Abstract
This paper highlights the advantages of an affordable multi-wavelength ground-based camera, called WaltRCam, for monitoring Aerosol Optical Depth (AOD) in a clear case over a peri-urban area. To simulate the performance of this low-cost camera, for which data are not yet available, we use data from an expensive hyperspectral camera (HSI) to mimic its characteristics. Our methodology is based on the construction of look-up tables using the DART (Discrete Anisotropic Radiative Transfer) 3D radiative transfer model. DART simulates the different spectra observed by the WaltRCam camera, which then provides the AODs for all image pixels in near-real-time. Moreover, DART is coupled to a 3D scale-model of the city of Toulouse (dating from 2014) to model complex urban geometries and to associate specific optical properties to the various objects that make up the environment. Moreover, we use a neural-network-based method to recognize the various objects in the image in order to take into account only pixels common between the observations. In this way, we take account of changes to the peri-urban area, such as vegetation growth, construction, demolition of buildings, etc. The results of this study show that the WaltRCam camera, by capturing eight wavelengths, can deliver convincing results compared with ground and satellite reference data, with a correlation coefficient of 0.9 and an average RMSE of less than 0.02.
1. Introduction
Air quality monitoring is usually carried out by in situ sensors, for which the performance is very high but that cover a small surface area [1]. Moreover, air quality regulatory monitoring relies on a small number of costly stations. Although numerical models can partly compensate for these limitations, they are often insufficiently constrained by actual observations, which can lead to inaccurate estimates [2,3,4]. The deployment of observation stations on a large-scale is not economically viable. In a first approach, this paper focuses on measuring the aerosol optical depth (AOD), which will allow the estimation of PM2.5 and PM10 (i.e., particles with a diameter smaller than 2.5 and 10 μm, respectively) in the future. Aerosols are tiny organic or inorganic chemical particles. They are composed of airborne liquid and solid particles with sizes ranging from a few nanometers to tens of micrometers, and they can originate from natural or anthropogenic sources [5]. Aerosols scatter and absorb solar radiation and have a significant impact on climate change, air pollution, visibility, and the ecological environment [6,7]. AOD provides a measure of columnar aerosol loading and can be obtained from either ground or space remote-sensing observations (e.g., [8]). Fine particles have a strong impact on human health, particularly during pollution peaks, and they can cause cardiovascular and pulmonary diseases as well as affect the central nervous system and cause cancer [9,10,11,12].
Spectral cameras are increasingly being used to monitor AODs and PMs. They are widely used onboard sun-synchronous satellite platforms such as Terra with MODIS (Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) [13] and PARASOL with POLDER (POlarization and Directionality of the Earth’s Reflectance) [14] instruments and onboard geostationary platforms such as MSG (Meteosat second generation) with SEVIRI (Spinning Enhanced Visible and Infra-Red Imager) [15]. At the surface, Chi-Wen Chen et al. (2020) [16] used hyperspectral imaging (HSI) to measure PM2.5 and PM10 concentrations. They used the spectral intensity of solar radiation and applied Beer–Lambert’s law as well as multivariate regression analysis to calculate these concentrations. Elcoroaristizabal et al. (2021) [17] proposed a tool for quantifying atmospheric carbonaceous aerosols in near-infrared using a camera with 288 wavelengths. However, most of these spectral cameras are not affordable for the majority of cities for hourly air quality measurements.
The aim of our work is to investigate the possibility of increasing the number of observations by using an affordable ground-based multi-wavelength camera placed at a strategic location on high ground to enable real-time air quality observations over a vast urban or peri-urban area. In this study, we focus on measuring the vertical aerosol optical depth over such an area during a nearly aerosol-free case. This is a first step before quantifying more-polluted events and evaluating particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10) in a future work.
To study this, we simulate, via hyperspectral images, the future low-cost multi-wavelength camera designed by the WaltR company, called hereafter WaltRCam, to obtain AOD information. We use a HySpex hyperspectral imager from Norsk Elektro Optikk [18] composed of 160 wavelengths (expensive equipment unreasonable for cities to afford on a large scale) to simulate the low-cost WaltRCam. We degraded the HySpex hyperspectral image to obtain an image composed of eight spectral bands with added noise: similar to the characteristics of the low-cost camera currently under development.
The goal with the simulated image is to measure the vertical AOD in near-real-time in the atmosphere as captured by the camera. To do this, we use the DART (Discrete Anisotropic Radiative Transfer) radiative transfer model, which is capable of taking into account the three-dimensional (3D) geometry of the urban area. Differently from SmartG [19] and ARTDECO [20] radiative transfer models, which assume a flat land surface, DART incorporates a 3D scale-model of the urban scene [21,22,23]. However, as peri-urban scenes are constantly evolving (due to changes in vegetation and/or buildings), and because 3D scale-models are costly to update, it is essential to remove any inconsistencies between the real and simulated images. Inconsistent areas are removed using a spectral classification method optimized for spatially coherent measurements using a neural network, which is fast in terms of computation time. Moreover, we set up a look-up table (LUT) generated with DART that associates each AOD value with the radiance measured at the camera. This approach allows us to pre-calculate radiances as a function of various AOD levels, which offers the advantage of generating near-real-time results. The AODs are then compared to AERONET (AErosol RObotic NETwork) [24] and MODIS (Moderate-Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) [13] observations to assess the quality and the added value of such camera observations.
We have organized the paper as follows: Section 2 presents a description of the multi-wavelength ground camera as well as the validation data. Section 3 presents the methods to estimate the AOD from the different images, including the processing chain, the DART radiative transfer model, and the LUT we used. Section 4 focuses on the presentation of our results. In particular, we highlight the AOD values we obtained and evaluate these results by comparing AODs from the camera with observations from AERONET and MODIS. Finally, conclusions are drawn and future work is considered.
2. Data
2.1. Camera Observation
To demonstrate that a multi-wavelength camera can monitor the AOD in near-real-time over a wider surface area compared to current measurement sensors, we simulate a dataset from the future WaltRCam using data from an HSI camera (HySpex). The high quality of the HySpex data is degraded by selecting only a few wavelengths and by adding random noise on the spectrum to match the characteristics of the WaltRCam. This much cheaper camera is still under development and should be deployed in a few months over the urban area of Toulouse in the south of France.
2.1.1. The HySpex Camera
The data we used are based on the hyperspectral acquisition system from the HySpex VNIR 1600 camera [25] developed by Norsk Elektro Optikk [18]. This upmarket camera was provided by the Office National d’Études et de Recherches Aérospatiales (ONERA) in Toulouse. It offers extensive, high-resolution spectral coverage, encompassing both the visible and short-wave infra-red (SWIR) spectra. This hyperspectral camera has a spectral resolution of 3 to 4 nm with 160 spectral bands. It measures radiances, i.e., light intensity per unit area in Wmsrnm, for all wavelengths. The main characteristics of the sensor are summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
Specifications of the HySpex VNIR-1600 camera [25,26].
