohydrological processes that have a potential cumulative soil water effect on transient rainfall runoff and flood. Moreover, CA-DUSRM is convenient for further application and development given its simple structure, simple rules, and reliable simulation results.
In the pipe convergence module of the IUFM, the dynamic wave analysis method is chosen because it can simulate complex flow states in almost all pipe flows. This method supports a small simulation time step (e.g., 5 s), which ensures stable simulation values. Other methods, such as the kinematic wave and diffusion wave analysis methods, do not take into account the variations in pressure and acceleration within the fluid when dealing with pipe flow problems; consequently, they are unable to accurately estimate the downstream backwater effect [62].
When using the multi-source dynamic diffusion inundation algorithm in the inundation module of the IUFM, flood range is determined by implementing a series of expansion processes from cells to cells and from depressions to depressions. By contrast, when using the common non-source inundation algorithm, flood range is determined just from the cells below the water level [30,31]. The simulation results from the inundation module of the IUFM are more realistic, taking into account the effects of both DEM and land-cover. By contrast, in non-source algorithm, only DEM data are generally used [63,64,65]. Moreover, the 2D shallow water equation is also commonly used for simulating inundation processes. The Iber hydrodynamic module solves the 2D shallow water equations using an unstructured finite volume solver over a computational mesh. This method can derive accurate flood velocity while reducing processing speed [24,66]. FLURB-2D ignores the convection term of shallow water equation to eliminate numerical instability. However, solving shallow water equation is still computationally intensive even for the simplified formulae [67,68].
In addition, when using the IUFM to simulate the whole flooding process for the rainfall event lasting nearly one day on 21 July 2012 over the entire study area, only an average time of 2.0 s per simulation step (total steps being flood duration divided by temporal grain for simulation (5 s)) was required by using an E5-2630 v4 processor (32 GB of memory) and an NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1070 graphics card (6 GB of dedicated memory and 16 GB of shared memory). Therefore, the IUFM can effectively balance the relationship between simulation accuracy and computational efficiency.
However, uncertainties may still exist in the simulation, mainly arising from the model structures and estimations of input variables and parameters when the model is applied.
4.1.1. Uncertainties from the Model Structures
Uncertainties in the model structures can be observed in the simulation framework, assumptions, established formulae, and selected temporal and spatial grains (resolutions) [69].
In the surface runoff module of the IUFM, the ecohydrological effects on surface runoff did not differ between grasses and shrubs or between broad-leaved and coniferous-leaved trees. This simplification is necessary when detailed vegetation information cannot be obtained even from high-resolution images. This simplification is also reasonable, given that the ecohydrological processes of ecosystems associated with vegetation are not critical during rainstorms. However, water cycle processes in a system were not isolated. For example, soil moisture is a result of the ecohydrological processes of ecosystems at a certain time and is a critical factor that determines the occurrence and intensity of surface runoff on pervious surfaces by affecting soil infiltration before and during rainstorms. There are certain differences in ecohydrological processes (such as transpiration and water absorption) and soil physical and chemical properties (such as soil bulk density, soil saturated hydraulic conductivity, and field water capacity) between grasses and shrubs and between broad-leaved and coniferous-leaved trees, which result in differences in soil water conditions and soil infiltration [70]. Therefore, identifying detailed vegetation types will help simulate surface runoff more accurately. In addition, further studies may identify low-impact development (LID) facilities in the study area and simulate their runoff reduction effects—for instance, by involving the LID module in the SWMM [71,72].
In the pipe convergence module of the IUFM, artificial drainage facilities such as reservoirs and pumping stations were not added to the drainage network. Thus, the effect of reservoirs and pumping stations on pipe flow and overflow could not be estimated, which might have resulted in a higher modeled flood depth, for example, in 2012 at Site B in the study area (Figure 8c). Further studies may identify artificial drainage facilities in the study area and refine the drainage network map to simulate their effects on surface runoff. In addition, the overland flow entering outlets is immediately transferred into the drainage network, which may be different from real situation [73]. And these circumstantial factors (e.g., inlets position, typology, and clogging conditions) may also have a significant impact on the water flow through the drainage networks [68,74,75,76].
In the inundation module of the IUFM, a cell-based simulation is conducted beyond the boundaries among different subcatchments so that a spatial distribution of waterlogging across subcatchments can be displayed; however, the cell-based simulation can underestimate the flood depth under the invariant overflow volume, particularly for small, inundated areas greatly affected by boundary cells. The cut-and-trial method, based on the water balance principle, simplifies the inundated processes; however, if the hydraulic mechanism of the inundated processes is combined, more detailed information (such as flood velocity) can be derived. Moreover, the introduction of overflow loss coefficients for different land-cover types is expected to present a more accurate flow expansion over the land surface; however, the effect of overflow loss was not considerable in an urban area dominated by impervious land-cover, as shown in Section 3.3.3.
