Classification of River Sediment Fractions in a River Segment including Shallow Water Areas Based on Aerial Images from Unmanned Aerial Vehicles with Convolution Neural Networks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
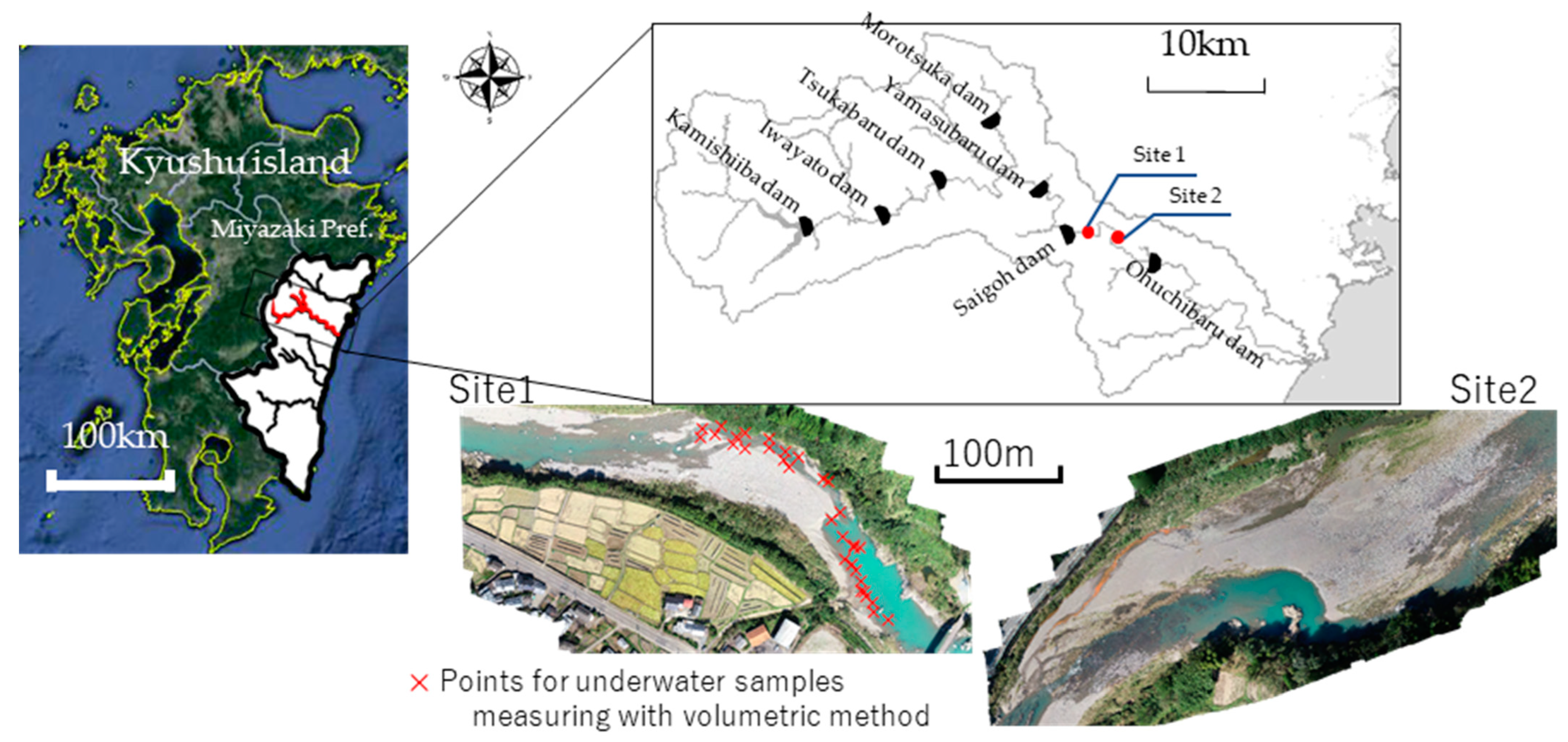
2.1. Study Area
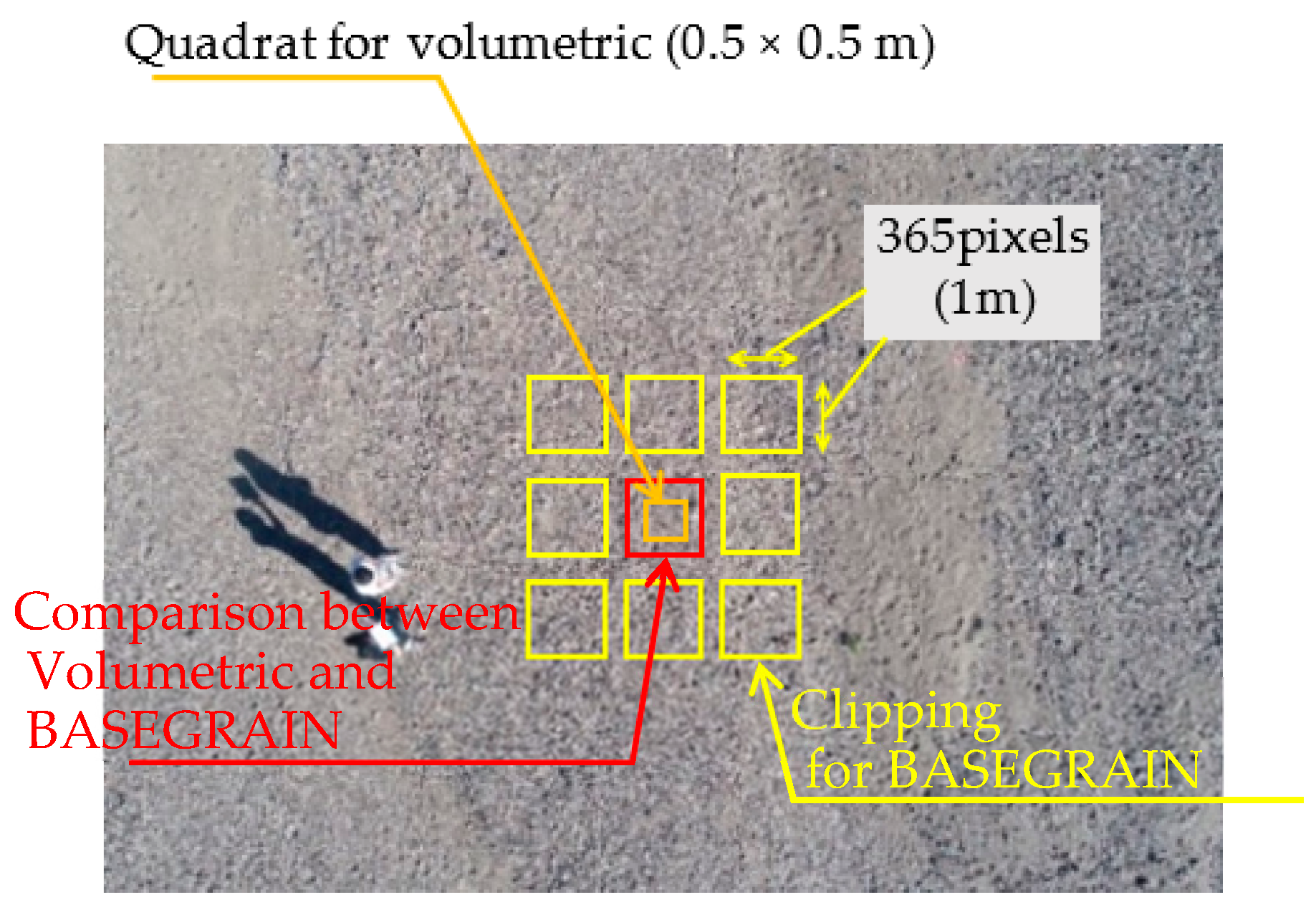
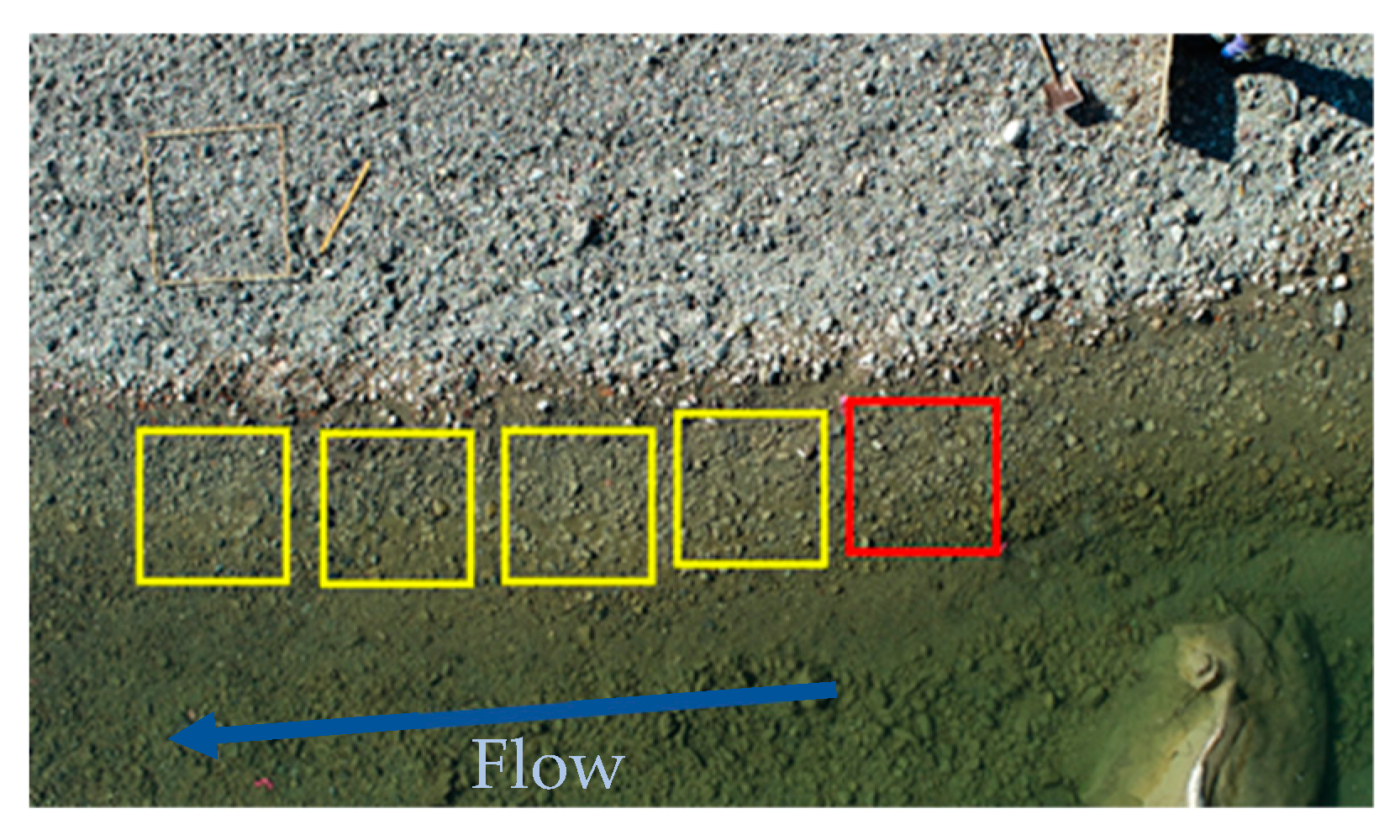
2.2. Aerial Photography and Sieving for Validation
2.3. Training and Test of the CNN
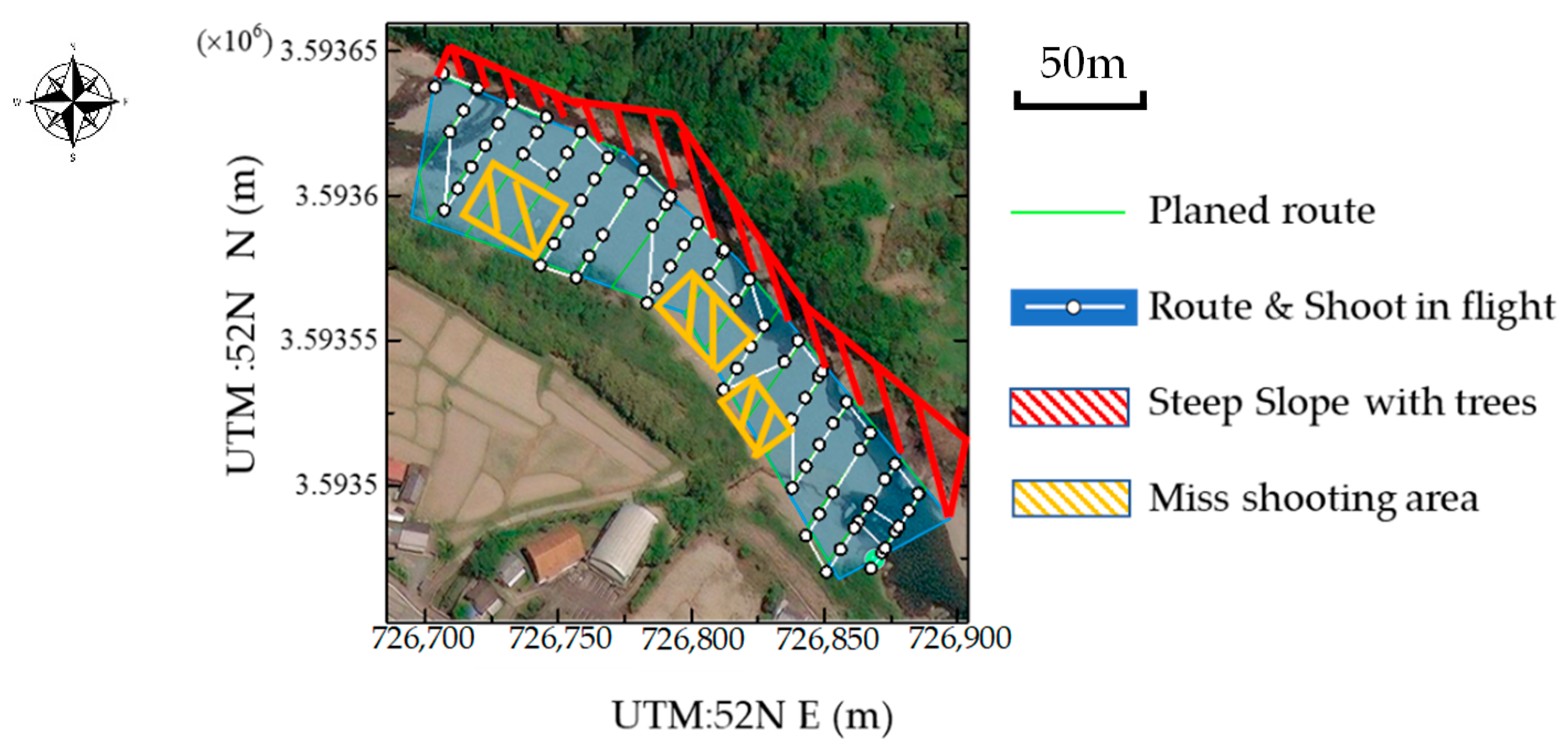
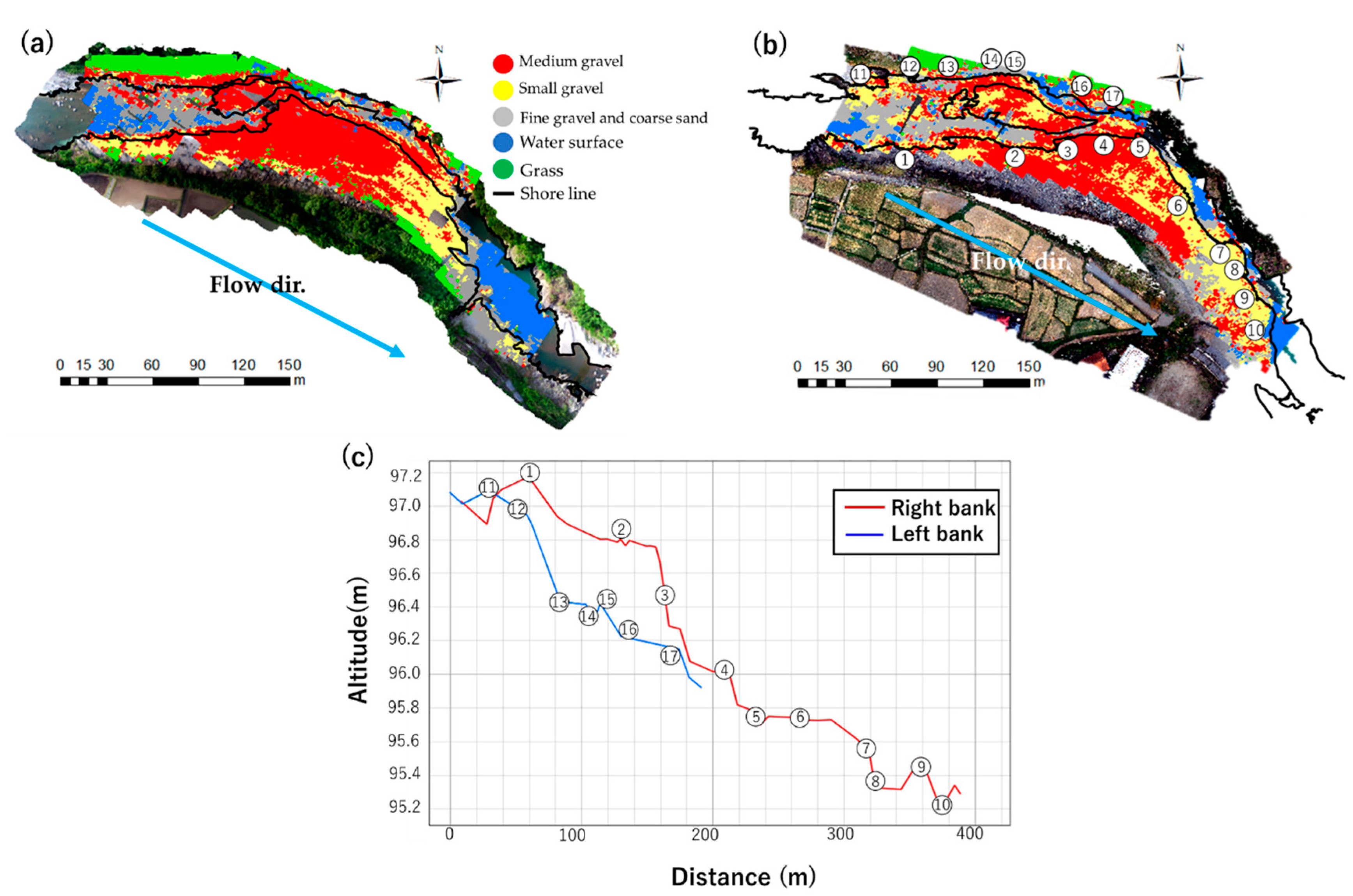
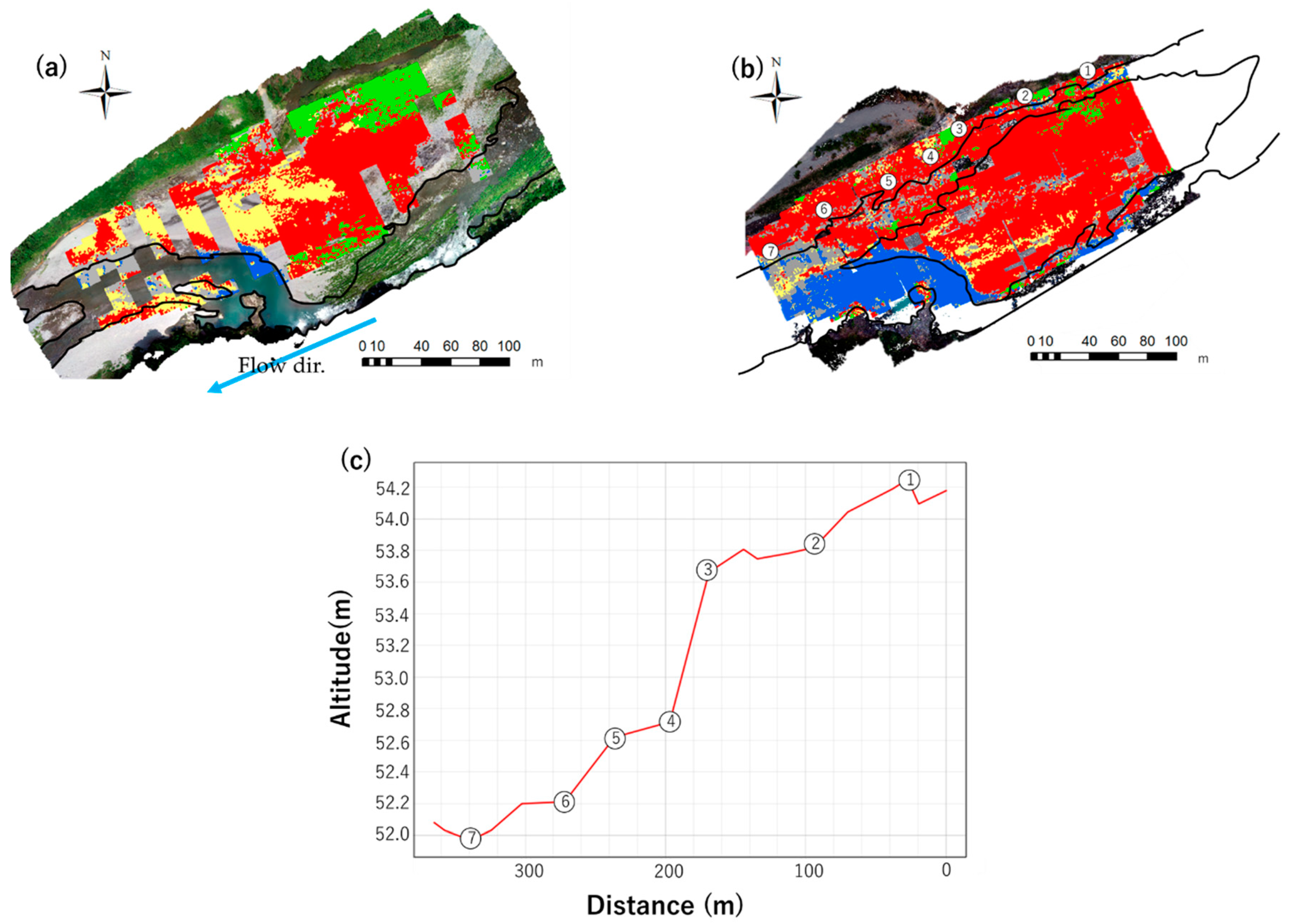
2.4. Projection of the Classification Results and Microtopographic Survey
3. Results
3.1. Classification of Terrestrial and Underwater Samples
3.2. Uniform Class Only for Class 3 of the Particle Size
4. Discussion
4.1. Reduction of the Error Factors using the Diversity of Training Data
4.2. Mapping of the Wide-Ranging Area
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- David, A.J.; Castillo, M.M. Stream Ecology: Structure and Function of Running Waters, 2nd ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 1–436. [Google Scholar]