This camera captures the scene line-by-line using a scanning method called pushbroom [27]. It scans the scene by collecting adjacent line slices to form a hyperspectral image consisting of a stack of 160 monochromatic images captured at a specific wavelength. The camera is positioned on a mechanical rotation bracket to capture a panoramic image about 130 degrees wide. For our study, the camera was positioned on 30 June 2020 at a strategic high point at the top of the Pech David belvedere in Toulouse in order to see a wide part of the city center and its southwest and western suburbs. The coordinates of the camera location are: latitude 43.5587; longitude 1.4465 at an altitude of 264 m. The weather conditions at the time of this occurrence were favorable, with a cloud-free day and a temperature between 18 and 25 °C. Wind strength fluctuated between 7 and 11 km·h. Visibility during the day was fairly stable, varying between 20 and 25 km [28], offering favorable conditions for clear-sky observations. The meteorological parameters presented ideal conditions for a nearly aerosol-free case.
2.1.2. The WaltRCam
The WaltRCam camera was designed by the WaltR company [29] in Toulouse. The camera is cheap, which makes it an ideal affordable tool for equipping large monitored areas such as cities and thus increasing the accuracy of air quality measurements. The price is approximately ten thousand euros, compared to several hundred thousand euros for a HySpex. This camera is designed to offer precise cost-effective measurement capabilities in the UV–visible spectral range at 11 wavelengths (300, 310, 330, 392, 460, 560, 610, 671, 780, 870, and 940 nm). The spectral bands have been carefully selected for measuring gases such as ozone and oxygen (300 to 392 and 940 nm, respectively) and aerosols (460 to 870 nm).
WaltRCam’s spectral acquisition system is based on filter wheel spectral scanning [30]. A motorized wheel made up of 11 interference filters is placed in front of the camera sensor. Each filter lets through a portion of the light radiation at a given wavelength. The camera builds a hyperspectral cube by acquiring monochromatic images. Each acquisition is an image of the scene taken at a given wavelength, and the collection of all hyperspectral image data corresponds to a complete revolution of the wheel. As this camera is still under development, we have simulated WaltRCam images by capturing HySpex wavelengths as close as possible to those of the WaltRCam: 414, 458, 560, 611, 672, 778, 870, and 938 nm. A full WaltRCam image is a composition of 30 smaller images (2048 × 2048 pixels) with a total definition of 61440 × 4096, which corresponds to a 220 degree panoramic view. The field of view (FOV) is degrees, and the pixel size is 6.6 m (slightly finer compared with the 24 m for a HySpex camera). The spectral width is identical on both cameras. Note that color images in the following article are obtained by using the 414, 560, and 672 nm wavelengths. Evaluation of the radiometric error of the WaltRCam has been carried out, and the tests in the laboratory have shown a maximum error of 6%. In this study, we use 10% in our simulation to avoid overestimating the results. Therefore, to mimic the noise of the WaltRCam compared to the HySpex camera, we have perturbed the spectra by adding 10% random noise. We have used the normal law centered around 0 with a standard deviation of 0.1. In this study, we have simulated WaltRCam images from HySpex images taken on 30 June 2020 at four different moments in the day (9:55, 11:02, 12:34, and 14:04 local time (LT), corresponding to UTC + 2).
2.2. Validation Data
To evaluate the WaltRCam AOD obtained with our methodology, which we present in the next section, we used the coincident AERONET ground-based and MODIS satellite observations.
2.2.1. AERONET
The AERONET network is a worldwide network of photometers measuring the optical and microphysical properties of aerosols from the ground: both on land and at sea [31]. The network is equipped exclusively with CIMEL sun photometers that measure incident radiation at eight wavelengths: 340, 380, 440, 500, 672, 870, 1020, and 1640 nm. For each wavelength, the AOD measured by the sun photometer has an accuracy between 0.01 and 0.02 [32], and the AOD at 550 nm is interpolated using the AODs at 440 and 672 nm to specifically compare with the MODIS AOD product. Hundreds of AERONET stations around the world produce continuous measurements (when weather and light conditions are sufficient). We used version 3.0 level 2.0 AERONET data from the Toulouse_MF station located at the Météo-France site in the suburbs of Toulouse. The data are available from http://aeronet.gsfc.nasa.gov/ (accessed on 27 December 2023). This data source is considered as the reference in terms of AOD validation [33,34].
2.2.2. MODIS
In our study, we use data acquired by the MODIS instrument, which was launched by NASA in 1999 onboard the Terra platform. This satellite is in a sun-synchronous orbit and is part of the Earth Observing System (EOS) program [35]. MODIS monitors ambient aerosol loading and selected aerosol properties over snow, ice-free land, and ocean surfaces. We use the AOD product at a wavelength of 550 nm obtained by the Dark Target (DT) algorithm used for the retrieval of the AOD [36]. The products are supplied with a horizontal (nadir) spatial resolution (pixel size) of 3 km × 3 km and a temporal resolution of 1 or 2 days. The quality of the MODIS data we use follows the recommendations of the MODIS aerosol team for quantitative analyses (Levy et al., 2013) [37]. Data on 30 June 2020 at 12:45 LT are available as a file (M*D04_3K) and can be downloaded from http://ladsweb.nascom.nasa.gov (accessed on 27 December 2023).
3. Methodology
3.1. Processing Chain
Figure 1 shows the different stages in the processing chain to obtain the AOD from the camera positioned on the ground. First, the experimental data obtained by WaltRCam are simulated using degraded HySpex data. Then, pixel classification is performed on this simulation in order to identify the class of each pixel (building, vegetation, etc.). The result is then compared to the image generated from a 3D scale-model for which each pixel class is also known. Then, colocated pixels for which the classes are different in the two images are removed using a similarity matrix. The DART radiative transfer model is configured with a given set of atmospheric characteristics and optical surface properties within the 3D environment described in the scale-model (called hereafter the Toulouse scale-model). DART allows us to build look-up tables (LUTs) based on different AOD values. The final step is to select the LUT that best represents the WaltRCam image and enables us to deduce the AOD. This section describes these steps in detail.
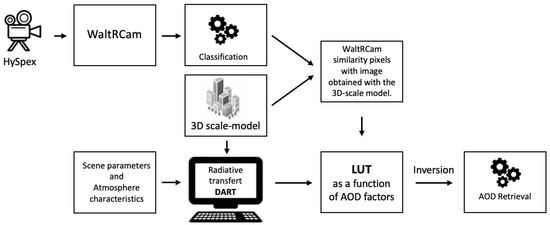
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the AOD calculation method. The WaltRCam image extracted from an HSI is compared with the image obtained from the 3D scale-model. This comparison includes a classification step in which pixels from non-identical classes are discarded. Radiative transfer is used to generate LUTs according to an AOD factor. After selecting the LUT with the radiance closest to that of WaltRCam, we estimate the AOD corresponding to the entire image.
3.2. The Toulouse 3D Scale-Model
3.2.1. Description
In this work, we use a Toulouse 3D scale-model, which was released in 2014 and that incorporates the topographical features of the terrain covering an area of 110 km. This scale-model has an accurate representation of the terrain (1 m resolution) of the greater Toulouse area. The camera was positioned in the model in the same location and at the same height (264 m) as the HySpex camera (on top of Pech David hill) to offer an ideal view of a vast peri-urban area. Note that the lowest point of the Toulouse 3D scale-model is at the altitude of 150 m.