This study set the temporal and spatial grains to 5 s and 5 m, respectively, to ensure simultaneous simulation efficiency and accuracy. Compared with the temporal grain of 1 s, using the grain of 5 s decreases the modeled total surface runoff by 1.57 mm (4.86%) and the modeled peak discharge by 0.44 mm (18.97%), yielding a delay of 4 s in the peak time by reducing the sampling frequency of the water exchange among cells, according to a systemic evaluation of the temporal grain effects on the modeled surface runoff process [19]. However, even for a depressed surface involving an underpass and its surrounding high-elevation regions, such as the study area, there are similar temporal dynamics of the modeled surface runoff when the temporal grains vary from 1 to 5 s [19]. Moreover, compared with the spatial grain of 1 m, the modeled total surface runoff increases by 2.52 mm (7.76%) and the modeled peak discharge increases by 0.23 mm (9.16%) when the spatial grain of 5 m is used. However, there is little difference in the temporal dynamics of the modeled surface runoff when the spatial grains vary from 1 to 5 m, even for a depressed surface with large undulations [19]. This indicates that the determined temporal grain of 5 s and spatial grain of 5 m in the present study are reliable for the timely dynamic simulation of urban surface runoff and floods.
4.1.2. Uncertainties from Estimations of Inputs
When the model is applied, the reliability of the model outputs depends primarily on the estimation precision of the input data, including the driving variables, initial variables, state variables, and parameters.
For the flood simulation, the key driving variable was precipitation, which directly affected surface runoff. If the error in the precipitation data doubles, the error in the modeled peak flood volume may reach 1.6 times that amount [77]. This study used a Chicago rain-pattern generator and cubic polynomial interpolation of hourly precipitation data to generate minute precipitation data. These methods have been used extensively to supplement fine temporal resolution precipitation data—for instance, when actual minute data cannot be obtained [38]. Although the generated data can present the main temporal trends and regional characteristics of precipitation, they necessarily differ from the actual data, which results in uncertainties in the modeled surface runoff and flooding processes [78]. In the future, minute (and even second) precipitation data that can be continuously measured by weather radars are expected to directly provide precipitation data for urban flood models [66,79].
Initial SWC is the key initial variable in the IUFM. In this study, a series of uncertainties existed during the entire process of estimating initial SWC values. For example, VWC values were first derived from a statistical relationship (Equation (9)) between the TVDIs inverted from Landsat images with a spatial resolution of 30 m and the corresponding VWC values from field measurements. The incomplete matching of spatial locations between remote sensing images and ground values and the inconsistency in the spatial resolution of the two data types were sources of uncertain VWC values. When converting VWC into SWC, the average bulk density value (rather than a cell-based value) was used for the entire study area. Ignoring the spatial heterogeneity of soil bulk density could enhance the uncertainty of the estimated SWC values. Finally, the downscaling of SWC values from 30 m to 5 m was based on the scale domain (60 m) identified from the spatial autocorrelation of the NDVI, assuming that soil moisture and vegetation growth varied within an approximate scale domain. If this assumption is not true—that is, different from NDVI—SWC has high spatial heterogeneity so that significant changes in SWC values occur within the range of 30 m to 5 m surrounding a site, then, directly downscaling SWC values from 30 m to 5 m can cause non-ignorable uncertainty.
The state variables in the IUFM mainly include the DEM and land-cover data. This study had spatial resolutions of 1.0 m and 2.0 m, respectively, which could meet the requirement for presenting spatial heterogeneity of terrain and land-cover in the study area. Therefore, these data resulted in little uncertainty from spatial grain in the modeled surface runoff and flooding processes. Although higher-resolution data can be obtained using light detection and ranging (LiDAR) technology in many other regions [80]; the use of unmanned aerial vehicle loaded with LiDAR is strictly controlled in downtown Beijing. In addition, we used the interpreted land-cover map for 2017 in the study area and did not consider the possible changes in surface runoff and floods caused by interannual changes in land-cover types. The Anhua Bridge study area, as a part of the central urban area of Beijing, hardly underwent large-extent changes in land-cover types during the 2010s, which was confirmed by the street view data from 2007 to 2016 on Baidu maps. Therefore, there was little uncertainty from temporal variation in land-cover data.