- Alexandre, C.M.; Ferreira, T.F.; Almeida, P.R. Fish assemblages in non-regulated and regulated rivers from permanent and temporary Iberian systems. River Res. Appl. 2013, 29, 1042–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, D.; Merino-Aguirre, R.; Angeler, D.G. Benthic invertebrate communities in regulated Mediterranean streams and least-impacted tributaries. Limnologica 2013, 43, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eekhout, J.P.C.; Hoitink, A.J.F. Chute cutoff as a morphological response to stream reconstruction: The possible role of backwater. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 3339–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsubaki, R.; Baranya, S.; Muste, M.; Toda, Y. Spatio-temporal patterns of sediment particle movement on 2D and 3D bedforms. Exp. Fluids 2018, 59, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L. Drone-based photogrammetry for riverbed characteristics extraction and flood discharge modeling in Taiwan’s mountainous rivers. Measurement 2023, 220, 113386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Tsubaki, R.; Toda, Y. Effects of vegetation distribution along river transects on the morphology of a gravel bed braided river. Acta Geophys. 2023. online first. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, T.; Kimura, I.; Shimizu, Y. Responses of bed morphology to vegetation growth and flood discharge at a sharp river bend. Water 2018, 10, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunte, K.; Abt, S.R. Sampling Surface and Subsurface Particle-Size Distributions in Wadable Gravel- and Cobble-Bed Streams for Analyses in Sediment Transport, Hydraulics, and Streambed Monitoring; General Technical Report RMRS-GTR-74; U. S. Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 2001; pp. 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellerhals, R.; Bray, D. Sampling procedure for Coarse Fluvial Sediments. J. Hydraul. Div. ASCE 1971, 97, 1165–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detert, M.; Weitbrecht, V. Automatic object detection to analyze the geometry of gravel grains—A free stand-alone tool. In River Flow 2012; Muños, R.M., Ed.; Taylor & Francis Group: London, UK, 2012; pp. 595–600. [Google Scholar]