The scale-model is composed of 28 objects: each defined by specific attributes such as form, size, location, and orientation in space (slate, slate-specific building, concrete, bitumen, wood, wood-specific building, brick, capitol, stairs, facade, hydro, metal, wall, marble, stone, stone-specific building, soil, soil-specific building, talus, terrace, roof, tile roof, zinc roof, sidewalk, vegetation, glass, and glass capitol). Each object is also of a class that has specific optical properties: the classes used in this study are trunk, leaves, grass, roof-tiles, building, and sky.
3.2.2. Camera Position Settings
The WaltRCam was positioned virtually in the Toulouse 3D scale-model in the same position as the HySpex camera using Blender 3D visualization software [38]. The technical characteristics of the camera, such as spatial and spectral resolution, sensitivity, FOV, focal length, and precise orientation of the sensor on a 3D axis, were also defined. The camera orientation is defined according to three axes—x (horizontal plane), y (rotation of the image), and z (vertical plane)—allowing great flexibility for capturing images at different angles and orientations. To obtain the position that best matches the scene captured by the camera, we calculated the Pearson correlation coefficient between the WaltRCam image and the image generated from the 3D scale-model, taking into account different configurations for the axes of the camera orientation. We selected the orientation configuration with the highest correlation coefficient, which indicates the best match between the scene observed and the 3D model view. This approach enables the camera orientation to be fine-tuned to maximize the similarities between the images. As a result, the 3D image of the field of study obtained corresponds exactly to the image measured from the WaltRCam. Each pixel in this image has a class that is provided by the 3D scale-model. Each object class is then assigned a surface reflectance according to the predominant material of which it is composed (see Section 3.4.1).
3.3. WaltRCam Object Classification
Due to the constant evolution of urban scenes, i.e., construction or demolition of buildings and changes to vegetation, and also due to the scarcity of Toulouse 3D scale-model updates, it is crucial to discard pixels that have a different class between the scale-model and the WaltRCam images. A pixel with a different class has different optical properties, resulting in bias when applying radiative transfer. In order to reduce this bias as much as possible, we removed pixels that do not correspond to the same class. To do this, we performed a classification on the WaltRCam image. This classification aims to assign a class to each pixel in the image, which is compared with the pixel class in the scale-model image. We used a method based on neural networks for automatic detection of the class of each pixel using a spectral and spatial pixel-by-pixel classification called SOC (Spatial and Spectral Optimized Classification; for more details, see [39]). Object detection approaches such as convolutional neural networks are very effective at detecting one or more objects [40] but cannot classify all the pixels in an image. The classification methods usually used for this type of problem, such as support-vector machine (SVM) and random forest, treat each pixel independently by analyzing only the spectral properties [41] but without considering the correlations between spatially adjacent pixels. However, neglecting the notion of neighborhoods (spatial dimensions) in classification can lead to situations for which the classes obtained are not spatially coherent [42]. Morphological profiles [43] have been used for this type of task, but they are very time-consuming [44], which is a major drawback for applications requiring fast, near-real-time results on large datasets. SOC using a neural network was optimized for this type of problem and is as fast as possible in terms of computation time. In the Toulouse 3D scale-model, an image is composed of six different classes: trunk, leaves, grass, roof, building, and sky. Differently, in the WaltRCam image, we have identified five classes: namely, vegetation (grouping together trunk, wood, and leaf), roof, building, horizon (distant pixels that are more difficult to identify), and sky. A subset of pixels was manually labeled (10,000 pixels) based on the classes identified for training (80% of the labeled pixels) and testing (20%) machine learning algorithms. Similar proportions of pixels for each class were labeled to limit possible errors or biases when training the neural network. We found a classification accuracy of about 99%. Figure 2 presents the classification strategy.
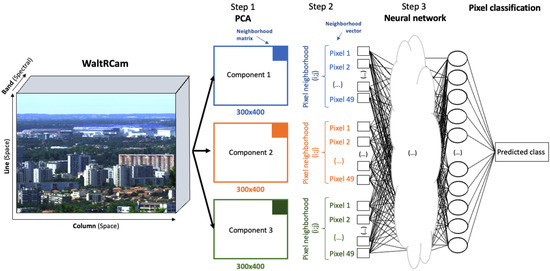
Figure 2.
Diagram showing the spatial and spectral optimized classification (SOC) strategy. Step 1 consists of applying a principal components analysis (PCA) on the original image to reduce its dimensionality. Step 2 consists of selecting a neighborhood matrix to include spatial features and obtain the neighborhood vector. Step 3 is the application of the neural network using the vector from Step 2. The neural network output values give the predicted classes.
3.4. The DART Model
The DART radiative transfer model has been being developed by CESBIO (Centre d’Etudes Spatiales de la Biosphère) since 1992 [45]. It simulates the interaction of light (electromagnetic radiation) with the atmosphere, clouds, aerosols, and land surfaces in three dimensions over a spectral range of about 0.25 m to 100 m (UV, VIS, and TIR) [21,22,23]. DART simulates the propagation of light beams (photons). Here, we use its Monte Carlo approach [46]. In addition to the 3D radiation budget, DART simulates spaceborne remote sensing images in terms of spectral reflectance and brightness temperature at any altitude. From the bottom of the atmosphere (BOA) to the top of atmosphere (TOA), it is possible to sense the atmosphere in any direction. The images are simulated for any experimental configuration (solar direction, state of the atmosphere, and optical and geometric properties of the environment) and instrument characteristics (fine or broad spectral band, spatial resolution, viewing direction, spectral sensitivity of the sensor, etc.). In DART, the gaseous atmosphere is defined by its optical scattering thickness, by the Rayleigh phase function, and by the vertical density and optical absorption thickness of the major gases (, , , , , , and ). Aerosols are defined by an optical depth, a 1D density profile, a single-scattering spectral albedo, and the combination of two Henyey–Greenstein phase functions. All atmospheric characteristics are defined in Section 3.4. Unlike radiative transfer models such as SmartG [19] or ARTDECO [20], which use scenes with surfaces assumed to be flat, DART has the advantage of simulating three-dimensional scenes, which takes into account the complex geometry of objects present in a city, such as natural elements (trees, crops, rivers, etc.) and urban elements (houses, roads, etc.). Each element in the scene is characterized by its geographical shape and is categorized according to different classes, which enables a surface reflectance property to be attributed to each object present in the scene.
3.4.1. Scene Parameters
The Toulouse 3D scale-model represents the landscape used within DART to calculate the radiative transfer in the simulation. As already described in Section 3.2, each object class is then assigned a surface reflectance according to the predominant material of which it is composed. DART offers a selection of around fifty surface reflectance spectra [47,48,49,50], each corresponding to a different material. Note that the sky class is not considered an object in the 3D scale-model and thus has no surface properties. The selections made for our simulation is summarized in Table 2 considering the surface reflectances we used in the DART model. The building class does not exist in the DART model; we assign a surface reflectance of 40% to buildings, which is an average value of granite surface reflectance in the wavelength range from 414 to 870 nm. The difficulty with finding the surface reflectance of buildings composed of different elements (windows, concrete white or pink wall, balconies, etc.) likely introduces some uncertainties in the surface reflectance of the buildings and then in the calculation of the spectrum. All the other surface reflectances are provided by the DART model.