There are many parameters in the IUFM, particularly those in the surface runoff and pipe convergence modules. These parameters are indispensable for deriving ecological, hydrological, and hydraulic processes [81]. However, these parameters, determined using various sources or methods, may cause output uncertainty. For example, the LAI values for grasses, shrubs, and trees in the study area were obtained from the NDVI-LAI look-up table. In this table, the corresponding NDVI and LAI values exhibit significant power-law relationships, which allowed LAI values to be accurately estimated from high-resolution (2 m) NDVI values in the present study. However, the NDVI-LAI relationships may change with the study area because of differences in the biophysical conditions of different areas [44,57]. This method also converts continuous NDVI and LAI values into classified values, reducing their spatial continuity. Moreover, if the interannual variation in LAI during the flood season cannot be ignored, then the assumed invariant LAI values from 2007 to 2016 will increase the uncertainty of the modeled ecohydrological and flooding processes. In future studies, more high-resolution NDVI values over more years will be necessary to weaken this assumption. For another example, although the structures and layout of drainage inlets are important factors affecting the flow conveyance through urban pipelines [75], the related studies require detailed drainage network data, and such detailed data may not be available [67]. Model studies considering the drainage inlets are mostly conducted in small areas [17] and laboratory settings [66]. In our drainage network data, there is pipe and node information along main roads (Figure 1), while more detailed information cannot be obtained in downtown Beijing given the data secrecy. Therefore, we discretized subcatchments based on the ultimate outlets rather than the finer inlets along the flow routes. Although the coarser drainage network data influenced the discretization degree of subcatchments, they did not weaken the function of the outlets of the subcatchments in linking surface runoff outflows with pipe networks; thus, they did not reduce the precision of simulated flood depth.
Calibrated parameters based on measurements in the study area were credible and feasible for simulations [82]. However, calibration problems cause uncertainties in the determined parameters. The actual flooding process was difficult to observe during severe rainstorms, especially at night or suddenly, and measured flooding data were not easily obtained from government departments or companies; therefore, measured data were always lacking. Moreover, most waterlogging phenomena have been observed at a single time; therefore, continuous observed data are always lacking. In summary, more data measured at different spaces and times are required to improve the reliability of the calibrated parameters.
4.2. Prevention and Control Measures for Urban Flood
In general, the main factors that cause urban flooding include natural rainstorms from external systems, physical terrain, underlying surfaces, and human drainage facilities within a system [83]. The entropy weight analysis for the area surrounding the North Moat (involving the Anhua Bridge study area) showed that among the internal factors, altitude difference had the greatest effect on floods, secondary drainage systems, and land-cover of the underlying surface.
4.2.1. Rainstorm Event
In the case of high rainfall intensity, which means a large rainfall volume over a short period, urban flooding is more likely to occur. Chang et al. (2023) analyzed multiple flood events using statistical methods and concluded that high rainfall intensity is an important factor causing severe floods [84]. Our study indicated complex and interlaced relationships between rainfall parameters and flood range, depth, volume, and duration. Our flood simulation of actual rainstorm events showed that the simultaneous occurrence of a larger rainfall volume and higher rainfall intensity always caused a larger flood range, depth, and volume (for instance, rainstorms on 6 August 2007) (Table 2 and Figure 7). The simultaneous occurrence of a larger rainfall volume and longer rainfall duration caused a longer flood duration (for instance, the rainstorms on 21 July 2012). A large flood depth greatly depends on a high rainfall intensity. For example, the maximum flood depth could reach 1.10 m when the rainfall of 99.40 mm occurred in 1.5 h and the average rainfall intensity reached 66.27 mm/h on 6 August 2007. In contrast, during the rainstorm on 20 July 2016, there existed no ponding because the rainfall of 106.0 mm lasted for 50 h and the average rainfall intensity was only 2.12 mm/h (Table 2 and Figure 7). Consequently, a large amount of rainwater could not be discharged in time and thus gathered under the concave bridge on 6 August 2007. In contrast, there was sufficient time to discharge rainwater even if overland flows could be generated at certain times on 20 July 2016.
Therefore, in the future, if we can analyze the causes and characteristics of extreme rainstorms and carry out more refined studies on urban rainstorm early warning and forecasting, we will be able to derive more scientific support for urban flood prevention and emergency response [85].
4.2.2. Terrain Factor
A depression can result in a significant altitude difference from its bottom to the ground level, which makes a depression a container for floods. During rainstorms, a large amount of surface runoff can rapidly expand to impervious roads and converge in depressions, forming ponding areas [86]. In particular, ponding is more easily formed under concave-down overpasses because of the low-lying terrain [4]. In this study, in the Anhua Bridge, a typical concave-down overpass, the maximum depth of the accumulated flood reached 2 m (e.g., on 1 August 2007 in Table 4 and Figure 9).
Therefore, local low-lying urban areas should receive more attention and reconstruction. For example, we can level the land or raise the terrain to reduce the altitude differences where conditions permit. Li et al. (2018) conducted a study in Shangqing Bridge, Beijing, and the results showed that when the elevation in low-lying areas increased by 1.5 m, the maximum flood depth decreased by 0.89 m [2]. If the reconstruction of the terrain is difficult, we can focus on drainage facilities, such as establishing impounding reservoirs and pumping stations, to pump out and drain floods in a timely manner.