- Detert, M.; Weitbrecht, V. User guide to gravelometric image analysis by BASEGRAIN. In Advances in River Sediment Research; Taylor & Francis Group: London, UK, 2013; pp. 1789–1796. [Google Scholar]
- Harada, M.; Arakawa, T.; Ooi, T.; Suzuki, H.; Sawada, K. Development of bed topography survey technique by underwater imaging progress for UAV photogrammetry. Proc. River Eng. 2016, 22, 67–72. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Hirao, S.; Azumi, T.; Yoshimura, M.; Nishiguchi, Y.; Kawai, S. Fundamental study on grain size distribution of river bed surface by analyzing UAV photograph. Proc. River Eng. 2018, 24, 263–266. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogan, J.; Chen, D. Remote sensing technology for mapping, and monitoring land-cover and land-use change. Prog. Plan. 2004, 61, 301–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochizuki, S.; Murakami, T. Vegetation map using the object-oriented image classification with ensemble learning. J. Forest. Plan. 2013, 18, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mtibaa, S.; Irie, M. Land cover mapping in cropland dominated area using information on vegetation phenology and multi-seasonal Landsat 8 images. Euro-Mediterr. J. Environ. Integr. 2016, 1, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurya, K.; Mahajan, S.; Chaube, N. Remote sensing techniques: Mapping and monitoring of mangrove ecosystem—A review. Complex Intell. Syst. 2021, 7, 2797–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilcher, M.; Udelhoven, T. Field Geometry and the Spatial and Temporal Generalization of Crop Classification Algorithms—A randomized approach to compare pixel based and convolution based methods. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taravat, A.; Wagner, M.P.; Bonifacio, R.; Petit, D. Advanced Fully Convolutional Networks for Agricultural Field Boundary Detection. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeepGlobe CVPR 2018—Satellite Challenge. Available online: https://deepglobe.org (accessed on 10 October 2023).