Table 2.
Surface reflectance (in %) of the object’s class in DART for the different wavelengths (in nm).
DART calculates solar angles based on the date recorded in the Gregorian calendar; it takes into account the year, month, day, hour, minute, and second as well as the model’s geographical position, including latitude, longitude, and altitude. These calculations are carried out using equations and models established by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) [51]. The surface temperatures were recorded on the day of the experiment by the Météo France in situ ground station located close to the study site. Table 3 shows the DART input parameters.

Table 3.
Solar angles (in degrees) and surface temperatures (K) for the 4 different LTs on 30 June 2020.
3.4.2. Atmosphere Characteristics
For the chemical composition of the atmosphere, we use the USSTD76 (U.S. Standard Atmosphere Model, see [52]) gas profiles from the MODTRAN radiative transfer model. The DART gas profiles are defined by their optical scattering thickness, by the Rayleigh phase function, and by the vertical density and optical absorption thickness of the major gases. In the spectral range considered in this study (400–900 nm), gas absorption (even ) plays a minor role in the absorption of radiation. We can only note there is a small contribution from the ozone () absorption band between 550 and 650 nm.
In addition, we selected RURALV23 from the DART database for the aerosol characteristics derived from the MODTRAN model [53]. In this database, the aerosols are defined by a 1D density profile, an aerosol optical depth, a simple-scattering spectral albedo, and the combination of two Henyey–Greenstein phase functions [53]. This database corresponds as best as possible to the characteristics of the peri-urban conditions of the experiment period with a visibility of 23 km, which is comparable to that of our study day.
3.5. AOD Retrieval
The AOD in the DART model can be modified either by importing a vertical profile of an aerosol extinction coefficient or by scaling the spectral AOD by a multiplicative factor (called hereafter the AOD factor). Here, we adopted the convenient latter approach. For example, an AOD factor k = 1 corresponds to the default spectral AOD value of the atmosphere selected in DART, i.e., RURALV23. The AOD values for this atmosphere are 0.42, 0.38, 0.31, 0.28, 0.25, 0.20, 0.17, and 0.15 for wavelengths 414, 458, 560, 611, 672, 778, 870, and 938 nm, respectively. The scaled AOD is calculated as follows:
where is the initial AOD value of the RURALV23 atmosphere for the wavelength , and k is the AOD factor. Figure 3 shows the radiance look-up tables as a function of wavelength for two AOD factors (0 and 0.5) and the WaltRCam’s corresponding radiance averaged for the entire image. The LUT clearly shows similar behavior and delineates the range of the WaltRCam values (represented in blue).
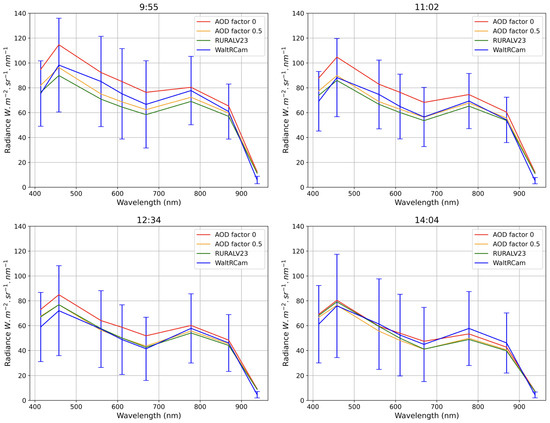
Figure 3.
Example of average spectra obtained from the LUT and WaltRCam for the entire image. A factor k = 1 corresponds to the default AOD of the atmosphere selected in DART, i.e., RURALV23 (green curve). A factor k = 0.5 indicates a 50% reduction in the default optical depth spectrum (orange curve). The red curve corresponds to an AOD factor = 0. The WaltRCam spectrum (blue curve) represents the average radiance and its associated standard deviation (blue vertical lines). The optimum multiplicative AOD factor leads to the closest spectrum compared to the WaltRCam spectrum.
For each pixel, we obtain the corresponding spectrum by changing the AOD factor from 0 to 2.5 with a step of 0.1, which leads to AOD values from 0 to 1, respectively. This provides the correspondence between the vertical AOD over the scene covered by DART and the radiance measured at the WaltRCam. This look-up table takes into account all the 3D parameters such as the different angles (angle of incidence on each 3D object) as well as the surface reflectance of the classes in the image.
In addition, to improve the accuracy, we added 10 more spectra between each two calculated spectra by performing a linear interpolation on both the calculated spectra and the corresponding AOD factor (e.g., [54]). Each pixel in the image therefore has 200 spectra that differ by their AOD multiplicative factor. Each pixel in the simulated image corresponds exactly to the pixels observed using the inconsistency image (Section 3.3). Each pixel of the WaltRCam image is associated with the value of the AOD factor that corresponds to the calculated radiance spectrum closest to the WaltRCam radiance spectrum and then to the DART vertical AOD. This correspondence is done when the normalized root-mean-square error (nRMSE) between the WaltRCam spectrum and the LUT spectrum for the different wavelengths is lowest and there is maximum correlation. The RMSE, nRMSE, and correlation are defined as:
where is the radiance of the WaltRCam and is the DART radiance for wavelength i and for AOD factor k. The nRMSE corresponds to the RMSE normalized by the difference between the minimum and maximum of the RMSE. This allows us to obtain a value between 0 and 1.
The Pearson correlation coefficient is the ratio between the covariances of two variables (WaltRCam spectrum and the LUT spectrum) and the product of their standard deviations and is defined as:
where the overbar corresponds to the temporal mean of each parameter. For each pixel, we select the AOD factor k corresponding to the nRMSE minimum. If this value is below the 10% threshold and has a correlation greater than 0.95, the k-value is retained; otherwise, the pixel is considered missing data. This is a compromise between the quality of the calculated results and the number of pixels to ensure good representativeness. After this step, each pixel is associated with an AOD factor. The spectral value of the AOD is then obtained by multiplying this factor by the spectral values of the AOD of the atmosphere selected when configuring DART (here, RURALV23). The viewing direction is accounted for in the DART radiative transfer model and does not induce any systematic variation in the AOD values. However, the classes that relate the object to the surface reflectance do not have the necessary detail in the 3D scale-model and induce some small systematic variations in the AOD values. Therefore, the AOD value of the image is obtained by averaging the values of all the pixels contained in the image. The results are presented in the next section.
4. Results
4.1. Simulation Presentation
The images captured on 30 June 2020 at 9:55, 11:02, 12:34, and 14:04 LT are presented in Figure 4. These images highlight the main advantage of a 3D approach by showing the impact of light variation over the course of the day, including the presence of shadows. Calculating radiative transfer in a peri-urban scene means that the geometric complexity of such an environment can be taken into account to make simulation results more realistic. The distance between the location of the camera and the background of the image is limited to 12 kilometers in the Toulouse 3D scale-model. Hills, forests, and a few buildings in the background of the image are not described in the simulated DART image. Areas of differences between the observed image and the simulated image are removed by correcting the simulated scene using SOC pixel classification (see Section 3.3).