4.2.3. Drainage System
Insufficient drainage capacity is another significant cause of urban flooding [59]. The drainage system of the Anhua Bridge was constructed primarily in the 1980s and 1990s, and most facilities are aging. The original standards designed for rainfall events with return periods of 1–3 years are extremely low [4] and unsuitable for increasingly frequent extreme rainstorms. The estimated drainage capacity for the six subcatchments in the study area averaged 0.38, and only for sub1 was approximately 0.60.
To mitigate waterlogging over the entire study area, priority should be given to sub3, sub4, and sub5 with the lowest drainage capacity, to improve their drainage capacities—for instance, by adjusting pipe parameters or establishing drainage facilities. Shi (2015) used the SWMM to simulate floods in a typical underpass bridge in Hangzhou and found that the flood volume was reduced by approximately 68% after increasing the pipe diameter from 400 mm to 500 mm and 800 mm to 1000 mm [28]. Moreover, drainage pipes should be checked frequently to remove sediment, silt, and garbage with rain to ensure smooth water flow in the pipelines.
4.2.4. Underlying Surface
In highly urbanized areas, the underlying surfaces primarily comprise asphalt, concrete, and other impervious surfaces. Predominantly impervious areas can considerably increase surface runoff and the probability of ponding [87]. In the six subcatchments of the Anhua Bridge study area, the proportions of impervious surfaces were greater than 61%, and the maximum could reach 89% (Figure 6). The mean surface runoff coefficients for the six subcatchments were greater than 0.43 (Figure 11a), indicating a high risk of severe ponding [88].
To reduce urban ponding risk, impervious cover can be decreased, or pervious cover can be increased by constructing or adding LID facilities such as green land, pervious pavement, and green roofs [89]. Our studies in the area surrounding the North Moat in Beijing found that only if the PPC in a subcatchment reached 20–30% could the subcatchment have better a mitigation effect on surface runoff [33]. In the Anhua Bridge study area, the PPC of sub3, sub5, and sub6 were 10.9%, 11.9%, and 18.4%, respectively, smaller than the minimum of the PPC threshold (20%). Therefore, for sub3, sub5, and sub6, rapid reduction in surface runoff can be achieved by increasing the pervious area by approximately 20–30%. For sub1 and sub2 with a PPC of 22%, a similar reduction effect can also be expected when the pervious area is increased to at least 30%. However, it may not be necessary to increase PPC to greater than the maximum of the PPC threshold (30%) because the hydrological effect of increasing PPC is not obvious as PPC is greater than 30% [52]. In addition, there is little possibility to increase PPC to a greater value during a short period in this highly urbanized area.
If it is not feasible to decrease the total impervious area or increase the total pervious area in a highly urbanized area, we can change the spatial configuration of the impervious or pervious patches under the invariant cover area. According to the results in Section 3.3.1, effective measures that can change the spatial configuration include decreasing the size of the largest impervious patch, increasing isolation among large impervious patches, and reducing the connection among different impervious patches [52]. Conversely, these measures include increasing the size of the largest pervious patch (for instance, by enlarging a green land park), decreasing isolation among small pervious patches (for instance, by increasing the size of each green land), and enhancing connections among different pervious patches (for instance, by adding vegetation corridors). Changing the spatial configuration of impervious or pervious patches can be a crucial approach to alleviating urban flooding and deserves more attention in current sponge city construction.
5. Conclusions
We developed an IUFM in which three sequential hydrological and hydraulic processes (surface runoff, overflow from drainage networks, and overflow expansion) were fully considered by combining a cell-based surface runoff module (CA-DUSRM), a subcatchment-based pipe convergence module, and a cell-based and across-subcatchment inundation module.
The surface runoff module in the IUFM based on grid cells can more accurately depict the complex underlying surface characteristics in urban areas. The rainfall runoff processes on pervious surfaces can be accurately described based on the SWC values immediately preceding the rainfall, estimated from the continuous daily ecohydrological processes, rather than from assumed or qualitative values. The pipe convergence module has the ability to simulate complex flow states in almost all pipes, with stable simulation values. The inundation module in the IUFM can realistically simulate the distribution of flood depth. The CA-based IUFM supports parallel operations, which can effectively balance the simulation precision and computational efficiency. Therefore, the IUFM has great potential for providing accurate and timely flooding information.
The IUFM was confirmed to be reliable for simulating rainstorm flooding processes in a typical concave-down overpass area in Beijing. We also successfully employed the model to infer flooding processes over the area surrounding the North Moat in Beijing with reliable results. Given its cell-based framework, the model is also potentially applicable to other urban areas, especially those with complex underlying surfaces. Further studies should focus on reducing model uncertainties in model structures (including the simulation framework, assumptions, established formulae, and temporal and spatial grains) and estimations of input variables and parameters.
