Abstract
The vertical aerosol layering of the troposphere is poorly documented in mountainous regions, particularly in the Alpine valleys, which are influenced by valley and mountain winds. To improve our knowledge of particulate matter trapped in the Annecy valley, synergetic measurements performed by a ground-based meteorological Raman lidar and a Rayleigh-Mie lidar aboard an ultralight aircraft were implemented as part of the Lacustrine-Water vApor Isotope inVentory Experiment (L-WAIVE) over Lake Annecy. These observations were complemented by satellite observations and Lagrangian modeling. The vertical profiles of aerosol optical properties (e.g., aerosol extinction coefficient (AEC), lidar ratio (LR), particle linear depolarization ratio (PDR)) are derived from lidar measurements at 355 nm during the period between 13 and 22 June 2019. The background aerosol content with an aerosol optical thickness (AOT) of 0.10 ± 0.05, corresponding to local–regional conditions influenced by anthropogenic pollution, has been characterized over the entirety of Lake Annecy thanks to the mobile ultralight payload. The aerosol optical properties are shown to be particularly variable over time in the atmospheric column, with mean LRs (PDRs) varying between 40 ± 8 and 115 ± 15 sr (2 ± 1 and 35 ± 2%). Those conditions can be disturbed by air masses that have recirculated over the valley, as well as by contributions from neighboring valleys. We have observed an important disruption in the atmospheric aerosol profiles by the arrival of an exceptionally dry air mass (RH ~ 30%), containing aerosols identified as coming from the Great Western Erg (AOT ~ 0.5, LR = 65 ± 10 sr, PDR = 20–35%) in the Sahara. These desert dust particles are shown to influence the entire atmospheric column in the Annecy valley. Such an experimental approach, coupling upward and downward lidar and spaceborne observation/Lagrangian modelling, was shown to be of significant interest for the long-term monitoring of the evolution of aerosol loads over deep valleys. It allows a better understanding of the influence of dust storms in the presence of severe convective weather processes.
1. Introduction
The vertical distribution of aerosols over Alpine valleys is still poorly documented. Meanwhile, the levels of fine particles in areas with dense urbanization or industrial and transportation activities continue to worry the inhabitants. Field experiments on air quality have been conducted in the past, but they have been conducted in extremely limited numbers; the issue of particle pollution in the Alpine valleys only reaches the public through mainstream press releases. The Pollution in the Alpine Valleys (POVA) program is one of the most impactful environmental research projects of the last decades [1]. It was principally oriented towards particulate pollution in the Chamonix and Maurienne valleys. From this project, anthropic emissions were reported to be fundamentally due to traffic, industries, residential heating, and some agricultural activities. Despite these findings, the societal issue associated with particulate pollution in the valleys is often underestimated by local stakeholders [2], whereas the health benefits of mitigation policies are no longer questioned [3,4].
As shown by [5], the air quality in Alpine valleys strongly depends on their specific topography, due to effects, including the aerosol origins in narrow valleys and certain atmospheric dynamic processes linked to steep valley walls. First established from observations in [6], the effects of these dynamic processes have been mainly investigated by modelling, in particular for studies of atmospheric pollution. The most prominent of these are TRANSALP [7,8], POLLUMET (Pollution and Meteorology) [9], and VOTALP (Vertical Transport of Pollutants in Alpine Valleys) [10,11].
As for other locations under scrutiny, most of the measurements of particulate pollution in the valleys are carried out near the surface (e.g., [1,12]), and few data are available on the air column from the surface to the free troposphere. However, knowledge of the vertical distribution of aerosols and their temporal evolution is necessary to understand and forecast events of particulate pollution and to inform populations (e.g., [13]). Though some efforts have been performed using other means [14,15], lidar measurements have a fundamental role to play here through the vertical and temporal resolutions they can offer [16,17,18,19,20,21]. The synergy between different types of lidar measurements also allows better identification of aerosol layers and helps ascertain their origins and variabilities over time [22,23,24].
Previous lidar measurements in the Alps by a ground-based scanning system during VOTALP have allowed us to identify the two aerosol layers associated with inversions typically induced by local and regional orography, as well as horizontal inhomogeneities in aerosol concentrations at the opening of the Mesolcina valley near Grono, Switzerland [25]. More recently, a ground-based micropulse lidar was used in the Italian valley of Aosta to quantify, for the first time, the direct radiative effect of aerosols during two cases— one with local pollution, and one during a dust transport event in June 2019 [26]. Nonetheless, the three-dimensional distribution of pollutants was only previously investigated during POVA in the Chamonix and Maurienne valleys [17], coupling in situ airborne and lidar measurements to highlight their sources, along with urban heat island effects.
A component of the Lacustrine-Water vApor Isotope inVentory Experiment (L-WAIVE) field campaign [27], conducted in the Annecy valley in the French Alps in June 2019, was dedicated to the study of aerosols. One of its main objectives was to document the three-dimensional extent and temporal evolution of aerosol layers above the Annecy valley in its complex topographic environment. This unprecedented experiment mainly involved the airborne Rayleigh-Mie lidar ALiAS (Airborne Lidar for Aerosol Study [28]) and the ground-based Raman WALI (Weather and Aerosol LIdar [29]).
The objective of this paper is to discuss the spatiotemporal evolution of the vertical profiles of aerosol optical properties measured during L-WAIVE, based on lidar samplings of different aerosol structures present in the Annecy valley from 13 to 21 June 2019. The observation period cannot be generalized to the whole year, but it is representative of a spring/summer situation. A detailed interpretation of these results will be presented to identify the origin of the particles, as well as their temporal and vertical variabilities. We will show that these observations, which were not widely available in the past, pinpoint notable mixing between aerosols emitted locally and those transported from distant sources of the Sahara.
In Section 2, the experimental setup is presented, as well as the methods used for the inversion of the lidar profiles. The temporal evolution of the optical properties of the aerosol layers is described in Section 3. Section 4 is dedicated to the discussion of local aerosol contribution to lidar profiles in relation to meteorological parameters. In Section 5, a case study involving disturbed environmental conditions in the valley due to a desert dust event is presented.
2. Materials and Methods
Our objective was to quantify the vertical distribution of aerosols in the Annecy valley using ground-based and airborne lidars. They are the only instruments that allow sampling the air column with the vertical and temporal resolution required to observe slight variations in aerosol plumes. The lidar data are supplemented by in situ measurements for calibration and validation purposes. In complement, to help identify the contributions of long-range atmospheric transports and their associated aerosol origin, we also used satellite observations and Lagrangian modelling.
2.1. Ground-Based Raman Lidar
We positioned the ground-based lidar in the village of Lathuile, on the southern bank of Lake Annecy (45°47′N, 6°12′E, altitude ~447 m above the mean sea level (a.m.s.l.) in the Haute-Savoie area of the French Alps) [27]. This location allowed us to limit the effects of slope winds, which have a considerable influence at distances between 50 and 200 m from the relief [5].
The ground-based lidar WALI (Weather and Aerosol Lidar, https://metclim-lidars.aeris-data.fr/wali/, last access: 15 January 2023) is an established mobile system, which samples the troposphere for aerosol [22], water vapor [29,30,31], and temperature retrievals [32]. It operates in the ultraviolet part of the spectrum, at the wavelength of ~355 nm, with a field-of-view (FOV) of 2 mrad, allowing for a full overlap of the emission and reception paths beyond ~200–300 m. Several aerosol optical parameters were retrieved from two cross-polarized channels coupled with a dinitrogen Raman elastic channel at ~387 nm [33,34,35]: the aerosol extinction coefficient (AEC), the lidar ratio (LR, ratio of the AEC and aerosol backscatter coefficient), the linear volume depolarization ratio (VDR), the particle linear depolarization ratio (PDR), and the aerosol optical thickness (AOT). The water vapor mixing ratio (WVMR) was derived using Raman channels at ~387 and ~407 nm for dinitrogen and water vapor, respectively [35]. The temperature was derived from two rotational Raman channels combining the Raman lines of both dinitrogen and dioxygen close to the elastic Cabannes line centered at 354.7 nm. The relative humidity (RH) was calculated by using the WVMR and temperature. For all altitude-dependent aerosol optical properties, the average vertical profiles were computed over 20 min with a vertical resolution of 30 m. In all Raman retrievals (water vapor, temperature), the lidar signal was averaged over 30 min, and the vertical resolutions decreased with altitude from 30 m near the ground to 360 m 5 km above ground level (a.g.l.).