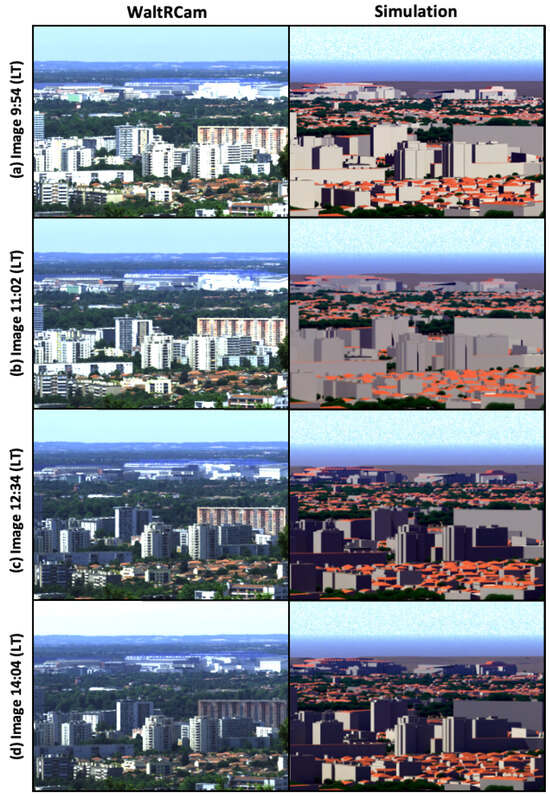

Figure 4.
(Left) Images observed by the WaltRCam camera. (Right) Images simulated by the DART model for 9:55, 11:02, 12:34, and 14:04 LT (from top to bottom). Note that the absence of details in the background shows the limits of the 3D scale-model, which is limited in the horizontal direction to a few km with respect to the location of the camera. This simulation corresponds to the RURALV23 atmosphere with an AOD factor of 0 to clearly distinguish the objects in the image.
4.2. Similarity Matrix
Figure 5 shows the same-class pixels between the scene as seen by the WaltRCam and by DART and its associated 3D scale-model. By examining the two results, the similarity image allows us to clearly visualize the regions where the two classes are similar, i.e., where the pixel belongs to the same class, and the areas where the pixels are different, i.e., where the pixel does not belong to the same class. This correction ensures that the DART simulation reflects the actual observed data as closely as possible. This allows us to refine the simulation results and obtain more accurate representations of the environment under study.

Figure 5.
Image of pixel class similarity. The white areas (deleted pixels) represent the pixels with a different class between the calculated classes and the WaltRCam classes (about 30% of the pixels in the image). Vegetation, roof, buildings, horizon, and sky are colored in black, red, grey, dark blue, and light blue, respectively.
Discarded pixels comprise about 30% of the pixels in the image. Among these pixels, 63% are within the vegetation class, while the building class accounts for 20% of these deletions, and around 17% are attributable to the roof class. Note that different class pixels concerning buildings and roofs are mostly visible in the background. This distribution of deleted pixels is significantly influenced by the time at which the image was captured, which took place at the beginning of the summer period. At this time of year, the vegetation is particularly dense, which explains the high percentage of discarded pixels associated with this class. It should also be noted that the scale-model used contains certain inaccuracies, particularly with regard to warehouses in the background, which justifies the high percentage of deletions for the building class.
4.3. WaltRCam and DART Spectra Correspondence
Table 4 summarizes the statistics used to assess the correspondence between the average of the selected spectra and the corresponding WaltRCam spectra. The nRMSE is about 3% for the four different local times. All day long, correlations between WaltRCam and DART spectra systematically show values of around 0.98. In terms of RMSE, the time 9:55 LT has the highest value, with 8.0 Wmsrnm, while at 12:34 LT, there is the lowest RMSE of 6.1 Wmsrnm. With the 10% nRMSE threshold and correlation greater than 0.95, a large number of pixels are conserved, with a minimum of 53% at 12:34 LT and a maximum of 58% of pixels at 11:02 LT. This corresponds to at least 61,000 pixels for 9:55 and least 67,000 pixels for 11:02. This amount of pixels allows us to obtain reliable results after averaging. Moreover, as a reminder, 30% of the pixels have already been discarded by the similarity matrix (Section 4.2), to which we have to add the pixels discarded by the threshold.

Table 4.
Statistics used to assess the correspondence between the average of the selected spectra and the corresponding WaltRCam spectrum: nRMSE (in %), Pearson correlation, RMSE in Wmsrnm, pixels conserved in %, and relative bias (excluding 938 nm) in %. The statistics are calculated for the experiment on 30 June 2020 for 4 different local times.
Note that the relative biases calculated for the first seven bands (excluding 938 nm) are 4%, 4%, 2%, and −1% for 9:55, 11:02, 12:34, and 14:04 LT, respectively. We have excluded the radiance values for the 938 nm band because they are very low (less than 5 Wmsrnm), and a small deviation significantly increases the relative bias. Figure 6 shows the average radiances calculated by DART for the entire image with the pixels selected according to our methodology.
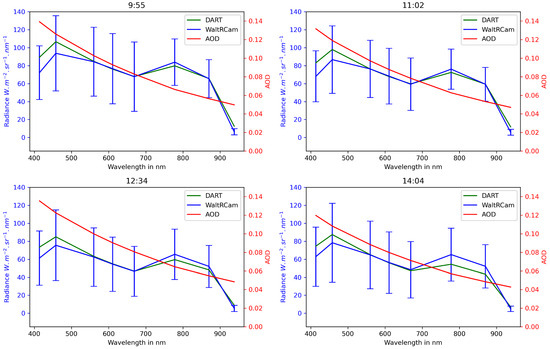
Figure 6.
Averaged WaltRCam spectrum for the entire image (blue curve); averaged calculated DART spectrum (green curve) for the entire image. The red curve represents the spectral AOD values calculated for each wavelength.
The figure also shows the average radiance measured by WaltRCam. A perfect simulation would be characterized by perfect superposition of these two curves. This figure clearly shows good correspondence between the two averaged spectra that can likely induce an estimation of AOD for each wavelength. The red curve represents the AOD values calculated in accordance with the method. As expected, for such a scene, AODs measured at smaller wavelengths are higher than AODs at greater wavelengths. The values obtained are compared with AERONET and MODIS satellite data in the following section.
4.4. Evaluation of AOD
4.4.1. AERONET
We evaluate the results by comparing the WaltRCam AOD with measurements taken by the closest AERONET station (see Section 2.2.1). Note that the AERONET measurements were taken with a small time difference from the WaltRCam data: 9:52, 10:59, 12:29, and 13:59 LT for AERONET and 9:55, 11:02, 12:34, and 14:04 LT for WaltRCam. We assume that this slight time difference does not affect the results. The evaluation is based on the common AERONET wavelengths: 440, 500, 672, and 870 nm. To do this, we perform logarithmic interpolation between the two nearest adjacent WaltRCam wavelengths, as recommended by authors from various publications (i.e., [55,56]). Figure 7 illustrates the comparison between WaltRCam and AERONET AOD for these different wavelengths as well as for the different hours in the day.
