Design of Extensible Structured Interferometric Array Utilizing the “Coarray” Concept
Abstract
1. Introduction
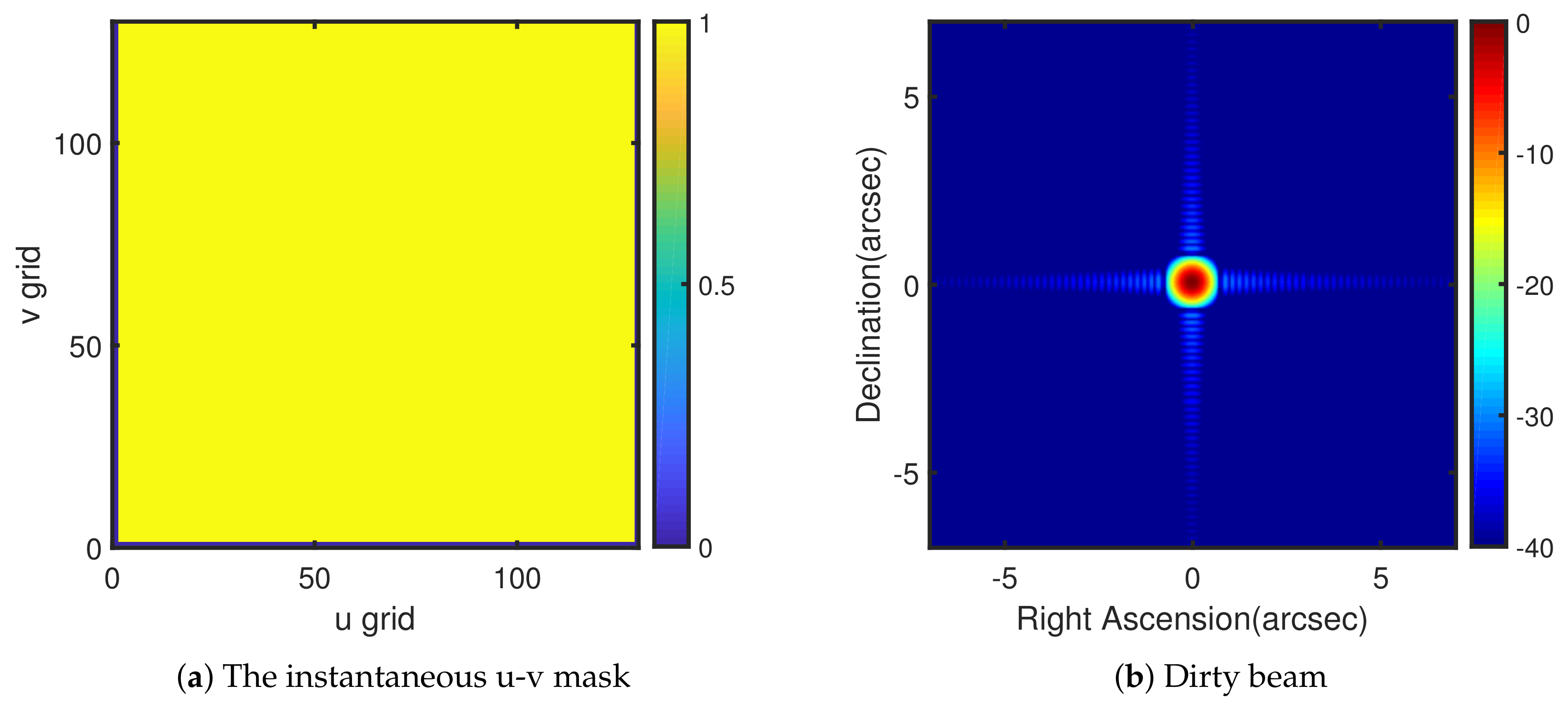
2. Coarray in Interferometric Synthesis Imaging
3. Extensible Interferometric Array Design
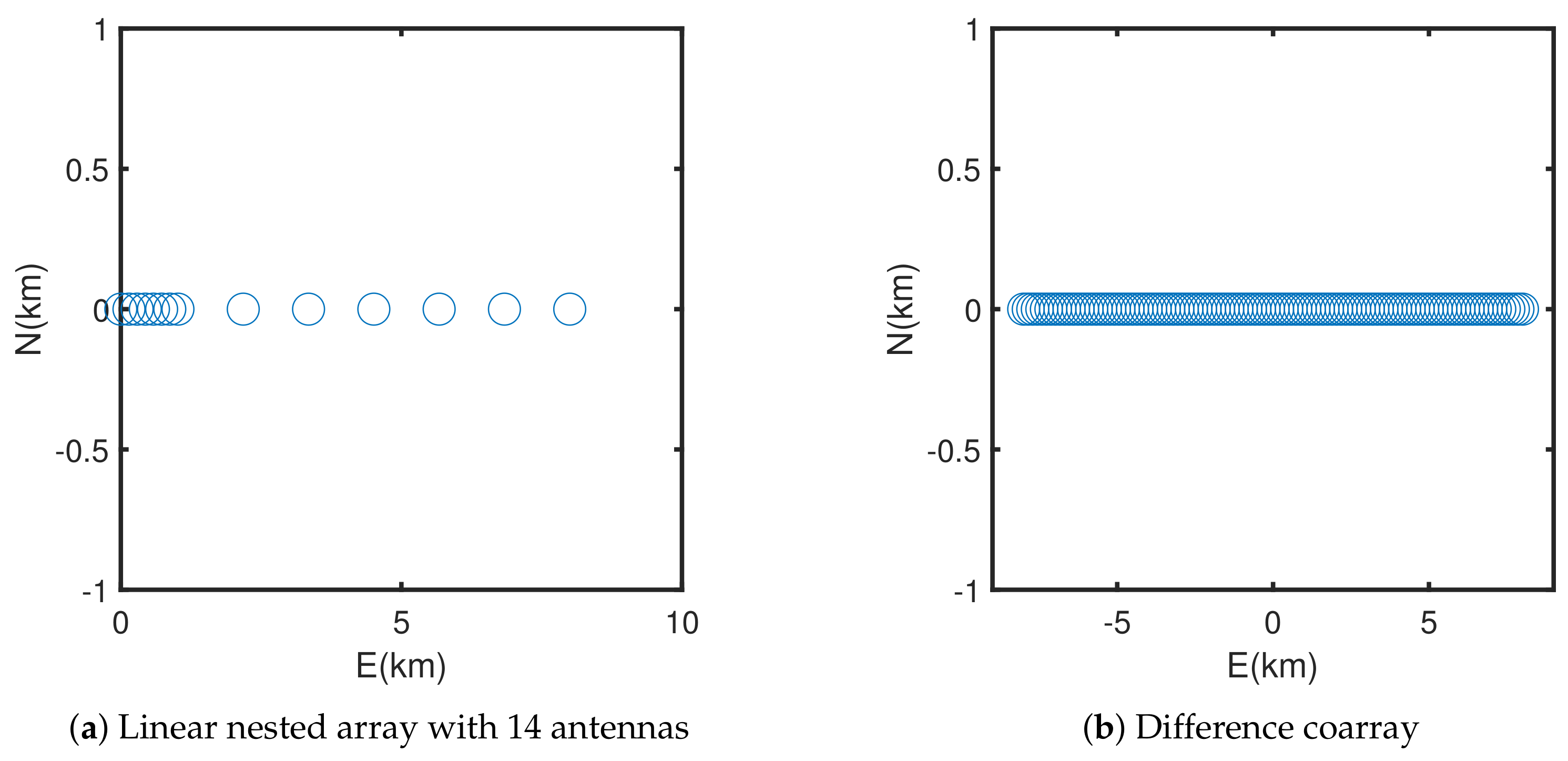
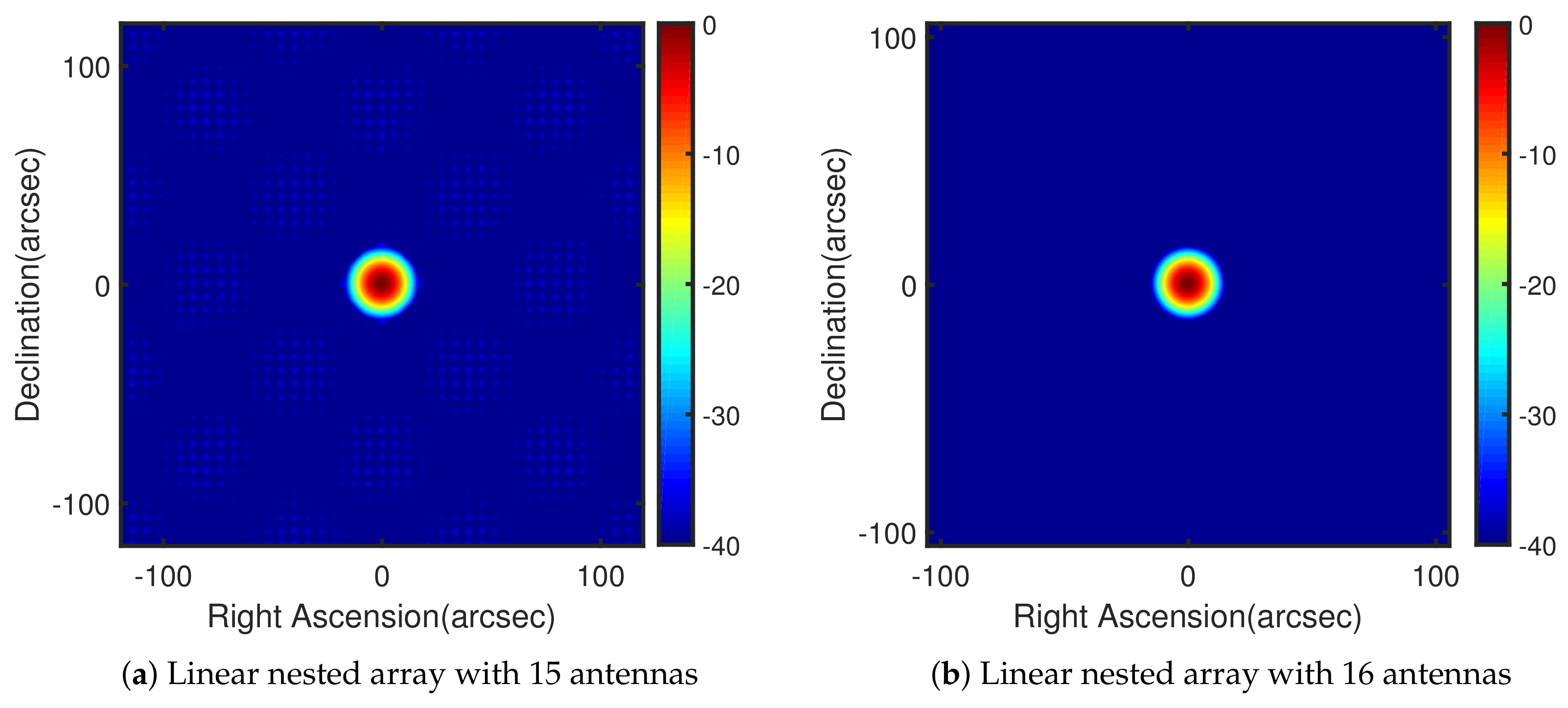
3.1. Linear Nested Array
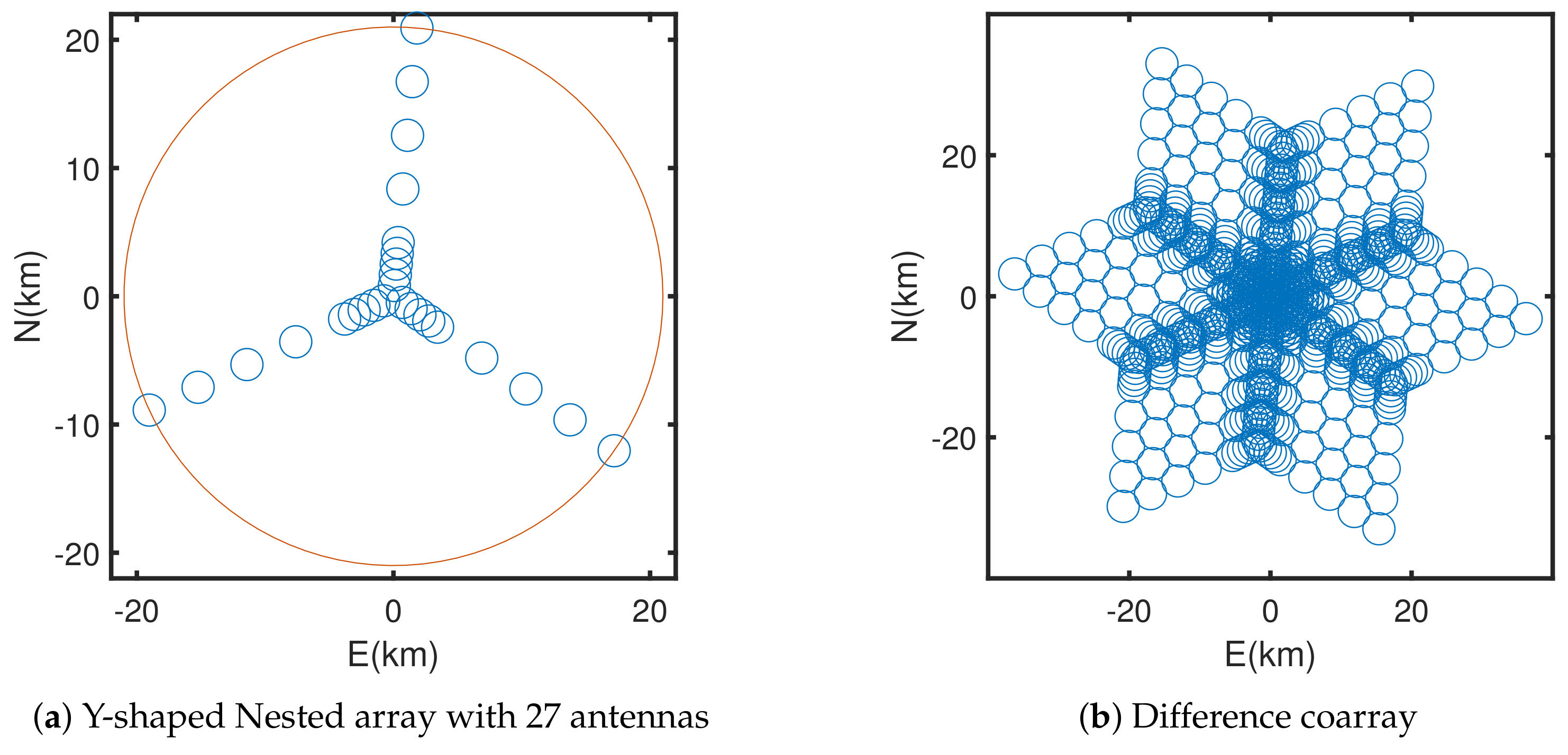
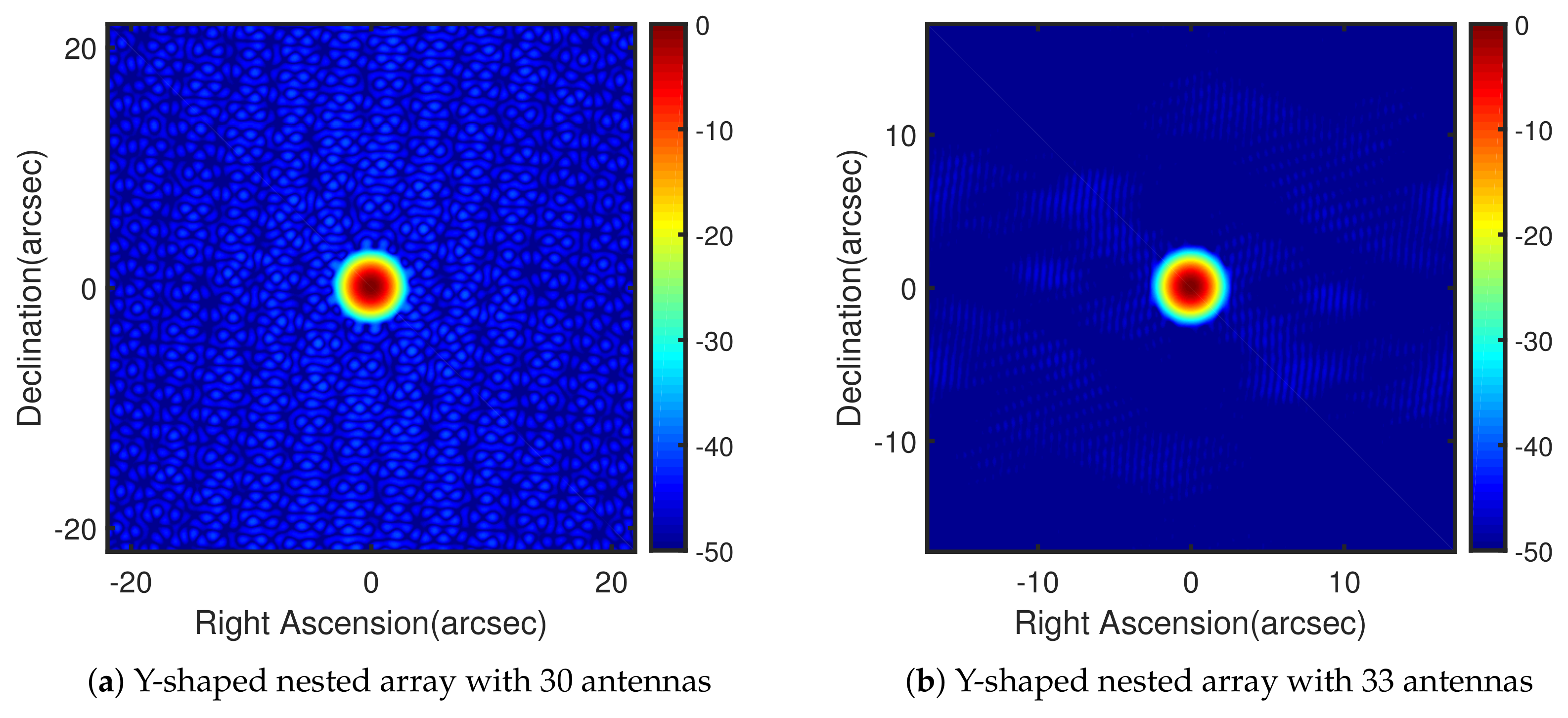
3.2. Y-Shaped Nested Array
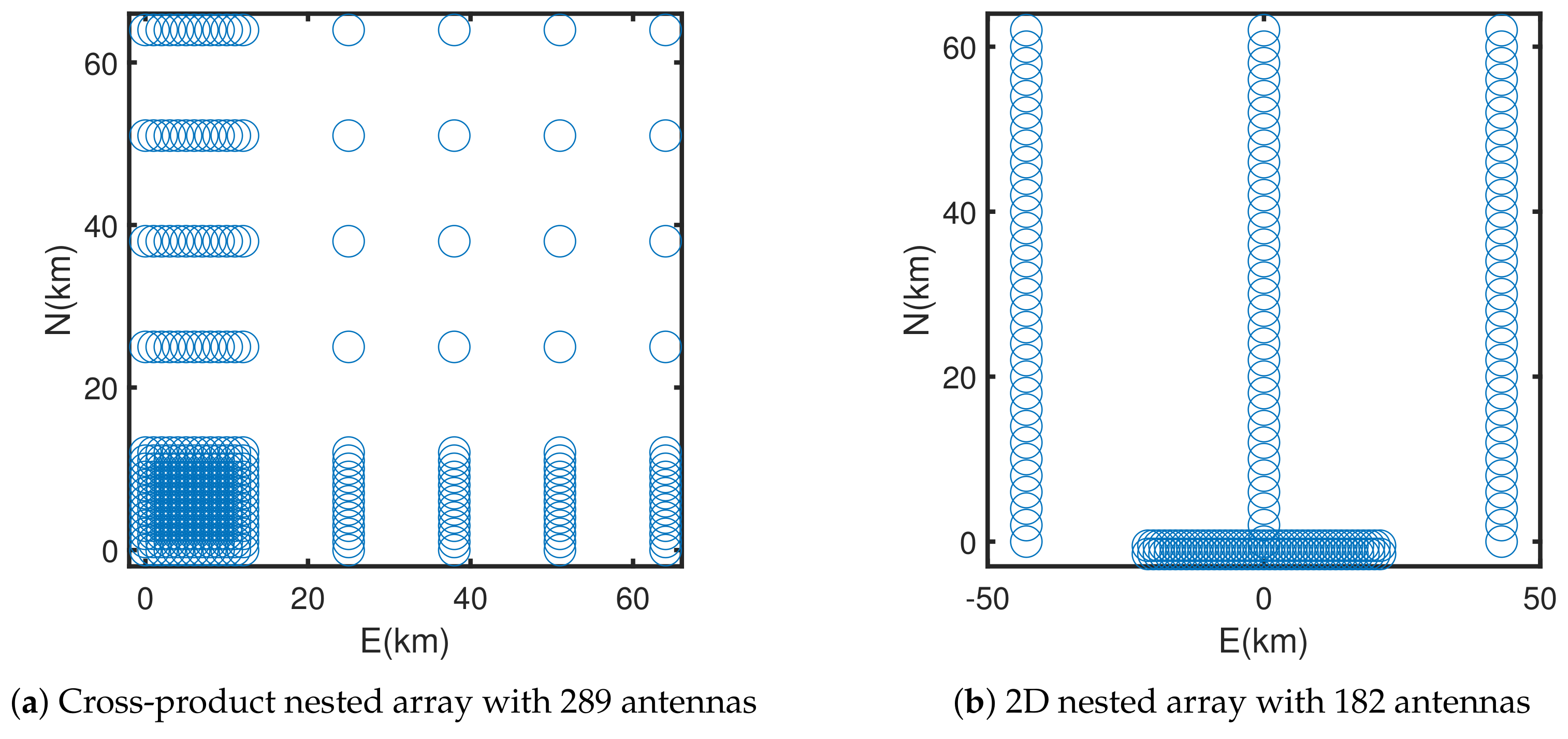
3.3. Cross-Product Nested Array
3.4. 2D Nested Array
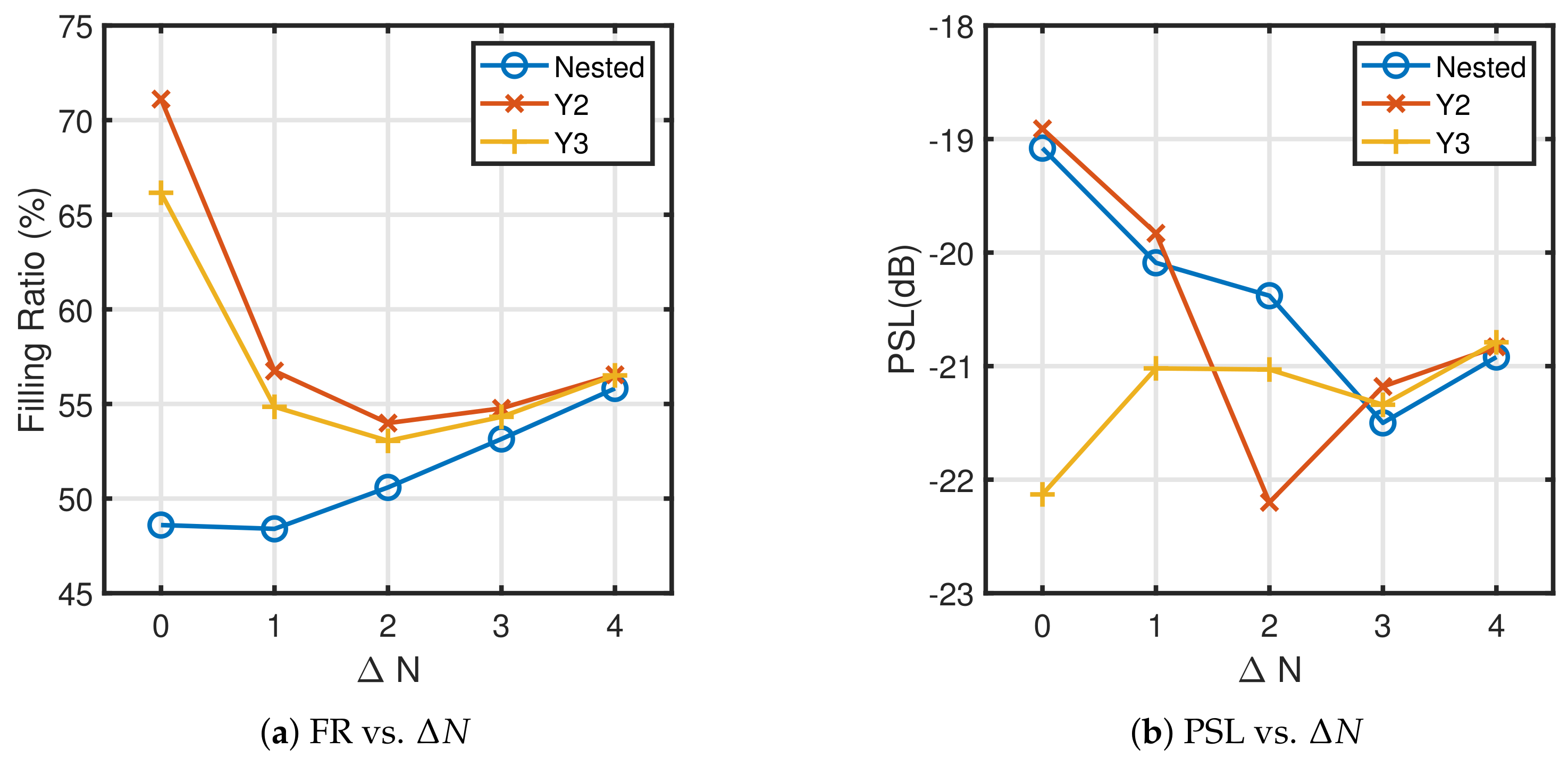
4. Simulation Results
4.1. Example 1: Linear Nested Array
4.2. Example 2: Y-Shaped Nested Array
4.3. Example 3: Cross-Product and 2D Nested Arrays
4.4. Example 4: Extensibility
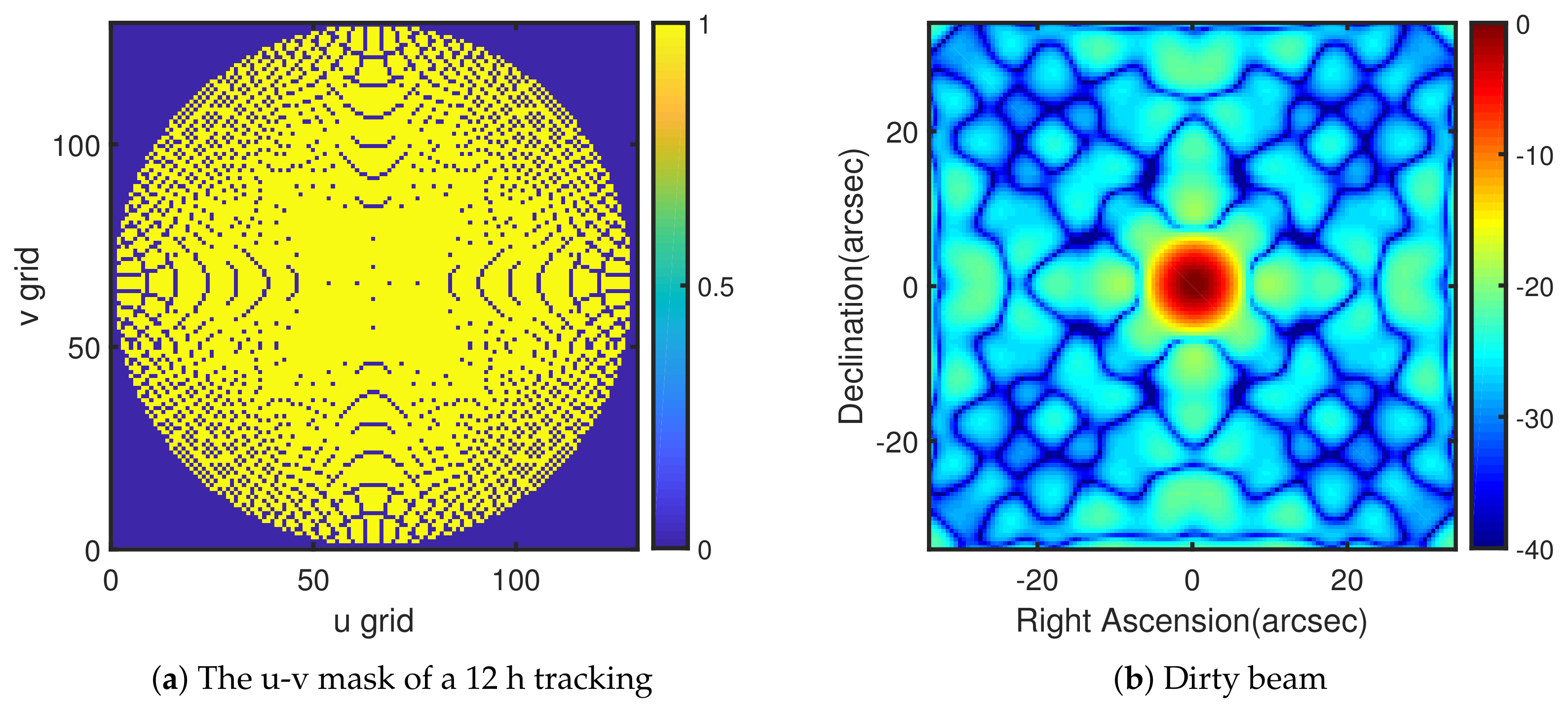
4.5. Example 5: Source Image Retrieval
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, X.; Wang, P.; Chen, V.C. Simultaneous measurement of radial and transversal velocities using interferometric radar. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2019, 56, 3080–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Gao, Y.; Li, J.; Xing, M. InSAR phase denoising: A review of current technologies and future directions. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2020, 8, 64–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josaitis, A.T.; Ewall-Wice, A.; Fagnoni, N.; De Lera Acedo, E. Array element coupling in radio interferometry I: A semi-analytic approach. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2022, 514, 1804–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, W.; Chen, V.C. Hand Gesture Recognition Using Radial and Transversal Dual Micromotion Features. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2022, 58, 5963–5973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Zhang, B.; Yu, H.; Chen, J.; Xing, M.; Hong, W. Sparse synthetic aperture radar imaging from compressed sensing and machine learning: Theories, applications, and trends. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2022, 10, 32–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viher, M.; Vuković, J.; Racetin, I. A Study of Tropospheric and Ionospheric Propagation Conditions during Differential Interferometric SAR Measurements Applied on Zagreb 22 March 2020 Earthquake. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Nan, R.; Peng, B.; Roddis, N.; Zhou, J. Optimization of interferometric array configurations by “sieving” u–v points. Astron. Astrophys. 2004, 414, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debary, H.; Mugnier, L.M.; Michau, V. Aperture configuration optimization for extended scene observation by an interferometric telescope. Opt. Lett. 2022, 47, 4056–4059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, A.R.; Moran, J.M.; Swenson, G.W. Interferometry and Synthesis in Radio Astronomy; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Cornwell, T. A novel principle for optimization of the instantaneous Fourier plane coverage of correlation arrays. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1988, 36, 1165–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogan, L. Optimizing a large array configuration to minimize the sidelobes. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2000, 48, 1075–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, N. A pseudodynamic programming technique for the design of correlator supersynthesis arrays. Radio Sci. 1969, 4, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, N.; Rahmat-Samii, Y. Analysis and particle swarm optimization of correlator antenna arrays for radio astronomy applications. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2008, 56, 1269–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveri, G.; Caramanica, F.; Massa, A. Hybrid ADS-based techniques for radio astronomy array design. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2011, 59, 1817–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffet, A. Minimum-redundancy linear arrays. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1968, 16, 172–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoctor, R.T.; Kassam, S.A. Array redundancy for active line arrays. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 1996, 5, 1179–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloom, G.S.; Golomb, S.W. Applications of numbered undirected graphs. Proc. IEEE 1977, 65, 562–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidyanathan, P.P.; Pal, P. Sparse sensing with co-prime samplers and arrays. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2011, 59, 573–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, P.; Vaidyanathan, P.P. Nested arrays: A novel approach to array processing with enhanced degrees of freedom. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2010, 58, 4167–4181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Ren, S.; Cao, S. Augmented nested arrays with enhanced DOF and reduced mutual coupling. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2017, 65, 5549–5563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Mao, Z.; Zhang, Y.D.; Huang, Y. Rank minimization-based Toeplitz reconstruction for DoA estimation using coprime array. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2021, 25, 2265–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoctor, R.T.; Kassam, S.A. The unifying role of the coarray in aperture synthesis for coherent and incoherent imaging. Proc. IEEE 1990, 78, 735–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, Y. On designing a supersynthesis antenna array. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1972, 20, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Veen, A.J.; Leshem, A.; Boonstra, A.J. Signal processing for radio astronomical arrays. In Proceedings of the Processing Workshop Proceedings, 2004 Sensor Array and Multichannel Signal, Barcelona, Spain, 18–21 July 2004; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2004; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Bracewell, R. Optimum spacings for radio telescopes with unfilled apertures. Natl. Acad. Sci. Natl. Res. Council. Publ. 1966, 1408, 243–244. [Google Scholar]
- Napier, P.J.; Thompson, A.R.; Ekers, R.D. The very large array: Design and performance of a modern synthesis radio telescope. Proc. IEEE 1983, 71, 1295–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, P.; Vaidyanathan, P.P. Nested arrays in two dimensions, Part I: Geometrical considerations. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2012, 60, 4694–4705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karastergiou, A.; Neri, R.; Gurwell, M.A. Adapting and expanding interferometric arrays. Strophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2006, 164, 552–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FR | 63.82 | 69.64 | 70.76 | 71.93 | 72.61 |
| PSL | −17.85 | −24.55 | −26.26 | −26.75 | −27.02 |
| Angular resolution | 0.66 | 0.57 | 0.50 | 0.45 | 0.41 |
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Angular resolution | 0.14 | 0.10 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.06 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Q.; Xue, C.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, R.; Sheng, W. Design of Extensible Structured Interferometric Array Utilizing the “Coarray” Concept. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1943. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15071943
Wang Q, Xue C, Zhang S, Zhang R, Sheng W. Design of Extensible Structured Interferometric Array Utilizing the “Coarray” Concept. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(7):1943. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15071943
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Qiang, Cong Xue, Shurui Zhang, Renli Zhang, and Weixing Sheng. 2023. "Design of Extensible Structured Interferometric Array Utilizing the “Coarray” Concept" Remote Sensing 15, no. 7: 1943. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15071943
APA StyleWang, Q., Xue, C., Zhang, S., Zhang, R., & Sheng, W. (2023). Design of Extensible Structured Interferometric Array Utilizing the “Coarray” Concept. Remote Sensing, 15(7), 1943. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15071943