- Golovanov, S.; Kurbanov, R.; Artamonov, A.; Davydow, A.; Nikolenko, S. Building Detection from Satellite Imagery Using a Composite Loss Function. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickenson, M.; Gueguen, L. Rotated Rectangles for Symbolized Building Footprint Extraction. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 215–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglovikov, V.I.; Seferbekov, S.; Buslaev, A.V.; Shvets, A. TernausNetV2: Fully Convolutional Network for Instance Segmentation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1806.00844. [Google Scholar]
- Buslaev, A.; Seferbekov, S.; Iglovikov, V.; Shvets, A. Fully Convolutional Network for Automatic Road Extraction from Satellite Imagery. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 1973–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costea, D.; Marcu, A.; Slusanschi, E.; Leordeanu, M. Roadmap Generation using a Multi-stage Ensemble of Deep Neural Networks with Smoothing-Based Optimization. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doshi, J. Residual Inception Skip Network for Binary Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Ehrlich, M.; Shah, S.; Davis, L.; Chellappa, R. Stacked U-Nets for Ground Material Segmentation in Remote Sensing Imagery. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samy, M.; Amer, K.; Eissa, K.; Shaker, M.; ElHelw, M. NU-Net: Deep Residual Wide Field of View Convolutional Neural Network for Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.; Li, C.; Shi, J. Dense Fusion Classmate Network for Land Cover Classification. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, U.; Chauhan, A.; Pai M, M.; Pai, R. DeepRivWidth: Deep learning based semantic segmentation approach for river identification and width measurement in SAR images of Coastal Karnataka. Comput. Geosci. 2021, 154, 104805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, F.; Boyd, D.; Ge, Y.; Foody, G.M.; Li, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, L.; Shang, C.; Li, X.; et al. Measuring River Wetted Width from Remotely Sensed Imagery at the Subpixel Scale with a Deep Convolutional Neural Network. Water Resour Res. 2019, 55, 5631–5649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nama, A.H.; Abbas, A.S.; Maatooq, J.S. Field and Satellite Images-Based Investigation of Rivers Morphological Aspects. Civ. Eng. J. 2022, 8, 1339–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamawaki, M.; Matsui, T.; Kawahara, M.; Yasumoto, Y.; Ueyama, K.; Kawazoe, Y.; Matsuda, K.; Hara, F. Study on enhancement of sandbar monitoring by deep learning -towards enhancement of management in Hojo-river. J. Jp. Soc. Civ. Eng. Ser. B2 2021, 77, I_511–I_516. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, T.S.; Marcato Junior, J.; Gonçalves, W.N.; Bressan, P.O.; Eltner, A.; Binder, F.; Singer, T. Deep learning applied to water segmentation. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2020, XLIII-B2-2020, 1189–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhadi, N.A.; Abdullah, A.F.; Bejo, S.K.; Mahadi, M.R.; Mijic, A. Deep Learning Semantic Segmentation for Water Level Estimation Using Surveillance Camera. Appl. Sci. 2020, 11, 9691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Fuentes, L.; Rossi, C.; Skinnemoen, H. River segmentation for flood monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data), Boston, MA, USA, 11–14 December 2017; pp. 3746–3749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, H.; Katayama, T.; Song, T.; Shimamoto, T. Semantic Segmentation of River Video for Efficient River Surveillance System. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Technical Conference on Circuits/Systems, Computers, and Communications (ITC-CSCC), Jeju, Republic of Korea, 25–28 June 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, R.; Li, J.; Chavez-Galaviz, J.; Mahmoudian, N. A Survey on the Deployability of Semantic Segmentation Networks for Fluvial Navigation. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision Workshops (WACVW), Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–7 January 2023; pp. 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Jin, J.; Wang, Y.; Fan, M.; Wang, N.; Zhang, Y. ICENETv2: A Fine-Grained River Ice Semantic Segmentation Network Based on UAV Images. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, B.; Pan, Y.; Lin, X.; Yang, K. Statistical Roughness Properties of the Bed Surface in Braided Rivers. Water 2022, 15, 2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piton, G.; Recking, A.; Le Coz, J.; Bellot, H.; Hauet, A.; Jodeau, M. Reconstructing depth-averaged open-channel flows using image velocimetry and photogrammetry. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 4164–4179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasington, J.; Vericat, D.; Rychkov, I. Modeling river bed morphology, roughness, and surface sedimentology using high resolution terrestrial laser scanning. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, W11519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenther, G.C.; Brooks, M.W.; Larocque, P.E. New capabilities of the ‘SHOALS’ airborne lidar bathymeter. Remote Sens. Environ. 2000, 73, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onaka, N.; Akamatsu, Y.; Mabu, S.; Inui, R.; Hanaoka, T. Development of a habitat prediction method for ruditapes philippinarum based on image analysis using deep learning. J. Jp. Soc. Civ. Eng. Ser. B1 2020, 76, I_1279–I_1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onaka, N.; Akamatsu, Y.; Koyama, A.; Inui, R.; Saito, M.; Mabu, S. Development of a sediment particle size prediction method for tidal flat based on image analysis using deep learning. J. Jp. Soc. Civ. Eng. Ser. B1 2022, 78, I_1117–I_1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedger, R.D.; Sundt-Hansen, L.; Foldvik, A. Evaluating the Suitability of Aerial Photo Surveys for Assessing Atlantic Salmon Habitat in Norway. NINA Report 2105. 2022. Available online: https://brage.nina.no/nina-xmlui/bitstream/handle/11250/2975990/ninarapport2105.pdf?sequence=5&isAllowed=y (accessed on 10 October 2023).