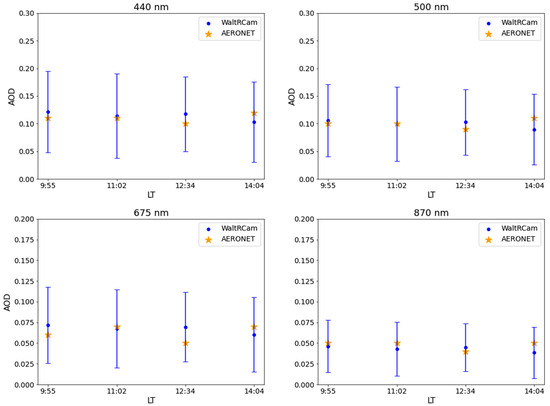
Figure 7.
AERONET AOD (orange stars) and WaltRCam AOD and its associated standard deviation (blue dots and vertical lines) at 440, 500, 675, and 870 nm as for 9:55, 11:02, 12:34, and 14:04 LT.
AOD values are fairly low and constant over the 4 h of measurement on 30 June 2020. The lowest wavelengths show the highest AOD values. In the environment of our experiment, we assume the aerosols are homogenous in terms of size and type. Therefore, light scattering by aerosols is likely more efficient at shorter wavelengths, meaning that aerosols tend to scatter more blue light (shorter wavelengths) than red light (longer wavelengths). Moreover, one can note that AERONET measurements are included within the variability of the WaltRCam measurements defined by the standard deviation calculated on all pixels of the image. Maximum AOD values are reached at 9:55 LT for all wavelengths: reaching 0.12, 0.11, 0.7, and 0.05 for the 440, 500, 675, and 870 nm wavelengths, respectively. In the same way, for these wavelengths, minimum AOD values are observed at 14:04 LT, and the measurements are 0.10, 0.09, 0.06, and 0.04, respectively. Measured AOD variability varies by around 0.07, 0.06, 0.04, and 0.03 depending on the wavelength considered. This variability could be reduced with the use of a more accurate 3D scale-model and an increase in the number of objects and classes to allow more accurate assignment of surface optical properties. Each urban element is indeed made up of objects with different surface reflectances. For example, a building may be covered by different materials, such as concrete, brick, plaster, etc., and may be painted different colors, each with its own surface reflectance. But we use a 3D scale-model that does not have this level of detail; instead, it groups all objects of the same class under the same surface reflectance. A more sophisticated scale-model could better represent the surface reflectance variability in a real urban environment, thereby increasing the accuracy of the results. Table 5 presents the statistics used to evaluate and compare the two AODs.

Table 5.
Bias, relative bias in %, and RMSE between the WaltRCam and AERONET AOD data. The statistics are calculated for the experiment on 30 June 2020 for 4 different times.
The errors obtained are reasonable compared to AERONET, with the highest bias being 0.014 at 12:34 and lowest bias being −0.015 at 14:04 LT. Note that biases are positive for 9:55 and 12:34 LT, indicating slight overestimation, while the bias is negative for 11:02 and 14:04 LT, suggesting slight underestimation. The relative bias is minimum at 11:02 LT at −3% and maximum at 12:34 LT at 20%. The RMSE is 0 for 11:02 LT and 0.02 for 12:34 LT and 14:04 LT. Figure 8 presents the comparison between WaltRCam and AERONET AODs. As already said, the WaltRCam results remain fairly close to the AERONET data, with a correlation coefficient of 0.9 and weak variability around the 1:1 line. The RMSE is 0.012, which is relatively low.
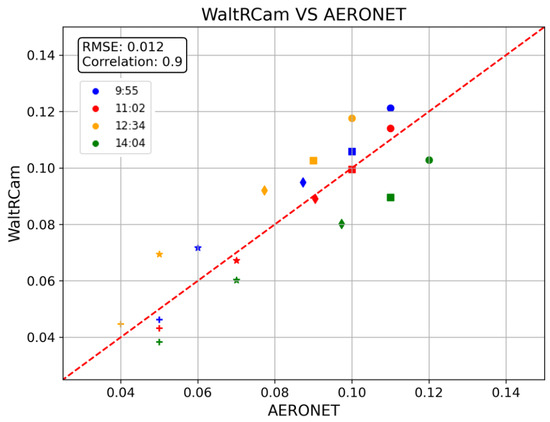
Figure 8.
Comparison of the AOD values of WaltRCam and AERONET. The colors blue, red, yellow, and green represent the different time measurements at 9:55, 11:02, 12:34, and 14:04 LT, respectively, on 30 June 2020. The wavelengths correspond to the following signs: circle = 440, square = 500, diamond = 550, star = 675, and plus sign = 870 nm.
4.4.2. MODIS
Finally, we evaluate the WaltRCam AOD data with the Terra satellite MODIS instrument data that was described in Section 2.2.2. MODIS mad a daily pass over the greater Toulouse area at 12:45 LT on 30 June 2020, which is close to the time of a WaltRCam measurement (12:34 LT). Figure 9 shows the AOD values measured at 550 nm over the greater Toulouse area. Each MODIS pixel corresponds to an area of 9 km (3 km × 3 km), whereas WaltRCam covers a smaller area corresponding to about a 3.3 km quadrilateral, as shown in this figure. MODIS AOD measurements are available over a part of the study area and give a similar result to the WaltRCam’s AOD for this specific zone. Note that MODIS pixels are coarse because of the DT algorithm, which likely discards non-convergent pixels. The AOD measured by MODIS in this area shows a value of 0.12 at 12:45 LT in a MODIS pixel colocated with the WaltRCam’s field of view, which provides an AOD value of 0.09 at 12:34 LT, and for the AERONET data, the AOD is 0.08. It should be noted that the MODIS instrument on the Terra satellite, as a sun-synchronous satellite, provides one AOD value per day, while the WaltRam camera can potentially provide several AOD values per hour. The observation frequency capability of the WaltRCam will allow measurement of diurnal AOD variations.
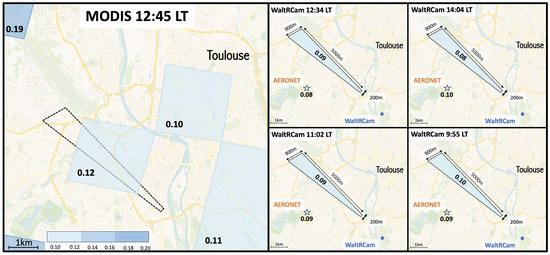
Figure 9.
(Left) MODIS AOD measurements for 550 nm at 12:45 LT (spatial resolution 3 km × 3 km). (Right) WaltRCam AOD measurements for 550 nm and corresponding AERONET AOD values for 9:55, 11:02, 12:34, and 14:04 LT on 30 June 2020. The AERONET station is located at the Météo-France site. The blue dot (CAM) is the location of the WaltRCam.