In application, immediately after an urgent rainstorm warning, the IUFM can provide accurate and rapid information on the spatial-temporal distribution of flood range, depth, and volume for the government and the people, based on which flood risk evaluation and waterlogging prevention and control measures can be issued in a timely manner. In addition, the exploration of factors that could have a significant effect on the flooding process also urged us to take continuous and regular measures during long-term storm water management, such as adjusting terrain, improving drainage systems, and increasing pervious cover.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/rs16101650/s1; Table S1: The parameters of the surface runoff module of IUFM (integrated urban flood model); Table S2: The parameters of the pipe convergence module of IUFM (integrated urban flood model); Table S3: Loss coefficients for different land-cover types in the inundation module of the IUFM (integrated urban flood model); Table S4: Spatial composition and configuration metrics for the impervious cover types from the landscape pattern analysis package FRAGSTATS 4.2.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.Y. and N.Z.; methodology, Y.Y., N.Z., H.Z., and C.F.; software, Y.Y. and C.F.; validation, Y.Y., N.Z., and H.Z.; formal analysis, Y.Y. and N.Z.; investigation, Y.Y., N.Z., and C.F.; resources, Y.Y.; data curation, Y.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.Y.; writing—review and editing, Y.Y., H.Z., and N.Z.; visualization, Y.Y.; supervision, N.Z.; project administration, N.Z.; funding acquisition, N.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Beijing Natural Science Foundation [grant number 8181001] and the Science and Technology Fundamental Resources Investigation Program [grant number 2022FY100100].
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ding, Z.; Li, J.; Li, L. Method for Flood Submergence Analysis Based on GIS Grid Model. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2004, 6, 56–60. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Pan, X.; Di, S.; Yang, M.; Su, Y. Diagnostic Analysis of the Waterlogging Influence Factors in Beijing City: A Case Study of Shangqingqiao Catchment. J. Nat. Resour. 2018, 33, 1940–1952. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, C.; Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Xiang, C.; Fu, X.; Luan, Q. Urban Storm Flooding: Characteristics and Management in Beijing. In Proceedings of the MATEC Web of Conferences; EDP Sciences: Les Ulis, France, 2018; Volume 246, p. 01042. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, J. Modeling Method and Reason Analysis of Urban Flooding in Concave-down Overpass Area. Hebei J. Ind. Sci. Technol. 2014, 31, 389–394. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Z.; Guo, W.; Li, N.; Xie, Y. Numerical Simulation of Urban Ponding in Beijing. Meteorol. Mon. 2015, 41, 1111–1118. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J. Research on the Water Infiltration Technology during the Rainy Seasons in the Recessed Overpass of Beijing. Urban Geol. 2016, 11, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, F.; Hu, H.; Guo, L. The Early Warning Methods on Risk Degree of Urban Rainstorm Flash Flood and Its Application in Beijing. Torrential Rain Disasters 2013, 32, 263–267. [Google Scholar]
- Agonafir, C.; Lakhankar, T.; Khanbilvardi, R.; Krakauer, N.; Radell, D.; Devineni, N. A Review of Recent Advances in Urban Flood Research. Water Secur. 2023, 19, 100141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatichi, S.; Vivoni, E.R.; Ogden, F.L.; Ivanov, V.Y.; Mirus, B.; Gochis, D.; Downer, C.W.; Camporese, M.; Davison, J.H.; Ebel, B.; et al. An Overview of Current Applications, Challenges, and Future Trends in Distributed Process-Based Models in Hydrology. J. Hydrol. 2016, 537, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossman, L.A.; Huber, W.C. Hydrology. In Storm Water Management Model Reference Manual; EPA/600/R-15/162A; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 2016; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, S.; Kumar, S. Urban Flood Modeling Using SWMM for Historical and Future Extreme Rainfall Events under Climate Change Scenario. Indian J. Ecol. 2020, 47, 48–53. [Google Scholar]
- Rossman, L.A.; Dickinson, R.E.; Schade, T.; Chan, C.C.; Burgess, E.; Sullivan, D.; Lai, F.H. SWMM 5—The next Generation of EPA’s Storm Water Management Model. J. Water Manag. Model. 2004, 12, 339–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, F.; Hu, J.; Lu, A.; Gan, Y. Building of Mathematical Model for Drainage System at an Underpass in Beijing. China Water Wastewater 2014, 30, 103–108. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, M.; Xu, Z.; Chu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Du, C. Simulation of Rainstorm Waterlogging Processes at the Lixia Overpass Bridge in Jinan City. South-North Water Transf. Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 16, 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- Agudelo-Otálora, L.M.; Moscoso-Barrera, W.D.; Paipa-Galeano, L.A.; Mesa-Sciarrotta, C. Comparison of Physical Models and Artificial Intelligence for Prediction of Flood Levels. Tecnol. Cienc. Agua 2018, 9, 209–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Chu, X. A New Modeling Approach for Simulating Microtopography-Dominated, Discontinuous Overland Flow on Infiltrating Surfaces. Adv. Water Resour. 2015, 78, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.-F.; Leandro, J. A Conceptual Time-Varying Flood Resilience Index for Urban Areas: Munich City. Water 2019, 11, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.; Yang, J.; Chi, Y.; Zhang, J. Dynamic Puddle Delineation and Modeling of Puddle-to-Puddle Filling-Spilling-Merging-Splitting Overland Flow Processes: Dynamic Puddle Delineation and Modeling of P2P Processes. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 3825–3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Zhang, N.; Habiyakare, T.; Yu, H. Development of a Cellular Automata-Based Distributed Hydrological Model for Simulating Urban Surface Runoff. J. Hydrol. 2023, 627, 130348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Jing, Y.; Liu, C.; Li, Y.; Shen, J. A Cellular Automaton Model for Grasshopper Population Dynamics in Inner Mongolia Steppe Habitats. Ecol. Model. 2016, 329, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Chen, N.; Du, W.; Wang, C.; Chen, C. A Cellular Automata Based Rainfall-Runoff Model for Urban Inundation Analysis Under Different Land Uses. Water Resour. Manag. 2021, 35, 1991–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, P.R.; Dalponte, D.D.; Vénere, M.J.; Clausse, A. Cellular Automata Algorithm for Simulation of Surface Flows in Large Plains. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 2007, 15, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mignot, E.; Li, X.; Dewals, B. Experimental Modelling of Urban Flooding: A Review. J. Hydrol. 2019, 568, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidolin, M.; Chen, A.S.; Ghimire, B.; Keedwell, E.C.; Djordjević, S.; Savić, D.A. A Weighted Cellular Automata 2D Inundation Model for Rapid Flood Analysis. Environ. Model. Softw. 2016, 84, 378–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, H. Applications of Advanced Technologies in the Development of Urban Flood Models. Water 2023, 15, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Lai, C.; Wang, Z.; Wu, X. Rapid Simulation of Urban Rainstorm Flood Base on WCA2D and SWMM Model. Adv. Water Sci. 2020, 01, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Zhang, N.; Habiyakare, T.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, H. Prospects of Eco-Hydrological Model for Sponge City Construction. Ecosyst. Health Sustain. 2021, 7, 1994885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, N.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, C.; Xu, S. Research on City Flyover Model of Water Logging. Ind. Control Comput. 2015, 28, 27–28. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Duan, Z.; Wang, Y. Urban Flooding Disaster Simulation Method for Concave-down Overpass Bridges by Developing SWMM. J. Beijing Univ. Technol. 2016, 42, 1422–1427. [Google Scholar]
- Lyu, H.-M.; Shen, S.-L.; Yang, J.; Yin, Z.-Y. Inundation Analysis of Metro Systems with the Storm Water Management Model Incorporated into a Geographical Information System: A Case Study in Shanghai. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 23, 4293–4307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.-M.; Jin, S.-G. A Methodology for Simple 2-D Inundation Analysis in Urban Area Using SWMM and GIS. Nat. Hazards 2019, 97, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Feng, S.; Yang, Z.; Wu, H. Primary Analysis of the Precipitation Characteristics for Beijing during the Period from 1950 to 2005. J. Irrig. Drain 2007, 26, 12–16. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, C.-H. Eco-Hydrological Effects of Urban Landscape Spatial Pattern Change and Simulation. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, N.; Yu, G. Simulation and Analysis of Water Balance for Vegetation Ecosystems on Landscape Scale. Clim. Environ. Res. 2006, 11, 425–440. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, N.; Liu, C. Simulated Water Fluxes during the Growing Season in Semiarid Grassland Ecosystems under Severe Drought Conditions. J. Hydrol. 2014, 512, 69–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gironás, J.; Roesner, L.A.; Davis, J. Storm Water Management Model Applications Manual; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2009; EPA/600/R-09/077. [Google Scholar]
- Karim, F.; Armin, M.A.; Ahmedt-Aristizabal, D.; Tychsen-Smith, L.; Petersson, L. A Review of Hydrodynamic and Machine Learning Approaches for Flood Inundation Modeling. Water 2023, 15, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jean, M.-È.; Duchesne, S.; Pelletier, G.; Pleau, M. Selection of Rainfall Information as Input Data for the Design of Combined Sewer Overflow Solutions. J. Hydrol. 2018, 565, 559–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beijing Urban Planning and Design Research Institute. Standard of Load Calculation for Municipal Infrastructure Planning 2017.