Lidar inversion methods can be found in the references cited at the beginning of this section as additional technical information on the lidar. For our N2-Raman lidar, the uncertainties of the retrieved optical properties of aerosols are well described in [35]. The relative error on the determination of AOT from the vibrational Raman channels is less than 2% for a signal-to-noise ratios (SNR) greater than 10. The uncertainty on the LR is between 5 and 10 sr, but it increases abruptly for AOTs below 0.1, and it strongly depends on SNR, as shown by [36]. For AEC higher than 0.05 km−1, the error on the PDR remains in the order of 1–2%, but it will increase sharply for lower AEC values.
Airborne in situ measurements were used, as in [31], for the calibration of the ground-based lidar to retrieve vertical water vapor and temperature profiles. The sources of error on measurements by the Raman channels of WALI are fully described in [32]. In this study, the bias has been shown to be negligible for water vapor, and it is below 0.4 °C for temperature. Random errors are consistent with theoretical noise levels extrapolated from known sources, namely, 0.03-0.4 g kg−1 (daytime–nighttime) under 2 km a.g.l. and 0.04 g kg−1 (nighttime), under 6 km a.g.l. for water vapor, and 0.4–0.7 °C (daytime-nighttime) under 2 km and 0.75 °C (nighttime) under 6 km a.g.l. for temperature. This is consistent with previous implementations of WALI [29,31,37] with only water vapor measurements. During L-WAIVE, uncertainties were again assessed by direct comparison to atmospheric soundings. With suitable SNR conditions (nighttime or daytime in the first 2 km of atmosphere), statistical errors remain below 3% for water vapor measurements, and they remain below 2.5 °C for temperature measurements (this is a result of larger random error, likely due to more horizontal variability between lidar and sonde). The resulting error on RH is around 10%, with less than 5% bias highlighted below 4 km a.g.l.
2.2. Ground-Based Hand-Held Sunphotometer
During the day, in parallel with the cloudless sky lidar measurements, a SolarLight® Microtops II manual sun photometer (https://solarlight.com/, last access: 15 January 2023) was used. It was equipped with 4 channels (340, 440, 675, and 870 nm) and with a water vapor channel at 936 nm. For use with the ground-based lidar, an Angstrom coefficient between 340 and 440 nm was calculated. Each value considered here is the average of three consecutive measurements. The manual spectrophotometer has been calibrated by the manufacturer and verified in comparison to the AERONET (https://aeronet.gsfc.nasa.gov/, last access: 15 January 2023) sun photometer of Palaiseau (Greater Paris area) before the campaign. The procedure was the same as that presented in [19]. The AOT accuracy is comparable to that of the automated Cimel sun photometer. Nevertheless, manual solar targeting induces an additional bias, which leads to an absolute uncertainty between 0.01 and 0.02, as compared to simultaneous measurements by an automated sun photometer [34]. The expected total uncertainty is, therefore, less than 0.04 on every channel.
2.3. Airborne Measurements
In order to complement measurements of the vertical distribution of aerosols and to collect information at other locations in the valley, we used a scientific payload onboard a Tanarg 912 XS ultralight from the company Air Creation, similar to the one described by Chazette and Totems (2017) [38]. The maximum total payload was approximately 250 kg, including the pilot. Flight durations were ~2 h, depending on flight conditions, with a cruise speed around 85–90 km h−1. The ultralight location was computed by a Global Positioning System (GPS) and an Attitude and Heading Reference System (AHRS), both part of the MTi-G components sold by XSens. The ultralight flew at altitudes lower than 3.5 km a.m.s.l. above the valley.
The onboard instruments are the following:
Rayleigh-Mie lidar. ALiAS (https://metclim-lidars.aeris-data.fr/alias/, last access: 15 January 2023) was especially developed by LSCE as an airborne payload dedicated to aerosols and clouds samplings [28,39]. It emits a pulse energy of 30 mJ in the ultraviolet spectrum at 355 nm with a 20 Hz pulsed Nd:YAG laser (Ultra) manufactured by Lumibird (https://www.lumibird.com/, last access: 15 January 2023). The acquisition system was based on a PXI (PCI eXtensions for Instrumentation) technology manufactured by National Instrument (https://www.ni.com/, last access: 15 January 2023). The receiver implements two channels for the detection of the elastic backscatter from the atmosphere in the parallel and perpendicular polarization planes relative to the linear polarization of the emitted radiation. The native resolution along the line-of-sight (LOS) is 0.75 m. It degraded to 30 m during data processing to improve the SNR. The FOV ~2 mrad ensures a full overlap of the transmit and receive paths, around 200–300 m from the emitter. For this study, we used lidar profiles obtained with a horizontal LOS. The inversion of lidar data on a horizontal LOS has already been described in [40] and in [41]. The so-called “top-down” inversion of lidar measurements at nadir are not well constrained. We will, therefore, discuss only the VDR, which is associated with lower uncertainties than the PDR.
Meteorological probe. The shielded meteorological probe for measuring temperature, pressure, and relative humidity was a Vaisala PTU-300. With a 1-min sampling time, this probe measures the atmospheric pressure within an uncertainty of 0.25 hPa, the air temperature within an uncertainty of 0.2 K, and relative humidity (RH) within a relative uncertainty of 2.5%.
Particle sizer. The particle sizer used was a Fidas® Frog manufactured by Palas (https://www.palas.de/en/, last access 15 January 2023). The measuring cell of the Fidas® Frog is identical to that of the Fidas® 200. The particle sizer operates on battery power with a volume flow of 1.4 L min−1 in environmental conditions of temperature, atmospheric pressure, and relative humidity (no drying). The particle size distribution is determined from 180 nm to 20 µm by means of an optical aerosol spectrometer using Lorenz-Mie scattered light analysis. The LED source homogeneously illuminates an optically differentiated measurement volume with white light. Each particle moving through this volume generates a scattered light impulse detected at an angle of 85° to 95° degrees. The amplitude of the impulse is a measure of the particle diameter, and the number of particles corresponds to the number of impulses. To allow in-flight measurement, while limiting missed particles, a sampling head has been custom designed and 3D-printed for the ultralight cruising airspeed to guarantee an isokinetic air flow at the entrance of the Fidas®. The Fidas® 200 optical particle sizer is TÜV-certified in the European Community for aerosol mass concentration measurements. The instrument was leased and calibrated by ADDAIR (https://www.addair.fr/, last access: 15 January 2023), the official dealer of Palas instruments. When comparing to measurements of aerosol mass concentration, the Pearson correlation coefficient was between 0.75 and 0.87 [42].
2.4. Modelling and Satellite Data
Modelling. Back trajectories were computed using the Hybrid Single Particle Lagrangian Integrated Trajectory (HYSPLIT) [43]. The model was initialized using the wind fields of the Global Forecast System (GFS) (http://www.ncep.noaa.gov/, last access: 14 February 2023) at 0.25° horizontal resolution. The endpoints of back trajectories were defined using the lidar profiles to determine both their temporal and altitude locations above the lidar when aerosol layers were present. We used the ensemble mode of HYSPLIT, which computes, simultaneously, 27 back trajectories for each endpoint. For each endpoint time, the endpoints have been distributed in altitude every 100 m within the altitude range, where the aerosol layer has been identified from lidar measurements. This allows for a more static consideration of back trajectories, which can then be represented by surface densities.