5. Conclusions
We show the advantages of an affordable ground-based multi-wavelength camera for measuring the vertical AOD of a vast peri-urban area. This camera, called the WaltRCam, can capture eight wavelengths (414, 458, 560, 611, 672, 778, 870, and 938 nm) and is currently under development and should soon be exploitable in the Toulouse area. For this study, the WaltRCam data were simulated using a HySpex hyperspectral camera. The urban scene of Toulouse is represented in 3D using a scale-model dating from 2014. This scale-model offers the possibility of reproducing complex urban configurations while assigning specific optical properties to the various elements that make it up. We perform classification on the WaltRCam image to distinguish the different objects and to ensure that the scale-model image corresponds exactly with the observed image. The aim of this classification is to assign a class (with the same optical properties) to each pixel in the WaltRCam image in order to discard any pixels that differ from the image generated by the scale-model. To do this, we use a learning method based on neural networks. In this way, we take into account changes in the peri-urban area, such as vegetation growth, construction, and demolition of buildings, and detect limits in the scale-model image. Using this technique, around 30% of the pixels are excluded from the observations: mainly because the vegetation is particularly dense at the end of June, which is not represented in the 3D scale-model. Secondly, to retrieve the AOD, we develop a methodology that relies on the construction of Look-Up Tables (LUTs) based on the DART radiative transfer model. Each image taken by the camera can deliver the vertical AOD representative of the 3D DART representation. These look-up tables take into account surface reflectance (pixel class) and all incident angles in the Toulouse 3D scale-model and simulate the spectra as observed by the WaltRCam. The closest spectrum is then selected, and an AOD value is calculated for all pixels in near-real-time. To demonstrate the usefulness of the technique, we use four images captured during a nearly clear case on 30 June 2020. On average, we obtain a good match between the LUT spectra and the WaltRCam spectra, with a correlation coefficient between 0.98 and 0.99 and an average RMSE of less than 8 Wmsrnm regardless of the time of day, which allows estimation of the AOD.
The AOD values are quite constant all day long, with AOD values between 0.08 and 0.10 for 550 nm. The results of this study show that the WaltRCam camera delivers convincing results compared with the AERONET data, with a relative bias ranging from −3% to 20% depending on the time, and with a correlation coefficient of 0.90 and an average RMSE of less than 0.02. In addition, we show similar AOD values compared to MODIS, but we provide a field of view almost twice as small (9 km compared to km). Using the WaltRCam images, future works will be to obtain AOD measurements with higher temporal resolution and with a time resolution of only a few tens of minutes. In addition to the smaller field of view, this represents a considerable advantage over the daily resolution currently obtained with MODIS satellite measurements. To follow up this study, we plan to apply the method in different atmospheric conditions using the WaltRCam observations, when available, and then extend our approach by deriving PM10, and PM2.5.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, V.B., J.-L.A., and R.T.; methodology, V.B. and J.-L.A.; DART software, N.L., J.-P.G.-E., and V.B.; investigation, X.C., J.-P.G.-E., and J.-L.A.; resources, J.A. and E.P.; data curation, J.A. and E.P.; writing—original draft preparation, V.B., J.-L.A., and R.T.; writing—review and editing, all; supervision, J.-L.A. and R.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The project is funded by the Région Occitanie and the University of Toulouse. The dataset was provided by the WaltR company. VB’s PhD has been funded by Région Occitanie and the University of Toulouse.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Toulouse town hall (M.P. Pagès) for providing the Toulouse city geo-database. We also thank the anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments that contribute to improve the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Pui, D.Y.; Chen, S.C.; Zuo, Z. PM2.5 in China: Measurements, sources, visibility and health effects, and mitigation. Particuology 2014, 13, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Semanjski, I.; Gautama, S.; Tsiligianni, E.; Deligiannis, N.; Rajan, R.T.; Pasveer, F.; Philips, W. A review of urban air pollution monitoring and exposure assessment methods. ISPRS Int. J.-Geo-Inf. 2017, 6, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahoz, W.A.; Schneider, P. Data assimilation: Making sense of Earth Observation. Front. Environ. Sci. 2014, 2, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Air Quality Near You. Available online: https://www.atmo-france.org (accessed on 15 November 2023).
- Kokhanovsky, A.A. The modern aerosol retrieval algorithms based on the simultaneous measurements of the intensity and polarization of reflected solar light: A review. Front. Environ. Sci. 2015, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Carlson, B.E.; Yung, Y.L.; Lv, D.; Hansen, J.; Penner, J.E.; Liao, H.; Ramaswamy, V.; Kahn, R.A.; Zhang, P.; et al. Scattering and absorbing aerosols in the climate system. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 363–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellouin, N.; Quaas, J.; Gryspeerdt, E.; Kinne, S.; Stier, P.; Watson-Parris, D.; Boucher, O.; Carslaw, K.S.; Christensen, M.; Daniau, A.L.; et al. Bounding global aerosol radiative forcing of climate change. Rev. Geophys. 2020, 58, e2019RG000660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, S.K.; Tesche, M.; Müller, D.; Noh, Y. Absorption aerosol optical depth components from AERONET observations of mixed dust plumes. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 607–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schraufnagel, D.E. The health effects of ultrafine particles. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, F.; Xiao, Q.; Gu, D.; Xu, M.; Tian, L.; Guo, Q.; Wu, Z.; Pan, X.; Liu, Y. Satellite-based short-and long-term exposure to PM2. 5 and adult mortality in urban Beijing, China. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ruan, Z.; Wang, X.; Yang, Y.; Mason, T.G.; Lin, H.; Tian, L. Short-term and long-term exposures to fine particulate matter constituents and health: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 247, 874–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Ambient Air Pollution: A Global Assessment of Exposure and Burden of Disease; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016.
- MODIS (Moderate-Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer). Available online: https://modis.gsfc.nasa.gov (accessed on 15 November 2023).
- Dubovik, O.; Herman, M.; Holdak, A.; Lapyonok, T.; Tanré, D.; Deuzé, J.; Ducos, F.; Sinyuk, A.; Lopatin, A. Statistically optimized inversion algorithm for enhanced retrieval of aerosol properties from spectral multi-angle polarimetric satellite observations. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2011, 4, 975–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceamanos, X.; Six, B.; Moparthy, S.; Carrer, D.; Georgeot, A.; Gasteiger, J.; Riedi, J.; Attié, J.L.; Lyapustin, A.; Katsev, I. Instantaneous aerosol and surface retrieval using satellites in geostationary orbit (iAERUS-GEO)–estimation of 15 min aerosol optical depth from MSG/SEVIRI and evaluation with reference data. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2023, 16, 2575–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.W.; Tseng, Y.S.; Mukundan, A.; Wang, H.C. Air pollution: Sensitive detection of PM2. 5 and PM10 concentration using hyperspectral imaging. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elcoroaristizabal, S.; Amigo, J. Near infrared hyperspectral imaging as a tool for quantifying atmospheric carbonaceous aerosol. Microchem. J. 2021, 160, 105619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norsk Elektro Optikk. Available online: https://www.neo.no (accessed on 15 November 2023).
- SmartG. Available online: https://www.hygeos.com/smartg (accessed on 15 November 2023).
- ArtDeco. Available online: http://precog.iiitd.edu.in/people/anupama (accessed on 15 November 2023).