- Arnell, V.; Harremoës, P.; Jensen, M.; Johansen, N.B.; Niemczynowicz, J. Review of Rainfall Data Application for Design and Analysis. J. Water Sci. Technol. 1984, 16, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Huang, G.; Zhang, H.; Wang, W. Urban Inundation Response to Rainstorm Patterns with a Coupled Hydrodynamic Model: A Case Study in Haidian Island, China. J. Hydrol. 2018, 564, 1022–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Hong, W. The Improvement of the Formula of Rainfall Interception by Vegetation. Syst. Sci. Compr. Stud. Agric. 1999, 15, 200–202. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Lei, T.; Zhang, G.; Cai, C.; Huang, Y.; Yang, X. A New Experimental Method for Observing Initial Soil Infiltration under Ring Infiltrometer. Nongye Jixie Xuebao Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2014, 45, 140–146. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, C.; Liu, K.; Zhou, T. Research on a Formula of Rainfall Interception by Vegetion. J. Soil Eros. Water Conserv. 1996, 2, 47–49. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, G. Retrieval of Leaf Area Index and Foliage Clumping Index from Remotely Sensed Data. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanjing University, Nanjing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Su, H.; Bai, F.; Li, G. Seasonal Dynamics in Leaf Area Index in Three Typical Temperate Montane Forests of China: A Comparison of Multi-Observation Methods. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2012, 36, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G. Studies on Species Composition and Landscape Aesthetics Evaluation of Urban Forest in Beijing. Ph.D. Thesis, Beijing Forestry University, Beijing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, W.; Liu, G.; Pan, J. Distribution of Available Soil Water Capacity in China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2005, 15, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Field Water Capacity Measurement and Results Analysis of Langfang National Drought Reporting Station. Groundwater 2016, 38, 25–26. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Z.; Sui, J.; Xu, R.; Li, X. Study on Soil Water Infiltration in Different Urban Green Space in Beijing. Chin. Landsc. Archit. 2019, 36, 105–108. [Google Scholar]
- Daly, E.; Porporato, A.; Rodriguez-Iturbe, I. Coupled Dynamics of Photosynthesis, Transpiration, and Soil Water Balance Part I: Upscaling from Hourly to Daily Level. J Hydrometeorol. 2009, 5, 559–566. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, N.; Luo, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, Q.; Jing, Y.; Wang, X.; Feng, C. Understanding the Effects of Composition and Configuration of Land Covers on Surface Runoff in a Highly Urbanized Area. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 125, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Wang, H.; Wang, X. The Runoff Curve Number of SCS-CN Method in Beijing. Geogr. Res. 2013, 32, 797–807. [Google Scholar]
- Neitsch, S.L.; Williams, J.R.; Arnold, J.G.; Kiniry, J.R. Hydrology in Soil and Water Assessment Tool Theoretical Documentation; Texas Water Resources Institute: College Station, TX, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, W.; Li, R.; Duan, Z. Digital Elevation Model Fusion by Landform Characteristics. J. Earth Inf. Sci. 2018, 20, 895–905. [Google Scholar]
- Markham, K.; Frazier, A.E.; Singh, K.K.; Madden, M. A Review of Methods for Scaling Remotely Sensed Data for Spatial Pattern Analysis. Landsc. Ecol. 2023, 38, 619–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Zhang, W. The Application of Remotely Sensed Data to the Estimation of the Leaf Area Index. Remote Sens. Land Resour. 2003, 3, 58–62. [Google Scholar]
- McGarigal, K.; Cushman, S.A.; Ene, E.; FRAGSTATS: Spatial Pattern Analysis Program for Categorical Maps. University of Massachusetts, Amherst. 2005. Available online: https://www.fragstats.org (accessed on 2 May 2024).
- Ramachandra, T.; Mujumdar, P.P. Urban Floods: Case Study of Bangalore. Disaster Dev. 2009, 3, 1–98. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Li, H. Rainstorm Model-Based Approach for Traffic Loss Evaluation under Condition of Urban Inundation. Water Resour. Power 2017, 35, 62–65. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X. Study on Site Optimization Design about Waterlogging Area in Beijing Inner City under the Perspective of Sponge City. Master’s Thesis, Beijing University of Technology, Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Todini, E. On the Convergence Properties of the Different Pipe Network Algorithms. In Proceedings of the Water Distribution Systems Analysis Symposium 2006; pp. 1–16.