- Carbonneau, P.E.; Dugdale, S.J.; Breckon, T.P.; Dietrich, J.T.; Fonstad, M.A.; Miyamoto, H.; Woodget, A.S. Adopting deep learning methods for airborne RGB fluvial scene classification. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 251, 112107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casado, M.R.; Gonzalez, R.B.; Kriechbaumer, T.; Veal, A. Automated identification of river hydromorphological features using UAV high resolution aerial imagery. Sensors 2015, 15, 27969–27989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milan, D.J.; Heritage, G.L.; Large, A.R.G.; Entwistle, N.S. Mapping hydraulic biotopes using terrestrial laser scan data of water surface properties. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2010, 35, 918–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, L.R.; Legleiter, C.J.; Overstreet, B.T.; Bell, T.W.; Hannon, J. Assessing the potential for spectrally based remote sensing of salmon spawning locations. River Res. Appl. 2020, 36, 1618–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedger, R.D.; Gosselin, P. Automated fluvial hydromorphology mapping from airborne remote sensing. River Res. Appl. 2023, 39, 1889–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takechi, H.; Aragaki, S.; Irie, M. Differentiation of River Sediments Fractions in UAV Aerial Images by Convolution Neural Network. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nukazawa, K.; Shirasaka, K.; Kajiwara, S.; Saito, T.; Irie, M.; Suzuki, Y. Gradients of flow regulation shape community structures of stream fishes and insects within a catchment subject to typhoon events. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 748, 141398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, D.; Nakane, Y.; Kajiwara, S.; Sakada, K.; Nishimura, K.; Fukaike, M.; Honjo, T. Macrozoobenthos distribution after flood events offshore the Mimi River estuary, Japan. Plankton Benthos Res. 2022, 17, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, K.; Matsunaga, M.; Itakiyo, T.; Oishi, H.; Nukazawa, K.; Irie, M.; Suzuki, Y. Tracing sediment transport history using mineralogical fingerprinting in a river basin with dams utilizing sediment sluicing. Intl. J. Sediment Res. 2022, 38, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nukazawa, K.; Kajiwara, S.; Saito, T.; Suzuki, Y. Preliminary assessment of the impacts of sediment sluicing events on stream insects in the Mimi River. Jp Ecol. Eng. 2020, 145, 105726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumi, T.; Yoshimura, T.; Asazaki, K.; Kaku, M.; Kashiwai, J.; Sato, T. Retrofitting and change in operation of cascade dams to facilitate sediment sluicing in the Mimikawa river basin. In Proceedings of the 25th Congress of International Commission on Large Dams, Stavanger, Norway, 14–20 June 2015; Volume Q99-R45, pp. 597–616. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura, T.; Shinya, H. Environmental impact assessment plan due to sediment sluicing at dams along Mimikawa river system. J. Disaster Res. 2018, 13, 709–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landwehr, T.; Kantoush, S.A.; Pahl-Wostl, C.; Sumi, T.; Irie, M. The effect of optimism bias and governmental action on siltation management within Japanese reservoirs surveyed via artificial neural network. Big Earth Data 2020, 4, 68–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Technical Standards for River Erosion Control—Research Version-4. Available online: https://www.mlit.go.jp/river/shishin_guideline/gijutsu/gijutsukijunn/chousa/ (accessed on 15 December 2023).
- Wentworth, C.K. A scale of grade and class terms for clastic sediments. J. Geol. 1922, 30, 377–392. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/30063207 (accessed on 15 December 2023). [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS’12), Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 3–6 December 2012; pp. 1097–1105. [Google Scholar]
- ImageNet Website. Available online: http://image-net.org/ (accessed on 28 September 2023).
- Zamir, A.R.; Sax, A.; Shen, W.; Guibas, L.; Malik, J.; Savarese, S. Taskonomy: Disentangling Task Transfer Learning. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 3712–3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newson, M.D.; Newson, C.L. Geomorphology, ecology and river channel habitat: Mesoscale approaches to basin-scale challenges. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2000, 24, 195–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