- Gastellu-Etchegorry, J.P.; Demarez, V.; Pinel, V.; Zagolski, F. Modeling radiative transfer in heterogeneous 3-D vegetation canopies. Remote Sens. Environ. 1996, 58, 131–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gastellu-Etchegorry, J.; Martin, E.; Gascon, F. DART: A 3D model for simulating satellite images and studying surface radiation budget. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 25, 73–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gastellu-Etchegorry, J.P. 3D modeling of satellite spectral images, radiation budget and energy budget of urban landscapes. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2008, 102, 187–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AERONET (AErosol RObotic NETwork). Available online: https://aeronet.gsfc.nasa.gov (accessed on 15 November 2023).
- Lenhard, K.; Baumgartner, A.; Schwarzmaier, T. Independent laboratory characterization of NEO HySpex imaging spectrometers VNIR-1600 and SWIR-320m-e. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 53, 1828–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenhard, K.; Baumgartner, A.; Gege, P.; Nevas, S.; Nowy, S.; Sperling, A. Impact of improved calibration of a NEO HySpex VNIR-1600 sensor on remote sensing of water depth. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 6085–6098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Høye, G.; Løke, T.; Fridman, A. Method for quantifying image quality in push-broom hyperspectral cameras. Opt. Eng. 2015, 54, 53102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weather Station of Toulouse-Blagnac. Available online: https://www.infoclimat.fr/observations-meteo/archives/30/juin/2020/toulouse-blagnac/07630.html (accessed on 15 November 2023).
- WaltR. Available online: https://waltr.fr (accessed on 15 November 2023).
- Eichenholz, J.M.; Barnett, N.; Fish, D. Sequential filter wheel multispectral imaging systems. In Proceedings of the Applied Industrial Optics: Spectroscopy, Imaging and Metrology, Tucson, AZ, USA, 7–8 June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I.a.; Tanré, D.; Buis, J.; Setzer, A.; Vermote, E.; Reagan, J.A.; Kaufman, Y.; Nakajima, T.; et al. AERONET—A federated instrument network and data archive for aerosol characterization. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 66, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eck, T.F.; Holben, B.; Reid, J.; Dubovik, O.; Smirnov, A.; O’neill, N.; Slutsker, I.; Kinne, S. Wavelength dependence of the optical depth of biomass burning, urban, and desert dust aerosols. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1999, 104, 31333–31349. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, J.; von Hoyningen-Huene, W.; Kokhanovsky, A.; Vountas, M.; Burrows, J. Trend analysis of aerosol optical thickness and Ångström exponent derived from the global AERONET spectral observations. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2012, 5, 1271–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldabash, M.; Bektas Balcik, F.; Glantz, P. Validation of MODIS C6. 1 and MERRA-2 AOD using AERONET observations: A comparative study over Turkey. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Missions: Earth Observing System (EOS). Available online: https://eospso.nasa.gov/mission-category/3 (accessed on 15 November 2023).
- Algorithme Dark Target MODIS. Available online: https://darktarget.gsfc.nasa.gov (accessed on 15 November 2023).
- Levy, R.; Mattoo, S.; Munchak, L.; Remer, L.; Sayer, A.; Patadia, F.; Hsu, N. The Collection 6 MODIS aerosol products over land and ocean. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 2989–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blender—A 3D Modelling and Rendering Package. Available online: http://www.blender.org (accessed on 15 November 2023).
- Boulisset, V.; Attié, J.L.; Tournier, R.; El Malki, N.; Ceamanos-Garcia, X.; Andrey, J.; Pequignot, E. Classification de surfaces dans une image hyperspectrale urbaine par réseau de neurones pour la qualité de l’air. In Proceedings of the 9ème Conférence Nationale sur les Applications Pratiques de l’Intelligence Artificielle APIA@ PFIA2023, Strasbourg, France, 6–7 July 2023; pp. 24–27. [Google Scholar]
- Audebert, N.; Le Saux, B.; Lefèvre, S. Deep learning for classification of hyperspectral data: A comparative review. IEEE Geosci. Remote. Sens. Mag. 2019, 7, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Fei, B. Medical hyperspectral imaging: A review. J. Biomed. Opt. 2014, 19, 010901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, M.; Webster, R. A geostatistical basis for spatial weighting in multivariate classification. Math. Geol. 1989, 21, 15–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauvel, M.; Tarabalka, Y.; Benediktsson, J.A.; Chanussot, J.; Tilton, J.C. Advances in spectral-spatial classification of hyperspectral images. Proc. IEEE 2012, 101, 652–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, L. A comparative study of spatial approaches for urban mapping using hyperspectral ROSIS images over Pavia City, northern Italy. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 3205–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Discrete Anisotropic Radiative Transfer Model. Available online: https://www.hyspex.com/hyperspectral-imaging/what-is-hsi/ (accessed on 15 November 2023).
- Kroese, D.P.; Rubinstein, R.Y. Monte carlo methods. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Stat. 2012, 4, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MODIS UCSB Emissivity Library. Available online: https://icess.eri.ucsb.edu/modis/EMIS/html/em.html (accessed on 15 November 2023).
- Spectroscopy Lab. Available online: https://www.usgs.gov/labs/spectroscopy-lab (accessed on 15 November 2023).
- ECOSTRESS Spectral Library—Version 1.0. Available online: https://speclib.jpl.nasa.gov (accessed on 15 November 2023).
- Kotthaus, S.; Smith, T.E.; Wooster, M.J.; Grimmond, C. Derivation of an urban materials spectral library through emittance and reflectance spectroscopy. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 94, 194–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NOAA Solar Calculator. Available online: https://gml.noaa.gov/grad/solcalc/ (accessed on 15 November 2023).
- Berk, A.; Bernstein, L.S.; Robertson, D.C. Modtran: A Moderate Resolution Model for LOWTRAN 7. Geophys. Lab. Tech. Rep. 1989, 89, 122. [Google Scholar]
- Berk, A.; Anderson, G.P.; Bernstein, L.S.; Acharya, P.K.; Dothe, H.; Matthew, M.W.; Adler-Golden, S.M.; Chetwynd, J.H., Jr.; Richtsmeier, S.C.; Pukall, B.; et al. MODTRAN4 radiative transfer modeling for atmospheric correction. In Proceedings of the Optical Spectroscopic Techniques and Instrumentation for Atmospheric and Space Research III, Denver, CO, USA, 19–21 July 1999; Volume 3756, pp. 348–353. [Google Scholar]
- Bingen, C.; Robert, C.; Hermans, C.; Vanhellemont, F.; Mateshvili, N.; Dekemper, E.; Fussen, D. A Revised Cross-Section Database for Gas Retrieval in the UV-Visible-Near IR Range, Applied to the GOMOS Retrieval Algorithm AerGOM. Front. Environ. Sci. 2019, 7, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, R.A.; Gaitley, B.J.; Garay, M.J.; Diner, D.J.; Eck, T.F.; Smirnov, A.; Holben, B.N. Multiangle Imaging SpectroRadiometer global aerosol product assessment by comparison with the Aerosol Robotic Network. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, D23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.; Remer, L.; Kleidman, R.; Mattoo, S.; Ichoku, C.; Kahn, R.; Eck, T. Global evaluation of the Collection 5 MODIS dark-target aerosol products over land. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 10399–10420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).