Satellite. The level 2, version 4 aerosol optical thicknesses of the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometers (MODIS, http://modis-atmos.gsfc.nasa.gov, last access: 14 February 2023 [44,45]), on board the Aqua and Terra platforms, have been used to study the horizontal spread and transport of aerosol plumes. The brightness temperature anomalies (BTA) of the Spinning Enhanced Visible and InfraRed Imager (SEVIR, [46]) thermal infrared channels offer the possibility to identify the location of uplift zones and high AOT plumes over the Sahara. For this purpose, we used the approach proposed by [47], which highlights the apparent cooling of the hot surface due to the presence of dust aerosols. A reference image of warmer temperatures was computed from a series of 21 successive images taken at 12:00 UTC, centered on 13 June 2019, after which the given image was compared with the reference image to detect anomalous cold areas.
3. Temporal Evolution during the Field Campaign
As will be seen hereafter, both vertical structures and concentrations of particulate pollutants are highly variable over the Lake Annecy valley over the course of a day and from one day to the next. Vertical structures can be highlighted on the AEC, PDR, RH, and temperature lidar profiles.
3.1. Aerosol Optical Properties
Figure 1 shows the temporal evolution of the optical properties of aerosols retrieved by the ground-based WALI over the entire L-WAIVE campaign.
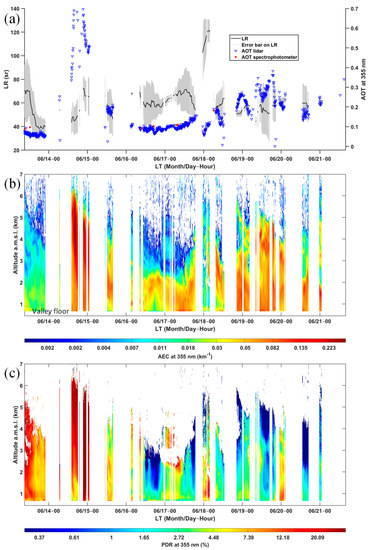
Figure 1.
Temporal evolution between 13 and 21 June 2019 of (a) lidar ratio (LR) (mean value as a black line and error bar in orange), as well as the aerosol optical thickness (AOT) at 355 nm derived from lidar measurements (blue triangles) and the handheld sun spectrophotometer (red dots); (b) the vertical profile of the aerosol extinction coefficient (AEC) at 355 nm; and (c) the vertical profile of the particle linear depolarization ratio (PDR) at 355 nm. White stripes along time correspond to cloudy periods when measurements could not be inverted.
3.1.1. Column-Integrated Parameters
The lidar-derived AOT and LR are presented in Figure 1a in low cloud free condition.
Remarkably high AOTs are reported, above 0.5 at 355 nm on 14 June. It is worth noting that, in cloud-free conditions, the AOT at 355 nm retrieved from the handheld sun spectrophotometer is close to the one derived from the ground-based lidar (red dots in Figure 1a). The latter may be slightly higher due to the lidar blind spot below 200 m a.g.l. The AOTs increase discernibly after the night of 18–19 June, from ~0.15 to ~0.4, in connection with the thickening of the aerosol layer. The histogram of AOTs over the period of the field experiment is presented in Figure 2. The majority of AOT values are distributed around 0.1, corresponding to particulate pollution which is lighter by a factor of two than that of the Greater Paris area in spring [48]. For higher AOTs, a non-local aerosol contribution must be considered.
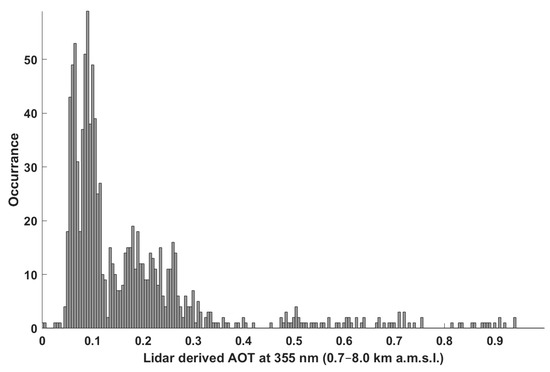
Figure 2.
Histogram of the aerosol optical thickness (AOT) at 355 nm, as derived from the ground-based lidar measurements for the altitude range of 0.7–8 km a.m.s.l. (south of Lake Annecy, ground level at ~0.45 km a.m.s.l.).
The LR is strongly dependent on the particle size and chemical composition of the aerosol via the complex refractive index of the particles [49]. It, therefore, allows us to trace the evolution of the aerosol composition in the atmospheric column over time (Figure 1a). The lowest values (~40–50 ± 10 sr) observed on 14 June may be associated with the presence of dust-like aerosols [50,51,52], whose exact origin remains to be determined. The LRs are generally higher on the other days of the campaign, and the maximum values reach ~115 ± 15 sr at 355 nm during the night of 18–19 June for several consecutive independent profiles. Such values are exceptional and are rarely retrieved in the literature. They correspond to the AOTs encountered at that time (Figure 1a), which are among the lowest measured during the campaign and may lead to higher errors for LR retrieval. This sudden increase in LR occurs when the regional circulation brings air from the mountain tops, thus decreasing the AOT. It is, therefore, difficult to assess the origin of the particles involved. A LR of 115 ± 15 sr is substantially higher than that previously observed over Paris (90 ± 16 sr, [53]) for pollution aerosols closely linked to motor traffic, although the error bars overlap noticeably. More common values, between 50 and 85 sr, are encountered quite often after 16 June. It should be noted that violent thunderstorms broke out on 16 June [27] and washed off a very large proportion of the aerosols present in the atmosphere. These thunderstorms, and more frequently the presence of low and medium altitude clouds, explain the occasional lack of data in Figure 1.
3.1.2. Vertical Profiles
The temporal evolution of the vertical profiles of AEC is shown in Figure 1b. The profiles show conspicuous structures, which allow the identification of the aerosol layers. The low atmosphere was, at first, strongly loaded by dust-like aerosols, up to more than 6 km a.m.s.l. on 14 June. The aerosol load then dropped, especially after the storms, yet an aerosol layer remained aloft on the afternoon of June 16 between ~1.5 and 2.5 km a.m.s.l. A similar layer was found on the night of 17–18 June. An upward expansion of the aerosol layer was noted on 19 June, which could be linked to more important thermal convection on that sunny day.
Derived from the VDR, the PDR is an optical parameter that allows us to easily differentiate aerosols according to their degree of sphericity [54,55]. As dust-like aerosols are much less spherical than pollution aerosols, they will show higher PDRs, as seen on 14 June in Figure 1c. PDR values above 20% are characteristic of dust-like particles mixed with pollution aerosols [22,52]. For pollution aerosols, the values generally remain below 2-4% during the day. Higher values are observed during the night, exceeding 10%, which could be the signature of a different origin of particles than during the day, both including dust-like particles. Aerosols with such PDRs can be observed mainly on 13–14 June, with a higher frequency being observed during the night.
The nature of aerosols varies vividly, not only from day to day, but even within the same day. An evolution as a function of altitude is also observed. Moreover, it is also evident over the horizontal extent of the valley, as shown in Figure 3 by the airborne lidar measurements on 18 June 2019, 11:00–12:30 LT (local time). The latter highlight a fall in VDR between the north and the south of the lake. This evolution may be associated with a rapid ageing of the aerosols, which become more hydrophilic and whose properties can thus potentially differ between the city of Annecy (located in the north of the valley) and the lidar ground station of Lathuile.