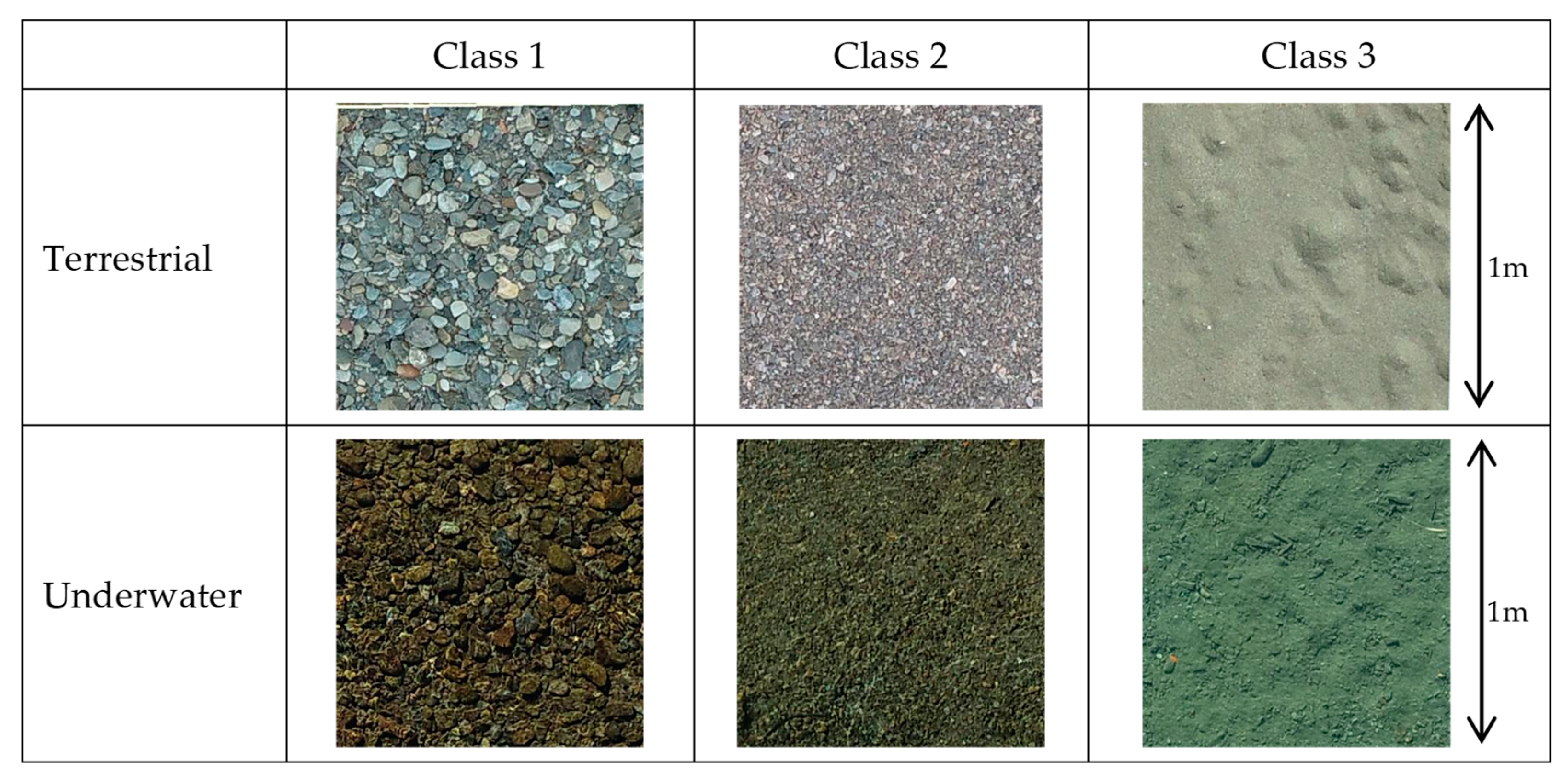




| Classification | Particle Size (mm) | Classification Name in This Study |
|---|---|---|
| Medium gravel | 64–24.5 | Class 1 |
| Small gravel | 24.5–2 | Class 2 |
| Fine gravel and coarse sand | 2> | Class 3 |
| Class 1 | Class 2 | Class 3 | Recall | F-Score | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class 1 | 67 | 8 | 0 | 89.3% | 86.4% |
| Class 2 | 13 | 58 | 18 | 65.2% | 70.3% |
| Class 3 | 0 | 10 | 22 | 68.8% | 61.1% |
| Precision | 83.8% | 76.3% | 55.0% | ||
| Micro Prec. | 75.0% | ||||
| Macro Prec. | 71.7% | ||||
| Micro Recall | 75.0% | ||||
| Macro Recall | 74.4% | ||||
| Overall Acc. | 75.0% | ||||
| Average Acc. | 71.7% | ||||
| Terrestrial | Underwater | Recall | F-Score | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class 1 | Class 2 | Class 3 | Class 1 | Class 2 | Class 3 | |||
| Class 1 | 56 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100.0% | 62.9% |
| Class 2 | 16 | 122 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 85.9% | 92.4% |
| Class 3 | 50 | 0 | 58 | 80 | 65 | 19 | 21.3% | 35.0% |
| Class 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | - |
| Class 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | - |
| Class 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 19 | 76.0% | 58.5% |
| Precision | 45.9% | 100.0% | 98.3% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 47.5% | ||
| Micro Prec. | 51.5% | |||||||
| Macro Prec. | 48.6% | |||||||
| Micro Recall | 51.5% | |||||||
| Macro Recall | 69.1% | |||||||
| Overall Acc. | 51.5% | |||||||
| Average Acc. | 48.6% | |||||||
| Terrestrial | Underwater | Both | Recall | F-Score | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class 1 | Class 2 | Class 1 | Class 2 | Class 3 | |||
| Class 1 | 113 | 6 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 94.2% | 93.3% |
| Class 2 | 5 | 115 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 92.0% | 93.1% |
| Class 1 | 4 | 1 | 78 | 18 | 11 | 69.6% | 81.2% |
| Class 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 48 | 12 | 78.7% | 68.1% |
| Class 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 11 | 94 | 88.7% | 83.1% |
| Precision | 92.6% | 94.3% | 97.5% | 60.0% | 78.3% | ||
| Micro Prec. | 85.5% | ||||||
| Macro Prec. | 84.5% | ||||||
| Micro Recall | 85.5% | ||||||
| Macro Recall | 84.5% | ||||||
| Overall Acc. | 85.5% | ||||||
| Average Acc. | 84.6% | ||||||
| Class 1 | Class 2 | Class 3 | Deep Pool | Grass | Recall | F-Score | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class 1 | 134 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 99.3% | 93.7% |
| Class 2 | 16 | 144 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 88.9% | 88.3% |
| Class 3 | 1 | 17 | 56 | 2 | 0 | 73.7% | 81.2% |
| Deep Pool | 0 | 2 | 5 | 73 | 0 | 91.3% | 93.6% |
| Grass | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 80 | 100% | 100% |
| Precision | 88.7% | 87.8% | 90.3% | 96.1% | 100% | ||
| Overall Acc. | 91.3% | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Irie, M.; Arakaki, S.; Suto, T.; Umino, T. Classification of River Sediment Fractions in a River Segment including Shallow Water Areas Based on Aerial Images from Unmanned Aerial Vehicles with Convolution Neural Networks. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16010173
Irie M, Arakaki S, Suto T, Umino T. Classification of River Sediment Fractions in a River Segment including Shallow Water Areas Based on Aerial Images from Unmanned Aerial Vehicles with Convolution Neural Networks. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(1):173. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16010173
Chicago/Turabian StyleIrie, Mitsuteru, Shunsuke Arakaki, Tomoki Suto, and Takuto Umino. 2024. "Classification of River Sediment Fractions in a River Segment including Shallow Water Areas Based on Aerial Images from Unmanned Aerial Vehicles with Convolution Neural Networks" Remote Sensing 16, no. 1: 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16010173
APA StyleIrie, M., Arakaki, S., Suto, T., & Umino, T. (2024). Classification of River Sediment Fractions in a River Segment including Shallow Water Areas Based on Aerial Images from Unmanned Aerial Vehicles with Convolution Neural Networks. Remote Sensing, 16(1), 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16010173