- Luo, P.; Luo, M.; Li, F.; Qi, X.; Huo, A.; Wang, Z.; He, B.; Takara, K.; Nover, D.; Wang, Y. Urban Flood Numerical Simulation: Research, Methods and Future Perspectives. Environ. Model. Softw. 2022, 156, 105478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, C.; Vojinovic, Z.; Price, R.; Sanchez, A. Modelling Infiltration Process, Overland Flow and Sewer System Interactions for Urban Flood Mitigation. Water 2021, 13, 2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, C.; Hill, A.A.; Urbano, L.D. A GIS-Based Model for Urban Flood Inundation. J. Hydrol. 2009, 373, 184–192. [Google Scholar]
- Costabile, P.; Costanzo, C.; Kalogiros, J.; Bellos, V. Toward Street-Level Nowcasting of Flash Floods Impacts Based on HPC Hydrodynamic Modeling at the Watershed Scale and High-Resolution Weather Radar Data. Water Resour. Res. 2023, 59, e2023WR034599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalvo, C.; Reyes-Silva, J.D.; Sañudo, E.; Cea, L.; Puertas, J. Urban Pluvial Flood Modelling in the Absence of Sewer Drainage Network Data: A Physics-Based Approach. J. Hydrol. 2024, 634, 131043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palla, A.; Colli, M.; Candela, A.; Aronica, G.T.; Lanza, L.G. Pluvial Flooding in Urban Areas: The Role of Surface Drainage Efficiency. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2018, 11, S663–S676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupka, M. A Rapid Inundation Flood Cell Model for Flood Risk Analysis. Ph.D. Thesis, Heriot-Watt University, Edinburgh, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.A.; Moser, A.; Anderson, M.; Zhang, C.; Rötzer, T.; Pauleit, S. Comparing the Infiltration Potentials of Soils beneath the Canopies of Two Contrasting Urban Tree Species. Urban For. Urban Green. 2019, 38, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Du, Y.; Meersmans, J.; Qiu, S. Linking Ecosystem Services and Circuit Theory to Identify Ecological Security Patterns. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakimdavar, R.; Culligan, P.J.; Finazzi, M.; Barontini, S.; Ranzi, R. Scale Dynamics of Extensive Green Roofs: Quantifying the Effect of Drainage Area and Rainfall Characteristics on Observed and Modeled Green Roof Hydrologic Performance. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 73, 494–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.-J.; Wang, C.-H.; Chen, A.S.; Djordjević, S. The Effect of Inclusion of Inlets in Dual Drainage Modelling. J. Hydrol. 2018, 559, 541–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Guan, M. Effects of Urban Drainage Inlet Layout on Surface Flood Dynamics and Discharge. J. Hydrol. 2024, 632, 130890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.-H.; Chang, T.-H.; Chen, W.-B. Effect of Inlet Modelling on Surface Drainage in Coupled Urban Flood Simulation. J. Hydrol. 2018, 562, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosco, C.; Gómez, M.; Russo, B.; Tellez-Alvarez, J.; Macchione, F.; Costabile, P.; Costanzo, C. Discharge Coefficients for Specific Grated Inlets. Influence of the Froude Number. Urban Water J. 2020, 17, 656–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobold, M.; Sušelj, K. Precipitation Forecasts and Their Uncertainty as Input into Hydrological Models. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2005, 9, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, Y.; Hsu, K.; Chang, F.-J.; Hong, Y.; Sorooshian, S. Merging Multiple Precipitation Sources for Flash Flood Forecasting. J. Hydrol. 2007, 340, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatone, F.; Szeląg, B.; Kiczko, A.; Majerek, D.; Majewska, M.; Drewnowski, J.; Łagód, G. Advanced Sensitivity Analysis of the Impact of the Temporal Distribution and Intensity of Rainfall on Hydrograph Parameters in Urban Catchments. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 25, 5493–5516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, L.; Zhang, T.; Kang, Y. Effect of DEM Data Sources and Resolutions on Watershed Flood Simulations. J. Hydroelectr. Eng. 2023, 42, 26–40. [Google Scholar]
- Pappenberger, F.; Bartholmes, J.; Thielen, J.; Cloke, H.L.; Buizza, R.; de Roo, A. New Dimensions in Early Flood Warning across the Globe Using Grand-Ensemble Weather Predictions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L10404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvello, M.; Finno, R.J. Selecting Parameters to Optimize in Model Calibration by Inverse Analysis. Comput. Geotech. 2004, 31, 410–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Wu, Z.; Liang, Q. Urban Flood Susceptibility Analysis Using a GIS-Based Multi-Criteria Analysis Framework. Nat. Hazards 2019, 97, 455–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, D.; Li, S.; Lai, Z. Effects of Extreme Precipitation Intensity and Duration on the Runoff and Nutrient Yields. J. Hydrol. 2023, 626, 130281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Rojas, J.L.; Moya-Alvarez, A.S.; Valdivia-Prado, J.M.; Piñas-Laura, M.; Kumar, S.; Abi Karam, H.; Villalobos-Puma, E.; Martínez-Castro, D.; Silva, Y. On the Dynamic Mechanisms of Intense Rainfall Events in the Central Andes of Peru, Mantaro Valley. Atmos. Res. 2021, 248, 105188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Sun, J.; Lin, B. A Large-Scale Waterlogging Investigation in a Megacity. Nat. Hazards 2022, 114, 1505–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Fu, Y.; Li, L. Spatiotemporal Variance Assessment of Urban Rainstorm Waterlogging Affected by Impervious Surface Expansion: A Case Study of Guangzhou, China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Nieto, J.; Lerner, D.; Saul, A.; Blanksby, J. GIS Water-Balance Approach to Support Surface Water Flood-Risk Management. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2012, 17, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Liu, Y.; Engel, B.A.; Chen, J.; Sun, H. Green Infrastructure Practices Simulation of the Impacts of Land Use on Surface Runoff: Case Study in Ecorse River Watershed, Michigan. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 233, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).