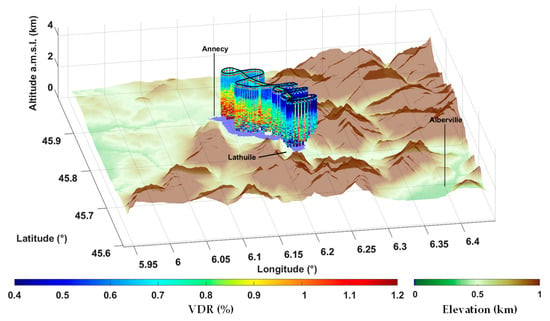
Figure 3.
Linear volume depolarization ratio (VDR) derived from the airborne lidar over Lake Annecy on 18 June 2019, 11:00–12:30 LT.
3.2. Meteorological Parameters Derived from the Ground-Based Lidar
The temporal evolution of the vertical temperature and RH profiles are shown in Figure 4. Below 2–3 km a.m.s.l., a marked temperature cycle is observed (Figure 4a), with the highest temperatures observed during the afternoon. These temperatures can be related to rising valley winds (see Figure 5b of [27]) and, conversely, the lowest nighttime temperatures are more frequently associated with mountain winds descending from the relief surrounding the measurement site. The temporal evolution of RH (Figure 4b) shows a less pronounced diurnal cycle due to the presence of precipitating clouds [27], which disrupt it, but also, at the beginning of the period, are related to the presence of dust-like particles likely advected from higher altitudes. The air mass above the measurement site on 13–15 June was much drier (RH < 30%) than usual. A more precise identification of the origin of this air mass will be presented in Section 5. We also note a warmer and drier lower troposphere (<2 km a.m.s.l.) on the afternoon of 19 June in connection with vertical mixing related to a more pronounced thermal convection, which is evidenced by the previous high PDR values.
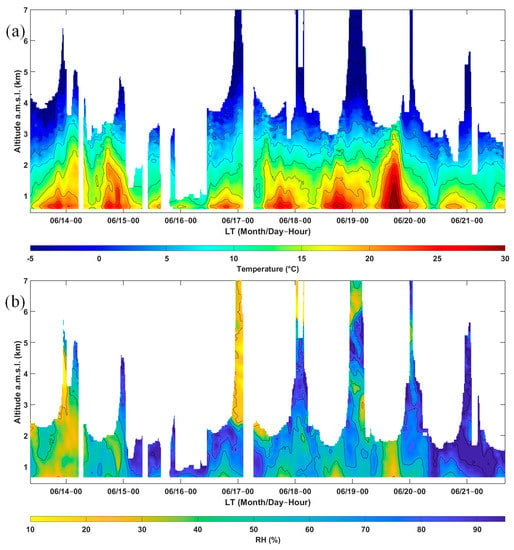
Figure 4.
Temporal evolution between 13–21 June 2019 of the vertical profiles of lidar-derived (a) temperature and (b) relative humidity (RH). Maximum range is chosen based on a threshold on signal to noise ratio (SNR) and uncertainty. White time stripes correspond to periods of clouds.
4. Local Aerosol Conditions in Connection with the Valley Winds
The aerosols in local–regional conditions have been observed between 17–19 June, when the AOT is weaker, between two periods of rainy thunderstorms. A diurnal cycle that is consistent with that of temperature is not clearly observed (Figure 1b and Figure 2) because aerosols from the ground are also mixed at higher altitudes via thermal convection at the hottest times of the day and can recirculate depending on the valley winds. To better demonstrate the evolution of aerosol transport during the day, we performed ascending and descending spiral flights over the southern part of the lake at different meteorological key times during the day from 18 to 19 June. The spiral measurements provided vertical profiles of AEC from horizontal lidar measurements that can be related to those derived from the ground-based lidar near the southwest shore of the lake. These results are shown in Figure 5 and Figure 6.
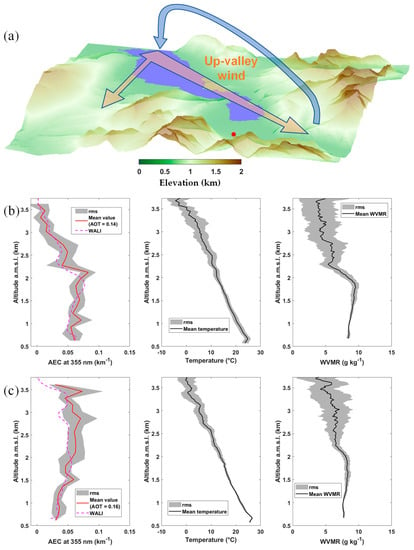
Figure 5.
(a) Schematic representing the circulation patterns in the Annecy valley associated with the vertical lidar profiles shown below, in (b,c). Vertical profiles of the aerosol extinction coefficient (AEC), temperature, and water vapor mixing ratio (WVMR) during ultralight flights on (b) 17 June 2019, 15:45–17:00 LT, as well as (c) 17 June 2019, 17:45–19:00 LT. The ground-based lidar location is indicated by a red dot.
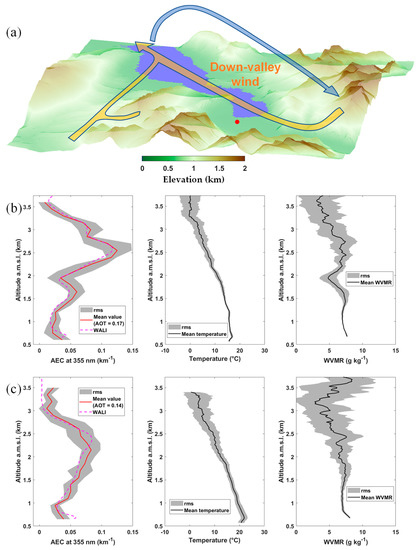
Figure 6.
(a) Schematic representing the circulation patterns in the Annecy valley associated with the vertical lidar profiles shown below, in (b,c). Vertical profiles of the aerosol extinction coefficient (AEC), temperature, and water vapor mixing ratio (WVMR) during ultralight flights on (b) 18 June 2019, 08:30–0945 LT and (c) 18 June 2019, 11:00–12:30 LT. The ground-based lidar location is indicated by a red dot.
During the afternoon (~1600–1700 LT) of 17 June (Figure 5), the wind in the planetary boundary layer (PBL, below ~2 km a.g.l.) rises along the valley (orange path in the diagram in Figure 5a) to recirculate from 2 km a.m.s.l. (blue path in the diagram) (see Figure 5b of [27]). This circulation favors aerosol uplift from the bottom to the top of the valley, as well as vertical mixing by thermal convection. As shown in the WVMR profiles, the lower layers appear well-mixed, up to about 1.8 km a.m.s.l., above which a significant depletion is observed. At about ~1800-1900 LT, the valley is cooling down, and we observe a weakening of the low layer circulation, which will transport less aerosols from Annecy, inducing a sign change in the vertical AEC gradient, which can be observed by comparing Figure 5b,c.
As the ultralight flights could not be carried out in the evening, when cold high-altitude air descends from the mountains, they were postponed to the morning of June 18 before the sun had heated the ground surface. The schematic in Figure 6a represents a return flow along the valley axis on the morning of 18 June 2019, 08:30–09:45 LT. The air circulation is reversed compared to the previous day, with a mountain wind descending below ~1.5 km a.m.s.l. As shown in Figure 5b of [27], the wind orientation is more variable above 2 km a.m.s.l., which may be related to various contributions from transverse valleys and to the effects of flows over the reliefs of similar mean altitude. We also note that the air in the lower layers is much colder than the day before due to subsidence from the mountain tops (Figure 6b,c). Based on this pattern, just above the local PBL (at ~1.6 km a.g.l.), the peak of AEC at about 2.5 km a.m.s.l. on Figure 6b can be explained by an upper-level redistribution of aerosols from source areas, such as the city of Annecy or transverse valleys, such as the highly industrialized Arve valley. On 18 June 2019, 1100-1230 LT, the peak is wider due to the onset of thermal convection, which will lead to the homogenization of aerosols in the first 2 km of the atmosphere. Note that the effect of homogenization are clearly visible in the WVMR profiles of Figure 6b,c. Pollution aerosols can thus be introduced by this process above the southern part of the lake. This may explain the higher particle concentrations on 19 June of up to 5 km a.m.s.l. (Figure 1b), preceding the stormy precipitation on 20 June.
5. Disturbed Conditions—Saharan Dust Event
The main cause of disturbance of aerosol composition over Alpine valleys is related to the large-scale transport of desert dust aerosols uplifted from above the Sahara. Traces of such events are found in the ice and snow mantle in the Alps [56]. Here, we analyze the case of 14–15 June 2019, where strikingly high PDR values were recorded from ground level to more than 6 km a.m.s.l.
5.1. Evidence of Dust-like Aerosols
5.1.1. What Can Be Inferred from the Weather Data
During the 14–15 June event, data from the European Center for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) show that the synoptic wind originated primarily from the Sahara and was advected over the Mediterranean Sea, south of the campaign location. In the Annecy valley, the wind sector is favorable to the Foehn effect. This phenomenon is generated by humid air masses, which undergo an ascendancy over the reliefs. Water vapor condenses on the windward side. In the valley, this results in a subsidence of dry air towards the valley ground surface, which is observed in the case of this dust transport event, where RH falls below 30% (Figure 3). This subsidence carries aerosols trapped in the air mass, and, as a result, particles can be observed from the surface up to several kilometers above the valley. Figure 7 shows the flight plan performed over the lake during an ultralight flight on 14 June, between 17:30 and 18:30 LT. The airborne meteorological measurements clearly show the drying of the air mass in the lower layers, and they are in good agreement with the ground-based lidar measurements in Figure 4b.
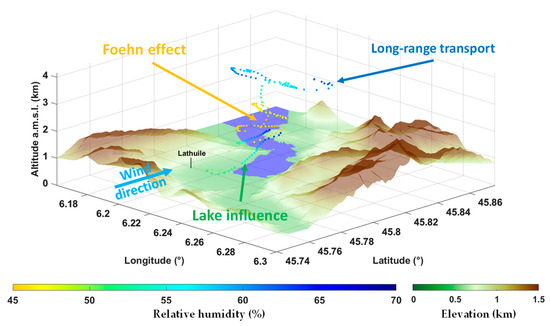
Figure 7.
Relative humidity (RH) measured by the meteorological probe on the ultralight on 14 June 2019, 17:30–18:30 LT.
5.1.2. Coherence between Ground-Based and Airborne Lidars
The measurements made with the airborne lidar are shown in Figure 8 for the same flight. In this figure, the AEC (Figure 8a) and VDR (Figure 8b) derived from the ground-based lidar over the period of the flight are also given. The profiles match very well with the AEC values up to ~3 km a.m.s.l., after which point a slight discrepancy is observed. This can be attributed to the different locations of the measurement profiles, but also to the fact that the ultralight covers a larger area and provides instantaneous samples for each altitude level, as opposed to the type of profile temporally averaged by the ground-based lidar.
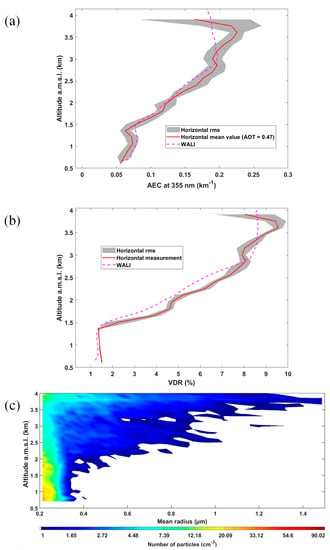
Figure 8.
Measurements performed on 14 June 2019, 17:30–18:30 LT. (a) Vertical profile of aerosol extinction coefficient (AEC) derived from the ground-based lidar (WALI, pink dotted line) and the airborne lidar ALiAS (solid red line). (b) Same as (a) for the linear volume depolarization ratio (VDR). The gray areas correspond to the statistical variability (rms). (c) Aerosol size distribution, as measured by the airborne particle sizer.
The presence of a major quantity of aerosols above the PBL is confirmed by both types of lidar measurement over the whole valley. These aerosols are highly depolarizing, as derived from both instruments. Note that the VDR is stable in the PBL (around 1.5%), and it increases very rapidly above it to reach 8 to 9%. These values correspond to PDRs of ~4 and 30%, respectively. In parallel, the measurements performed from the ground with the handheld sun spectrophotometer show exceptionally low Angstrom exponent values, between 0 and 0.2 on that day. Such values are representative of the presence of a coarse mode of desert dust-like particles in the atmospheric column, generally centered between 1 and 2 µm in radius (e.g., [57]). The depolarization values show that this mode is mostly located above the PBL, in the free troposphere, subject to mesoscale circulation.
5.1.3. Dust Signature on Particle Size Measurements
The optical particle sizer aboard the ultralight confirms this conclusion. Indeed, its airborne measurements show a supermicron aerosol mode, with increasing preponderance as a function of altitude (Figure 8c), from the PBL top (~2 km a.m.s.l.) to the maximum flight altitude (~4 km a.m.s.l.) in the free troposphere. As shown in Figure 8c, these coarse aerosols are not noticeably transferred into the PBL, which shows a pronounced temperature inversion at its top at the time of the flight (~1800 LT).
5.1.4. Variability of the LR, AEC, and PDR in the Dust Layer
The contribution of desert dust to the aerosol load in the air column is highly variable as a function of altitude, as confirmed by the particle size plotted against altitude (Figure 8c). So far, we have assumed a constant LR value as a function of altitude. While this assumption is acceptable for local aerosol layers, it is most unlikely during this long-range transport episode. To extract a distinctive profile of the LR in the dust layer up to 6 km a.m.s.l., an optimal signal-to-noise ratio is required, and therefore nighttime measurements with substantially less noise are favored. We have thus assessed the LR profile, as in [22]. The result is shown in Figure 9 for LR and associated profiles of AEC and PDR. As in the case of Figure 1b, at the same time, the aerosol layer peaks at ~3.5 km a.m.s.l., with AEC being ~0.16 km−1.
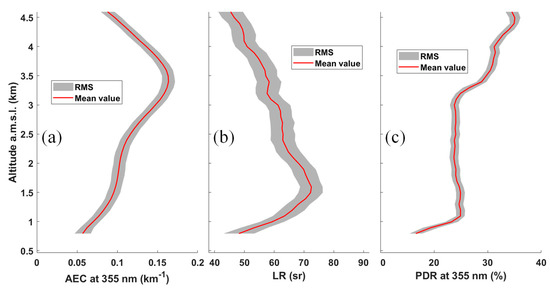
Figure 9.
Mean vertical profiles (red solid line) with 50 m vertical resolution of (a) the aerosol extinction coefficient (AEC), (b) lidar ratio (LR), and (c) particle linear depolarization ratio (PDR) between 14 June 2019, 22:00 and 15 June, 06:00 LT. The uncertainties on the lidar-derived optical parameters are shown as gray areas.
The LR, AEC, and PDR profiles, with their uncertainties (shaded area), are given in Figure 9. The LR ranges from ~50 sr at ground level to 75 sr at about 1.5 km a.m.s.l., which corresponds to the contribution of larger particles to the particle size distribution in Figure 8c, and it decreases continuously to ~4.5 km below 50 sr. When compared to Figure 1a, which gives values between 45 and 70 sr over the same period, the results appear consistent. Indeed, the calculated mean LR corresponds to the LR profile, weighted by the aerosol backscatter coefficient profile. Nonetheless, there is a strong variability in the LR profile, which is the signature of the heterogeneous character of dust layers along altitude. Pure desert dust aerosols are more likely to be found in the upper part of the profile (LR ~50 sr). Below this, they are probably mixed with local dust-like or pollution aerosols.
The PDR values remain close to those calculated with a constant LR and clearly show an increase with distance from the surface. PDR values of 20% near the ground are representative of aerosol mixtures with dust-like particles, whilst those at higher altitudes, around 30%, are representative of pure desert aerosols [22]. A rapid transition is noted between 3 and 3.5 km a.m.s.l., where the PDR increases from ~25% to ~30–35%. This gap, also observable on the meteorological profiles (see Figure 4), corresponds to the transition between mesoscale and synoptic air masses, where air mass histories can be different and where strong wind shears are often observed. It is located at the average altitude of the surrounding mountain range. Note that wind shears induce turbulence in the free troposphere that mixes air masses vertically, but desert aerosol transport occurs primarily in the free troposphere (above 3 km a.m.s.l.).
5.2. Saharan Dust Origin
To complete this study, we will now identify the origin of the air mass that transported dust-like aerosols over the Alps. For this purpose, we use reanalyses of meteorological fields and satellite observations.
5.2.1. Evidence of Transport and Horizontal Spread
Three-day back trajectories are computed between 4 and 6 km a.m.s.l. above the ground-based lidar using HYSPLIT. The choice of this altitude range is made considering (i) the maximum altitude where desert dust particles were seen by the ground-based lidar and (ii) the altitude of transition between mesoscale and synoptic air masses. Figure 10a shows the associated surface density of the back trajectory locations. On 13 June, the air masses are close to the surface, where potential desert dust sources are located. They are then lifted to higher altitudes as they cross the Mediterranean Sea.
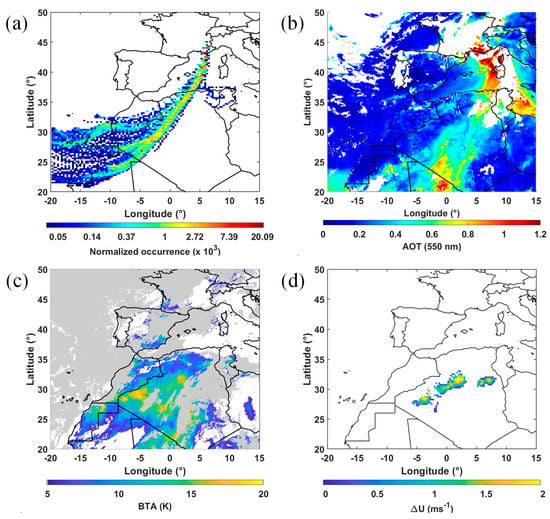
Figure 10.
(a) Normalized occurrence of the contribution to the air masses going over the ground-based lidar on 14 June 2019, at 16:00 UTC. The calculations have been performed using three–day back trajectories in ensemble mode between 4 and 6 km a.m.s.l., in steps of 0.1 km. (b) aerosol optical thickness (AOT) at 550 nm derived from MODIS on 14 June 2019. (c) Brightness temperature anomaly (BTA) on 13 June 2019, at 12:00 UTC. The cloud mask has been applied, here colored in gray. (d) Weighted difference between the horizontal velocity (U10) and the friction velocity ( at 10 m a.g.l. ().
The horizontal extent of this dust aerosol plume over the Western Mediterranean is well identified from MODIS-derived AOT at 550 nm. Figure 10b shows a daily synthesis of MODIS-derived AOTs for 14 June, between ~12:00 and 16:00 UTC, where the transport of desert aerosols towards the south-east of France is clearly highlighted. It is worth noting that, with time, Saharan aerosol plumes move from west to east over the Mediterranean area [57], so that they have a meridional position, which evolves during the transport. This explains the spatial shift of the back trajectories and MODIS-derived AOTs.
5.2.2. Dust Source Location
On the path of the back trajectories plotted in Figure 9a, the BTA on June 13 from Figure 10c reveals very clearly the presence of dust aerosols over the Great Western Erg, east of Morocco (~31°N~2°E), as well as all along the Moroccan–Algerian border, around 30°N.
Not all areas on those back trajectories are necessarily sources of dust from wind erosion. To locate the source area of dust aerosols more accurately, we compare horizontal winds with threshold friction velocities, both at 10 m a.g.l. (U10 and , respectively), determined over the Sahara from the map of the estimated aerodynamic roughness, established by [58]. The threshold friction velocities are those determined in the work of [59]. The U10 winds are from the fifth European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts Reanalysis (ERA5) at 0.25° horizontal resolution. It is defined that the uplift of dust aerosol is likely if ∆U = 1.1 − U10 is positive. ∆U is shown in Figure 10d. The coincidences between the areas defined by the BTAs and ∆U clearly identify the Great Western Erg as the source of the desert aerosols observed over the Annecy valley.
6. Conclusions
The L-WAIVE field campaign was an opportunity to sample the aerosol-laden air masses over Lake Annecy, where the atmospheric circulation typical of Alpine valleys can amplify the particulate contribution to local air masses. Few studies of this type are available yet, whilst the settlement of mountain valleys is increasing globally, in response to population growth and the search for less anthropized environments.
Air masses above the Annecy valley were sampled using 355 nm Raman lidar measurements, which made it possible to trace the optical properties of the aerosols, as well as the atmospheric moisture and temperature profiles, and this highlighted their strong heterogeneity over time and as a function of altitude. This heterogeneity is linked to the dynamic processes in the valley. More particularly, this was related to the diurnal upward/downward cycle of the valley and mountain winds, coupled with the synoptic meteorological conditions. Thus, LRs ranging from 40 to 115 ± 15 sr were observed, as well as PDRs varying between 2 and 35%. High LR values predominantly correspond to pollution aerosols and are associated with traffic and industrial pollution. Lower values are likely associated with local emissions of dust-like aerosols mixed with the pollution aerosols.
During L-WAIVE, in Foehn conditions generated by southerly winds, an important contribution of dust aerosols from the Sahara has been observed. These aerosols radically modify the average optical properties of the customary valley aerosol mixtures. They increase the AOT, which can exceed 0.5 at 355 nm, whereas it is normally 0.1 at the same wavelength during non-disruptive conditions. The non-spherical characteristics of these particles immediately induce an increase in the PDR in the layers above the PBL, which reaches values between 25 and 35%. In the PBL, the desert dust aerosols have mixed by subsidence with the local aerosols, which leads to intermediate PDR values (10–20%) between those of local pollution (~1–5%) and dust aerosols (~30%). This shows that, even in a steep valley, the air dynamic associated with the relief can drastically influence the local aerosol content via subsidence, which can bring aerosols transported in the free troposphere down to the valley floor.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, campaign coordination, methodology and writing—original draft preparation, P.C.; instruments development and preparation, J.T.; field campaign, data processing, writing—review and editing, P.C. and J.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the WaVIL project (WAter Vapor and Isotope Lidar) of Agence Nationale de la Recherche, grant number ANR-16-CE01-0009.
Data Availability Statement
Data can be downloaded from https://metclim-lidars.aeris-data.fr/en/homepage/ (last access: 15 January 2023), upon request to the first author of the paper. ERA5 data were downloaded from the Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S) Climate Date Store (https://cds.climate.copernicus.eu/#!/search?text=era5&type=dataset, last access: 15 January 2023).
Acknowledgments
Friendly acknowledgements to local authorities of the town of Lathuile: R. Aumaître, H. Bourne, F. Lambert; instrument providers F. Arthoud (USMB); D. Crucciani for his welcome at the Delta Evasion airfield; ultralight pilot F. Toussaint. The authors thank C. Flamant for his support as the WaVIL project coordinator, as well as campaign participants A. Baron, E. Dieudonné, F. Maignan, P. Doira, and C. Diana for their help in the field.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Jaffrezo, J.L.; Aymoz, G.; Cozic, J. Size Distribution of EC and OC in the Aerosol of Alpine Valleys during Summer and Winter. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2005, 5, 2915–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascal, M.; Yvon, J.M.; Corso, M.; Blanchard, M.; De Crouy-Chanel, P.; Medina, S. Conditions for a Meaningful Health Impact Assessment for Local Stakeholders: The Example of the Arve Valley in France. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, C.A.; Dockery, D.W. Health Effects of Fine Particulate Air Pollution: Lines That Connect. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2006, 56, 709–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoek, G.; Krishnan, R.M.; Beelen, R.; Peters, A.; Ostro, B.; Brunekreef, B.; Kaufman, J.D. Long-Term Air Pollution Exposure and Cardio-Respiratory Mortality: A Review. Environ. Health Glob. Access Sci. Source 2013, 12, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brulfert, G.; Chemel, C.; Chaxel, E.; Chollet, J.P. Modelling Photochemistry in Alpine Valleys. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2005, 5, 2341–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteman, C.D.; McKee, T.B. Break-up of Temperature Inversions in Deep Mountain Valleys: Part II. Thermodynamic Model. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1982, 21, 290–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löffler-Mang, M.; Zimmermann, H.; Fiedler, F. Analysis of Ground Based Operational Network Data Acquired during the September 1992 TRACT Campaign. Atmos. Environ. 1998, 32, 1229–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosetti, P.; Anfossi, D.; Cieslik, S.; Graziani, G.; Lamprecht, R.; Marzorati, A.; Nodop, K.; Sandroni, S.; Stingele, A.; Zimmermann, H. Mesoscale Transport of Atmospheric Trace Constituents across the Central Alps: TRANSLAP Tracer Experiments. Atmos. Environ. 1998, 32, 1257–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehning, M.; Richner, H.; Kok, G.L. Pollutant Transport over Complex Terrain: Flux and Budget Calculations for the Pollumet Field Campaign. Atmos. Environ. 1996, 30, 3027–3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wotawa, G.; Kromp-Kolb, H. The Research Project VOTALP—General Objectives and Main Results. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 1319–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grell, G.A.; Emeis, S.; Stockwell, W.R.; Schoenemeyer, T.; Forkel, R.; Michalakes, J.; Knoche, R.; Seidl, W. Application of a Multiscale, Coupled MM5/Chemistry Model to the Complex Terrain of the VOTALP Valley Campaign. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 1435–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffrezo, J.L.; Aymoz, G.; Delaval, C.; Cozic, J. Seasonal Variations of the Water Soluble Organic Carbon Mass Fraction of Aerosol in Two Valleys of the French Alps. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2005, 5, 2809–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sartelet, K.N.N.; Bocquet, M.; Chazette, P.; Sicard, M.; D’Amico, G.; Léon, J.F.F.; Alados-Arboledas, L.; Amodeo, A.; Augustin, P.; et al. Assimilation of Lidar Signals: Application to Aerosol Forecasting in the Western Mediterranean Basin. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 12031–12053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordova, A.M.; Arévalo, J.; Marín, J.C.; Baumgardner, D.; Raga, G.B.; Pozo, D.; Ochoa, C.A.; Rondanelli, R. On the Transport of Urban Pollution in an Andean Mountain Valley. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2016, 16, 593–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Lu, G.; Che, Y.; Zhong, S.; Ma, S.; Li, P.; et al. Cable-Car Measurements of Vertical Aerosol Profiles Impacted by Mountain-Valley Breezes in Lushan Mountain, East China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 768, 144198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beniston, M.; Wolf, J.P.; Beniston-Rebetez, M.; Kolsch, H.J.; Rairoux, P.; Woste, L. Use of Lidar Measurements and Numerical Models in Air Pollution Research. J. Geophys. Res. 1990, 95, 9879–9894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chazette, P.; Couvert, P.; Randriamiarisoa, H.; Sanak, J.; Bonsang, B.; Moral, P.; Berthier, S.S.; Salanave, S.; Toussaint, F. Three-Dimensional Survey of Pollution during Winter in French Alps Valleys. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 1035–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savov, P.B.; Skakalova, T.S.; Kolev, I.N. Lidar Investigation of the Temporal and Spatial Distribution of Atmospheric Aerosols in Mountain Valleys. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2002, 41, 528–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, J.; Shrestha, P.; Barros, A.P. Mapping Aerosol Intrusion in Himalayan Valleys Using the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) and Cloud-Aerosol Lidar and Infrared Pathfinder Satellite Observation (CALIPSO). Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 6382–6392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoff, R.M.; Harwood, M.; Sheppard, A.; Froude, F.; Martin, J.B.; Strapp, W. Use of Airborne Lidar to Determine Aerosol Sources and Movement in the Lower Fraser Valley (LFV), BC. Atmos. Environ. 1997, 31, 2123–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolev, N.; Grigorov, I.; Kolev, I.; Devara, P.C.S.; Raj, P.E.; Dani, K.K. Lidar and Sun Photometer Observations of Atmospheric Boundary-Layer Characteristics over an Urban Area in a Mountain Valley. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2007, 124, 99–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chazette, P.; Totems, J.; Ancellet, G.; Pelon, J.; Sicard, M. Temporal Consistency of Lidar Observations during Aerosol Transport Events in the Framework of the ChArMEx/ADRIMED Campaign at Minorca in June 2013. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 2863–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansmann, A.; Riebesell, M.; Weitkamp, C. Measurement of Atmospheric Aerosol Extinction Profiles with a Raman Lidar. Opt. Lett. 1990, 15, 746–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groß, S.; Freudenthaler, V.; Schepanski, K.; Toledano, C.; Schäfler, A.; Ansmann, A.; Weinzierl, B. Optical Properties of Long-Range Transported Saharan Dust over Barbados as Measured by Dual-Wavelength Depolarization Raman Lidar Measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 11067–11080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnuth, W.; Trickl, T. Transport Studies with the IFU Three-Wavelength Aerosol Lidar during the VOTALP Mesolcina Experiment. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 1425–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasano, G.; Diémoz, H.; Fountoulakis, I.; Cassardo, C.; Kudo, R.; Siani, A.M.; Ferrero, L. Vertical Profile of the Clear-Sky Aerosol Direct Radiative Effect in an Alpine Valley, by the Synergy of Ground-Based Measurements and Radiative Transfer Simulations. Bull. Atmos. Sci. Technol. 2021, 2, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chazette, P.; Flamant, C.; Sodemann, H.; Totems, J.; Monod, A.; Dieudonné, E.; Baron, A.; Seidl, A.; Steen-Larsen, H.C.; Doira, P.; et al. Experimental Investigation of the Stable Water Isotope Distribution in an Alpine Lake Environment (L-WAIVE). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 10911–10937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chazette, P.; Dabas, A.; Sanak, J.; Lardier, M.; Royer, P. French Airborne Lidar Measurements for Eyjafjallajökull Ash Plume Survey. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 7059–7072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chazette, P.; Marnas, F.; Totems, J. The Mobile Water Vapor Aerosol Raman LIdar and Its Implication in the Framework of the HyMeX and ChArMEx Programs: Application to a Dust Transport Process. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 1629–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Totems, J.; Chazette, P. Calibration of a Water Vapour Raman Lidar with a Kite-Based Humidity Sensor. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 1083–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Totems, J.; Chazette, P.; Raut, J.J.-C. Accuracy of Current Arctic Springtime Water Vapour Estimates, Assessed by Raman Lidar. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2019, 145, 1234–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Totems, J.; Chazette, P.; Baron, A. Mitigation of Bias Sources for Atmospheric Temperature and Humidity in the Mobile Raman Weather and Aerosol Lidar (WALI). Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2021, 14, 7525–7544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komppula, M.; Mielonen, T.; Arola, A.; Korhonen, K.; Lihavainen, H.; Hyvärinen, A.P.; Baars, H.; Engelmann, R.; Althausen, D.; Ansmann, A.; et al. Technical Note: One Year of Raman-Lidar Measurements in Gual Pahari EUCAARI Site Close to New Delhi in India-Seasonal Characteristics of the Aerosol Vertical Structure. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 4513–4524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansmann, A.; Riebesell, M.; Wandinger, U.; Weitkamp, C.; Voss, E.; Lahmann, W.; Michaelis, W. Combined Raman Elastic-Backscatter LIDAR for Vertical Profiling of Moisture, Aerosol Extinction, Backscatter, and LIDAR Ratio. Appl. Phys. B Photophys. Laser Chem. 1992, 55, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royer, P.; Chazette, P.; Lardier, M.; Sauvage, L. Aerosol Content Survey by Mini N2-Raman Lidar: Application to Local and Long-Range Transport Aerosols. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 7487–7495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieudonné, E.; Chazette, P.; Marnas, F.; Totems, J.; Shang, X. Raman Lidar Observations of Aerosol Optical Properties in 11 Cities from France to Siberia. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Totems, J.; Chazette, P.; Shang, X.; Flamant, C.; Raut, J.-C.; Doerenbecher, A.; Ducroq, V.; Bock, O.; Marnas, F. Water Vapor Measurements by Mobile Raman Lidar over the Mediterranean Sea in the Framework of HyMex: Application to Multi-Platform Validation of Moisture Profiles. In Proceedings of the EPJ Web of Conferences, The 27th International Laser Radar Conference (ILRC 27), New York City, NY, USA, 5–10 July 2015; Volume 119. [Google Scholar]
- Chazette, P.; Totems, J. Mini N2-Raman Lidar Onboard Ultra-Light Aircraft for Aerosol Measurements: Demonstration and Extrapolation. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chazette, P.; Totems, J.; Baron, A.; Flamant, C.; Bony, S. Trade-Wind Clouds and Aerosols Characterized by Airborne Horizontal Lidar Measurements during the EUREC4A Field Campaign. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2020, 12, 2919–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chazette, P.; Sanak, J.; Dulac, F. New Approach for Aerosol Profiling with a Lidar Onboard an Ultralight Aircraft: Application to the African Monsoon Multidisciplinary Analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 8335–8341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chazette, P.; Baron, A.; Flamant, C. Mesoscale Spatio-Temporal Variability of Airborne Lidar-Derived Aerosol Properties in the Barbados Region during EUREC4A. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 1271–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuula, J.; Friman, M.; Helin, A.; Niemi, J.V.; Aurela, M.; Timonen, H.; Saarikoski, S. Utilization of Scattering and Absorption-Based Particulate Matter Sensors in the Environment Impacted by Residential Wood Combustion. J. Aerosol Sci. 2020, 150, 105671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, A.F.; Draxler, R.R.; Rolph, G.D.; Stunder, B.J.B.B.; Cohen, M.D.; Ngan, F.; Stein, A.F.; Draxler, R.R.; Rolph, G.D.; Stunder, B.J.B.B.; et al. NOAA’s HYSPLIT Atmospheric Transport and Dispersion Modeling System. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 2059–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmonson, V.V.; Barnes, W.L.; Maymon, P.W.; Montgomery, H.E.; Ostrow, H. MODIS: Advanced Facility Instrument for Studies of the Earth as a System. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1989, 27, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.C.; Mattoo, S.; Munchak, L.A.; Remer, L.A.; Sayer, A.M.; Patadia, F.; Hsu, N.C. The Collection 6 MODIS Aerosol Products over Land and Ocean. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 2989–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmetz, J.; Pili, P.; Tjemkes, S.; Just, D.; Kerkmann, J.; Rota, S.; Ratier, A. An Introduction to Meteosat Second Generation (MSG). Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2002, 83, 977–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legrand, M.; Cautenet, G.; Buriez, J.C. Thermal Impact of Saharan Dust over Land. Part II: Application to Satellite IR Remote Sensing. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1992, 31, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chazette, P.; Royer, P. Springtime Major Pollution Events by Aerosol over Paris Area: From a Case Study to a Multiannual Analysis. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 8101–8119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raut, J.-C.; Chazette, P. Retrieval of Aerosol Complex Refractive Index from a Synergy between Lidar, Sunphotometer and in Situ Measurements during LISAIR Experiment. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2007, 7, 2797–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesche, M.; Ansmann, A.; Müller, D.; Althausen, D.; Engelmann, R.; Freudenthaler, V.; Groß, S. Vertically Resolved Separation of Dust and Smoke over Cape Verde Using Multiwavelength Raman and Polarization Lidars during Saharan Mineral Dust Experiment 2008. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114, D13202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiridis, V.; Balis, D.; Giannakaki, E.; Kazadzis, S.; Arola, A.; Gerasopoulos, E. Characterization of the Aerosol Type Using Simultaneous Measurements of the Lidar Ratio and Estimations of the Single Scattering Albedo. Atmos. Res. 2011, 101, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, D.; Lee, K.-H.; Gasteiger, J.; Tesche, M.; Weinzierl, B.; Kandler, K.; Müller, T.; Toledano, C.; Otto, S.; Althausen, D.; et al. Comparison of Optical and Microphysical Properties of Pure Saharan Mineral Dust Observed with AERONET Sun Photometer, Raman Lidar, and in Situ Instruments during SAMUM 2006. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, 7211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raut, J.-C.C.; Chazette, P. Assessment of Vertically-Resolved PM10 from Mobile Lidar Observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 8617–8638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrendt, A.; Nakamura, T. Calculation of the Calibration Constant of Polarization Lidar and Its Dependency on Atmospheric Temperature. Opt. Express 2002, 10, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, J.M.; Vaughan, M.A.; Hostetler, C.A.; Hunt, W.H.; Winker, D.M. Calibration Technique for Polarization-Sensitive Lidars. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2006, 23, 683–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodemann, H.; Palmer, A.S.; Schwierz, C.; Schwikowski, M.; Wernli, H. The Transport History of Two Saharan Dust Events Archived in an Alpine Ice Core. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 667–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamonou, E.; Chazette, P.; Balis, D.; Dulac, F.; Schneider, X.; Galani, E.; Ancellet, G.; Papayannis, A. Characterization of the Vertical Structure of Saharan Dust Export to the Mediterranean Basin. J. Geophys. Res. 1999, 104, 22257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marticorena, B.; Chazette, P.; Bergametti, G.; Dulac, F.; Legrand, M. Mapping the Aerodynamic Roughness Length of Desert Surfaces from the POLDER/ADEOS Bi-Directional Reflectance Product. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 25, 603–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, B.; Marticorena, B.; Bergametti, G.; Léon, J.F.; Mahowald, N.M. Modeling Mineral Dust Emissions from the Sahara Desert Using New Surface Properties and Soil Database. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).